Showing 27 items matching "uterine device"
-
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Dilator, uterine, Goodell's
... Uterine device... by him from colleagues initially. Uterine device Dilation Forster ...Mostl likely donated by Dr Frank Forster, possibly collected by him from colleagues initially.Uterine dilator, Goodell's, stamped inside the blades '22". Manufacturers logo stamped on near netral screw joint, Medical symbol, serpent entwined around a sword with crown on top.uterine device, dilation, forster, frank -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Dilator, uterine, Palmer's
... Uterine device... by him from colleagues initially. Uterine device Dilation Forster ...Most likely donated by Dr Frank Forster, possibly collected by him from colleagues initially.Uterine dilator, Palmer's. Broken handle lever. illustrated in Tiemann, George The American Armaterium, page 503.uterine device, dilation, forster, frank -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Dilator, uterine, Goodell's
... Uterine device... by him from colleagues initially. Uterine device Dilation Forster ...Most likely donated by Dr Frank Forster, possibly collected by him from colleagues initially.Uterine dilator, Goodell's, stamped inside the blades '23". Manufacturers unknown.uterine device, dilation, forster, frank -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Dilator, uterine, Goodell's
... Uterine device... by him from colleagues initially. Uterine device Dilation Forster ...Most likely donated by Dr Frank Forster, possibly collected by him from colleagues initially.Uterine dilator, Goodell's, stamped inside the blades '23". Manufacturers unknown.uterine device, dilation, forster, frank -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Dilator, uterine, Gardner's
... Uterine device... by him from colleagues initially. Uterine device Dilation Forster ...Most likely donated by Dr Frank Forster, possibly collected by him from colleagues initially.Uterine dilator, Gardner's, stamped on blade "HIGHEST STAND...(ard). Worn away- This item must have had great usage.uterine device, dilation, forster, frank -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Dilator, uterine, Wathern's
... Uterine device... by him from colleagues initially. Uterine device Dilation Forster ...Most likely donated by Dr Frank Forster, possibly collected by him from colleagues initially.Uterine dilator, Wathern's. No manufacturer's stamp.uterine device, dilation, forster, frank -
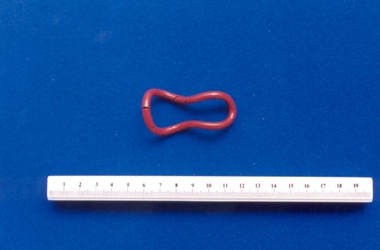 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Barnes-Hodges style pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster, Barnes Hodges, England
... Pessary. Intra-uterine contraceptive device, consisting... that of the inventor. Intrauterine device Pessary. Intra-uterine contraceptive ...Uterine and anal pessaries were in use in the early 1900s. Both size and shape of the pessary varied considerably. Pessaries were often round ('ring' pessaries) or irregular shape, depending on the maker. The name of the pessarty was usually that of the inventor.Pessary. Intra-uterine contraceptive device, consisting of red rubber outer covering over wire or vulcanite in an irregular shape. Most likely hand made. Inscribed "PATENTED" at .intrauterine device -
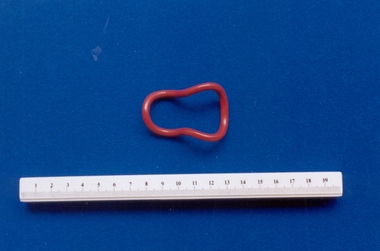 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Smith-Hodges style pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster
... was usually hand made and was in demand as an intra-uterine device... and was in demand as an intra-uterine device in the 1960s ...This is Albert Smith's modification of a Hodges pessary. Uterine and anal pessaries were in use from the early 1900s onwards. The shape and style of pessaries varied with the introduction of new O & G techniques, and the materials they were made from varied with the maker. The Hodges-Smith pessary was usually hand made and was in demand as an intra-uterine device in the 1960s. For the prevention of uterine or abdominal infection, this type of pessary was changed frequently.Small, irregular vulcanite/wire pessary, covered with red rubber. Inscribed "PATENT".pessary, intrauterine device -
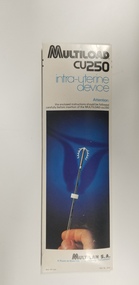 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Multiload CU250 IUDs associated with Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, Multilan S.A, 1984
... /CU250/intra-uterine/device/Attention:/the enclosed instructions... on the front of the box reads 'MULTILOAD/CU250/intra-uterine/device ...Multiload is an IUD, an intrauterine device used for contraception. The plastic used in this IUD is a mixture of high density polyethylene, ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer and barium sulphate in a weight ratio 44/36/20. (MIMS, October 2013)This is one of a collection of items received from the practice of Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, FRCOG, Launceston, Tasmania.Two flat boxes containing Multiload CU250 intrauterine devices. Front of box carries an image of a hand holding an IUD inserter, with the Multiload IUD at the top of the inserter, above a blue background on which an image of a uterus has been superimposed. Text printed on the front of the box reads 'MULTILOAD/CU250/intra-uterine/device/Attention:/the enclosed instructions should be followed carefully before insertion of the MULTILOAD-cu250'. Manufacturer's information is printed on the bottom section of the front of the box. Back of box is printed with distributor information. One box is sealed, and the other box has been opened. Back of sealed box carries a sticker which reads 'Date of manufacture: /12-08-1984'. Opened box contains a Multiload IUD in a sealed packet, a brochure outlining the recommended procedure for insertion, a booklet outlining prescribing information, and another booklet entitled 'Everything you have to know about Multiload'. The packaging of the IUD inside the opened box is labelled with an expiry date of 16/10/1984.intrauterine device -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Multiload CU250 IUDs associated with Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, Multilan S.A, 1984
... 'MULTILOAD/CU250/intra-uterine/device/Attention:/the enclosed... on the front of the box reads 'MULTILOAD/CU250/intra-uterine/device ...Multiload is an IUD, an intrauterine device used for contraception. The plastic used in this IUD is a mixture of high density polyethylene, ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer and barium sulphate in a weight ratio 44/36/20. (MIMS, October 2013)This is one of a collection of items received from the practice of Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, FRCOG, Launceston, Tasmania.Two flat boxes containing Multiload CU250 intrauterine devices. Front of each box carries an image of a hand holding an IUD inserter, with the Multiload IUD at the top of the inserter, above a blue background on which an image of a vagina has been superimposed. Text printed on the front of the box reads 'MULTILOAD/CU250/intra-uterine/device/Attention:/the enclosed instructions should be followed carefully before insertion of the MULTILOAD-cu250'. Manufacturer's information is printed on the bottom section of the front of the box. Back of each box is printed with distributor information. One box is sealed, and one box is unsealed. Unsealed box contains one IUD, sealed inside a sterile plastic pocket. Back of sterile pocket is printed with an expiration date of 06-12-1984. The IUD is in the form of a small plastic rod, or stem, with two small flexible side-arms. Each side arm has five small protrusions. A copper wire is wound around the stem. A nylon thread with two ends is attached to the bottom end of the stem. Back of sealed box carries a sticker which reads 'Date of manufacture: /12-08-1984'.intrauterine device -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Duke's stem pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster
Part of the collection of Dr Frank Forster. The philosophy of this object was to keep the uterus dilated. It was commonly believed at this time that the cervix was the cause of dysmenorrhoea. The stem pessary was an object used to rectify uterine displacements - either anteversion or retroversion. The device consisted of a stem which is introduced into the uterus, the stem was then attached to an ovoid flange or ball, on which the cervix uteri then rested. Connected to this flange was an external part or wire frame, which in turn was attached at one extremity to a flat tubular portion, passing into the vagina. This was then fixed to the intrauterine portion. The wire frame was then made to press on to the pubis, so that the pessary could be kept in position in utero.Pessary, Duke's stem design. Metal pessary with hollow stem, and a rounded flange at one end. The flange has eight small holes surrounding the central hole. The stem is flexible and is made from coiled metal which has then been attached (perhaps by soldering) to the flange.pessary, intrauterine device -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Duke's stem pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster
Part of the collection of Dr Frank Forster. The philosophy of this object was to keep the uterus dilated. It was commonly believed at this time that the cervix was the cause of dysmenorrhoea. The stem pessary was an object used to rectify uterine displacements - either anteversion or retroversion. The device consisted of a stem which is introduced into the uterus, the stem was then attached to an ovoid flange or ball, on which the cervix uteri then rested. Connected to this flange was an external part or wire frame, which in turn was attached at one extremity to a flat tubular portion, passing into the vagina. This was then fixed to the intrauterine portion. The wire frame was then made to press on to the pubis, so that the pessary could be kept in position in utero.Pessary, Duke's stem design. Metal pessary with hollow stem, and a rounded flange at one end. The flange has six small holes surrounding the central hole. The stem is flexible and is made from coiled metal which has then been attached (perhaps by soldering) to the flange.pessary, intrauterine device -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Peaslee pessaries associated with Dr Frank Forster
Stem pessaries were instruments used for rectifying uterine displacement, either ante or retroversion. The pessary consisted of a stem and bulb or ball. The stem was introduced into the vagina, and the bulb rested against the cervix/uteri. An external wire frame could be attached to the bulb. The wire frame would be positioned to press on the pubis, thus keeping the pessary in position in utero. Although this pessary has been recorded as Peaslee's it is very similar in appearance to Thomas's galvanic stem pessaries. Stem pessaries were used in rectifying uterine displacement, either acute or retroversion. A pink tag was attached by string to one of the stems inscribed "Peaslee's/ Uterine/ Stem " "...?TID" on other side.Two Peaslee's intrauterine stem pessaries. Copper single stem pessaries with rounded top, stamped with the number seven on the top.intrauterine device, pessary -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Simpson's galvanic pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster, c. 1880 to 1920
... Part of the collection of Dr Frank Forster. Intrauterine device ...Part of the collection of Dr Frank Forster.Uterine stem pessary. Pessary is made of copper coated lead with upper oval shaped bulb. Bulb of the pessary is made of copper and oval has a small hole in the top centre. The upper part of the stem is made of copper and the lower section is made of lead and tapers to a blunt end. On the upper outer right side on the bulb is the figure "6".intrauterine device, pessary -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Uterine flushing tube associated with Professor Bruce Mayes, c1932
Item originally belonged to Professor Bruce Mayes, University of Sydney c1950-65. According to Professor Warren Jones the item had been in a back room of the medical facility and Professor Mayes gave it to Warren Jones, otherwise it may have been thrown out. Warren Jones took it with him to Adelaide where he practiced from 1975. This item may have originally been imported from Germany.Uterine flushing tube, possibly Bozeman-type. Curved metal device in a loose 's' shape, with a bulbous point at one end, just above two circular metal loops which sit either side of main metal stem. Manufacturer is unknown.obstetric delivery -
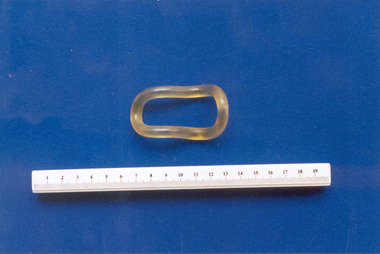 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Hodges-style pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster
Uterine and anal pessaries were in use from the early 1900s onwards. The size and shape of the pessary varied greatly, and the variation of the original Hodges pessary is evident in many catalogues over a period of sixty years. Celluloid appliances were made in many different colours (ie. blue, pink, white, yellow). The use of celluloid gradually decreased during the late 1960s.Yellow celluloid (plastic) pessary. intrauterine device -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Divided Hodges-style pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster
Uterine and anal pessaries were in use from the early 1900s onwards. The size and shape of the pessary varied greatly, and the variation of the original Hodges pessary is evident in many catalogues over a period of sixty years.Black vulcanite pessary divided at one end, leaving a gap of approximately 1.5cm.intrauterine device -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Uterine stem pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster
The pessary was originally regarded as an instrument and made from cork, ivory, hard rubber or gum-elastic. In later times, they were made from black vulcanite, flexible tin, soft copper wire covered with Indian rubber, and celluloid. The form of the pessary was and still is variable -either round, oval, or moulded in some cases combining three or four curves depending on the size of the pessary. In ancient times, medicated pessaries were made from emollient. astringent and aperient. Several of these are still used, but in more modem times are called vaginal suppositories. Anal suppositories are still used to suppress the pain of haemorrhoids.Moulded black vulcanite pessary. Pessary is irregular in shape, and in the "eyeglass" stem style.pessary, intrauterine device -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Hodges-style pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster
Uterine and anal pessaries were in use from the early 1900s onwards. The size and shape of the pessary varied greatly, and the variation of the original Hodges pessary is evident in many catalogues over a period of sixty years. Celluloid appliances were made in many different colours (ie. blue, pink, white, yellow). The use of celluloid gradually decreased during the late 1960s.Hodges -style intrauterine pessary, made of black vulcanite.intrauterine device -
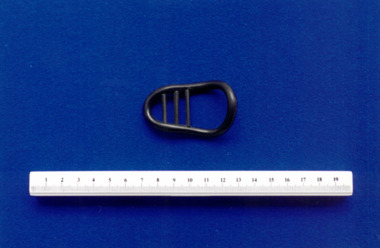 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Hodges-style pessary with cross bars, associated with Dr Frank Forster
Both uterine and anal pessaries were in use from the early part of the 1900s. This particular type of pessary was in general use from the 1960s to the mid 1970s.Hodges-style intrauterine pessary with three cross bars.intrauterine device -
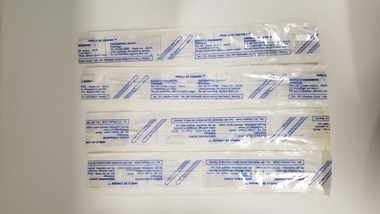 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Collection of Pipelle curettes associated with Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, Prodimed, c.1989
Used for endometrial biopsy. As described on packaging - 'For histologic biopsy on the uterine mucosal lining or sample extracting of uterine menstrual content.'This is one of a collection of items received from the practice of Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, FRCOG, Launceston, Tasmania.Four curettes, each in an individually sealed package. Each package is labelled 'Unimar/Pipelle TM Endometrial/suction curette.' Distributed by Unimar (USA), manufactured by Prodimed (France). Batch dated 'OCT 89'.intrauterine device -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Uterine catheter used by Dr Fritz Duras
This instrument was used by Dr Fritz Duras (1896-1965), who moved to Australia from Germany in 1937. As his father was Jewish, Duras was forced to leave Germany , and came to Australia to take up a post as director of physical education at Melbourne University. Metal catheter with internal wire. Catheter is in a vague 's' shape, with a thinner and thicker section. A loop at one end it attached to a wire which can be slid in and out of the device. There are two small round attachments at the thinner end of the device which function as grips. obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Instrument - Dührssen-style 8 bladed dilator, Unknown
Alfred Dührssen (23 March 1862 – 11 October 1933) was a German gynecologist and obstetrician born in Heide, Schleswig-Holstein, at the time part of Denmark. He studied medicine at the University of Marburg, as well as the Kaiser-Wilhelm-Akademie für das militärärztliche Bildungswesen (Kaiser-Wilhelm-Academy for Military Physicians). In 1886, he became an obstetrical assistant to Adolf Gusserow (1836-1906) in Berlin, and in 1888 he began work as a lecturer at the University of Berlin. In 1892 he opened a private clinic for obstetrics and gynecological diseases. Dührssen was a prominent figure in modern German gynecology, being remembered for his pioneer work in surgical practices such as vaginal Caesarean section (vaginalen Kaiserschnitt). He was an advocate of institutional births for all pregnancies, and proposed that pregnant women undergo screening processes to uncover possible difficulties prior to giving birth. (Wikipedia) Metal uterine dilator consisting of a handle, a short shaft, and eight prongs. The prongs each have a bump/curve in the prong towards the top, to allow them to bend around the shaft of the instrument and meet at their tips. There is a second 'bump' in the prongs just before the tips. The tip of each prong has five ridges to assist with grip. The handle of the device is a flat, rounded handle, which is turned to open the prongs and set them at various degrees of diameter. There is a gauge on the shaft of the instrument which ranges from 0-12, showing the current setting of the instrument. There is also a pin and T-shaped slot arrangement located just above the start of the prongs, which has been engraved '8' on the left hand side, and '1' on the right hand side. Each prong is also engraved with a number at the base of the prong, reading '1' to '8'. gynaecology -
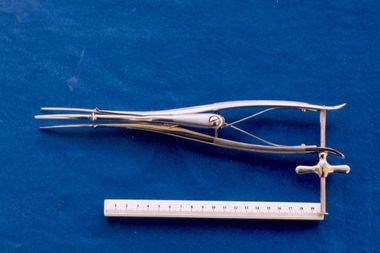 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sims-type uterine dilator used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward
Used for probing a woman's uterus through the cervix, to measure the length and direction of the cervical canal and uterus. Dilators are primarily used to open and dilate the cervix to gain access to the uterine cavity but can also be used as sounds. This device was included with other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, given to RANZCOG from Box Hill Hospital labour ward in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill Hospital combined with St George's Hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett.Three bladed Sims uterine dilator, consisting of upper blade, lower blade, bridge, and wingnut. Blades are polished stainless steel with matte steel handles. Upper surface inscribed, (trademark) MADE IN GERMANY INOXIDABLE", "21"."21"box hill hospital -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Uterine catheter used by Dr Fritz Duras and Dr Michael Kloss
This instrument was used by Dr Fritz Duras (1896-1965), who moved to Australia from Germany in 1937. As his father was Jewish, Duras was forced to leave Germany, and came to Australia to take up a post as director of physical education at Melbourne University. This instrument was part of a collection of instruments given to his son-in-law, Dr Michael Kloss, who was an obstetrician. Dr Kloss subsequently had it engraved and used it in his own practice, before donating the item to the College. Metal uterine catheter. Catheter is in a vague 's' shape, with a rounded tip at one end and a hole in the catheter just above the tip. There is a small oval shaped attachment at the proximal end of the device for grip. One side of the instrument is engraved with the word 'Kloss'. The number '10' is engraved at the proximal end of the catheter. Internal wire section may be missing from this catheter.'Kloss'obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Instrument - Bossi-style uterine dilator
Four-pronged metal surgical instrument. Consists of a handle and a short shaft with a metal cross shaped base section to which four long, curved prongs are attached. Each prong is capped by a detachable foot, consisting of a grooved metal sleeve with a base that forms the shape of a quarter circle. When the device is closed, the four feet line up with each other to form a complete circle at the base. There is large handle with four spokes at the top of the device for opening and closing the instrument, and a circular knob is affixed to the top of the handle to lock it in place when required. The shaft of the instrument is engraved with gauge markings to measure how open the instrument is when in use.obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Equipment - Mark-7 disposable uterine sound associated with Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, Searle Laboratories, 1984
... . Intrauterine device Disposable uterine sound in sterile sealed ...Used to measure the depth/distance of the uterus. Uterine sounds are particularly useful for ensuring safe and accurate IUD placement.This is one of a collection of items received from the practice of Dr Lachlan Hardy-Wilson, FRCOG, Launceston, Tasmania.Disposable uterine sound in sterile sealed packaging. Label inside packaging reads 'Mark-7 brand of disposable uterine sound/ONE STERILE UNIT/NO. 154'. Label also includes manufacturer information, a sterile packaging warning, and a caution about sale of the item being restricted to physicians. The number '026' is printed on the back of the packaging.intrauterine device
