Showing 6 items matching "weather measurement"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Record Book, Commonwealth Meteorological Bureau, Meteorological Observations, May 1945
... weather measurement... May 1945 weather history weather measurement weather record ...This book of meteorological observations is dated May 1945. The book was published by the Commonwealth Meteorological Bureau, Victora Division. It was printed by L. F. Johnston, Commonwealth Government Printer, Canberra. Readings were recorded daily for barometric pressure, temperature, rain and wind velocity. At the end of each month, they were posted to the central Branch in Melbourne. These Meteorological Observations are an important accurate record of the local weather since the decades. They are part of Flagstaff Hill's Meteorological Observations collection of over seventy record books dating from the late 19th century. The collected information gives a picture of the weather patterns for the months and seasons, which then allows for warnings of events out of the normal or extreme, such as forecasting floods or droughts.Meteorological Observations, dated May 1945. Small brown cardboard printed cover with printed pages prepared for adding records. Published by the Commonwealth of Australia. Printed text includes "Commonwealth Meteorological Bureau / DIVISION NO. 5 VICTORIA / METEOROLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS " and "The Observer who takes each set of readings is requested to put his initials at the bottom of each column" "flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, meteorological observations, commonwealth meteorological bureau, commonwealth meteorologist, central meteorological bureau, division no. 5 victoria, weather readings, weather records, may 1945, weather history, weather measurement, weather record -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Record Book, Commonwealth Meteorological Bureau, Meteorological Observations, November 1948
... weather measurement... weather measurement weather record Division No 3 Queensland ...This book of Warrnambool's meteorological observations is dated November 1948. The book was published by the Commonwealth Meteorological Bureau, Victora Division. It was printed by L. F. Johnston, Commonwealth Government Printer, Canberra. It was originally printed for Division 3, Queensland but has been overwritten with 'Vic' [Victoria] and used for Warrnambool. Readings were recorded daily for barometric pressure, temperature, rain and wind velocity. At the end of each month, they were posted to the central Branch in Melbourne.These Meteorological Observations are an important accurate record of the local weather since the decades. They are part of Flagstaff Hill's Meteorological Observations collection of over seventy record books dating from the late 19th century. The collected information gives a picture of the weather patterns for the months and seasons, which then allows for warnings of events out of the normal or extreme, such as forecasting floods or droughts.Meteorological Observations record book. Recordings were taken at Warrnambool in November 1948. Small red cardboard printed cover with printed pages prepared for adding records. Published by the Commonwealth of Australia. The book was printed for Queensland; the cover has been altered by hand to read Vic [Victoria], but the fly page has not been altered.Printed cover text includes "Central Meteorological Bureau" "METEOROLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS DIVISION No. 3 QUEENSLAND" Handwritten on cover "VIC" "Nov 1948."flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, meteorological observations, commonwealth meteorological bureau, weather readings, weather records, weather history, weather measurement, weather record, division no 3 queensland, victoria, november 1848 -
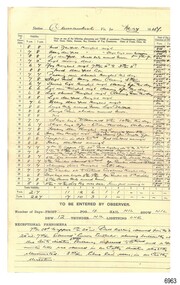 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageJournal - Record Book, Meteorological Observations, 1947-1948
... weather measurement... measurement weather forecast weather history Carrington Harbour Master ...This bundel of twenty pages of meteorological observations covers the period between March 1947 and April 1948 but there are some gaps. The bundle includes handwritten records on pre-printed forms from the Commonwealth Government and brief records on plain paper. There are calculations for monthly totals of information such as rainfall, and there are some comparisons between the years. One of the forms has handwriting in three directions, which is quite unusual. Readings were recorded daily for barometer, temperature and wind. There was also a section for comments on Exceptional Phenomena such as storms and fog. . It was one of the many duties of the Lighthouse Keeper or his Assistant to keep these records and make the mathematical calculations required by the Government. Information gathered from Lighthouse Keepers' letters tells of the large amount of time taken for this detailed work and the lack of payment made for such a responsibility. The quite detailed record for May, June and July 1947 were signed by C Carrington, Harbour Master for Warrnambool. Captain Carrington was responsible to the Harborus Board. He was responsibilite for the fortnightly training of the Warrnambool Lifeboat Crew on the practice of lifesaving and using the Rocket Rescue equipment. These Meteorological Observations are an important accurate record of the local weather since the late 1899s. They are part of Flagstaff Hill's Meteorological Observations collection of over seventy record books dating from the late 19th century. The collected information gives a picture of the weather patterns for the months and seasons, which then allows for warnings of events out of the normal or extreme, such as forecasting floods or droughts.Meteorological Observations for Warrnambool March 1947 to May 1948. A bundle of unbound sheets of paper joined at the top left corner with a metal fastener. The pages are ordered from most recent on top to the oldest on bottom. The older records are on pre-printed forms and include many handwritten details. The more recent records are handwritten on plain paper. There is a line for each day of the month and lines for calculations at the bottom of the page. The handwritten Information includes readings for Barometer, Temperature, Wind and Rain. Printed: "COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA METEROLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS / Division No. 5, Vic. "flagstaff hill, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, maritime museum, maritime village, meteorological observations, weather records, meteorology, barometer readings, temperature records, barometer records, wind records, rain records, commonwealth of australia, division 5, weather measurement, weather forecast, weather history, carrington, harbour master -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Lead line
The lead line or hand lead is a simple navigational instrument used as a depth finder to measure the depth of water under the ship’s keel and to take samples of the sea bed. The long line may be marked at regular intervals with tags of different coloured and textured fabric, such as rope, leather and cloth. Each tag was a code to represent a certain depth. The leadsman’s eyes and hands could distinguish the depth easily as he drew in the lead line, day or night and in poor weather conditions. A standard set of codes for the tags was used so that the depth of the sea could be easily and quickly read. The measurement used was a Fathom, which equals 1.83 metres. The codes were: - 2 fathoms = 2 strips of leather 3 fathoms = 3 strips of leather 5 fathoms = white duck fabric 7 fathoms = red bunting fabric 10 fathoms = leather with a hole 13 fathoms = blue serge fabric 15 fathoms = white duck fabric 17 fathoms = red bunting 20 fathoms = 2 knots The lead weight could be between 7 -14 pounds (3.5 – 6.5kg) and the rope would be approximately 25 fathoms (45m). The hollowed-out end of the weight would hold a stick substance such as tallow or wax, which would pick up samples from the sea bed which would show whether the vessel was close to, or far away from, the shore. The leadsman would stand at the front of the vessel and cast the lead line into the sea. When it hit bottom he would note the tag marker nearest the surface of the water and call out his finding. Then he would haul it up again and examine the kind of matter that adhered to the end of the weight, whether it be sand, mud, gravel, or the colour of it. This information would be given to the ship’s helmsman or navigator and would help indicate the proximity to the land.This handheld lead is an example of early marine navigational equipment used by sailors to travel the seas to measure the depth of the water and sample the nature of the seabed. It helps to understand the history and progress made from the very basic to the sophisticated technology of today.Lead line, sounding line or depth finder. The long length of rope has a heavy lead weight attached to the end. Coloured fabric tags are tied onto the rope at regular intervals, representing different depths. The concave base of weight holds sticky substances such as tallow or beeswax, providing an adhesive surface to collect samples of sea bed like sand, shells or pebbles. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, lead line, depth finder, hand lead, sounding lin, leadsmane, navigation instrument, leadline, hand lead line -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesInstrument - Mercury Barometer and Thermometer, A.L. Franklin, Early twentieth century
A Fortin style mercury barometer from well-known Australian instrument maker, A.L.Franklin. The column of mercury is supported by the pressure of air on the free surface of the mercury in the cistern at the bottom. Its level can be adjusted to a datum using the screw at the bottom and then the height of the column can be accurately read off using a vernier scale at the top. Attached to a backing timber board with a thermometer. Thermometer made by Townson and Mercer. Metal vertical hanging eyelet.A.L.Franklin, established 1919, scientific instrument makers, Brookvale, NSW; A.L Franklin Sydney No. 457; Townson and Mercer Distributors Pty Ltd throughout Aust and NZ.;weather station, soil science, science, student outside activities, measurements, air pressure, atmospheric pressure, air temperature, artifact -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionPrototype fuel moisture meter
Bushfire behaviour is influenced by many things including temperature, relative humidity, forest type, fuel quantity and fuel dryness, topography and even slope. Wind has a dominant effect on the Rate of Spread (ROS), and also bushfire size, shape and direction. Fuel arrangement is as important as fuel quantity (tonnes/ha). Fibrous and ribbon bark, together with elevated and near-surface scrub fuels act as ladders which lead flames into the tree canopy. But the availability of fuel to burn depends largely on its moisture content. When it exceeds 20-25% not much will burn, whereas 12-15% is generally ideal for fuel reduction burning, but if the moisture content drops as low as 7-10% virtually everything will ignite, and fire behaviour becomes extreme. During the afternoon of the Ash Wednesday bushfires on 16 February 1983 fuel moisture contents were recorded at Stawell as low as 2.7%. Fine fuels like leaves and bark can rapidly absorb moisture after a shower of rain, or from the air when the Relative Humidity (RH) is high, and the temperature is low. Conversely, they can also dry out very quickly. So even though the overall fuel quantity in the forest doesn’t change, the fine fuel availability can increase rapidly from zero after rain to many tonnes per hectare as the fuel dries out. This can happen over a few hours on hot and windy days. Heavy fuels like logs on the ground take longer to dry out. Since the 1930s foresters, firefighters and researchers have been working to develop quick and reliable techniques for measuring fuel moisture content. One of the most accurate methods is slowly drying a sample of fuel in a conventional oven for 24-48 hours to remove all the moisture and measuring the weight difference, but this takes time and is not practical in the field when rapid measurements are needed. But oven drying is often used as a benchmark to compare other methods. Microwave ovens are faster but can cause uneven drying and even char the fuel. They are also not very practical for use in the field. Some mathematical models rely on weather records such as rainfall, wind speed, evaporation, cloud cover, shading, relative humidity, slope, aspect and season of the year to predict soil and fuel moisture. The Keetch-Byram Drought Index of soil dryness is the most common. But complex fuels with leaves, twigs, grass etc make the predictive models often inadequate for fine fuels. The most common technique in Victorian forests until recently was the trusty Speedy Moisture Meter. Originally developed in England during the 1920s for measuring moisture in wheat and other grains it was adapted for Australian forest fuels in the 1950s (I think). Fuel was first ground using a Spong mincer, often attached to the bullbar of a vehicle, and a small sample placed into the Speedy together with a measure of calcium carbide and then sealed. A chemical reaction created gas pressure which was read on the external dial. There were important techniques with cleaning, mincing and using the chemicals with the Speedy to give reliable readings, but it was quick, inexpensive, robust, portable and practical in the field. It was used routinely before igniting a fuel reduction burn or measuring fuel moisture differentials on slash burns. But in about 1996, Karen Chatto and Kevin Tolhurst from the Department’s Creswick Research Station developed the Wiltronics Fuel Moisture meter which measured electrical resistance. Wiltronics is an Australian owned company operating from Ballarat. The final result was a kit that was portable, accurate and could reliably measure fuel moisture contents between 3% and 200%. Although expensive, it is now widely used by fire agencies around the world which has virtually relegated the Speedy to the back cupboard.Prototype Fuel moisture meterT-H Fine Fuel Meterforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, forest measurement
