Showing 36 items
matching National%20Trust, themes: 'aboriginal culture','creative life','gold rush','kelly country','land and ecology'
-

Women's Suffrage
... solo and 18 group exhibitions since 1985. Her artworks are held in private collections nationally and internationally. 'moving landscape' was produced by Fern Smith in celebration of the 100 years of Women’s Suffrage in Victoria. The palette.... Bindi Cole is an emerging artist and photographer. In 2007 she won the Victorian Indigenous Art Photography Award and was also a finalist in the National Photographic Portrait Prize (National Portrait, Canberra). ...2008 marked the centenary of the right for Victorian non-indigenous women to vote.
During 2008 the achievements of the tenacious indigenous and non-indigenous women who forged a path through history were celebrated through an array of commemorative activities.
How the right to vote was won…
In 1891 Victorian women took to the streets, knocking door to door, in cities, towns and across the countryside in the fight for the vote.
They gathered 30,000 signatures on a petition, which was made of pages glued to sewn swathes of calico. The completed petition measured 260m long, and came to be known as the Monster Petition. The Monster Petition is a remarkable document currently housed at the Public Records Office of Victoria.
The Monster Petition was met with continuing opposition from Parliament, which rejected a total of 19 bills from 1889. Victoria had to wait another 17 years until 1908 when the Adult Suffrage Bill was passed which allowed non-indigenous Victorian women to vote.
Universal suffrage for Indigenous men and women in Australia was achieved 57 years later, in 1965.
This story gives an overview of the Women’s Suffrage movement in Victoria including key participants Vida Goldstein and Miles Franklin, and the 1891 Monster Petition. It documents commemorative activities such as the creation of the Great Petition Sculpture by artists Susan Hewitt and Penelope Lee, work by artists Bindi Cole, Louise Bufardeci, and Fern Smith, and community activities involving Kavisha Mazzella, the Dallas Neighbourhood House, the Victorian Women Vote 1908 – 2008 banner project, and much more…
Further information can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site Women's Rights
Learn more about the petition and search for your family members on the Original Monster Petition site at the Parliament of Victoria.
Educational Resources can be found on the State Library of Victoria's 'Suffragettes in the Media' site.
-
 Megan Cardamone
Megan CardamoneGanagan
... by the Maritime Museums of Australia Project Support Scheme, supported by the Australian Government through the Australian National Maritime Museum. Ganagan means ‘deep water’ in the Taungurung language. CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander ...I dreamt about weaving a net. So I did just that. I wove a net! When I started weaving my net my mind wandered back in time and I thought about how it must have been for my ancestors who lived along the mighty Murray River.
GLENDA NICHOLLS Waddi Waddi/Yorta Yorta/Ngarrinjeri
Glenda Nicholls entered her Ochre Net into the Victorian Indigenous Art Awards in 2012 and was the winner of the Koorie Heritage Trust Acquisition Award.
When Glenda’s Ochre Net came into the Trust’s care, it inspired this exhibition of artworks and stories relating to waterways and their significance to Koorie people. Powerful spiritual connections to waterways, lakes and the sea are central to Koorie life and culture.
The works shown in Ganagan Deep Water come from the Trust’s collections and represent many Koorie cultural groups from south-eastern Australia.
The Ganagan Deep Water exhibition at the Koorie Heritage Trust was sponsored by Melbourne Water.
This online component of the Ganagan exhibition is sponsored by the Maritime Museums of Australia Project Support Scheme, supported by the Australian Government through the Australian National Maritime Museum.
Ganagan means ‘deep water’ in the Taungurung language.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users of this website are warned that this story contains images of deceased persons and places that could cause sorrow.
-
 Malcolm McKinnon
Malcolm McKinnonJohn Teasdale – Chronicle of a Country Life
... produced particularly for regional viewers. John continued in this role for thirty years, until changing technology eventually made the role of 'regional stringers' obsolete. The Teasdale film collection constitutes a nationally significant record ...These little films from Victoria's Western Plains are about the actual and the everyday.
They have no hint of sensationalism in them. They are plain and utterly honest. They tell us about tractors and farming machinery. About fire and flood and snow. We glimpse Anzac Day and are touched by the irony of people remembering in a time and place few people remember or think about today. But there is no sentimentality in these films either. They are just plain good. - Martin Flanagan.
John Teasdale (1936 – 2004) was a farmer at Rupanyup in the Victorian Wimmera. He was also a keen and highly accomplished cinematographer, filming consistently for over 50 years to create a long-term record of working life on a family farm and of community life in a particular part of rural Victoria.
When television arrived in Australia in 1956, John successfully applied to the ABC to become a 'stringer' cameraman, shooting regional footage that was frequently included in state-wide news broadcasts and in segments produced particularly for regional viewers. John continued in this role for thirty years, until changing technology eventually made the role of 'regional stringers' obsolete.
The Teasdale film collection constitutes a nationally significant record of working and community life in a small Australian dry-land farming community, reflecting enormous changes in farming practices as well as transformations in the character and scale of community life in and around Rupanyup. At a time when many dry-land farming communities are actively reinventing themselves as their underlying social and economic structures change dramatically, John Teasdale’s films provide a critical point of reference and affirmation.
Artist and filmmaker Malcolm McKinnon, with the support of John Teasdale’s family, is undertaking ongoing work to interpret and celebrate this rich and resonant archive.
-
 Kate Luciano
Kate LucianoSchool Days: Education in Victoria
... and neglected children, unable to afford an education. Common and National schools charged a fee too high for Melbourne’s poorest. Dirty, ill-clothed and poor, these children were quickly excluded from respectable schools or were simply unable to sacrifice...Teaching was one of the few professions open to Australian women in the 19th century. By 1866, women made up 48 per cent of the teaching profession in Victoria. Under the National School Board (1848–62) and Board of Education (1862–72), married ...The exhibition, School Days, developed by Public Record Office Victoria and launched at Old Treasury Building in March 2015, is a history of more than 150 years of schooling in Victoria.
It is a history of the 1872 Education Act - the most significant education reform in Victoria, and a world first! It is a history of early schooling, migrant schooling, Aboriginal schools, women in education, rural education and, of course, education during war time (1914-1918).
This online exhibition is based on the physical exhibition School Days originally displayed at Old Treasury Building, 20 Spring Street, Melbourne, www.oldtreasurybuilding.org.au and curated by Kate Luciano in collaboration with Public Record Office Victoria.
-

But That's Another Story
... . Participating museums: Granya Pioneer Museum, Man From Snowy River Museum, Tallangatta & District Heritage Group, Wodonga Historical Society. Supported by: the Commonwealth Government’s Regional Arts Fund, Regional Arts Victoria, National Museum of Australia ...This innovative collaboration between community museums and local artists captures the unique living memories and rich cultural heritage of communities along the Murray River between Wodonga and Corryong.
Seven short films were created as part of the project:
Nox-All Rabbits: How do you deal with a plague of rabbits? With Nox-All. Rabbiting was a way of life in Victoria, especially during the plague of 1932. Rabbits were a source of food and income (the felt from their pelts used in Akubra hats), and thought by some to be "better than chickens".
Jim Simpson's knitted war trophy: During World War II Jim Simpson's aircraft was shot down over Germany and he became a prisoner of war at Stalag IVB. Jim's ingenuity helped to keep prisoners warm, and ultimately resulted in an extraordinary memorial.
Old time music in the blood: Nariel Creek residents have music in the blood, so much so that they've been told their accordion style is special, using all four fingers at once. The Nariel old time style of Australian traditional music and dance continues with the Nariel Creek Folk Festival.
A history of engine power: Watch out... refurbishing engines can become an addiction. The gem of this collection of over 150 engines is an 1866 Ransom Sims engine, one of only 5 in the world, which has been lovingly restored.
The Saleyards Made Wodonga: Cattle were one of the biggest industries in Wodonga, and the saleyards a focal point town, not least because plum pudding was served in the luncheon room all year round.
The Icon of Wodonga: You need more than a trickle of water to fight a fire. The Wodonga water tower was welcomed as it brought the 'luxury' of water to town, and when it was decommissioned the community rallied to prevent its demolition.
The Saw Doctor's Wagon: The 'Sharpening King' and his family travelled throughout eastern Australia sharpening knives in their 'road urchin'. A circus-like wagon, the urchin was first pulled by horses, then a Chevron truck, and finally, by a David Brown tractor.
Participating museums: Granya Pioneer Museum, Man From Snowy River Museum, Tallangatta & District Heritage Group, Wodonga Historical Society.
Supported by: the Commonwealth Government’s Regional Arts Fund, Regional Arts Victoria, National Museum of Australia, City of Wodonga, Shire of Towong, Museums Australia (Vic) and Arts Victoria. Auspice organisation: Murray Arts
-
 Open House Melbourne
Open House MelbourneModern Melbourne
... practice was also instrumental in design of the Melbourne Olympic Swimming Stadium and in setting up the National Trust in Victoria....Collaboration between Robin Boyd and Mary and Grant Featherston on the furnishings and fit out of the National Gallery of Victoria (NGV) offices. ...Modern Melbourne is a series of filmed interviews and rich archival material that documents the extraordinary lives and careers of some of our most important architects and designers including Peter McIntyre, Mary Featherston, Daryl Jackson, Graeme Gunn, Phyllis Murphy, Allan Powell and Peter Elliott.
Melbourne’s modernist architects and designers are moving into the later stages of their careers. Their influence on the city is strong and the public appreciation of their early work is growing – they have made an indelible mark on Melbourne. Much of their mid-century modernist work and latter projects are now represented on the Victorian Heritage Register.
Many of the Modern Melbourne subjects enjoyed a working relationship and a friendship with Robin Boyd, the influential architect who championed the international modernist movement in Melbourne.
-
 Wind & Sky Productions
Wind & Sky ProductionsMany Roads: Stories of the Chinese on the goldfields
... the Irish and the Welsh. In the 1850s Chinese people quickly became the largest national sub-group outside of the British on the goldfields. At the height of Chinese migration to Victoria they made up over one-fifth of the male goldfields population...: National Library of Australia. ...In the 1850s tens of thousands of Chinese people flocked to Victoria, joining people from nations around the world who came here chasing the lure of gold.
Fleeing violence, famine and poverty in their homeland Chinese goldseekers sought fortune for their families in the place they called ‘New Gold Mountain’. Chinese gold miners were discriminated against and often shunned by Europeans. Despite this they carved out lives in this strange new land.
The Chinese took many roads to the goldfields. They left markers, gardens, wells and place names, some which still remain in the landscape today. After a punitive tax was laid on ships to Victoria carrying Chinese passengers, ship captains dropped their passengers off in far away ports, leaving Chinese voyagers to walk the long way hundreds of kilometres overland to the goldfields. After 1857 the sea port of Robe in South Australia became the most popular landing point. It’s estimated 17,000 Chinese, mostly men, predominantly from Southern China, walked to Victoria from Robe following over 400kms of tracks.
At the peak migration point of the late 1850s the Chinese made up one in five of the male population in fabled gold mining towns of Victoria such as Ballarat, Bendigo, Castlemaine, Beechworth and Ararat. It was not just miners who took the perilous journey. Doctors, gardeners, artisans and business people voyaged here and contributed to Victoria’s economy, health and cultural life. As the nineteenth century wore on and successful miners and entrepreneurs returned home, the Chinese Victorian population dwindled. However some chose to settle here and Chinese culture, family life, ceremony and work ethic became a distinctive feature of many regional Victorian towns well into the twentieth century.
By the later twentieth century many of the Chinese relics, landscapes and legacy of the goldrush era were hidden or forgotten. Today we are beginning to unearth and celebrate the extent of the Chinese influence in the making of Victoria, which reaches farther back than many have realised.
-

The Apinis Loom
... Woven on a table loom, this rug was made in the late seventies when rug weaving was popular. Anita has used some yarn dyed with eucalyptus leaves. The pattern is a typically Latvian design called ‘rosepath’ and is used in the national dress ...When Latvian refugees Anna and Ervins Apinis arrived in Australia in 1950 they brought with them a loom built of wood salvaged from bombed out German ruins, along with Anna's precious notebooks full of traditional fabric designs.
Anna Strauss was born in 1913 in Latvia. She attended weaving lessons in Leipaja from 1930 to 1933 and spent hours at the nearby Ethnographic Museum recording traditional fabric designs in her notebooks.
She married Ervins Apinis, an engineer, in 1938 and they had a son but soon World War II changed their lives. Ervins was conscripted into the German army while Anna fled Latvia, finally ending up in Memmingen Displaced Persons camp in Germany in 1945. There, they were finally reunited, remaining in the camp for five years until they migrated to Australia in 1950.
When they arrived at Parkes Holding Centre in New South Wales, they were so exhausted from their long journey, they slept on a huge wooden crate containing the traditional Latvian loom they had brought with them, built of wood scavenged from bombed German ruins. This loom is now at the Immigration Museum in Melbourne.
Anna continued her weaving traditions, passing her knowledge to her daughter Anita.
-

Panorama: A question of perspective
... the landscape is often tantamount to the formation and delineation of our personal, communal, and national identities. The term panorama was first coined to describe the eponymous device invented by the British painter Robert Barker which became a popular ...TarraWarra Museum of Art is located in the picturesque Yarra Valley in Victoria, Australia.Visitors to the Museum are afforded a spectacular, resonant and panoramic experience of ‘nature’ through the north facing windows. The view stretches towards the distant Toolangi rainforest across planted vines, native bushland and farmland.
The region is surrounded by a spectacular mountain range that includes Mt Baw Baw, Mt Donna Buang, Mt Juliet, Mt Riddell and Mt Toolebewong. As these names attest, we are situated in an area of significant Indigenous history and colonisation. Tarrawarra is a Wurundjeri word that translates approximately as ‘slow moving water’ and is the name given to the area in which the Museum is located.
The Yarra Valley sunsets, soundscapes, seasonal changes, Indigenous histories, ecological vulnerabilities and environmental challenges are in a complex and ever changing entanglement. Since 2012, the Museum has explored this context through special exhibitions and commissions, forums and performances, screenings and lectures. As such, the Museum has sought to understand the complexity of our site, and with that, the broader intersections between art and landscape. Artists provide us the opportunity to ‘see’ the landscape in a different way. They imagine it, call it into being, reflect upon it, animate it, unravel its hidden histories, and expose its ecological sensitivities.
Panorama, the exhibition, was an integral part of this ongoing conversation and imaginative exploration. Our intention was not so much to write a narrative history of Australian landscape painting. Rather, it was to be attuned to the intermingling of voices, points of view, perspectives - colonial and modern, contemporary and Indigenous – that comprise the uniquely Australian persistence to unravel the ‘patter’ of nature.
As a phenomenon to which we are all very accustomed, it is easy to overlook the simple fact that for a landscape to come into being it requires a ‘point of view’, a subjective consciousness to frame a particular expanse of the natural world. As the art historian Simon Schama remarks in his landmark survey on the genre, Landscape and Memory, ‘it is our shaping perception that makes the difference between raw matter and landscape’. [i] The centrality of the viewer’s position in constructing a vista is clearly evident in terms such as ‘perspective’, ‘prospect’, and ‘view point’ which are synonymous with ‘position’, ‘expectation’, and ‘stance’. This highlights that there is always an ineluctable ideological dimension to the landscape, one that is intimately entwined with a wide range of social, economic, cultural and spiritual outlooks. Turning to the notion of the panorama, a brief survey of its conception and infiltration into everyday speech, reveals how our way of seeing the landscape is often tantamount to the formation and delineation of our personal, communal, and national identities.
The term panorama was first coined to describe the eponymous device invented by the British painter Robert Barker which became a popular diversion for scores of Londoners in the late 18th century. Consisting of a purpose built rotunda-like structure on whose cylindrical surface landscape paintings or historical scenes were displayed, ‘The Panorama’ contained a central platform upon which viewers observed the illusionistic spectacle of a sweeping 360 degree vista. With its ambitious, encyclopaedic impulse to capture and concentrate an entire panoply of elements into a singular view, it is telling that this construction would soon give rise to an adjective to describe, not only an expansive view extending in all directions, but also a complete and comprehensive survey of a subject. As the curators Jean-Roch Bouiller and Laurence Madeline argue, these different meanings convey ‘the very essence of the panoramic phenomenon: the central role of perspective, a certain appropriation of the world that follows, the feeling of dominating a situation simply due to having a wide and complete view’.[ii] Indeed, as art historian Michael Newman reveals, the whole notion of the panorama originated in military conceptions of the landscape as a battlefield, whereby strategic vantage points are key to tactical planning.[iii] Underlying its transformation into a form of popular entertainment, the panorama is rooted in a particular form of political authority based on surveying, mapping and commanding the subject of the view.
In this exhibition, the term panorama was invoked to acknowledge that ways of perceiving the landscape have their own histories which have arisen out of particular social, political and cultural contexts. As the landscape architect Anne Whiston Spirn contends: ‘In every landscape are ongoing dialogues; there is “no blank slate”; the task is to join the conversation’.[iv]However, far from claiming to present an unbroken view or a complete survey, Panorama challenged the very notion of a single, comprehensive monologue by presenting a series of works which engaged with the discourse of landscape in a diverse range of voices. Taking advantage of the tremendous depth and strength of the TarraWarra Museum of Art collection gifted by its founders Eva Besen AO and Marc Besen AC, the exhibition was staged in two parts, with a different selection of paintings exhibited in each half. Displayed in distinct groupings which explored alternative themes and concerns, Panorama highlighted the works of key artists who have redefined, expanded and interrogated the idea of the landscape in ways which suggest that it is far from settled.
Further Information
[i] Simon Schama, Landscape and Memory, New York: Vintage Books, 1996, p. 10.
[ii] Jean-Roch Bouiller and Laurence Madeline, Introductory text for the exhibition I Love Panoramas, MuCEM and the Musées d’Art et d’Histoire, Geneva, 4 November 2015 - 29 February 2016, URL: http://www.mucem.org/en/node/4022
[iii] See ‘The Art Seminar’ in Landscape Theory, (eds. Rachael Ziady DeLue and James Elkins), New York and London: Routledge, 2008, p. 130.
[iv] Anne Whiston Spirn, ‘“One with Nature”: Landscape, Language, Empathy and Imagination’ in Landscape Theory, 2008, p. 45.
-

Drought Stories
... Lindsay Smith, retired farmer and Chairman of Snape Reserve, near Little Desert National Park, talks to John Francis about the impact of drought, mineral sands mining and tree planting on river health, and how farmers have adapted to drought. ...“The social impact it has is huge, but the footy club survives," says Charlie Gillingham, mixed farmer from Murrabit.
In this story the community talks about drought: its social impact, resilience, changes to farming practises, changing weather patterns and water trading.
The median annual rainfall of the Wimmera and northern plains of Victoria is 420mm. But this median does not convey the deluges that sometimes double the figure, or the dry spells that can halve it. Like semi-arid places elsewhere, the climate cycle of this region is variable.
Aboriginal people have had thousands of years to adapt to the fluctuations, whilst recent settlers are still learning.
The introduction of the Land Act of 1869 accompanied by the high rainfall La Niña years of the early 1870s brought selectors to northern Victoria and the Wimmera. A series of dry years in the 1880s initiated storage and channel projects to assist them to stay.
Irrigation was introduced in 1886 to settle the northern plains and was expanded under closer settlement legislation. The drought years from 1895 to 1902 came to be known as the Federation Drought. Water supplies dried up completely in the El Niño years of 1914 and 1915 and people took the opportunity to picnic in the empty bed of the River Murray.
Drought hit again during World War Two, and then in the period 1965-8. The drought of 1982-3 was short but devastating. Our most recent drought, lasting more than a decade, broke late in 2010 with extensive flooding.
Policy responses have changed over the years and with the recent onset of human induced climate change, continual adaptation will be required.
In 2009, the History Council of Victoria captured resident’s experiences in the project titled Drought Stories: a spoken and visual history of the current drought in Victoria. There were two aims to the project: to create a historic record of the experience, and to strengthen community capacity in rural and regional areas through telling and listening to local stories.
Two types of collections were produced: Drought Stories Local Collections, held by historical societies, and the Drought Stories Central Archive, a selection of interviews held by the State Library of Victoria.
The History Council of Victoria believes that the project material provides a rich resource to assist researchers understand Australian society at a crucial and revealing stage of adjustment to the Australian environment.
Legislation and other land records are held at the Public Record Office Victoria.
-

Seeing the Land from an Aboriginal Canoe
... In this extended audio interview at Fyans Creek, Brambuk National Park and Cultural Centre, Halls Gap, Djab Wurrung and Jardwadjali language country, Jamie Lowe, a Djab Wurrung man, talks about the founding of the Brambuk Cultural Centre, how canoes ...This project explores the significant contribution Aboriginal people made in colonial times by guiding people and stock across the river systems of Victoria.
Before European colonisation Aboriginal people managed the place we now know as Victoria for millennia. Waterways were a big part of that management. Rivers and waterholes were part of the spiritual landscape, they were valuable sources of food and resources, and rivers were a useful way to travel. Skills such as swimming, fishing, canoe building and navigation were an important aspect of Aboriginal Victorian life.
European explorers and colonists arrived in Victoria from the 1830s onwards. The newcomers dispossessed the Aboriginal people of their land, moving swiftly to the best sites which tended to be close to water resources. At times it was a violent dispossession. There was resistance. There were massacres. People were forcibly moved from their traditional lands. This is well known. What is less well known is the ways Aboriginal people helped the newcomers understand and survive in their new environment. And Victoria’s river system was a significant part of that new environment.
To understand this world we need to cast ourselves back into the 19th century to a time before bridges and cars, where rivers were central to transport and movement of goods and people. All people who lived in this landscape needed water, but water was also dangerous. Rivers flooded. You could drown in them. And in that early period many Europeans did not know how to swim. So there was a real dilemma for the newcomers settling in Victoria – how to safely cross the rivers and use the rivers to transport stock and goods.
The newcomers benefited greatly from Aboriginal navigational skills and the Aboriginal bark canoe.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images of deceased persons and images of places that could cause sorrow.
-

SCOOT
... The Scoot – CBN (now known as Culture Victoria ) project explored the potential for location-based games to work across Melbourne’s key cultural sites: the Australian Centre for the Moving Image (ACMI), National Gallery of Victoria, Melbourne Museum ...Scoot is a location based game produced to explore mobile phone technology and as a playful way to engage with Melbourne’s key cultural institutions. Scoot was created by artist Debra Polson through the Queensland University of Technology and produced by ACMI in collaboration with various cultural partners.
The Australian Centre for the Moving Image (ACMI) is a world leading cultural institution dedicated to celebrating and exploring games. As the first cultural centre in the world to have a dedicated games lab space, ACMI has been involved in the development and research of location based games.
Such location-based gaming allows for the development of relationships between people and spaces. Participant awareness of Melbourne’s cultural resources increases as they feel more comfortable engaging in the history and identity of the city via its arts institutions.
Artist and academic Debra Polson currently lectures in the field of interaction design at the Queensland University of Technology and is a project leader at the Australasian CRC for Interaction Design (ACID). Debra has worked as an interface designer on interactive games and various other multimedia productions and continues to design location-based games.
Her research interests lie in new immersive forms of game play that blur the edges between the digital and physical realms with a particular focus on the community interactions that emerge from these experiences and the potential for new multi-modal forms of entertainment and education within those communities.
Currently researchers and artists have been experimenting with ways to apply new forms of mobile technologies combined with digital media to examine new ways for people to interact in both physical and virtual spaces. Debra Polson has been particularly interested in how effectively they enhance the relationships between location, participants and cultural activities.
-

William Barak
... Judith Ryan, senior curator of Indigenous Art in the National Gallery of Victoria, discusses the life and work of William Barak. ...Diplomat, artist, story-teller and leader, Wurundjeri (Woiwurung) man William Barak worked all his life to protect the rights and culture of his people, and to bridge the gap between settlers and the land’s original custodians.
Barak was educated at the Yarra Mission School in Narrm (Melbourne), and was a tracker in the Native Police as his father had been, before becoming ngurungaeta (clan leader). Energetic, charismatic and mild mannered, he spent much of his life at Coranderrk Reserve - a self-sufficient Aboriginal farming community in Healesville.
Barak campaigned to protect Coranderrk, worked to improve cross-cultural understanding and created many unique artworks and artifacts, leaving a rich cultural legacy for future generations.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images and voices of deceased persons, and images of places that could cause sorrow.
Further information on William Barak can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site.
-

Women on Farms
... Icon selected to represent the Glenormiston Gathering. "The object decided on was $1,000.00 in Perpetuity National Bank Account. This amount was available because our budget was for 150-200 registrants and we had [340]. This was beyond our ...In 1990, a group of rural and farming women met in Warragul for what was to be the inaugural Women on Farms Gathering.
A group of local women had developed the idea while involved in a Women on Farms Skill Course. It was to prove inspirational, and the gatherings have been held annually ever since, throughout regional Victoria.
The Women on Farms Gathering provides a unique opportunity for women to network, increase their skills base in farming and business practices, share their stories and experience a wonderful sense of support, particularly crucial due to the shocking rural crises of the last decade. Importantly, the gatherings help promote and establish the notion of rural women as farmers, business women and community leaders.
The relationship between Museums Victoria and the Women on Farms Gathering is a model of museums working with living history.
-
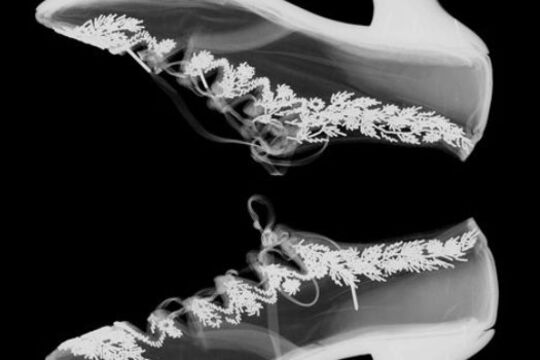
The Fashion Detective
... This Bodice, c.1885, was presented to the National Gallery of Victoria by Miss Bostock in 1963 and attributed to Worth by virtue of an incomplete label attached to the inner waistband. Today, however, suspicions about this attribution have arisen ...The NGV’s fashion archive contains countless works about which we know little.
We don’t know who made them, who wore them, when or why, or indeed, what happened in them! For the curator, such works are endlessly intriguing; a form of ‘material evidence’ to examine and explicate.
In 2014, the NGV’s Fashion Detective exhibition took a selection of unattributed nineteenth century garments and accessories from the Australian fashion and textiles collection as the starting point for a series of investigations. Using forensics and fiction as alternate interpretative methods, the exhibition considered the detective work that curators and conservators do and where this can lead, as well as the role of storytelling in making visible the social life of clothes.
From fakes and forgeries to poisonous dyes, concealed clues and mysterious marks to missing persons, Fashion Detective was a series of ‘cases’ that each followed a different path of analysis.
Some relied on empirical study and science to reach conclusions, others were purposefully speculative - the inspired hypothesis of leading crime writers Garry Disher, Kerry Greenwood, Sulari Gentill and Lili Wilkinson.
A playful exhibition about modes of enquiry, Fashion Detective considered the different ways in which we can decode objects in order to reveal what is normally concealed, and challenged the visitor to reappraise what they see and what they know.
-

Felon Families
... Felon Families: Stories of women prisoners and their families Diane Gardiner Old Melbourne Gaol National Trust of Australia (Victoria) Life in the colony of Victoria during the nineteenth century could be fraught with difficulties for families ...Stories of Women Prisoners and their Families
"Life in the colony of Victoria during the 19th century could be fraught with difficulties for families and, particularly, for women. The problems they encountered in hard times were exacerbated by distance from the support and friendship of their extended families. If women found themselves unable to cope, the repercussions for the whole family could be tragic.
The stories and images of women who passed through Victoria’s penal system in the 19th century include: Elizabeth Scott, a young girl forced into marriage, living in an isolated part of the country, and the first woman hanged in Victoria; the baby farmer Frances Knorr; Martha Needle who's story is unusual because her crimes arose not out of the severe circumstances of colonial Victoria but from universal, age-old family and personal dysfunction; Emma Williams a single mother who drowned her baby son and brought the Champion newspaper to claim in October 1895 that her case would "exhibit Victoria to the world as the very lowest and most degraded of all civilised communities"; and Janet Dibden who wrote poetry while imprisoned at the Old Melbourne Gaol. It also includes Ellen Kelly the mother of bushranger Ned Kelly, who told her son "Die brave, die like a Kelly" before he was hanged."
The text above has been abstracted from an essay Felon families: Stories of women prisoners and their families written by Diane Gardiner for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The full text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
