Showing 25 items
matching John%20Alexander, themes: 'built environment','kelly country','land and ecology','sporting life'
-
 Brian Allison
Brian AllisonJohn Harry Grainger
... John Harry Grainger...Life of John Harry Grainger...John Grainger was born on 30 November 1854 at 1 New Street, Westminster. His parents were John Grainger, Master Tailor and Mary Ann Grainger, née Parsons. Little is known about Grainger’s early life prior to emigrating to Australia. Winifred...Architect and Civil Engineer John Harry Grainger was a creative figure, largely overlooked by history. He receives a brief mention in the much-examined life story of his famous son, the composer and pianist Percy Grainger, where he is depicted ...Architect and Civil Engineer
John Harry Grainger was a creative figure, largely overlooked by history. He receives a brief mention in the much-examined life story of his famous son, the composer and pianist Percy Grainger, where he is depicted as a proud but ineffectual father.
Grainger's prolific output as an architect and his extraordinary talents for bridge building have not yet received due recognition.
The material presented here is sourced from the Grainger Museum Collection at the University of Melbourne. Additional material is held in the Public Record Office of Victoria and in the State Library of Victoria collections.
-
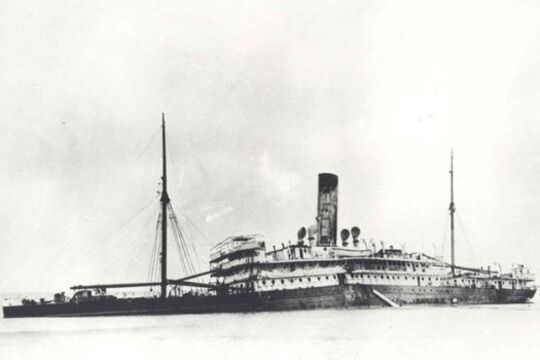
Tales from the deep
... John Black Oral History...Essay: John Black Oral History...This is the transcript of an interview conducted with John Black by Kate Fielding....John Black is one of Australia’s early underwater explorers. He began his career in abalone diving in 1951 and became involved in the new and developing sport of scuba diving in the 1960s....As the rest of the world became enthralled in the exciting and mysterious world of scuba diving - devouring the anecdotes of early adventurers such as Jacques-Yves Cousteau and Lloyd Bridges - Victoria’s own pioneers were hard at work. John Black ...As the rest of the world became enthralled in the exciting and mysterious world of scuba diving - devouring the anecdotes of early adventurers such as Jacques-Yves Cousteau and Lloyd Bridges - Victoria’s own pioneers were hard at work.
John Black is one of Australia’s early underwater explorers. He began his career in abalone diving in 1951 and became involved in the new and developing sport of scuba diving in the 1960s.
At the time, specialty equipment was hard to get so John and his colleagues used the DIY attitude to create boats out of wooden planks and Victa lawnmower engines and breathing equipment using hoses and hotel CO2 gas tanks. With these extraordinary apparatus they were among the first to enter the pristine underwater wilderness of the Gippsland coast.
John’s stories describe the evolution of diving gear, the triumphs and near-misses of working in a burgeoning field and the excitement of being the first to dive on the remains of Victoria’s spectacular shipwrecks.
John was interviewed as part of the Heritage Victoria East Gippsland Oral Histories project in 2003. This story includes audio extracts from his interview and a transcript of his full interview.
-
 Malcolm McKinnon
Malcolm McKinnonJohn Teasdale – Chronicle of a Country Life
... John Teasdale – Chronicle of a Country Life.... We glimpse Anzac Day and are touched by the irony of people remembering in a time and place few people remember or think about today. But there is no sentimentality in these films either. They are just plain good. - Martin Flanagan. John Teasdale ...These little films from Victoria's Western Plains are about the actual and the everyday.
They have no hint of sensationalism in them. They are plain and utterly honest. They tell us about tractors and farming machinery. About fire and flood and snow. We glimpse Anzac Day and are touched by the irony of people remembering in a time and place few people remember or think about today. But there is no sentimentality in these films either. They are just plain good. - Martin Flanagan.
John Teasdale (1936 – 2004) was a farmer at Rupanyup in the Victorian Wimmera. He was also a keen and highly accomplished cinematographer, filming consistently for over 50 years to create a long-term record of working life on a family farm and of community life in a particular part of rural Victoria.
When television arrived in Australia in 1956, John successfully applied to the ABC to become a 'stringer' cameraman, shooting regional footage that was frequently included in state-wide news broadcasts and in segments produced particularly for regional viewers. John continued in this role for thirty years, until changing technology eventually made the role of 'regional stringers' obsolete.
The Teasdale film collection constitutes a nationally significant record of working and community life in a small Australian dry-land farming community, reflecting enormous changes in farming practices as well as transformations in the character and scale of community life in and around Rupanyup. At a time when many dry-land farming communities are actively reinventing themselves as their underlying social and economic structures change dramatically, John Teasdale’s films provide a critical point of reference and affirmation.
Artist and filmmaker Malcolm McKinnon, with the support of John Teasdale’s family, is undertaking ongoing work to interpret and celebrate this rich and resonant archive.
-

Young and Jackson Hotel
... John Batman... and old, and only those of vicious proclivities." John Russell (7 May, 1883)...The Young and Jackson Hotel, built in the 1850s, is one of Australia's most well known hotels. It was built, as the Princes Bridge Hotel, on part of an allotment originally purchased by John Batman in 1837. Young and Jackson were both born in Dublin ...The Young and Jackson Hotel, built in the 1850s, is one of Australia's most well known hotels. It was built, as the Princes Bridge Hotel, on part of an allotment originally purchased by John Batman in 1837.
Young and Jackson were both born in Dublin, and "chummed together" to New Zealand chasing the Otago gold deposits in 1861. It is not known when they came to Victoria, but they purchased the lease on the Princes Bridge Hotel in 1875.
-

St Paul's Cathedral
... John Barr..., the towers he designed (but were not built at the time) were shafted for a new design by Australian architect John Barr. ...Refusing to set foot in the colony, the eminent Gothic Revivalist architect William Butterfield resorted to sending extremely detailed architectural drawings and plans of St Paul's Cathedral to Australia.
He even produced life-size drawings of columns, window tracery and other features, to ensure the antipodeans could get nothing wrong.
In the end however, he was defeated by distance, and St Paul's was completed by the Australian firm Reed, Henderson and Smart, and later, in the 1930s, the towers he designed (but were not built at the time) were shafted for a new design by Australian architect John Barr.
-
 Museums Victoria
Museums VictoriaTime Flies in Museum Collections: Ornithology in Victoria
... Lithograph: Australian Pelican, Pelecanus conspicillatus from 'Birds of Australia' by John Gould, Vol. 7, Plate 74...Early immigrants to Victoria included highly-skilled amateur naturalists. One such man was John Cotton, scientist, artist and poet. Cotton’s manuscripts and illustrations record a snapshot of birdlife in Victoria just as it was about... charts the history of amateur and professional ornithology in Victoria. Whilst the big names such as John Gould (1804–1881), are represented, the very local, independent bird observers such as John Cotton (1801-1849) and Archibald James Campbell (1853 ...Natural science collections are vast treasure troves of biological data which inform current research and conservation.
Alongside bird skins, nests, eggs and DNA samples sits a magnificent collection of rare books, illustrations and images which charts the history of amateur and professional ornithology in Victoria.
Whilst the big names such as John Gould (1804–1881), are represented, the very local, independent bird observers such as John Cotton (1801-1849) and Archibald James Campbell (1853–1929) made some of the most enduring contributions.
The collections also document the bird observers themselves; their work in the field, building collections, their efforts to publish and the growth of their ornithological networks. Captured within records are changes in ornithological methods, particularly the way data is captured and published.
However the data itself remains as relevant today as it did when first recorded, 160 years of collecting gives us a long-term picture of birdlife in Victoria through space and time.
-

Burke and Wills: Have Camels Will Travel
... Document: Agreement between George Landells, John Driscoll, John Drakeford and John King...Agreement between George Landells and John Driscoll, John Drakeford and John King that the three men will act as camel attendants on the passage between India and Australia, in exchange for free passage on the voyage. John King and John Drakeford.... Partly in response to his fame, Landells was appointed second in command of the Burke and Wills expedition. He was also appointed officer in charge of the camels. Landells recruited John Drakeford and John King, who had helped him bring the animals from ...Dromedary camels were introduced to Australia in 1840. The first significant shipment, however, was made to service the Burke and Wills expedition, which was the first exploring party to use camels, as well as horses, for transporting supplies.
In 1858, George Landells, who had worked as a horse trader in India, wrote to the Victorian Government explaining how the camel was ideally suited to the Australian landscape. He offered to travel to India and purchase camels on behalf of the Victorian government for use in exploration, and as the basis of a breeding stud. The government’s Board of Science and Zoological Gardens Committee agreed that the camel would be useful on the Australian continent, and Landells was authorised to borrow money from the Indian Government and make the purchase.
Landells traveled through India, Pakistan and Afghanistan to source the animals, engaging eight camel drivers to assist him on the journey from Karachi to Melbourne in December 1859, arriving mid-June 1860.
He was hailed for his travels through the ‘very unsettled’ lands by the English Scindian Newspaper, and similarly lauded in Melbourne where the ‘exotic’ animals caused a sensation, as did their handlers, identified variously as Indians, Sepoys, and Malays.
Partly in response to his fame, Landells was appointed second in command of the Burke and Wills expedition. He was also appointed officer in charge of the camels.
Landells recruited John Drakeford and John King, who had helped him bring the animals from Karachi to Melbourne, and four of the eight handlers: Samla (described by Becker as a Hindu), Dost Mahomet (or Botan), from Guznee; Esau Khan (or Hissand or Isaah), Belooch, who came from Mahadpoor in the Punjab, and another man from Kelat.
The expedition party departed Melbourne with 26 camels. As the expedition progressed, Landells and Burke disagreed over their treatment and Landells resigned in Menindee.
Four of the 26 camels were left at Menindee. Dost Mahomet stayed with 16 at the Coopers Creek depot. Burke and Wills took six animals with them on their trek to the Gulf and John King, travelled with them, to care for. Some of the animals strayed or were lost, others were abandoned. Burke, Wills, Charlie Gray and John King ate the last of them, as they struggled back from the Gulf of Carpentaria.
However the Burke and Wills Expedition was not the end of the story. Camels had proved their worth in negotiating the harsh and dry Australian interior and camels became an increasingly important form of transport in the Australian inland. Between 1870 and 1900, over 15,000 camels and 2000 cameleers were brought to Australia. The cameleers were commonly known as “Afghans” although small in number, they made a vital contribution to Australia’s exploration and development.
Feral camels now roam across outback Australia. In response, markets for live camels and camel meat have developed. It is more than likely that the descendents of Landells’ camels are among those that now roam the Australian continent.
-
 Carissa Goudey
Carissa GoudeyMaking & Using Transport on the Goldfields
... John McCartney ...During the nineteenth century, horse-drawn vehicles were an essential part of life in rural Victoria.
In Ballarat, local coachbuilding firms assisted with the town’s growth in more ways than providing passage to the diggings. Horse-drawn vehicles were vital for the delivery of goods, responding to emergencies and often symbolised one’s social standing.
The Gold Rush ushered in a period of incredible growth for colonial Victoria. Ballarat’s escalating population and burgeoning industries highlighted the need for horse-drawn transport – not only for getting to the diggings, but also for delivering goods and building material, responding to emergencies and performing significant social rituals.
In the early nineteenth century, the goldfields were dominated by vehicles either imported from England or English-style vehicles built locally. Coaches, carriages and carts were typically constructed part-by-part, one at a time. As a result, each vehicle was highly unique.
By the mid-1850s, the American coachbuilding tradition had arrived on the goldfields. The American method, which had been developing since the 1840s, relied on mass-produced, ready-made components. In comparison to English designs, American coaches were known to be more reliable for goldfields travel; they were primed for long-distance journeys on rough terrain and were less likely to tip over.
As the nineteenth century progressed, a plethora of English, American and European vehicles populated Ballarat – both locally made and imported. The abundance of coaches, carriages and carts – and their value to the Ballarat community – can be seen in photographs and objects catalogued here on Victorian Collections.
-
 State Library Victoria / Public Records Office Victoria
State Library Victoria / Public Records Office VictoriaNed Kelly
... john kelly ...Ned Kelly, the most famous of our 'Wild Colonial Boys', was born in 1855.
He was raised in harsh poverty in Northern Victoria, and became an expert bushman; by his teens he had developed a reputation as a bushranger. Kelly and his 'gang' were proclaimed outlaws when they killed three policemen, accounts of which differ.
So began the prolonged hunt, which ended with Kelly's capture in Glenrowan, in iconic home-made armour made from plough parts. Ned Kelly was executed in 1880, hanged in the Melbourne Goal by order of Sir Redmond Barry. Barry was instrumental in the foundation of the State Library of Victoria where, perhaps ironically, Kelly's "manifesto", the Jerilderie letter and the armour are held.
Kelly's Irish heritage, his contempt for and success in humilating the authorities, his harsh and some say unfair treatment, his bad luck and his daring and notoriety have ensured Kelly's place as folk hero.
View videos and other Kelly artefacts from the State Library of Victoria Ergo site:
Capture of the Kelly Gang
Ned Kelly's Armour
The Life of Ellen Kelly, Ned Kelly's mother
The Jerilderie Letter
Ned Kelly's death mask
-
 Megan Cardamone
Megan CardamoneTennis in Pictures
... John Alexander ...Today, for many Australians, especially Melburnians, watching and attending the tennis, and supporting favourite players is a popular aspect of summer.
What was it like to be a top player in times past and how has every aspect of tennis - the travel, the venues, the people, the social context - changed over time?
Tennis Australia collects and preserves items of tennis heritage as a way of safekeeping the history of Australian tennis. Among its holdings are a large number of historical images. It also fosters relationships with champions of the past so that emerging players can learn from their experience.
In 2015, two of these champions - Thelma Coyne Long and Neale Fraser - shared their memories of significant images in the Tennis Australia collection.
The result is this story: Tennis In Pictures, in which two tennis greats reminisce and share in a very personal way their memories about fascinating moments in our sporting history.
Thelma Coyne Long recalls the overseas trip in 1938 with three other female team-mates, the long ship journey, the excitement and novelty of travel and the confining attitudes towards women and female athletes in 1930s Australia.
As he examines historic Davis Cup images, Neale Fraser is reminded of some of his greatest team and individual triumphs and fondest memories from a lifelong tennis career.
-

The Ross Sea Party
... Photograph: John King Davis, 'John Lachlan Cope Standing on the Deck of a Ship', c. 1907 - 1931..., Australian and New Zealand governments agreed to fund the rescue. In January 1917 the Aurora re-entered the Ross Sea under the command of John King Davis and with Ernest Shackleton aboard. On January 10 the 7 remaining men of the Ross Sea stores party...Andrew Keith Jack notes John King Davis as the compiler of this photograph. Davis (1884-1967) was a notable Antarctic navigator and Captain of the Aurora on the January 1917 relief mission that rescued the Ross Sea Party. John Lachlan Cope was born... in the process. The seven survivors (including Jack, Richards and Gaze) were eventually rescued in 1917 by Shackleton and John King Davis. In total, the party’s sledging journeys encompassed 169 days, greater than any journey by Shackleton, Robert Scott, or Roald ...As Shackleton’s ambitious 'Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition' of 1914 foundered, the Ross Sea party, responsible for laying down crucial supplies, continued unaware, making epic sledging journeys across Antarctica, to lay stores for an expedition that would never arrive.
In 1914 Ernest Shackleton advertised for men to join the Ross Sea Party which would lay supply deposits for his 'Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition'. Three Victorians were selected for the ten-man shore party: Andrew Keith Jack (a physicist), Richard Walter Richards (a physics teacher from Bendigo), and Irvine Owen Gaze (a friend of Jack’s).
The Ross Sea party commenced laying supplies in 1915 unaware that Shackleton’s boat Endurance had been frozen in ice and subsequently torn apart on the opposite side of the continent (leading to Shackleton’s remarkable crossing of South Georgia in order to save his men). Thinking that Shackleton’s life depended on them, the Ross Sea Party continued their treacherous work, with three of the men perishing in the process. The seven survivors (including Jack, Richards and Gaze) were eventually rescued in 1917 by Shackleton and John King Davis.
In total, the party’s sledging journeys encompassed 169 days, greater than any journey by Shackleton, Robert Scott, or Roald Amundsen – an extraordinary achievement.
Jack, Gaze and others in the party took striking photographs during their stay. Jack later compiled the hand coloured glass lantern slides, which along with his diaries, are housed at the State Library of Victoria.
-
 Open House Melbourne
Open House MelbourneModern Melbourne
... Photograph: John and Phyllis Murphy's wedding day...Phyllis Murphy was one of two female graduates of architecture in 1949 at the University of Melbourne. She launched a practice with her husband John Murphy and the firm quickly became known for their interpretation of modernist design. The Murphy...Architects Peter McIntyre, Kevin Borland, John and Phyllis Murphy and their engineer Bill Irwin won the right to design and build the Olympic Swimming Stadium in a competition - due to their innovative and economical design. ...Modern Melbourne is a series of filmed interviews and rich archival material that documents the extraordinary lives and careers of some of our most important architects and designers including Peter McIntyre, Mary Featherston, Daryl Jackson, Graeme Gunn, Phyllis Murphy, Allan Powell and Peter Elliott.
Melbourne’s modernist architects and designers are moving into the later stages of their careers. Their influence on the city is strong and the public appreciation of their early work is growing – they have made an indelible mark on Melbourne. Much of their mid-century modernist work and latter projects are now represented on the Victorian Heritage Register.
Many of the Modern Melbourne subjects enjoyed a working relationship and a friendship with Robin Boyd, the influential architect who championed the international modernist movement in Melbourne.
-

Drought Stories
... Audio: John Gledhill talks about the impact of drought and water trading on farmers in northern Victoria...David Eltringham, Horsham Rural City Technical Services Manager, talks to John Francis about the impacts of ongoing drought in the Shire. ...“The social impact it has is huge, but the footy club survives," says Charlie Gillingham, mixed farmer from Murrabit.
In this story the community talks about drought: its social impact, resilience, changes to farming practises, changing weather patterns and water trading.
The median annual rainfall of the Wimmera and northern plains of Victoria is 420mm. But this median does not convey the deluges that sometimes double the figure, or the dry spells that can halve it. Like semi-arid places elsewhere, the climate cycle of this region is variable.
Aboriginal people have had thousands of years to adapt to the fluctuations, whilst recent settlers are still learning.
The introduction of the Land Act of 1869 accompanied by the high rainfall La Niña years of the early 1870s brought selectors to northern Victoria and the Wimmera. A series of dry years in the 1880s initiated storage and channel projects to assist them to stay.
Irrigation was introduced in 1886 to settle the northern plains and was expanded under closer settlement legislation. The drought years from 1895 to 1902 came to be known as the Federation Drought. Water supplies dried up completely in the El Niño years of 1914 and 1915 and people took the opportunity to picnic in the empty bed of the River Murray.
Drought hit again during World War Two, and then in the period 1965-8. The drought of 1982-3 was short but devastating. Our most recent drought, lasting more than a decade, broke late in 2010 with extensive flooding.
Policy responses have changed over the years and with the recent onset of human induced climate change, continual adaptation will be required.
In 2009, the History Council of Victoria captured resident’s experiences in the project titled Drought Stories: a spoken and visual history of the current drought in Victoria. There were two aims to the project: to create a historic record of the experience, and to strengthen community capacity in rural and regional areas through telling and listening to local stories.
Two types of collections were produced: Drought Stories Local Collections, held by historical societies, and the Drought Stories Central Archive, a selection of interviews held by the State Library of Victoria.
The History Council of Victoria believes that the project material provides a rich resource to assist researchers understand Australian society at a crucial and revealing stage of adjustment to the Australian environment.
Legislation and other land records are held at the Public Record Office Victoria.
-
 Amy Tsilemanis
Amy TsilemanisTalking Shop: Ballarat in Business & City Life at Ballaarat Mechanics' Institute
... in this story.This exhibition was curated by Amy Tsilemanis at the BMI who worked with artists Pauline O'Shannessy-Dowling and Margie Balazic, collector John Kerr and Ballarat businesses, council, and schools to create a 'generative' exhibition where material ...Between January and April 2019, the Ballaarat Mechanics' Institute hosted the exhibition Talking Shop, exploring a world of Peters ice cream cones, milk bars, vintage advertising, historic photographs and ephemera.
This nostalgia was complemented by contemporary photographs and creative responses exploring Ballarat’s shops and businesses. Community events throughout the exhibition invited the people of Ballarat to contribute their images and memories to the BMI collection, and are shared here in this story.
This exhibition was curated by Amy Tsilemanis at the BMI who worked with artists Pauline O'Shannessy-Dowling and Margie Balazic, collector John Kerr and Ballarat businesses, council, and schools to create a 'generative' exhibition where material and collaborations could grow.
Wanting to know more about Ballarat’s booming business history? Take a digital tour of the exhibition here: https://invictoria.com.au/talking-shop-exhibition
-

Seeing the Land from an Aboriginal Canoe
... Photograph: John Henry Harvey, 'Smith’s Crossing, Yea River, Toolangi', c. 1875-1938... of John Hunter Kerr’s station in 1849 shows the ute of the day – a horse and cart. John Hunter Kerr was an early photographer and a pastoralist, taking property on the Loddon Plains near Boort, near the border of Dja Dja Wurrung and Wemba Wemba language ...This project explores the significant contribution Aboriginal people made in colonial times by guiding people and stock across the river systems of Victoria.
Before European colonisation Aboriginal people managed the place we now know as Victoria for millennia. Waterways were a big part of that management. Rivers and waterholes were part of the spiritual landscape, they were valuable sources of food and resources, and rivers were a useful way to travel. Skills such as swimming, fishing, canoe building and navigation were an important aspect of Aboriginal Victorian life.
European explorers and colonists arrived in Victoria from the 1830s onwards. The newcomers dispossessed the Aboriginal people of their land, moving swiftly to the best sites which tended to be close to water resources. At times it was a violent dispossession. There was resistance. There were massacres. People were forcibly moved from their traditional lands. This is well known. What is less well known is the ways Aboriginal people helped the newcomers understand and survive in their new environment. And Victoria’s river system was a significant part of that new environment.
To understand this world we need to cast ourselves back into the 19th century to a time before bridges and cars, where rivers were central to transport and movement of goods and people. All people who lived in this landscape needed water, but water was also dangerous. Rivers flooded. You could drown in them. And in that early period many Europeans did not know how to swim. So there was a real dilemma for the newcomers settling in Victoria – how to safely cross the rivers and use the rivers to transport stock and goods.
The newcomers benefited greatly from Aboriginal navigational skills and the Aboriginal bark canoe.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images of deceased persons and images of places that could cause sorrow.
-
 Wind & Sky Productions
Wind & Sky ProductionsMany Roads: Stories of the Chinese on the goldfields
... Drawing: John Alloo's Chinese Restaurant ...In the 1850s tens of thousands of Chinese people flocked to Victoria, joining people from nations around the world who came here chasing the lure of gold.
Fleeing violence, famine and poverty in their homeland Chinese goldseekers sought fortune for their families in the place they called ‘New Gold Mountain’. Chinese gold miners were discriminated against and often shunned by Europeans. Despite this they carved out lives in this strange new land.
The Chinese took many roads to the goldfields. They left markers, gardens, wells and place names, some which still remain in the landscape today. After a punitive tax was laid on ships to Victoria carrying Chinese passengers, ship captains dropped their passengers off in far away ports, leaving Chinese voyagers to walk the long way hundreds of kilometres overland to the goldfields. After 1857 the sea port of Robe in South Australia became the most popular landing point. It’s estimated 17,000 Chinese, mostly men, predominantly from Southern China, walked to Victoria from Robe following over 400kms of tracks.
At the peak migration point of the late 1850s the Chinese made up one in five of the male population in fabled gold mining towns of Victoria such as Ballarat, Bendigo, Castlemaine, Beechworth and Ararat. It was not just miners who took the perilous journey. Doctors, gardeners, artisans and business people voyaged here and contributed to Victoria’s economy, health and cultural life. As the nineteenth century wore on and successful miners and entrepreneurs returned home, the Chinese Victorian population dwindled. However some chose to settle here and Chinese culture, family life, ceremony and work ethic became a distinctive feature of many regional Victorian towns well into the twentieth century.
By the later twentieth century many of the Chinese relics, landscapes and legacy of the goldrush era were hidden or forgotten. Today we are beginning to unearth and celebrate the extent of the Chinese influence in the making of Victoria, which reaches farther back than many have realised.
