Showing 27 items
matching Yarra%20Ranges%20Regional%20Museum, themes: 'a diverse state','built environment','creative life','family histories','land and ecology','sporting life'
-
 Isaac Douglas Hermann & Heather Arnold
Isaac Douglas Hermann & Heather ArnoldCarlo Catani: An engineering star over Victoria
... A Straighter Yarra...Map: Yarra River improvements... and shallow Yarra.... line between Caulfield and South Yarra and so the family moved to Wyndham, 39 Blessington Street in St Kilda. Catani died on July 20, 1918 at the age of 66 and Kate died August 6, 1925, aged 68. They are both buried at the Brighton General Cemetery ...After more than forty-one years of public service that never ended with his retirement, through surveying and direct design, contracting, supervision, and collaborative approaches, perhaps more than any other single figure, Carlo Catani re-scaped not only parts of Melbourne, but extensive swathes of Victoria ‘from Portland to Mallacoota’, opening up swamplands to farming, bringing access to beauty spots, establishing new townships, and the roads to get us there.
-

Moomba
... Yarra River...Moomba is one of Australia's most enduring festivals, first held in 1955. It is held every Labour Day weekend and can feature a float parade, stalls, fireworks and water sports on the Yarra. One of the more idiosyncratic events is the Birdman Rally ...Moomba is one of Australia's most enduring festivals, first held in 1955.
It is held every Labour Day weekend and can feature a float parade, stalls, fireworks and water sports on the Yarra. One of the more idiosyncratic events is the Birdman Rally, where competitors jump off a 4m platform into the Yarra, wearing homemade "wings".
Popular rumour holds that Moomba's naming was the result of a subtle Aboriginal joke, and that while organisers believed Moomba to signify, "let's get together and have good time", the true meaning of the word is rather more salacious.
-

William Barak
... Yarra Mission School...When farmer John Batman first rowed down the Yarra River (the Birrarung), he was excited to see acres of lush green land – ideally suited, he thought, to farming. In 1835, at the age of 12 years, Barak witnessed the first and only bid for a '... at the Yarra Mission School in Narrm (Melbourne), and was a tracker in the Native Police as his father had been, before becoming ngurungaeta (clan leader). Energetic, charismatic and mild mannered, he spent much of his life at Coranderrk Reserve - a self ...Diplomat, artist, story-teller and leader, Wurundjeri (Woiwurung) man William Barak worked all his life to protect the rights and culture of his people, and to bridge the gap between settlers and the land’s original custodians.
Barak was educated at the Yarra Mission School in Narrm (Melbourne), and was a tracker in the Native Police as his father had been, before becoming ngurungaeta (clan leader). Energetic, charismatic and mild mannered, he spent much of his life at Coranderrk Reserve - a self-sufficient Aboriginal farming community in Healesville.
Barak campaigned to protect Coranderrk, worked to improve cross-cultural understanding and created many unique artworks and artifacts, leaving a rich cultural legacy for future generations.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images and voices of deceased persons, and images of places that could cause sorrow.
Further information on William Barak can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site.
-

Early Photographs - Landscapes and Streetscapes
... Yarra River... waterfalls, to the already altered Yarra River, to the dusty corner of Spring and Bourke Streets. Further material can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site: Early Street Names of Melbourne ...Antoine Fauchery and Richard Daintree's images offer rare fine quality images of early Victorian landscapes and Melbourne streets of the late 1850s.
Antoine Fauchery and Richard Daintree's Sun Pictures of Victoria was the first photographic album of Australian scenes made available for sale to the public.
Using the latest in photographic techniques of the time, the Fauchery-Daintree images offer rare fine quality images of early Victorian landscapes and Melbourne streets of the late 1850s; from pristine waterfalls, to the already altered Yarra River, to the dusty corner of Spring and Bourke Streets.
Further material can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site: Early Street Names of Melbourne
-

Melbourne and Smellbourne
... Yarra River..., but there was still no sewerage system. An appalling stench wafted from the many cesspits and open drains. 'Nightsoil' (as human waste was politely referred to) polluted the streets and ran into the Yarra. Nightsoil collectors frequently dumped their loads on public ...Over the last 150 years Victoria has experienced a number of landmark capital works and landscaping projects in response to its changing economic, environmental and cultural relationship to water. The sewerage system that we take for granted today had to be built from scratch.
For all the grandeur that was 'Marvellous Melbourne' in the 1880s, the city was nicknamed 'Smellbourne', and for good reason. The building of Yan Yean Reservoir in the 1850s had ensured the availability of fresh water, but there was still no sewerage system.
An appalling stench wafted from the many cesspits and open drains. 'Nightsoil' (as human waste was politely referred to) polluted the streets and ran into the Yarra. Nightsoil collectors frequently dumped their loads on public roads. Ignorance and neglect of the hygienic disposal of human waste had devastating results at this time when hundreds died in a savage outbreak of typhoid.
Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works
In 1891 the Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was created. It immediately began plans to build an underground drainage system linked to a pumping station at Spotswood, located on the western banks of the mouth of the Yarra River. The sewage flowed by gravity to Spotswood, where it was then pumped to the Werribee Treatment Farm.
Spotswood Pumping Station
Spotswood Pumping Station built to pump Melbourne's sewage to Werribee, was finished in 1897. At the pumping station, steam engines (later replaced by electrical ones) worked to pump the sewage up a rising main to join the major sewer outfall at the head of the pumping mains near Millers Road at Brooklyn. The outfall sewer then carried the sewage to the Werribee Treatment Farm where it was purified and discharged into the sea.
Werribee Farm
Werribee was the perfect site for the MMBW's new sewage farm. The farm was the Board's most important project, and one of the largest public works undertaken in Australia in the nineteenth century.
Land at Werribee was cheaper than at Mordialloc - the other site considered. Rainfall was low compared with the rest of Melbourne, which meant the land would adapt well to irrigation. Werribee was also 9 miles (14.4 KM) away from the nearest boundary of the metropolitan district (Williamstown), and 24 miles (38.6 KM) away from the influential and well-to-do suburb of Brighton. The Chirnside family sold 8,857 acres (3.2 hectares) to the Board for 17 pounds per acre.
The Earl of Hopetoun, Governor of Victoria, turned the first sod of earth in a ceremony on May 1892, which marked the beginning of the building of the outfall sewer near Werribee.
Connection!
On 5 February 1898, a ceremony marked the official connection of Melbourne to the new sewerage system. Guests - politicians, board members, city councillors and federal delegates - boarded a steamer to watch the Governor, Lord Brassey, raise the penstock (the partition between the smaller and larger sewers) at the Australian Wharf. They then visited the pumping station at Spotswood and the sewage farm at Werribee. Horses and carts conveyed the 180 guests around the farm.
After lunch and toasts, many of which looked forward to the future of a federated Australia, MMBW Chairman Mr Fitzgibbon proudly declared it "was not a question of how much the scheme was going to cost, but how much it was going to save in the lives of the citizens." Before the work was completed he hoped to see those puny punsters and petty wits who spoke of Melbourne as Marvellous Smellbourne constrained to speak of her as one of the sweetest and healthiest cities of the world.
-

William Buckley
... Yarra River... accounts of his life. Many of the images of the first European settlement on the banks of the Yarra River include Buckley as a pale giant clad in animal skins, approaching the newcomers. His name lives on in Australian slang with the ironic saying “you’ve ...After convict William Buckley’s escape from a Victorian settlement he was discovered by the Wathaurang people who thought this pale, 198cm giant carrying a spear was the ghost of one of their leaders.
Buckley had arrived at Port Phillip from England in 1803 with about 300 soldiers, settlers and convicts after being sentenced to transportation for life. Before the Port Phillip and Sullivan Bay (Victoria’s first official European settlement) settlement was abandoned, Buckley escaped. He wandered alone for weeks before he was befriended by the Wathaurang people.
Over the next 32 years Buckley lived with the Wathaurang, learnt their language and customs, married and had a daughter. In 1835 he finally emerged to meet Batman’s colonising party and tried to work as an intermediary between settlers and aborigines, but felt he wasn’t trusted by either.
His name lives on in Australian slang with the ironic saying “you’ve got Buckley’s chance” or “Buckley’s hope”.
Further material can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site:-
William Buckley's Escape
Buckley and the Aborigines
Buckley's return to European life
-
 Lauren McAlary
Lauren McAlaryCollecting Fire: A new kind of practice
... Yarra Ranges Regional Museum ...The fires of February 2009 left an indelible mark on the histories of Victoria’s community collecting organisations; whether through blackened ash markings or by the absence of once cherished objects and ephemera.
This exploration of Victoria’s collecting response to the Black Saturday bushfires is inspired by Liza Dale‐Hallett, Rebecca Carland and Peg Fraser’s reflections on the Victorian Bushfires Collection project, in 'Sites of Trauma: Contemporary Collecting and Natural Disaster'.
-

Seeing the Land from an Aboriginal Canoe
... Functional object: Woi wurrung, Yarra Canoe, c. 1860...Woi wurrung Bark Canoe This rare artefact is the only remaining 19th century Aboriginal canoe from the Melbourne region. It was collected by the Buchan family in Kew, Victoria, probably from the banks of the Yarra River in Studley Park, in the 1870s ...This project explores the significant contribution Aboriginal people made in colonial times by guiding people and stock across the river systems of Victoria.
Before European colonisation Aboriginal people managed the place we now know as Victoria for millennia. Waterways were a big part of that management. Rivers and waterholes were part of the spiritual landscape, they were valuable sources of food and resources, and rivers were a useful way to travel. Skills such as swimming, fishing, canoe building and navigation were an important aspect of Aboriginal Victorian life.
European explorers and colonists arrived in Victoria from the 1830s onwards. The newcomers dispossessed the Aboriginal people of their land, moving swiftly to the best sites which tended to be close to water resources. At times it was a violent dispossession. There was resistance. There were massacres. People were forcibly moved from their traditional lands. This is well known. What is less well known is the ways Aboriginal people helped the newcomers understand and survive in their new environment. And Victoria’s river system was a significant part of that new environment.
To understand this world we need to cast ourselves back into the 19th century to a time before bridges and cars, where rivers were central to transport and movement of goods and people. All people who lived in this landscape needed water, but water was also dangerous. Rivers flooded. You could drown in them. And in that early period many Europeans did not know how to swim. So there was a real dilemma for the newcomers settling in Victoria – how to safely cross the rivers and use the rivers to transport stock and goods.
The newcomers benefited greatly from Aboriginal navigational skills and the Aboriginal bark canoe.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images of deceased persons and images of places that could cause sorrow.
-

Como House and the Armytage Family
... gardeners and a coachman. Como was just over 54 acres in area (21.9 hectares) and, like all the large properties around South Yarra and Toorak, both supported and was supported by a large number of working-class retainers. Despite the severe economic...The Armytage family owned Como House in South Yarra for nearly 95 years. The property was managed by the women of the family for more than seventy years from 1876 to 1959. The history of the Armytage family, and the families who worked for them ...The Armytage family owned Como House in South Yarra for nearly 95 years. The property was managed by the women of the family for more than seventy years from 1876 to 1959. The history of the Armytage family, and the families who worked for them, provides an insight into almost a century of life on a large estate.
Como was purchased in 1864 by Charles Henry Armytage and it became the home of Charles, his wife Caroline, and their ten children. Charles died in 1876 and Caroline in 1909. Their daughters Leila, Constance, and Laura lived on at Como and left an indelible impression there.
The last surviving children of Charles and Caroline - Constance and Leila - sold Como to The National Trust of (Vic) in 1959. Como was the first house acquired by the Trust. One of the most significant aspects of this purchase was the acquisition of the complete contents of the house. The Armytage sisters realized that if Como was to survive as an expression of their family and its lifestyle, it must remain intact as a home. They also left an extensive archive of diaries, letters, journals and photographs.
Boasting one of Melbourne’s finest gardens, an inspiring historic mansion, and an impressive collection of antique furniture, the property provides a glimpse into the privileged lifestyle of its former owners; one of Australia’s wealthiest pioneer families.
Life can be seen to contain two major elements: the animate and the inanimate. While the inanimate bricks and mortar, objects and pathways, help in our understanding of this family, it is the animate, the social history, which makes Como come alive.
The text above has been abstracted from an essay The Armytage Family of Como written by Adrea Fox for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The entire text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
-

History in Place
... Arts Centre and Yarra Ranges Museum. The project is a partnership between the Heritage Council of Victoria, the History Teachers' Association of Victoria and Culture Victoria. The pilot was funded by the Telematics Trust. During the History in Place ...The History in Place project connects teachers and students with their local history via a community collecting society or museum.
History in Place provides an innovative and practical implementation of the new Australian Curriculum in History and Victoria's Framework of Historical Themes. It provides a framework for students to engage with their local history and heritage in a fun and challenging way using digital technologies. The program has been designed for grades 5 and 6, but has also been used for year 9s.
History in Place can be initiated either by schools or by community museums and heritage organisations. Students use collection items and interviews with local experts to create short films using tablet devices.
This story includes examples of what happens during a day of History in Place, examples of student films from the program pilot and an education toolkit (available from the Education Resources tab below) which includes course materials, instructional materials and everything that a museum and school need to implement the program.
The pilot program partnered 6 primary schools from across Victoria with local museums.
Museums participating in the pilot were: Barwon Park, Burke Museum, CO.AS.IT Museum, Golden Dragon Museum, the Mildura Arts Centre and Yarra Ranges Museum.
The project is a partnership between the Heritage Council of Victoria, the History Teachers' Association of Victoria and Culture Victoria. The pilot was funded by the Telematics Trust.
During the History in Place pilot, students used the Linking History site to research their films. Linking History is an experimental pilot in the practical application of linked open data, and is part of Portrait of a Nation: History In Place Access Project which is a Centenary of Canberra project, proudly supported by the ACT Government and the Australian Government.
-
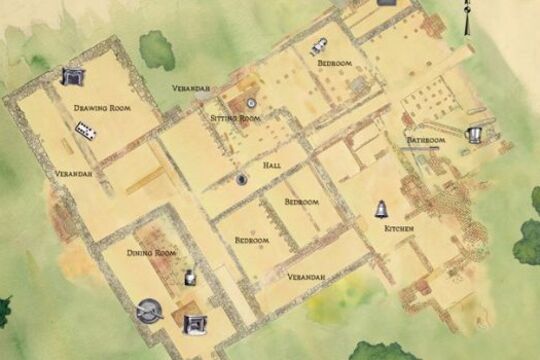
Viewbank: Unearthing a Colonial Homestead
... Viewbank Homestead was one of the first grand homesteads built on the outskirts of Melbourne. Built around 1840, Viewbank was located near the junction of the Yarra and Plenty Rivers in Heidelberg. The homestead was built in two phases. Originally ...Viewbank Homestead was one of the first grand homesteads built on the outskirts of Melbourne. Built around 1840, Viewbank was located near the junction of the Yarra and Plenty Rivers in Heidelberg.
The homestead was built in two phases. Originally a four room house, it was renovated and expanded in the 1850s and 1860s after it was acquired by wealthy squatter Dr Robert Martin.
Viewbank was destroyed by a professional demolition team in the early 1920s, long after the Martin family moved away from the area. By then, the house had fallen into disrepair and locals believed that it was haunted. For most of the 20th century, cattle grazed over the ruins and knowledge of the former grand homestead slipped from public knowledge until archaeologists returned to the site to unlock its secrets.
Between 1996 and 1999, Heritage Victoria conducted three excavations at the site with help from archaeologists from Melbourne, La Trobe and Flinders Universities, and more than 140 archaeology students and community members.
The archaeologists uncovered the stone foundations of the house and remnants of hand-made brick walls, fireplaces and other features. A range of artefacts were found during the excavation including children’s toys, coins, gaming tokens, thimbles and pins. A network of servant’s bells, fragments of marble fireplaces, and pieces of richly decorated plaster cornices reflect the affluence of the Martin family.
This story is made up of audio interviews with an archaeologist, an historian and a conservator. They discuss the Viewbank excavation, describe the artefacts found there and explain the process of their conservation at the Heritage Victoria conservation laboratory.
The Viewbank Homestead is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register. For more information on the Viewbank or other heritage sites visit The Victorian Heritage Database.
-
 Koorie Heritage Trust / NGV Australia / State Library Victoria
Koorie Heritage Trust / NGV Australia / State Library VictoriaKoorie Art and Artefacts
... William Barak was a leader of the Wurundjeri and King of the Yarra Yarra. He was considered 'bridge builder of the Kulin nation' leaving a strong legacy as a prominent leader, spokesperson, artist, activist and cultural ambassador for his people... Barak Last of the Yarra Tribe 18/12/97' is inscribed on the club in cursive script in black ink. ...Koorie makers of art and artefacts draw upon rich and ancient cultural traditions. There are 38 Aboriginal Language Groups in Victoria, each with unique traditions and stories. These unique traditions include the use of geometric line or free flowing curving lines in designs.
This selection of artworks and objects has been chosen from artworks made across the range of pre-contact, mission era and contemporary times and reflects the richness and diverse voices of Koorie Communities. It showcases prehistoric stone tools, works by 19th century artists William Barak and Tommy McRae right through to artworks made in the last few years by leading and emerging Aboriginal artists in Victoria.
The majority of the items here have been selected from the extensive and significant collections at the Koorie Heritage Trust in Melbourne. The Trust’s collections are unique as they concentrate solely on the Aboriginal culture of south-eastern Australia (primarily Victoria). Over 100,000 items are held in trust for current and future generations of Koorie people and provide a tangible link, connecting Community to the past.
Within the vibrant Koorie Community, artists choose their own ways of expressing identity, cultural knowledge and inspiration. In a number of short films Uncle Wally Cooper, Aunty Linda Turner and Aunty Connie Hart practice a range of traditional techniques and skills. These short documentaries show the strength of Koorie culture today and the connection with past traditions experienced by contemporary Koorie artists.
Taungurung artist Mick Harding draws upon knowledge from his Country about deberer, the bogong moth: "The long zigzag lines represent the wind currents that deberer fly on and the gentle wavy lines inside deberer demonstrate their ability to use those winds to fly hundreds of kilometres to our country every year."
Koorie artists today also draw inspiration from the complex and changing society we are all part of. Commenting on his artwork End of Innocence, Wiradjuri/Ngarigo artist Peter Waples-Crowe explains: "I went on a trip to Asia early in the year and as I wandered around Thailand and Hong Kong I started to think about Aboriginality in a global perspective. This series of works are a response to feeling overwhelmed by globalisation, consumerism and celebrity."
Koorie culture is strong, alive and continues to grow.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images and voices of deceased persons, and images of places that could cause sorrow.
-

Panorama: A question of perspective
... TarraWarra Museum of Art is located in the picturesque Yarra Valley in Victoria, Australia.Visitors to the Museum are afforded a spectacular, resonant and panoramic experience of ‘nature’ through the north facing windows. The view stretches towards ...TarraWarra Museum of Art is located in the picturesque Yarra Valley in Victoria, Australia.Visitors to the Museum are afforded a spectacular, resonant and panoramic experience of ‘nature’ through the north facing windows. The view stretches towards the distant Toolangi rainforest across planted vines, native bushland and farmland.
The region is surrounded by a spectacular mountain range that includes Mt Baw Baw, Mt Donna Buang, Mt Juliet, Mt Riddell and Mt Toolebewong. As these names attest, we are situated in an area of significant Indigenous history and colonisation. Tarrawarra is a Wurundjeri word that translates approximately as ‘slow moving water’ and is the name given to the area in which the Museum is located.
The Yarra Valley sunsets, soundscapes, seasonal changes, Indigenous histories, ecological vulnerabilities and environmental challenges are in a complex and ever changing entanglement. Since 2012, the Museum has explored this context through special exhibitions and commissions, forums and performances, screenings and lectures. As such, the Museum has sought to understand the complexity of our site, and with that, the broader intersections between art and landscape. Artists provide us the opportunity to ‘see’ the landscape in a different way. They imagine it, call it into being, reflect upon it, animate it, unravel its hidden histories, and expose its ecological sensitivities.
Panorama, the exhibition, was an integral part of this ongoing conversation and imaginative exploration. Our intention was not so much to write a narrative history of Australian landscape painting. Rather, it was to be attuned to the intermingling of voices, points of view, perspectives - colonial and modern, contemporary and Indigenous – that comprise the uniquely Australian persistence to unravel the ‘patter’ of nature.
As a phenomenon to which we are all very accustomed, it is easy to overlook the simple fact that for a landscape to come into being it requires a ‘point of view’, a subjective consciousness to frame a particular expanse of the natural world. As the art historian Simon Schama remarks in his landmark survey on the genre, Landscape and Memory, ‘it is our shaping perception that makes the difference between raw matter and landscape’. [i] The centrality of the viewer’s position in constructing a vista is clearly evident in terms such as ‘perspective’, ‘prospect’, and ‘view point’ which are synonymous with ‘position’, ‘expectation’, and ‘stance’. This highlights that there is always an ineluctable ideological dimension to the landscape, one that is intimately entwined with a wide range of social, economic, cultural and spiritual outlooks. Turning to the notion of the panorama, a brief survey of its conception and infiltration into everyday speech, reveals how our way of seeing the landscape is often tantamount to the formation and delineation of our personal, communal, and national identities.
The term panorama was first coined to describe the eponymous device invented by the British painter Robert Barker which became a popular diversion for scores of Londoners in the late 18th century. Consisting of a purpose built rotunda-like structure on whose cylindrical surface landscape paintings or historical scenes were displayed, ‘The Panorama’ contained a central platform upon which viewers observed the illusionistic spectacle of a sweeping 360 degree vista. With its ambitious, encyclopaedic impulse to capture and concentrate an entire panoply of elements into a singular view, it is telling that this construction would soon give rise to an adjective to describe, not only an expansive view extending in all directions, but also a complete and comprehensive survey of a subject. As the curators Jean-Roch Bouiller and Laurence Madeline argue, these different meanings convey ‘the very essence of the panoramic phenomenon: the central role of perspective, a certain appropriation of the world that follows, the feeling of dominating a situation simply due to having a wide and complete view’.[ii] Indeed, as art historian Michael Newman reveals, the whole notion of the panorama originated in military conceptions of the landscape as a battlefield, whereby strategic vantage points are key to tactical planning.[iii] Underlying its transformation into a form of popular entertainment, the panorama is rooted in a particular form of political authority based on surveying, mapping and commanding the subject of the view.
In this exhibition, the term panorama was invoked to acknowledge that ways of perceiving the landscape have their own histories which have arisen out of particular social, political and cultural contexts. As the landscape architect Anne Whiston Spirn contends: ‘In every landscape are ongoing dialogues; there is “no blank slate”; the task is to join the conversation’.[iv]However, far from claiming to present an unbroken view or a complete survey, Panorama challenged the very notion of a single, comprehensive monologue by presenting a series of works which engaged with the discourse of landscape in a diverse range of voices. Taking advantage of the tremendous depth and strength of the TarraWarra Museum of Art collection gifted by its founders Eva Besen AO and Marc Besen AC, the exhibition was staged in two parts, with a different selection of paintings exhibited in each half. Displayed in distinct groupings which explored alternative themes and concerns, Panorama highlighted the works of key artists who have redefined, expanded and interrogated the idea of the landscape in ways which suggest that it is far from settled.
Further Information
[i] Simon Schama, Landscape and Memory, New York: Vintage Books, 1996, p. 10.
[ii] Jean-Roch Bouiller and Laurence Madeline, Introductory text for the exhibition I Love Panoramas, MuCEM and the Musées d’Art et d’Histoire, Geneva, 4 November 2015 - 29 February 2016, URL: http://www.mucem.org/en/node/4022
[iii] See ‘The Art Seminar’ in Landscape Theory, (eds. Rachael Ziady DeLue and James Elkins), New York and London: Routledge, 2008, p. 130.
[iv] Anne Whiston Spirn, ‘“One with Nature”: Landscape, Language, Empathy and Imagination’ in Landscape Theory, 2008, p. 45.
-

Nyernila - Listen Continuously: Aboriginal Creation Stories of Victoria
... was celebrated through the ngargee held during Pareip.The bagurrk of the Boon Wurrung decorated their yarra with murnong flowers and purple flower of the guyeem apple. They drummed on drums made from walert skins stretched tightly between their barring...Boon Wurrung: The Filling of the Bay - The Time of ChaosMany years ago the biik we now call greater Melbourne extended right out to the warreeny. Nairm (Port Phillip Bay) was then a large flat grassy plain. The Yarra River, as it is known today ...This story is based on the unique publication Nyernila – Listen Continuously: Aboriginal Creation Stories of Victoria.
The uniqueness is differentiated by two significant and distinguishing features. It is the first contemporary compilation of Victorian Aboriginal Creation Stories told by Victorian Aboriginal People, and it is the first to extensively use languages of origin to tell the stories.
‘Nyernila’ to listen continuously – a Wergaia/Wotjobaluk word recorded in the 20th century. To listen continuously. What is meant by this term. What meaning is being attempted to be communicated by the speaker to the recorder? What is implied in this term? What is the recorder trying to translate and communicate to the reader?
‘Nyernila’ means something along the lines of what is described in Miriam Rose Ungemerrs ‘dadirri’ – deep and respectful listening in quiet contemplation of Country and Old People. This is how our Old People, Elders and the Ancestors teach us and we invite the reader to take this with them as they journey into the spirit of Aboriginal Victoria through the reading of these stories.
Our stories are our Law. They are important learning and teaching for our People. They do not sit in isolation in a single telling. They are accompanied by song, dance and visual communications; in sand drawings, ceremonial objects and body adornment, rituals and performance. Our stories have come from ‘wanggatung waliyt’ – long, long ago – and remain ever-present through into the future.
You can browse the book online by clicking the items below, or you can download a PDF of the publication here.
nyernila
nye
ny like the ‘n’ in new
e like the ‘e’ in bed
rn
a special kind of ‘n’
i
i like the ‘i’ in pig
la
la
-

Against the Odds: The victory over conscription in World War One
... at the Yarra Bank, and, just before the 1917 referendum, on a tour through regional areas of Victoria. Shortly after World War One ended, Lavender moved to Adelaide to live with her son, who was practising as a doctor. Lavender died in 1923, aged 65...., with several thousand more looking on It started from the Guild Hall (now Storey Hall) and proceeding to the Yarra Bank. The march was led by Madge Gardiner, the 8 year old daughter of Edith, Vice President of the Women’s Political Association. Madge ...In October 1916 and December 1917 two contentious referendums were held in Australia, asking whether the Commonwealth government should be given the power to conscript young men into military service and send them to war overseas.
These campaigns were momentous and their legacy long-lasting. This is the only time in history that citizens of a country have been asked their opinion about such a question, and the decisive 'No' vote that was returned remains the greatest success of the peace movement in Australia to date. Yet the campaigns split families, workplaces and organisations, and left an imprint on Australian politics that lasted for decades.
Many of the actors and events that were central to these campaigns were based in the northern Melbourne suburbs of Brunswick and Coburg. In many ways, these localities were a microcosm of the entire campaign. Against the Odds: The Victory Over Conscription in World War One tells the story of the anti-conscription movement in Australia during World War 1 through this lens.
-
 Open House Melbourne
Open House MelbourneModern Melbourne
... Peter McIntyre purchased the 9-acre block of land in 1947 for £200 when he was 19 years old. The terrain was difficult, with steep cliffs and prone to flooding from the Yarra River. ...Modern Melbourne is a series of filmed interviews and rich archival material that documents the extraordinary lives and careers of some of our most important architects and designers including Peter McIntyre, Mary Featherston, Daryl Jackson, Graeme Gunn, Phyllis Murphy, Allan Powell and Peter Elliott.
Melbourne’s modernist architects and designers are moving into the later stages of their careers. Their influence on the city is strong and the public appreciation of their early work is growing – they have made an indelible mark on Melbourne. Much of their mid-century modernist work and latter projects are now represented on the Victorian Heritage Register.
Many of the Modern Melbourne subjects enjoyed a working relationship and a friendship with Robin Boyd, the influential architect who championed the international modernist movement in Melbourne.
