Showing 76 items with themes 'Built Environment' or 'Immigrants And Emigrants'
-

Melbourne and Smellbourne
Over the last 150 years Victoria has experienced a number of landmark capital works and landscaping projects in response to its changing economic, environmental and cultural relationship to water. The sewerage system that we take for granted today had to be built from scratch.
For all the grandeur that was 'Marvellous Melbourne' in the 1880s, the city was nicknamed 'Smellbourne', and for good reason. The building of Yan Yean Reservoir in the 1850s had ensured the availability of fresh water, but there was still no sewerage system.
An appalling stench wafted from the many cesspits and open drains. 'Nightsoil' (as human waste was politely referred to) polluted the streets and ran into the Yarra. Nightsoil collectors frequently dumped their loads on public roads. Ignorance and neglect of the hygienic disposal of human waste had devastating results at this time when hundreds died in a savage outbreak of typhoid.
Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works
In 1891 the Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) was created. It immediately began plans to build an underground drainage system linked to a pumping station at Spotswood, located on the western banks of the mouth of the Yarra River. The sewage flowed by gravity to Spotswood, where it was then pumped to the Werribee Treatment Farm.
Spotswood Pumping Station
Spotswood Pumping Station built to pump Melbourne's sewage to Werribee, was finished in 1897. At the pumping station, steam engines (later replaced by electrical ones) worked to pump the sewage up a rising main to join the major sewer outfall at the head of the pumping mains near Millers Road at Brooklyn. The outfall sewer then carried the sewage to the Werribee Treatment Farm where it was purified and discharged into the sea.
Werribee Farm
Werribee was the perfect site for the MMBW's new sewage farm. The farm was the Board's most important project, and one of the largest public works undertaken in Australia in the nineteenth century.
Land at Werribee was cheaper than at Mordialloc - the other site considered. Rainfall was low compared with the rest of Melbourne, which meant the land would adapt well to irrigation. Werribee was also 9 miles (14.4 KM) away from the nearest boundary of the metropolitan district (Williamstown), and 24 miles (38.6 KM) away from the influential and well-to-do suburb of Brighton. The Chirnside family sold 8,857 acres (3.2 hectares) to the Board for 17 pounds per acre.
The Earl of Hopetoun, Governor of Victoria, turned the first sod of earth in a ceremony on May 1892, which marked the beginning of the building of the outfall sewer near Werribee.
Connection!
On 5 February 1898, a ceremony marked the official connection of Melbourne to the new sewerage system. Guests - politicians, board members, city councillors and federal delegates - boarded a steamer to watch the Governor, Lord Brassey, raise the penstock (the partition between the smaller and larger sewers) at the Australian Wharf. They then visited the pumping station at Spotswood and the sewage farm at Werribee. Horses and carts conveyed the 180 guests around the farm.
After lunch and toasts, many of which looked forward to the future of a federated Australia, MMBW Chairman Mr Fitzgibbon proudly declared it "was not a question of how much the scheme was going to cost, but how much it was going to save in the lives of the citizens." Before the work was completed he hoped to see those puny punsters and petty wits who spoke of Melbourne as Marvellous Smellbourne constrained to speak of her as one of the sweetest and healthiest cities of the world.
-
 History Teachers' Association of Victoria / Royal Historical Society of Victoria
History Teachers' Association of Victoria / Royal Historical Society of VictoriaMacRobertson's Confectionery Factory
MacRobertson Steam Confectionery Works was a confectionery company founded in 1880 by Macpherson Robertson and operated by his family in Fitzroy, Melbourne until 1967 when it was sold to Cadbury.
This story accompanies the 'Nail Can to Knighthood: the life of Sir Macpherson Robertson KBE' exhibition which took place at the Royal Historical Society of Victoria in 2015.
-

Dimitri Katsoulis, Greek Puppet Master
Traditional Greek shadow puppet theatre evolved from the Turkish model, which dates back to at least the 16th century.
The central figure is the character Karaghiozis, who relies on his wit and cunning to extricate himself from precarious situations. He and other characters are involved in humorous and satirical moral tales that comment on social and political life.
Dimitri Katsoulis immigrated to Melbourne in 1974 to escape the Junta regime that repressed Greek artists. He had trained in Greece with theatre and film companies as an actor and technician, as well as in shadow puppetry with masters of the art form. While earning a living in a Melbourne metal factory, he co-founded the Children's Theatre of Melbourne. Dimitri performed Greek shadow puppetry until 1991, exploring contemporary and controversial issues such as women's equality, and the isolation of migrant women and children.
-
 Jane Routley and Elizabeth Downes
Jane Routley and Elizabeth DownesFlinders Street Station
The current Flinders Street Station building has been part of the lives of Melbournians for over 100 years.
Inspired by the launch of the latest competition to put forward proposals for its restoration and reinvigoration, and to highlight some of the amazing Flinders Street-related material in Victoria's cultural collections, I will be celebrating the past, present and future of my favorite station.
Over the next few months, I will be recording impressions and stories found whilst exploring the station as it exists today, trawling the internet for related sounds and images (such as this timelapse) and featuring some of the wonderful images of the station that are held in Victoria's cultural collections. As a taster for my future posts, here's a selection of images that I've found.
-

The Apinis Loom
When Latvian refugees Anna and Ervins Apinis arrived in Australia in 1950 they brought with them a loom built of wood salvaged from bombed out German ruins, along with Anna's precious notebooks full of traditional fabric designs.
Anna Strauss was born in 1913 in Latvia. She attended weaving lessons in Leipaja from 1930 to 1933 and spent hours at the nearby Ethnographic Museum recording traditional fabric designs in her notebooks.
She married Ervins Apinis, an engineer, in 1938 and they had a son but soon World War II changed their lives. Ervins was conscripted into the German army while Anna fled Latvia, finally ending up in Memmingen Displaced Persons camp in Germany in 1945. There, they were finally reunited, remaining in the camp for five years until they migrated to Australia in 1950.
When they arrived at Parkes Holding Centre in New South Wales, they were so exhausted from their long journey, they slept on a huge wooden crate containing the traditional Latvian loom they had brought with them, built of wood scavenged from bombed German ruins. This loom is now at the Immigration Museum in Melbourne.
Anna continued her weaving traditions, passing her knowledge to her daughter Anita.
-
 Carissa Goudey
Carissa GoudeyMaking & Using Transport on the Goldfields
During the nineteenth century, horse-drawn vehicles were an essential part of life in rural Victoria.
In Ballarat, local coachbuilding firms assisted with the town’s growth in more ways than providing passage to the diggings. Horse-drawn vehicles were vital for the delivery of goods, responding to emergencies and often symbolised one’s social standing.
The Gold Rush ushered in a period of incredible growth for colonial Victoria. Ballarat’s escalating population and burgeoning industries highlighted the need for horse-drawn transport – not only for getting to the diggings, but also for delivering goods and building material, responding to emergencies and performing significant social rituals.
In the early nineteenth century, the goldfields were dominated by vehicles either imported from England or English-style vehicles built locally. Coaches, carriages and carts were typically constructed part-by-part, one at a time. As a result, each vehicle was highly unique.
By the mid-1850s, the American coachbuilding tradition had arrived on the goldfields. The American method, which had been developing since the 1840s, relied on mass-produced, ready-made components. In comparison to English designs, American coaches were known to be more reliable for goldfields travel; they were primed for long-distance journeys on rough terrain and were less likely to tip over.
As the nineteenth century progressed, a plethora of English, American and European vehicles populated Ballarat – both locally made and imported. The abundance of coaches, carriages and carts – and their value to the Ballarat community – can be seen in photographs and objects catalogued here on Victorian Collections.
-

A Station with a Town Attached
"Don't you overlook that Maryborough station, if you take an interest in governmental curiosities. Why, you can put the whole population of Maryborough into it, and give them a sofa apiece, and have room for more." Mark Twain, during his 1895 tour of Australia.
Twain’s remark stuck, and Maryborough became known as the railway station with a town attached.
Why was Maryborough chosen for one of the nation's grandest stations? Was it meant for Maryborough, Queensland? Was it indeed a ‘governmental curiosity’, a monumental bureaucratic mistake?
In fact, neither is the case. The Maryborough Station tells a much larger story: the vision for a rail-connected Victoria in the age that preceded the motor engine. Maryborough would be a crucial junction between the Wimmera, Geelong, Ararat, Warrnambool, Ballarat, Bendigo and Melbourne, especially for freight such as wheat.
The original station was built in 1874 but, as part of the 'Octopus Act' of 1884, Parliamentarians began arguing the case for a grander station.
The new Queen Anne style red brick building with stucco trimmings and Dutch-Anglo influences was erected in 1890-1, with 25 rooms, an ornate clock tower, Flemish gables, oak wall panels, a large portico, and a spectacular platform veranda - the longest in country Victoria.
Here, oral histories, expert opinions and archival photographs from local collections are presented, giving us a sense of the station's importance, its role in an earlier era and, as a magnificent late 19th century Australian building, the place it continues to hold in the district.
-

Goldfields Stories: Dai gum san, big gold mountain
It may come as a surprise to some that the oldest Imperial Dragon in the world, Loong, is to be found in Bendigo, Victoria.
In 1851 gold was found in the Bendigo region. News reached China and by 1853 Chinese miners started to arrive at Dai Gum San (Big Gold Mountain). By 1855 there were up to 4000 Chinese in the Bendigo goldfields, about one fifth of the population.
By the 1860s, Bendigo was becoming a wealthy and established town, and in 1869 The Bendigo Easter Fair and Procession was initiated to raise funds for the Bendigo Benevolent Asylum and Hospital. By 1871, the Chinese, keen to support the wider community, joined the procession, providing music, theatre and acrobatic displays. Their position as the main attraction at the Fair was confirmed by 1879.
All of the costumes, flags and musical instruments were imported from China, with no expense spared. For the 1882 Fair, 100 cases of processional regalia were imported. In 1892 a further 200 cases arrived, along with Loong, the Imperial five-clawed dragon, who made his first appearance that year.
The traditions established in the 1860s by the Bendigo Chinese community continue to this day. As well as providing the main attraction in the Bendigo Easter Festival, ceremonies such as the Awakening of the Dragon are conducted. These traditions reflect uniquely preserved traditions, many of which were lost or discontinued in mainland China. They also reflect traditions, such as the main celebration taking place at Easter rather than Chinese New Year, that trace the history of the Chinese in Victoria.
The remarkable collection of 19th Century processional regalia that has been preserved by the Chinese community in Bendigo is held in the Golden Dragon Museum. It is not only a collection of world significance but, importantly, it contextualises and preserves the living heritage of both Victoria and China.
-

Made in Bendigo, Cold Beer!
In 1857 at the height of the gold rush, with people pouring into Central Victoria from all over the world, three brothers from Denmark – Moritz, Julius and Jacob Cohn – founded a small cordial factory in the booming town of Bendigo.
They went on to build an empire and, through introducing lager, which is served cold, to the country, changed the drinking preferences of Australians.
Cordial was a necessity at the time as water was considered unpalatable. The Cohn cordial products were successful and the brothers went on to produce other staples such as fruit preserves. The Cohn Brothers were canny businessmen and at the peak of their success Cohn products were sold across the country and exported to the United Kingdom and Asia. The brothers went on to hold prominent positions on the local Council, and were part of the group that founded the Bendigo Land and Building Society, which became the Bendigo Bank.
Traces of the impact that Cohn products had on the daily lives of Australians, particularly those in Central Victoria, can be found in vintage bottles, wooden crates and signs that have been collected and preserved.
The legacy of their business and civic activities are told through interviews with their descendent, Helen Bruinier, Bendigo Art Gallery Curator, Sandra Bruce, and Frank Barr, the sign painter of the Cohn’s Cordial sign in Bridge Street, Bendigo.
-

Melbourne Trams: Step aboard!
'Introduction to Melbourne Trams: Step aboard!'
Written by Carla Pascoe, May 2012
Trams are what make Melbourne distinctive as a city. For interstate and overseas visitors, one of the experiences considered compulsory is to ride a tram. When Melbourne is presented to the rest of the world, the tram is often the icon used. The flying tram was one of the most unforgettable moments of the Opening Ceremony of the 2006 Commonwealth Games. When Queen Elizabeth II visited Australia in 2011, she was trundled with regal dignity along St Kilda Road in her very own ‘royal tram’.
The history of trams is closely bound up with the history of this southerly metropolis. Melbourne’s tram system originated during the 1880s economic boom when the Melbourne Tramway and Omnibus Company opened the first cable line. Cable tram routes soon criss-crossed much of the growing city and cable engine houses can still be seen in some inner suburbs, such as the grand building on the south-east corner of Gertrude and Nicholson streets, Fitzroy. Some older passengers like Daphne Rooms still remember riding cable cars.
In the late 19th century, cable and electric tram technologies were vying for supremacy. Australia’s first electric tram line opened in 1889, running through what was then farmland from Box Hill station to Doncaster. The only surviving clue that a tram line once traversed this eastern suburb is the eponymous Tram Road, which follows the former tram route in Doncaster.
Gradually, various local councils joined together to create municipal Tramways Trusts, constructing electric lines that extended the reach of the cable system. In 1920 the tram system came under centralised control when the Melbourne and Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB) consolidated the routes and began electrifying all cable lines.
Manpower shortages during World War II meant that Australian women stepped into many roles previously reserved for men. The tramways were no exception, with women being recruited as tram conductors for the first time. After the war, tram systems were slowly shut down in cities around both Australia and the world, as transport policies favoured the motor vehicle. But thanks to the stubborn resistance of MMTB Chairman, Sir Robert Risson, as well as the wide, flat streets that characterise the city’s geography, Melbourne retained its trams.
Melbourne’s tram industry has always possessed a unique workplace culture, characterised by fierce camaraderie and pride in the role of the ‘trammie’ (the nickname for a tram worker). Many Trammies, like Bruce MacKenzie, recall that they joined the tramways because a government job was seen as a job for life. But the reason they often remain for decades in the job is because of the strong bonds within the trammie ‘family’. This is partly due to the many social events and sporting clubs that have been attended by Trammies, as Bruce MacKenzie remembers. It is also because the demands of shift work bond people together, explains Roberto D’Andrea.
The tram industry once employed mainly working-class, Anglo-Australian men. After World War II, many returned servicemen joined the ranks, bringing a military-style discipline with them. With waves of post-war migration the industry became more ethnically diverse, as Lou Di Gregorio recalls. Initially receiving Italian and Greek workers from the 1950s and 1960s, from the 1970s the tramways welcomed an even broader range of Trammies, from Vietnamese, South American, Turkish and other backgrounds.
Trammies perform a wide range of tasks critical to keeping the system running, including driving, track maintenance, tram maintenance, time tabling, customer service and more. But just as designs of ‘rolling stock’ have changed - from the beloved veteran W class trams to the modern trams with their low floors, climate control and greater capacity - so too have the jobs of Trammies changed over time. Bruce MacKenzie remembers joining the Preston Workshops in the 1950s when all of Melbourne’s fleet was constructed by hand in this giant tram factory. Roberto D’Andrea fondly recalls the way that flamboyant conductors of the 1980s and 1990s would perform to a tram-load of passengers and get them talking together. As a passenger, Daphne Rooms remembers gratefully the helping role that the connies would play by offering a steadying arm or a piece of travel advice.
Trams have moved Melburnians around their metropolis for decades. As Daphne maintains, ‘If you can’t get there by tram, it’s not worth going’. Everyone has memories of their experiences travelling on trams: some funny, some heart-warming and some frustrating. Tram driver, Lenny Bates, tells the poignant story of the blind boy who would sometimes board his tram on Collins Street and unhesitatingly call out the names of the streets they passed. As the films in this collection demonstrate, every passenger has their routes that they customarily ride and these routes take on a personal meaning to their regulars. You could say that every tram line has its own distinct personality. Whilst the way the tram system is run inevitably changes across time, one thing has been constant: trams have always played a central role in the theatre of everyday life in Melbourne.
-

Melbourne's Homes
These house plans from the late 19th and early 20th Centuries, give us an indication of how those with the means to build larger houses lived.
Servant's quarters, groom's rooms, sculleries, stables, parlours and children's areas give us clues to social attitudes, relationships to children and employees, social mores and living conditions.
-
 Judy Scurfield
Judy ScurfieldJourney's End
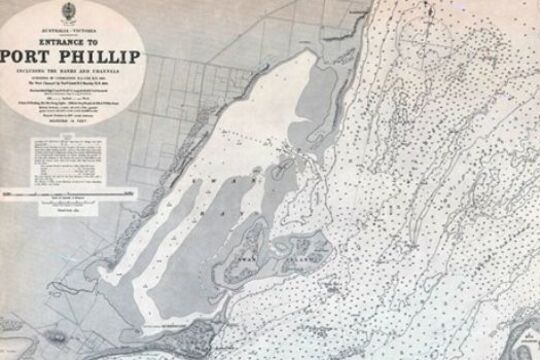
Try to imagine yourself on board a sailing ship in the 19th century...
Approaching the entrance to Port Phillip Bay, which is known to be a particularly dangerous harbour entrance, being very narrow (only 2 and a half kilometers across), fringed with rocky reefs, and turbulent because of the tides meeting the ocean swells of Bass Strait.
If you were the Captain you needed an accurate chart showing sea-depths, the coastline and its hazards, but also the navigational aids such as lighthouses and beacons which would guide you into port. You would also have needed a book of sailing directions...
Judy Scurfield, librarian at the State Library of Victoria, asks us to imagine the entry through the most hazardous Port Phillip Heads.
Further material can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site: Thomas Pierson (Diaries of an early arrival chronicle first impressions of Melbourne).
-
 Erin Wilson
Erin WilsonUrban Fringe
Melbourne is an expanding city, with a growing population and sprawling urban development. It is predicted that by 2056 an additional 4 million people will settle in Greater Melbourne, increasing the population from 5 million to 9 million people over the next 30 years (1). While some expansion is vertical, in the form of high-rise developments, much of this growth is across the peri-urban fringe, described simply as ‘areas on the urban periphery into which cities expand’ (2) or ‘which cities influence’ (3).
In Melbourne, these peri-urban areas of most rapid growth are currently the local government areas of Cardinia, Casey, Hume, Melton, Mitchell, Whittlesea and Wyndham. With population growth comes the inevitable expansion of infrastructure, services and transportation. As the fringes of the city continue to sprawl, what was once the urban fringe and green edge of the city has to be negotiated, as it is increasingly encroached upon.
The artists and photographers in Urban Fringe examine these spaces on the fringe of the expanding city of Melbourne, where urban and natural environments meet, clash and coexist. Beginning with white colonisation and the myth of ‘terra nullius’, these artists discuss the treatment of the Greater Melbourne environment over time, consider the cost of progress, and explore protest and the reclamation of space.
-

Migrants Enriching Australia
Migrants Enriching Australia was born of a project to assist ethnic community groups preserve and manage their material heritage.
This story consists of 21 story objects - including videos, audio recordings, images and text - and two educational resources available at the bottom of the page.
During the research a few people emerged who vividly carried a particular story about immigration and settlement to Victoria. These included Peter Yiannoudes who introduced Greek films to Melbourne in the 1950s. He carried his portable projector on a train and visited small country towns and even a farmhouse around Victoria, in order to share this dynamic Greek heritage with Greek expatriates.
Janina Archabuz (Pani Babscha) is a Polish grandmother who carefully designed and sewed multiple copies of intricate costumes for a Polish dance troupe in Ardeer, in Melbourne’s west. Janina is self-taught, however the costumes are exquisitely sewn and meticulously detailed. These costumes gave the Polish group visibility when performing traditional dances in the community, and contributed to their community’s transition from being Poles to being Australians of Polish origin.
The research for the Multicultural Communities’ Collection Project revealed incredibly rich collections – their photographs, documents, costumes and memorabilia from their countries of origin, their community members’ journeys to Australia and the process of settlement into this country and this state - held by community groups, each different and many reliant on individuals who valued their history and their community identity. The project was based on the idea that understanding of and control over community heritage strengthens community identity, which in turn contributes to an Australia which is enriched by diverse ethnic groups living side by side harmoniously.
The Multicultural Communities’ Collection Project began in 2011 - firstly as a project of the then Arts Victoria and later Museums Australia (Victoria). It involved visiting up to 40 ethno specific community groups and providing them with professional assistance to preserve and store their material heritage. There was also training in the documentation and digitisation of these collections, and including them in the web based cataloguing system, Victorian Collections.
Ethnic Communities Council of Victoria (ECCV) is the peak body for Victoria’s multicultural communities and have been advocating their needs and concerns to government for 40 years. It is the principle liaison point between multicultural communities, the government and the wider community. The ECCV welcomed the opportunity to facilitate these two films for Culture Victoria, to share more broadly these stories about immigrants and how they have enriched our community.
-

Restoring St Nicholas
St Nicholas church in Humffray St, Ballarat East, was built in 1867. Originally named the Bible Christian Church, it was built by Cornish miners in the evenings and weekends after they had returned from their work at the diggings.
Like most buildings of its time it was built to last, constructed of solid brick with lime mortar. By the 1970s, the mortar was crumbling and the church community of the time re-mortared it with cement, a process we now know was incorrect for buildings of its age. The cement mortar, combined with rising damp, caused salt attack in many of the original bricks and the building literally began to crumble.
In 2009 the Greek Orthodox community of St Nicholas approached the City of Ballarat, Heritage Victoria and the trade school at the University of Ballarat to form a unique partnership to restore the church. This project allowed young apprentices to learn traditional trade skills and practice the technique of mixing and using lime mortar. In the process, the humble church has had its life extended, and the Greek community have a religious and cultural centre they can use for generations to come.
-
 Brian Allison
Brian AllisonJohn Harry Grainger
Architect and Civil Engineer
John Harry Grainger was a creative figure, largely overlooked by history. He receives a brief mention in the much-examined life story of his famous son, the composer and pianist Percy Grainger, where he is depicted as a proud but ineffectual father.
Grainger's prolific output as an architect and his extraordinary talents for bridge building have not yet received due recognition.
The material presented here is sourced from the Grainger Museum Collection at the University of Melbourne. Additional material is held in the Public Record Office of Victoria and in the State Library of Victoria collections.
