Showing 20 items with themes 'Gold Rush' or 'Family Histories'
-
 Carissa Goudey
Carissa GoudeyMaking & Using Transport on the Goldfields
During the nineteenth century, horse-drawn vehicles were an essential part of life in rural Victoria.
In Ballarat, local coachbuilding firms assisted with the town’s growth in more ways than providing passage to the diggings. Horse-drawn vehicles were vital for the delivery of goods, responding to emergencies and often symbolised one’s social standing.
The Gold Rush ushered in a period of incredible growth for colonial Victoria. Ballarat’s escalating population and burgeoning industries highlighted the need for horse-drawn transport – not only for getting to the diggings, but also for delivering goods and building material, responding to emergencies and performing significant social rituals.
In the early nineteenth century, the goldfields were dominated by vehicles either imported from England or English-style vehicles built locally. Coaches, carriages and carts were typically constructed part-by-part, one at a time. As a result, each vehicle was highly unique.
By the mid-1850s, the American coachbuilding tradition had arrived on the goldfields. The American method, which had been developing since the 1840s, relied on mass-produced, ready-made components. In comparison to English designs, American coaches were known to be more reliable for goldfields travel; they were primed for long-distance journeys on rough terrain and were less likely to tip over.
As the nineteenth century progressed, a plethora of English, American and European vehicles populated Ballarat – both locally made and imported. The abundance of coaches, carriages and carts – and their value to the Ballarat community – can be seen in photographs and objects catalogued here on Victorian Collections.
-

Early Photographs - Gold
These images are part of the first photographic series of Australian scenes presented for sale to the public. Produced by the studio of Antoine Fauchery and Richard Daintree in 1858, these photograph are from a series of 53 collectively known as the Fauchery-Daintree Album.
Using the latest collodion wet-plate process, Fauchery and Daintree produced their collection of albumen silver prints at a time when the sales of photographs were flourishing.
Antoine Fauchery and Richard Daintree produced iconic images of both early gold diggers and the landscapes scarred by the exploding search for gold, which attracted miners from all over the world and created the boom that made Melbourne the fastest growing metropolis of the time.
Antoine Fauchery and Richard Daintree were both migrants who tried their luck on the goldfields – Daintree coming out from England in 1853, Fauchery from France in 1852.
Unsuccessful on the goldfields, in 1857 they combined forces to produce a series of photographs titled Sun Pictures of Victoria, capturing important early images of the goldfields, Melbourne Streets, landscapes and portraits of Indigenous Victorians. Using the new collodion wet-plate process, they created albumen silver prints of a rare quality for the time.
Further information on Antoine Fauchery's time in Melbourne can be found at the State Library of Victoria's Ergo site.
-

Rippon Lea Estate
"Do you remember the garden in which you grew up, or the part the backyard played in your family life? Imagine if you had actually grown up in one of Australia's finest gardens.
Created in the English-landscape tradition which traces its roots back to Capability Brown and Humphry Repton, Rippon Lea is one of Australia's most important historic homes, exemplifying the lifestyle of wealthy families living in 19th and 20th century Australian cities. Although its architecture and that of its outbuildings is impressive, it is the mansion’s gardens, which are truly remarkable, both for their landscape qualities and because they have survived many threats and changes in the past 130 years.
Today, the amenities offered by a typical garden are still greatly valued: a safe place for children to play, somewhere to dry the washing, a plot for vegetables and a flower garden that adds colour and produces blooms for the home. Today as then, the scale differs but the experience of owning a garden - with its balance of utility and ornament - is essentially the same.
The National Trust of Australia (Victoria) now runs Rippon Lea as a museum, conserving the architecture and the landscape, and presenting the social history of the owners and their servants. Visitors to Rippon Lea enter a mansion preserved as the Jones family lived in it after their 1938 modernisation. In the pleasure garden the Sargood era is evoked by the staging of a range of performing arts events including opera, theatre, chamber music and outdoor activities."
The text above has been abstracted from an essay Solid Joys and Lasting Treasure: families and gardens written by Richard Heathcote for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The entire text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
-

History in Place
The History in Place project connects teachers and students with their local history via a community collecting society or museum.
History in Place provides an innovative and practical implementation of the new Australian Curriculum in History and Victoria's Framework of Historical Themes. It provides a framework for students to engage with their local history and heritage in a fun and challenging way using digital technologies. The program has been designed for grades 5 and 6, but has also been used for year 9s.
History in Place can be initiated either by schools or by community museums and heritage organisations. Students use collection items and interviews with local experts to create short films using tablet devices.
This story includes examples of what happens during a day of History in Place, examples of student films from the program pilot and an education toolkit (available from the Education Resources tab below) which includes course materials, instructional materials and everything that a museum and school need to implement the program.
The pilot program partnered 6 primary schools from across Victoria with local museums.
Museums participating in the pilot were: Barwon Park, Burke Museum, CO.AS.IT Museum, Golden Dragon Museum, the Mildura Arts Centre and Yarra Ranges Museum.
The project is a partnership between the Heritage Council of Victoria, the History Teachers' Association of Victoria and Culture Victoria. The pilot was funded by the Telematics Trust.
During the History in Place pilot, students used the Linking History site to research their films. Linking History is an experimental pilot in the practical application of linked open data, and is part of Portrait of a Nation: History In Place Access Project which is a Centenary of Canberra project, proudly supported by the ACT Government and the Australian Government.
-

Nyernila - Listen Continuously: Aboriginal Creation Stories of Victoria
This story is based on the unique publication Nyernila – Listen Continuously: Aboriginal Creation Stories of Victoria.
The uniqueness is differentiated by two significant and distinguishing features. It is the first contemporary compilation of Victorian Aboriginal Creation Stories told by Victorian Aboriginal People, and it is the first to extensively use languages of origin to tell the stories.
‘Nyernila’ to listen continuously – a Wergaia/Wotjobaluk word recorded in the 20th century. To listen continuously. What is meant by this term. What meaning is being attempted to be communicated by the speaker to the recorder? What is implied in this term? What is the recorder trying to translate and communicate to the reader?
‘Nyernila’ means something along the lines of what is described in Miriam Rose Ungemerrs ‘dadirri’ – deep and respectful listening in quiet contemplation of Country and Old People. This is how our Old People, Elders and the Ancestors teach us and we invite the reader to take this with them as they journey into the spirit of Aboriginal Victoria through the reading of these stories.
Our stories are our Law. They are important learning and teaching for our People. They do not sit in isolation in a single telling. They are accompanied by song, dance and visual communications; in sand drawings, ceremonial objects and body adornment, rituals and performance. Our stories have come from ‘wanggatung waliyt’ – long, long ago – and remain ever-present through into the future.
You can browse the book online by clicking the items below, or you can download a PDF of the publication here.
nyernila
nye
ny like the ‘n’ in new
e like the ‘e’ in bed
rn
a special kind of ‘n’
i
i like the ‘i’ in pig
la
la
-
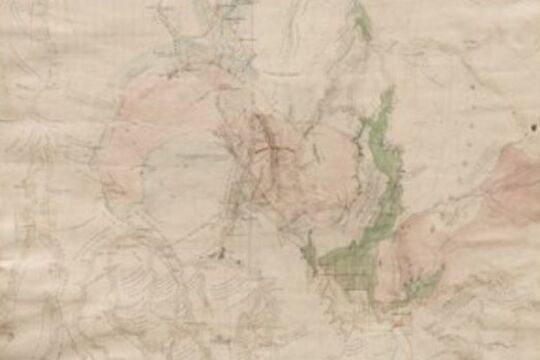
Mapping Great Change
This series of films and stories is centred on a beautiful and complex map with the ungainly name: Plan of the General Survey from the Town of Malmsbury to the Porcupine Inn, from the sources of Forest Creek to Golden Point, shewing the Alexandrian Range, also Sawpit Gully, Bendigo and Bullock Creeks.
In many ways, the map is a mirror of our times: the map is a record of the 'critical years' between 1835 and 1852 in which the dispossession of Aboriginal people of Victoria was allowed to occur; we contemporary people are in the "critical decade" for making the changes necessary to avoid catastrophic climate change.
If we fail to act effectively in this decade, it will be as loaded with moral and practical consequences for coming generations as the moral and policy failures of our colonial ancestors was for the Traditional Owners of the land.
-

Lola Montez, Star Attraction
When gold fever gripped central Victoria in the 1850s, hundreds of thousands of people arrived from all over the world, including Africa, the Americas, China, Europe and India.
The tent cities that appeared overnight brought people together regardless of whether they were rich or poor, aristocrat or convict, man or woman, lucky or unlucky. Everyone co-existed side by side, creating a society in a state of flux. With roles less fixed, it was a relatively liberal time.
But by 1856 the teeming, transgressive society began to settle. Ballarat was becoming an established town where men were comfortable to bring their wives and families. The process of social stratification, and the rise of associated moral agendas, began to take hold.
It was into this atmosphere that international sensation, Lola Montez, arrived.
Montez was born Maria Eliza Dolores Rosanna Gilbert in Ireland in 1818. Self-made, creative and charismatic, she mixed with notable figures of her day, including George Sand and Emperor Nicholas I of Russia. She was politically influential, and the consort to King Ludwig I of Bavaria, who made her Countess of Landsfeld. Her other lovers included composer Franz Liszt and writer Alexandre Dumas.
Montez was hugely popular and controversial, just as pop star, Madonna, was a century later. Crowds descended on the Victoria Theatre in the Goldfields to witness her notorious 'Spider Dance', a titillating version of a tarantella.
Through Montez and her 'Spider Dance' (as represented by the interpretive theatre presented at the Sovereign Hill Outdoor Museum), this story explores the broader social forces at play on the goldfields at the time she visited.
The story also includes several moving postcards, giving snapshots of life on the goldfields in the nineteenth century.
-

Como House and the Armytage Family
The Armytage family owned Como House in South Yarra for nearly 95 years. The property was managed by the women of the family for more than seventy years from 1876 to 1959. The history of the Armytage family, and the families who worked for them, provides an insight into almost a century of life on a large estate.
Como was purchased in 1864 by Charles Henry Armytage and it became the home of Charles, his wife Caroline, and their ten children. Charles died in 1876 and Caroline in 1909. Their daughters Leila, Constance, and Laura lived on at Como and left an indelible impression there.
The last surviving children of Charles and Caroline - Constance and Leila - sold Como to The National Trust of (Vic) in 1959. Como was the first house acquired by the Trust. One of the most significant aspects of this purchase was the acquisition of the complete contents of the house. The Armytage sisters realized that if Como was to survive as an expression of their family and its lifestyle, it must remain intact as a home. They also left an extensive archive of diaries, letters, journals and photographs.
Boasting one of Melbourne’s finest gardens, an inspiring historic mansion, and an impressive collection of antique furniture, the property provides a glimpse into the privileged lifestyle of its former owners; one of Australia’s wealthiest pioneer families.
Life can be seen to contain two major elements: the animate and the inanimate. While the inanimate bricks and mortar, objects and pathways, help in our understanding of this family, it is the animate, the social history, which makes Como come alive.
The text above has been abstracted from an essay The Armytage Family of Como written by Adrea Fox for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The entire text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
-

Chinese Australian Families
Dreams of Jade and Gold: Chinese families in Australia's history
From the 1840s onwards, Chinese people have come to Australia inspired by dreams of happiness, longevity and prosperity - of 'jade and gold' in a new and strange land. For most of that time, Chinese people in Australia have been predominantly male. Most of them were temporary sojourners who came to earn money for their families back in the village - most did not intend to settle in Australia.
Despite the predominance of male sojourning, a small proportion of Chinese men in nineteenth-century Australia brought their wives and children to live with them, or married here. As Australian-born children of these families grew to adulthood, their parents would seek brides and grooms on their behalf amongst other Chinese families in Australia.
The majority of post-1905 Chinese brides of Chinese-Australian sons were never able to settle here. Some children were born in China or Hong Kong. Some were born in Australia. Families like this were split for decades, until immigration laws were relaxed.
In the nineteenth century, many of the Chinese men who wanted wives in Australia married or lived de facto with non-Chinese women. At least 500 European-Chinese partnerships are estimated to have occurred before 1900.
Despite repeated waves of racism and official discrimination from the 1840s to the 1970s, a sizeable number of families of Chinese background have put down roots in this country.
In 1973 the Whitlam government abolished racist provisions in immigration laws. Since then, the number of ethnic Chinese migrants has increased dramatically. They have come primarily as family groups - not as sojourners, but as permanent immigrants. They come not only from China and Hong Kong, but also from Malaysia, Singapore, Vietnam, Cambodia and Indonesia, as well as from further afield. The Chinese are now a highly visible and generally accepted part of the Australian community of cultures.
The text above has been abstracted from an essay 'Dreams of Jade and Gold: Chinese families in Australia's history' written by Paul Macgregor for the publication The Australian Family: Images and Essays. The full text of the essay is available as part of this story.
This story is part of The Australian Family project, which involved 20 Victorian museums and galleries. The full series of essays and images are available in The Australian Family: Images and Essays published by Scribe Publications, Melbourne 1998, edited by Anna Epstein. The book comprises specially commissioned and carefully researched essays with accompanying artworks and illustrations from each participating institution.
-

Walhalla: fires, floods and tons of gold
In a remote, steep, and heavily timbered valley in the Victorian Alps, in the summer of 1862-63, a small party of prospectors found encouraging signs of gold at the fork of a tributary of the Thomson River. It was December. By February of the next year an immense quartz reef had been discovered.
This reef – Cohen’s Reef - yielded over 50 tonnes of gold, making Walhalla one of Victoria’s richest and most vibrant towns, and home to thousands: with hotels, shops, breweries, churches, school, jail and its own newspaper. It also had its own photographic studio, headed by the Lee brothers.
Several albums still survive of Walhalla at its peak, providing a fascinating, evocative photographic record of a 19th century mining town; capturing a moment that was to be shortlived.
In 1910 the railway arrived, but too late: the gold was disappearing. The town emptied out and began its long sleep, until the 1980s when restorations began in earnest, and electricity finally arrived in 1998.
William Joseph Bessell (ex Councillor of the Shire of Walhalla) was presented this series of photos in 1909 on the eve of his departure from Walhalla.
-
 Isaac Douglas Hermann & Heather Arnold
Isaac Douglas Hermann & Heather ArnoldCarlo Catani: An engineering star over Victoria
After more than forty-one years of public service that never ended with his retirement, through surveying and direct design, contracting, supervision, and collaborative approaches, perhaps more than any other single figure, Carlo Catani re-scaped not only parts of Melbourne, but extensive swathes of Victoria ‘from Portland to Mallacoota’, opening up swamplands to farming, bringing access to beauty spots, establishing new townships, and the roads to get us there.
-

Family Stories
From the nuclear to the extended family, from groups of close friends, communities and neighbourhoods, to one on one relationships: family means many different things to different people.
Family describes our most cherished, and sometimes most difficult, relationships. In this collection of digital stories and videos, Victorians share their family stories.
Family stories include stories of immigration; disadvantage and survival, indigenous life, stories of sickness and health; life and death; childhood and old age.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that some of the videos in this story may contain images of deceased persons and images of places that could cause sorrow.
-
 Walter Barber
Walter BarberThe Dreamer & the Cheerful Thing
Some months after my grandfather Bob Snape’s death in 1977 I collected two old trunks full of memorabilia from his last home, in Sandringham.
What a treasure it turned out to be: jammed full of papers, comprising correspondence, diaries, short stories, a poem or two, much of it typed, some of it hand-written, some official-looking documents and some music scores roughly sorted into manila folders, and a variety of souvenirs and ephemera. There were also half a dozen ordnance maps, aerial photographs of some Western Front battlefields and some battered old albums containing postcards, of WW1 France and Belgium, but also of England and Wales. These have since been catalogued on the Warrnambool RSL Victorian Collections page.
Bob’s treasure trove tells the story of his experiences during the war, and that of his younger brother Harold who also fought. Bob was a prolific correspondent and diarist, whilst Harold’s own tiny pocket diary alone ran to approximately 40,000 words. Near the end of his life, Bob told me, “You can burn the lot for all I care. You decide when I’m gone....”
Walter J.R. Barber
-

Ballarat Underground
The story of Ballarat is tied to the story of mining, with hundreds of thousands of people flocking there in the 1850s to seek their fortune. The few lucky ones became wealthy, but most were faced with the harsh reality of needing a regular income. The Ballarat School of Mines was established in 1870 to train men in all aspects of mining.
When the First World War was declared in 1914, thousands of Ballarat men enlisted. Many of these men were miners who had trained at the Ballarat School of Mines and worked in the town’s mining industries. Their skills were recognised, and tunnelling companies were created to utilise them in strategic and secretive ways. Underground (literally) campaigns were designed where the men tunnelled underneath enemy lines to lay explosives. The intention: to cause significant destruction from below. It was dangerous and cramped work, not for the faint hearted.
One hundred years on, local collecting organisation Victorian Interpretive Projects, in conjunction with Ballarat Ranges Military Museum, is asking local residents and relatives of former Ballarat miners to share their photographs, objects and stories.
This is the story of the miners who left Ballarat to fight in the First World War. It is also the story of the people seeking to commemorate them through research and family history, enabling an ongoing legacy through contributions to the public record.
-
 Wind & Sky Productions
Wind & Sky ProductionsMany Roads: Stories of the Chinese on the goldfields
In the 1850s tens of thousands of Chinese people flocked to Victoria, joining people from nations around the world who came here chasing the lure of gold.
Fleeing violence, famine and poverty in their homeland Chinese goldseekers sought fortune for their families in the place they called ‘New Gold Mountain’. Chinese gold miners were discriminated against and often shunned by Europeans. Despite this they carved out lives in this strange new land.
The Chinese took many roads to the goldfields. They left markers, gardens, wells and place names, some which still remain in the landscape today. After a punitive tax was laid on ships to Victoria carrying Chinese passengers, ship captains dropped their passengers off in far away ports, leaving Chinese voyagers to walk the long way hundreds of kilometres overland to the goldfields. After 1857 the sea port of Robe in South Australia became the most popular landing point. It’s estimated 17,000 Chinese, mostly men, predominantly from Southern China, walked to Victoria from Robe following over 400kms of tracks.
At the peak migration point of the late 1850s the Chinese made up one in five of the male population in fabled gold mining towns of Victoria such as Ballarat, Bendigo, Castlemaine, Beechworth and Ararat. It was not just miners who took the perilous journey. Doctors, gardeners, artisans and business people voyaged here and contributed to Victoria’s economy, health and cultural life. As the nineteenth century wore on and successful miners and entrepreneurs returned home, the Chinese Victorian population dwindled. However some chose to settle here and Chinese culture, family life, ceremony and work ethic became a distinctive feature of many regional Victorian towns well into the twentieth century.
By the later twentieth century many of the Chinese relics, landscapes and legacy of the goldrush era were hidden or forgotten. Today we are beginning to unearth and celebrate the extent of the Chinese influence in the making of Victoria, which reaches farther back than many have realised.
-

Eureka Stories
What is Eureka and what happened there?
In the early hours of 3 December 1854 a force of police and other troops charged a reinforced camp constructed by miners on the Eureka gold diggings. About 150 diggers were inside the stockade at the time of the attack. In the fighting, 4 soldiers and about 30 other people were killed, and another 120 people taken prisoner. Thirteen people from the stockade were charged with treason – these men were either tried and found not guilty, or charges against them were dropped.
Many people think of the Eureka Stockade as a battle between the diggers (rebellious Irish fighting for democracy) and the police and colonial militia (the forces of the British Crown in the Colony). It’s nice to have a single story to make sense of everything. Eureka, however, is not a single simple narrative. Several stories intertwine and involve many of the same people and places. Let’s look at some of them.
The Hated Gold Licences
In 1854, people mining for gold around Victoria had to pay a monthly fee of 30 shillings for the right to mine, regardless of how much gold they found. Someone who had been looking for gold unsuccessfully for months still had to pay the same fee as someone who was pulling out gold by the pound. Diggers argued that it was an unfair tax, imposed on them without their consent, as they did not have the right to vote. (After the Goldfields Royal Commission the licensing fee was changed to a tax on gold when it was being exported.)
Not only did the diggers resent the licence fee, they were angry at the way the goldfields police went about checking that miners had licences. Diggers claimed that police were beating people up or chaining them to trees if they could not produce a licence, and undertaking unnecessary inspections on people they didn’t like. Resentment of the licence fee and the conduct of police in their “licence hunts” was expressed across the Victorian goldfields.
The Unfair Treatment of Diggers by the Police and Justice System
People around the Victorian goldfields were also unhappy with the lack of thoroughness with which police had investigated a number of goldfields crimes. They were concerned about what they thought was the unfair and secretive way people were charged and convicted of crimes. There were claims by people living on the goldfields that it was necessary to bribe police and government officials in order to do business and stay safe. As the goldfields populations increased, tensions between the goldfields communities and police and other government officials rose.
In Ballarat a series of events (a murder, an arrest and a hotel burning) in late 1854 involving police and Ballarat locals led to the arrests of three men for burning down the Eureka Hotel. These arrests caused enormous disquiet in the area, adding weight to calls by the Ballarat Reform League and other organisations around the goldfields for a fundamental change to the system of government in the Colony – the next element in our Eureka story.
Demands for a Democratic Political System
Since the early 1850s people had been calling for the government to abandon the gold licensing system, remove the gold commissioners, and provide the Colony with a better policing and justice system. Despite an investigation by the Victorian parliament into the goldfields in 1853 (a Legislative Council Select Committee) the government did not make significant changes. By November 1854 an organisation called the Ballarat Reform League had formed in response to official inaction and had written a Charter of democratic rights. They organised a "monster meeting" in Ballarat on 11 November 1854, to have it accepted, and met with Governor Hotham on 27 November 1854, to demand his acceptance of the Charter, and the release of the three prisoners charged with burning down the Eureka Hotel.
Population Explosion
The people calling for these changes to taxes, justice and political participation came from many different parts of the world, such as the United States, Canada, England, Ireland, Scotland, Italy, Germany. This corner of South-Eastern Australia was rapidly changing as thousands and thousands of people arrived to search for gold. Many of these people were educated and from middle-class or merchant backgrounds. The domination of squatters running sheep on large land holdings was being challenged by dense populations of people in goldrush regions generating enormous wealth in the colony, and a desire from these recent arrivals to take up land, and have a say in the making of laws.
We have looked at some parts of the Eureka story; at what unfolded around the colony as a result of this mix of people, events and system of government. There are many other stories about Eureka. To find out more, you can explore the stories through original documents at Eureka on Trial.
