Showing 34 items with the theme 'Land And Ecology'
-

Seeing the Land from an Aboriginal Canoe
This project explores the significant contribution Aboriginal people made in colonial times by guiding people and stock across the river systems of Victoria.
Before European colonisation Aboriginal people managed the place we now know as Victoria for millennia. Waterways were a big part of that management. Rivers and waterholes were part of the spiritual landscape, they were valuable sources of food and resources, and rivers were a useful way to travel. Skills such as swimming, fishing, canoe building and navigation were an important aspect of Aboriginal Victorian life.
European explorers and colonists arrived in Victoria from the 1830s onwards. The newcomers dispossessed the Aboriginal people of their land, moving swiftly to the best sites which tended to be close to water resources. At times it was a violent dispossession. There was resistance. There were massacres. People were forcibly moved from their traditional lands. This is well known. What is less well known is the ways Aboriginal people helped the newcomers understand and survive in their new environment. And Victoria’s river system was a significant part of that new environment.
To understand this world we need to cast ourselves back into the 19th century to a time before bridges and cars, where rivers were central to transport and movement of goods and people. All people who lived in this landscape needed water, but water was also dangerous. Rivers flooded. You could drown in them. And in that early period many Europeans did not know how to swim. So there was a real dilemma for the newcomers settling in Victoria – how to safely cross the rivers and use the rivers to transport stock and goods.
The newcomers benefited greatly from Aboriginal navigational skills and the Aboriginal bark canoe.
CULTURAL WARNING: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users are warned that this material may contain images of deceased persons and images of places that could cause sorrow.
-

1956 Flood
In 1956, a monster flood overwhelmed the banks of the Murray and Darling Rivers, producing floodwaters in surrounding towns and rural areas that reached over 30 feet above normal levels.
The Murray Darling Environmental Foundation's 1956 Flood video features historical footage - including photographs and wonderful super8 film from personal collections - that document the rise and flow of the waters, and the monumental effort mobilised to tackle them.
It is presented here in 3 extracts.
The full video is over 25 minutes long, and copies can be obtained from:
Emma Bradbury, Murray Darling Association, Post Office Box 1268, Echuca 3564
Email: [email protected]
-
 Isaac Douglas Hermann & Heather Arnold
Isaac Douglas Hermann & Heather ArnoldCarlo Catani: An engineering star over Victoria
After more than forty-one years of public service that never ended with his retirement, through surveying and direct design, contracting, supervision, and collaborative approaches, perhaps more than any other single figure, Carlo Catani re-scaped not only parts of Melbourne, but extensive swathes of Victoria ‘from Portland to Mallacoota’, opening up swamplands to farming, bringing access to beauty spots, establishing new townships, and the roads to get us there.
-
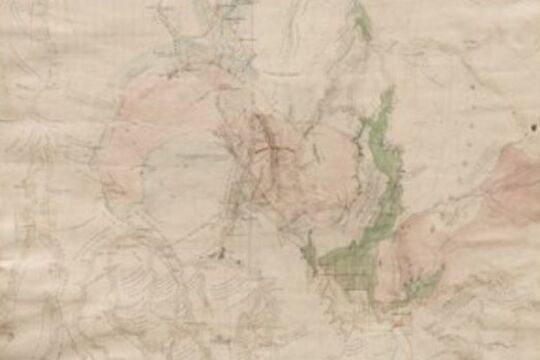
Mapping Great Change
This series of films and stories is centred on a beautiful and complex map with the ungainly name: Plan of the General Survey from the Town of Malmsbury to the Porcupine Inn, from the sources of Forest Creek to Golden Point, shewing the Alexandrian Range, also Sawpit Gully, Bendigo and Bullock Creeks.
In many ways, the map is a mirror of our times: the map is a record of the 'critical years' between 1835 and 1852 in which the dispossession of Aboriginal people of Victoria was allowed to occur; we contemporary people are in the "critical decade" for making the changes necessary to avoid catastrophic climate change.
If we fail to act effectively in this decade, it will be as loaded with moral and practical consequences for coming generations as the moral and policy failures of our colonial ancestors was for the Traditional Owners of the land.
-

Panorama: A question of perspective
TarraWarra Museum of Art is located in the picturesque Yarra Valley in Victoria, Australia.Visitors to the Museum are afforded a spectacular, resonant and panoramic experience of ‘nature’ through the north facing windows. The view stretches towards the distant Toolangi rainforest across planted vines, native bushland and farmland.
The region is surrounded by a spectacular mountain range that includes Mt Baw Baw, Mt Donna Buang, Mt Juliet, Mt Riddell and Mt Toolebewong. As these names attest, we are situated in an area of significant Indigenous history and colonisation. Tarrawarra is a Wurundjeri word that translates approximately as ‘slow moving water’ and is the name given to the area in which the Museum is located.
The Yarra Valley sunsets, soundscapes, seasonal changes, Indigenous histories, ecological vulnerabilities and environmental challenges are in a complex and ever changing entanglement. Since 2012, the Museum has explored this context through special exhibitions and commissions, forums and performances, screenings and lectures. As such, the Museum has sought to understand the complexity of our site, and with that, the broader intersections between art and landscape. Artists provide us the opportunity to ‘see’ the landscape in a different way. They imagine it, call it into being, reflect upon it, animate it, unravel its hidden histories, and expose its ecological sensitivities.
Panorama, the exhibition, was an integral part of this ongoing conversation and imaginative exploration. Our intention was not so much to write a narrative history of Australian landscape painting. Rather, it was to be attuned to the intermingling of voices, points of view, perspectives - colonial and modern, contemporary and Indigenous – that comprise the uniquely Australian persistence to unravel the ‘patter’ of nature.
As a phenomenon to which we are all very accustomed, it is easy to overlook the simple fact that for a landscape to come into being it requires a ‘point of view’, a subjective consciousness to frame a particular expanse of the natural world. As the art historian Simon Schama remarks in his landmark survey on the genre, Landscape and Memory, ‘it is our shaping perception that makes the difference between raw matter and landscape’. [i] The centrality of the viewer’s position in constructing a vista is clearly evident in terms such as ‘perspective’, ‘prospect’, and ‘view point’ which are synonymous with ‘position’, ‘expectation’, and ‘stance’. This highlights that there is always an ineluctable ideological dimension to the landscape, one that is intimately entwined with a wide range of social, economic, cultural and spiritual outlooks. Turning to the notion of the panorama, a brief survey of its conception and infiltration into everyday speech, reveals how our way of seeing the landscape is often tantamount to the formation and delineation of our personal, communal, and national identities.
The term panorama was first coined to describe the eponymous device invented by the British painter Robert Barker which became a popular diversion for scores of Londoners in the late 18th century. Consisting of a purpose built rotunda-like structure on whose cylindrical surface landscape paintings or historical scenes were displayed, ‘The Panorama’ contained a central platform upon which viewers observed the illusionistic spectacle of a sweeping 360 degree vista. With its ambitious, encyclopaedic impulse to capture and concentrate an entire panoply of elements into a singular view, it is telling that this construction would soon give rise to an adjective to describe, not only an expansive view extending in all directions, but also a complete and comprehensive survey of a subject. As the curators Jean-Roch Bouiller and Laurence Madeline argue, these different meanings convey ‘the very essence of the panoramic phenomenon: the central role of perspective, a certain appropriation of the world that follows, the feeling of dominating a situation simply due to having a wide and complete view’.[ii] Indeed, as art historian Michael Newman reveals, the whole notion of the panorama originated in military conceptions of the landscape as a battlefield, whereby strategic vantage points are key to tactical planning.[iii] Underlying its transformation into a form of popular entertainment, the panorama is rooted in a particular form of political authority based on surveying, mapping and commanding the subject of the view.
In this exhibition, the term panorama was invoked to acknowledge that ways of perceiving the landscape have their own histories which have arisen out of particular social, political and cultural contexts. As the landscape architect Anne Whiston Spirn contends: ‘In every landscape are ongoing dialogues; there is “no blank slate”; the task is to join the conversation’.[iv]However, far from claiming to present an unbroken view or a complete survey, Panorama challenged the very notion of a single, comprehensive monologue by presenting a series of works which engaged with the discourse of landscape in a diverse range of voices. Taking advantage of the tremendous depth and strength of the TarraWarra Museum of Art collection gifted by its founders Eva Besen AO and Marc Besen AC, the exhibition was staged in two parts, with a different selection of paintings exhibited in each half. Displayed in distinct groupings which explored alternative themes and concerns, Panorama highlighted the works of key artists who have redefined, expanded and interrogated the idea of the landscape in ways which suggest that it is far from settled.
Further Information
[i] Simon Schama, Landscape and Memory, New York: Vintage Books, 1996, p. 10.
[ii] Jean-Roch Bouiller and Laurence Madeline, Introductory text for the exhibition I Love Panoramas, MuCEM and the Musées d’Art et d’Histoire, Geneva, 4 November 2015 - 29 February 2016, URL: http://www.mucem.org/en/node/4022
[iii] See ‘The Art Seminar’ in Landscape Theory, (eds. Rachael Ziady DeLue and James Elkins), New York and London: Routledge, 2008, p. 130.
[iv] Anne Whiston Spirn, ‘“One with Nature”: Landscape, Language, Empathy and Imagination’ in Landscape Theory, 2008, p. 45.
-

Paintings Porcelain and Photography
Geelong Gallery was established in 1896 by twelve passionate citizens who believed Victoria's second largest and fastest growing city deserved an art institution befitting an aspiring metropolis. Since then, Geelong Gallery has established a collection of some 6,000 items – significant amongst these items are their holdings of paintings, porcelain and photography.
The gallery’s collection of Australian painting tells the history of the region from colonial times to the early twentieth century. Eugene von Guerard’s View of Geelong provides a sweeping panorama of Geelong seen from a vantage point near the village of Ceres in the nearby Barrabool Hills in 1856. While Arthur Streeton’s painting Ocean blue, Lorne, one of the gallery’s most recent acquisitions, depicts a shimmering summery sky, a view through slender young gum trees and down to the pristine sand and aquamarine ocean below in the 1920’s.
Geelong Gallery has a large and specialised collection of British painted porcelain spanning 1750 – 1850. It is one of the most significant holdings in Australia and is part of a bequest by well-known local citizen Dorothy McAllister. A fine example is the 'Buckingham Palace' card tray by renowned manufacturer Worcester dating to the 1840’s.
The gallery’s photographic collection is very much of the twentieth century, but not without references to earlier times and other works in the collection. Polixeni Papapetrou’s photograph In the Wimmera 1864 #1 created in 2006 examines the narrative of the ‘lost child’ and refers to Frederick McCubbin’s late nineteenth century paintings of children ‘lost’ or at least wandering absent-mindedly through the Australian bush.
-

Murray Darling Palimpsest #6
In 2006, Mildura Palimpsest became the Murray Darling Palimpsest, emphatically underscoring the identity of the region and its environmental interdependence.
The Murray Darling Palimpsest, staged in locations throughout the Murray Darling Basin, continues Palimpsest’s direct engagement with issues of environmental and social sustainability. With land and water use no longer in the background, Palimpsest is remarkable in its recognition that art affects attitudes, and reflects the engagement and connection many contemporary artists have to the environment; perhaps the most pressing issue we now face.
In 2006, Palimpsest brought together artists, scientists, environmentalists and other academics and commentators with the future of the Murray Darling Basin firmly in sight.
-

Murray Darling Palimpsest #5
Mildura is situated just south-east of the confluence of two of Australia’s great rivers: the Darling and the Murray.
As water and land use creep up to the top of our national agenda, the Mildura region emerges as one of Australia’s most contested places, with small ‘block’ farmers, multinational companies, State and Federal politics, among others, entering the debate.
As such, it was perhaps the most natural place for the biennial Palimpsest expositions and symposiums to arise. Following on from Mildura’s famous sculpture triennials, Palimpsest plays on the idea of the landscape as palimpsest, written and rewritten over both physically and with layers of meaning. Palimpsest engages directly with land, land use, water and issues of sustainability, involving artists, and scientists and other experts, spearheading the creative exploration of key environmental issues.
-
 Rohan Long
Rohan LongVictorians & Native Birds: An evolving relationship
The people of Victoria have had a constantly changing relationship with their native birdlife.
Ever-present and iconic, we’ve put Australian birds on official state heraldry and on tomato sauce bottles and biscuit packets. There has always been an immense fondness and respect for our unique birds. However, attitudes towards wildlife generally and birds specifically have undergone seismic paradigm shifts over the last few hundred years.
Looking at objects catalogued here on Victorian Collections, we can map this change and trace the ways that Victorians have interacted with birds, from Indigenous spirituality to citizen science programs.
-
 Lauren McAlary
Lauren McAlaryCollecting Fire: A new kind of practice
The fires of February 2009 left an indelible mark on the histories of Victoria’s community collecting organisations; whether through blackened ash markings or by the absence of once cherished objects and ephemera.
This exploration of Victoria’s collecting response to the Black Saturday bushfires is inspired by Liza Dale‐Hallett, Rebecca Carland and Peg Fraser’s reflections on the Victorian Bushfires Collection project, in 'Sites of Trauma: Contemporary Collecting and Natural Disaster'.
-
 Museums Victoria
Museums VictoriaTime Flies in Museum Collections: Ornithology in Victoria
Natural science collections are vast treasure troves of biological data which inform current research and conservation.
Alongside bird skins, nests, eggs and DNA samples sits a magnificent collection of rare books, illustrations and images which charts the history of amateur and professional ornithology in Victoria.
Whilst the big names such as John Gould (1804–1881), are represented, the very local, independent bird observers such as John Cotton (1801-1849) and Archibald James Campbell (1853–1929) made some of the most enduring contributions.
The collections also document the bird observers themselves; their work in the field, building collections, their efforts to publish and the growth of their ornithological networks. Captured within records are changes in ornithological methods, particularly the way data is captured and published.
However the data itself remains as relevant today as it did when first recorded, 160 years of collecting gives us a long-term picture of birdlife in Victoria through space and time.
-
 Jary Nemo and Lucinda Horrocks
Jary Nemo and Lucinda HorrocksCollections & Climate Change
The world is changing. Change is a natural part of the Earth’s cycle and of the things that live on it, but what we are seeing now is both like and unlike the shifts we have seen before.
Anthropogenic change, meaning change created by humans, is having an impact on a global scale. In particular, human activity has altered the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere, causing the world’s climate to change.
Already in the state of Victoria we are seeing evidence of this change around us. In the natural world, coastal waters are warming and bringing tropical marine species to our bays. Desert animals are migrating to Victoria. Alpine winters are changing, potentially putting plants and animals at risk of starvation and pushing species closer to the margins. In the world of humans, island and coastal dwellers deal with the tangible and intangible impacts of loss as sea levels rise, bush dwellers live with an increased risk of life-threatening fires, farmers cope with the new normal of longer droughts, and we all face extreme weather events and the impacts of social and economic change.
This Collections and Climate Change digital story explores how Victoria’s scientific and cultural collections help us understand climate change. It focuses on three Victorian institutions - Museums Victoria, the Royal Botanic Gardens Victoria and Parks Victoria. It looks at how the information gathered and maintained by a dedicated community of researchers, curators, scientists, specialists and volunteers can help us understand and prepare for a hotter, drier, more inundated world.
The story is made up of a short documentary film and twenty-one examples highlighting how botanical records, geological and biological specimens and living flora and fauna provide a crucial resource for scientists striving to map continuity, variability and change in the natural world. And it helps us rethink the significance of some of Victoria’s cultural collections in the face of a changing climate.
-

The Ross Sea Party
As Shackleton’s ambitious 'Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition' of 1914 foundered, the Ross Sea party, responsible for laying down crucial supplies, continued unaware, making epic sledging journeys across Antarctica, to lay stores for an expedition that would never arrive.
In 1914 Ernest Shackleton advertised for men to join the Ross Sea Party which would lay supply deposits for his 'Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition'. Three Victorians were selected for the ten-man shore party: Andrew Keith Jack (a physicist), Richard Walter Richards (a physics teacher from Bendigo), and Irvine Owen Gaze (a friend of Jack’s).
The Ross Sea party commenced laying supplies in 1915 unaware that Shackleton’s boat Endurance had been frozen in ice and subsequently torn apart on the opposite side of the continent (leading to Shackleton’s remarkable crossing of South Georgia in order to save his men). Thinking that Shackleton’s life depended on them, the Ross Sea Party continued their treacherous work, with three of the men perishing in the process. The seven survivors (including Jack, Richards and Gaze) were eventually rescued in 1917 by Shackleton and John King Davis.
In total, the party’s sledging journeys encompassed 169 days, greater than any journey by Shackleton, Robert Scott, or Roald Amundsen – an extraordinary achievement.
Jack, Gaze and others in the party took striking photographs during their stay. Jack later compiled the hand coloured glass lantern slides, which along with his diaries, are housed at the State Library of Victoria.
-

Ash Wednesday 30
On 16 February 1983 the Ash Wednesday bushfires burned approximately 210,000 hectares of land, 2,080 homes were destroyed and 75 people, including 47 Victorians, lost their lives.
Among the 47 Victorians killed were volunteer Country Fire Authority (CFA) firefighters from Panton Hill, Nar Nar Goon, Narre Warren and Wallacedale brigades.
Many businesses, stores, equipment, machinery, stock and other assets were lost. The total cost of the property damage in Victoria was estimated to be over $200 million.
These web pages were created to commemorate the 30th anniversary of the Ash Wednesday Bushfires in 2013.
The Victorian Government invited people to share their stories of recovery, healing and hope as a tribute to those who experienced a natural disaster, and as an inspiration to all Victorians.
A collection of selected stories and short films have now been published here.
-
 Amanda Ahmed and Mali Moir
Amanda Ahmed and Mali MoirAn Eye for Eucalypts
In his hometown of Ararat, Stan Kelly (1911 – 2001) was known as an engine driver and as a talented painter of plants and flowers. A determined amateur, Stan painted at home on a small table and shared his talent by teaching botanical art in Ararat. Today, many Australians travelling overseas carry his artwork in their pocket.
Kelly is now recognised as one of Australia’s premier botanical illustrators, especially respected for his works on eucalypts. His first book, Australian Eucalypts in Colour, was published in 1949. His most celebrated work, Eucalypts Volumes I & II, was first published in 1969 and became a core reference for students of Australian botany.
Kelly received an Order of Australia Medal in 1980. In 2009, he was posthumously honoured when a selection of his botanical illustrations was adapted for the ‘N’ series Australian passport.
The Langi Morgala Museum in Ararat houses a permanent exhibit on Stan Kelly and his work, including a fine collection of his paintings.
A collection of over 500 of Kelly’s watercolour paintings is held by the National Herbarium of Victoria, Royal Botanic Gardens Melbourne.
-

Savoy Ladies Group
The Italian community of Myrtleford, in the picturesque Ovens Valley in alpine North Eastern Victoria, arrived mainly to work in the tobacco industry which once thrived in the area. The region now has a distinctive Italian-Australian culture with settled second, third and fourth generation Italian families.
Tobacco farming was a lonely experience for many of the Italian women who migrated to Myrtleford. Unlike their husbands, the women stayed largely on the farms and lacked social contact outside of their immediate circle. Once their children grew up and mechanisation changed the labour requirements on the farms, women were frequently on their own.
The Myrtleford Savoy Ladies Group was founded in 1983 by nuns concerned about the social isolation of women in the area. It has been a great success, forming a network of companionship amongst women of Italian heritage to this day.
Cultural Warning: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander users of this website are warned that this story contains images of deceased persons and places that could cause sorrow.
