Showing 1653 items in the category Documentation with item type Plan
-
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan - Subdivision Plan, Camberwell Mountain View Estate, 1923
The Kew Historical Society collection includes almost 100 subdivision plans pertaining to suburbs of the City of Melbourne. Most of these are of Kew, Kew East or Studley Park, although a smaller number are plans of Camberwell, Deepdene, Balwyn and Hawthorn. It is believed that the majority of the plans were gifted to the Society by persons connected with the real estate firm - J. R. Mathers and McMillan, 136 Cotham Road, Kew. The Plans in the collection are rarely in pristine form, being working plans on which the agent would write notes and record lots sold and the prices of these. The subdivision plans are historically significant examples of the growth of urban Melbourne from the beginning of the 20th Century up until the 1980s. A number of the plans are double-sided and often include a photograph on the reverse. A number of the latter are by noted photographers such as J.E. Barnes.The so-called Camberwell Mountain View Estate was a subdivision on ‘the corner [of] Burke Road, Eyre and Wills Streets, Deepdene’. The Estate was not the first attempt to subdivide this land holding. In 1884, 1888 and 1894 the Belmore Park subdivision proposed 18 allotments for this parcel of land. The final stages of the Belmore Park subdivision occurred during the Depression of the 1890s. Apart from perhaps one block facing Burke Road, which is unnumbered in the Mountain View Estate subdivision, the rest must have remained unsold. The later subdivision would redraw the original 18 allotments, creating 22 new lots. In the Locality Plan on the left side of the subdivision plan, Deepdene Station, which formed part of the Outer Circle Railway is represented, as is the location of Deepdene Primary School. A selling point was the proposed extension of the Burke Road tram beyond its terminus at Cotham Road. The extension did not eventuate.subdivision plans - camberwell, mountain view estate -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan, 'Burnley Park', 1987
Tracing paper copy dated July 1987. Landscape Graphics - Assignment One, 'Burnley Park' Site Plan. Scale 1:100. Includes contours and existing trees.burnley park, trees, landscape graphics -
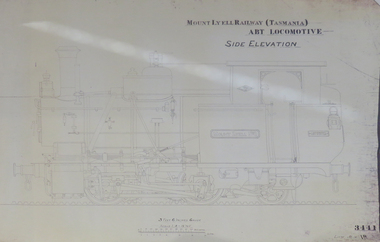 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPlan, Mount Lyell Railway (Tasmania) ABT Locomotive Side Elevation, undated
On 29 March 1893 the Mount Lyell Mining and Railway Company was formed. This Tasmanian mining company was often referred to as Mount Lyell. Mount Lyell, and was the dominant copper mining company of the Tasmanian West Coast from 1893 to 1994, and was based in Queenstown, Tasmania. After consolidation of leases and company assets at the beginning of the twentieth century, Mount Lyell was the major company for the communities of Queenstown, Strahan and Gormanston. It closed in 1994. The Mount Lyell mining operations produced more than a million tonnes of copper, 750 tonnes of silver and 45 tonnes of gold since mining commenced in the early 1890s – which is equivalent to over 4 billion dollars worth of metal in 1995 terms.Copy of a plan of a locomotive.mount lyell, locomotive, mount lyell railway, quuenstown, tasmania, strahan, gormamston, railway -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPlan, Kew! Kew!, 1888
The Land Boom of the 1880s accelerated the rate of subdivisions in Kew. This subdivision, 'Kew! Kew!' was also impacted by, or resulted from, the decision by the Victorian Government to construct the Outer Circle railway. Construction of the railway began in 1888 and was completed in 1891. Plan of an 1888 subdivision bounded by Bulleen Road (now High Street), Gladstone Street (now Campbell Street?), Park Street (now Adeney Avenue), and Belmore Road (now Harp Road). The 16 lots in the proposed subdivision are bisected by the route of the Outer Circle railway, and next to the proposed Normanby Station (later renamed East Kew). On the plan, local landmarks such as the tram terminus, the Harp of Erin hotel, and the station are located. The street where the lots are numbered , was called Welsh Street on the plan as this was the name of the vendor. Surrounding land owners are also named: G. Smith Esq, Matthew Maher Esq, and Maurice Neligan Esq.outer circle railway, land subdivisions -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyPlan - Shelter shed, Borough of Sandridge, Mar 1877
Hand drawn plan and elevation of tiny shelter shed "at manure depot in common", Sandridge 1877.Signed by Edward Wilson and Charles Clay (Surveyor)local government - borough of sandridge, built environment - civic, edward wilson, charles clay -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyPlan - Fire Reel Shed, Port Melbourne Courthouse, Engineer, Borough of Port Melbourne, Jun 1889
Plan with elevation, for fire reel shed behind courthouse, 1889Borough of Port Melbourne Stamp (Town Clerk's Office):Signed by E. CLARK 21-6-1889 and Stephen SPADIER, Contractor:witnessed by E.C. CROCKFORDfire and fire services, built environment - civic, edward clark, edward c crockford, town clerks -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPlan - Plan / Line Drawings - Portland Harbour Trust Slipway Bilge Blocks Trawler Halcyon, Victoria, 23/04/1980
PORT OF PORTLAND AUTHORITYFront: '42' - black texta, top right corner -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyPlan - Walter Avenue, Port Melbourne, Town of Port Melbourne, 1893 - 1919
Plan of Walter Avenue showing various cross sections, date unknown.engineering - roads streets lanes and footpaths, walter avenue, loans program -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyPlan - Floor Plan Club Hotel
Floor plan for main building and out building of Club Hotel Lakes Entrance Victoriahotels, plans, businesses, construction -
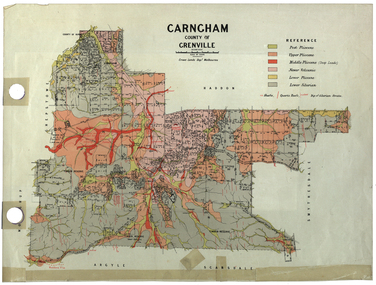 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPlan, Carngham, County of Grenville
A plan of Carngham, Victoria.snake valley, timber reserve, poverty point, recreation reserve, carngham, county of ripon, county of grenville, plan -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyPlan - Tram and roadworks, Rouse Street between Esplanade East and Esplanade West, Engineering Department, Town of Port Melbourne, Mar 1893
Plan for tram and road works in Rouse Street between Esplanades East and West and adjacent to Lagoon Loan Works 1893 plan 19; relates to specification 99.1Signed by JJ Bartlett (Mayor) 14.3.1893engineering - roads streets lanes and footpaths, sandridge lagoon, transport - tramways, arthur victor heath, town clerks, james john bartlett, mayors -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumPlan (Item) - Plan Dassault Breguet/Dornier Alpha Jet Ex GAF
-
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPlan - Ship Plan / Mould, n.d
Wooden pattern for mould for boat fittings. Rectangular, two cylinders of different diameters, one on top of the other, attached. Painted yellow/orange, underside white. -
 Bialik College
Bialik CollegePlan (item) - Extensions to Bialik College, c. 1990s and 2002
Plans for extensions to Bialik College, 429 Auburn Rd, Hawthorn, created by Ron Unger & Associates Architects, c. 1990s. Includes a plan for the new Primary School playground, 2002. Please contact [email protected] to request access to this record.1990s -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyPlan - Sandridge, 1859
1859 plan of Sandridge. Photocopy made from joined photocopies. Appears that original was joined or reinforced by narrow tapetown planning, sandridge, land sales -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyPlan - Annotated and handcoloured by Peter Libbis to indicate his research into Libbis family residences and hotels on copy of a section of an MMBW map, Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works, c. 1980s
Peter LIBBIS obtained these copies from the MMBW when he researched his family history in the 1980s. He has annotated them, colour in hotels etc. Donated to Society in 1997.One of a group of 19 photocopies of various 20th century MMBW plans, annotated/coloured in to indicate residences of Libbis family and local hotels, by Peter LIBBIS in family and hotel research - Railway yards, Ross and Clark, South Graham c 1950sbusiness and traders - hotels, built environment - domestic, transport - railways, melbourne and metropolitan board of works, libbis family -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan - Photocopy, Sunshine Planning Scheme, 1993
Photocopies. 18.02.1993. (1) 5 copies Map User Guide - Sunshine Planning Scheme. List of Zones, Reservations and additional Planning Controls. (2) Sunshine Planning Scheme - Local Section. Zones and Reserved Land Map No 2. (3) Map No 3. (4) Map No 4. Used in planning Native Garden Woodlandsunshine, reservations, native garden, planning scheme, victoria department of planning and development -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan, Garden Advisory Centre Summer House. Landscape working drawing 1:50, 1985
Copy of Landscape Working Drawing for the Agriculture Research Institute by the Public Works Department, Victoria No 85-523 L1/1 dated 30.01.1985. Scale 1:50.garden advisory centre, summer house, agriculture research institute, victoria public works department, landscape drawing, burnley gardens -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyPlan - Annotated and handcoloured by Peter Libbis to indicate his research into Libbis family residences and hotels on copy of a section of an MMBW map, Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works, c. 1980s
Peter LIBBIS obtained these copies from the MMBW when he researched his family history in the 1980s. He has annotated them, colour in hotels etc. Donated to Society in 1997.One of a group of 19 photocopies of various 20th century MMBW plans, annotated/coloured in to indicate residences of Libbis family and local hotels, by Peter LIBBIS in family and hotel research - Bay/Crockford area, Ingles to Bridgebusiness and traders - hotels, built environment - domestic, transport - railways, melbourne and metropolitan board of works, libbis family -
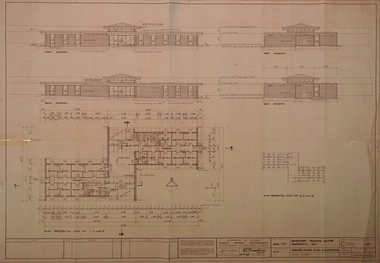 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Plan - SANDHURST BOYS CENTRE COLLECTION: SANDHURST TRAINING CENTRE BUILDING PLANS, 21/08/1969
Sandhurst Training Centre residential unit ground floor plan and elevations; prepared by Public Works Department for the Government of Victoria. 21/8/1969. Includes floor plan for residential units nos 1,4,5 comprising 12 bedrooms, 2 toilet blocks, living hall, crafts and tea room, laundry. The plan for units 2,3,6 is a mirror image. Also included are elevations for north, south, east and west views. Drawn Aug 1968 Senior Designing Architect John F Swan, Chief Architect D C Bradbury. .bendigo, institutions, sandhurst boys centre, sandhurst boys centre plans;, john f swan, d c bradbury -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyPlan - Plan Port Melbourne Town Hall, c.2024
Port Melbourne Town Hall Survey Planport melbourne town hall -
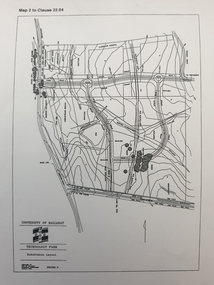 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPlan, Ballarat Technology Park plans, c1998
.1) Alotment plan .2) contour planballarat technology park, mount helen campus, canadian wetlands, ballarat to buninyong railway line, sub-division layout -
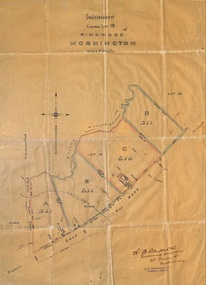 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPlan, Subdivision of Crown Lot 19, Ringwood, Victoria - circa 1915
Surveyor's map on wax paperSubdivision map includes Mullum Creek, Government Road to Anderson's Creek, later Warrandyte Road, Government Road to Lillydale, later Whitehorse Road, small creek bridge, later Sandy Creek at Ringwood Lake. Buildings marked include Roman Catholic Church, O.J. Pratt's House and Pratt's butcher shop (photos attached). Map by A.B. Bruford & Co., Licensed Surveyor, 47 Queen Street, Melbourne. -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan, City of Hawthorn. Proposed Walking Track - Yarra Bank, Burwood to Barkers, 1986
City of Hawthorn. Drawing No P26/9 dated November 1986.hawthorn, yarra bank, pridmore park reserve, walking tracks -
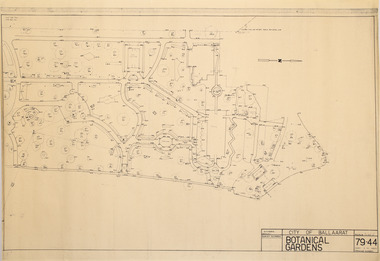 Friends of Ballarat Botanical Gardens History Group
Friends of Ballarat Botanical Gardens History GroupPlan - Survey Plan A, G. Creek, City of Ballarat Botanical Gardens
HistoricSurvey map on papersurvey map, city of ballaarat, ballarat botanical gardens -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumPlan (item) - Bristol Aeroplane 170 schematic drawings, Gusset Outer Wing
Bristol Aeroplane Company -
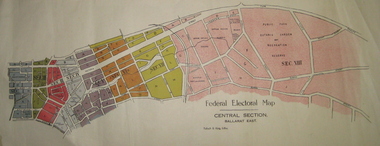 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPlan - Plans, Tulloch & King, Federal Electoral Map Subdivision of Ballarat, c1901
It is thought that these are the first federal electorial plans for the Subdivision of Ballarat. The first member of Ballarat was Alfred Deakin.May of the Federal subdivision of Ballarat, with each section depicted in a different colour. The plans include Lake Wendouree, Central Ballarat subdivision; Soldiers Hill subdivision; Ballarat East subdivision, and Central Section Ballarat East, including the Ballarat East Botanic Garden .ballarat, federation, alfred deakin, elections, plan, electoral division, electoral map, polling -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionPlan - Plan - Parking Plans Edgar Street Heywood, n.d
'Bower Bird' Museum, HeywoodParking plan for Edgar Street Heywood. Angle parking.Front: Back - 'Parking Heywood' - Red Pen -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncPlan, A Master Plan for Central Park Stawell, 2000
Grey Cover. Fawn binder a4 SizeMay 2000 Prepared for the Northern Grampians Shire Councilsport, central park, northern grampians shire -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesPlan, Pat de Moulpied, Rose Garden, 1988
Most of these plans were held in Geoff Olive's office. (1) Preliminary concept South-East corner Burnley Gardens Re-design Proposals, Amenity Horticulture III, drawn by Pat de Moulpied 1988. Original turf path destroyed after Garden Week to be replaced with paving donated by Boral. (2) Rose Garden Site Analysis by Peter Jans, Parks & Gardens 1989, pencil on paper. On reverse, "B. Site Analysis & Design Changes. (3) 2 copies pencil on tracing paper, Planting plan. (4) Planting plan on tracing paper. (5) Planting plan (roughly final version?), 1 tracing paper, 6 photocopies. (6) Notes from Geoff Olive addressed to James Hitchmough. Also photocopies of 1 - 5 and some rough sketches. Notes made by Guide Jean Corbett on the History of the Rose.pat de moulpied, peter jans, gardens, geoff olive, andrew smith
