Showing 111 items
matching machine wheel
-
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyCream Separator
Dairy farms used cream separators to separate the milk and the cream before using it themselves or selling it to the dairy companies, shops or directly to the public.This cream separator was used by P & R Creamer on their dairy farm in the Kiewa Valley.3 parts - top brass lid with hollow cylinder enclosed across its top and extending beyond its circumference. 2. Stainless Steel hollow cylinders that fit the base and the lid but has 2 long curved spouts extending out - one for the milk and one for the cream to come out 3. Black cast iron stand that houses the gear mechanisms that drive the separator cones. The gear speed reduction wheel is on one side. "Alfa-Laval MOB / 80 Gall Capacity per hr / 48 Rev of Crank per Minute / Alfa-Laval Separator / Co. Ltd / 299 Sussex St. / Sydney" - on bottom side of the machinedairy; cream separator; kiewa valley; creamer family -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietySewing Machine
... . There is a compartment in the base, right of the wheel of the machine, which.... There is a compartment in the base, right of the wheel of the machine, which ...Sewing machines were used by some ladies to mend and make clothes for the family as shops were some distance away and bought clothes were much more expensive. The sewing machines were also used to sew items for fund raising e.g.. Church and School fetes.Used in the Kiewa Valley.The machine has a brown wood veneer base and a lid with a metal handle in the centre of the top. There is a long screw that fits in a hole at the top of the lid. The screw can be lifted out and used to open and take off the lid. Inside there is a black metal machine which is fitted onto the wooden base. There is a compartment in the base, right of the wheel of the machine, which holds an instruction manual and a tube of ""Singer" lubricant for electric machines". The light, above the needle is covered by bakelite. A leather belt runs around the wheel on the right to enable the machine to run. There is a foot pedal and an electric cord attached."Singer Manufacturing Company" - gold embossed "No. EL 249 355" - oval disc "99K" - disc "Singer Manfg. Co. - discsewing machine; singer manufacturing company; kiewa valley -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumBadge - UNIT BADGES, RACT
Badges used to identify units within the RACT (Royal Australian Corp of Transport).1. Square material blue patch with red round borders and yellow writing and picture of a vehicle. Other side, white felt. 2. Round light blue patch with brown spoked boat wheel. White writing and inside wheel picture of white crane vehicle on red background and white machine on blue background.1. Embroidered "Amphibious Transport RACT"and "41 PL". 2. Embroidered "Melbourne Water Transport RACT".passchendaele barracks trust collection., ract, cloth badges -
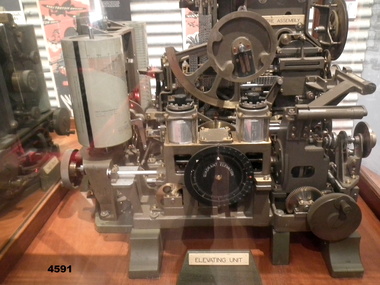 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumEquipment - VICKERS No1 MK III A.A. PREDICTOR, Commonwealth Government Ordnance Factory, c. 1942
This piece of equipment was used to predict the flight path of an aircraft in order for anti-aircraft artillery to fire accurately at an approaching enemy airborne target. A crew of six operated the machine with information ready to be relayed to a gun within 50 seconds. The predictor was manufactured at the Commonwealth Government Ordnance Factory, Maribyrnong.The item is made primarily from metal, is square shaped and bolted to a wooden base. Numerous hand operated wheel dials attached to gauges which input information related to wind speed, bearings and elevation are visible. Each of the four sides has a specific task with three sides being labelled - Elevation Unit, Wind Calculator, Bearing Unit. The item is housed in a glass and wood display case. Attached to the front of the display case: 'VICKERS A.A. PREDICTOR No1 MK III MANUFACTURED BY ORDNANCE FACTORY MARIBYRNONG'pedictor, military equipment, ordnance, anti-aircraft guns -
 Shepparton RSL Sub Branch
Shepparton RSL Sub BranchConcinnium Machine (Cigarette Roller)
Could have been used by WW1 TroopsPossibly used by WW1 & 2 troops and civilians.Nickle Plated Split and Hinged Brass Cylinder containing six serated nickle plated rollers with gears and Nickle Plated rotateable brass wheel. Wheel held on by brass screw. Hinge is the full length of cylinder. Concinnum Machine Evans Patient London to hinged lid.Concinnium Machine Evans Patient London to hinged lid. To the wheel, Evans Concinnium and arrows pointing to the direction.concinnium machine, cigarette, smoking -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPulley
Pulleys date back to Ancient Egypt circa 1800BC. it is a simple machine used to lift weights.Used by residents of the Kiewa Valley.Steel pulley. A pulley is a wheel on an axle or shaft enabling a taut cable or belt passing over the wheel to move and change direction, or transfer power between itself and a shaft.pulley, pulley machine -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical SocietySewing machine, 1895 -1910
Donor, Connie Cruikshank was grand-daughter of Poppy Kerr whose father was the first doctor in Orbost. Machine belonged to her grandmother, Mrs Hilda Kerr(Temple).This item is significant for its use by an influential and well-known Orbost identity. It is also an example of a common domestic appliance of the late 19th-early 20th century.Hand-operated sewing machine. Black with gold designs, large metal turning wheel. All set on large polished block of wood.Wertheim Francfortsewing-machine kerr-dr temple-hilda cruikshank-connie wertheim -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyhand drill
The invention of a hand drill is credited to Arthur James Arnot and William Blanch Brain of Melbourne, Australia who patented the electric drill in 1889. In 1895, the first portable handheld drill was created by brothers Wilhem & Carl Fein of Stuttgart, Germany. Hand-powered devices have been used for millennia. However, during the last quarter of the 19th century a radically improved generation of tools appeared. These tools took advantage of modern mass production machinery and processes (like interchangeable parts) and an increased availability in superior material (metal instead of wood). One of the outcomes included an array of new drilling machines. These human-powered tools were a vast improvement over earlier tools.This item is an example of a commonly used domestic tool - pre power tools.A Stanley hand drill with two wooden handles. The red wheel is painted metal. On red wheel - STANLEY ENGLANDwoodwork tool hand-drill -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societysewing machine, late 1860's - 1870's
The early settlers of Orbost had to be self sufficient making their own clothes, tableware, bed coverings, furnishings and equipment. Many women were skilled dressmakers and craft workers. This item reflects that time.A small black hand-cranked lockstitch sewing machine. It has a backwards C-shaped body. The wheel and base are decorated with a gold pattern. On the end above the needle assembly is a brass plate The balance wheel has a handle. The pattern on the wheel is a gold border with two gold, red and green stars formed by interwoven triangles. On the cloth plate is stamped "Patent March 1867 Heron Gresham" with some indecipherable marks.sewing-machine needlework -
 Cheese World Museum
Cheese World MuseumToy, sewing machine, c1960
Hand-operated toy sewing machine has red metal base with name inscribed in gold; creamy-white plastic body has a gold scroll decoration with 5 red spots. The operating wheel is silver metal with a black knob on the handle. The working parts are silver-coloured metal.Little Bettylittle betty, allansford, toys, sewing machines -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Sewing Machine, late 19th or early 20th century
... -village textile machines sailmaker's machine maritime sewing ...This Eclipse model, treadle operated sewing machine was made by the Oldham Sewing Machine Company in Greater Manchester U.K.. It was used by sailmakers for sewing sails with box shape top and slim neck. Sewing machine, foot treadle, for sewing sails with box shape top and slim neck. Brand is Eclipse. Cast iron base is bolted to square wooden table-top with drawer under table. Drawer has 3 partitions and wood fitting with 5 drilled holes for needle storage, lock has diamond shaped, decorative metal surrounds; half of inside drawer is painted black. Decorative metal stand, painted green, with 2 foot pedals; 1 foot pedal drives the wheel wheel. Padals both have "ECLIPSE" cast into the iron.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, textile machines, sailmaker's machine, maritime sewing machine -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMachine - Guillotine, c. 1880's
... of the machine turns a large spoked wheel, which rotates a large gear... of the machine turns a large spoked wheel, which rotates a large gear ...This guillotine is a hand operated machine specifically designed to cut through multiple sheets of paper or card. It has a very heavy and sharp single blade knife mounted between vertical guides or runners. The main users of a machine like this is in by the printing and publication binding industry. Book binding companies use a guillotine to evenly trim the pages of a book after it has been bound. The way the guillotine is used is - paper or card is stacked squarely on the flat table and pushed firmly against the back guide - the handle below the table at the front of the machine is wound around, which brings the back guide forward, pushing the paper stack forward and positioning the centre of the stack below the vertical frame - the upper wheel is wound around, which brings the clamp and firmly in position on top of the paper, to hold it very firmly - the large wheel on the side of the machine is turned around to lower the long sharp blade down onto the pages and cut them through. The sharp edge of the blade is protected somewhat from becoming blunt; a block of wood sits in the table under the stack of paper An early model of a guillotine was patented in 1837 by Thirault, who built a model with a fixed blade. Guillotines similar in principal to this one were patented by Guillaume Massiquot in 1844 and 1852. Over the years many improvements have been made and operation has moved from man power to electricity. Oscar Friedheim Ltd. was the importer and wholesaler of a large range of machinery and equipment for the printing and bookbinding industry. He sold most of his equipment under his own name. On this guillotine or paper cutter he refers to the origin of the guillotine’s manufacture only as “German Manufacrure”. A reference book “Commercial Bookbinding: a description of the processes and the various machines used" by Geo. Stephen, 1910, recommends Oscar Friedheim, amongst others, for the supply of “reliable cutting machines for hand or power”. It also recommends Oscar Friedheim’s for a wide range of other printing machinery and processes. OSCAR FRIEDHEIM LIMITED, LONDON Oscar Friedheim Ltd. was established in 1884 and operated from Ludgate in London. The company was an importer and wholesale supplier in the 1880’s, offering machinery and equipment for the printing and packaging industry for the UK and Ireland. The company became incorporated in 1913. An advertisement of 1913 includes a telegraphic code plus two telephone numbers for Oscar Friedheim Ltd and invites readers to call at the Ludgate, London, showrooms to see the machines working. The company later became Friedheim International Ltd. The book titled “Friedheim, A Century of Service 1884-1984 by Roy Brewer, celebrates Oscar Friedheim’s achievements. Friedheim International currently operates from Hemel Hempstead, on the northern outskirts of London UK. It promotes itself as “… the leading supplier of finishing, converting and packaging machinery to the printing, graphic arts, and highly varied packaging industries in the UK and Ireland. The company’s policy is simple – “employ the best people, work with the best equipment manufacturers in the world, and treat our customers as partners!” The company still sells guillotines. The guillotine is significant for its ability to represent aspects of the printing trade in Warrnambool and in a typical port town circa 1850 to 1910. It represents communication methods and processes used in the time before electrically powered equipment became common in industry.Guillotine (or paper cutter), hand operated. Metal framework with vertical guides, stand and metal mechanical parts including wheels and gears. Table with back guide; handle below front of table winds to move the back guide. A wheel at top of machine winds to adjust pressure of the clamp on the work on the table below it. The cutting blade fits between vertical guides; a timber insert in the table below the blade helps minimise the loss of sharpness of the blade. A handle on the side of the machine turns a large spoked wheel, which rotates a large gear, causing the blade to move up and down. Makers details are on a small oval plaque with embossed maker’s details is screwed onto main body. Maker is O Friedheim, London, and the machine is of German manufacture, circa late 1880’s.Maker’s plaque inscribed "O. FRIEDHEIM / London / German Manufacture"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, printing machinery, printer’s guillotine, paper guillotine, paper cutter machine, oscar friedheim ltd london, friedheim international ltd, bookbinding industry, printing industry -
 Blacksmith's Cottage and Forge
Blacksmith's Cottage and ForgeSewing machine
A domestic sewing machine used for dressmaking and handcrafts which was operated by hand.A hand sewing machine with a cast metal body and gold leaf decoration on the 'arm'. It stands on four 'legs/feet' with a kidney shaped base. The driving wheel is grooved for a belt. This has no handle. All cogs move.domestic, needlework, sewingmachine, stitching, dressmaking, needlecraft -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Mechanics' Magazine vol. 3, 1825 (exact)
Hardcovered book, half leather bound with marbled paper. Formerly book number 4040 from the Ballaarat East Public Library. Contents include: new pit-saw, self-moving carriage (car), Lord Worcestor's steam engine, extinction of fires, Cameron's Soda Water Apparatus, Newton's Lectures on Astronomy, coining at the Royal Mint, mechanical geometry, lifting ships by steam, voltaic-mechanic agent, steam navigation, portable hand-mill, Brown's pneumatic engine, Bell's invention for saving lives from shipwreck, triple pump, cycloidal chuck, potato-washer, sand clock, Galvanic electricity, perpetual motion, Hadley's Quadrent, Wollaston's Night-Bolt, rope bridges, boring machinery, locomotive steam-engines, new London Bridge, naval architecture, steam and water wheel, Spencer's Patent Forge, boat with wings, ivory profile portraits, Jenning's Gas burner, Ramage's Telescope, washing machine, tallow lamp, iron masts, self regulating pendulum, prismatic compass, simple blowpipe. Includes image of Henry Brougham, and many drawings of inventions.non-fictioncar, newton, fire, shipwreck, bell, naval architecture, locomotive, ballaarat east public library, ballarat east public library, ballarat east library, henry brougham, potassium, meridian lines, pit saw, self moving carriage, lord worcestor, steam engine, cameron s, soda water, astronomy, royal mint, mechanical geometry, lifting ships by steam, voltaic mechanic agent, steam navigation, hand mill, brown s pneumatic engine, triple pump, cycloidal chuck, potato washer, sand clock, galvanic electricity, perpetual motion, hadley s quadrent, wollaston s night bolt, rope bridges, boring machinery, steam engines, new london bridge, steam and water wheel, spencer s patent forge, boat with wings, ivory profile portraits, jenning s gas burner, ramage s telescope, washing machine, tallow lamp, iron masts, self regulating pendulum, prismatic compass, simple blowpipe, bookplate -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionNewspaper, The Machinery Market, 02/12/1889
It's assumed that this journal was read at the Ballarat School of MinesA small illustrated journal with advertisements and pictures. pages 328-356 (and 26 pages of illustrated advertisements). Illustrations include machinery, corn crushers, condensers, chlorination plants. stea, hammers, steam engines, steam pumps, lamps, saw bench, leather belting, casks, barrels, machinery, boiler, cohran and co, birkenhead, stern, cowles syndicate company, electric smelting works, aluminium manufacturing, w t glover and co, rope machine, steam travelling crane, webster wood fibre machine, automatic govenor expansion gear, international exhibition edinburgh, beacon light, air propeller, well boring tools and pumps, cochran and co.'s launch, tug and boat building yard, s.s. jeanette, cochran boiler, cochran and co's boiler shop, stern wheel steamer, s.s. esperanca, cowles syndicate co, milton, w.t. glover & co.'s patent compound rope making machine, bendh drilling machine, steam launch, bicycle, well-boring tools -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWheel
... . 280mmW x 280mmD x 45mmH. Part of a machine/engine Wheel ...Wheel metal painted red, 6 spokes with hole in centre with groove. 280mmW x 280mmD x 45mmH. Part of a machine/engineflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Dentist Drill, Late 19th century
The design of this and other similar treadle powered dental engine (or dentist drill) was in common use by dentists from the 1870’s into the 1920's. When electricity became accessible to most communities the electrically powered dental engines began to take over from the treadle power. Over the ages teeth were extracted using picks and scissors and other gouging instruments. Bow drills, hand drills and even a "bur thimble" drill were later used to prepare cavities for filling. Some drills were made bendable by attaching flexible shanks between the metal bur and the handle, giving access to the teeth at the back of the mouth. Other mechanical devices were introduced along the way, such as clockwork drills, but they were hard to handle and inefficient. Over the centuries “dentistry has been performed by priests, monks and other healers. This was followed by barbers; the barber’s chair may well have been the precursor to the dental chair. “(SA Medical Heritage Society Inc.) In 1871 James Morrison patented the first commercially manufactured 'foot treadle dental engine', the first practica dental engine although others had been introduced as early as 1790 (by John Greenwood). Handmade steel burs or drills were introduced for dental handpieces, taking advantage of the significant increase in the speed of the drill. In 1891 the first machine-made steel burs were in use. The treadle drill reduced the time to prepare a cavity from hours to less than ten minutes. In 1876 the Samuel S. White Catalogue of Dentist Instruments listed a 12 ½ inch wheel diameter dental engine, with 14 bright steel parts, for sale at US $55 In today’s market, this is the equivalent to US $1200 approx. The specifications of that dental engine are very similar to the this one in our Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s collection. It is interesting to note that workings of a similar treadle dentist drill were used and modified to power a treadle spinning wheel of one of the volunteer spinners at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The foot treadle dental engine was a milestone in dental history. “Historic importance of treadle powered machines; they made use of human power in an optimal way” (Lowtech Magazine “Short history of early pedal powered machines”) The invention of a machine to speed up the process of excavation of a tooth lead to the invention of new burs and drills for the handpieces, improving speed and the surgical process of dentistry. They were the fore-runner of today’s electrically powered dental engines. This treadle-powered dentist drill, or dentist engine, is made of iron and steel and provides power for a mechanical dental hand-piece that would be fitted with a dental tool. The drill has a three footed cast iron base, one foot being longer than the other two. A vertical C shaped frame is joined into the centre of the base, holding an axle that has a driving-wheel (or flywheel) and connecting to a crank. A slender, shoulder height post, made from telescoping pipes, joins into the top of this frame and is height adjusted by a hand tightened screw with a round knob. On the post just above the frame is a short metal, horizontal bar (to hold the hand-piece when it is not in use). A narrow tubular arm is attached to the top of the stand at a right angle and can move up and down. At the end of the arm is a firmly fixed, flexible rubber hose protected for a short distance by a sheath of thin metal. At the end of the hose there is a fitting where the drill’s hand-piece would be attached; a small, silver coloured alligator clip is also at the end. A treadle, or foot pedal, is hinged to the heel to the long foot of the base, and joined at the toe to the crank that turns the driving-wheel. There is a spring under the toe of the treadle. The metal driving-wheel has a wide rim. Touching the inside of the rim are four tubular rings that bulge towards the outside of the driving-wheel, away from the pole, and all meet at the hub of the axle. The axle is bulbous between the inside of the driving-wheel and the frame then passes through the frame and is attached on the other side. The driving-wheel has a groove around which a belt would sit. The belt would also fit around a pulley on the arm, at the top of the post. The pulley is joined to a rod inside the arm and this spins the drill's hand-piece and dental tool holder. The two shorter feet of the base are made from a long metal bar that has been curved outwards, and its centre is bolted to the base of the pole. Under the ends of the curved legs of the base are wedge shaped feet. The driving-wheel is decorated in light coloured paint on both sides, each side having three sets of floral decals evenly spaced around them, and each about a sixth of the wheel's circumference. Similar decoration is along the sides of the frame. The foot pedal has decorative cutout patterns in the centre of the foot and at the toe. On the long foot of the stand is some lettering with a fine, light coloured border around it. The lettering is hard to read, being a dark colour and flaking off. There are also remnants of fine, light coloured flourishes. The foot pedal has lettering of the maker’s trade mark cast into the metal at the ball of the foot. Lettering on the base is peeling and difficult to read. The foot pedal has a trade mark cast into it that looks like a combination of ‘C’ , ‘S’ , ‘A’, ‘R’. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dentist, teeth, dental drill, dental engine, treadle drill, foot powered drill, treadle engine, orthodontics, dental surgery, james morrison -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Dentist Drill, Late 19th century
The design of this and other similar treadle powered dental engine (or dentist drill) was in common use by dentists from the 1870’s into the 1920's. When electricity became accessible to most communities the electrically powered dental engines began to take over from the treadle power. Over the ages teeth were extracted using picks and scissors and other gouging instruments. Bow drills, hand drills and even a "bur thimble" drill were later used to prepare cavities for filling. Some drills were made bendable by attaching flexible shanks between the metal bur and the handle, giving access to the teeth at the back of the mouth. Other mechanical devices were introduced along the way, such as clockwork drills, but they were hard to handle and inefficient. Over the centuries “dentistry has been performed by priests, monks and other healers. This was followed by barbers; the barber’s chair may well have been the precursor to the dental chair. “(SA Medical Heritage Society Inc.) In 1871 James Morrison patented the first commercially manufactured 'foot treadle dental engine', the first practica dental engine although others had been introduced as early as 1790 (by John Greenwood). Handmade steel burs or drills were introduced for dental handpieces, taking advantage of the significant increase in the speed of the drill. In 1891 the first machine-made steel burs were in use. The treadle drill reduced the time to prepare a cavity from hours to less than ten minutes. In 1876 the Samuel S. White Catalogue of Dentist Instruments listed a 12 ½ inch wheel diameter dental engine, with 14 bright steel parts, for sale at US $55 In today’s market, this is the equivalent to US $1200 approx. The specifications of that dental engine are very similar to the this one in our Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s collection. It is interesting to note that workings of a similar treadle dentist drill were used and modified to power a treadle spinning wheel of one of the volunteer spinners at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The foot treadle dental engine was a milestone in dental history. “Historic importance of treadle powered machines; they made use of human power in an optimal way” (Lowtech Magazine “Short history of early pedal powered machines”) The invention of a machine to speed up the process of excavation of a tooth lead to the invention of new burs and drills for the handpieces, improving speed and the surgical process of dentistry. They were the fore-runner of today’s electrically powered dental engines. This treadle-powered dentist drill, or dentist engine, is made of iron and steel and provides power for a mechanical dental handpiece that would be fitted with a dental tool. On the foot is painted lettering naming it "The Brentfield" and there is a fine line of light coloured paint creating a border around the name. The paint under the lettering is peeling off. The drill has a Y-shaped, three footed cast iron base, one foot being longer than the other two. A vertical frame is joined into the centre of the base, holding an axle that has a driving-wheel (or flywheel) and connecting to a crank. A slender, shoulder height post, made from adjustable telescoping pipes, joins into the top of this frame. On the post just above the frame is a short metal, horizontal bar (to hold the hand-piece when it is not in use). A narrow tubular arm is attached to the top of the stand at a right angle and can move up, down and around. There is a pulley each side of the joint of the arm and a short way along the arm is fitted a short metal pipe. A little further along the arm a frayed-ended cord hangs down from a hole. At the end of the arm is another pulley and a joint from which hangs a long, thin metal pipe with two pulleys and a fitting on the end. A treadle, or foot pedal, is joined to the long foot of the base, and joined at the toe to the crank that turns the driving-wheel. The metal driving-wheel has a wide rim. Touching the inside of the rim are four tubular rings that bulge towards the outside of the driving-wheel, away from the pole, and all meet at the hub of the axle. The axle fits between the inside of the driving-wheel and the frame then passes through the frame and is attached on the other side. The driving-wheel has a groove around which a belt would sit. The belt would also fit around a pulley on the arm, at the top of the post. The pulley is joined to a rod inside the arm and this spins the drill's hand-piece and dental tool holder. The foot pedal has a cross-hatch pattern on the heel and the ball of the foot has tread lines across it. The end of the toe and the instep areas have cut-out pattern in them. "The ____/ Brentfield / __ DE IN L___" (Made in London) painted on the long foot of the base. Marked on the drill connection is “Richter De Trey, Germany”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dentist, teeth, dental drill, dental engine, treadle drill, foot powered drill, treadle engine, orthodontics, dental surgery, james morrison, the brentfield, richter de trey, german dental fitting, london dental drill -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, Ballarat School of Mines Annual Report 1888, 1888
Ballarat School of Mines Annual Report 1888. President's Annual Report, Constitution and Statute of Affiliation, Monetary prize by R. M. Serjeant for Treatment of Ores, Balance Sheet: Liabilities and Assets, Certificates Granted by the Council, Fees, Honorary Correspondents, Life Governors, Number of Students attending the School of Mines, Office Bearers, Report of the Curator of the Museum and Library, Report of the Superintendent of Laboratories, Report of the Lecturer on Machine Drawing, Report of the Lecturer on Mechanical Engineering, Report of the Lecturer on Telegraphy, Report of the Lecturer on Botany, Report of the Lecturer on Freehand and Model Drawing, Report of the Lecturer on Materia, Medica and Physiology, Report of the Hon. Secretary St John Ambulance Association, Examinations Held, Scale of Charges for Assays and Analyses, Statement of Receipts and Expenditure for the year 1888 and Special Trust Funds, Statistics - Students Attending Lectures, Subjects and Lecturers, Subscriptions and Donations from 1st January to 31st December 1888, Time Table. Ballarat School of Mines annual Report. Cover attached by tape on booklet, spine missing, 108 pages. ballarat school of mines, annual report, the hon sir william foster stawell, president, andrew anderson, vice president, alf. mica smith - professor of chemistry and metallurgy, f. m. krause - professor of geology and minealogy, j. h. horwood - mechanical engineering, machine drawing and design, mining, mathematics, henry j. hall - freehand and model drawing, daniel walker - chemistry and physics, w. e. burbridge - demonstrator of chemistry and metallurgy, w. d. campbell - telegraphy, george day - botany, j. f. usher - materia, medica, pharmacy and physiology, gilbert j. dawbarn, e. thornton, charles kent - auditor, andrew berry - registrar, t. h. thompson jp - mayor of the city of ballarat, james russell jp - mayor of the town of ballarat, daniel brophy jp - chairman of the band and albion consols, walter gude, elizabeth phillips, thomas commons, kate porritt, emily mary wheeler, grace shrigley, george clendinning, rose ditchburn, cecelia h. murphy, eliza a. turpie, rebecca walton, george g. zilles, william menzies, john waters sutherland, h.w. sutherland, alfred kerr, william coltman, alfred j. dunstan, arthur bregazzi, maggie miller, serna davey, william thomas grownow, sarah davies, anna bella cravno, william corbould, thomas copeland, robert john gribble, henry lipson hancock, leigh george hancock, harry m. martell, ivan rosenblum, john la gerche, samuel barrell, walter reed bechercaise, william treloar, adolf gode, arthur e. lilburne, carl werner, isaac bernstein, george kidd, arthur lynch, henry coltman, josiah wasley, david curtain, martha maud berry, mary ann cameron, harriet mary mitchell, anna s. schloo, ellen fussell, lavinia treloar, mary drury, annie winifred eastwood, annie louisa gatliff, mary gatliff, james edward gribble, frank uren, alfred curthoys, william edwin kernot, j. ditchburn, john bradshaw, david michael curtain, alfred ernest campbell kerr, walter nettleton, william henry keast, george ja,es, donald mcgregor, john king, john bailey bullen, john trevan, patrick murray, josiah curnow, tobert taplin, samuel earnest figgis, w.h. keast -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Functional object - Laundry equipment, Mangle, c1900
The mangle was used in the laundry at Key's, Exchange Hotel. This large, iron framed, manual, machine with 3 cylinders for rolling and pressing washed clothes was a prominent and necessary piece of equipment used by early settler women in Moorabbin Shire 1800 to mid 1900sThis large Mangle was used at The Exchange Hotel, Nepean Highway, Cheltenham , built in 19thC , now known as The Tudor Inn.A large, iron framed, manual, machine with 3 cylinders, for rolling and pressing washed clothes, connected by cogs manually operated by turning a side wheel with a large crank handle.On an oval plate at base of iron frame 'W. Summerscales / & Sons / Keighley Englandclothing, brighton, moorabbin, linen, washing machine, bentleigh, market gardeners, laundry equipment, mangle, early setters pioneers -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - FOUNDRY
sepia print mounted on grey board. Adult males (some in working clothes) assembled in lean to of engineering machine shop. Some machinery - pumps, lathe etc. Vertical wall of main building in background. Lorry wheel in right lower foreground.organization, business, foundry -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - BURNT GULLY PHOTOS, 1924
Burnt Gully - possibly near Woodvale. a. Black and white photo: men standing behind, alongside bagged grain. Steam farm engine on RH side. Written on rear of photo: threshing team at lunch engine Ruston Procter steam. 8 horse power, single cylinder, working pressure 75 lbs per square inch. 80 revs per minte. Fly wheel 6 feet in diameter. b. Pilcher's thresher on Robert Riley's farm, Burnt Gully. Bullock drivers Bill Pilcher, Paddy Mulcair. Bullock drawn threshing machine, large group of men standing alongside and to rear of machine. Two men standing on top of thresher. Steam traction engine on far left of photo. c. Pioneer log cabin Burnt Gully, the home of the Grafton family, demolished about 1930. Hut of slab construction, with corruated iron roof over timber slats. Chimney of logs and slabs topped with bricks on LH side of house. Steam farm machine in background on LH side.unknownagriculture, farm, grafton familyh, robert riley, bill pilcher, paddy mulcair, burnt gully. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - BUTTON CARRIER BENDIGO, early 1900's ?
Sepia photo: Four wheeled cart with canvas top situated on deck of ship, alongside wharf which has large verandah type structure running length of it. Carts with large piles of bags visible behind wharf building. Workmen standing alongside cart, C. Button carriers Bendigo, printed on side of cart. Furniture Packed & Stored printed across topside of below canvas top. Winding machine with man holding lever on RH side of photo.organization, business, c. button carriers, bendigo -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Model, Swift Boat
The boat has grey body and black bottom stands on two legs base. The control room is half of the deck. It has 1 soldier at the front, 1 soldier in the cockpit and 2 soldiers controlling the stiring wheel. At the back of the boat, a soldier controls a machine gun.SWIFT BOAT Used for Inland water operations By "Brown Water Navy"model boat, swift boat, brown water navy -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Model, Caddilac-Gage V-100 'Commando' Recon Veh
Model wheeled armoured vehicle with TSO turret with twin machine guns. Troop carrier. Olive drab on orange plinth.White US Army stars front and sides/White number 10 on side. US Army 1ZC 12868cadillac-gage, v100, 'commando' recon vehicle -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Model, Half Track Troop Carrier
Wheeled front, tracked rear. Solid half sides. Caged roof. Machine gun in troop bay. Bush bash roller on bumper bar and fold down armoured windscreen with observation slits.m3, half track truck, troop transport, white motor company, model -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyMachine - W & A PENTLAND Wheel Hub, c.1950
... Machine W & A PENTLAND Wheel Hub ...William PENTLAND arrived in Sandrisge in 1864 and set up his own coach building business in 1880.The firm was located between Ingles & Raglan Streets on the east side of Crockford Street. As well as coach building - and later motor body building - the firm were wheelwrights and blacksmiths.Round brass wheel hub cap from W & A PENTLAND, Port MelbourneW & A Pentland Port Melbourne Buildersw & a pentland, business & traders - manufacturing, william pentland -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, 29/071956
The Slingsby T31 is a two seat training glider that came available in 1951. It is, in effect, a two seat version of the single seat Kirby Tutor. The T31 was marketed by Slingsby Sailplanes both as complete aircraft and kits of parts for assembly. The Australian Gliding Museum’s example (currently registered as VH-GDB) is one of five of this type to grace Australian skies. Three including GDB were assembled in Australia from kits supplied by Slingsby’s in England, the other two were delivered as completed airframes. To date only four remain of which two are airworthy. This aircraft began flying in at Caversham in Western Australia (the then home of the Gliding Club of Western Australia) in July 1956. It was badly damaged in a crash in June 1958. The wreckage was sent to Schneiders in Adelaide for repair. However, the Club decided against having the repairs done, opting instead to buy a new ES52 Kookaburra. After a couple of years, the wreck was purchased by a member of the Waikerie Gliding Club whereupon the glider was rebuilt with some modifications, including a more rounded and better streamlined fuselage nose. It returned to the air in October 1961 at Clare in South Australia. The ownership of VH-GDB passed through a number of clubs, including at Dubbo in New South Wales, Wimmera in Victoria and Pioneer Valley at Mackay in Queensland. Eventually, it came into the hands of Bill Riley of Tocumwal in New South Wales who held it in storage for many years. Riley donated the aircraft to the Museum. It has been restored to airworthiness and is flown at vintage glider rallies and on Museum open days. This exhibit is an excellent example of a Slingsby T31 Tandem Tutor, a type of glider that was used by a number of clubs in the 1950s and 1960s for dual training of pilots to the solo capability.The Slingsby T31b Tandem Tutor is an open cockpit, tandem, two-seater glider with high, pylon mounted two piece wing supported by double, wire braced, steel tube struts. The glider is fitted with a main wheel, rubber-block sprung, wooden nose skid and steel leaf sprung, brass shod tailskid. The basic controls of aileron, rudder and elevator are not supplemented with pitch trim. Wing lift spoilers and both aerotow and winch releases are fitted. The instrument panels in both cockpits are fitted with an airspeed indicator, cosim variometer and altimeter. This red and silver painted wood and fabric covered aircraft is in excellent condition having been restored to full airworthy status by the Australian Gliding Museum. SLINGSBY – T31b (nose – both sides) DB Australian Gliding Museum (rudder – both sides) It has been given Serial Number GFA/HB/12 and is registered as VH-GDBaustralian gliding, glider, sailplane, slingsby, tandem tutor, t31, gliding club of western australia, waikerie gliding club, wimmera soaring club, pioneer valley soaring club -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, 1940
The “Coogee” is an intermediate single seat sailplane designed and built by Tom Proctor in 1940. Only one was built. It was first flown at Stuart Hill near Bendigo Victoria in January 1941 and was maintained in flying condition until 1967. The aircraft was flown extensively by the Victorian Motorless Flight Group (now the Melbourne Gliding Club) and Geelong Gliding Club and several subsequent owners. This exhibit is a "one off" Australian designed and built glider similar in some respects to the Hutter H17. Its usage is relevant to the history of gliding in Victoria in the post war years. Also the aircraft provides an insight into gliding technology in Australia in the 1940s. Wood and fabric single seat glider sailplane with strutted wings and strutted tailplane – features metal framed perspex canopy, central fuselage skid and wheel, small tail skid, instruments include airspeed, turn and bank indicator; variometer and altimeter. Metal parts include struts and fairing covering wing joint. All surfaces are pink doped – awaiting painting.australian gliding, glider, sailplane, coogee, tom proctor, victorian motorless flight group, geelong gliding club -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, 1952-1953
This aircraft, the first glider built by Schneiders after they immigrated to Australia, was test flown on 3 January 1953 by Dave Darbyshire and Owen Lewis. It is the only machine of its type. It is essentially a Grunau Baby 2B with a Perspex enclosed cockpit, wing airbrakes and a landing wheel. However, the wing design came from an existing Grunau 3 type that was being built in Germany. The glider has given extensive service for a number of owners – including the Gliding Club of Victoria, Sunraysia Gliding Club, Millicent Gliding Club, Max Bugler of Morwell and Garth Hudson of Brighton in Victoria. Prior to being donated to the Australian Gliding Museum in January 2001 the glider had logged over 2200 hours flying time from over 9000 flights. The glider is an improved Grunau Baby design that Edmund Schneider built after coming to Australia.Single seat glider of wood and fabric construction, with steel wing struts. Currently painted crème with yellow details. Underside of fuselage is painted orange.australian gliding, grunau, grunau baby, schneider, gliding club of victoria, sunraysia gliding club, millicent gliding club, darbyshire, lewis, bugler, hudson
