Showing 88 items
matching property law
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Jarrod Watt, Street Protests in Hong Kong against proposed extradition laws, 2019, 17/06/2019
Carrie Lam, Hong Kong’s chief executive, had plenty of political support in the territory’s pro-Beijing legislature to pass a bill that would allow extraditions to mainland China. The legislators were set to begin discussing the bill in early June, and intended to vote on it just weeks later. A series of protests took place, and after a June 16 protest saw the largest turnout yet, Ms. Lam made a major concession: She postponed the bill, at least temporarily. It was an undeniable victory for the protesters — but it did little to quell the unrest. Since the bill could later be reintroduced, protesters felt they remained in danger. The police tactics to break up the demonstrations on June 12, including the use of more than 150 tear gas canisters to push protesters far away from the government office, created a new set of demands from the protesters. Now, instead of just calling for the withdrawal of the bill and Ms. Lam’s resignation, they said they wouldn’t be content unless there was an independent investigation of officers’ conduct. They also wanted the release of protesters arrested on June 12, and for the government to rescind its description of the demonstrations as a “riot,” a designation that carries legal significance. None of that has happened. Many analysts say Ms. Lam is unlikely to step down, nor would Beijing accept her resignation if she offered it. She has more wiggle room on the other demands, but has not indicated any willingness to budge. The Hong Kong Protests are a leaderless, digital movement.There is no single leader or group deciding on or steering the strategy, tactics and goals of the movement. Instead, protesters have used forums and messaging apps to decide next steps. Anyone can suggest a course of action, and others then vote on whether they support it. The most popular ideas rise to the top, and then people rally to make them happen. At its best, this structure has empowered many people to participate and have their voices heard. Protesters say it keeps them all safe by not allowing the government to target specific leaders. Their success in halting the extradition bill, which was shelved by the territory’s chief executive, speaks to the movement’s power. Despite the lack of a clear leader, protesters have shown extensive coordination at the demonstrations, having planned the specifics online beforehand. Supply stations are set up to distribute water, snacks, gloves, umbrellas and shields made of cardboard. Volunteer first aid workers wear brightly colored vests. People form assembly lines to pass supplies across long distances, with protesters communicating what they need through a series of predetermined hand signals. Anyone walking in dangerous areas without a helmet or a mask is quickly offered one. No individual can speak on behalf of the protesters, which makes negotiations difficult, if not impossible. (https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/02/world/asia/hong-kong-protest-explained.html, accessed 07/07/2019) Hong Kong’s amended extradition law would allow the extradition of suspects to mainland China for the first time. Supporters say the amendments are key to ensuring the city does not become a criminal refuge, but critics worry Beijing will use the law to extradite political opponents and others to China where their legal protections cannot be guaranteed. The government claims the push to change the law, which would also apply to Taiwan and Macau, stems from the killing last year of a Hong Kong woman while she was in Taiwan with her boyfriend. Authorities in Taiwan suspect the woman’s boyfriend, who remains in Hong Kong, but cannot try him because no extradition agreement is in place. Under the amended law, those accused of offences punishable by seven years or more in prison could be extradited. The new legislation would give Hong Kong’s leader, known as the chief executive, authority to approve extradition requests, after review by the courts. Hong Kong’s legislature, the legislative council, would not have any oversight over the extradition process. Many Hong Kongers fear the proposed extradition law will be used by authorities to target political enemies. They worry the new legislation spells the end of the “one country, two systems” policy, eroding the civil rights enjoyed by Hong Kong residents since the handover of sovereignty from the UK to China in 1997. Many attending the protests on Sunday said they could not trust China as it had often used non-political crimes to target government critics, and said they also feared Hong Kong officials would not be able to reject Beijing’s requests. Legal professionals have also expressed concern over the rights of those sent across the border to be tried. The conviction rate in Chinese courts is as high as 99%. Arbitrary detentions, torture and denial of legal representation of one’s choosing are also common. Many in the protests on Sunday 09 June 2019 said they felt overwhelmed by a sense of helplessness in the face of mainland China’s increasing political, economic and cultural influence in Hong Kong. Hong Kong’s top political leader is not elected by ordinary voters but by a 1,200-strong election committee accountable to Beijing. Half of its legislature are chosen through indirect electoral systems that favour pro-Beijing figures. Many Hong Kongers also cited the jailing of leaders and activists from the 2014 Occupy Central movement– a 79-day mass civil disobedience movement – as well as the disqualification of young localist lawmakers as signs of the erosion of civil freedoms. Resentment towards China has been intensified by soaring property prices – with increasing numbers of mainland Chinese buying properties in the city – as well as the government’s “patriotic education” drive, and the large numbers of mainland tourists who flock to Hong Kong. Many Hong Kongers are also concerned about China’s growing control over the city’s news media, as they increasingly self-censor and follow Beijing’s tacit orders. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/jun/10/what-are-the-hong-kong-protests-about-explainerPhotograph of a crowd or protestors against proposed extradition laws gathering on the streets of Causeway Bay, Hong Kong, leading down to the gathering area. carrie lam, hong kong protests, extraditions, protest, protestors -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour, Jarrod Watt, Street Protests in Hong Kong against proposed extradition laws, 2019, 17/06/2019
Carrie Lam, Hong Kong’s chief executive, had plenty of political support in the territory’s pro-Beijing legislature to pass a bill that would allow extraditions to mainland China. The legislators were set to begin discussing the bill in early June, and intended to vote on it just weeks later. A series of protests took place, and after a June 16 protest saw the largest turnout yet, Ms. Lam made a major concession: She postponed the bill, at least temporarily. It was an undeniable victory for the protesters — but it did little to quell the unrest. Since the bill could later be reintroduced, protesters felt they remained in danger. The police tactics to break up the demonstrations on June 12, including the use of more than 150 tear gas canisters to push protesters far away from the government office, created a new set of demands from the protesters. Now, instead of just calling for the withdrawal of the bill and Ms. Lam’s resignation, they said they wouldn’t be content unless there was an independent investigation of officers’ conduct. They also wanted the release of protesters arrested on June 12, and for the government to rescind its description of the demonstrations as a “riot,” a designation that carries legal significance. None of that has happened. Many analysts say Ms. Lam is unlikely to step down, nor would Beijing accept her resignation if she offered it. She has more wiggle room on the other demands, but has not indicated any willingness to budge. The Hong Kong Protests are a leaderless, digital movement.There is no single leader or group deciding on or steering the strategy, tactics and goals of the movement. Instead, protesters have used forums and messaging apps to decide next steps. Anyone can suggest a course of action, and others then vote on whether they support it. The most popular ideas rise to the top, and then people rally to make them happen. At its best, this structure has empowered many people to participate and have their voices heard. Protesters say it keeps them all safe by not allowing the government to target specific leaders. Their success in halting the extradition bill, which was shelved by the territory’s chief executive, speaks to the movement’s power. Despite the lack of a clear leader, protesters have shown extensive coordination at the demonstrations, having planned the specifics online beforehand. Supply stations are set up to distribute water, snacks, gloves, umbrellas and shields made of cardboard. Volunteer first aid workers wear brightly colored vests. People form assembly lines to pass supplies across long distances, with protesters communicating what they need through a series of predetermined hand signals. Anyone walking in dangerous areas without a helmet or a mask is quickly offered one. No individual can speak on behalf of the protesters, which makes negotiations difficult, if not impossible. (https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/02/world/asia/hong-kong-protest-explained.html, accessed 07/07/2019) Hong Kong’s amended extradition law would allow the extradition of suspects to mainland China for the first time. Supporters say the amendments are key to ensuring the city does not become a criminal refuge, but critics worry Beijing will use the law to extradite political opponents and others to China where their legal protections cannot be guaranteed. The government claims the push to change the law, which would also apply to Taiwan and Macau, stems from the killing last year of a Hong Kong woman while she was in Taiwan with her boyfriend. Authorities in Taiwan suspect the woman’s boyfriend, who remains in Hong Kong, but cannot try him because no extradition agreement is in place. Under the amended law, those accused of offences punishable by seven years or more in prison could be extradited. The new legislation would give Hong Kong’s leader, known as the chief executive, authority to approve extradition requests, after review by the courts. Hong Kong’s legislature, the legislative council, would not have any oversight over the extradition process. Many Hong Kongers fear the proposed extradition law will be used by authorities to target political enemies. They worry the new legislation spells the end of the “one country, two systems” policy, eroding the civil rights enjoyed by Hong Kong residents since the handover of sovereignty from the UK to China in 1997. Many attending the protests on Sunday said they could not trust China as it had often used non-political crimes to target government critics, and said they also feared Hong Kong officials would not be able to reject Beijing’s requests. Legal professionals have also expressed concern over the rights of those sent across the border to be tried. The conviction rate in Chinese courts is as high as 99%. Arbitrary detentions, torture and denial of legal representation of one’s choosing are also common. Many in the protests on Sunday 09 June 2019 said they felt overwhelmed by a sense of helplessness in the face of mainland China’s increasing political, economic and cultural influence in Hong Kong. Hong Kong’s top political leader is not elected by ordinary voters but by a 1,200-strong election committee accountable to Beijing. Half of its legislature are chosen through indirect electoral systems that favour pro-Beijing figures. Many Hong Kongers also cited the jailing of leaders and activists from the 2014 Occupy Central movement– a 79-day mass civil disobedience movement – as well as the disqualification of young localist lawmakers as signs of the erosion of civil freedoms. Resentment towards China has been intensified by soaring property prices – with increasing numbers of mainland Chinese buying properties in the city – as well as the government’s “patriotic education” drive, and the large numbers of mainland tourists who flock to Hong Kong. Many Hong Kongers are also concerned about China’s growing control over the city’s news media, as they increasingly self-censor and follow Beijing’s tacit orders. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/jun/10/what-are-the-hong-kong-protests-about-explainerPhotograph of a crowd on the streets of Hong Kong to protest against proposed extradition laws, heading towards Admiralty. carrie lam, hong kong protests, extraditions, protest, protestors, admiralty -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour Photograph, Street Protests in Hong Kong against proposed extradition laws, 2019, 17/06/2019
Carrie Lam, Hong Kong’s chief executive, had plenty of political support in the territory’s pro-Beijing legislature to pass a bill that would allow extraditions to mainland China. The legislators were set to begin discussing the bill in early June, and intended to vote on it just weeks later. A series of protests took place, and after a June 16 protest saw the largest turnout yet, Ms. Lam made a major concession: She postponed the bill, at least temporarily. It was an undeniable victory for the protesters — but it did little to quell the unrest. Since the bill could later be reintroduced, protesters felt they remained in danger. The police tactics to break up the demonstrations on June 12, including the use of more than 150 tear gas canisters to push protesters far away from the government office, created a new set of demands from the protesters. Now, instead of just calling for the withdrawal of the bill and Ms. Lam’s resignation, they said they wouldn’t be content unless there was an independent investigation of officers’ conduct. They also wanted the release of protesters arrested on June 12, and for the government to rescind its description of the demonstrations as a “riot,” a designation that carries legal significance. None of that has happened. Many analysts say Ms. Lam is unlikely to step down, nor would Beijing accept her resignation if she offered it. She has more wiggle room on the other demands, but has not indicated any willingness to budge. The Hong Kong Protests are a leaderless, digital movement.There is no single leader or group deciding on or steering the strategy, tactics and goals of the movement. Instead, protesters have used forums and messaging apps to decide next steps. Anyone can suggest a course of action, and others then vote on whether they support it. The most popular ideas rise to the top, and then people rally to make them happen. At its best, this structure has empowered many people to participate and have their voices heard. Protesters say it keeps them all safe by not allowing the government to target specific leaders. Their success in halting the extradition bill, which was shelved by the territory’s chief executive, speaks to the movement’s power. Despite the lack of a clear leader, protesters have shown extensive coordination at the demonstrations, having planned the specifics online beforehand. Supply stations are set up to distribute water, snacks, gloves, umbrellas and shields made of cardboard. Volunteer first aid workers wear brightly colored vests. People form assembly lines to pass supplies across long distances, with protesters communicating what they need through a series of predetermined hand signals. Anyone walking in dangerous areas without a helmet or a mask is quickly offered one. No individual can speak on behalf of the protesters, which makes negotiations difficult, if not impossible. (https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/02/world/asia/hong-kong-protest-explained.html, accessed 07/07/2019) Hong Kong’s amended extradition law would allow the extradition of suspects to mainland China for the first time. Supporters say the amendments are key to ensuring the city does not become a criminal refuge, but critics worry Beijing will use the law to extradite political opponents and others to China where their legal protections cannot be guaranteed. The government claims the push to change the law, which would also apply to Taiwan and Macau, stems from the killing last year of a Hong Kong woman while she was in Taiwan with her boyfriend. Authorities in Taiwan suspect the woman’s boyfriend, who remains in Hong Kong, but cannot try him because no extradition agreement is in place. Under the amended law, those accused of offences punishable by seven years or more in prison could be extradited. The new legislation would give Hong Kong’s leader, known as the chief executive, authority to approve extradition requests, after review by the courts. Hong Kong’s legislature, the legislative council, would not have any oversight over the extradition process. Many Hong Kongers fear the proposed extradition law will be used by authorities to target political enemies. They worry the new legislation spells the end of the “one country, two systems” policy, eroding the civil rights enjoyed by Hong Kong residents since the handover of sovereignty from the UK to China in 1997. Many attending the protests on Sunday said they could not trust China as it had often used non-political crimes to target government critics, and said they also feared Hong Kong officials would not be able to reject Beijing’s requests. Legal professionals have also expressed concern over the rights of those sent across the border to be tried. The conviction rate in Chinese courts is as high as 99%. Arbitrary detentions, torture and denial of legal representation of one’s choosing are also common. Many in the protests on Sunday 09 June 2019 said they felt overwhelmed by a sense of helplessness in the face of mainland China’s increasing political, economic and cultural influence in Hong Kong. Hong Kong’s top political leader is not elected by ordinary voters but by a 1,200-strong election committee accountable to Beijing. Half of its legislature are chosen through indirect electoral systems that favour pro-Beijing figures. Many Hong Kongers also cited the jailing of leaders and activists from the 2014 Occupy Central movement– a 79-day mass civil disobedience movement – as well as the disqualification of young localist lawmakers as signs of the erosion of civil freedoms. Resentment towards China has been intensified by soaring property prices – with increasing numbers of mainland Chinese buying properties in the city – as well as the government’s “patriotic education” drive, and the large numbers of mainland tourists who flock to Hong Kong. Many Hong Kongers are also concerned about China’s growing control over the city’s news media, as they increasingly self-censor and follow Beijing’s tacit orders. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/jun/10/what-are-the-hong-kong-protests-about-explainerCrowds mass on Queens Way in Hong Kong as an estimated 2 million people march in protest at the government's refusal to withdraw a controverisal law allowing people to be extradited to mainland China. Chants demanded the chief executive apologise and the legislation be withdrawn, while many held signs protesting police violence. Nearly 2 million protesters flooded the streets of Hong Kong on Sunday, organisers claimed, delivering a stunning repudiation of Chief Executive Carrie Lam Cheng Yuet-ngor’s governance and forcing a public apology out of the city’s leader over her campaign to bulldoze a controversial extradition bill through the legislature. A day after Lam suspended her push for the bill, expecting it to defuse a crisis that has seen violent clashes between mostly young protesters and police, the centre of Hong Kong was brought to a complete standstill as the masses marched to chastise her for refusing to withdraw the bill or apologise when first asked to, and declaring that nothing short of her resignation would satisfy them now. (https://www.scmp.com/news/hong-kong/politics/article/3014737/nearly-2-million-people-take-streets-forcing-public-apology ) carrie lam, hong kong protests, extraditions, protest, protestors, admiralty -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photograph - Photograph, Black & White Mrs J.L.Smith & Butcher, 1915
The Butcher Mr Bill Ellin delivering meat to Mrs J.L.Smith in front of the house Law Muir Den 510 Centre Rd Bentleigh c 1915. Groceries, Ice, Milk, Bread, Eggs, Poultry were delivered to housewives by the traders in horse drawn carts, Also Hawkers and Pedlars plied their wares by visiting the cottages. John Logan Smith 1860-1932 , the son of Irish immigrants James and Marianne Smith was born at their home near the 'Toll Gates' on Point Nepean Road and Dendy Street. East Brighton. At that time the area had many orchards that were later replaced by market gardens. J.L.Smith at first rented a cottage 'Law Muir Den' & Shed from Mr Box and commenced business as a wood merchant - sawing logs into shorter pieces using one horse to power the saw. He purchased the property, added to the buildings , began trading in fuel and fodder as well and installed a chaff cutting mill powered by 10hp steam engine. The business prospered 1909 following the death of Tommy Bent, J/L Smith was nominated for Councillor of the Shire of Moorabbin. WW1 1914 - 18 both John and Mary Ann supported local War Relief Auxiliaries and their son Vic served as a Signaler in AIF. As Motor transport was increasing 1926 J L Smith built a small Garage on the opposite corner (Woolworths Supermarket 2005) , employed a good mechanic ( Reg Hunt ) and developed another successful business. The Grain Store was managed by family until 1930. In 1932 JL Smith assisted a man whose car had broken down, pushing it to the garage and sadly suffered a heart attack and died. He is buried in Cheltenham Cemetery. J.L.Smith was an early settler in East Brighton now Bentleigh and established successful Wood cutting, Grain & Chaff cutting and Motor garage businesses in Centre Road . He was elected Councillor of the Shire of Moorabbin and, with Mary Ann, his family were involved with local Church, Red Cross, and other community organizations.A Black and white photograph c 1915 showing the Butcher delivering meat to Mrs J.L Smith Bentleighsmith j l, smith mary ann, stanley helen, smith vic, smith harry redvers, chaff cutter, horse drawn carts, toll gates brighton, motor cars 1900, steam engines, early settlers, bentleigh, parish of moorabbin, city of moorabbin, county of bourke, moorabbin roads board, shire of moorabbin, henry dendy's special survey 1841, bent thomas, charman s, highett william, ormond francis, market gardeners, vineyards, orchards, william ellin, butcher -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photograph - Washing Day at 'Law Muir Den' Mrs J L Smith c1910, c1910
Mrs J.L.Smith and Ada Smith in the backyard of the house Law Muir Den 510 Centre Rd Bentleigh c 1910. . The early settler women usually devoted a whole day to washing as it was very labourious. A fire was lit in a stone pit and a large tub of water boiled. Soap that had been made, usually in the previous Autumn, from fat drippings and caustic soda, was flaked into the tub to form suds. The clothes were moved around in the tub with a long wooden paddle that was also used to lift the clothes out of the tub into another tub of cold rinsing water..Stains were removed by scrubbing soap on the cloth against a scrubbing board. Clothes were wrung by hand or a mechanical wringer and hung on the clothes line to dry. Mary Ann Smith was married John Logan Smith 1860-1932 who at first rented a cottage 'Law Muir Den' & Shed from Mr Box and commenced business as a wood merchant - sawing logs into shorter pieces using one horse to power the saw. He purchased the property, added to the buildings , began trading in fuel and fodder as well and installed a chaff cutting mill powered by 10hp steam engine. The business prospered As Motor transport was increasing 1926 J L Smith built a small Garage on the opposite corner (Woolworths Supermarket 2005) , employed a good mechanic ( Reg Hunt ) and developed another successful business. J.L.Smith was an early settler in East Brighton now Bentleigh and established successful Wood cutting, Grain & Chaff cutting and Motor garage businesses in Centre Road . He was elected Councillor of the Shire of Moorabbin and, with Mary Ann, his family were involved with local Church, Red Cross, and other community organizations.Photograph, Black & White, showing 2 women washing clothes in a large tub, set over a fire in a stone pit, in the back yard. Clothes are hanging from a rope line strung between 2 trees and held up with a wooden 'prop' -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photograph, Black & White J. L. Smith Hay & Grain Store Bentleigh c1910, c1910
John Logan Smith 1860-1932 , the son of Irish immigrants James and Marianne Smith was born at their home near the 'Toll Gates' on Point Nepean Road and Dendy Street. East Brighton. At that time the area had many orchards that were later replaced by market gardens. J.L.Smith at first rented a cottage 'Law Muir Den' & Shed from Mr Box and commenced business as a wood merchant - sawing logs into shorter pieces using one horse to power the saw. He purchased the property, added to the buildings , began trading in fuel and fodder as well and installed a chaff cutting mill powered by 10hp steam engine. The business prospered 1909 following the death of Tommy Bent, J/L Smith was nominated for Councillor of the Shire of Moorabbin. WW1 1914 - 18 both John and Mary Ann supported local War Relief Auxiliaries and their son Vic served as a Signaler in AIF. As Motor transport was increasing 1926 J L Smith built a small Garage on the opposite corner (Woolworths Supermarket 2005) , employed a good mechanic ( Reg Hunt ) and developed another successful business. The Grain Store was managed by family until 1930. In 1932 JL Smith assisted a man whose car had broken down, pushing it to the garage and sadly suffered a heart attack and died. He is buried in Cheltenham Cemetery. J.L.Smith was an early settler in East Brighton now Bentleigh and established successful Wood cutting, Grain & Chaff cutting and Motor garage businesses in Centre Road . He was elected Councillor of the Shire of Moorabbin and, with Mary Ann, his family were involved with local Church, Red Cross, and other community organizations.Black & white photograph of the Hay & Grain Store of John Logan Smith 1860-1932 on the corner of Jasper Rd and Centre Rd Bentleigh ( East Brighton) c1910. A Horse drawn cart loaded with hay and another outside the first building used by J L Smith -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photograph, Black & White, J.L.Smith Hay & Grain Store c1916 Bentleigh, 1916
John Logan Smith 1860-1932 , the son of Irish immigrants James and Marianne Smith was born at their home near the 'Toll Gates' on Point Nepean Road and Dendy Street. East Brighton. At that time the area had many orchards that were later replaced by market gardens. J.L.Smith at first rented a cottage 'Law Muir Den' & Shed from Mr Box and commenced business as a wood merchant - sawing logs into shorter pieces using one horse to power the saw. He purchased the property, added to the buildings , began trading in fuel and fodder as well and installed a chaff cutting mill powered by 10hp steam engine. The business prospered 1909 following the death of Tommy Bent, J/L Smith was nominated for Councillor of the Shire of Moorabbin. WW1 1914 - 18 both John and Mary Ann supported local War Relief Auxiliaries and their son Vic served as a Signaler in AIF. As Motor transport was increasing 1926 J L Smith built a small Garage on the opposite corner (Woolworths Supermarket 2005) , employed a good mechanic ( Reg Hunt ) and developed another successful business. The Grain Store was managed by family until 1930. In 1932 JL Smith assisted a man whose car had broken down, pushing it to the garage and sadly suffered a heart attack and died. He is buried in Cheltenham Cemetery J.L.Smith was an early settler in East Brighton now Bentleigh and established successful Wood cutting, Grain & Chaff cutting and Motor garage businesses in Centre Road . He was elected Councillor of the Shire of Moorabbin and, with Mary Ann, his family were involved with local Church, Red Cross, and other community organizations.Black & White photograph of J L Smith Hay & Grain Store and Crushing Mill Jasper Rd / Centre Rd Bentleigh 1916. A veranda has been added to the store, new signage attached and a Gas light and hitching post are in foreground. 3 Horse drawn carts loaded with grain bags and drivers sitting on top of loadV. Smithgas street light, hitching posts, smith vic, photography, smith j l; smith mary ann, stanley helen, smith vic, smith harry redvers, chaff cutter, horse drawn carts, toll gates brighton, motor cars 1900, steam engines, early settlers, bentleigh, parish of moorabbin, city of moorabbin, county of bourke, moorabbin roads board, shire of moorabbin, henry dendy's special survey 1841, were j.b.; bent thomas, o'shannassy john, king richard, charman s, highett william, ormond francis, maynard dennis, market gardeners, vineyards, orchards -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photographs, x 2 ,Black & White, F Smith Horse drawn cart loaded, Baled Straw, Grain, c1920
John Logan Smith 1860-1932 , the son of Irish immigrants James and Marianne Smith was born at their home near the 'Toll Gates' on Point Nepean Road and Dendy Street. East Brighton. At that time the area had many orchards that were later replaced by market gardens. J.L.Smith at first rented a cottage 'Law Muir Den' & Shed from Mr Box and commenced business as a wood merchant - sawing logs into shorter pieces using one horse to power the saw. He purchased the property, added to the buildings , began trading in fuel and fodder as well and installed a chaff cutting mill powered by 10hp steam engine. The business prospered 1909 following the death of Tommy Bent, J/L Smith was nominated for Councillor of the Shire of Moorabbin. WW1 1914 - 18 both John and Mary Ann supported local War Relief Auxiliaries and their son Vic served as a Signaler in AIF. As Motor transport was increasing 1926 J L Smith built a small Garage on the opposite corner (Woolworths Supermarket 2005) , employed a good mechanic ( Reg Hunt ) and developed another successful business. The Grain Store was managed by family until 1930. In 1932 J L Smith assisted a man whose car had broken down, pushing it to the garage and sadly suffered a heart attack and died. He is buried in Cheltenham Cemetery. J.L.Smith was an early settler in East Brighton now Bentleigh and established successful Wood cutting, Grain & Chaff cutting and Motor garage businesses in Centre Road . He was elected Councillor of the Shire of Moorabbin and, with Mary Ann, his family were involved with local Church, Red Cross, and other community organizations.2 x Black & White photographs showing horse drawn carts loaded with (a) Hay and (b) bags of grain outside J.L.Smith Grain & Chaff Store Centre Rd Bentleigh c1920smith frank, smith arch, smith tom, smith j l; smith mary ann, stanley helen, smith vic, smith harry redvers, chaff cutter, horse drawn carts, toll gates brighton, motor cars 1900, steam engines, early settlers, bentleigh, parish of moorabbin, city of moorabbin, county of bourke, moorabbin roads board, shire of moorabbin, henry dendy's special survey 1841, were j.b.; bent thomas, o'shannassy john, king richard, charman s, highett william, ormond francis, maynard dennis, market gardeners, vineyards, orchards -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - VICTORIA POLICE GAZETTES COLLECTION: GAZETTE FROM JUNE 1863, as above
Victoria Police Gazette No. 25 dated Thursday, June 18, 1863, containing notices about: murder, arson, highway robbery and stealing from the person, housebreaking and stealing from dwelling houses, felonies and offences not otherwise described, miscellaneous information, inquests, courts, property lost, property found, horses and cattle, escaped prisoners, deserters from merchant vessels, ticket of leave holders and extracts from Otago Police gazette. Also a list and description of horses and cattle reported to the police as stolen during the week ending 16th June, 1863, a list and description of horses and cattle reported to the police as found or those recovered by the police and not claimed during the week ending 16th June, 1863, a list of prisoners to whom tickets of leave have been issued and a list of prisoners reported as discharged from the penal establishments during the week ending 17th June, 1893.Victoria Policeessential services, police, victoria police gazette, victoria police gazette, law and order -
 Stratford and District Historical Society
Stratford and District Historical SocietyChest
Thought to have been made and used by one of the two Struss brothers who were both carpenters in Scotland before coming to Victoria in 1848 and 1854. They dealt in hardware, living and selling in Walhalla, Woods Point and Matlock. It finally became the property of Elsa Struss of South Yarra, the sister-in-law of the donor. Many tradesmen had chests such as this to carry and store tools.Large wooden box/trunk, painted Mission Brown. Three tin braces support each corner joint. Four hinges, two at the back and two inoperational at the front. Lid corners and edges braced with tin strips and shaped corners. Loop and hasp at front. Metal handles on the side. Pink paint on base.trades -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Brett Baker, Indigenous language and social identity : papers in honour of Michael Walsh, 2010
For almost 40 years, Michael Walsh has been working alongside Indigenous people: documenting language, music and other traditional knowledge, acting on behalf of claimants to land in the Northern Territory, and making crucial contributions to the revitalisation of Aboriginal languages in NSW. This volume, with contributions from his colleagues and students, celebrates his abiding interest in and commitment to Indigenous society with papers in two broad themes. ?Language, identity and country? addresses the often complex relations between Aboriginal social groups and countries, and linguistic identity. In ?Language, identity and social action? authors discuss the role that language plays in maintaining social identities in the realms of conversation, story-telling, music, language games, and in education. ?Language and Social Identity in Australian Indigenous Communities? will be of interest to students of linguistics, Indigenous studies, anthropology, and sociology. Contents: 1. Introduction /? Rod Gardner ... [et al.] 2. Michael Walsh : a personal reflection /? Ros Fraser 3. Place and property at Yintjingga/?Port Stewart under Aboriginal Law and Queensland Law /? Bruce Rigsby and Diane Hafner 4. Linguistic identities in the eastern Western Desert : the Tindale evidence /? Peter Sutton Juwaliny : dialectal variation and ethnolinguistic identity in the Great Sandy Desert /? Sally Dixon 6. Who were the 'Yukul'? and who are they now? /? Brett Baker 7. Colonisation and Aboriginal concepts of land tenure in the Darwin region /? Mark Harvey 8. Aboriginal languages and social groups in the Canberra region : interpreting the historical documentation /? Harold Koch 9. The Kuringgai puzzle : languages and dialects on the NSW Mid Coast /? Jim Wafer and Amanda Lissarrague 10. Dawes' Law generalised : cluster simplification in the coastal dialect of the Sydney language /? David Nash 11. Space, time and environment in Kala Lagaw Ya /? Lesley Stirling 12. Turn management in Garrwa mixed-language conversations /? Ilana Mushin and Rod Gardner 13. Laughter is the best medicine : roles for prosody in a Murriny Patha conversational narrative /? Joe Blythe 14. Collaborative narration and cross-speaker repetition in Umpila and Kuuku Ya'u /? Clair Hill 15. Co-narration of a Koko-Bera story : giants in Cape York Peninsula /? Paul BlackMaps, b&w photographs, charts, word listslanguage and identity, language maintenance, language and culture, language and country -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Terri Janke, Our culture : our future : report on Australian Indigenous cultural and intellectual property rights, 1998
In 1997, ATSIC released the discussion paper Our Culture: Our Future: Proposals for the Protection and Recognition of Indigenous Cultural and Intellectual Property, and invited public comment on the need for protecting and recognising Indigenous Cultural and Intellectual Property Rights. The report extracted here was developed in the light of over 70 submissions received on this discussion paper, and also in consultation with a National Indigenous Reference Group and other relevant individuals, communities and organisations. The Report details the types of rights Indigenous people seek in relation to their cultures and considers the application of current laws. It also makes recommendations for a comprehensive range of measures for improving the level of protection, including legal and non-legal reforms.colour illustrations, chartsindigenous cultural and intellectual property, intellectual property, copyright, native title -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, c late 1980s
The series of photographs show a number of sites included in the Rupertswood Estate. By 1851 William Clarke had acquired 31,375 acres of land in the Sunbury district. The foundation stone for Rupertswood Mansion was laid on 29th August 1874 by Mrs. W. J. Clarke, daughter-in-law of 'Big Bull'. The Salesian Fathers bought the Rupertswood property in June 1927 and established Salesian College.A coloured photograph of an open valley with scrub which is part of the original Rupertswood Estate. This land is north of the mansion and existing Salesian College.rupertswood estate, clarke, william j. t. 'big bull', salesian brothers, george evans collection -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, c late 1980s
The series of photographs show a number of sites included in the Rupertswood Estate. By 1851 William Clarke had acquired 31,375 acres of land in the Sunbury district. The foundation stone for Rupertswood Mansion was laid on 29th August 1874 by Mrs. W. J. Clarke, daughter-in-law of 'Big Bull'. The Salesian Fathers bought the Rupertswood property in June 1927 and established Salesian College.A coloured photograph of a herd of Fresian cows crossing a small bridge on the Rupertswood Estate. The cows were from the agricultural studies faculty at Salesian College.rupertswood estate, clarke, william j. t. 'big bull', salesian brothers, george evans collection -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, c late 1980s
The series of photographs show a number of sites included in the Rupertswood Estate. By 1851 William Clarke had acquired 31,375 acres of land in the Sunbury district. The foundation stone for Rupertswood Mansion was laid on 29th August 1874 by Mrs. W. J. Clarke, daughter-in-law of 'Big Bull'. The Salesian Fathers bought the Rupertswood property in June 1927 and established Salesian College.A coloured photograph of the bluestone and iron rail bridge over the Jacksons Creek on the Rupertswood Estate. One stone pylon at the top of the embankment and an iron pylon are visible along with the stone wall at the base of the embankment and part of the iron span. A post and wire fence is in the foreground.rupertswood estate, clarke, william j. t. 'big bull', salesian brothers, george evans collection -
 Rutherglen Historical Society
Rutherglen Historical SocietyNewspaper article, Historic former post office for sale, 7/02/2018
Article from the Corowa Free Press, Wednesday 7th February 2018, page 7, relating to the former Wahgunyah Post Office, at 5 Foord Street, Wahgunyah. The building was built in 1863 by John Foord for his daughter and son-in-law, Roderick Killborn. It ceased to operate as a post office in 1942. The present owner is Ms Jenny Tutton, who bought the property about two years ago. It is now on sale in the price range $445,000 to $485,000.Newspaper article with coloured photograph of a brick building.wahgunyah, post offices, wahgunyah post office, john foord, roderick kilborn, real estate sales -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photograph, Denise Kinnane, Barn at Rabelofs, Sweden, 2007
The barn is situated near Råbelöv castle, and near the small medieval church adjacent to the property, that is a popular baptismal and wedding church. Råbelöv Castle is a castle in Kristianstad Municipality, Scania, in southern Sweden. The castle was built in 1637. In this year, Christopher Ulfeld Råbelöf's current main building, his and his wife's initials were still on the north end. He died in 1657 and was succeeded at Råbelöf first by his son Björn, then by his nephew Otto. Both died young, whereby Christopher's son Ebbe, married to Hedewig, daughter of Christian IV and his second wife, Kirsten Munck, took office in 1663. In 1676 - 1678 Kristianstad was held by the Danes, but was besieged by Charles XI. The siege staff were located at Råbelöf, both on the enclosed yard and on a moat surrounded by a islet just west of the farm. During this time, Råbelöf was held by Ebbe's daughter Anna Catharina, married to Carl Gustaf Skytte. The latter settled for a time in 1712 on the fortified island within the moat to protect himself from the then ravaging plague. From the Skåne trip in 1749, Linnaeus describes homes and a lovely garden with mulberry and walnut trees, grapes, lavender and white lilies in abundance. The owner was then Anna Catharina Ridderschantz, married to Ludvig Gustaf von Böhnen. She made 1763 Råbelöf and Odersberga fidei committee for the benefit of her three daughters. The Fidei Commission letter is difficult to interpret when it comes to the time after the three daughters, something that several times caused bitter heritage disputes. In 1782 the entire farm burned, the main building was badly damaged and the family moved to Råbelöf belonging to Odersberga, which then had completely new buildings, those that are still there today. Only in 1833 then did the fidei commissioner Fredrik von Rosen return to Råbelöf. The main building had then been cut down and fitted with a new south gable. According to fidei commission rules, Råbelöf returned to the von Böhnen family in 1864. Accession did not become presumed Celestine von Böhnen but instead her older brother Axel. Celestine was married to John William Kennedy. The fide commission went to her and John Williams son James Kennedy. The family could then look back on a number of tortuous legal proceedings between John William and his wife Celestine on the one hand and Axel and his wife Elsa Maria on the other. James was a chamberlain, sitting in the first chamber where he fought socialism. This led to the large agricultural workers' strike in 1907 that was concentrated on Kennedy's three farms Råbelöf, Odersberga and Hammarsjö. In 1906, his eldest son Douglas, the future fidei commissioner, took his life. Four years later another son took his life. James and his wife took the disasters hard, they fell ill. The young son Gilbert got in 1908, only 22 years old, took over responsibility for the farm. James son Gilbert Kennedy took over as Fidei Commissioner in 1916 and they became known as outstanding farmers with, among other things, grazing for dairy cows and fruit growing as specialties. He passed away in 1946 and was succeeded by his son Douglas, who gave continuity to Råbelöf's position with among other things, a new barn with loose running and slatted floors in 1965. Douglas Kennedy held the farm 61 years before he passed away in 2007. He became the last fidei commissioner, the property became a fideicommissie corporation inherited by his sister-in-law John Murray, who in turn in 2010 left it his children Caroline Murray Karlsson and Johan Murray. Since October 2014, Johan Murray has been the sole owner.Digital photograph of a Barn at Rabelofs, Swedenkristianstadt, kennedy, sweden, råbelöv, church, castle, barn -
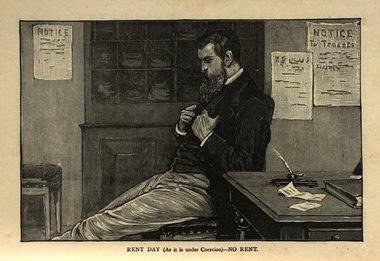 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, Rent Day (as it is under coercion) - No Rent, c1864, c1864
Protection of Person and Property Act 1881 The ''Protection of Person and Property Act 1881'' was one of more than 100 Coercion Acts passed by the Parliament of United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland between 1801 and 1922, in an attempt to establish law and order in Ireland. The 1881 Act was passed by parliament and introduced by Gladstone. It allowed for persons to be imprisoned without trial. On 13 October 1881, the Act was used to arrest Charles Parnell after his newspaper, the ''United Ireland'', had attacked the Land Act. On Gladstone's return to office in 1880, William Edward Forster was made Chief Secretary for Ireland. He carried the Compensation for Disturbance Bill through the Commons, only to see it thrown out in the Lords. On 24 January 1881, he introduced a new Coercion Bill in the House of Commons, to deal with the growth of the Irish National Land League. Despite a 41-hour long fillibuster in the House by the Irish Parliamentary Party, the bill passed, among its provisions being one enabling the British government in Ireland to arrest without trial persons "reasonably suspected" of crime and conspiracy. However those arrested were often not always suspect, only supportive of the Irish National Land League's movements. Over 100 such acts were passed, some of the more notable of which were "An Act for the more effectual Suppression of Local Disturbances and Dangerous Associations in Ireland", "The Protection of Life and Property in Certain Parts of Ireland Act", and the "Protection of Person and Property Act 1881". An Irish Coercion Bill was proposed by Sir Robert Peel to calm the increasing difficult situation in Ireland as a result of the Great Famine 1844–47. The Bill was blocked and this led, in part, to Peel's retirement as Prime Minister. Later attempts to introduce Irish coercion acts were blocked by the filibustering of Joseph Biggar. As a response to the Plan of Campaign of the mid-1880s the new Chief Secretary for Ireland Arthur Balfour secured a tough Perpetual Crimes Act (1887) (or Coercion Act) aimed at the prevention of boycotting, intimidation, unlawful assembly and the organisation of conspiracies against the payment of agreed rents. The Act resulted in the imprisonment of hundreds of people including over twenty MPs. The so-called ''Crimes Act'' (or "Coercion" Act) was condemned by the Catholic hierarchy since it was to become a permanent part of the law and did not have to be renewed annually by parliament, but the Papacy issued the bull Link: "Saepe Nos" in 1888 which was uncritical of the Acts. Trial by jury was abolished. An influential analysis of the pros and cons of the Act was published in 1888 by W. H. Hurlbert, a Catholic Irish-American author. Many hundreds were imprisoned at times under the Acts, including many prominent politicians and agrarian agitators, Joseph Biggar, Alexander Blane, Michael Davitt, John Dillon, James Gilhooly, Patrick Guiney, Matthew Harris, John Hayden, J. E. Kenny, Andrew Kettle, Denis Kilbride, Pat O'Brien, William O'Brien, James O'Kelly, Charles Stewart Parnell, Douglas Pyne, Willie Redmond, Timothy Sullivan. [http://shelf3d.com/i/Irish%20Coercion%20Act, accessed 13/12/2013]A many sits on a table holding the lapels of his Jacket. ballarat irish, cabin, rent, tenants, quill, biggar, davitt -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumBook, State Electricity Commission of Victoria (SECV), "Rules of the Australian Tramway and Motor Omnibus Employees Association", 1937 to 1951
Set of five books that were the property of Jock Menzies, a SEC Ballarat driver. .1 - same as btm3655 - "Rules of the Australian Tramway and Motor Omnibus Employees Association" - 1939. .2 - same as btm3135 - "The Australian Tramway and Motor Omnibus Employees' Association / Agreement / Ballarat, Bendigo and Geelong" - 1937 .3 - same btm3112 - "Electric Tramways of the State Electricity Commission of Victoria By-Law No. 1" - August 1951. .4 - same as btm3068 - "State Electricity Commission of Victoria - Tramways - Rules Governing Employees - May 1936" .5 - same as btm3116 - "Rules Governing Employees" - see btm8078i1.pdf for a full scan of the book. This version is slightly different to other versions,All items have notations on the cover and inside - notes made by Jock.trams, tramways, ballarat, geelong, bendigo, atmoea, unions, agreements, uniforms, sec, rules, regulations, by laws, motormen, conductors -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumDocument - Rule Book, Melbourne and Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), "Rules and Regulations", 30/05/1957 12:00:00 AM
Sixty eight page, sewn book within brown Rexene heavy card covers with printed self end papers. Titled "Melbourne and Metropolitan Tramways Board / Rules and Regulations / relating to drivers, conductors and employees concerned in any aspect of electric tram and motor omnibus operation." Dated 30/5/1957 Has stamped number "790" in bottom. Printing number 1/228. Provides for 226 General Rules - in four sections - General, Tram system only, Bus system only, Accident prevention and procedure (Tram and Bus), and By-Law Nos. 11 and 16, General and Lost property. On both inside covers are printed messages about wearing uniforms, being courteous and safety. On the back pages are printed Long Service Certificate and Certificate of Service. Has a number of amendments adhered to the relevant pages - rules 116, 144j, 15, 160, 216. "Ballarat Tramway Preservation Society Catalogue No. 308" in ink. trams, tramways, rules, regulations, by laws, mmtb, drivers, conductors -
 Otway Districts Historical Society
Otway Districts Historical SocietyMinute Book, Beech Forest Butter Factory Minute Book, 18/3/1902 - 6/2/1905, 18 March 1902
A meeting was held in Gardner's Hall, Beech Forest, for the purposes of considering the advisability of having butter factory established in the Beech Forest district. It was eventually agreed that a butter factory should be established, that provisional directors should be appointed, and upwards of 400 shares were taken up immediately. A second meeting was held on 20 May 1902 of about 40 dairymen. The meeting became a meeting of shareholders resolving to expedite the registration of the company and other preliminary matters. The election of directors then took place. Another meeting of shareholders held on the 15 July 1902 resolved to purchase a property and have the by-laws accepted. An Extraordinary General Meeting was held on 6 August 1902 to confirm all the resolutions passed by the Board.A ledger containing the records of the Beech Forest Butter Factory Minute Book from 18 March, 1902, the date the Butter Factory starts, until 6 February, 1905.Beech Forest Butter Factory Minutes Book Donated to the Otway District Historical Society Inc. by the Colac & District Family History Group Inc. 1st May 2013beech forest; butter, factory, 1902, 1905, minute book, -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - COCKS FAMILY HISTORY
Forty four pages of the Cocks Family History including Acknowledgements and an introductory letter from David James Cocks. No page seven. The Cock Family came England and on arrival in Victoria the letter 's' was added to their surname. Robinson Cock came to Australia at the request of his brother-in-law, John Hunter Patterson, who owned Moorabbee Station, where he started to work. It also tells of the properties owned, horses they bred, dairy farms and later shops in Melbourne which various family members had.person, family, cocks family, cocks family history, david james cocks, robinson cocks, john hunter patterson, bendiog library, mary ann cocks (nee reeves), gwendolyn nellie pegg (nee cocks), herbert james robinson cocks (jim), leslie vincent kennett cocks (les), victor hugh cocks (hugh), herbert victor thomas cocks (bert), nellie cocks (nee mills), leslie robinson cocks, catherine cnatrill (nee cocks), herbert arthur cocks, eve ellen cocks (nee scott), leonard gibb cocks (len), raymond cocks, ingrid cocks (nee petersen), phyllis hope cocks (nee phillips), 'kimbolton', 'mcivor', john ormond randell, latrobe library, melbourne university archives, queensberry hill press, brown prior anderson p/ltd, john cock, katherine robinson, john cock, catherine shepperson -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - PETER ELLIS COLLECTION: CONTRACT OF SALE
Copy of Contract of Sale of Real Estate and associated papers for property located in Flora Lane, Flora Hill which was purchased by Peter Ellis on 26 May 1993. Contract is in booklet with other loose papers. Contract includes General Conditions, Particulars of Sale, Special Conditions, Guarantee, Vendors Statement to the Purchaser, Shire of Strathfieldsaye Land Information Certificate, Planning Certificate Request for Building Approval Particulars, Coliban Region Water Authority Information Statement, Property Inquiry Application Form, Request for Property Information from Vic roads, Advice on Mine Subsidence Hazard (Department of Energy & Minerals), Map, Copy of Certificate of Title and Folder Numbers. Loose pages include Building Control Act 1981 Inspection Notice, two plans of building, Three plans (Coliban Water Asset Location) of Flora Lane where property is situated, 2 dated 13/11/2007 (have New Carport drawn beside house) and 1 dated 22/11/2007. Last page has specifications for car port.bendigo, house, peter ellis oam, peter ellis collection, reiv, law institute of victoria, real estate institute of victoria ltd, e j gannaway, peter n ellis, ray white bendigo pty ltd, e m monotti & son, rogers and every, craig watts, shire of strathfieldsaye, coliban region water authority, sec, g & fc of vic, telecom, vicroads, bruce l phillips, k deps?, department of energy and minerals, robert james sanderson, t flanagan, land titles office victoria, harston partridge & co pty ltd -
 RMIT GSBL Justice Smith Collection
RMIT GSBL Justice Smith CollectionBook, Collins, C. M, The value of property compensation and land tax : being a treatise on the principles to be adopted in the valuation of all kinds of property, whether for compensation, rating, or any other purpose, and an exhaustive exposition of the law relating to Federal Land Tax, 1949
Third editioncompensation (law) -- australia, eminent domain -- australia, tax assessment -- australia, real property -- valuation -- australia, real property tax -- australia, land value taxation -- australia -
 RMIT GSBL Justice Smith Collection
RMIT GSBL Justice Smith CollectionReport, Priorities : report no. 22 : April 1989, 1989
Report no. 22 April 1989ISBN: 0724195947 (corrected)real property -- victoria, priorities of claims and liens -- victoria, land titles -- registration and transfer -- victoria -
 RMIT GSBL Justice Smith Collection
RMIT GSBL Justice Smith CollectionBook, Edwards, Douglas W, The law of fraudulent and voluntary conveyances; being a treatise on the Statute of Elizabeth against fraudulent alienations, and on the law of voluntary dispositions of property, 1908
Previous owners: T. H. Smith, T. W. SmithThird editiontransfer (law), fraudulent conveyances -- great britain -
 RMIT GSBL Justice Smith Collection
RMIT GSBL Justice Smith CollectionBook, Williams, Joshua, Principles of the law of real property, intended as a first book for the use of students in conveyancing, 1920
... Principles of the law of real property, intended as a first.... W. Smith real property -- great britain ISBN: 0665654596 ...Previous owners: T. H. Smith, T. W. SmithTwenty Third edition- re-arranged and partly re-written by his son, Williams, Cyprian. TISBN: 0665654596real property -- great britain -
 RMIT GSBL Justice Smith Collection
RMIT GSBL Justice Smith CollectionBook, Williams, Cyprian. T et al, Principles of the law of personal property intended for the use of students in conveyancing, 1926
... Principles of the law of personal property intended for the... of the law of personal property intended for the use of students ...Previous owners: T. H. Smith, T. W. SmithEighteenth edition Also known as: Williams on person propertypersonal property -- great britain -
 RMIT GSBL Justice Smith Collection
RMIT GSBL Justice Smith CollectionBook, Stevens and Sons Limited, The law of real property, 1959
... The law of real property.... W. Smith real property -- great britain land tenure -- law ...Previous owners: T. H. Smith, T. W. SmithSecond editionreal property -- great britain, land tenure -- law and legislation -- great britain -
![Journal series, Fleet Street patent law reports, [1968]](/media/collectors/54a9bcce2162f11b1cc120f2/items/54ebf4f02162f10f9cbf4e79/item-media/54ebf6b42162f10f9cbf6c0f/item-fit-380x285.jpg) RMIT GSBL Justice Smith Collection
RMIT GSBL Justice Smith CollectionJournal series, Fleet Street patent law reports, [1968]
Previous owner: J. McL. EmmersonNo. of volumes: 47 Volume range: 1967-1974 (large) & Vol. 1 (1975) - Vol. 40 (2013) Later title: Fleet street reports of industrial property cases from the Commonwealth and Europe Editors: Lunzer, R. ([1967] - 1969) Haywood, R. (1969 - 1972) Fysh, M. (1973 - 1994) Vitoria, M. (1995 - 2011) Clark, F. (2012 - 2013)industrial property -- europe -- cases, industrial property -- great britain -- cases, patent laws and legislation -- great britain -- cases, patent laws and legislation -- europe -- cases
