Showing 986 items matching "shillings"
-
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Equipment - Adding Machine
Built on a cast iron base the machine is designed for Sterling currency with a full-keyboard that has five decimal columns for pounds, three columns for shilling and pence, one column for the 10 and 11 pence keys and three farthing (1/4 penny) keys. The machine was imported and distributed by Chartres Pty. Ltd, Capel Court, 375-377 Collins Street MelbourneHand operated comptometer or adding machine with side handle. Sterling currency with full-keyboard with columns for Pounds Shillings and Pence'Chartres Pty Ltd/Capel Court/375-377 Collins Street Melbourne/23359'commerce, office equipment / stationery, bookkeeping -
 Anglesea and District Historical Society
Anglesea and District Historical SocietyPostal Note, 1933
Australian Postal Note made out to the Postmaster at Hamilton to pay Miss H.M. Thomson - four shillings, at any time within six months from the last day of the month of issue on account of the Postmaster General. The purchaser must fill in the office of payment and names of payee.232512 VICTORIA / COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA / To the Postmaster at . . . . . . . Hamilton / Pay .. . . . . . . Miss H.M. Thomson / FOUR SHILLINGS / POUNDAGE / THREE HALF PENCEpostal note, money order, postmaster general -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyprogram, December 1925
This event - horse racing - was held to raise funds for the Orbost District Hospital and the Trustees of Marlo Reserve funds. It was used by F.E. Richardson of Bete Bolong at the Marlo picnic Races on Boxing Day 1925. It cost one shilling. Frank Richardson was the son of Mark Richardson, son of pioneer, Samuel Richardson.This program is significant in that it is a souvenir of a local event which no longer takes place. A small folded card program for the Marlo Picnic Races on Boxing Day 1925. Text is in black print. This Official Program cost 1s (one shilling)recreation horse-racing marlo-picnic-races -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Document, Receipt WCC
This receipt issued to the Warrnambool Club by the Shire of Warrnambool is for ‘materials’ supplied. It is not known what type of material the Warrnambool Club was buying but it could not have been very important as the total cost was only four shillings. The Warrnamnbool Club was (and is) in the City of Warrnambool. This club was a gentlemen’s club established in 1873 and the building that still exists today was built in 1877. This receipt has little significance as it is a 1951 purchase by the Warrnambool Club for an unknown item of little value. This is a small green receipt slip issued by the Shire of Warrnambool in 1951 to the Warrnambool Club for materials received. The paper has printed black lines and handwritten information (pencil) and has been torn from a larger receipt book, perhaps leaving a copy for the Shire records. ‘Shire of Warrnambool, received from W’bool Club, the sum of four shillings, E.C.Fairbridge, Rate Collector, 24/10/51’.warrnambool club, shire of warrnambool -
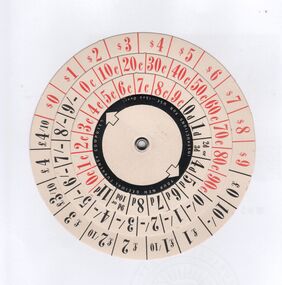 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Ephemera - Decimal currency computer, Win Jennings Collection, 1966
Conversion of Australian currency from pounds/shilling/pence to dollars/cents. on 14 February 1966.Circular paper computer used by hand to convert pounds/shilling/pence to dollars/cents, or the reverse calculation. Printed in 1965/64 for the conversion of Australian currency which was affected on 14 February 1966. Printed in red and black on four circular plains. Printed by Earles Printing Pty Ltd for Ultra Publicity Pty Ltd, 104 Wellington parade, East Melbournebendigo, decimal converter -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Ports and Harbours, Ports and Harbours, Tender for Warrnambool Light, 24-06-1902
... shillings ...The document confirms that the Tender for the supply of gas to the Warrnambool Light, also known as the Lighthouse, by the Warrnambool Gas Works was successful. The Tender was issued by the Engineer in Charge, Ports and Harbours, Melbourne, for a the period ending 30th June 1903, at the offered rate of 10/- (ten shillings) per 100.0 c/f (cubic feet). The Manager of the Warrnambool Gas Works expected to follow this acceptance with a visit to the Collector of Customs to sign the Conditions of Contract and Bond. The light of Warrnambool's Lady Bay Lighthouse was originally powered by oil. Later it was converted to gas, followed by electricity, then solar power, and finally to battery power. The Warrnambool Gas Company operated the gas works from the 1870's to the late 1920's.This document connects Warrnambool's Lady Bay Lighthouse to the Warrnambool Gas Works during the first decade of the 20th century. It documents to process of a Government department requesting Tenders for the supply of goods to operate a service, the the formal documentation required at that time.Pale green rectangular paper with template text printed in black and completed in black ink script. Letterhead of the Department of Ports and Harbours, Melbourne, and addressed to the Gas Works, Warrnambool, dated 24th June 1902, for the supply of gas to the Warrnambool Light until 30th June 1903 at the cost of Ten Shillings per 100 cubic feet."24th [June] 1902" Warrnambool [Light]" "Manager W'bool Gas Wks" "supply of gas to" "1903" "10/- per 100.0 c/f" "Collector of Customs" " The Manager / Gas Works / Warrnambool" [Signature] "for" [Engineer in Charge, Ports and Harbours]flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, department of ports and harbours, ports and harbours, ports and harbours melbourne, warrnambool light, warrnambool lighthouse, warrnambool gas works, w'bool gas works, gas works, gas supply, early 1900s, early 20th century, shillings, cubic feet, collector of customs, customs, warrnambool customs, engineer in charge, lady bay lighthouse, warrnambool gas company -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Ports and Harbours, Ports and Harbours, Tender for Warrnambool Light, 24-06-1904
... shillings ...The document confirms that the Tender for the supply of gas to the Warrnambool Light, also known as the Lighthouse, by the Warrnambool Gas Works was successful. The Tender was issued by the Engineer in Charge, Ports and Harbours, Melbourne, for a the period ending 30th June 1905, at the offered rate of 10/- (ten shillings) per 100.0 c/f (cubic feet). The Manager of the Warrnambool Gas Works expected to follow this acceptance with a visit to the Collector of Customs to sign the Conditions of Contract and Bond. The light of Warrnambool's Lady Bay Lighthouse was originally powered by oil. Later it was converted to gas, followed by electricity, then solar power, and finally to battery power. The Warrnambool Gas Company operated the gas works from the 1870's to the late 1920's.This document connects Warrnambool's Lady Bay Lighthouse to the Warrnambool Gas Works during the first decade of the 20th century. It documents to process of a Government department requesting Tenders for the supply of goods to operate a service, the the formal documentation required at that time.Pale cream rectangular paper with template text printed in black and completed in black ink script. Letterhead of the Department of Ports and Harbours, Melbourne, and addressed to the Gas Works, Warrnambool, dated 24th June 1904, for the supply of gas to the Warrnambool Light until 30th June 1905 at the cost of Ten Shillings per 100 cubic feet."24th [June] 1904" Warrnambool [Light]" "Manager W'bool Gas Wks" "supply of gas to" "1905" "10/- per 100.0 c/f" "Collector of Customs" " The Manager / Gas Works / Warrnambool" [Signature] "for" [Engineer in Charge, Ports and Harbours]flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, department of ports and harbours, ports and harbours, ports and harbours melbourne, warrnambool light, warrnambool lighthouse, warrnambool gas works, w'bool gas works, gas works, gas supply, early 1900s, early 20th century, shillings, cubic feet, collector of customs, customs, warrnambool customs, engineer in charge, lady bay lighthouse, warrnambool gas company -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomBook, Hints to NON-COMS in the AUSTRALIAN MILITARY FORCES, 1915
A light card covered book, compiled by Lt R Stupart, containing hints on various subjects including duties, the art of instructing, military courtesy. dress and discipline Copyright One Shillinghandbook, nco training, 1915 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Ports and Harbours, Ports and Harbours, Tender for Warrnambool Light, 24-06-1907
... shillings ...The document confirms that the Tender for the supply of maintenance to the Warrnambool Light, also known as the Lighthouse, by the Warrnambool Gasworks was successful. The Tender was issued by the Engineer in Charge, C. Maclean, Ports and Harbours, Melbourne, for a the period ending 30th June 1908, at the offered rate of 10/- (ten shillings) per 100.0 c/f (cubic feet). The Manager of the Warrnambool Gasworks expected to follow this acceptance with a visit to the Collector of Customs to sign the Conditions of Contract and Bond. The light of Warrnambool's Lady Bay Lighthouse was originally powered by oil. Later it was converted to gas, followed by electricity, then solar power, and finally to battery power. The Warrnambool Gas Company operated the gas works from the 1870's to the late 1920's.This document connects Warrnambool's Lady Bay Lighthouse to the Warrnambool Gas Works during the first decade of the 20th century. It documents to process of a Government department requesting Tenders for the supply of goods to operate a service, the the formal documentation required at that time.Pale cream rectangular paper with template text printed in black and completed in black ink script. Letterhead of the Department of Ports and Harbours, Melbourne, and addressed to the Gas Works, Warrnambool, dated 25th June 1907, for the supply of maintenance to the Warrnambool Light until 30th June 1908 at the cost of Ten Shillings per 100 cubic feet. A purple stamped signature is also added and initialled in red pen."25th [June] 1907" Warrnambool [Light]" "Manager W'bool Gasworks" "supply of gas to" "1908" "10/- per 100.0 c/f" "Collector of Customs" " The Manager / Warrnambool Gasworks" [Signature] "for" [Engineer in Charge, Ports and Harbours] Stamped " C. -. Maclean"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, department of ports and harbours, ports and harbours, ports and harbours melbourne, warrnambool light, warrnambool lighthouse, warrnambool gas works, w'bool gas works, gas works, gas supply, early 1900s, early 20th century, shillings, cubic feet, collector of customs, customs, warrnambool customs, engineer in charge, lady bay lighthouse, warrnambool gas company, gasworks, warrnambool gasworks, maintenance, c. - maclean -
 Hand Tool Preservation Association of Australia Inc
Hand Tool Preservation Association of Australia IncCoin
This item is part of the Thomas Caine Tool Collection, owned by The National Trust of Australia (Victoria) and curated by the Hand Tools Preservation Association of Australia.coin, 1922 shilling with chain attachment -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncCurrency - Money, 1940's
Japanese One Shilling Invasion Currencystawell -
 Wonga Park Community Cottage History Group
Wonga Park Community Cottage History GroupCoins, 6 Australian pre decimal, ie pre 1966
1946 Two shillings, 1952 One shilling, 1946 sixpence, 1951 threepence, 1961 penny and 1961 halfpenny, mounted on a card and labelled -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Container - PHARMACY COLLECTION: BULL DOG BRAND SALVE JAR, 1920's
Object. Small amber glass jar with gold coloured metal lid. Label showing " British Bulldog as trademark for Bulldog Brand Salve, the herbal ointment". Price 1/-. (Price has been overwritten so as to read 2/-.). For Catarrh, Piles, Eczema, Cuts, Burns, Sores, etc..On label original price of 1/- (Shilling) has been overwritten with pen and ink to read 2/- (Shilling). A832.medicine, first aid, bulldog brand salve -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomBooklet, Capt W Stanley Lewis MSc, FRGS, Military Map Reading for the New Army, Feb 1941
Soft covered booklet covering various details of military maps and how to read them. Price Two shillings and six pencemanual, map reading -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumBooklet, Reminiscences of Clunes, 1925
Printed for the Back to Clunes Reunion November 14 to 21, 1925Blue soft cover booklet, 15 pagesPrinted on Front; Price-ONE SHILLINGback to clunes 1925, state school jubilee -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook, Knitting, Lincoln Book 28, c.1960
Knitting book produced by the Lincoln Mills, Coburg and containing knitting patterns for women's garments.Knitting book, 16pp. Front cover printed in colour with a photograph of a woman wearing a blue knitted cardigan with a matching blue knitted skirt and blue knitted hair band. Contains photos and patterns for women's knitted garments.Lincoln / BOOK 28 / THREE SHILLINGSknitting, lincoln mills (australia) limited, coburg, patterns, fashion -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaLetter - Correspondence, 29/06/1951
Allan's mother comments on the high cost of living in Sydney; lamb chops are six shillings and eight-pence a pound and only four shillings a pound in Melbourne. They have brought six pounds of butter with them as butter is very difficult to buy in Sydney. She and Allan's step-father Kip Hayes are staying with 'Jim' and enjoying catching up with friends and relatives. She has sent Allan a cake for his 23rd birthday which is on the 2 July.Quinn CollectionThree-page letter written on three sheets of lined, cream-coloured paper (0876.a1-3), headed McCleay Regis and dated 29/06/51. (This should probably be Macleay Regis). The matching envelope (0876.b) is addressed to Mr A. Quinn, C/- General Delivery, G.P.O., Oslo, Norway. It is postmarked Sydney and bears an Australian 1 shilling, 6 pence stamp. On the back are two indistinct postmarks and an unidentifiable square stamp which appears to have been reversed.Letter commences "Allan Dear,"......and concludes "...From your Mum."letters-from-abroad, allan quinn, oslo, alette andersen, sydney, kip hayes -
 Sunshine and District Historical Society Incorporated
Sunshine and District Historical Society IncorporatedReceipt (1912), HUGH V. McKAY - SUNSHINE HARVESTER, 6 March 1912
Interpreting from the details that can be read it is believed that on 6/3/1912 Mr. M. Norton paid by cheque the sum of 5 Pounds 19 Shillings and 5 Pence, of which 5 Pounds 3 Shillings and 11 Pence was for a Summons possibly issued on 23/2/1912, while 15 Shillings and 6 Pence was the charge for the costs of the Summons. This is not a document issued by a Court of Law so use of the word 'Summons' is confusing to us at this stage. Was it just standard practice to send out a bill and call it a Summons, or was Mr. Norton late in paying and so had to pay an extra charge after being 'summoned' a second time. Could this receipt be part of a 'promissory note' exchange, payment for which had to be summoned? Another thing that can't be explained at this stage is the use of the symbol % after the amount of money written in figures, just after the Pence amount. The symbol for Pence in those days, and until decimal currency, was d as can be seen from the Duty Stamp. In 1912 and before did % also stand for Pence when the money amount was written by hand, or could it have been a shorthand way of indicating something like 'portion of amount'? This receipt is very intriguing and so we will endeavour to try to fully understand the information it contains. If any person can provide information that may assist us, then please contact the Sunshine & District Historical Society. The receipt is significant to our Society because it was issued by Sunshine Harvester / Hugh V. McKay more than 100 years ago. It also appears to contain information that at this stage is not fully understood, such as the use of the % sign, and why the word summons is used. Of further interest, but perhaps not surprising for the times, is that only Mr. is printed on the receipt. It appears that they never expected to issue these type of receipts to females.Very light tan coloured paper receipt No.1773 issued on 6/3/1912 by Sunshine Harvester / Hugh V. McKay to Mr M. Norton. The receipt has fire damage on the left side and so some details are missing. Details are hand written in ink in the spaces provided. A greenish coloured one penny (1d) Victoria Stamp Duty stamp is affixed.6 3 1912 ......ved by Cheque from Mr. M Norton ......ne the sum of Five ...... nineteen Shillings and five Pence, with ......being £5.3.11% of Enclosed Summons 23. 2.12 & 15/6 % Costs of Same.receipt no. 1773, sunshine harvester, hugh v. mckay, mr m. norton, 1912, victoria stamp duty, 1d -
 Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub Branch
Running Rabbits Military Museum operated by the Upwey Belgrave RSL Sub BranchCurrency
British Military Authority 1 shilling notedocuments, rn -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyBook, Richard Watson, The Life of The Rev. John Wesley, A.M, 1851
The life of The Rev. John Wesley, A.M. sometime fellow of Lincoln College, Oxford and founder of the Methodist Societies.An old rare damaged brown heavily embossed patterned hardcover book, The Life of The Rev. John Wesley, A.M. by Richard Watson. The spine is missing. There are loose pages particularly at the front with pencil and ink inscriptions. A sewing pin is holding the black and white portrait of John Wesley to the endpaper. The spine edge inside has grey tape holding the endpapers together. There are dirty marks, severe tanning and foxing noted all through this 1851 edition. 485p. with a few pages at the back of further religious works by the publisher John Mason.non-fictionThe life of The Rev. John Wesley, A.M. sometime fellow of Lincoln College, Oxford and founder of the Methodist Societies.religion, biography, methodist church history -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Certificate - Document, receipt burial 1890 Martha Jones, c1880
James Jones was the son of Philip Jones, a Chairmaker, and Ann Jones who settled in East Brighton after the sale of land c1852 in the area of the Henry Dendy Special Survey of 1841. Mary Ann Moore was the daughter of Thomas Moore, a Gardener, and Sarah Harris who also settled in Brighton c1852. James and Mary Ann Jones settled and raised their family in East Brighton now Bentleigh. Mr John Herron resided at 4 Vickery St Bentleigh until 1989. Sadly Martha Jones born 1888 died in 1890 and James Jones had to purchase a plot at Brighton General Cemetery for her burial. A further 2 children were interred in 1893 and 1900 then Mary Ann in 1903 and James in 1940James Jones and Mary Ann Moore were born in Brighton c1857 and c 1859 into pioneer market gardener families in the area of the Dendy Special Survey of 1841. They married in 1883 and raised their family in East Brighton, now Bentleigh. Sadly infectious diseases took the lives of many infants throughout the Colony of Victoria due to the poor state of water supply and sewerage disposal and locally the swamps of the Elster Creek were a constant breeding ground. Martha Jones born 1888 died 1890 and was interred in Brighton General Cemetery in a family plot purchased by her father James Jones. An original paper receipt No. 2844 for payment 22 January 1890 by James Jones to Brighton General Cemetery of 3 pounds 1 shilling for burial of Martha Jones aged approx. 2 years in a plot 4 feet x 8 feet. Fees include family grave at 2 pounds 2 shillings, Sinking to 7 feet at 14 shillings and Label 5 shillings .No. 2844( hand written) / BRIGHTON GENERAL CEMETERY / RECEIVED 22 January 18 90 / of Mr James Jones ( hand written ) the sum of £3. 1 being the / following charges in Wesleyan Portion No. / Compt. Name of deceased Martha Jones / Signed S Simmonds (handwritten) Secretary Along left side G.H Orford Printer “ Southern Cross Office” Bay St. Brighton melbourne, brighton, moorabbin, water supply, pioneers, bentleigh, dendy henry, market gardeners, early settlers, jones mary ann, wesleyan church, jones james, vaccination, typhoid, dendys special survey 1841, infectious diseases, elster creek, jones martha, brighton general cemetery, orford g h, printers, southern cross office, bay street brighton -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - FRANK J EVERY COLLECTION: C SMITH PAINTER INVOICE
Handwritten invoice. White Hills, 13/02/1912. Mr F. Every to C. Smith - Painter. Painting fence at Raglan Street 3 pounds 15 shillings and Painting fence at Main Street 4 pounds 15 shillings, total 8 pounds 10 shillings. Paid with thanks 14/02/1912. Signed C. Smith. There is a 1 shilling stamp duty attachedbusiness, retail, smith painter -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaDocument - Statement of earnings (linked to group certificate registration number 00291), Issued 26 January 1945
Tax certificate of Allan QuinnThis certificate gives an indication of the level of wages in 1945 and the amount of tax paid. Triplicate version of group certificate marked statement of earnings.Issued 26 January 1945 for tax of 2 pounds, 12 shillings and 9 pence on earnings of 79 pounds, 10 shillings. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Queen Victoria Women's Centre
Queen Victoria Women's CentreBanner, Shilling Fund Banner, c.1996
Used for several QVWC events including grand opening weekend, and fundraising events. Cream satin banner with purple text 'Shilling Fund' -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1887
This Great Britain one shilling coin is dated 1887, which is during the reign of Queen Victoria. There were over 4 million of these coins minted. Queen Victoria succeeded King William IV to the British Throne in 1837 – she was only 18 years old at the time – and she ruled until 1901. This 1887 Great Britain shilling was struck as part of new coinage of gold and silver commemorating the Golden Jubilee of Queen Victoria 1837-1887. This design continued until 1893. The obverse image of Queen Victoria, called the ‘Junior Head’, was engraved by Joseph Edgar Boehm and adapted from his engraving for the Jubilee Medal. The design on the reverse is based on the design of the George IV shilling, 1823-1825. Inscription translations: - Obverse side: “Victoria by the Grace of God, Queen of the British territories, Defender of the Faith”. - Reverse side "Evil to him who evil thinks”. British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This one shilling coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. There are three main groups of shillings produced during Queen Victoria’s reign:- - The Young Head; 1837-1887, in 8 different versions, on the obverse showing the Queen’s maturing face over 50 years. - The Junior Head; 1887-1892, minted when Queen Victoria had been reigning for 50 years. Her head was smaller on the coins minted 1887-1889 than on those shillings minted 1889-1892. - The Old Head; 1893-1901, shows the veiled head of Queen Victoria. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. This silver shilling is also of significance to Australia as part one of the British Colonies ruled by Queen Victoria. It is part of the special silver and gold coins minted 1887-1893 to celebrate the 50 years Jubilee of Queen Victoria’s reign 1837-1887. Coin, Great Britain Shilling, 1887. Silver coin, round. Obverse; Queen Victoria head, ‘Junior Head’, looking left. Reverse; crown on quartered shield within band of text, above year. Shield has 2 quarters with 3 lions on each, one quarter with a lion, one quarter with a harp. Inscriptions on both sides of coin.Obverse “VICTORIA DEI GRATIA BRITT REGINA F : D :” Reverse “HONI . SOIT . QUI . MAL . Y . PENSE” and “1887” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1887, queen victoria currency, queen victoria 50 years golden jubilee shilling, colonial australia currency, joseph edgar boehm, numismatics
