Showing 438 items matching "surgical instruments"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Spirit burner, early 1900's
... surgical instrument... historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once... to sterilize surgical instruments (W.R. Angus Collection)... medical equipment surgical instrument dr ryan nhill base hospital ...This spirit burner was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Spirit or alcohol burner, round squat shape, clear glass base and bulbous top with cotton wick inside; wick has metal holder. Top sits on base, to snuff flame. Suitable for liquid fuel such as methylated spirits; heat from flame is used to sterilize surgical instruments (W.R. Angus Collection)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, spirit burner, alcohol burner, glass spirit burner, metical equipment, dr w r angus, medical equipment, surgical instrument, dr ryan, nhill base hospital, flying doctor, medical history, medical treatment, mira hospital -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSurgical instrument set, early 20th century
... Surgical instrument set...surgical instrument set... medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once...Surgical instrument set in wooden case contains instruments... historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once ...This object was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s SS Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Surgical instrument set in wooden case contains instruments for ophthalmic (eye) surgery. Case has hinged lid, lock, removable compartment; inlaid brass strips, nameplate on lid, brass hook closures. Lined with purple fabric and fitted to hold surgical instruments; brass protective strip under tips of sharp instruments. Contains 8 fine instruments and 3 long, glass head pins. Scissors have corrosion. (Set is incomplete). Inlaid cream strip along inside edge with black print "ARNOLD & SONS" WEST SMITHFIELD LONDON" Instrument have varying impressed marks "MAYER & MELTZER, LONDON or "M&M LONDON" or "M&M Co" or "GRESCOE" (W.R. Angus Collection) Inlaid cream strip along inside edge with black print "ARNOLD & SONS" WEST SMITHFIELD LONDON" Instrument have varying impressed marks "MAYER & MELTZER, LONDON or "M&M LONDON" or "M&M Co" or "GRESCOE"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, surgical instrument set, dr w r angus, medical equipment, surgical instrument, dr ryan, ophthalmology, s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, flying doctor, medical history, medical treatment, mira hospital, medical education, medical text book -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Photograph, Gibbons, Denis, Correct Terminology
... medical and surgical instruments at the NVA/VietCong K76A Hospital... medical and surgical instruments at the NVA/VietCong K76A Hospital ...Denis Gibbons (1937 – 2011) Trained with the Australian Army, before travelling to Vietnam in January 1966, Denis stayed with the 1st Australian Task Force in Nui Dat working as a photographer. For almost five years Gibbons toured with nine Australian infantry battalions, posting compelling war images from within many combat zones before being flown out in late November 1970 after sustaining injuries. The images held within the National Vietnam Veterans Museum make up the Gibbons Collection. A black and white photograph of a Doctor from 1st Australian Field Hospital, Vung Tau, South Vietnam, inspects captured medical and surgical instruments at the NVA/VietCong K76A Hospital and advised an Intelligence Officer from 6 RAR/NZ (ANZAC) of the correct terminology during Operation Marsden on Nui May Tao Mountainphotograph, 6rar/nz, k76a hospital, nui may tao mountain, operation marsden, gibbons collection catalogue, doctor, nva/vc, 6 rar/nz (anzac), 1st australian field hospital, captured medical supplies, nva/vietcong, denis gibbons -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSurgical instrument, early 20th century
... Surgical instrument...surgical instrument...This surgical instrument was donated to Flagstaff Hill... Surgical instrument of plated meta, from the W.R. Angus... Warrnambool great-ocean-road This surgical instrument was donated ...This surgical instrument was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Surgical instrument of plated meta, from the W.R. Angus Collectionl. The long flat instrument is curved up into an elongated ‘S’ shape, pointed at one end with an oval hole 1.5cm from the tip. The other end is rounded and has an oval hole about 1.25cm long, starting close to its end. The surface is pitted in places. There is a residue of a dark brown substance on the tip. Once part of Dr T.F. Ryan's medical practice.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, surgical instrument, dr t f ryan, dr angus, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, surgical instrument, dr t f ryan, dr angus, medical equipment, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical history -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumAuroscope, Elliots & Australian Drug Pty Ltd
... , . 33 Bligh St. Sydney. Manufactures and importers of Surgical... Station, Melbourne until 1984. Auroscope: a medical instrument ...Used by Manning Chemist, Flinders Street Railway Station, Melbourne until 1984.Auroscope: a medical instrument consisting of a magnifying lens and light; used for examining the external ear (the auditory meatus and especially the tympanic membrane)Housed in a black box with velvet lining: a black metal tube for holding batteries to power the globe, with screw base and top. Top holds a metal attachment with an eye piece and glass lenses. Box also contains three other attachments.On lining of box lid 'Elliots and Australian Drug Pty Ltd, . 33 Bligh St. Sydney. Manufactures and importers of Surgical Instruments'.,. On label attached inside box 'Manning Chemist Fluinders St. Raoilway Station, Melbourne, Phone MA 33 48'. -
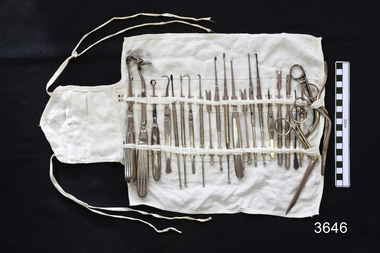 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSurgical Kit, late 19th century
... surgical instrument... surgical instruments for Ear Nose and Throat surgery. I was useful... surgical instruments (Ear Nose Throat).... T.F. Ryan's to hold surgical instruments for Ear Nose ...This surgical kit holder was used by Dr T.F. Ryan's to hold surgical instruments for Ear Nose and Throat surgery. I was useful for both holding these particular instruments and for keeping them together whilst they were sterilised. It was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, including the instruments, by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Surgical kit holder once belonging to Dr T.F. Ryan, part of the W.R. Angus Collection. Roll-up kit, right weight, flexible canvas, 21 loops for instruments, with fastening and tying tapes, plus 6 pockets for needles and sutures. Fabric is suitable for sterilising by boiling or autoclave treatment. Name tag, sewn on, with red embroidery, "DR T.F. RYAN" Used by Dr Ryan to store ENT surgical instruments (Ear Nose Throat).Name tag, sewn on, with red embroidery, "DR T.F. RYAN" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, surgical kit, fabric sutrical instrument holder, surgery -
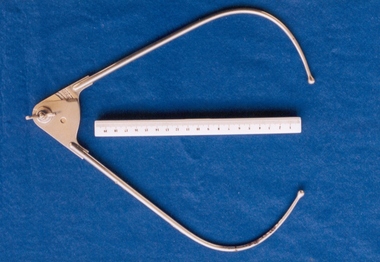 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Pelvimeter used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward
... in Aesculapius Surgical Instruments p. 2195. ... Surgical Instruments p. 2195. This instrument was included ...A pelvimeter is used in obstetrics for measurement of the female pelvis, with the aim of attempting to determine whether there will be any potential issues with a vaginal birth. The style of this pelvimeter is similar to Collyer's pelvimeter as depicted in Aesculapius Surgical Instruments p. 2195. This instrument was included with other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, given to RANZCOG from Box Hill Hospital labour ward in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill Hospital combined with St George's Hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett.Pelvimeter. Similar in style to Collyer's pelvimeter. Has adjustable arms hinged with a wingnut, and a scale graduated in inches and centimetres.obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Chassaignac gynaecological ecraseur associated with Dr Frank Forster
... . Tiemann & Co Surgical Instruments USA. .... Tiemann & Co Surgical Instruments USA. Destructive instruments ...Used to remove polyps or other growths, using a tightening chain to gradually lacerate the growth, minimizing haemorrhage. Devised by Charles Marie Edouard Chassaignac (1805-1879) who was a surgeon in Paris. The manufacturer of this item was possibly Geo. Tiemann & Co Surgical Instruments USA. Metal ecraseur, Chassaignac's design. The straight shaft can be extended, and has a straight handle at one end and a metal loop at the other. destructive instruments -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Obstetric forceps used by Dr Michael Kloss, Jetter and Scheerer
... Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker... Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded ...Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded in Germany in 1867. Their company symbol is that of a serpent curled around a rod, surmounted by a coronet/crown. This instrument was part of a collection of instruments used by Dr Michael Kloss in his medical practice. Dr Kloss subsequently donated this collection to the College.Metal forceps, consisting of two blades which lock together with a pin fitting. The handle of one of the forceps blades is engraved with the word 'Kloss', both on the outside and on the inner aspect. The number '26' is engraved on the inner aspect of both blades near the pin joint. The upper shaft of one blade is engraved with the word 'HOSON'. The blade is also engraved with a derivation of the Rod of Asclepius, featuring a serpent wrapped around a rod, with the entire design topped by a crown.'Kloss' '26' 'HOSON'obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Surgical spreader used by Dr Michael Kloss, Jetter and Scheerer
... Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker... Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded ...Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded in Germany in 1867. Their company symbol is that of a serpent curled around a rod, surmounted by a coronet/crown. This instrument was part of a collection of instruments used by Dr Michael Kloss in his medical practice. Dr Kloss subsequently donated this collection to the College.Metal spreader. Instrument consists of two arms and a set of spring loaded handles, with a pin lock to lock the spreader at particular apertures. Each arm ends with a 'z' shaped section with a narrow foot. The outside of each foot is grooved for grip. One arm of the spreader is engraved with a derivation of the Rod of Asclepius, featuring a serpent wrapped around a rod, with the entire design topped by a crown. Each arm is engraved with the number '355' on the inner aspect near the join point.obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Ovum forceps used by Dr Michael Kloss
... Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker... Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded ...Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded in Germany in 1867. Their company symbol is that of a serpent curled around a rod, surmounted by a coronet/crown. This instrument was part of a collection of instruments used by Dr Michael Kloss in his medical practice. Dr Kloss subsequently donated this collection to the College.Metal ovum forceps. Instrument resembles a set of scissors, with a ratchet adjacent to the handle to lock them at particular apertures. The end of each arm of the scissors ends with a metal loop, with grooves on the inner aspects of the loops for grip. The inner aspect of the forceps are engraved with the number '99'. The forceps are also engraved with a derivation of the Rod of Asclepius, featuring a serpent wrapped around a rod, with the entire design topped by a crown.obstetrics -
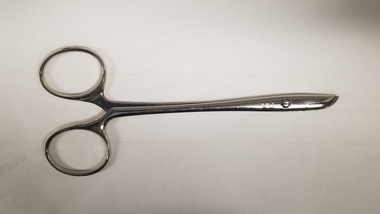 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Surgical scissors used by Dr Michael Kloss, Jetter and Scheerer
... Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker... Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded ...Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded in Germany in 1867. Their company symbol is that of a serpent curled around a rod, surmounted by a coronet/crown. This instrument was part of a collection of instruments used by Dr Michael Kloss in his medical practice. Dr Kloss subsequently donated this collection to the College.Metal surgical scissors. Consists of two arms with handle grips, a narrow shaft, and small cutting blades at the end of each arm. The inner aspect of the scissors is engraved with the number '47'. The shaft is engraved with a derivation of the Rod of Asclepius, featuring a serpent wrapped around a rod, with the entire design topped by a crown.'47'obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Commemorative ashtray presented to Dr Frank Forster, c. 1965, Rocket & Co, London
... ] The ashtray was made by Rocket & Co, a manufacturer of surgical...] The ashtray was made by Rocket & Co, a manufacturer of surgical ...This item was a gift to Dr Frank Forster from colleagues (and possibly students) whilst he was working at the Hosptial for Women at Soho, London, c 1965. [Source: Librarian Hilary Belton] The ashtray was made by Rocket & Co, a manufacturer of surgical instruments. Geofrey Bishop and Bryan Hibbard also have similar ashtrays.Chrome ashtray, consisting of a triangular base with three cigarette rests. At the centre of the base, on a central stem/pedestal, is a set of replica miniature forceps.dr frank forster, obstetric delivery, ephemera -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Surgical scraper used by Dr Michael Kloss, Jetter and Scheerer
... and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded in Germany... and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded in Germany ...The '3' on this instrument indicated it was size 3. Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded in Germany in 1867. Their company symbol is that of a serpent curled around a rod, surmounted by a coronet/crown. This instrument was part of a collection of instruments used by Dr Michael Kloss in his medical practice. Dr Kloss subsequently donated this collection to the College.Metal scraper. Instrument consists of a large, six sided handle section, a short, thin shaft and a small, oval shaped scoop at the end of the shaft. The handle at the proximal end is in the shape of an elongated teardrop, hollowed out at centre. The number '3' is engraved on the shaft of the instrument. The shaft is also engraved with a derivation of the Rod of Asclepius, featuring a serpent wrapped around a rod, with the entire design topped by a crown.'3'obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Surgical scraper used by Dr Michael Kloss, Jetter and Scheerer
... and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded in Germany... and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded in Germany ...The '3' on this instrument indicated it was size 3. Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded in Germany in 1867. Their company symbol is that of a serpent curled around a rod, surmounted by a coronet/crown. This instrument was part of a collection of instruments used by Dr Michael Kloss in his medical practice. Dr Kloss subsequently donated this collection to the College.Metal scraper. Instrument consists of a large, six sided handle section, a short, thin shaft and a small, round scoop at the end of the shaft. The handle at the proximal end is in the shape of an elongated teardrop, hollowed out at centre. The number '3' is engraved on the shaft of the instrument. The shaft is also engraved with a derivation of the Rod of Asclepius, featuring a serpent wrapped around a rod, with the entire design topped by a crown.'3'obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Medical instrument tray
... An important part of any surgical room, instrument trays... An important part of any surgical room, instrument trays are used ...An important part of any surgical room, instrument trays are used to organise and hold instruments during surgery.Square metal instrument tray.surgery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, Physiological Principles in Treatment, 1930
... medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once... historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once ...This book was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969.The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Book Title- 'Physiological Principles in Treatment' by Brown and Hilton, 6th edition. Red hard cover book with title stamped into cover. Approximately 464 pages.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, physiological principles in treatment, medical book 1930 -
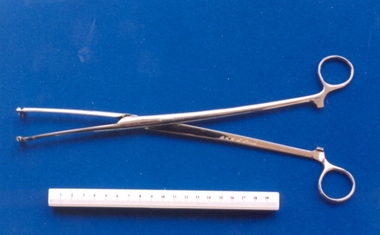 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Placenta praevia forceps used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward, Ramsay
... Bros Catalogue of Surgical Instruments and Appliances, c1930, p... Catalogue of Surgical Instruments and Appliances, c1930, p 940 ...Similar to Willett's placenta praevia forceps [see Down Bros Catalogue of Surgical Instruments and Appliances, c1930, p 940]. John Abernethy Willett (1872 -1932) modified an existing pair of surgical scalp forceps for use in bringing down the head of a foetus in the case of placenta praevia. As the safety of c-sections increased and fetal viability became a dominant consideration, these were used only for the dead/pre-viable foetus. (Source: Baskett, Thomas. 'On the Shoulders of Giants - Eponyms & Names in O&G'.) This was included with other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, from Box Hill Hospital labour ward given to RANZCOG in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill hospital combined with St Geroge's Hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett.Pair of long handled forceps, placenta praevia style. Inscribed "B.H.H.L Ward" inner handle."B.H.H.L Ward"destructive instruments -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Gellhorn pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster
... ." (Dr. A.J.Helm-Montigue, Down Bros Ltd. Surgical Instruments... Bros Ltd. Surgical Instruments and Appliances, p. 1038 ...This is the 'old' style of Gelhorn pessary, which is similar in appearance to the Matthews-Duncan disc and stem and the Simpson's shelf gutta-percha. "This type of pessary was used in cases of complete procidenture... thus preventing dragging on the posterior wall of the bladder and the associated incontinence of which most patients complained. When wearing a large pessary with a small pessary, the uterus often came down beside the pessary." (Dr. A.J.Helm-Montigue, Down Bros Ltd. Surgical Instruments and Appliances, p. 1038.Black vulcanite pessary . Consists of a rigid short think stem with bulb at the distal end, and a solid flange at the proximal end.intrauterine device, pessary -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Cervical suture needle used by Dr Fritz Duras and Dr Michael Kloss, Jetter and Scheerer
... University. Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker... and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded in Germany ...This instrument was used by Dr Fritz Duras (1896-1965), who moved to Australia from Germany in 1937. As his father was Jewish, Duras was forced to leave Germany, and came to Australia to take up a post as director of physical education at Melbourne University. Jetter and Scheerer were a surgical instrument maker founded in Germany in 1867. Their company symbol is that of a serpent curled around a rod, surmounted by a coronet/crown. This instrument was part of a collection of instruments given to his son-in-law, Dr Michael Kloss, who was an obstetrician. Dr Kloss subsequently had it engraved and used it in his own practice, before donating the item to the College. Metal instrument used for cervical sutures. Instrument consists of a handle and shaft. The end of the shaft is curved so as the tip of the instrument is almost perpendicular to the handle. The end of the shaft is in the shape of a loop to allow for sutures to be passed through it. The handle of the instrument is engraved with the word 'KLOSS'. The shaft of the needle is engraved with an image of the Rod of Asclepius, featuring a serpent wrapped around a staff, topped by a crown.'KLOSS' obstetrics -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook, Bainbridge Veterinary Instruments
... . Published by Bainbridge Bros., surgical and veterinary instrument...-and-the-bellarine-peninsula "Bainbridge Veterinary Instruments", catalogue ..."Bainbridge Veterinary Instruments", catalogue, c.1988. Published by Bainbridge Bros., surgical and veterinary instrument makers and precision engineers, North Fitzroy.Book / catalogue of veterinary instruments produced by Bainbridge Bros., c.1988.animal health, bainbridge bros, veterinary instruments -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageClothing - Lingerie, Gladys Angus, wife of Dr. W.R. Angus, late 1920's
... that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments.... The Collection that includes historical medical equipment, surgical ...This pair of silk split-leg drawers was handmade by Gladys Angus for her trousseau in 1929 when she married Dr. Angus. The design became popular in the mid-1800's and continued into the early 1900's. It is part of the W.R.Angus Collection and was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. The Collection that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. Dr Angus was the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool.This garment is an example of the beautiful handmade clothing produced in Australian homes in the early 20th century. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Lingerie, split-leg drawers, beige silk, handmade, with scalloped finish on legs and drawer string waist. Each leg is finished separately then drawn together at the waist by a ribbon drawer-string, with the legs overlapping slightly. It is part of the W.R. Angus Collection. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, handmade lingerie, lingerie 1920's, silk lingerie, split leg drawers, split-leg drawers, early 20th century, ladies underwear, women's underwear, underwear, silk inderwear, undergarment -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Letter Scale, 1920s to 1960s
... , surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan..., surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan ...This scale was owned by Dr Angus, whose training and experience included chemistry and pharmacy. This is a sliding balance scale. The object to be weighed, such as a letter or a dose of medicine, is placed on the square metal plate and the weight, the slider, is moved along the notched metal arm and adjusted until the arm is horizontal, then reading is recorded of the figure the pointer on the slider is positioned. This design of small is often referred to as a letter scale. This item was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969.The scale is significant as an example of 20th century measuring and weighing equipment. It is also important for its association with the W.R. Angus Collection, which is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being a historical example of medicine, administration, household equipment and clothing from the late 19th to the mid-20th centuries. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Scale; a small sliding balance letter scale. The scale has a flat metal platform and a toothed metal balance arm with cylindrical brass weight. These are attached to a decorative metal stand that is mounted onto a shaped lacquered black wooden base. The sliding weight causes the arm to pivot on the stand. The arm is marked into equal-length segments from 0 to 8. Each segment is marked into halves. There is no maker’s mark. The scale is part of the W.R. Angus Collection.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, dr w r angus, letter scale, postal scale, balance scale, single arm scale, chemist scale, pharmacy scale, office equipment, retail equipment, sales equipment, measuring instrument, weighing instrument, technical instrument, medications, w.r. angus collection -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Hodges-style pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster, medium
... Tiemann & Co Surgical Instruments catalogue.1989. page 486... Surgical Instruments catalogue.1989. page 486.] The pessary ...This type of pessary was often used for uterine malpositions and displacements and usually made from vulcanite. This particular object is known as Hodges moulded pessary. [Source: George Tiemann & Co Surgical Instruments catalogue.1989. page 486.] The pessary was originally regarded as an instrument and made from cork, ivory, hard rubber or gum-elastic. In later times, they were made from black vulcanite, flexible tin, soft copper wire covered with Indian rubber, and celluloid. The form of the pessary was and still is variable -either round, oval, or moulded in some cases combining three or four curves depending on the size of the pessary. In ancient times, medicated pessaries were made from emollient. astringent and aperient. Several of these are still used, but in more modem times are called vaginal suppositories. Anal suppositories are still used to suppress the pain of haemorrhoids. Moulded black vulcanite pessary. Pessary is irregular in shape, and medium size. "I.T.A.Y." inscribed on upper curve.pessary, intrauterine device -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Hodges-style pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster, large
... Tiemann & Co Surgical Instruments catalogue.1989. page 486... Surgical Instruments catalogue.1989. page 486.] The pessary ...This type of pessary was often used for uterine malpositions and displacements and usually made from vulcanite. This particular object is known as Hodges moulded pessary. [Source: George Tiemann & Co Surgical Instruments catalogue.1989. page 486.] The pessary was originally regarded as an instrument and made from cork, ivory, hard rubber or gum-elastic. In later times, they were made from black vulcanite, flexible tin, soft copper wire covered with Indian rubber, and celluloid. The form of the pessary was and still is variable -either round, oval, or moulded in some cases combining three or four curves depending on the size of the pessary. In ancient times, medicated pessaries were made from emollient. astringent and aperient. Several of these are still used, but in more modem times are called vaginal suppositories. Anal suppositories are still used to suppress the pain of haemorrhoids.Moulded black vulcanite pessary. Pessary is irregular in shape, and large size.pessary, intrauterine device -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Hodges-style pessary associated with Dr Frank Forster
... Tiemann & Co Surgical Instruments catalogue.1989. page 486... Surgical Instruments catalogue.1989. page 486.] The pessary ...This type of pessary was often used for uterine malpositions and displacements and usually made from vulcanite. This particular object is known as Hodges moulded pessary. [Source: George Tiemann & Co Surgical Instruments catalogue.1989. page 486.] The pessary was originally regarded as an instrument and made from cork, ivory, hard rubber or gum-elastic. In later times, they were made from black vulcanite, flexible tin, soft copper wire covered with Indian rubber, and celluloid. The form of the pessary was and still is variable -either round, oval, or moulded in some cases combining three or four curves depending on the size of the pessary. In ancient times, medicated pessaries were made from emollient. astringent and aperient. Several of these are still used, but in more modem times are called vaginal suppositories. Anal suppositories are still used to suppress the pain of haemorrhoids.Moulded black vulcanite pessary. Pessary is irregular in shape.intrauterine device -
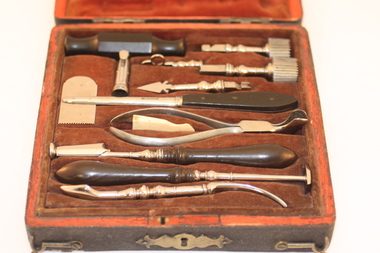 Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Museum and Archives
Royal Australasian College of Surgeons Museum and ArchivesTrephine case
... of surgical instruments contains, in a wooden case covered... & SKULL SAW IN CASE OF SURGICAL INSTRUMENTS: EIGHTEENTH OR EARLY ...From Neurological Society of Australia. Wooden case with key. Contents (12 parts) include trephines, various sizes; perforator; key; ebony trephine handle; Hey skull saw; elevator; steel forceps; brush; lenticular; five pointed rugine. 18th or early 19th century.TREPHINE & SKULL SAW IN CASE OF SURGICAL INSTRUMENTS: EIGHTEENTH OR EARLY NINETEENTH CENTURY. This set of surgical instruments contains, in a wooden case covered with shagreen: two trephines and a perforator , with a key to remove the trephine centring pins a detachable ebony handle a Hey skull saw with the name BLACKWELL an elevator a pair of steel forceps a bone or ivory brush to clean the trephines a lenticular a 5-pointed rugine. The trephines are conical, with slight tapering to prevent over- penetration; they are approximately 17 and 20 mm in diameter. Each has a sharp centring point, which 5 can be removed. Hand trephines are operated with one hand, being rotated like a gimlet, by alternating pronation and supination of the forearm, which also exe1ts downward pressure. The skull saw was used where trephining was difficult, as in some depressed fractures; it was popularised by William Hey (1736-1819) of Leeds, though described by earlier writers. Hey, a Yorkshireman, studied in St George's Hospital, London, but worked with great distinction in the Leeds General Infirmary. The lenticular, a curious instrument seen in many eighteenth century illustrations, was used to smooth the margins of bone defects. The rugine could be used to scrape granulations. The design of the trephines and of most of the other instruments strongly suggests an English origin, probably in the eighteenth century. A very similar trephine is figured by the London surgeon Percivall Pott2 in 1779. Bennion l [ists three instrument makers named Blackwell, none earlier than 1817. Most of the instruments have been plated, presumably with nickel, at a date that must be much later. The nickel plating shows little sign of wear. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Field Stretcher, Australian Defence Force, 1939-1942
... medical equipment, surgical instruments, and material once... medical equipment, surgical instruments, and material once ...This field stretcher was the property of Dr. William Roy Angus. It was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments, and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (both of Nhill, Victoria), as well as Dr Angus’ belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926, plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. W R Angus served with the Australian Department of Defence as a Surgeon Captain during World War II from 1942 to 1945, in Ballarat, Victoria, and Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence, he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material used for making dentures.The stretcher is an example of portable medical and emergency equipment used by the military and emergency services in the 19th and early 20th centuries. It is significant for its connection to Dr W R Abgus, who practised medicine in the community, the Australian Army and the Flying Doctor service from the 1920s to 1960s. He was also Warrnambool's last Port Medical Officer.Medical Field Stretcher: cream coloured canvas with wooden poles through side hems and a leather strap with buckle to keep parts together when folded or rolled up. This stretcher is part of the W.R. Angus Collection.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, stretcher, field stretcher, first aid, military equipment, medical equipment, emergency equipment, dr w r angus, canvas stretcher, patient transport, world war ii, ww2, australian department of defence, military doctor, medic, military stretcher, field gear, army stretcher, litter, adf, folding stretcher, w.r. angus -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumBottle, glass, post 1856
... OF Drugs, Chemicals, Patent Medicines, Surgical Instruments... Instruments, And Surgical and Medical Appliances generally, H, FRANCIS ...Henry Francis was previously in business at the goldfields at Ballarat, before coming to Melbourne in 1856. TROVE : Advocate (Melbourne, Vic. : 1868 - 1954), Saturday 19 July 1879, page 11. H. F R A N C I S & CO (Late FRANCIS & SWIFT) DISPENSING AND FAMILY CHEMISTS, M , 31 BOURKE ST. EAST, Melbourne. IMPORTERS OF Drugs, Chemicals, Patent Medicines, Surgical Instruments, And Surgical and Medical Appliances generally, H, FRANCIS & Co. solicit attention to their large and complete stock of WATER AND AIR-PROOF GOODS, Beds, Cushions, Mattresses. Pillows, Hot Water Bottles, Bed Sheeting, Portable Baths, Elastic Stockings, Ladies' Abdominal Belts, Shoulder Braces, Trusses, &c., Which, owing to their buying Direct from the Manufacturer, through their London agents, they are now able to supply at much' more reasonable rates than have hitherto obtained. THE GERMAN & FRENCH MINERAL WATERS Hunyadi Janos, Friedrichshall, Carlebad, Vichy, Pullna, Vale, &c., &c., Continually in stock, and supplied in quantities to suit purchasers. DISPENSARY AND RETAIL ESTABLISHMENT: 31 Bourke Street East; Melbourne. Wholesale Laboratory—Dawson Place, Swanston St, MEDICINE CHESTS SUPPLIED & REFITTED. TROVE : Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 - 1957), Thursday 17 January 1957, page 9 'ANTINOIS EAR PLUGS Ensure mental rest; soothe the nerves in factories, plane, or train travel 3 pairs, 2/6, post free H. Francis & Co., Box 5Ó2H, Melb.' Aqua tinted clear glass rectangular with angled corners in section bottle for stopper seal, with graduations on two sides for dosage quantities. Embossed text on front , angled sides and base.Embossed on base 'K' over '4616'. On one angled side graduation marks for one tablespoon doses, on other side graduation marks for two tablespoon doses, on front 'H. FRANCIS & Co'. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBadge - BMA Ladies Badge, Stokes, 1935
... and surgical equipment and instruments from the doctors Edward... and surgical equipment and instruments from the doctors Edward ...The badge was issued by the British Medical Association 'BMA'. It is known as the Female Relative's Bade or Ladies' Badge. It was manufactured in Melbourne in 1935 by Stokes of Melbourne. The BMA badge is one of a set of badges collected by Dr W R Angus from the organisations in which he was involved. They are now part of Flagstaff Hill’s comprehensive W.R. Angus Collection, donated by the family of Dr W R Angus, surgeon and oculist. The W.R. Angus Collection: - The W.R. Angus Collection includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. It includes historical medical and surgical equipment and instruments from the doctors Edward and Thomas Ryan of Nhill, Victoria. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1927 at Ballarat, the nearest big city to Nhill where he began as a Medical Assistant. He was also Acting House surgeon at the Nhill hospital where their two daughters were born. During World War II He served as a Military Doctor in the Australian Defence Forces. Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool in 1939, where Dr Angus operated his own medical practice. He later added the responsibility of part-time Port Medical Officer and was the last person appointed to that position. Both Dr Angus and his wife were very involved in the local community, including the planning stages of the new Flagstaff Hill and the layout of the gardens there. Dr Angus passed away in March 1970.This badge is significant for connecting Doctor Angus with organisations that support men and women who performed military service for Australia. The badge was specifically for a female relative of the person who did service, showing compassion for women. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The Collection includes historical medical objects that date back to the late 1800's.This BMA badge is an overall rectangular shape made in a silver metal. It has a raised oval section in the centre. The badge has embossed text and a basket weave background pattern within the metal. It is a Ladies Badge, made for the women connected to members of the British Medical Association. It was made in Melbourne in 1935. This badge is part of a set of badges collected by Dr W R Angus. the set represents organisations that he was involved in, and is part of the W.R. Angus Collection.Front embossed; “BMA” “LADIES” “BADGE. Back embossed; “MELBOURNE / 1935 “ “STOKES MELB”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, w.r. angus, badge, bma, british medical association, ladies’ badge, female relative's badge, military service, stokes, melbourne, w.r. angus collection
