Showing 2378 items
matching first place
-
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumDecorative object - Swinging Clock, Charles Frederick Falck, 1855
This clock was made by Charles Frederick Falck who was a watchmaker and jeweller in Beechworth from 1863-1908. Falck was born in Körlin, Prussia on May 22nd in 1833 and died at the age of 75 in 1908. Ovens and Murray Advertiser, Beechworth: edition June 13, 1908 OBITUARY: Falck was brought up to the business of watch-making, in which he developed exceptional mechanical ingenuity. Attracted by the favourable prospects held out by the Australian discoveries of gold he, like many other young adventurous spirits, left his native land to seek his fortune in the great southern Eldorado, arriving in Adelaide in 1854, and shortly after came to Melbourne where he worked as a journeyman, and subsequently started in business on his own account. Feeling inclined to test his fortune on the goldfields, he went to Blackwood but, meeting with little success, he returned to Melbourne where he was married. In 1862, he moved to Beechworth, where he commenced business as watchmaker and gold-buyer. He then embarked in vine-growing on the Sydney road, but eventually resumed his business avocations. His skill in practical horology was evinced in a clock of his own design and manufacture, surmounted by a golden eagle, which was exhibited at the first Melbourne Exhibition in 1856, and which afterwards formed a pre-eminent attraction in the window of his business premises in Ford Street. For many years, he filled the position of timekeeper to the Beechworth Racing Club, with complete satisfaction also at various sports meetings. He leaves a family of six sons and one daughter (Mrs. Jas. Broadfoot) all arrived at maturity. The funeral, which was well attended by a number of residents, took place at the Beechworth Cemetery on Sunday, the burial service being performed by the Ven. Archdeacon Potter. The cortege was capably supervised by Mr. D. Wilson, undertaker. The clock was returned to Beechworth in 2020 through the generous support of the Copland Foundation. Given that Mr. C. F. Falck traded as a watchmaker and jeweller in Beechworth for 45 years and traded with the 1855 clock mounted in his front window, there is a direct link between the clocks and the social, cultural and economic life of nineteenth century Beechworth at time when the town was developing and expanding in response to gold mining. This clock represent the significant skill and expertise of Charles Falck as an horologist. Medium-sized pendulum clock featuring a carved gilt wood eagle with wings outstretch (épandre - expanded with wing-tips directed upwards) and perched above a pendulum rod that holds a silver dial clock face within a reeded sunburst surround. The clock has an eight-day fuse movement with dead beat escapement wound from the clock face. C. F. F. FALCK / EXHIBITION 1856 / MELBOURNEburke museum, copland foundation, beechworth, leonard joel, auction, purchase, clock, pendulum, eagle, eagle clock, charles frederick falck, c. f. falck, falck, horology, pendulum clock, melbourne -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumDecorative object - Swinging Clock, Charles Frederick Falck, 1870
This clock was made by Charles Frederick Falck who was a watchmaker and jeweller in Beechworth from 1863-1908. Falck was born in Körlin, Prussia on May 22nd in 1833 and died at the age of 75 in 1908. Ovens and Murray Advertiser, Beechworth: edition June 13, 1908 OBITUARY: Falck was brought up to the business of watch-making, in which he developed exceptional mechanical ingenuity. Attracted by the favourable prospects held out by the Australian discoveries of gold he, like many other young adventurous spirits, left his native land to seek his fortune in the great southern Eldorado, arriving in Adelaide in 1854, and shortly after came to Melbourne where he worked as a journeyman, and subsequently started in business on his own account. Feeling inclined to test his fortune on the goldfields, he went to Blackwood but, meeting with little success, he returned to Melbourne where he was married. In 1862, he moved to Beechworth, where he commenced business as watchmaker and gold-buyer. He then embarked in vine-growing on the Sydney road, but eventually resumed his business avocations. His skill in practical horology was evinced in a clock of his own design and manufacture, surmounted by a golden eagle, which was exhibited at the first Melbourne Exhibition in 1856, and which afterwards formed a pre-eminent attraction in the window of his business premises in Ford Street. For many years, he filled the position of timekeeper to the Beechworth Racing Club, with complete satisfaction also at various sports meetings. He leaves a family of six sons and one daughter (Mrs. Jas. Broadfoot) all arrived at maturity. The funeral, which was well attended by a number of residents, took place at the Beechworth Cemetery on Sunday, the burial service being performed by the Ven. Archdeacon Potter. The cortege was capably supervised by Mr. D. Wilson, undertaker. The clock was returned to Beechworth in 2020 through the generous support of the Copland Foundation and the Friends of the Burke. Given that Mr. C. F. Falck traded as a watchmaker and jeweller in Beechworth for 45 years and traded with the 1855 clock mounted in his front window, there is a direct link between the clocks and the social, cultural and economic life of nineteenth century Beechworth at time when the town was developing and expanding in response to gold mining. This clock represent the significant skill and expertise of Charles Falck as an horologist. Large swinging clock featuring a carved gilt wood eagle with its wings outstretched (abaisé - expanded with wing-tips lowered) and perched above a pendulum rod that holds a silvered dial clock face within a reeded sunburst surround. (Similar to #2019.056.01) The clock has an eight-day fuse movement with dead beat escapement wound from the clock face. C. F. FALCK / WATCHMAKERburke museum, copland foundation, beechworth, leonard joel, auction, purchase, clock, pendulum, eagle, eagle clock, charles frederick falck, c. f. falck, falck, horology, pendulum clock, melbourne -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, 1859
Taken in Beechworth 1859, this photograph depicts the south side of Ford street looking towards the Methodist Church. The Methodist Church was built in 1857, and was the first permanent church building on the Ovens goldfields. It was one of the first permanent churches built on the Victorian goldfields, and the first on the Ovens goldfield. It demonstrates the rapid development which occurred in the goldfield towns following the discovery of gold in the early 1850s. It reflects the importance of Methodism in Victoria at this time, and the early activities of the Wesleyan Methodist Church in taking their religious message to the gold miners. [https://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/104] The buildings ceased being used as a church in 1966 when the Methodist and Congregational churches in Beechworth amalgamated.Black and white rectangular photograph. Image is printed on matte photographic paper. Obverse: NO INSCRIPTION Reverse: 7775 Ford St Looking Southwest 1859 Burke Museum Beechworth beechworth, ford street, methodist church, 1859 -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPostcard, 30/07/1942
The postcard image depicts the torpedo tubes with caps in position of a Japanese midget submarine that was involed in the attack on Sydney Harbour on May 31st, 1942. On the 31st of May 1942, in the midst of World War Two, Sydney found itself under attack from three Japanese midget submarines that entered Sydney Harbour under the cover of night. The first submarine became trapped in anti-torpedo nets and the third submarine was sunk in Taylor Bay. The second submarine fired on the heavy cruiser the USS Chicago. One of the torpedoes exploded near the depot ship the HMAS Kuttabul, killing 21 sailors.Black and white rectangular postcard printed on cardReverse: 7525-1/ POST CARD/ 2/ This postcard is a/ souvenir of the Exhibition/ of Japanese Midget Sub-/ marines sunk in Sydney Har-/ bour on the night of Sunday,/ May 31st, 1942, the night/ that the first attack on/ Sydney by a foreign power/ took place and was/ frustrated./ caps of the/ torpeto tubes/ 30th JULY 1942/ SERIAL No. 2/ Torpedo tubes of Japanese midget submarine with/ caps in position/military album, beechworth, burke museum, ww2, world war two, wwii, maritime, sydney harbour, sydney, japanese, japan, submarine, torpedo -
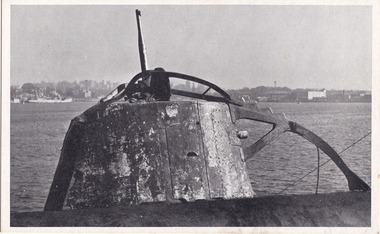 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPostcard, 30/07/1942
The postcard image depicts the conning tower of a Japanese midget submarine that was involed in the attack on Sydney Harbour on May 31st, 1942.On the 31st of May 1942, in the midst of World War Two, Sydney found itself under attack from three Japanese midget submarines that entered Sydney Harbour under the cover of night. The first submarine became trapped in anti-torpedo nets and the third submarine was sunk in Taylor Bay. The second submarine fired on the heavy cruiser the USS Chicago. One of the torpedoes exploded near the depot ship the HMAS Kuttabul, killing 21 sailors.Black and white rectangular postcard printed on cardReverse: 7525-2/ POST CARD/ 3/ This postcard is a/ souvenir of the Exhibition/ of Japanese Midget Sub-/ marines sunk in Sydney Har-/ bour on the night of Sunday,/ May 31st, 1942, the night/ that the first attack on/ Sydney by a foreign power/ took place and was/ frustrated./ 30th JULY 1942/ SERIAL No. 3/ Conning tower of Japanese midget submarine/ The Con. Tower/ military album, beechworth, burke museum, ww2, world war two, wwii, maritime, sydney harbour, sydney, japanese, japan, submarine -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPostcard, 30/07/1942
The postcard image depicts a sunken Japanese midget submarine, that was involved in the attack on Sydney Harbour on May 31st, 1942, being raised from the waters of the Sydney Harbour by a winch system, as groups of onlookers stand upon the decks of surrounding boats.On the 31st of May 1942, in the midst of World War Two, Sydney found itself under attack from three Japanese midget submarines that entered Sydney Harbour under the cover of night. The first submarine became trapped in anti-torpedo nets and the third submarine was sunk in Taylor Bay. The second submarine fired on the heavy cruiser the USS Chicago. One of the torpedoes exploded near the depot ship the HMAS Kuttabul, killing 21 sailors.Black and white rectangular postcard printed on cardReverse: 7525-3/ POST CARD/ 4/ This postcard is a/ souvenir of the Exhibition/ of Japanese Midget Sub-/ marines sunk in Sydney Har-/ bour on the night of Sunday,/ May 31st, 1942, the night/ that the first attack on/ Sydney by a foreign power/ took place and was/ frustrated./ 30th JULY 1942/ SERIAL No. 4/ Raising the Japanese midget submarine/ The sub after/ being lifted out of/ the water, note/ the cause from depth/ charges./military album, beechworth, burke museum, ww2, world war two, wwii, maritime, sydney harbour, sydney, japanese, japan, submarine, torpedo -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPostcard, 30/07/1942
The postcard image depicts the propeller of a Japanese midget submarine that was involved in the attack on Sydney Harbour on May 31st, 1942.On the 31st of May 1942, in the midst of World War Two, Sydney found itself under attack from three Japanese midget submarines that entered Sydney Harbour under the cover of night. The first submarine became trapped in anti-torpedo nets and the third submarine was sunk in Taylor Bay. The second submarine fired on the heavy cruiser the USS Chicago. One of the torpedoes exploded near the depot ship the HMAS Kuttabul, killing 21 sailors.Black and white rectangular postcard printed on cardReverse: 7525-4/ POST CARD/ 1/ This postcard is a/ souvenir of the Exhibition/ of Japanese Midget Sub-/ marines sunk in Sydney Har-/ bour on the night of Sunday,/ May 31st, 1942, the night/ that the first attack on/ Sydney by a foreign power/ took place and was/ frustrated./ 30th JULY 1942/ SERIAL No. 1/ Propellers and rudders of Japanese midget/ submarine/ Propellor/ with protecting/ bands./military album, beechworth, burke museum, ww2, world war two, wwii, maritime, sydney harbour, sydney, japanese, japan, submarine -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPostcard, 30/07/1942
The postcard image depicts a salvage team winching a Japanese midget submarine that was involed in the attack on Sydney Harbour on May 31st, 1942, out of the waters of the Sydney Harbour. The winch and salvage team are situated in front of a dock shed on a pier.On the 31st of May 1942, in the midst of World War Two, Sydney found itself under attack from three Japanese midget submarines that entered Sydney Harbour under the cover of night. The first submarine became trapped in anti-torpedo nets and the third submarine was sunk in Taylor Bay. The second submarine fired on the heavy cruiser the USS Chicago. One of the torpedoes exploded near the depot ship the HMAS Kuttabul, killing 21 sailors.Black and white rectangular postcard printed on cardReverse: 7525-5/ POST CARD/ This postcard is a/ souvenir of the Exhibition/ of Japanese Midget Sub-/ marines sunk in Sydney Har-/ bour on the night of Sunday,/ May 31st, 1942, the night/ that the first attack on/ Sydney by a foreign power/ took place and was/ frustrated./ 30th JULY 1942/ SERIAL No. 6/ The salvage part at work on a Japanese midget/ submarine/ Bringing the sub/ to the surface/military album, beechworth, burke museum, ww2, world war two, wwii, maritime, sydney harbour, sydney, japanese, japan, submarine -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph
Taken on an unknown date, depicted is a portrait of a young, unidentified male soldier kneeling beside a grave in a cemetery. He is dressed in an Australian military uniform. The cemetery pictured is the Arnos Vale Cemetery in Bristol, United Kingdom. There are multiple crosses marking graves in this photograph, all marked in memory of different soldiers who fought with the Australian Imperial Force (AIF) during World War I. It is believed that the soldier who is kneeling was also part of the Australian Imperial Force. This can be inferred by the chevron rank insignia visible on the uniform. The placement of this insignia on the sleeve of the right arm suggests that this soldier was either a Warrant Officer or a Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO). Another signifier of the Australian Imperial Force uniform are the three inverted chevron stripes positioned on the lower part of the left sleeve, near the wrist. These are called Good Conduct Stripes and were worn by Warrant Officers and NCOs. This patch consisted of a single chevron stripe for each year of military service meeting certain requirements of good conduct. Additionally, the man in this photograph is also wearing a 'Rising Sun' collar badge on his coat. Australia, unlike most other Commonwealth countries, did not adopt metal regimental badges during the First World War. All units were issued with the Australian Army General Service Badge, better known as the 'Rising Sun’ badge. This insignia is almost always identified with the Australian Imperial Force. Furthermore, the grave that this unidentified soldier is kneeling next to is the resting place of Private John James (J. J.) Simpson. He was born in Stanley, Victoria in 1883. He enlisted in the Australian Imperial Force in Melbourne, Victoria on 12 July, 1915, with the service number 4909. John James Simpson was then posted to the 60th Company Depot at Seymour for military recruit training. John James Simpson was reported wounded in action in France on 19 July, 1916. He was admitted to 13th General Hospital, France with gunshot wounds to his legs. From Boulogne, France, he traveled to the United Kingdom aboard the Hospital Ship 'St. Denis' for medical care. Upon arrival, he was admitted to 2nd Southern General Hospital, Bristol, England on 27 July, 1916. John James Simpson passed away from his wounds on 1 August, 1916. He was 33 years old.The record is historically significant due to its connection to World War I. This conflict is integral to Australian culture as it was the single greatest loss of life and the greatest repatriation of casualties in the country's history. Australia’s involvement in the First World War began when the Australian government established the Australian Imperial Force (AIF) in August 1914. Immediately, men were recruited to serve the British Empire in the Middle East and on the Western Front. The first significant Australian action of the war was the Australian Naval and Military Expeditionary Force’s (ANMEF) landing on Rabaul on 11 September 1914. The ANMEF took possession of German New Guinea at Toma on 17 September 1914 and of the neighbouring islands of the Bismarck Archipelago in October 1914. On 25 April 1915, members of the AIF landed on Gallipoli in Turkey with troops from New Zealand, Britain, and France. This specific event holds very strong significance within Australian history. The record has strong research potential. This is due to the ongoing public and scholarly interest in war, history, and especially the ANZAC legend, which is commemorated annually on 25 April, known as ANZAC Day.Sepia rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper mounted on card.Obverse: A.I.F. / AUSTRALIA / 441, PTE.T. / T (?) / 26B (?) / 6.1.17 / (?) / LANGTON RD. / ST. ANNES PK. / BRISTOL / A.I.F. / AUSTRALIA. / 708, GNR B.L.CRAWFORD. / FR / 5 D.A.C. / 13.2.17 / A.I.F. / AUSTRALIA. / 4481, P (?) D.MORRIS. / (?) / 31.12.(?) / A.I.F. / AUSTRALIA. / 4909, PTE J.J.SIMPSON. / 608(?) / 1.8.16 / Winchester / LANGTON RD. / ST. ANNES PK / BRISTOL / Reverse: 2641 /military album, military, war, world war i, wwi, australian imperial force, aif, j. j. simpson, uniform, cemetery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Bick Iron, Prior to 1950
A Bick or coopers anvil is a tool used to fabricate the iron hoops that a cooper would produce to hold a barrel together. The hoops are first cut to the required length and then beaten into shape and riveted on the Bick or Tee anvil. They are then driven into place on the barrel with a hammer and iron tipped, wedged shaped driver.The subject Item is used as a tool to produce steel hoops for wooden barrels but at this time cannot be associated with an historical event, person or place, provenance is therefore unknown, item assessed as a collection asset as it is believed to have been produced and used before 1950.Bick Iron or Coopers Anvil, attaches to a removeable wooden base, Metal anvil with pointed end & flat shaped topNoneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, brick iron, anvil, coopers tools, barrel making, barrels -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageScale, 1920
Inventor Biography: Percival Everitt was a Norfolk-born engineer and regarded as the father of the coin-op industry. in 1884 he patented one of his many inventions the coin-operated scales. For many people, it was their first exposure to coin-operated machines. As a young man in 1877, Everitt invented a hay and corn pitcher, a turnip thinner in 1878 and an “Automatic Travelling Anchor” in 1880. But he hit his stride in 1883 with the first postcard-vending machine over a hundred of which he distributed around London. Everitt went on to invent the one penny scale which prompted the formation of the Weighing Machine Company in 1885. Further inventions followed a blow tester in 1887 also the machine for testing a person grip in 1888 and the dispensing machine that opera glasses could be hired from in 1889 also the fortune-telling machine in 1890. He also invented a mechanism to shut coin slots when vending machines were empty, but then as now vandals posed a problem by jamming paper into the slot. Everitt sadly did not make his fortune he died suddenly in February 1893, in his late forties with £71 to his name. Penny Slot Weighing Machine: When the Australian colonies federated to form the Commonwealth of Australia in 1901 their post and telegraph departments were merged to form the national Postmaster General's (PMG) Department. The subject scale is an automatic public weighing machine, No.387, made in England by George Salter and Co. of West Bromwich. The Australasian Automatic Weighing Machine Co. Ltd in 1923 tendered for the right to place Automatic Weighing Machines on railway and tram premises throughout New South Wales subsequently for five-year terms in return for a fixed payment per machine and a portion of the revenue to the NSW Government. The company also made arrangements with the Postmaster General's Department to place machines outside post offices across the country. Weights were measured in stones and pound's up to 20 stone (127 kg) and average weights were shown separately for men, women, boys and girls by various heights in feet and inches. The subject item has had its scale change by the Eastern Scale Company to metric and it is believed to have occurred shortly after April 2000 as the company was first registered and began trading on this date. This weighing machine was originally installed by the Australasian Automatic Weighing Machine Co. Ltd at Warrnambool Post Office and was made by the firm, George Salter and Company, in West Bromwich, England to the Percival Everitt patent. Salter advertised that these machines were suitable for hotels, pleasure gardens, theaters, exhibition halls, clubs, baths and places of public resort. The company had been established in 1760 by the brothers, Richard and William Salter, manufacturing springs and pocket steelyards (spring balances). After several generations, the company was taken over by a nephew, George, and in 1884 the Salter trademark was registered to show a Staffordshire knot pierced by an arrow. The company's expanded range of products included the first coin-operated public weighing machines in the 1880s and in 1895 the first English made typewriter. When the last George Salter died in 1917, the company passed into the hands of other relatives but continued to grow before being bought out by Staveley Industries in 1973. Despite several subsequent mergers, the Salter name continues today on home ware products such as digital scales.A very rare example of a penny in the slot weighing machine imported into Australia and used in public places the item is significant as it gives a snapshot into community life at the time where the public could go and get weighed given there were no personal weighing machines or equipment that people could use at home. So if they needed to post a letter or go on a train journey they could use a machine to check their weight. Whats interesting is that this patent by Percival Everitt was the worlds first slot machine and the start of casino, arcade and other types of slot machines. Personal weighing scale metal large silver painted penny coin operated. Weight measurements are in stones and pounds. Australian Automatic Weighing Machine 60 lb Everitt Patent. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Washboard, 1900-1920s
The Mother Hubbard Roller Washboard was the hottest selling door-to-door item in America in the early 1900s. Its patented design featured threaded maple rollers that rolled in opposite directions. The touch could be light because the screw threads did all the work. It carried the Good Housekeeping Seal of Approval. The first roller washboard was made in Dover Illinois by the Hubbard brothers who ran their large sawmill there in the town where they were born. As the sales began coming in, they moved their plant in 1904 to LaMoille for better shipping facilities. In 1916 the sawmill was moved to Mendota Ill. and in addition to the washboards, the plant specialized in sawing walnut logs and forming them into roughs for gun stocks. All during the 1920s, the Mother Hubbard Washboard factory was a busy place. The boards were not made after 1935 once the electric washing machine became popular. This washboard appears to be a variation on the Hubbard system to get around their patented protection for washboards with rollers, the rollers appear to be made from maple indicating an American Manufacturer. The manufacturer of the subject item is unclear at this time.An unusual washboard with horizontal flutes designed to circumvent the Hubbard Brothers patent for washboards with rollers and vertical flutes. It makes the item rare and possibly made in Australia early 1900s and gives insight into how various companies tried to improve or get around other manufactures patented designs.Wooden washboard with rotating fluted rollers rectangular in shape and has 2 legsNoneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, washing equipment, washboard, hubbard brothers, domestic laundry -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Needle Pin Case, 1860 to 1900
Knitting, as a household task, has been traced back to 1100 AD where archaeologists in Egypt found remnants of socks. Evidently socks or stockings became a household necessity and creating them by knitting was the easiest way to get a good fit. The Tudors wore hand knit caps and King Henry the VIII made hand knit silk stockings, imported from Spain, a fashion staple. Meanwhile in Paris in 1525, men formed one of the first worker's unions for hand knitters. Knitting by machine first appeared during this same period and with the spread of fashion of the silk stockings and the basic needs of people to keep warm helped to fuel the popularity of knitting. By the 1850's, knitting machines were common place and apprenticing in such a factory, was considered honourable employment. But the main tool of knitting has always remained the needle, that is said to have it's origins in Arabia. The first needles were made of copper and looked more like hooks than needles. In other locations around the world, knitting needles have been found constructed from wood, ivory, bone, bamboo, amber and iron as well. They are also known as woods, skewers or wires depending where in the world they are found. Context: Edwin Rodgers was born in Lincolnshire England estimated at 1830-1832, records document that he was working as a Miller in Jan 1863 and that he resided in Warrnambool until his death in 1887. The knitting needle case is believed to belong to his wife Ellen Amelia (nee Heywood), daughter of George Heywood and Dinah Turton. She had married Mr Edwin Rodgers on 30 Jan 1863 in Warrnambool, and they had continued to resided in Warrnambool. Ellen Amelia Heywood was born Oct to Dec 1839 in Stockport, Cheshire England & christened on 5 Jul 1840 in St Thomas, Stockport, Cheshire. She died on 8 Dec 1922 in 284 Merri Street, Warrnambool, Victoria 10 and was buried on 11 Dec 1922 in the Warrnambool Cemetery.A significant item that belonged to one of the early families of Warrnambool and as such is regarded by the Warrnambool community as significant because it helps to document Warrnambool's development.Medium sized cardboard foldable maroon knitting pin case with numbered sections to fit relevant sized metal pins 10 in all case called the peacock knitting pin case.On lid of case written in italic Mrs E A Rodgers, Warrnambool 1860-1922, Wife of Edwin Rodgersflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Military group, Warrnambool First Volunteer Corps 1860, Taken May 24th, 1860, presented to Mayor in 1887
This Photograph is one of a number of photographs of the Warrnambool Militia. The photograph entitled "Warrnambool First Volunteer Corps" is dated 24th May 1860. (The First Volunteer Corps began in 1855.) It was presented by James Astley Bromfield (former Mayor of Warrnambool) to Major Walter Helpmann, head of Warrnambool’s 1st Volunteer Corps in 1887. The photograph shows the Corps lined up for inspection in Timor Street, Warrnambool. The location is outside what is now the Archie Graham Centre and the camera is looking west towards Liebig Street. The town band is in the right rear corner and spectators surround the Corps. The names listed on the back of the photograph are "1. R.Bushe (Captain in command), 2. Basil Spence, 3. Thomas Mickle, 4. Alfred Davies (Sergeant), 5. Cawthray, 6. Andrew Kerr, 7. Charles Scoborio, 8. Lacy, 9. James Hider, 10. D. O’Mullane, 11. William Norman, 12. Crouthers (or Cowthers ?), 13. Francis Breckon, 14. Russ, 15. Benjamin Wycherley, 16. C. A. Cramer (Sergeant), 17. James Coulstock, 18. Robert Newton (Sergeant), 19. J.A. Bromfield, 20. Singleton (supernumery), 21. Mostyn (Drill Instructor)," On the left of the picture is Billy Adams, Barnes (road contractor) and James Mason (Bootmaker). On the right of the picture is The Band. This is one of a collection of photographs showing the development of the Warrnambool Militia from its inception as the First Volunteer Corps in 1855. The collection is of local significance as it parallels the development of the town and includes images of significant local people. A number of Warrnambool streets are named after members of the Militia. It is also historically significant because of its connection to the unrest that was taking place in Europe at this time. Photograph of Warrnambool First Volunteer Corps 1860, sepia coloured, mounted on cream card. The photograph shows the Corps lined up for inspection in Timor Street Warrnambool. The location is outside what is now the Archie Graham Centre and the camera is looking west towards Liebig Street. The town band is in the right rear corner and spectators surround the Corps. Photograph taken 24th May 1860. Has names listed on reverse side. The protograph was presented to Mayor Helpman, by Bromfield, May 1887. Title printed below base of photo on the mounting board "May. 24. WARRNAMBOOL First VOLUNTEER CORPS. 1860" On the back of the photograph is a numbered list of names, handwritten in ink. Also on the back are presentation details "Presented to Mayor Helpman, by Bromfield, May 1887". warrnambool, wolunteer corps, militia, helpmann, bromfield, flagstaff hill, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Telescope, 1752-1900
The discovery of the first telescope in 1608 can be attributed to Hans Lippershey of the Netherlands when he discovers that holding two lenses up some distance apart bring objects closer. He applies for a patent on his invention and this becomes the first documented creation of a telescope. Then in 1668, Newton produces the first successful reflecting telescope using a two-inch diameter concave spherical mirror. This opened the door to magnifying objects millions of times far beyond what could ever be obtained with a lens. It wasn’t until 1729 that Chester Moor Hall develops an achromatic lens (two pieces of glass with different indices of light refraction combined produce a lens that can focus colours to almost an exact point resulting in much sharper images but still with some distortion around the edges of the image. Then in 1729 Scottish instrument maker James Short invents the first parabolic and elliptic, distortion-less mirror ideal for reflecting telescopes. We now come to John Dollond who improves upon the achromatic objective lens by placing a concave flint glass lens between two convex crown glass lenses. This had the effect of improving the image considerably. Makers Information: John Dollond (1707-1761) London England he was a maker of optical and astronomical instruments who developed an achromatic (non-colour distorting) refracting telescope and practical heliometer. A telescope that used a divided lens to measure the Sun’s diameter and the angles between celestial bodies. The son of a Huguenot refugees Dollond learned the family trade of silk weaving. He became proficient in optics and astronomy and in 1752 his eldest son, Peter joined his father in an optical business, in 1753 he introduced the heliometer. In the same year, he also took out a patent on his new lenses. He was elected a fellow of the Royal Society in May 1761 but died suddenly in November and his share in the patent passed to his son Peter. In subsequent squabbles between Peter and the many London opticians who challenged his patent, Peter’s consistent position was that, whatever precedents there may have been to his achromatic lenses, his father had independently reached his practical technique on the basis of his theoretical command of Newtonian optics. As a result of maintaining his fathers patent, Dollond s became the leading manufacturer of optical instruments. For a time in the eighteenth and nineteenth century the word 'Dollond' was almost a generic term for telescope rather like 'Hoover; is to vacuum cleaner. Genuine Dollond telescopes were considered to be amongst the best. Peter Dollond (1731-1820) was the business brain behind the company which he founded in Vine Street, Spitalfields in 1750 and in 1752 moved the business to the Strand London. The Dollonds seem to have made both types of telescopes (reflecting and refracting), possessing the technology to produce significant numbers of lenses free of chromatic aberration for refracting telescopes. A Dollond telescope sailed with Captain Cook in 1769 on his voyage to observe the Transit of Venus. Thomas Jefferson and Admiral Lord Nelson were also customers of the Dollonds. Dollond & Co merged with Aitchison & Co in 1927 to form Dollond & Aitchison, the well-known high street chain of opticians, now fully part of Boots Opticians. They no longer manufacture but are exclusively a retail operation. John Dollond's experiments in optics and how different combinations of lenses refract light and colour gave a better understanding of the divergent properties of lenses. That went on to inform and pave the way for the improvement of our understanding of optics that are represented today. Dollond was referred to in his time as the "Father of practical optics" as a leader in his field he received many prestigious awards. The telescope in the collection is a good example of one of Dollonds early library telescopes and its connection with one of England's 18th-century pioneers in optical development is in itself a significant and an important item to have within the collection. One tube ships day & Night Telescope brass inner tube with timber main tube covered in leather. Unavailable to inspect Inscriptions to determine authenticity.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, telescope, dolland, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, royal national life boat institution -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Telescope, Early 18th Century
This Dollond Day or Nigh telescope was designed to be used in any light conditions, as its name implies. Telescopes are optical instruments designed to make objects appear to be larger or closer. The discovery of the first telescope in 1608 can be attributed to Hans Lippershey of the Netherlands when he discovers that holding two lenses up some distance apart bring objects closer. He applies for a patent on his invention and this becomes the first documented creation of a telescope. Then in 1668, Newton produces the first successful reflecting telescope using a two-inch diameter concave spherical mirror. This opened the door to magnifying objects millions of times far beyond what could ever be obtained with a lens. It wasn’t until 1729 that Chester Moor Hall develops an achromatic lens (two pieces of glass with different indices of light refraction combined produce a lens that can focus colours to almost an exact point resulting in much sharper images but still with some distortion around the edges of the image. Then in 1729 Scottish instrument maker James Short invents the first parabolic and elliptic, distortion-less mirror ideal for reflecting telescopes. We now come to John Dollond who improves upon the achromatic objective lens by placing a concave flint glass lens between two convex crown glass lenses. This had the effect of improving the image considerably. Makers Information: John Dollond (1707-1761) London England he was a maker of optical and astronomical instruments who developed an achromatic (non-colour distorting) refracting telescope and practical heliometer. A telescope that used a divided lens to measure the Sun’s diameter and the angles between celestial bodies. The son of a Huguenot refugees Dollond learned the family trade of silk weaving. He became proficient in optics and astronomy and in 1752 his eldest son, Peter joined his father in an optical business, in 1753 he introduced the heliometer. In the same year, he also took out a patent on his new lenses. He was elected a fellow of the Royal Society in May 1761 but died suddenly in November and his share in the patent passed to his son Peter. In subsequent squabbles between Peter and the many London opticians who challenged his patent, Peter’s consistent position was that, whatever precedents there may have been to his achromatic lenses, his father had independently reached his practical technique on the basis of his theoretical command of Newtonian optics. As a result of maintaining his fathers patent, Dollond s became the leading manufacturer of optical instruments. For a time in the eighteenth and nineteenth century the word 'Dollond' was almost a generic term for telescope rather like 'Hoover; is to vacuum cleaner. Genuine Dollond telescopes were considered to be amongst the best. Peter Dollond (1731-1820) was the business brain behind the company which he founded in Vine Street, Spitalfields in 1750 and in 1752 moved the business to the Strand London. The Dollonds seem to have made both types of telescopes (reflecting and refracting), possessing the technology to produce significant numbers of lenses free of chromatic aberration for refracting telescopes. A Dollond telescope sailed with Captain Cook in 1769 on his voyage to observe the Transit of Venus. Thomas Jefferson and Admiral Lord Nelson were also customers of the Dollonds. Dollond & Co merged with Aitchison & Co in 1927 to form Dollond & Aitchison, the well-known high street chain of opticians, now fully part of Boots Opticians. They no longer manufacture but are exclusively a retail operation. John Dollond's experiments in optics and how different combinations of lenses refract light and colour gave a better understanding of the divergent properties of lenses. That went on to inform and pave the way for the improvement of our understanding of optics that is represented today. Dollond was referred to in his time as the "Father of practical optics" as a leader in his field he received many prestigious awards. The telescope in the collection is a good example of one of Dollond's early library telescopes. Its connection with one of England's 18th century pioneers in optical development makes it a significant and an important item to have within the collection.Telescope: Dollond's Telescope, Day or Night model navigational instrument. Telescope is mounted on wooden tripod stand that has folding legs. Brass telescope with leather sheath over barrel, adjustable angle fitting with brass wing nuts that join the legs to the top frame, which is then joined to the telescope pole by an adjustable screw fitting. Manufactured by Dollond, London. Inscription reads "Dollond London, Day or Night" and "DOLLOND LONDON"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, telescope, dollond, dollond london, day & night telescope, floor-standing telescope, optical instrument, john dollond, peter dollond, achromatic telescope, heliometer, light refraction, instrument maker, lens, transit of venus, astronomical telescope, concave lens, library telescope, dollond telescope, day or night, day or night telexcope, scientific instrument, navigation, navigational instrument, astronomy -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Auger Bit, William A Ives, 1860-1950
William A Ives worked in New Haven, Connecticut, and surrounding towns of Wallingford and Hamden from 1868 to 1917 and was a prolific inventor of braces and other wood boring tools between 1868 and 1884, when he received a dozen patents for these devices. William A. Ives lived in the New Haven CT area, and his first auger-making activity took place in the town of Hamden. At first in association with the Churchill family who had been manufacturing tools in the area at least as early as 1863. That firm's works had created "Augerville" in Hamden, starting earlier, possibly as early as 1830. Ives became active as part of the Hamden Manufacturing Co. until 1875 (it is thought he may also have started his own business in the interim), and the William A. Ives & amp; Co. was established by 1877. This continued, until William's death in 1888, when The Hamden Mfg. Company became its successor. Ives also registered the name "Mephisto" trademark name with the US patent office that was to be used in connection with augers, auger bits, machine bits as of June 1st, 1909, appearing on items up until at least 1922. It also appears that the trademark was licensed by the Mephisto Tool Co of Hudson New York who continued to manufacture tools under this trademark. Item is significant because its maker was the inventor of the wood auger boring bit and his patent has been used ever since on many different types of bits with little change to the original design.Auger wood screw bit W A Ives Patent Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Spectacles and case, c. 1969
The history of spectacles The earliest form of spectacles are generally agreed to have been invented in Northern Italy in the thirteenth century. Over hundreds of years of innovation and refinement, they have been perfected into the stylish and functional designs you see today worn by millions of people to correct their eyesight. Here's a look at the key moments that defined the history of spectacles. Thirteenth century - Rivet spectacles The earliest form of spectacles was simply two mounted lenses riveted together at the handle ends. They had no sides and were secured to the face by clamping the nose between the rims, some of which had notches which may have been intended to improve the grip. Even then the wearer could only keep them in place by remaining relatively still and would normally support them with the hand. These spectacles contained convex lenses for the correction of presbyopic long-sightedness and were generally suited only to those few who lived beyond their forties and had the ability to read. Sixteenth century - Nose spectacles Nose spectacles were in more common use by the early sixteenth century. These often had a bow-shaped continuous bridge, almost of a modern appearance, that was sometimes flexible depending upon the material, for example leather or whalebone. The bridge was as much an area to be gripped as to rest on the nose. Spectacles were still usually held in place with the hand whilst being used temporarily for a brief period of reading or close inspection. By now the lenses could be used to correct both long and short sight. The general design changed little through the seventeenth century, though certain refinements increased the flexibility and comfort for some wearers. In some localised areas, notably in Spain, people experimented with ear loops made of string. This allowed them to walk around with their spectacles on. Eighteenth century - Temple glasses Only in the eighteenth century did the first modern eyewear, or ‘glasses’ as we would understand them, start to appear. The lenses might be glass, rock crystal or any other transparent mineral substance and were prone to smashing if the spectacles fell off, so there was an impetus to develop frames that could be worn continuously and would stay in place. London optician Edward Scarlett is credited with developing the modern style of spectacles which were kept in place with arms, known as ‘temples’. These were made of iron or steel and gripped the side of the head but did not yet hook over the ears because often the ears were concealed beneath a powdered wig, such as was fashionable at the time. As temples developed they were made with wide ring ends through which the wearer could pass a ribbon, thus tying the spectacles securely to the head. As spectacles were no longer primarily for use in sedentary activities, people began to be noticed out and about in their spectacles and might come to be identified as a ‘spectacle wearer’. By the end of the eighteenth century, people who needed correction for both distance and near could choose bifocals. Nineteenth century - Pince-nez Pince-nez were a nineteenth century innovation that literally translates as ‘pinching the nose’. They had a spring clip to retain the item in place under its own tension. Sometimes this clip was too tight and the wearer struggled to breathe. If it was too loose the pince-nez could fall off so, for safety and security, they were often connected to the wearer's clothing by a cord or a chain to avoid them being dropped or lost. Pince-nez were sometimes chosen by people who felt that large spectacles were too prominent and drew attention to a physical defect. They were also suitable for mounting lenses that could correct astigmatism. Twentieth century spectacles Spectacle wearing continued to become more widespread, key developments being the supply of spectacles to troops in the First World War, cheaper spectacles being subsidised through insurance schemes arranged by friendly societies, and the beginning of the National Health Service in 1948, when free spectacles were made available to all who might benefit from them. This normalised spectacle wearing and led to a significant increase in the scale of production. Entirely separate categories of women’s spectacles and sports eyewear both emerged in the 1930s. The latter half of the twentieth century saw spectacles become more fashionable and stylish as frames with different shapes, materials, and colours became available. Plastics frames, in particular, allowed a greater choice of colours and textured finishes. Plastic lenses were more durable and could be made lighter and thinner than glass, spurring a renewed interest in rimless designs. Designer eyewear bearing popular high-street brand names encouraged patients to regard spectacles as a desirable commodity, even as a fashion accessory, not just a disability aid. https://www.college-optometrists.org/the-british-optical-association-museum/the-history-of-spectacles These spectacles and case were used by Dr. Angus in his surgery in Warrnambool to test patients' eye sight. They were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII 1941-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Spectacles and case, from the W.R. Angus Collection and used by Dr. Angus for testing the sight of his patients. Black rimmed spectacles in tan, open ended pouch. Inscription is stamped into frame and printed in gold lettering on the case. c. 1969 Inscriptions read on spectacles;“52 (square) 18” and “RODENSTOCK > ELBA < 130“ and printed in gold lettering on the pouch “DOBBIE BROS. / OPTOMETRISTS & OPTICIANS / 173 EXHIBITION ST. MELBOURNE”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, spectacles and case, optical testing, optometrist examination, dobbie bros melbourne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Spectacles and Case, 1930s - 1960s
The history of spectacles The earliest form of spectacles are generally agreed to have been invented in Northern Italy in the thirteenth century. Over hundreds of years of innovation and refinement, they have been perfected into the stylish and functional designs you see today worn by millions of people to correct their eyesight. Here's a look at the key moments that defined the history of spectacles. Thirteenth century - Rivet spectacles The earliest form of spectacles was simply two mounted lenses riveted together at the handle ends. They had no sides and were secured to the face by clamping the nose between the rims, some of which had notches which may have been intended to improve the grip. Even then the wearer could only keep them in place by remaining relatively still and would normally support them with the hand. These spectacles contained convex lenses for the correction of presbyopic long-sightedness and were generally suited only to those few who lived beyond their forties and had the ability to read. Sixteenth century - Nose spectacles Nose spectacles were in more common use by the early sixteenth century. These often had a bow-shaped continuous bridge, almost of a modern appearance, that was sometimes flexible depending upon the material, for example leather or whalebone. The bridge was as much an area to be gripped as to rest on the nose. Spectacles were still usually held in place with the hand whilst being used temporarily for a brief period of reading or close inspection. By now the lenses could be used to correct both long and short sight. The general design changed little through the seventeenth century, though certain refinements increased the flexibility and comfort for some wearers. In some localised areas, notably in Spain, people experimented with ear loops made of string. This allowed them to walk around with their spectacles on. Eighteenth century - Temple glasses Only in the eighteenth century did the first modern eyewear, or ‘glasses’ as we would understand them, start to appear. The lenses might be glass, rock crystal or any other transparent mineral substance and were prone to smashing if the spectacles fell off, so there was an impetus to develop frames that could be worn continuously and would stay in place. London optician Edward Scarlett is credited with developing the modern style of spectacles which were kept in place with arms, known as ‘temples’. These were made of iron or steel and gripped the side of the head but did not yet hook over the ears because often the ears were concealed beneath a powdered wig, such as was fashionable at the time. As temples developed they were made with wide ring ends through which the wearer could pass a ribbon, thus tying the spectacles securely to the head. As spectacles were no longer primarily for use in sedentary activities, people began to be noticed out and about in their spectacles and might come to be identified as a ‘spectacle wearer’. By the end of the eighteenth century, people who needed correction for both distance and near could choose bifocals. Nineteenth century - Pince-nez Pince-nez were a nineteenth century innovation that literally translates as ‘pinching the nose’. They had a spring clip to retain the item in place under its own tension. Sometimes this clip was too tight and the wearer struggled to breathe. If it was too loose the pince-nez could fall off so, for safety and security, they were often connected to the wearer's clothing by a cord or a chain to avoid them being dropped or lost. Pince-nez were sometimes chosen by people who felt that large spectacles were too prominent and drew attention to a physical defect. They were also suitable for mounting lenses that could correct astigmatism. Twentieth century spectacles Spectacle wearing continued to become more widespread, key developments being the supply of spectacles to troops in the First World War, cheaper spectacles being subsidised through insurance schemes arranged by friendly societies, and the beginning of the National Health Service in 1948, when free spectacles were made available to all who might benefit from them. This normalised spectacle wearing and led to a significant increase in the scale of production. Entirely separate categories of women’s spectacles and sports eyewear both emerged in the 1930s. The latter half of the twentieth century saw spectacles become more fashionable and stylish as frames with different shapes, materials, and colours became available. Plastics frames, in particular, allowed a greater choice of colours and textured finishes. Plastic lenses were more durable and could be made lighter and thinner than glass, spurring a renewed interest in rimless designs. Designer eyewear bearing popular high-street brand names encouraged patients to regard spectacles as a desirable commodity, even as a fashion accessory, not just a disability aid. https://www.college-optometrists.org/the-british-optical-association-museum/the-history-of-spectacles The company Optical Prescription Spectacle Makers (OPSM ) was formed in Sydney in 1932 and publically listed in 1953. These spectacles and case were used by Dr. Angus when testing patients' eyes. The spectacles and case were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII 1941-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Spectacles and case, from the W.R. Angus Collection and used by Dr. Angus testing the sight of his patients. Metal case covered in red leather, black velvet lining. Tan rimmed spectacles. Maker is OPSM. Inscriptions on case, inside case and on spectacle rim.Inscribed on spectacle arms “CONTORA”. Inscription on case in gold print “OPSM Optical Prescription Spectacle Makers Pty Ltd”. Inscription on white oval label inside case is illegible. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, spectacles and case, optical testing, optometrist examination, opsm optical prescription spectacle makers -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Spectacles and Case, Mid 20th Century
The history of spectacles The earliest form of spectacles are generally agreed to have been invented in Northern Italy in the thirteenth century. Over hundreds of years of innovation and refinement, they have been perfected into the stylish and functional designs you see today worn by millions of people to correct their eyesight. Here's a look at the key moments that defined the history of spectacles. Thirteenth century - Rivet spectacles The earliest form of spectacles was simply two mounted lenses riveted together at the handle ends. They had no sides and were secured to the face by clamping the nose between the rims, some of which had notches which may have been intended to improve the grip. Even then the wearer could only keep them in place by remaining relatively still and would normally support them with the hand. These spectacles contained convex lenses for the correction of presbyopic long-sightedness and were generally suited only to those few who lived beyond their forties and had the ability to read. Sixteenth century - Nose spectacles Nose spectacles were in more common use by the early sixteenth century. These often had a bow-shaped continuous bridge, almost of a modern appearance, that was sometimes flexible depending upon the material, for example leather or whalebone. The bridge was as much an area to be gripped as to rest on the nose. Spectacles were still usually held in place with the hand whilst being used temporarily for a brief period of reading or close inspection. By now the lenses could be used to correct both long and short sight. The general design changed little through the seventeenth century, though certain refinements increased the flexibility and comfort for some wearers. In some localised areas, notably in Spain, people experimented with ear loops made of string. This allowed them to walk around with their spectacles on. Eighteenth century - Temple glasses Only in the eighteenth century did the first modern eyewear, or ‘glasses’ as we would understand them, start to appear. The lenses might be glass, rock crystal or any other transparent mineral substance and were prone to smashing if the spectacles fell off, so there was an impetus to develop frames that could be worn continuously and would stay in place. London optician Edward Scarlett is credited with developing the modern style of spectacles which were kept in place with arms, known as ‘temples’. These were made of iron or steel and gripped the side of the head but did not yet hook over the ears because often the ears were concealed beneath a powdered wig, such as was fashionable at the time. As temples developed they were made with wide ring ends through which the wearer could pass a ribbon, thus tying the spectacles securely to the head. As spectacles were no longer primarily for use in sedentary activities, people began to be noticed out and about in their spectacles and might come to be identified as a ‘spectacle wearer’. By the end of the eighteenth century, people who needed correction for both distance and near could choose bifocals. Nineteenth century - Pince-nez Pince-nez were a nineteenth century innovation that literally translates as ‘pinching the nose’. They had a spring clip to retain the item in place under its own tension. Sometimes this clip was too tight and the wearer struggled to breathe. If it was too loose the pince-nez could fall off so, for safety and security, they were often connected to the wearer's clothing by a cord or a chain to avoid them being dropped or lost. Pince-nez were sometimes chosen by people who felt that large spectacles were too prominent and drew attention to a physical defect. They were also suitable for mounting lenses that could correct astigmatism. Twentieth century spectacles Spectacle wearing continued to become more widespread, key developments being the supply of spectacles to troops in the First World War, cheaper spectacles being subsidised through insurance schemes arranged by friendly societies, and the beginning of the National Health Service in 1948, when free spectacles were made available to all who might benefit from them. This normalised spectacle wearing and led to a significant increase in the scale of production. Entirely separate categories of women’s spectacles and sports eyewear both emerged in the 1930s. The latter half of the twentieth century saw spectacles become more fashionable and stylish as frames with different shapes, materials, and colours became available. Plastics frames, in particular, allowed a greater choice of colours and textured finishes. Plastic lenses were more durable and could be made lighter and thinner than glass, spurring a renewed interest in rimless designs. Designer eyewear bearing popular high-street brand names encouraged patients to regard spectacles as a desirable commodity, even as a fashion accessory, not just a disability aid. https://www.college-optometrists.org/the-british-optical-association-museum/the-history-of-spectacles These spectacles and case from F.G. and R.G. Bennett of Warrnambool were used by Dr. Angus to test his patients' eye sight. They were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII 1941-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Spectacles and case, from the W.R. Angus Collection and used by Dr. Angus testing the sight of his patients. Metal case covered in blue leather, blue velvet lining. Orange/yellow rimmed spectacles, one lens covered with cardboard. White oval label inside case. Inscription on case with maker’s details in gold print.Inscription on case reads “F. G. & R. G. BENNETT / WARRNAMBOOL”. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, spectacles and case, optical testing, optometrist examination, f.g. and r.g. bennett of warrnambool -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph, Freeman & Co, second half 19th century
Mr. Robert Martin - First Church of England was a clergyman stationed at Orbost - 1884-1891. Mr Martin, who was appointed by Bishop Moorhouse of Melbourne, to be Stipendiary Reader in charge of the district in 1885. Prior to that, Mr Martin, a retired sea captain, had unofficially conducted services in all sorts of places, where a congregation could be gathered together, though his business officially was that of a fire insurance argent. (more information in October 2007 Newsletter)This item is associated with churches in Orbost.A black / white portrait photograph, head and shoulders, of a middle - aged man with a white beard.It is an oval shaped photograph set in a cream cardboard mount.on front at bottom - Freeman & Co Sydneymartin-robert church-of-england-orbost church-orbost -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph, late 19th century - early 20th century
This is a photograph of the four daughters of Mrs George Thomas. L -R : Elleen Parsons, Julia Eaton, Eva Murray and Violet Gay. George Thomas and Gtranny Thomas lived at Newmerella on Grand View Road until the 1950's. In the Newmerella Koorie Community, there were about 15 families. The family was a very well-respected local Aboriginal family. . George was a stockman for Jas Stirling. From Colin Thomas "I learned that George Thomas was Kitty Johnson’s oldest son. As a young boy George had been found by the Reverend John Bulmer, in addition to other young Aboriginal children in the bush around the Lake Tyers area. He had gathered them all together and took them onto the reserve at the Mission. After quite a number of years had passed George had met and fallen in love with a young half-caste girl, known as Agnes Patterson. Agnes was of Monaro descent and came from New South Wales. George and Agnes got married at Lake Tyers. Because of the half-caste act George and Agnes had to leave the reserve along with their nine girls. They moved to Newmerella, situated outside the township of Orbost. This was the place that George and his wife and children came to call home. Soon after, George and Agnes would add to their family bringing the total of children to fourteen, the last five of whom were boys. At the time of the First World War George’s boy’s volunteered their services and joined the army. When in Europe one of the boys sustained an injury which caused the loss of an arm. Following the end of the war the boys came home, as men." The Thomas family was a well-respected family in Newmerell in the late 19th and first half of the 20th century. The daughter were well known for their needlework and craft skills.A black / white photograph of four women wearing log skirts / dresses and elaborate hats, two sitting on a log and two standing on either side.thomas-family newmerella koori-family -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societynewspaper clipping, Orbost Forty Years Ago, 1929?
The first hotel built in Orbost was the Club in 1885 an old wooden place on the corner built for J. A. Petersen of the Mitchell Hotel Bairnsdale, with the licence in the name of Mr Thomas Maguire (stepson of Petersen). In June 1889 there was a rush to Mackenzie River, about 28 miles from Orbost, on Twelve Mile Creek. An estimated 80 men rushed the ground, but yields were patchy and large numbers eventually left. They were coming and going almost daily.The Club Hotel was the first hotel built in Orbost and remains a significant building in the town. It was an important hub for the township with many whole town meetings held there.A yellowed black / white newspaper clipping of a photograph of people with a horse and cart outside a one-storey hotel building. It is glued onto a piece of cardboard.Caption at bottom - "View taken in 1889 of the Old Orbost Club Hotel"orbost-club-hotel -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photographs, Snowy River Mail, March 12 1980
These photographs were taken at the 1980 annual Orbost Show. The first photograph is of Mr Frank Rourke congratulating Combienbar rider, Gavin Chester, East Gippsland Olympian ( a member of the 1980 Australian team which did not compete in Moscow). He won the title of Champion Show Jumper riding his mount "Blue Trick" on Monday March 10 1980. The second photograph shows Mr Frank Rourke placing the winning ribbon around the neck of Gavin Chester's winning mount, "Blue Trick" The third photograph is the winner of the coveted R.L.Fisher Memorial Plate won by Eric Musgrave being congratulated by Mr Frank Rourke. Frank Rourke was the Gippsland and Northern manager. G. & N. sponsored the event which carried a prize of $500. On the left in this photograph is Mr J. Horstman, ring four judge.This is a pictorial record of a significant event in Orbost. This item is also associated with the Orbost Agricultural Society 's Annual Show which has been a major event in Orbost for over a century. Agricultural shows are an important part of cultural life in small country towns and the Orbost Show is an integral part of Orbost 's agricultural history.Three black / white photographs of a rider on horseback receiving congratulations. There are details on labels on the back of each photograph.orbost-show equestrian chester-gavin musgrave-eric show-jumping -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPainting, "Wantirna" - Water colour on paper by Winifred Miles (1884-1944), Undated, later than 1910
"Alexander Colquhoun [Herald art critic 1914-1922 and feature writer for the Age 1926-1941] ... took private students in the first decade of the century, and one of these was Winifred Miles, who after her marriage in 1910 lived the remainder of her life in Ringwood. ... (She) began by doing charcoal studies of animals when she was in Balranald, but in later years moved to oils and then watercolours, travelling around Ringwood to find places to paint by means of a pony-driven governess-cart. She won prizes for paintings in the Royal Melbourne Shows." - Hugh Anderson - Ringwood, Place of Many Eagles [p.217].Painting with cardboard border in glass-fronted frame. One of two undated paintings by Winifred Miles' viewed from the same vantage point in Wantirna. (See Registration Number 4851) -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPencil sketch, Winifred Miles, "Family dog - Mick" - Graphite on paper by Winifred Miles, 1922
"Alexander Colquhoun [Herald art critic 1914-1922 and feature writer for the Age 1926-1941] ... took private students in the first decade of the century, and one of these was Winifred Miles, who after her marriage in 1910 lived the remainder of her life in Ringwood. ... (She) began by doing charcoal studies of animals when she was in Balranald, but in later years moved to oils and then watercolours, travelling around Ringwood to find places to paint by means of a pony-driven governess-cart. She won prizes for paintings in the Royal Melbourne Shows." - Hugh Anderson - Ringwood, Place of Many Eagles [p.217].Pencil drawing with cardboard border in glass-fronted frame. -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPainting, Winifred Miles, "Creek Bed" - Oil on canvas by Winifred Miles (1884-1944), Undated, later than 1910
"Alexander Colquhoun [Herald art critic 1914-1922 and feature writer for the Age 1926-1941] ... took private students in the first decade of the century, and one of these was Winifred Miles, who after her marriage in 1910 lived the remainder of her life in Ringwood. ... (She) began by doing charcoal studies of animals when she was in Balranald, but in later years moved to oils and then watercolours, travelling around Ringwood to find places to paint by means of a pony-driven governess-cart. She won prizes for paintings in the Royal Melbourne Shows." - Hugh Anderson - Ringwood, Place of Many Eagles [p.217].Painting with cardboard border in glass-fronted frame. -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPainting, Winifred Miles, "Tree - East Ringwood Golf Links" - Oil on paper by Winifred Miles (1884-1944), Undated, later than 1910
"Alexander Colquhoun [Herald art critic 1914-1922 and feature writer for the Age 1926-1941] ... took private students in the first decade of the century, and one of these was Winifred Miles, who after her marriage in 1910 lived the remainder of her life in Ringwood. ... (She) began by doing charcoal studies of animals when she was in Balranald, but in later years moved to oils and then watercolours, travelling around Ringwood to find places to paint by means of a pony-driven governess-cart. She won prizes for paintings in the Royal Melbourne Shows." - Hugh Anderson - Ringwood, Place of Many Eagles [p.217].Unframed painting with cardboard border. -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPainting, Winifred Miles, "Mullum Road" (Ringwood) - Water colour on paper by Winifred Miles (1884-1944), Undated, later than 1910
"Alexander Colquhoun [Herald art critic 1914-1922 and feature writer for the Age 1926-1941] ... took private students in the first decade of the century, and one of these was Winifred Miles, who after her marriage in 1910 lived the remainder of her life in Ringwood. ... (She) began by doing charcoal studies of animals when she was in Balranald, but in later years moved to oils and then watercolours, travelling around Ringwood to find places to paint by means of a pony-driven governess-cart. She won prizes for paintings in the Royal Melbourne Shows." - Hugh Anderson - Ringwood, Place of Many Eagles [p.217].Painting with cardboard border in glass-fronted frame. One of two undated paintings by Winifred Miles' viewed from the same vantage point on Mullum Mullum Road in Ringwood. (See Registration Number 4848)Sticker on back of frame - "Ringwood Framing Gallery, 233 Whitehorse Road Ringwood, Phone 8704930" -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyPainting, Winifred Miles, "Mullum Road" (Ringwood) - Water colour on paper by Winifred Miles (1884-1944), Undated, later than 1910
"Alexander Colquhoun [Herald art critic 1914-1922 and feature writer for the Age 1926-1941] ... took private students in the first decade of the century, and one of these was Winifred Miles, who after her marriage in 1910 lived the remainder of her life in Ringwood. ... (She) began by doing charcoal studies of animals when she was in Balranald, but in later years moved to oils and then watercolours, travelling around Ringwood to find places to paint by means of a pony-driven governess-cart. She won prizes for paintings in the Royal Melbourne Shows." - Hugh Anderson - Ringwood, Place of Many Eagles [p.217].Painting with cardboard border in glass-fronted frame. One of two undated paintings by Winifred Miles' viewed from the same vantage point on Mullum Mullum Road in Ringwood. (See Registration Number 4847)Sticker on back of frame - "Ringwood Framing Gallery, 233 Whitehorse Road Ringwood, Phone 8704930"
