Showing 745 items matching "loch ard shipwreck"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Ceramic Piece, Minton Potteries, ca. 1877
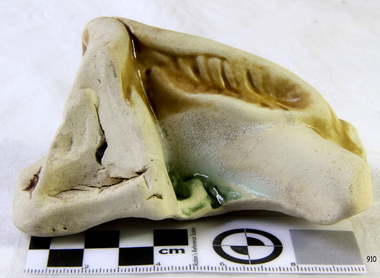
... they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck ...The ceramic piece is one of five porcelain fragments washed up from the Loch Ard wreck near Port Campbell, Victoria. These shards resemble the foot and leg of a large bird, and legend has it that another bird had drifted ashore at the same time as the Loch Ard peacock. This figurine is on display at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and regarded as the most valuable shipwreck relic. It is believed that all five fragments could belong to another peacock or a Minton porcelain stork that had been photographed in a Home Beautiful magazine in 1928. This stork appeared to be missing a leg and foot, and experts have hypothesised that the five fragments could belong to this stork, the whereabouts of which are currently unknown. History of the Loch Ard: The Loch Ard got its name from ”Loch Ard” a loch which lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic. The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the Loch Ard tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of Loch Ard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into Loch Ard Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition in. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register.The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collections historically significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.Ceramic shard, broken piece of pottery with some diagonally carved features. It is possibly a peacock leg section and green foliage. The ceramic piece has remnants of a coloured glaze.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, ceramic, porcelain, piece, fragment, ceramic bird, loch ard, shipwreck, salvage, recover, 1877, 1878, minton, shard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Ceramic Piece, Minton Potteries, ca 1877
... Loch Ard Gorge and took the two shipwreck survivors ...The ceramic piece is one of five porcelain fragments washed up from the Loch Ard wreck near Port Campbell, Victoria. These fragments resemble the foot and leg of a large bird, and legend has it that another bird had drifted ashore at the same time as the Loch Ard peacock. This figurine is on display at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and regarded as the most valuable shipwreck relic. It is believed that all five fragments could belong to another peacock or a Minton porcelain stork that had been photographed in a Home Beautiful magazine in 1928. This stork appeared to be missing a leg and foot, and experts have hypothesised that the five fragments could belong to this stork, the whereabouts of which are currently unknown. A brief history of the Loch Ard (1873-1878): - The sailing ship Loch Ard was one of the famous Loch Line of ships that sailed the long voyage from England to Australia. Barclay, Curdle and Co. built the three-masted iron vessel in Glasgow in 1873. It had sailed three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of recently married, 29-year-old Captain Gibbs. It was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, and a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. Other cargo included items intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The Loch Ard had been sailing for three months and was close to its destination on June 1, 1878. Captain Gibbs had expected to see land at about 3 am, but the Loch Ard ran into a fog that greatly reduced visibility, and there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. The fog lifted at 4 am, and the sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast were much closer to them than Captain Gibbs expected. He tried to manage the vessel but failed, and the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. The top deck loosened from the hull, and the masts and rigging crashed down, knocking passengers and crew overboard. The lifeboat was launched by Tom Pearce but crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. He clung onto its overturned hull and sheltered under it. He drifted out to sea, and the tide brought him back to what is now called Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore and found a cave for shelter. A passenger, Eva Carmichael, had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening and was confronted by towering cliffs above the ship. She was soon swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He swam out and dragged her to the shelter of the cave. He revived her with a bottle of brandy from a case that had washed up on the beach. Tom scaled a cliff in search of help and followed some horse hoof prints. He came from two men from Glenample Station, three and a half miles away. He told the men of the tragedy and then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. They reached Loch Ard Gorge and took the two shipwreck survivors to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome and was presented with a medal and some money. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collections historically significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.Ceramic piece, broken, with remnants of burgundy, green and yellow glaze. The piece has been shaped. It could be a peacock leg section with green foliage with glaze. Noneflagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, ceramic, porcelain, piece, fragment, ceramic bird, loch ard, shipwreck, salvage, recover, 1877, 1878, minton, shard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCeramic - Ceramic Piece, Minton Potteries, ca 1877
... Loch Ard Gorge and took the two shipwreck survivors ...The ceramic piece is one of five porcelain fragments washed up from the Loch Ard wreck near Port Campbell, Victoria. These fragments resemble the foot and leg of a large bird, and legend has it that another bird had drifted ashore at the same time as the Loch Ard peacock. This figurine is on display at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and regarded as the most valuable shipwreck relic. It is believed that all five fragments could belong to another peacock or a Minton porcelain stork that had been photographed in a Home Beautiful magazine in 1928. This stork appeared to be missing a leg and foot, and experts have hypothesised that the five fragments could belong to this stork, the whereabouts of which are currently unknown. A brief history of the Loch Ard (1873-1878): - The sailing ship Loch Ard was one of the famous Loch Line of ships that sailed the long voyage from England to Australia. Barclay, Curdle and Co. built the three-masted iron vessel in Glasgow in 1873. It had sailed three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of recently married, 29-year-old Captain Gibbs. It was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, and a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. Other cargo included items intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The Loch Ard had been sailing for three months and was close to its destination on June 1, 1878. Captain Gibbs had expected to see land at about 3 am, but the Loch Ard ran into a fog that greatly reduced visibility, and there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. The fog lifted at 4 am, and the sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast were much closer to them than Captain Gibbs expected. He tried to manage the vessel but failed, and the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. The top deck loosened from the hull, and the masts and rigging crashed down, knocking passengers and crew overboard. The lifeboat was launched by Tom Pearce but crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. He clung onto its overturned hull and sheltered under it. He drifted out to sea, and the tide brought him back to what is now called Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore and found a cave for shelter. A passenger, Eva Carmichael, had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening and was confronted by towering cliffs above the ship. She was soon swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He swam out and dragged her to the shelter of the cave. He revived her with a bottle of brandy from a case that had washed up on the beach. Tom scaled a cliff in search of help and followed some horse hoof prints. He came from two men from Glenample Station, three and a half miles away. He told the men of the tragedy and then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. They reached Loch Ard Gorge and took the two shipwreck survivors to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome and was presented with a medal and some money. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collections historically significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.Ceramic piece, broken with remnants of glaze. It has been shaped. It may be from a peacock leg section.Noneflagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, ceramic, porcelain, piece, fragment, ceramic bird, loch ard, shipwreck, salvage, recover, 1877, 1878, minton, shard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageNewspaper - Newspaper clipping, The Loch Ard : An Epic Wreck : Death of Eva Carmichael, ca. April 1934
... ), the only female survivor of the LOCH ARD shipwreck in 1878. She... LOCH ARD, which is now listed on the Victorian Heritage ...“On the 8th April 1934, at her residence in Bedford, England, Eveline Victoria Townshend, widow of the late Thomas Achilles Townshend, C.E. of County Cork, Ireland, died in her 74th year. Mrs Townshend was the Eva Carmichael who, with the late Tom Pearce, were the only two survivors of the ship Loch Ard, which was wrecked near Port Campbell, on 1st June, 1878 ....”. [Transcription of the article is attached]. Captain Gibbs was master of the Loch Ard, an iron clipper of 1623 tons, which was wrecked on Mutton Bird Island, one mile east of Sherbrook River. The two survivors, Carmichael, a passenger and Pearce, a member of the crew, were washed through the mouth of the gorge, which now bears the name of the ill-fated ship. The impact of the ship was so violent that the deck was torn clean off the hull, which now lies in 70 fathoms of water. (edited version of the same article)The newspaper article is of local, state and national historical significance for its association with the wreck of the sailing ship LOCH ARD, which is now listed on the Victorian Heritage Register S417. The article records an eye witness account of the rescue of the only two survivors from the Loch Ard wreck. A newspaper cutting from the Warrnambool Standard in 1934. It contains the obituary notice of Eva Carmichael (Townshend), the only female survivor of the LOCH ARD shipwreck in 1878. She died on 8 April 1934, a widow in England, in her 74th year. This original newspaper cutting has yellowed and creased with age. The article in the cutting is incomplete. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, warrnambool standard, eva carmichael, loch ard, eveline townshend, tom pearce, eveline victoria townsend, thomas achilles townshend, county cork, ireland, loch ard survivors, port campbell victoria, royal reade, 1-6-1878, w. c. till, eye witness account, george ford, glenample homestead, princetown, gibson, w. shields, mckenzie, robertson, robert strasenburg, loch venacher, robert pearce, tss hobsons bay -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Lead shot, Before 1878
... by Flagstaff Hill divers from the Loch Ard shipwreck site in 1976... they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck ...The objects are a sample of medium caliber lead shot raised by Flagstaff Hill divers from the Loch Ard shipwreck site in 1976. Included in the vessel’s cargo manifest were 22 tonnes of lead shot, packed into her holds in cloth bags and wooden casks. These 49 pieces of 7 mm diameter lead shot are identical in size and smoothness. Each one also bears the same slightly raised square of residual metal left behind by the process of pouring molten lead into individual but identical moulds through a small (square) opening. These pieces of shot can be compared with contrast pieces in the Maritime Village collection, which are examples of shot tower pellet production; an industrial technique more suited to the creation of uniformly spherical balls that do not need subsequent trimming. In conventional shot tower production, lead is heated in a cauldron at the top of a 150-160 feet tower, and poured through a copper lattice that divides the metal into falling droplets. As these droplets fall, they spin into small spheres and gradually cool, before finishing in a pool of water at the bottom of the tower. However the maximum size of lead shot, and the economic efficiency of shot tower production, is limited by the practical height of the drop. Larger diameter lead shot must fall further in order to cool evenly and sufficiently to avoid shape distortion on hitting the water at the base. This sample of larger 7 mm lead shot, although mass produced, appears to have been manufactured under the traditional and more labour intensive mould system. They are therefore distinct from the other samples of smaller gauged and shot tower produced lead shot that were being imported on the Loch Ard . In terms of metallurgical technology these 7 mm shot are more closely related to an artifact in our Collection (No. 5241) — a forged set of pincers or pliers with two facing cups at the end. When the pincers are closed, the cups join to form a single mould. Molten lead is poured through a small (circular) opening left at the top of the mould. When cooled the pincers are opened, breaking the mould and releasing the lead shot. The excess metal left over from the pouring operation at the top of the ball is then trimmed off using the scissor like cutting edges on the inner side of the pliers handles. In this manner, individual shooters were able to make their own ammunition for their shotguns. History of the Loch Ard: The Loch Ard got it’s name from ”Loch Ard” a loch which lies to the west of Aberfoyle, and to the east of Loch Lomond. It means "high lake" in Scottish Gaelic.The vessel belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many vessels from England to Australia. The Loch Ard was built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the vessel was a three-masted square-rigged iron sailing ship that measured 79.87 meters in length, 11.58 m in width, and 7 m in depth with a gross tonnage of 1693 tons with a mainmast that measured a massive 45.7 m in height. Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of 29-year-old Captain Gibbs, who was newly married. The ship was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were other items included that were intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. Then at 3 am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land. But the Loch Ard was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4 am the fog lifted and a lookout aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head-on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and Loch Ard's bow swung back towards land. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time the ship was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves subsequently broke over the ship and the top deck became loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael a passenger had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke the open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a complete state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached Loch Ard Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the Loch Ard tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of Loch Ard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some items were washed up into Loch Ard Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced in March 1982. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton majolica peacock- one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne 1880 International Exhibition in. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artifact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The shipwreck of the Loch Ard is of significance for Victoria and is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register Ref S 417. Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard and its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck. The collections object is to also give us a snapshot into history so we are able to interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. The collections historically significance is that it is associated unfortunately with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history. A quantity of forty-nine (49) loose round lead shot of 7 mm diameter retrieved from the wreck of the Loch Ard. All are smooth round spheres with the same small raised square of excess lead on one face.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, shipwreck artefact, shot, lead shot, shot towers, shot mould, colonial imports, practical metallurgy -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Pill bottle, Circa 1878
... Loch Ard Gorge and took the two shipwreck survivors ...This small pill bottle has been handmade by a glass blower. The battles and seamless concave sides and base show that the glass was blown into a shaped mould. The rough lip shows that the glass was snapped off at the mouth and roughly ground. This was an inexpensive way to produce a bottle. The bottle was recovered from the Loch Ard, wrecked in 1878. A brief history of the Loch Ard (1873-1878): - The sailing ship Loch Ard was one of the famous Loch Line ships that sailed from England to Australia. Barclay, Curdle and Co. built the three-masted iron vessel in Glasgow in 1873. It had sailed three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its fateful voyage. Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of recently married, 29-year-old Captain Gibbs. It was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. Onboard were straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, and a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. Other cargo included items intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition of 1880. The Loch Ard had been sailing for three months and was close to its destination on June 1, 1878. Captain Gibbs had expected to see land at about 3 am but the Loch Ard ran into a fog that greatly reduced visibility and there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. The fog lifted at 4 am and the sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast were much closer to them than Captain Gibbs expected. He tried to manage the vessel but failed and the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. The top deck loosened from the hull, and the masts and rigging crashed down, knocking passengers and crew overboard. The lifeboat was launched by Tom Pearce but crashed into the side of Loch Ard and capsized. He clung onto its overturned hull and sheltered under it. He drifted out to sea and the tide brought him back to what is now called Loch Ard Gorge. He swam to shore and found a cave for shelter. A passenger, Eva Carmichael, had raced onto the deck to find out what was happening and was confronted by towering cliffs above the ship. She was soon swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He swam out and dragged her to the shelter of the cave. He revived her with a bottle of brandy from a case that had washed up on the beach. Tom scaled a cliff in search of help and followed some horse hoof prints. He came from two men from Glenample Station, three and a half miles away. He told the men of the tragedy and then returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. They reached Loch Ard Gorge and took the two shipwreck survivors to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome and was presented with a medal and some money. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost her family in the tragedy. The glass pill bottle is associated with the shipwreck of the Loch Ard and of significance for Victoria as the wreck is registered on the Victorian Heritage Register ( S 417). Flagstaff Hill has a varied collection of artefacts from Loch Ard of which the pill bottle is one. Its collection is significant for being one of the largest accumulation of artefacts from this notable Victorian shipwreck of which the subject item is a small part. The collections objects give us a snapshot of how we can interpret the story of this tragic event. The collection is also archaeologically significant as it represents aspects of Victoria's shipping history that allows us to interpret Victoria's social and historical themes of the time. Through is associated with the worst and best-known shipwreck in Victoria's history.Small clear green-hue glass pill bottle, rectangular in shape and chipped lip. Sides and base are seamless and concave and varying thickness. Glass has bubbles and imperfections. A sticker is attached. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, loch ard, 1878 shipwreck, handblown bottle, pill bottle, small bottle, medicine bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Light Bracket, Before 1878
... would have found a ready market. The LOCH ARD shipwreck ...This pressed brass artefact is a highly decorative side bracket for distancing a gas lamp flame from the internal wall of a building. It is hollow and made of light gauge metal, with an innovative aesthetic design, but no internal piping to transport gas. It was recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. There are similar artefacts in the Flagstaff Hill collection. The LOCH ARD left Gravesend (London) on 2 March 1878, bound for Melbourne, with a crew of 37, 17 passengers, and a diverse and valuable cargo of manufactured goods, luxury items, and refined metal. Some of the cargo was destined for display at Melbourne’s first International Exhibition in 1880. At 3 am, 1 June 1878, the ship was wrecked against the high limestone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island on Victoria’s south west coast near Port Campbell. Only two people survived the disaster — Tom Pearce, a male crew member, and Eva Carmichael, a female passenger. The cargo proved too difficult to salvage in the vessel’s exposed condition and was largely written off. The manifest of goods in the LOCH ARD’s holds included “Fittings gas (4 cases)”. The gas lighting of streets, public buildings, and the dwellings of wealthier private citizens was already well-advanced in the cities and major towns of the Australian colonies. In 1841 Sydney was the first to be gas-lit with 23 street lamps, 106 hotel lamps, and 200 private residences connected to the Darlinghurst “gasometer” by an underground network of metal pipes. “The dim days of oil and tallow are gone by!” pronounced one newspaper, flushed with civic pride. The 1850s Gold Rush promoted a similar attitude of confidence and affluence in the Colony of Victoria. In 1855 Melbourne was connected to its own system of subterranean gas pipes despite the same high rates of 25 shillings per 1000 cubic feet being charged, (reduced to 15 shillings in 1865 with cheaper sources of coal). By1858 Kyneton had its own gasworks to light the town (fuelled by eucalyptus leaves) and Geelong followed suit in 1860. Had the LOCH ARD reached its intended destination in 1878, it is probable that the 4 cases of brass gas light fittings on board would have found a ready market.The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance — Victorian Heritage Register S417. The gas light bracket is an example of lamp fittings and plumbing from the late 19th century.A pressed brass lighting bracket recovered from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. It would be used for attaching, but simultaneously offsetting, a gas nozzle to a wall. Highly decorative in an unusually ‘modern’ or ‘art-deco’ style, with sweeping curves dissected by angular geometric pattern, and supporting a short, vertical bar with a gas nozzle on top. It is constructed of light gauge metal, with splitting along seams, and some delicate tracery is missing. Outer surface has been polished, removing sediment, but greenish oxidation remains in dents and joins. warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck artefact, maritime museum, gas lamps, gas lighting, gas works, brass fittings, gas pipes, loch ard, 1878 shipwreck, victorian affluence, colonial gas lighting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLetter
... . It is dated 21 January 1884, five and a half years after the LOCH ARD... they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck ...This original letter was handwritten and dated 21 January 1884. The author is Eveline V. Carmichael, of 29 Montpellier Villa, Cheltenham. Eva Carmichael was the only woman survivor of the iron clipper LOCH ARD, which was wrecked on 1 June 1878, at the subsequently named Loch Ard Gorge near Port Campbell. The letter was written to Mr J Archibald, first curator of the Warrnambool Mechanics Institute Museum, and was in response to a letter he wrote to Miss Carmichael on 1 December 1883. A complete transcript of Eva’s letter is attached as a Hard Copy Supplementary File. The letter first addressed the subject of her reply. She writes, “Thank you very much for thinking of me with regard to the volume of Longfellows Poems that have been found by Mr HW Davis [at Loch Ard Gorge], the book is not mine, nor did it belong to any members of my family. We had a ‘Longfellows’, but our book had a green cover.” The rescued book is on display at Flagstaff Hill (541) and has a blue cover. Another interesting aspect to her letter is its reference to the only other survivor from the LOCH ARD. As a postscript she writes, “You will be glad to hear that Tom Pearce is now on board the HMS Solvent. I heard from him last month he wrote from the West-Indies and seemed well and in good spirits. I have not seen him since we parted in Melbourne. I believe he is to be married next year, or perhaps this, but I do not know the young lady.” Tom Pearce was the young, male, able seaman who had risked his life to save her. In the months after the shipwreck, an excited public press speculated of a romantic connection between the two survivors, but this was clearly not the case. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Number S417 Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. A photocopy of a letter, handwritten in ink on both sides of 4 small sheets of thick, light blue paper. The letter is in neat cursive script. The writing originally covered 7 sides of the note paper and has been reproduced as 7 separate pages. It is dated 21 January 1884, five and a half years after the LOCH ARD shipwreck. The letter is from Eva Carmichael, one of only 2 survivors from that disaster, and is addressed to J. Archibald, first curator of the Warrnambool Mechanics Institute Museum. The copies include the reproduction of a typed index card which accompanies the original letter. The card states: “Photographic copy of the letter written by Eva Carmichael to Mr J Archibald, first Curator of the Warrnambool Museum. The original letter is kept with other documents, but the writing being on both sides of the note-paper it was not possible to read in its entireity when on display”.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, loch ard, survivor’s letter, eva carmichael, longfellow’s poems, warrnambool mechanics institute museum, joseph archibald, henry davis -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
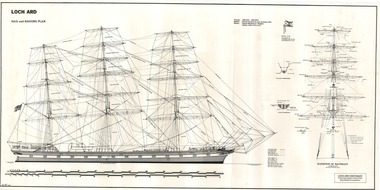
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Ship Model Plans, Loch Ard, October 1977
... of the tragic LOCH ARD shipwreck on Victoria’s south west coast in 1878... of the tragic LOCH ARD shipwreck on Victoria’s south west coast in 1878 ...These two framed model ship plans are from more than 650 produced for the LOCH ARD Centenary (1878-1978) Commemoration Committee. These plans were originally researched, designed and distributed in 1977 to assist entrants in the Committee’s Ship Model Competition. The competition was arranged as a means of creating public interest and awareness for the 100th anniversary of the tragic LOCH ARD shipwreck on Victoria’s south west coast in 1878. The main subject specified for modelling was “The Loch Ard ― Iron Wool Clipper 1873”. “The plans were drawn by Mr P Webb to the order of the Committee through Mr P Williams, organizer of the competition. The details were based on all available information which resulted in considerable historical research…and received favourable comment from model makers because of their attention to detail…In excess of 650 sets of plans were sold before entries closed…Many plans were probably purchased by collectors and interested persons for historical reference. An illustrated historical story sheet…was prepared and enclosed with the plans…” (‘Loch Ard Shipwreck Centenary 1878-1978 Report’, November 1978). An example of the attention to historical detail delivered on the plans is the inclusion of the following useful information about the original vessel: “Tonnage….1,693 G.R.T., 1,624 N.R.T. Builders….Charles Connell & Co., Ltd., Scotstoun, 1873. Owners….General Shipping Co., Glasgow, (Aitken Lilburn & Co., Ltd.)”. The quality of research and drafting makes these framed copies of considerable interpretive value to related items from the LOCH ARD shipwreck on display at Flagstaff Hill. They were originally mass produced but are now out of print. Flagstaff Hill retains other (unframed) copies in storage. The plans, in conjunction with the scale Ship Model of the LOCH ARD also on display, are of interpretive significance to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The plans provide historical and technological context to artefacts from the shipwreck, increasing understanding and appreciation of those objects. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Two framed model ship plans of the LOCH ARD. These are detailed and researched plans from the original vessel, drawn to scale and printed on good quality paper, and framed behind glass to be hung on display. One slightly smaller plan “Lines, Decks and Details” portrays the hull lines as a body plan (straight on at the bow), a sheer plan (full side view), and a half breadth plan (a top-down view of deck to keel), as well as two top-down views of the upper decks and main deck with fittings and details of specific fixtures. One slightly larger “Sail and Rigging Plan” presents a side on, above deck view of masts and shrouds and a front on, above deck view showing “Elevation of Mainmast Looking Aft”. Each plan bears the draftsman’s initials and date of completion (“P.A.W. 10/77”). The larger plan also includes a boxed label attributing the project to the “LOCH ARD CENTENARY Commemoration Committee Ship Model Competition.”Smaller plan: heading “LOCH ARD: LINES, DECKS and DETAILS”; initials “P.A.W. 10/77”. Larger plan: heading “LOCH ARD: SAIL and RIGGING PLAN”; initials “P.A.W. 10/77”; label “LOCH ARD CENTENARY Commemorative Committee Ship Model Competition”. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, ship model plans, loch ard model plans, sailing ship, loch ard centenary -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Ship Model Plans, Webb Warships Pty Ltd, Loch Ard Clipper Ship, 1874; Model Construction Plan Set, 1978
... of the Loch Ard Shipwreck Centenary through Mr P Williams... of the Loch Ard Shipwreck Centenary through Mr P Williams ...The plans are presented in a keepsake folder. They show marks of sections copied and assembled together. Overall, the plans are similar to those drawn by Mr P Webb to the order of the Loch Ard Shipwreck Centenary through Mr P Williams, the organizer of the Centenary competition. “The details were based on all available information which resulted in considerable historical research…and received favourable comment from model makers because of their attention to detail…In excess of 650 sets of plans were sold before entries closed…Many plans were probably purchased by collectors and interested persons for historical reference. An illustrated historical story sheet…was prepared and enclosed with the plans…” (‘Loch Ard Shipwreck Centenary 1878-1978 Report’, November 1978). An example of the attention to historical detail on the plans is the inclusion of the following useful information about the original vessel … Tonnage….1,693 G.R.T., 1,624 N.R.T. Dimensions, Builders….Charles Connell & Co., Ltd., Scotstoun, 1873. Owners….General Shipping Co., Glasgow, (Aitken Lilburn & Co., Ltd.), and the ship’s fate. The plans, in conjunction with the scale Ship Model of the LOCH ARD also on display, are of interpretive significance to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The plans provide historical and technological context to artefacts from the shipwreck, increasing understanding and appreciation of those objects. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history.Model ship plans for building the LOCH ARD. The three sets of plans are presented in a textured cream card folder with the supplier’s details and an oval cameo drawing of the LOCH ARD. The plans are detailed and drawn to scale. They and printed on good quality paper with details, scale and legends. Sheet 1: Sails and Rigging Sheet 2: Lines, Decks and Details Sheet 3: Masts and Spars Details include deck fittings, the wheel, lights and the shipping company’s house flag. The ship model plans are copyrighted in 1977 and 1978 to Webb Warships Pty Ltd. The folder has details of four locations; Australia, USA, UK and New Zealand. Sheet has a handwritten inscription.On Folder: "LOCH ARD CLIPPER SHIP, 1874, MODEL CONSTRUCTION PLAN SET, WEBB WARRIORS PTY LTD." "CONTENTS COPYRIGHT (C) 1978, WEBB WARSHIPS PTY LTD" "WEBB WARSHIPS PTY LTD, PO BOX 50, WILLIAMSTOWN, VICTORIA 3016, AUSTRALIA" Handwritten inscription on sheet 3: "834" "THE FLOATING DRYDOCK, PO BOX 16066, PHILADELPHIA, PENNA. 14114, USA" "SAMBROOK MARINE (PLANS), 84 BROAD ST. TEDDINGTON, MIDDLESEX, UK" "BYMODELS, PO BOX 3037, FORBURY, DUNEDIN, NEW ZEALAND" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, ship model plans, loch ard model plans, sailing ship, loch ard centenary, webb warriors pty ltd, 1977, 1978, centenary competition -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle
... Possibly from the shipwreck Loch Ard... bottom Height 11" Possible from the shipwreck of the Loch Ard.... Warrnambool great-ocean-road Possibly from the shipwreck Loch Ard ...Possibly from the shipwreck Loch ArdBrown glass bottle with concretion. Bottle has concave bottom Height 11" Possible from the shipwreck of the Loch Ard.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch ard, bottle, brown glass -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Fob watch, 1814
... connection with the Loch Ard shipwreck, it was purchased at auction... connection with the Loch Ard shipwreck, it was purchased at auction ...Watchmaker History: James McCabe was born in 1748. He was the son of Patrick McCabe, a notable watchmaker from Lurgan in County Armagh, Ireland. James McCabe immigrated to London in 1775 and established his business in Bells Building, Fleet Street, on 2nd April 1781. He was made an Honorary Freeman of the Clockmakers Company. The House of McCabe was renowned for the sheer variety of its designs, and the creativity and prestige of its manufacture were celebrated and revered by owners worldwide. These pieces remain highly collectable today and fetch increasingly higher prices at auction houses worldwide. Watch association with the Loch Ard: The watch was saved from the sea when discovered on the body of Mrs Rebecca Carmichael from Dublin and handed to Eva Carmichael, the only family member to survive the fatal wreck of the Loch Ard on 1st June 1878. Eva gifted the watch to her husband, Thomas Achilles Townsend when they married in 1884; his name is engraved on the rear movement cover. The watch was held by the family until 2011 when they decided to bring the watch, to Australia for auction. At this time the watch was in the possession of Eva Carmichael's grandson, Robert Townsend. Given its connection with the Loch Ard shipwreck, it was purchased at auction by Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village on 25th October 2011 to add to its Loch Ard collection and is currently referred to as the Carmichael watch. It is now on display alongside the Minton Peacock, which also survived the Loch Ard shipwreck, and other artefacts from the collection. James McCabe was originally a Belfast watchmaker who had moved his business to London. At the time James McCabe was much esteemed for producing fine watches and clocks, especially for export to India. Only the best watches were inscribed “James McCabe” and many with highly decorated cases were intended for the Indian market. Contemporary newspaper accounts of the watch's discovery echoed a Carmichael family tradition that the watch had been intended as a gift from the City of Dublin to King George IV to mark his planned visit to the city in 1821, however, there is no evidence to support this theory. Dr Evory Carmichael, according to some accounts, bought this watch from a nobleman for about £100 at some point and so it travelled with him on his final fateful journey to Australia. Today we can only guess at the actions of Mrs Carmichael in the chaos and darkness of the pre-dawn shipwreck. Perhaps the two items that were found on her body, the watch and a locket, were items that reminded her of those she held most dear, her husband and her family. When Mrs Carmichael's body was washed ashore the watch was found secreted in the waistband of her dress. In its own right the watch is of artistic and monetary value and is a rare and beautiful object depicting watch making in the early 19th century. It is a historically significant object in it’s own right and there is additional importance, surviving a significant event in the maritime history of Victoria. The wreck of the Loch Ard, Victoria's greatest maritime disaster has also been declared an event of National Significance because of its strong connection to Australia's immigration and maritime history. The watch, together with the Loch Ard Peacock, make up the two most significant shipwreck artefacts in Australia. Both of these items are of great social significance to not only local people but the wider Australian community. Funding for the watches purchase came from six local trusts and one anonymous citizen and is now on permanent display. Both these artefacts symbolise and helps to interpret the stories of survival along the Shipwreck Coast. Fob Watch, known as the "Carmichael Watch" or the "Loch Ard Watch". 1814 fob pocket watch belonging to the Carmichael family, recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard. Fob watch (or pocket watch)and winding key, made by James McCabe and Son, of Cornhill, London. The watch is in excellent condition and its design is decorative and intricate. The gold face is covered by glass. The gold rear cover is hinged over a silver inner cover that includes the winding hole. The watch has a knob with a swinging ring from which it can be hung. The dial of the gold watch face is textured and has raised Arabic numerals and every minute is marked around the perimeter by a dot, with the 5-minute dots slightly larger. The numerals and dots are a different coloured gold than the rest of the face. The centre of the face has a wavy pattern fanning out to the base of the numerals. The hour and minute hands are of a dark colour. The stems of the hands are a wavy shape and finish with spade shaped tips; the tip of the hour hand is larger than that of the minute hand. The hour hand reaches to the base of the numerals and the minute hand is long enough to rest between the minute dots. The back of the watch is decorated with a detailed design on a textured gold background. The design is embossed in coloured metals; gold, silver, greenish-gold and pink. In the centre is a dove resting on leaves of a pot plant that sits on a silver circular base. Another dove is flying above it, and their beaks touch together. On the right of the base of the pot plant is a dog resting on its hind legs, body facing away from the plant and head twisted around to look at the birds. On the sides of this design and meeting at the base are sprigs of leaves and buds. Around this central design is a rope-like border. Around the perimeter of the case is a border of leaves and budding stems. The inside of this cover has embossed hallmarks, numbers and etched markings indicating that the watch is 18 carat gold, made by James McCabe, assayed in London in 1814 and the case may have been made by Daniel Willmott, case maker. The silver inner workings cover has a full name beautifully engraved on it. There is a winding hole that accesses a square-ended lever for the key to fit over. The handle of the watch is a twisted gold knob with a hollow ‘D’-shaped swinging ring attached to the end of it. This knob also has a hallmark.On the silver inner workings cover “Thomas Achilles Townshend” is engraved, underscored by a thin, delicately decorated line. On the gold handle is the logo of a crown with “18”’ next to it. Inside the gold rear case is stamped “DW’. Under that is etched “JAN 77 II”. Underneath this are 3 logos; a logo “leopard, crowned”’, a logo “ crown on top of 18”, and a logo “T”. Under these 3 symbols is part of a stamp that could possibly be “IMC”. Under this is “ ’ 5 9 4 ”. Other numbers, symbols and letters are etched into this case including “15001”, “2/5/19”. Others are difficult to read.warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, maritime museum, shipwrecked artefact, shipwreck artefact, carmichael, townshend, townsend, carmichael watch, loch ard watch, pocket watch, loch ard, 1st june 1878, james mccabe, thomas walker, robert townshend, loch ard gorge, great ocean road, victoria., memorial headstone -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLetter
... survivor of the LOCH ARD shipwreck in 1878. It tells of Eva’s..., sole female survivor of the LOCH ARD shipwreck in 1878 ...This letter was written to Alisdair Loch, 10 Beaconsfield Parade, Lindfield (Sydney) NSW, from Frank Townshend Esq., 3 The Square, Holywell, Wotton-under-Edge, Gloucestershire, England. Its author is a son of Eva Carmichael/Townshend, sole female survivor of the LOCH ARD shipwreck in 1878. It tells of Eva’s struggle in the sea after the LOCH ARD hit the rocks, and of her rescue by the only other survivor, young seaman Tom Pearce. It also relates her return to a privileged life in Ireland, her subsequent marriage to another member of the Anglo-Irish ascendancy, and her three sons. In some places the letter seems in historical error, which is not surprising given the dates involved and the time that elapsed between them (Eva shipwrecked 1878, Son’s birth 1887, Eva’s death 1934, Son’s letter 1962). The writer makes clear he is relying on his memory of what his mother had told him, and he is usually forthright in declaring those things he cannot remember, or remembers indistinctly. An interesting paragraph in the letter answers the contemporary newspaper speculation about a possible romance between the two survivors: “She [his mother, Eva Carmichael] received many proposals of marriage, perhaps a dozen, including one from Tom Pearce. Tom Pearce was, I think, an apprentice. She spoke of him sometimes as a ‘cabin boy’. From his photograph, he was a fine, handsome young man. The reason she declined his offer of marriage was largely the fruit of class distinction, I think; class prejudice being very strong in Ireland, in those days.” The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance ― Victorian Heritage Number S417Typed copy of a letter from Frank Townshend, LOCH ARD survivor Eva Carmichael’s son in England, to Alasdair Loch, Sydney NSW. It is dated 8 March 1962 and consists of four pages. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, letter, frank townshend, eva carmichael, loch ard, alasdair loch, tom pearce -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLetter
... survivor of the LOCH ARD shipwreck in 1878. The letter is in reply... ordeal as the only female survivor of the LOCH ARD shipwreck ...This letter is a photographed copy of a typed transcript of an original. It is dated 28 March 1962 and was written by Ian F. Sloane Esq. of Savernake Station, NSW. Sloane’s great uncle, Hugh Gibson, was the owner of Glenample Station, Vic., where Eva Carmichael stayed to recuperate from her ordeal as the only female survivor of the LOCH ARD shipwreck in 1878. The letter is in reply to an earlier inquiry for information about the LOCH ARD tragedy from Alasdair Loch, 10 Beaconsfield Parade, Lindfield NSW. Most of the letter consists of tantalising asides: about trips to Glenample in 1916 and 1917 and the digging up of an old piano at Loch Ard Gorge; the possession of his uncle’s personal account of the shipwreck and its aftermath; the existence of a painting of Eva when she was staying at the Glenample homestead in 1878; and the disputed ownership of “a very old black iron box” containing letters from relatives of the shipwreck victims (who Hugh Gibson had written to advising of their unhappy fate). Unfortunately the letter, written in haste prior to Sloane’s departure overseas, contains no substantive information. However it concludes with an interesting footnote concerning Eva’s emotional recovery at Glenample. Sloane’s postscript states: “Miss Carmichael was very well after the wreck, full of fun and laughter, until she suddenly cracked, and had a nervous breakdown…Mrs Gibson…got a young girl, the same age as Eva, as her companion[…She] proved trumps and saved Eva’s mind. They became lifelong friends. Both wrote to my aunt till they died. Miss Carmichael stayed about 6 months at Glenample I think.” The shipwreck of the LOCH ARD is of State significance ― Victorian Heritage Number S417A photographic copy of a typed letter-transcript. The original letter was written to Alasdair Loch, Lindfield NSW, and is from Ian F. Sloane Esq. of Savernake Station NSW. It is dated 28 March 1962 and is two pages long.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, letter, alasdair loch, ian f sloane, sloane, loch ard, hugh gibson, eva carmichael, glenample station, tom pearce, glenample homestead -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLetter, Henry Davis, Editor, Warrnambool Standard, 11-10-1883
... with one of the survivors from the LOCH ARD shipwreck in 1878... connection with one of the survivors from the LOCH ARD shipwreck ...This letter was written by Henry Davis, editor of the Warrnambool Standard, to Joseph Archibald, curator of the Warrnambool Museum. Dated 11 October 1883, it refers to Davis’s recovery of a saturated volume of ‘Longfellow’s Poems’ from the sea at Loch Ard Gorge. The retrieval of this book, and its possible connection with one of the survivors from the LOCH ARD shipwreck in 1878, prompted Archibald’s letter of 1 December 1883 to Eva Carmichael, and Eva’s reply of 21 January 1884 (No, it was not her book). Miss Carmichael’s reply to Archibald’s inquiry (2290.4) and the water-damaged book itself (541) are both in the Flagstaff Hill collection along with this letter from Davis, which connects the two. The Davis letter reads: “Dear Sir, ― This book was found by me in the waves which broke on the sands [….] the Gorge where Tom Pearce rescued Miss Carmichael after the wreck of the ill-fated ‘Loch Ard’. I ran in with the receding waves and picked up the soddened volume, and, coincidentally, the first illustrations that met my gaze, on parting its dripping pages, was that portraying the fair maiden in the ‘Wreck of the [Hersperus’.] On the Bluff, 200 feet above me, were the dead forms of Mrs and one of the Misses Carmichael, whilst [by] them, stiff and [….] were two gentlemen passengers [by] the wreck[ed] [v]essel]. Having just left them before [….] [my] capture in the Gorge, you may imagine [m]y feelings on alighting upon, under such circumstances, Longfellow’s beautiful and sympathetic poem. Yours truly, H.W. Davis.” The book referred to here is The Poetical Works of Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, 1877, Nimmo, London. It is on display under glass in the Great Circle Gallery at the Maritime Village, alongside a typed transcript of the Davis letter. A 1996 audit of the rare book collection at Flagstaff Hill notes: “Inscribed ‘Loch Ard June 1 1878’ in pencil within ― believed to be a salvage from the shipwreck”. The letter is connected to the salvaged items from the 1878 LOCH ARD shipwreck, which is of State significance ― Victorian Heritage Number S417Letter from H. Davis, editor of the Warrnambool Standard, to J. Archibald, curator of the Warrnambool Museum. It was handwritten in ink on “Standard Office, Warrnambool” letterhead note paper, and dated 11 October 1883. The cursive script appears carelessly written and the original single sheet of paper is in poor condition (torn and creased). At some stage the original document has been backed with stiff cardboard and then sealed in a clear plastic cover.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, loch ard, longfellow’s poems, eva carmichael, joseph archibald, henry davis, warrnambool standard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Tap, mid-late 19th century
... the Loch Ard shipwreck, wrecked on Mutton Bird Island, east of Port... the Loch Ard shipwreck, wrecked on Mutton Bird Island, east of Port ...This type of large, brass tap is typical of the plumbing fittings manufactured in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The tap has encrustations and concretion inside, showing that it had been in the sea for quite some time. The pipe leading to the spout is squashed, nicked and appears to have been sawn or broken off. It could have once been part of the plumbing from a ship, perhaps from one of the boilers used in the kitchen, for bathing or for laundry or cleaning. The name “BEST” on the tap signifies that it could have been made by Robert Best who began his Birmingham brass foundry c. 1840, and even though The information from the donor is that tap was given to her father (1906-1982) who lived in the Warrnambool district. It was likely given by a cray fisherman or diver, who said that the tap came from the Loch Ard shipwreck, wrecked on Mutton Bird Island, east of Port Campbell, Victoria, on 1st June 1878. This could easily be the case but there is no provenance for it. ROBERT BEST, BRASS FOUNDRY Circa 1840 Robert Best founded his brass foundry business and was referred to as a Brass Chandelier of Birmingham”. In 1864 an advertisement in the Journal of Gas Lighting, Water Supply, & Sanitary Improvement announces Best and Hobson, late Robert Best, 100 Charlotte Street Birmingham, manufacturers of Chandeliers, Brass and iron fittings, Steam and Water-cocks etc. gas apparatus of every description, Plumber's brass foundry, with works at Birmingham and Great Bridge, Staffordshire. In 1867 Best & Lloyd was formed, after Best and Hobson went into liquidation, manufacturing at the Cambray Works of Wattville Road, Handsworth. It was a light industrial engineering works and one of the owners was Robert Dudley Best’s father. Robert Dudley Best (1892-1984) later took over the business of Best & Lloyd. The company is still in business at Downing Street, Smethwick, Birmingham. In 1878, brass ship furniture and bell fittings stamped “BEST” was made by William Udal & Co., who advertised as manufacturers of BEST cast and stamped brass foundry goods. This large brass tap is typical of industrial tapware of the mid-late 19th and 20th centuries. The location of the tap, when found, is associated with the Warrnambool district and could have easily been from a shipwreck due to the encrustation found inside the tap. Due to its design and manufacturer, the tap is associated with the mid-late 19th and early 20th-century manufacture of plumbing fittings. Tap, brass, heavy-duty, with butterfly handle. The design and style are typical of the plumbing of the late 1800s. Inscription pressed into the handle, within rectangular border "BEST". Encrustation and concretion are inside the tap spout. “BEST” on one side of the tap handle (Also, a label from the donor attached to the tap “from the wreckage of the LOCH ARD")flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, robert best brass foundry, best and hobson, best & llyod, birmingham brass foundry, brass tap, best brand tap, heavy duty brass tap, industrial brass tap, boiler tap, 19th century plumbing, 19th century tapware, 19th century plumbing fitting, tap with butterfly handle, tap salvaged from shipwreck, brass fittings, steam engine fittings, water-cock fitting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Bottle, 1870s-1910s
... titled ‘Glass Bottles from the Loch Ard Shipwreck (1878.... It is possible that this bottle was recovered from the Loch Ard, wrecked ...This clear, green tinged, Half Whirley (or Whirly) salad oil bottle has been handmade by a glassblower from 1870s-1910s. A bottle with such elaborate decoration would have been sought after as there was no need to decant the sauce into another jug or bottle to make it acceptable for table service. It is possible that this bottle was recovered from the Loch Ard, wrecked in 1878. A diver found the bottle on a shipwreck in the coastal waters of Victoria about 100 years from when it was made. The diver who found this bottle has recovered objects from several different shipwrecks between the late 1950s and early 1970s. A sizeable proportion of those objects was from the wreck of the famous clipper ship Loch Ard. This salad oil bottle may very well have been amongst that ship’s cargo. It is part of the John Chance Collection. A paper titled ‘Glass Bottles from the Loch Ard Shipwreck (1878): A Preliminary Study’ by Iain Stuart, (published in Australian Historical Archaeology, 9, 1991) included a study of twelve salad oil bottles from the wreck of the Loch Ard. The bottles were of this same Half Whirley design (half meaning that it was Whirley on the upper half but not on the lower half of the body), as well as the same colour and size. A diagram of one of these twelve bottles matches the bottle in our collection. The paper mentions that eleven of the twelve bottles have a number on their base, just as this one has. It is estimated that foreign and salad oil bottles totalled four percent of all of the bottles carried as cargo on the ship. The Half Whirley bottle has side seams from below the lip to the base, indicating that the bottle was made in a two-piece mould that included the heel, body, shoulder and neck. The fancy ‘whirly’ twist pattern and panelled sides would have been cut into the mould’s inner surface. The uneven thickness of the ridge around the base comes from adding a separately moulded and embossed base after the bottle was removed from the mould. The applied finish (mouth and lip) was also added to the bottle. The elongated bubbles in the glass are evidence of the glass being mouth blown into the mould, thus forming the shape and pattern from the inside shape of the mould. The bottle probably had a glass stopper with a round top and wedge-shaped shank with a ground surface, allowing the bottle to be re-sealed. The ring between upper and lower lip allows the closure to be sealed and anchored. The embossed numbers are either “133” or “833” and may represent a particular bottle pattern, manufacturer or filler. Although the bottle is not currently linked to a particular shipwreck, it is recognised as being historically significant as an example of bottles imported for use in Colonial Victoria in the mid-to-late 19th century. This whirley salad oil bottle is matches the whirley salad oil bottles recovered from the Loch Ard in the 1990s, adding depth of interpretation to the array of salvaged Loch Ard artefacts in Flagstaff Hill’s collection. The salad oil bottle is an example of the type of food condiment containers that were used in Victoria’s early days. The bottle is also significant as it was recovered by John Chance, a diver in Victoria’s coastal waters in the late 1960s to early 1970s. Items that come from several wrecks, including the Loch Ard, have since been donated to the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village’s museum collection by his family, illustrating this item’s level of historical value. Bottle; glass Half Whirley salad oil bottle, green-tinged, with some opalescence. Handmade, elaborately decorated bottle with round neck and base, and five-sided body. Applied double lip; straight upper, flared lower. The lower neck and shoulder have twisted spiral whirley patterns in the glass. The body tapers slightly inwards towards the base. It has five plain panels, one wider than the others. Side seams run from below the lip to the heel. The heel of the bottle is uneven in width, height and density where it joins the body of the bottle. The base is not level. Embossed characters on base. Glass has elongated bubbles towards the base and orange-brown sediment inside, on one side. Embossed "133" or “833” (the first character may be an “8”) flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, john chance, glass bottle, antique bottle, handmade, mouth blown, blown bottle, 19th century bottle, collectable, bottle, green glass, tinged green, two piece mould, food bottle, oil bottle, salad oil bottle, whirley, whirly, half whirley, condiment bottle -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Clock Parts, Bef. 01-06-1878
... of Loch Ard shipwreck artefacts, including the gold watch... of Loch Ard shipwreck artefacts, including the gold watch ...The clock parts were discovered in 1980 by Julie Wilkins, a Victorian scuba diver who had already experienced more than 500 dives in Australia and overseas. She was holidaying in Peterborough, Victoria, and looking forward to discovering more about the famous Loch Ard ship, wrecked in June 1878 at Mutton Bird Island. The fast Glasgow-built clipper ship was only five years old when the tragedy occurred. There were 54 people on board the vessel and only two survived Julie's holiday photograph of Boat Bay reminds her of her most memorable dive. Submerged in the calm, flat sea, she was carefully scanning around the remains of the old wreck when, to her amazement, a gold coin and a small gold cross suddenly came up towards her. She excitedly cupped them in her hands and then stowed the treasures safely in her wetsuit and continued her dive. She soon discovered a group of brass carriage clock parts and some bottles of champagne. It was a day full of surprises. The items were easily recognisable, without any build-up of encrustations or concretion. Julie secretly enjoyed her treasures for twenty-four years then packed them up for the early morning train trip to Warrnambool. After a short walk to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village, her photograph was taken as she handed over her precious find. She told her story to a local newspaper reporter, lunched a café in town then took the late afternoon train home. Her generous donation is now part of a vast collection of Loch Ard shipwreck artefacts, including the gold watch and the Minton Majolica model peacock. This group of brass clockwork parts is incomplete. The pieces were in the ocean for over 100 years before Julie recovered them from the Loch Ard wreck. Their size would suit the works of a carriage clock, with a mainspring and weight to power the clock movement, a pendulum to measure the clock's speed, arbours, posts, pillars and at least one other plate. They would have been mounted inside a protective case with a small door to easily access the clock face for setting the time and accessing the key's winding hole. The clock cases were usually made from decorative gilt brass with a glass front and a carrying handle. The parts include a weighted second hand with a decorative four-pronged finish at one end, a rounded weight at the other, and a hole for attaching it to the clock face. The gear teeth profiles are ‘cycloidal’, an arch shape with vertical sides, which is common for antique clocks. Modern clockworks have ‘involute’ teeth with sloping sides and a squared-off top. The brass carriage clock parts are an example of a mechanical clock produced in the 1870s. The clock's design is a part of the chain of technological improvements in methods for timekeeping. Its cycloidal gear teeth were the forerunner of the more modern involute gears. The group of clock parts includes a weighted hand or arm for signifying the seconds. This feature was uncommon in portable Victorian-era clocks. The clock parts are also significant for their association with the ill-fated sailing ship Loch Ard, wrecked in 1878. The travelling clock or officer’s clock may have been part of the cargo destined for the 1880 Melbourne Exhibition, or the personal possession of one of the people on board the vessel. Brass clockwork parts from a mechanical clock, sixteen pieces. Parts comprise a plate, large gears or wheels, small pinions or wheels with fine teeth, wheels with cogs, and a weighted second hand. The parts were from a carriage clock ca. 1878. They were recovered from the wreck of the sailing ship Loch Ard.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, loch ard, wreck of the loch ard, 1878, mutton bird island, peterborough, scuba diver, 1980s, shipwreck artefact, relic, clock, mechanical, clock parts, time, timekeeper, horology, chronometry, cogs, time keeping device, scientific instrument, chronometer, john harrison, longitude, carriage clock, coach clock, portable clock, travelling clock, travel clock, traveller’s clock, officer’s clock, weighted second hand, victorian era, cycloidal gear teeth, brass clock, julie wilkins -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Gold Cross, Bef. 01-06-1878
... generous donation is now part of a vast collection of Loch Ard... generous donation is now part of a vast collection of Loch Ard ...The gold cross was discovered by Victorian scuba diver Julie Wilkins, who had already experienced more than 500 dives in Australia and overseas. She was holidaying in Peterborough, Victoria, and looking forward to discovering more about the famous Loch Ard ship, wrecked in June 1878 at Mutton Bird Island. The fast Glasgow-built clipper ship was only five years old when the tragedy occurred. There were 54 people on board the vessel and only two survived Julie's holiday photograph of Boat Bay reminds her of her most memorable dive. Submerged in the calm, flat sea, she was carefully scanning around the remains of the old wreck when, to her amazement, a gold coin and a small gold cross suddenly came up towards her. She excitedly cupped them in her hands, then stowed the treasures safely in her wetsuit and continued her dive. She soon discovered a group of brass carriage clock parts and some bottles of champagne. It was a day full of surprises. The items were easily recognisable, without any build-up of encrustations or concretion. Julie secretly enjoyed her treasures for twenty-four years then packed them up for the early morning train trip to Warrnambool. After a short walk to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village, her photograph was taken as she handed over her precious find. She told her story to a local newspaper reporter, lunched a café in town then took the late afternoon train home. Her generous donation is now part of a vast collection of Loch Ard shipwreck artefacts, including the gold watch and the Minton Majolica model peacock. The small decorative cross dates back to on or before 1878, when the Loch Ard had set sail. The loop and ring have been added, perhaps as a pendant, pocket watch accessory or similar purpose. It may have been worn for ‘good luck’ or a ‘blessing’ on the long journey to Australia, where ships had to carefully navigate the treacherous Bass’s Strait before arriving at their destination of Melbourne. Sadly, many met their fate on that short stretch of ocean aptly named the Shipwreck Coast. The cross is very recognisable even though it was exposed to the wrecking of the ship, its consequent movement, and the sea's turbulence. Its scratched, pitted and worn condition, and the damage near the loop, is part of its story. The red-brown-black discolouration is similar to that found on other gold coins, sometimes called the ‘corrosion phenomena’. Studies suggest the possible cause is contaminants in the minting process reacting to the coins’ environment. Three edges of the cross have slightly raised narrow ridges of gold which could have been cause by the gold being cast liquid gold into a mould.This gold cross pendant is significant as a symbol of Christianity, a sign of hope and safety, and a sample of the religious following on board the Loch Ard, although not everyone wears a cross for this reason. This cross is a sample of jewellery owned by people migrating to Australia in the late 19th century. The cross and the guinea recovered together from the wreck of the Loch Ard are made of gold and help interpret the financial status of some of those on board.Gold cross; yellow gold with decorative hand engraved foliage design on the front, fitted loop and ring on top. The simple Latin or Roman variation of the cross, with an elongated vertical arm, has no figure on it and the reverse has no decoration. The right, left and base edges have sections of narrow, long slightly raised ridges. The top edge has remnants of red-black colour. Victorian era cross, ca. 1878. The cross was recovered from the wreck of the ship Loch Ard.Engraved foliage design. Slightly raised long ridges on sides and base edges. flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, gold cross, religious cross, religious trinket, religious jewellery, engraved cross, cross pendant, cross with ring, victorian era, 1878, antique cross, crucifix, religious symbol, christian symbol, christian jewellery, contamination phenomena, gold corrosion, good luck, lucky charm, blessing, pendant, loch ard, wreck of the loch ard, mutton bird island, peterborough, scuba diver, 1980s, shipwreck artefact, relic, latin cross, roman cross, pectoral cross, julie wilkins -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, circa 1895
... Loch Ard was bound for Melbourne in 1878 loaded... known as Loch Ard Gorge following the shipwreck. Cargo ...Loch Ard was bound for Melbourne in 1878 loaded with passengers and cargo when it ran into a rocky reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: an apprentice, Tom Pearce and a young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. The wreck of Loch Ard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island and much of the cargo has been salvaged. Some was washed up into what is now known as Loch Ard Gorge following the shipwreck. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. The photograph is significant for its association with the wreck of the Loch Ard. This wreck has been protected as a Historic Shipwreck since 11 March 1982, under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976) Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from Loch Ard is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register. The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the Loch Ard, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. The Loch Ard collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Photograph of rocks of Loch Ard Gorge in background, a man is sitting on small rock in the foreground. Reverse has hand writing in pen and inkReverse hand writing “The Loch Ard Gorge / showing the rock / on which Miss Carmichael / was clinging when Pearce / first saw her” and “Mr J Swinton / Warrnambool / March 1895”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, photograph -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph, late 19th century
... Loch Ard was bound for Melbourne in 1878 loaded... known as Loch Ard Gorge following the shipwreck. Cargo ...Loch Ard was bound for Melbourne in 1878 loaded with passengers and cargo when it ran into a rocky reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: an apprentice, Tom Pearce and a young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. The wreck of Loch Ard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island and much of the cargo has been salvaged. Some was washed up into what is now known as Loch Ard Gorge following the shipwreck. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. The photograph is significant for its association with the wreck of the Loch Ard. This wreck has been protected as a Historic Shipwreck since 11 March 1982, under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976) Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from Loch Ard is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register. The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The Loch Ard collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the Loch Ard, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. The Loch Ard collection meets the following criteria for assessment: Criterion A: Importance to the course, or pattern, of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion B: Possession of uncommon, rare or endangered aspects of Victoria’s cultural history. Criterion C: Potential to yield information that will contribute to an understanding of Victoria’s cultural history. Black and White photograph of Thomas Pearce. Taken on July 22nd 1878 by the Photographic Society of Victoria. Registered copyright July 24th 1878. Reverse has printed maker’s information.Printed green text “PHOTOGRAPHIC / SOCIETY OF VICTORIA / MELBOURNE / REGISTERED COPYRIGHT / JULY 24th 878” and “NONE ARE GENUINE UNLESS WITH / SIGNATURES THUS” and “PRESIDENT / VICE PRESIDENT / SECRETARY” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, photograph, thomas pearce, loch ard, photographic society of victoria -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Guinea Coin, The Royal Mint, 1793 George III Spade Guinea, 1793
... generous donation is now part of a vast collection of Loch Ard... generous donation is now part of a vast collection of Loch Ard ...The coin was discovered by Julie Wilkins, a Victorian scuba diver who had already experienced more than 500 dives in Australia and overseas. She was holidaying in Peterborough, Victoria, and looking forward to discovering more about the famous Loch Ard ship, wrecked in June 1878 at Mutton Bird Island. The fast Glasgow-built clipper ship was only five years old when the tragedy occurred. There were 54 people on board the vessel and only two survived Julie's holiday photograph of Boat Bay reminds her of her most memorable dive. Submerged in the calm, flat sea, she was carefully scanning around the remains of the old wreck when, to her amazement, a gold coin and a small gold cross suddenly came up towards her. She excitedly cupped them in her hands, then stowed the treasures safely in her wetsuit and continued her dive. She soon discovered a group of brass carriage clock parts and some bottles of champagne. It was a day full of surprises. The items were easily recognisable, without any build-up of encrustations or concretion. Julie secretly enjoyed her treasures for twenty-four years then packed them up for the early morning train trip to Warrnambool. After a short walk to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village, her photograph was taken as she handed over her precious find. She told her story to a local newspaper reporter, lunched a café in town then took the late afternoon train home. Her generous donation is now part of a vast collection of Loch Ard shipwreck artefacts, including the gold watch and the Minton Majolica model peacock. The coin is a British 1793 George III Gold Spade Guinea. It was already 83 years old when the Loch Ard had set sail. The loop and ring have been added, perhaps as a pendant, pocket watch accessory or similar purpose. It may have been worn for ‘good luck’ on the long journey to Australia, where ships had to carefully navigate the treacherous Bass’s Strait before arriving at their destination of Melbourne. Sadly, many met their fate on that short stretch of ocean aptly named the Shipwreck Coast. The coin is very recognisable even though it was exposed to the wrecking of the ship, its consequent movement, and the sea's turbulence. Its bent, scratched, buckled, split, dinted and worn condition is part of its story. The red-brown-black discolouration is similar to that found on other gold coins, sometimes called the ‘corrosion phenomena’. Studies suggest the possible cause is contaminants in the minting process reacting to the coins’ environment. The GEORGE III GOLD SPADE GUINEA: - The British Guinea was introduced in 1663 and was circulated until 1814. It was made of 22 carat gold, was 25 to 26 cm in diameter and weighed 8.35 grams. It had a value of 21 British shillings. The guinea coin ceased circulation after 1816 and was replaced by the one-pound note. However, the term ‘guinea’ continued to represent 21 shillings. King George (1738-1820) had six gold guinea designs minted during his reign from 1760 and 1820. Each of the six had different obverse portraits, all facing the right. There were three different reverse sides. The Spade Guinea was the fifth issue of the coin, introduced in 1787 and produced until 1799. The reverse shows a royal crown over a flat-topped shield with the Royal Arms of Great Britain, used in Scotland between 1714 and 1800. The shield images are, from left to right, top to bottom, the Arms of England and Scotland, the Arms of France, the Arms of Ireland, and the Arms of the House of Hanover. The Gold Guinea is also part of Australia’s history. It was the first coin mentioned in the announcement of Governor King of New South Wales his Australian Proclamation of a limited variety and denomination of coins accepted for use in the Australian Colony. The historic and decorative George III Spade Guinea has been reproduced for special collections of coins. However, replicas and imitations have also been made as souvenirs for tourists, as gaming tokens and chips for gamblers, and as ‘fake’ coins for profit. These coins differ in many ways; they may be only half the weight of the genuine coin. Often have a small stamp on the obverse with “COPY” or the manufacturer’s name or initials. Some have scalloped edges, some have dates that are different to the original dates of issue, and some even have text in Latin that translates as something very different to the original coin.The King George III Guinea was only produced from 1663 to 1814 and was the first English coin to be mechanically minted. The coin is the fifth edition of the King George III Guinea, the Spade Guinea, was only produced between 1787 and 1799. It is the only edition with this portrait of King George and the only one with the Royal Coat of Arms of Great Britain in Scotland on the reverse side. This edition was also the last guinea in circulation, because the sixth edition was reserved as the Military guinea. This edition of the Guinea is unique; This coin is the only guinea in our collection. It was minted in 1793, so it is now over 230 years old. The Gold Guinea is part of Australia’s history; it was the first coin in the list of coins for use in the Australian Colonies, mentioned by Governor King of New South Wales in his Australian Proclamation speech of 1800. The George III Spade Guinea was included in the Limited Edition Sherwood 12 Coin Collection of Notable Coinage of Australia. This coin is the only known guinea coin recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard. It was already 85 years old when the ship was wrecked.Gold coin; British. 1793, King George III of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1760-1820), Spade Guinea. Yellow gold coin with gold metal loop mount and a gold ring through the loop. The design is the fifth issue of the George III Gold Guinea. The obverse relief is a portrait of George III facing right. Reverse relief is a crown above the Coats of Arms (1801-1816) of flat top spade-shaped shield divided into four quadrants that depict crowned lions, fleur de lies, a harp. These images are identified as, from left to right, top to bottom, England and Scotland, France, Ireland and Hanover. Inscriptions are minted around the rims of each side. The coin is dated 1793. Its surface has dark areas on both sides and the reed edge and surfaces are well worn. The loop mount is bent and the ring is buckled. The coin was recovered from the wreck of the ship Loch Ard.Obverse text; 'GEORGIVS III DEI GRATIA' (translates to George the Third, by the Grace of God) Obverse relief; (King George III bust, facing right, laurel wreath on head) Reverse text; 'M.B.E.ET.H.REX.F. D.B.ET.L.D. S.R.I.A.T.ET.E' '1793' (translates to: King of Great Britain, France and Ireland, Defender of the Faith, Duke of Brunswick and Lüneburg, Arch-Treasurer and Elector of the Holy Roman Empire) Reverse relief; a spade-shaped image i.e. (Crown with fleer de lies, above Shield with crowned lions in different postures, a harp, and other details)flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, royal mint, british coin, currency, guinea, military guinea, australian currency, british guinea, gold coin, spade guinea, king george iii, george iii, fifth portrait, arms of england and scotland, arms of france, arms of ireland, arms of the house of hanover, coins, gold coins, gold medallion, georgian era, 1793, numismatics, contamination phenomena, gold corrosion, good luck, lucky charm, pendant, lucky coin, trade, loch ard, wreck of the loch ard, 1878, mutton bird island, peterborough, scuba diver, 1980s, guinea coin, gold guinea, shipwreck artefact, relic, julie wilkins -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Sample, Before 1878
... and timber washed ashore in the days following the LOCH ARD shipwreck... in the days following the LOCH ARD shipwreck, adding “but those were ...On a piece of paper subsequently glued near one end of its curved upper face, this length of planed and polished hardwood timber bears the inscription: “A [p]iece of w[r]ec[k] of the Loch Ard wrecked near Sherbroke River”. The timber is carefully worked with rich dark colouring and a uniformly moulded design, suggesting that it was part of a fitting or furnishing that was publicly visible and prominent. If the artefact is what it is declared to be, then it is possible that it formed part of the ship’s railings or companionway stairs. The LOCH ARD was a 1,693 ton, 3 masted barque, built on the Clyde in 1873. In an age of increasing competition for the emigrant passenger trade from steam-driven vessels, special attention was paid to her wooden furnishings and fittings. The Loch Line owners prided themselves on their attractive, distinctively painted, sailing ships. Below decks, where cargo and third class passengers were stowed, was made of iron. But everything above deck, and on show to the saloon and second class passengers, was carved and varnished timber. Captain Daish’s 1878 report for the ship’s underwriters notes “a quantity of general Cargo washed up in a confused mass” in the cove and “a number of Cases, Casks and Bales; also deals and boards floating about in some of the gorges” further west of the shipwreck. Contemporary newspaper accounts also reported a large quantity of cargo and timber washed ashore in the days following the LOCH ARD shipwreck, adding “but those were speedily removed by persons who came down from Port Campbell, Scott’s Creek and other places with carts and pack horses”. The appearance and good condition of this wood artefact, and the aged patina and dated hand-writing style of its pasted on inscription, support the suggestion that it was ‘souvenired’ from the floating debris of the LOCH ARD at or near the 1878 date of its foundering off Mutton Bird Island. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The Loch Ard wreck is of state significance – Victorian Heritage Register S417. However there is a lack of documented provenance that limits the interpretive value of this piece of timber (for example, its potential to interpret nineteenth century souveniring and scavenging from shipwrecks along the south west coast of Victoria). Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. A length of hardwood timber, planed and varnished to smooth finish on three sides, with two unfinished tongues protruding from each end (one broken off), possibly from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The front or upper face is moulded and routed to a regular, linear (skirting board type) design along its entire length, the two sides flat planed. One side contains two inserted dowel rods that have been broken off. The bottom face has not been finished to the same standard. The sample is good quality wood that has retained its density and weight and shows no evidence of having been submerged in seawater for any length of time. Glued on to the upper face of the length of timber near the right hand end is a deteriorated square of paper bearing an inscription. The paper, peeling back and with torn edges, is stuck over an original wood stain but under a subsequent layer of varnish. The faded ink words are indecipherable where paper is missing, but written carefully in an old fashioned cursive script.The inscription on the paper reads: “A [p]iece of w[r]ec[k] of the Loch Ard wrecked near Sherbroke River”. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, nineteenth-century souveniring, shipwreck scavenging, loch line sailing ships, wood sample -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLead shot, Before 1878
... raised from the LOCH ARD shipwreck site by Flagstaff Hill divers... calibre lead shot raised from the LOCH ARD shipwreck site ...The objects comprise a quantity of small calibre lead shot raised from the LOCH ARD shipwreck site by Flagstaff Hill divers in 1976. The Maritime Village’s collection has companion pieces. The three masted, iron hulled, LOCH ARD was wrecked against the tall limestone cliffs of Mutton Bird Island in the early hours of the first of June 1878. Included in her diverse and valuable cargo were 22 tons of lead shot, packed in cloth bags and wooden casks. Bulk quantities of lead shot, uniformly round balls of dull grey metal ranging from 2mm “birdshot” to 8mm “buckshot”, were routinely exported to the Australian colonies. Shot was used mostly as projectiles fired from smooth bored guns to bring down moving targets such as wild ducks and small game. It was also useful as ballast, when a dense, “pourable” weight was required to fill cavities or establish volume within a measuring container. The production of consistently round spheres of lead shot required the pouring of molten metal through a sieve and then a long drop through the atmosphere to a water filled basin for final cooling and collection. This “shot tower” process was first patented by William Watts of Bristol in 1782. His calculation of a 150 feet fall was not only to form evenly spherical droplets through surface tension, but also to provide partial cooling and solidification to each shot before they hit the water below. The value of his innovation was the minimising of indentation and shape distortion, avoiding the expense of re-smelting and re-moulding the lead. Lead shot was already being produced in Australia at the time the LOCH ARD loaded her cargo and left Gravesend on the second of March 1878. James Moir constructed a 157 feet circular stone shot tower near Hobart in 1870, with a peak annual production of 100 tons of lead shot sold in 28 pound linen bags. However colonial demand exceeded this source of local supply. The continued strength of the market for lead shot in the Colony of Victoria prompted substantial investment in additional productive capacity in Melbourne in the next decade. In 1882 Richard Hodgson erected the 160 feet round chimney-shaped Clifton Hill shot tower on Alexandra Parade (VHR H0709) and in 1889 Walter Coop built the 160 feet square tower-shaped Melbourne Central shot tower on La Trobe Street (VHR H0067). At its peak, the Coop Tower produced 6 tons of lead shot per week, or 312 tons per annum. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The shipwreck of the LOCH ARD is of State significance – Victorian Heritage Register S417 Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. A quantity of lead shot pellets retrieved from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. There are 242 loose 2mm pieces and 17 loose 4mm pieces. They are in good condition, with some shape distortion and sedimentary concretion, and shot tower made.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, lead shot, colonial industry, melbourne shot towers, victorian metallurgy, colonial imports -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Earthenware jar, Bailey & Co, circa 1878
... the shipwreck Loch Ard. The jar could have been from the ship's cargo... recovered from the shipwreck Loch Ard. The jar could have been from ...The handmade earthenware jar was one of a group of artefacts in the McCulloch Collection that were recovered from the shipwreck Loch Ard. The jar could have been from the ship's cargo or personal effects. There are other jars in our collection that were recovered from the Loch Ard. The object is now one of the shipwreck artefacts in Flagstaff Hill’s Mc Culloch Collection, which includes items recovered from the wrecks of the Victoria Tower (wrecked in 1869) and Loch Ard (wrecked in 1878). They were salvaged by a diver in the early 1970s from the southwest coast of Victoria. Advanced marine technology had enabled divers to explore the depths of the ocean and gather its treasures before protective legislation was introduced by the Government. The artefacts were donated to Queensland’s Department of Environment and Heritage Protection (EHP) by a passionate shipwreck lover and their locations were verified by Bruce McCulloch. In 2017 the Department repatriated them to Flagstaff Hill where they joined our vast collection of artefacts from Victoria’s Shipwreck Coast. The Loch Ard: - The three-masted, square-rigged iron ship Loch Ard belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. The ship was built in Glasgow in 1873. The Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. The Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo included straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that were intended for display in the 1880 Melbourne International Exhibition, including the famous Loch Ard Peacock. On June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land but visibility was reduced by fog. As it lifted, the sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came much closer than expected. The captain was unable to steer away and the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. The top deck was loosened from the hull, the masts and rigging came down and knocked passengers and crew overboard, and even the lifeboat crashed into the side of the ship and capsized. Of the 54 people on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael. The well-packed Minton porcelain peacock also survived, safe inside its crate. Much of the cargo was washed up, smashed and broken, and some was salvaged. Other cargo is still with the wreck at the base of Mutton Bird Island, now protected by Government law. The artefact is an example of cargo or personal items on board a ship in 1878. It provides a reference point for classifying and dating similar items. This artefact is significant for its association with the sailing ship Loch Ard, one of the best-known, and one of the worst, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from Loch Ard is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history. Container, round brown earthenware jar with a wide mouth, thick lip, a wide neck that tapers slightly inwards towards the shoulder, and a body that tapers slightly inward towards the base. The glazed surface is rough. The variegated colours of the clay also has small dark speckles. There are several chips and dents on the jar. The inscription is stamped into the lower edge. Made by Bailey & Co., England. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.Inscription “Bailey [&] Co / ENGLAND” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, white star line, victorian heritage register, sailing ship loch ard, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, migrant ship 1878, cargo ship 1878, stoneware jar, domestic container, kitchenware, kitchen storage, bailey & co england, shipwreck artefact, wreck dive, mcculloch collection, bruce mcculloch, 1878, sailing ship, earthenware, stoneware, domestic jar -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Lamp Fitting, circa 1878
... in the McCulloch Collection that were recovered from the shipwreck Loch Ard... the shipwreck Loch Ard and were donated together. The fitting could have ...This gas pipe fitting was one of a group of artefacts in the McCulloch Collection that were recovered from the shipwreck Loch Ard and were donated together. The fitting could have been from the ship's cargo or a ship’s fitting. Lamps from this era were fuelled by gas. There are other gas lamp fittings in our collection that were recovered from the Loch Ard The object is now one of the shipwreck artefacts in Flagstaff Hill’s Mc Culloch Collection, which includes items recovered from the wrecks of the Victoria Tower (wrecked in 1869) and Loch Ard (wrecked in 1878). They were salvaged by a diver in the early 1970s from the southwest coast of Victoria. Advanced marine technology had enabled divers to explore the depths of the ocean and gather its treasures before protective legislation was introduced by the Government. The artefacts were donated to Queensland’s Department of Environment and Heritage Protection (EHP) by a passionate shipwreck lover and their locations were verified by Bruce McCulloch. In 2017 the Department repatriated them to Flagstaff Hill where they joined our vast collection of artefacts from Victoria’s Shipwreck Coast. The Loch Ard: - The three-masted, square-rigged iron ship Loch Ard belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. The ship was built in Glasgow in 1873. The Loch Ard made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. The Loch Ard left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo included straw hats, umbrellas, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionery, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that were intended for display in the 1880 Melbourne International Exhibition, including the famous Loch Ard Peacock. On June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land but visibility was reduced by fog. As it lifted, the sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came much closer than expected. The captain was unable to steer away and the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. The top deck was loosened from the hull, the masts and rigging came down and knocked passengers and crew overboard, and even the lifeboat crashed into the side of the ship and capsized. Of the 54 people on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael. The well-packed Minton porcelain peacock also survived, safe inside its crate. Much of the cargo was washed up, smashed and broken, and some was salvaged. Other cargo is still with the wreck at the base of Mutton Bird Island, now protected by Government law. The artefact is an example of cargo or personal items on board a ship in 1878. It provides a reference point for classifying and dating similar items. This artefact is significant for its association with the sailing ship Loch Ard, one of the best-known, and one of the worst, shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from Loch Ard is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the Loch Ard. The Loch Ard collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. It is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history. Brass decorative gas lamp fitting. Two flat arms of different lengths are joined on either side of a fitting that has a fleur-de-lis-like design. The shorter arm has a J-shaped brass pipe fitted to it with a decorative threaded cube joint part way along, and ends with a triangular tap and knob. The longer arm is also J-shaped and ends with a feather design on it. There are remnants of green paint on the cube fittings and the knob. Recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, wreck dive, mcculloch collection, bruce mcculloch, loch ard, 1878, loch line, victorian heritage register, sailing ship, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, migrant ship 1878, cargo ship 1878, lamp fitting, gas lamp fitting, ship’s fitting, ship’s lamp, brass lamp fitting, lighting, domestic lighting, ship’s lighting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePocket Knife, before 1878
... known as Loch Ard Gorge following the shipwreck. Amongst... the shipwreck. Amongst artefacts salvaged from the Loch Ard is the now ...Found on board the "Loch Ard" . 'Loch Ard" left Gravesend, England on 2nd March 1878, under the command of Captain Gibb, bound for Melbourne loaded with passengers and cargo. On June 1st 1878, almost at the end of her journey, she ran into a rocky reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: an apprentice, Tom Pearce and a young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. The wreck of Loch Ard still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island and much of the cargo has been salvaged. Some was washed up into what is now known as Loch Ard Gorge following the shipwreck. Amongst artefacts salvaged from the Loch Ard is the now famous Minton Peacock Statue which was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition to be held in 1880 HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The "Loch Ard" is registered on the National Shipwreck database and is protected as an Historic "Shipwreck. It is one of Australia's and Victoria's most tragic and most famous shipwrecks. The quantity of luxury and commercial items carried as cargo show the type and quality of goods passengers migrating to Australia at that time were bringing with them Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Small pocket knife salvaged from the wreck of the Loch Ard. It has a dark brown cover on one side. Reverse side is only partly there. Both blades are missingflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, pocket knife, knife, tool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Photograph of Loch Ard Gorge. Photograph taken some distance from the Gorge. Three men in the Gorge and outlines of steps can be seen. Right hand side of the photograph is written "Loch Ard Gorge"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, photograph of loch ard gorge, photograph -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePainting
HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Painting of The Loch Ard oil on board depicting wreck. It shows stormy sea and coastline in background. Ship appears to be capsized.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, painting -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Literary Work, Henry Wardsworth Longfellow, The Poetical Works of Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, (short title on cover is ‘Longfellow’s Poetical Works’), 1877
... from the sea at Loch Ard Gorge soon after the shipwreck ...This well-produced but water-damaged book of Longfellows Poetry, was part of the former Warrnambool Mechanics Institute Library and Museum collection. The custody of this collection was assumed by Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in the 1970s. Supporting provenance indicates the book was retrieved from the sea at Loch Ard Gorge soon after the shipwreck of the same name in June 1878. This book was given to the Warrnambool Museum curator Joseph Archibald by its finder, the Warrnambool Standard editor Henry Davis in October 1883. A letter from Mr Davis describing the poignant circumstances of his discovery is also in the Flagstaff Hill collection. A transcript of this letter is displayed next to the book in the Great Circle Gallery at the Maritime Village (reg. no. 2292). The story behind this book prompted Mr Archibald to write to the sole surviving female passenger from the LOCH ARD, Eva Carmichael, asking if the book was hers. Miss Carmichael replied by handwritten letter in January 1884, advising that the volume of poems did not belong to her: “We had a ‘Longfellow’, but our book had a green cover”. This letter is also in the Flagstaff Hill collection (reg. no. 2290.4).The book is rare as it has survived a shipwreck in relatively good condition. It is an example of personal possessions carried by a shipboard passenger in the 1870s. It holds significance for its connection to the renowned poet, Henry Wardsworth Longfellow. The book is important for its probable association with the wreck of the vessel Loch Ard in 1878. The LOCH ARD shipwreck is of State significance and is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register S417. A volume of poetry by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow. It is bound in blue-purple cloth on thick board, with black lettering and curling-vine design, framed by gold border. In the centre of the front cover is a raised smooth-white ellipse with crimped edges, now worn bare but with traces of an original brightly coloured floral design. This white centre of supple leather is also framed by a decorative gold border. The upper case lettering on the front cover reads ‘Longfellow’s Poetical Works’. The edges of the blue material are faded and worn. The pages are corrugated by water damage but their original gold-edged condition is still evident. The front and back covers are scored with singed holes approximately 1.5cm diameter, situated about the centre edge of each side and in roughly corresponding positions. These holes may be from an original book-latch or fastening. However they have since been damaged by a hot piercing object, which has blackened the holes and extended the damage into the enclosed pages. The spine of the book features a stylised oak tree in gold, rising from bared roots to serrated leaves and acorns. The letters “LON[DON]” at the top of the spine and “W.P.NI[MM]O” at the bottom. The book cover has separated from the majority of stitched pages, along with a number of title pages, which are now loosed from the binding. The books condition is fragile from a handling perspective, but stable in terms of further deterioration. ‘Inscribed “Loch Ard June 1 1878” in pencil within ― believed to be a salvage from the shipwreck’ (Mechanics Institute Library auditor, June 1996).warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, longfellow’s poems, loch ard, eva carmichael, warrnambool mechanics institute library, warrnambool museum, joseph archibald, henry davis, william p. nimmo, poetry, heny longfellow, henry wadsworth longfellow, poetical works, 1870s, 1877, longfellow’s poetical works
