Showing 389 items matching "melbourne water supply"
-
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, 1907
This photograph was taken four years after bicycles were purchased by the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) and is a record of the first mode of transport used by their Trained nurses, and a record of the change of head ware needed now bicycles were in use. The uniforms were grey with white collar, belt and cuffs and a red Maltese cross was in the centre of the pith helmet. Prior to the use of bicycles the trained nurses walked to their patients and had become exhausted, particularly in summer. The bicycles were a solution to this problem, and now they could visit more patients and the Society's areas (districts) could be extended. In February 1885, 50 years after Melbourne was founded, it was recognized that nursing care was needed for the sick poor in inner Melbourne. The Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS), the first such Society in Australia, was founded with one Trained nurse, called 'Nurse' in those days, and a second employed six months later. They worked in the now CBD, ie from Spencer Street to Spring Street and from Victoria Parade to Flinders Street. From its inception the Society was at the forefront of health care. They provided high quality nursing care; educated their patients in the curing and prevention of disease; teaching the importance of cleanliness and good nutrition, both by verbal instruction and demonstration, even supplying soup and milk when needed. At that time they walked the streets and lane ways amid the slums of inner Melbourne carrying their nursing bag containing lotion, ointments, powders, liniment, bandages, dressings, a case of spirits, and the Nurse's own clean apron, soap and small towel. They supplied equipment on loan, such as earthenware hot water bottles, splints, urinals, bed pans, bed cradles, feeding mugs, and air-cushions as well as providing blankets, clean bed linen, and nightdresses as necessary. Trained Midwives began home births in late 1893 taking midwifery bundles and providing clothes for the babe and mother as needed. This was arduous work, particularly in the heat of summer. Permission to use bicycles was given to the Nurses in 1898 and the Society decided to purchase their own in 1903. A business man offered ‘new free wheel’ bicycles at £13 each which included maintenance for one year. Bells and wooden frames were added, at a cost of £5 per frame, so the Nurses could carry extra equipment. Nurses’ bags were strapped to the handlebars. Soup was made for those in need 2-3 times a week and if patients could not arrange to have it collected the soup was delivered by the Nurses on their bicycles. The use of bicycles caused a change in uniform, with white pith helmets, and veils covering them and tied under their chin, now being used. The Nurses provided high quality nursing care to a range of people, often in destitute situations, some lying on rags on the floor as they had no bed, others with just a bed and maybe a thin blanket, a chair and nothing else. Their ages ranged from babes, children, adults to the elderly. The Nurses gave medications as ordered by a Doctor, dressed wounds e.g. to the injured, and surgical cases, and to those with leg ulcers; attended to patients with ‘surgical ailments’ such as ‘hip disease’; gave care to those with acute illnesses such as bronchitis, pleurisy, pneumonia, measles, and scarlet fever, as well as those with chronic illnesses such as consumption (tuberculosis), heart disease, arthritis, cancer, debility, neuritis and paralysis. Over the years the Nurses complained that their veils became wet in the rain and asked for a change of uniform but this did not occur until 1921. Bicycles continued to be used in inner areas until 1945. Black and white photo of a group of ten (one partially hidden at rear) Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) trained nurses, with each standing with their bicycles in front of a spiked metal fence.The Nurses are wearing their MDNS uniform long grey frocks with white collar, cuffs and belt and white pith helmets with a central Maltese cross. Nursing bags are strapped to five of the bicycles. A large pedestal urn is seen to the left behind the fence between the 3rd and 4th nurse. Bushes and trees are seen in the background. melbourne district nursing society, mdns, nurses, uniforms, mdns transport, mdns equipment, rdns, royal district nursing service -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, c.1985
The RDNS Sisters are both holding the 1st day Cover Envelope issued by the Australian Postal Department in 1985 to commemorate the founding of the Melbourne District Nursing Society on the 17th of February 1885. A stamp is in the right hand top corner of the envelope. The main body of the stamp is pale blue. On the top of the stamp, written in deeper blue/grey, are the words "Centenary of District Nursing Services 1985" Below this, and to the right, is a pale bone colour original sign on a metal fence which reads, in white capital letters, "Melbourne District Nursing Society" Standing on the left in the foreground is a MDNS Trained nurse (Nurse) in her long grey uniform frock with white collar, cuffs and belt. She is wearing a grey helmet style hat which has a white hat band with a red Maltese cross in the centre. Her black shoes can also be seen. She is holding a bicycle; only the front wheel and part of the frame and the handlebars, which have a brown nursing bag strapped to them, can be seen, The nursing bag and handlebars cover part of the MDNS sign. At the bottom of the stamp, on a strip of white background, are the words in capital letters "Australia 33c". Below the stamp is a rectangular1st mark. On the left half of the envelope are some sketches of several two storey buildings either side of a set of steps. Some adults and children are standing on the steps as well as in the foreground; some are sketched and others dressed in various coloured clothing. In the foreground right in front of steps, stands a lady with her hair drawn up and wearing along grey frock and white apron; partly seen against her right side is a small child dressed in brown. Sister Willie Fleming is the Supervisor of the RDNS Sunshine Centre and Sister Phillipa Kariko is Supervisor of Essendon Centre. They are wearing their RDNS uniforms of white short sleeve blouses under royal blue V neck tunic style frocks. The RDNS insignia is round and has royal blue writing on a white background. In Melbourne in 1885 it was recognized that skilled nursing was needed to care for the sick poor in their own homes. On the 17th of February a meeting was held with prominent Melbourne citizens, five gentlemen and fourteen ladies. ‘Dr. Caffyn and Rev. Charles Strong explained the objects and scope of District Nursing Societies that had been formed in towns in UK’. On that day the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) was founded, the first District Nursing Service in Australia. Subsequent meetings were held to form a Committee and to draw up a Code of Rules of the Society. It was decided only nurses who had attended a Nurses Training School at a Hospital and were fully qualified would be employed by the Society, and that the Nurses would keep a daily journal of their work. After interviewing several candidates, the first Nurse, Mrs. Ferguson, was employed with a salary of £100 per annum and commenced work on the 1st of May 1885. She was employed for three months initially, but this was soon extended, “on the understanding she will make arrangements to live in the more immediate vicinity of her district”. A Doctor was consulted before any person was seen. In rotation, a member of the Superintendence Sub-Committee supervised the Nurse’s visits and could assist to alleviate some of the poor social conditions they found. Though only Trained nurses were employed, the term ’Nurse’ was used in those days, not the term ‘Sister’ that is used these days. A second Trained nurse, Mrs. Joanna Cannon, was employed in late 1885, with a trial period of six months which was extended. The two Nurses worked in the now CBD, ie from Spencer Street to Spring Street and from Victoria Parade to Flinders Street. At that time they walked the streets and lane ways amid the slums of inner Melbourne carrying their nursing bags containing lotion, ointments, powders, liniment, bandages, dressings, a case of spirits, and the Nurse's own clean apron, soap and small towel. They supplied equipment on loan, such as earthenware hot water bottles, splints, urinals, bed pans, bed cradles, feeding mugs, and air-cushions as well as providing blankets and clean bed linen, and nightdresses as necessary. From its inception the Society was at the forefront of health care and liaised with Doctors. They provided high quality nursing care to a range of people, often in destitute situations, some lying on rags on the floor as they had no bed, others with just a bed and maybe a thin blanket, a chair and nothing else. Their ages ranged from babes, children, adults to the elderly. The Nurses gave medications as ordered, dressed wounds e.g. to the injured, and surgical cases, and to those with leg ulcers; attended to patients with ‘surgical ailments’ such as ‘hip disease’; gave care to those with acute illnesses such as bronchitis, pleurisy, pneumonia, measles, and scarlet fever, as well as those with chronic illnesses such as consumption (tuberculosis), heart disease, arthritis, cancer, debility, neuritis and paralysis. They educated their patients, and their carers, in the curing and prevention of disease; teaching the importance of hygiene, cleanliness, ventilation and good nutrition. They taught them, by verbal instruction and demonstration, how to make poultices, to make and apply bandages, apply medical appliances such as splints; and the Nurses supplied milk, beef tea and they cooked soup when needed. As the work increased a third Nurse was employed but this was arduous work, particularly in the heat of summer and many Nurses only remained with the Society for several months. A Midwifery Service commenced in August 1893 with Nurse Fowler the first trained Midwife. She had previously worked with the Society carrying out General nursing. The Society expanded its areas using public transport and with the Society purchasing bicycles in 1903, before procuring its first cars to cope with the influx of patients during the Spanish influenza epidemic in 1919, though these were sold in 1927 due to their poor condition..A Motor Auxiliary was formed in 1929 to take Sisters to patients, and some Sisters used their own cars; even a motorcycle was used by one Sister in 1933. All these forms of transport were intermingled and in the early 1950s, and now as Melbourne District Nursing Service, seven Ford Prefect cars were bought followed by twelve Ford Anglia vehicles in 1955. Having received Royal patronage; the now Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) had its own fleet of Holden vehicles by the mid 1960s and the Motor Auxiliary ceased operating in 1971 as by then all staff employed were required to have a driving licence. Seat-belts had been introduced to Victoria in 1959 and District fitted them to their cars from 1962, even though they did not become compulsory until 1970. The Holden vehicles were replaced with grey Holden Torana vehicles. After several years the fleet was changed to white Toyota Corolla vehicles. The Melways Directory of maps was introduced in 1966, which was a boon to the Sisters, though it was a few years before it went beyond Seville, so a large paper map was used by the Sisters visiting patients in the areas passed Seville. By 2009 there were 598 cars in the fleet and the Sisters travelled 9 million 200,000 kilometres – this is equivalent to 12 trips to the moon and back. Over its years of expansion the RDNS Trained nurses (Sisters), continued to visit patients in their homes and gave best practice care in many fields of nursing, and to people of many cultures. Initial visits not only assessed the specific nursing situation but the situation as a whole. Their patients ranged in age from babes, children, adults to the elderly and referrals were taken from Hospitals, General Practitioners and allied Health facilities. Some of the care the Sisters provided is as follows: – Post-Natal care given to mother and babe, Wound Care following various types of surgery, accidents, burns, cancer, leg ulcers etc. Supervising and teaching Diabetic Care, including teaching and supervising people with Diabetes to administer their own Insulin, and administering Insulin to those unable to give their own injections. Administering other injections and setting up weekly medication boxes. The Sisters performed Catheterizations on adults suffering from conditions such as Quadriplegia, Paraplegia, Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Motor Neurone Disease (MND) and Guillan-Barre Syndrome, and when required at school on children for e.g. those with Spina Bifida. The Sisters visited those requiring Cystic Fibrosis support and care; those requiring Haemo-Oncology care, including visiting children at school; those requiring Home Enteral Feeding care, and those requiring IV therapy at home and home Dialysis. Palliative Care was given including pain relief with the use of syringe drivers, personal care as needed, and advice and support to both patient and family. The Sisters provided Stoma management to those needing Urostomy, Ileostomy and Colostomy care and those requiring Continence care. HIV/AIDS nursing care was provided; visits to Homeless Persons were made. Personal care was given to patients ranging in age and with varying mobility problems, such as Amputees, those with MS, MND, Guillan-Barre Syndrome, Poliomyelitis, Quadriplegia, Paraplegia, Acquired Brain Injury, to those following a Cerebrovascular Accident (Stroke), those with severe Arthritis and those with a form of Dementia. When necessary the elderly were assisted with personal care and advice given on safety factors with the use of hand rails, bath or shower seats, and hand showers. Rehabilitation with an aim towards independence remained at the forefront of the Sister’s minds and when possible using aids and instruction on safe techniques enabled the person to become fully independent. All care included giving advice and support to the patient and their Carers. The Sisters liaised with the persons Doctor, Hospital and allied Health personal when necessary. On the left of the black and white photograph is Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS), Sister Willie Fleming, who has curly blonde hair, and on the right, Sister Phillipa Kariko, who has short dark hair. They are standing outside Essendon RDNS Centre.. They are both wearing their RDNS summer uniform of dark V neck tunic style frocks, with emblazoned RDNS insignia on its upper left, over short sleeve white blouses, Each are holding an envelope with writing, sketched buildings and figures on the envelopes left side, and a stamp is on the upper right corner. Below the stamp is writing in a rectangle. Behind the Sisters is a brick wall with them hiding some of the white capital letters of the words 'District Nursing Service' and 'Essendon Centre'. Windows and part of the fascia of the building is seen behind this.Handwritten informationmelbourne district nursing society, melbourne district nursing service, mdns, royal district nursing service, rdns, rdns centre, sister willie fleming, sister phillipa kariko, rdns 1st day cover centenary envelope -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
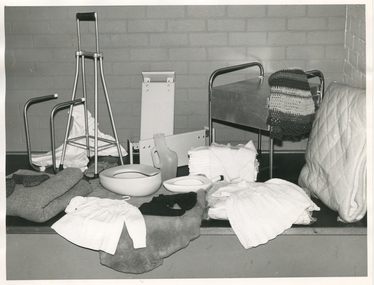
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Photograph, black and white, Barry Sutton, 1973
The equipment items in this photograph are loaned out to Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) patient's to use in their homes. They are returned to RDNS and sterilized, or cleaned with disinfectant, whichever is appropriate, once they are no longer required. The material items are given to patient's as required. Many of these items are made and donated by RDNS Auxiliary members. From its inception in 1885, the two Trained nurses (Nurses) of the Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) worked in the now CBD, ie from Spencer Street to Spring Street and from Victoria Parade to Flinders Street. At that time they walked the streets and lane ways amid the slums of inner Melbourne carrying their nursing bags containing lotion, ointments, powders, liniment, bandages, dressings, a case of spirits, and the Nurse's own clean apron, soap and small towel. They supplied equipment on loan, such as earthenware hot water bottles, splints, urinals, bed pans, bed cradles, feeding mugs, and air-cushions as well as providing blankets and clean bed linen, and nightdresses and clothes as necessary. The Society was at the forefront of health care and continued to liaise with Doctors as the Society expanded. The Nurses provided high quality nursing care to a range of people, often in destitute situations, some lying on rags on the floor as they had no bed, others with just a bed and maybe a thin blanket, a chair and nothing else. Their ages ranged from babes, children, adults to the elderly. The Nurses gave medications as ordered, dressed wounds e.g. to the injured, and surgical cases, and to those with leg ulcers; attended to patients with ‘surgical ailments’ such as ‘hip disease’; gave care to those with acute illnesses such as bronchitis, pleurisy, pneumonia, measles, and scarlet fever, as well as those with chronic illnesses such as consumption (tuberculosis), heart disease, arthritis, cancer, debility, neuritis and paralysis. They educated their patients, and their Carers, in the curing and prevention of disease; Over the years items were given and equipment was loaned and demonstrated to patients, and if appropriate, to their family members to enable them to care for their loved ones in their homes. The Trained nurses had the rehabilitation of their patients in the forefront of their minds to ensure they were able to live as independently as possible in their own homes. As the years passed the Trained nurses changed from being called 'Nurse' to 'Sister' and the Society changed its name. In the 1970s, now with Royal patronage, and known as Royal District Nursing Service ( RDNS), they contracted a Private and then employed, a Physiotherapist who taught RDNS Sisters the correct transferring techniques, including the use of a hoist when this became available. RDNS Sisters taught and used these techniques in patient’s homes to undertake safe transfer of the patient and to reduce physical strain on RDNS nursing staff and family members. Each RDNS Centre had a room or shed where equipment for loan was kept, and Headquarters also kept additional equipment which could be transported to Centres as required. This black and white photograph shows some of the equipment loaned, along with some to be given, to Royal District Nursing Service (RDNS) patients as required. Rear L-R - a white long nightdress with dark embroidery and buttons on the front and embroidery on the edge of the short sleeves. Next are two wooden bath seats; a square metal commode with lid and with its round legs extended to form handles on the left and right sides. A folded dark and white striped crocheted rug hangs over one of the handles. In the centre L-R, is a metal bed cradle, a metal 4 prong walking stick, bed pans, male urinal, stack of nappies with a white child's knitted jumper hanging over them, and a doona. In the front, L-R is a grey blanket, dark coloured bed socks, a sheepskin with a white smocked baby dress sitting on it, and a white babies nightgown on a clear plastic covered white bundle. A black mat sits under these items and a cream brick wall is in the background. Barry Sutton LS 47royal district nursing service, rdns, rdns equipment, rdns auxiliaries -
 Melton City Libraries
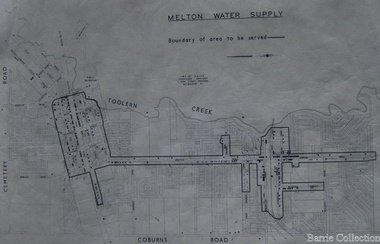
Melton City LibrariesMap, Melton Water Supply, Unknown
The development that had arguably the greatest impact in encouraging population growth in the shire during this period, was the establishment of a reliable water supply for the district. This had been a major concern of the local community for over 100 years, since the Melton township was first founded. Despite various schemes over the years to create a reliable water supply, the district was still dependent on bores, wells and tanks when the Melton Waterworks Trust was established in 1961 to address Melton’s water woes. With the opening of the Djerriwarrh Dam in December 1963, the shire’s residents finally had access to a reticulated water supply.Map shows the boundary of the area where the water will be serviced in the towncouncil -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesDocument, Minns Family Reunion, 2004
"A perpetual spring in the adjacent creek provided a steady supply of fresh water to the site on which the homestead is built. Although we can not be certain of the identity of the builder, the first stage of ‘The Willows’ homestead appears to have been constructed in the mid 1850s. The house is situated on Crown Allotment No.1 (No Section), Parish of Kororoit, an allotment of 5 acres 3 roods 4 perches. Although it had surveyed the land, the Crown did not offer it for sale until 22nd November 1861, at which time it was purchased by Charles March Williams. (Although the property is directly opposite and immediately adjacent to the Township of Melton, and was sold as ‘Suburban Allotment 33’, it was situated within the Shire of Braybrook rather than the Shire of Melton until 1917.) Considerable improvements had taken place on the land prior to the Crown sale. When CM Williams purchased the allotment in November 1861 he paid £23.5.0 for the land itself, and valued the improvements at £400. Even allowing for some exaggeration by Williams, this is an extremely high valuation for improvements, and must have included a house. Some local research has claimed that in 1858 Williams had taken over the interest of a Mr Parkinson in the property, and that Parkinson built the house upon taking possession of the land c.1855. It was definitely built by 1861, when a map shows a square building on the site marked as ‘House’. The property is important in the district for its association with the establishment of the pound. The district pound had been established in 1854, when George Scarborough of Mount Cottrell (Mt Cottrell Road, south of Greigs Road) was appointed pound-keeper. Scarborough resigned in 1857. The pound was moved to Melton following agitation from local farmers and Charles March Williams appointed pound-keeper on 26th April 1858. Williams, the son of a doctor, had been born in London. Reminiscences of local residents of the time, as recorded in the Express newspaper, note Williams’ success in breeding horses on the property. Sales of up to 60 guineas were noted. Whether this was from Williams’s own stock or from unclaimed pound stock is not made clear. Williams appeared before a government inquiry in 1860 and advocated registration of all stock brands in the State. Williams died in 1862 leaving a widow, Catherine, and five living children aged 15 years to five months. At the time of his death Williams had entered negotiations with one Matthew Devenish and had a mortgage of £100 on allotments 1 and 2, Parish of Kororoit. Catherine Williams was appointed pound-keeper on 2 September 1863, with her eldest son Charles as her assistant. Her tenure was short for on 22nd March 1864 George Minns senior paid Matthew Devenish £135 for allotments 1 and 2 Parish of Kororoit (considerably less than Williams had claimed the property was worth in 1861) and on the same day paid William Tullidge £45 for the adjoining allotments 3 and 4. In April 1867, James Ebden Minns, the newly married son of George senior became the owner of The Willows property having entered into a mortgage arrangement with his father to the extent of £200. At the time George Minns was residing in Kaarimba having left Melton in 1867 for a short trip to England and upon his return having taken up a selection in the Kaarimba district with his son Frederick who had a hotel licence there. James paid out the mortgage on 2-1-1873. James Minns was appointed pound-keeper in 1872; in 1885 the pound was moved elsewhere and Minns purchased the old pound site and added it to his farm. The Willows residence underwent a major change about this time. A two room extension, similar in style but with a lower elevation was added to the original rear of the house with a chimney matching the distinctive originals. Window arrangements did not match the original but became a feature of the façade when the new addition became the front of the building. Six buttresses were attached to the east and west walls of the old building, two to the south wall and the whole rendered with mortar to give the appearance of dressed stonework around the windows. Galvanized iron was placed over the shingles and a verandah added on three sides. By 1876 The Willows was the homestead for a thriving mixed farm of 340 acres of which 156 was rented from a H. Ruck. In October of that year the Australasian travelling reporter visited and reported on the property. In common with the nearly every other property in the district the farm had ‘recently’ (generally within the last two years) abandoned cultivation of crops, and turned over completely to cattle pasture. Butter making was the principal occupation of the farm, which had about 50 head of cattle, a large proportion of which were milking cows. The reporter also noted that a ‘large number of pigs are kept upon this farm and are found to be very profitable stock’. Their manure was used in an orchard and garden in which ‘large quantities of lucerne and prairie grass are grown for the use of stock when ordinary feed is scarce’. Two bores attached to deep brick lined wells supplied water for the house in addition to the farm. A commodious timber barn and necessary sheds had also been constructed. Access to the property was improved following the construction of the bluestone ford across the creek c.1887, when the recreation ground came into use. Prior to this date it may have been that the crossing referred to as ‘Mr Minns bridge’ was used. This appears to have been a flimsy structure and has but two references in Council reports in the Melton Express in the 1880’s. It is believed that in the late 1890’s a timber building was added near the rear of the building to house a kitchen, ablutions and laundry rooms and rooms for seasonal workers. This was attached to the house by means of a trellised walkway using the original front entry to the house (long since the back door). A photograph of this building appears in a local history of Melton. This was demolished in recent decades during the period when the house was tenanted (after the Minns family had left). James Minns son, George, took over the property following his marriage to Alice Walsh in 1903. James and Caroline moved into a house on the former JH Games property at the eastern end of Henry Street. George held the position of Shire Secretary for Melton for 40 years. He was a most prominent member of the community being Secretary to, among others, the Melton Coursing Club, the Shooting Club and the Cemetery Trust. He also rode with the hunting parties who sported across the Plains and were entertained at Mount Kororoit. George and Alice had one son, Norman who followed his father into local government and became Secretary of the Shire of Werribee completing a record term in this position. George retired to Werribee in 1951, where he died in 1965. The National Trust records note that James Ebden Minns and his sons were ‘leading men of the district, Justices of the Peace, and Shire Councillors’. It claims that Sir Thomas Bent was a frequent visitor. The Willows passed into the hands of George’s grandson, Bruce Minns and the property was let for a number of years. In the 1960s it became vacant and was subject to vandalism. Major structural problems arose with the part demolition of the roof, the loss of windows and doors and holes dug into and under the floorboards. The outbuildings were particularly targeted. Following widespread public support, the Shire of Melton purchased the house, with 3.75 acres of land, in 1972. In 1975 the Shire of Melton and the Melton and District Historical Society were successful in nominating the building for National Trust classification, and then the Australian Heritage Commission’s Register of the National Estate. The AHC particularly noted its ‘townscape importance’. It was envisaged that the farmhouse would form ‘a picturesque centrepiece to Melton’s planned … historical park, along with Dunvegan bluestone cottage … and similar structures as they become available.’ In a time of great Melton’s ‘satellite city’ development the Council spelt out its broader vision in its submission to the AHC: ‘Melton is destined to become, by the end of the present century, a city of between 75,000 and 100,000 people. Significant relics of the past, such as ‘The Willows’, regrettably will be rare in that situation. It is essential that sufficient tangible links with Melton’s pioneering days remain to promote in the new community a sense of history and continuity’. Under the direction of ‘The Willows’ Restoration Committee and consultant architect John Hitch, all outbuildings, with the exception of the garage and toilet, were demolished and the dwelling house restored. Finances were provided by the Shire of Melton and the National Estate Grants Program, and considerable amount of voluntary labour was provided by the local community. The orchard was removed, and remaining wooden buildings were relocated to provide an open vista for visitors to the Park. The property was furnished with donations from district families keen to preserve this example of pioneer life in the area. The Willows became the headquarters of the Melton and District Historical Society". Invitation to the family reunion at the Willowslocal identities, pioneer families -
 Tarnagulla History Archive
Tarnagulla History ArchiveTelegram: Mayor of Tarnagulla to the Minister of Mines, Melbourne, 22nd February 1865
Murray Comrie Collection. A telegram sent from James Ray, Mayor of Tarnagulla to the Minister for Mines, Melbourne on 22nd February 1865. Reads: "On behalf of the people of Tarnagulla I have to ask that the permission granted to two miners to draw off water from the Public Reservoir be suspended until a petition now in course of signatures by the miners can be forwarded. The public here have no other water supply within five miles."tarnagulla, post office, telegrams, minister mining, mining, water, reservoir, recreation reserve, resources -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesPhotograph, Construction of Dam Wall- Melton Water Supply, 1963
Photographs of the construction of the dam wall for Melton's water supplylocal significant events, council, local architecture, local identities -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Administrative record - Warrnambool Water Trust Notebook, late 19th century (1892-1900)
This notebook appears to be the Warrnambool Water Trust Records of two contracts in 1892 . (The reference is written as 'W.W.Trust'.) The first contract, with the contractors, Coates and Reed, is for the excavation for settling tanks and clear water basin and a reservoir in Liebig Street and there are 60 pages giving details of these works - labour, masonry, concreting, fencing etc. The second contract with the contractor, William Kellas, is for the erection of a cottage and an engine shed and boiler room (7 pages). The Warrnambool Water Trust was set up in 1891 and the first project was the supply of water from the Merri River near Wollaston to a reservoir and tower in Liebig Street and this notebook concerns some details of this early water supply scheme. This notebook is of some interest as it supplies details of a late 19th century Warrnambool water supply scheme and so should be of value to local history researchers This is a notebook with a red leather cover and pages with printed headings and ruled red lines. The pages contain handwriting in black ink. The cover has a label (partly torn) with handwriting.Returns Contracts 1 & 2warrnambool water supply, warrnambool water board, 19th century water in warrnambool -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesNewspaper - Newspaper Cutting, The Leader, Horticultural Notes, 1893
Copy of article in "The Leader" (Melbourne) on 7 January, 1893. Yan Yean water supplied to Burnley Gardens.the leader, yan yean, reservoir, irrigation, burnley gardens -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Art Gallery at Clifton Pugh's Artists' Colony, Dunmoochin, Barreenong Road, Cottles Bridge, 5 February 2008
Art Gallery with mural painted by Clifton Pugh (1924-1990) at his Artists' Colony, Dunmoochin, Barreenong Road, Cottles Bridge. Following military service in the second world war, Clifton Pugh studied under artist Sir William Dargie at the National Gallery School in Melbourne as well as Justus Jorgensen, founder of Montsalvat. For a while he lived on the dole but also worked packing eggs for the Belot family saving sufficient to purchase six acres (2.4 ha) of land at Barreenong Road, Cottles Bridge. He accumulated more land and persuaded several other artists and friends to buy land nearby, resulting in a property of approximately 200 acres, stablishing it as one of the first artistic communes in Australia alongside Montsalvat in Eltham. It was around 1951 that Pugh felt he had '"done moochin' around" and so the name of the property evolved. He bought timber from Alistair Knox to build his house on the crest of a hill. Inspired by local goldminer's huts, it was a one room wattle-and-daub structure with dirt floor. Over the years it expanded with thick adobe walls made from local clay, high ceilings and stone floors. All materials other than the local earth were sourced from second hand materials, most found at wreckers' yards. Artists from across the nation were drawn to Dunmoochin, with several setting up houses and shacks on the property, maintaining their independence but sharing their artistic zeal. Artists who worked or resided at Dunmoochin included Mirka Mora, John Perceval, Albert Tucker, Fred Williams, Charles Blackman, Arthur Boyd and John Olsen. In 2002, Pugh's house along with its treasure trove of art and a library of some 20,000 books was destroyed by fire. Traces of Pugh's home remain with the presence of the Victorian doorframe archway with leadlight of intricate design, procured from a demolished Melbourne mansion; and two bronze life-sized female statues created by Pugh and cast by Matcham Skipper. In place of Pugh's house rose two double-storey mud-brick artists' studios topped with corrugated iron rooves curved like the wings of a bird with accommodation for seven. The original studios, gallery and other buildings survived the fire. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p153 It’s not surprising that artist Clifton Pugh was drawn to Cottles Bridge to establish his artists’ colony Dunmoochin. Undisturbed by the clamour of modern life at Barreenong Road, Pugh was surrounded by the Australian bush he loved, and where his ashes were later scattered. The 200 acres (81ha) of bushland, broken by glimpses of rolling hills, has more than 50 species of orchids and Pugh shared his property with native animals including kangaroos, emus, phascogales, wombats, and diverse bird life. Pugh encouraged these creatures to join him in the bush by creating, with Monash University, a holding station where the animals were raised. Dunmoochin inspired Pugh for such paintings as in a book on orchids and the Death of a Wombat series.1 But his love for the bush was accompanied by the fear that Europeans were destroying it and much of his painting illustrated this fear and his plea for its conservation.2 However it was his house rather than the surrounding bush that was to be destroyed. Tragically in 2002 Pugh’s house, with its treasure of art and library of 20,000 art books, was destroyed by fire. Traces of the beauty of Pugh’s home still remain, however, in the magnificent Victorian doorframe archway with leadlight of intricate design procured from a demolished Melbourne mansion; and two bronze life-sized female statues created by Pugh and cast by Matcham Skipper. Now in place of Pugh’s house, are two double-storey mud-brick artists’ studios topped with corrugated roofs curved like birds’ wings, with accommodation for seven. The original studios, gallery and other buildings remain.3 Pugh grew up on his parents’ hobby farm at Briar Hill and attended the Briar Hill Primary School, then Eltham High School and later Ivanhoe Grammar. At 15 he became a copy boy for the Radio Times newspaper, then worked as a junior in a drafting office. Pugh was to have three wives and two sons. After serving in World War Two in New Guinea and Japan, Pugh studied under artist Sir William Dargie, at the National Gallery School in Melbourne.4 Another of his teachers was Justus Jörgensen, founder of Montsalvat the Eltham Artists’ Colony. Pugh lived on the dole for a while and paid for his first six acres (2.4ha) at Barreenong Road by working as an egg packer for the Belot family. Pugh accumulated more land and persuaded several other artists and friends to buy land nearby, resulting in the 200 acre property. They, too, purchased their land from the Belot family by working with their chickens. Around 1951 Pugh felt he had ‘Done moochin’ around’ and so the name of his property was born. Pugh bought some used timber from architect Alistair Knox to build his house on the crest of a hill. Inspired by local goldminers’ huts it was a one-room wattle-and-daub structure with a dirt floor. It was so small that the only room he could find for his telephone was on the fork of a tree nearby.5 Over the years the mud-brick house grew to 120 squares in the style now synonymous with Eltham. It had thick adobe walls (sun-dried bricks) made from local clay, high ceilings and stone floors with the entire structure made of second-hand materials – most found at wreckers’ yards. Pugh’s first major show in Melbourne in 1957, established him as a distinctive new painter, breaking away from the European tradition ‘yet not closely allied to any particular school of Australian painting’.6 Pugh became internationally known and was awarded the Order of Australia. He won the Archibald Prize for portraiture three times, although he preferred painting the bush and native animals. In 1990 not long before he died, Pugh was named the Australian War Memorial’s official artist at the 75th anniversary of the landing at Gallipoli. Today one of Pugh’s legacies is the Dunmoochin Foundation, which gives seven individual artists or couples and environmental researchers the chance to work in beautiful and peaceful surroundings, usually for a year. By November 2007, more than 80 people had taken part, and the first disabled artist had been chosen to reside in a new studio with disabled access.1 In 1989, not long before Pugh died in 1990 of a heart attack at age 65, he established the Foundation with La Trobe University and the Victorian Conservation Trust now the Trust for Nature. Pugh’s gift to the Australian people – of around 14 hectares of bushland and buildings and about 550 art works – is run by a voluntary board of directors, headed by one of his sons, Shane Pugh. La Trobe University in Victoria stores and curates the art collection and organises its exhibition around Australia.2 The Foundation aims to protect and foster the natural environment and to provide residences, studios and community art facilities at a minimal cost for artists and environmental researchers. They reside at the non-profit organisation for a year at minimal cost. The buildings, some decorated with murals painted by Pugh and including a gallery, were constructed by Pugh, family and friends, with recycled as well as new materials and mud-bricks. The Foundation is inspired by the tradition begun by the Dunmoochin Artists’ Cooperative which formed in the late 1950s as one of the first artistic communes in Australia. Members bought the land collaboratively and built the seven dwellings so that none could overlook another. But, in the late 1960s, the land was split into private land holdings, which ended the cooperative. Dunmoochin attracted visits from the famous artists of the day including guitarists John Williams and Segovia; singer and comedian Rolf Harris; comedian Barry Humphries; and artists Charles Blackman, Arthur Boyd and Mirka Mora. A potters’ community, started by Peter and Helen Laycock with Alma Shanahan, held monthly exhibitions in the 1960s, attracting local, interstate and international visitors – with up to 500 attending at a time.3 Most artists sold their properties and moved away. But two of the original artists remained into the new millennium as did relative newcomer Heja Chong who built on Pugh’s property (now owned by the Dunmoochin Foundation). In 1984 Chong brought the 1000-year-old Japanese Bizan pottery method to Dunmoochin. She helped build (with potters from all over Australia) the distinctive Bizan-style kiln, which fires pottery from eight to 14 days in pine timber, to produce the Bizan unglazed and simple subdued style. The kiln, which is rare in Australia, is very large with adjoining interconnected ovens of different sizes, providing different temperatures and firing conditions. Frank Werther, who befriended Pugh as a fellow student at the National Gallery Art School in Melbourne, built his house off Barreenong Road in 1954. Werther is a painter of the abstract and colourist style and taught art for about 30 years. Like so many in the post-war years in Eltham Shire, as it was called then, Werther built his home in stages using mud-brick and second-hand materials. The L-shaped house is single-storey but two-storey in parts with a corrugated-iron pitched roof. The waterhole used by the Werthers for their water supply is thought to be a former goldmining shaft.4 Alma Shanahan at Barreenong Road was the first to join Pugh around 1953. They also met at the National Gallery Art School and Shanahan at first visited each weekend to work, mainly making mud-bricks. She shared Pugh’s love for the bush, but when their love affair ended, she designed and built her own house a few hundred yards (metres) away. The mud-brick and timber residence, made in stages with local materials, is rectangular, single-storey with a corrugated-iron roof. As a potter, Shanahan did not originally qualify as an official Cooperative member.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, art gallery, clifton pugh, dunmoochin, cottlesbridge, cottles bridge, barreenong road -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Doorway of Clifton Pugh's former house at Dunmoochin, Barreenong Road, Cottles Bridge, 5 February 2008
Following military service in the second world war, Clifton Pugh studied under artist Sir William Dargie at the National Gallery School in Melbourne as well as Justus Jorgensen, founder of Montsalvat. For a while he lived on the dole but also worked packing eggs for the Belot family saving sufficient to purchase six acres (2.4 ha) of land at Barreenong Road, Cottles Bridge. He accumulated more land and persuaded several other artists and friends to buy land nearby, resulting in a property of approximately 200 acres, stablishing it as one of the first artistic communes in Australia alongside Montsalvat in Eltham. It was around 1951 that Pugh felt he had '"done moochin' around" and so the name of the property evolved. He bought timber from Alistair Knox to build his house on the crest of a hill. Inspired by local goldminer's huts, it was a one room wattle-and-daub structure with dirt floor. Over the years it expanded with thick adobe walls made from local clay, high ceilings and stone floors. All materials other than the local earth were sourced from second hand materials, most found at wreckers' yards. Artists from across the nation were drawn to Dunmoochin, with several setting up houses and shacks on the property, maintaining their independence but sharing their artistic zeal. Artists who worked or resided at Dunmoochin included Mirka Mora, John Perceval, Albert Tucker, Fred Williams, Charles Blackman, Arthur Boyd and John Olsen. In 2002, Pugh's house along with its treasure trove of art and a library of some 20,000 books was destroyed by fire. Traces of Pugh's home remain with the presence of the Victorian doorframe archway with leadlight of intricate design, procured from a demolished Melbourne mansion; and two bronze life-sized female statues created by Pugh and cast by Matcham Skipper. In place of Pugh's house rose two double-storey mud-brick artists' studios topped with corrugated iron rooves curved like the wings of a bird with accommodation for seven. The original studios, gallery and other buildings survived the fire. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p155 It’s not surprising that artist Clifton Pugh was drawn to Cottles Bridge to establish his artists’ colony Dunmoochin. Undisturbed by the clamour of modern life at Barreenong Road, Pugh was surrounded by the Australian bush he loved, and where his ashes were later scattered. The 200 acres (81ha) of bushland, broken by glimpses of rolling hills, has more than 50 species of orchids and Pugh shared his property with native animals including kangaroos, emus, phascogales, wombats, and diverse bird life. Pugh encouraged these creatures to join him in the bush by creating, with Monash University, a holding station where the animals were raised. Dunmoochin inspired Pugh for such paintings as in a book on orchids and the Death of a Wombat series.1 But his love for the bush was accompanied by the fear that Europeans were destroying it and much of his painting illustrated this fear and his plea for its conservation.2 However it was his house rather than the surrounding bush that was to be destroyed. Tragically in 2002 Pugh’s house, with its treasure of art and library of 20,000 art books, was destroyed by fire. Traces of the beauty of Pugh’s home still remain, however, in the magnificent Victorian doorframe archway with leadlight of intricate design procured from a demolished Melbourne mansion; and two bronze life-sized female statues created by Pugh and cast by Matcham Skipper. Now in place of Pugh’s house, are two double-storey mud-brick artists’ studios topped with corrugated roofs curved like birds’ wings, with accommodation for seven. The original studios, gallery and other buildings remain.3 Pugh grew up on his parents’ hobby farm at Briar Hill and attended the Briar Hill Primary School, then Eltham High School and later Ivanhoe Grammar. At 15 he became a copy boy for the Radio Times newspaper, then worked as a junior in a drafting office. Pugh was to have three wives and two sons. After serving in World War Two in New Guinea and Japan, Pugh studied under artist Sir William Dargie, at the National Gallery School in Melbourne.4 Another of his teachers was Justus Jörgensen, founder of Montsalvat the Eltham Artists’ Colony. Pugh lived on the dole for a while and paid for his first six acres (2.4ha) at Barreenong Road by working as an egg packer for the Belot family. Pugh accumulated more land and persuaded several other artists and friends to buy land nearby, resulting in the 200 acre property. They, too, purchased their land from the Belot family by working with their chickens. Around 1951 Pugh felt he had ‘Done moochin’ around’ and so the name of his property was born. Pugh bought some used timber from architect Alistair Knox to build his house on the crest of a hill. Inspired by local goldminers’ huts it was a one-room wattle-and-daub structure with a dirt floor. It was so small that the only room he could find for his telephone was on the fork of a tree nearby.5 Over the years the mud-brick house grew to 120 squares in the style now synonymous with Eltham. It had thick adobe walls (sun-dried bricks) made from local clay, high ceilings and stone floors with the entire structure made of second-hand materials – most found at wreckers’ yards. Pugh’s first major show in Melbourne in 1957, established him as a distinctive new painter, breaking away from the European tradition ‘yet not closely allied to any particular school of Australian painting’.6 Pugh became internationally known and was awarded the Order of Australia. He won the Archibald Prize for portraiture three times, although he preferred painting the bush and native animals. In 1990 not long before he died, Pugh was named the Australian War Memorial’s official artist at the 75th anniversary of the landing at Gallipoli. Today one of Pugh’s legacies is the Dunmoochin Foundation, which gives seven individual artists or couples and environmental researchers the chance to work in beautiful and peaceful surroundings, usually for a year. By November 2007, more than 80 people had taken part, and the first disabled artist had been chosen to reside in a new studio with disabled access.1 In 1989, not long before Pugh died in 1990 of a heart attack at age 65, he established the Foundation with La Trobe University and the Victorian Conservation Trust now the Trust for Nature. Pugh’s gift to the Australian people – of around 14 hectares of bushland and buildings and about 550 art works – is run by a voluntary board of directors, headed by one of his sons, Shane Pugh. La Trobe University in Victoria stores and curates the art collection and organises its exhibition around Australia.2 The Foundation aims to protect and foster the natural environment and to provide residences, studios and community art facilities at a minimal cost for artists and environmental researchers. They reside at the non-profit organisation for a year at minimal cost. The buildings, some decorated with murals painted by Pugh and including a gallery, were constructed by Pugh, family and friends, with recycled as well as new materials and mud-bricks. The Foundation is inspired by the tradition begun by the Dunmoochin Artists’ Cooperative which formed in the late 1950s as one of the first artistic communes in Australia. Members bought the land collaboratively and built the seven dwellings so that none could overlook another. But, in the late 1960s, the land was split into private land holdings, which ended the cooperative. Dunmoochin attracted visits from the famous artists of the day including guitarists John Williams and Segovia; singer and comedian Rolf Harris; comedian Barry Humphries; and artists Charles Blackman, Arthur Boyd and Mirka Mora. A potters’ community, started by Peter and Helen Laycock with Alma Shanahan, held monthly exhibitions in the 1960s, attracting local, interstate and international visitors – with up to 500 attending at a time.3 Most artists sold their properties and moved away. But two of the original artists remained into the new millennium as did relative newcomer Heja Chong who built on Pugh’s property (now owned by the Dunmoochin Foundation). In 1984 Chong brought the 1000-year-old Japanese Bizan pottery method to Dunmoochin. She helped build (with potters from all over Australia) the distinctive Bizan-style kiln, which fires pottery from eight to 14 days in pine timber, to produce the Bizan unglazed and simple subdued style. The kiln, which is rare in Australia, is very large with adjoining interconnected ovens of different sizes, providing different temperatures and firing conditions. Frank Werther, who befriended Pugh as a fellow student at the National Gallery Art School in Melbourne, built his house off Barreenong Road in 1954. Werther is a painter of the abstract and colourist style and taught art for about 30 years. Like so many in the post-war years in Eltham Shire, as it was called then, Werther built his home in stages using mud-brick and second-hand materials. The L-shaped house is single-storey but two-storey in parts with a corrugated-iron pitched roof. The waterhole used by the Werthers for their water supply is thought to be a former goldmining shaft.4 Alma Shanahan at Barreenong Road was the first to join Pugh around 1953. They also met at the National Gallery Art School and Shanahan at first visited each weekend to work, mainly making mud-bricks. She shared Pugh’s love for the bush, but when their love affair ended, she designed and built her own house a few hundred yards (metres) away. The mud-brick and timber residence, made in stages with local materials, is rectangular, single-storey with a corrugated-iron roof. As a potter, Shanahan did not originally qualify as an official Cooperative member.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, art gallery, clifton pugh, dunmoochin, cottlesbridge, cottles bridge, barreenong road -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - LETTER DESCRIBING BENDIGO'S GRANDEST BUILDINGS
Bendigo's Grandest Buildings are the Public Offices (1883-7) and the Law Courts (1892-6). Like the Town Hall they were described as Italian Renaissance in Design, but have high mansard roofs which give them a distinctly French air. They are so pompously Bendigonian that they stand well with Vahland's work, but in fact they originated in the Public Works Department, the architect for both being W.G. Watson. The building containing the Public Offices and Post Office has a frontage of 155 feet to Pall Mall and 100 feet to Williamson Street, and it was designed to include the post and telegraph offices and the postmaster's quarters. Public access was from the porch facing Pall Mall, and on the first floor were the police, water supply and crown lands departments, reached by a stair from the porch on the short façade. It was the largest building of its type outside of Melbourne, and was built in the grandest fashion of ornately stuccoed brick on a foundation of Harcourt granite, faced above ground level with bluestone. The floors of the porches and landings of the main stair are of encaustic tiles, the interior woodwork is of French polished cedar, and the major public rooms have coffered and enriched ceilings and cornices, and ornamentally panelled walls divided by pilasters. The building is surmounted by a tower rising to 130 feet, containing a great clock made by Thomas Gaunt of Melbourne, the chimes played on five bells weighing a total of three tons.bendigo, buildings, state offices -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Report, Metropolitan Town Planning Commission, "Metropolitan Town Planning Commission - Darling to Glen Waverley Railway - 1927", May. 1927
Report - 20 pages + 5 Maps stapled and then glued bound within a light green grey light card folder titled "Metropolitan Town Planning Commission - Special Report on the Development of the area serviced by the Darling to Glen Waverley Railway - 1927". Report looks the development that could be undertaken along the proposed Glen Waverley rail line, its town planning, Garden City type layouts, rail level crossings, new arterial roads, open spaces, financial arrangements, sewerage and water supply, zoning, legislation and conclusion. Dated 6/5/1927. Plans show possible garden city type layouts, arterial roads, possibilities within existing sub-divisions. Note that Mr. Strickland was a member of the Commission undertaking this work.Has in ink on the bottom edge "17th June 1919"trams, tramways, mmtb, tramways, development, town planning, glen waverley, darling -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
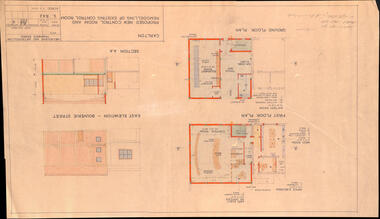
Melbourne Tram MuseumDrawing, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), "Carlton - Proposed new control room and remodelling of existing control room", May. 1961
Drawing - titled - "Carlton - Proposed new control room and remodelling of existing control room", coloured with a water colour brush, showing the proposed extensions to the Carlton control room, drawing Number S842, dated 9-5-1961. Shows the ground and first floors, mess room, offices, stairs and control room layout. Has the external elevations and sections.Has some pencil notations front and back re lights and sketch.trams, tramways, carlton, control centre, power supply, electrical engineering, electrical switching -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPhotograph - Digital Image, Sydney Road, Coburg, looking south from near Bell St, c1920
Digital Image of Sydney Road, Coburg, looking south from near Bell St, showing the track repair work to remove bricks from the rails that were resulting in damage to the track foundations by letting water into the track. Photo supplied for identification purposes May 2020, by the Editor, Australian Railway History - see htd4680doc for email correspondence. Image belongs to the ARHS NSW Div. Rail Resource Centre No. 117413 Was used in the June 2020 issue of Australian Railway History - see Reg Item 4684. In the background are the Commercial Bank of Australia, A. M. Hadden Chemist, Walkers Stores, Joblings Boots, a Lending Library with advertisements for "The Age", "The Argus" and "The Herald".trams, tramways, sydney road, coburg, track repairs, trackwork -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Specification - set of 7 - worker ammenties etc, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), mid 1950s
Seven documents for the supply and delivery of equipment and sheds for track workers - All undated. 1 - "Five oil-fired 25 gallon urns for boiling water" - 4 sheets 2 - "Two (2) mobile bitumen heaters - oil fired" - 6 sheets 3 - "Six (6) mobile tool boxes" - 4 sheets 4 - "Three hundred (300) barricade posts and six hundred (600) barricade rails - 4 sheets 5 - "Five (5) portable gangers' offices" - 5 sheets 6 - "Two (2) portable lamp cabins" - 7 sheets 7 - "Four (4) mobile conveniences" - 4 sheetsYields information about the MMTB tender for track workers facilities and equipment.Set of seven documents - foolscap sheets stapled in top left hand corner and hole punched along the top edge.mmtb, tramways, contracts, purchases, trackwork, tools -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumMagazine, Engineers Australia, Journal of the Institution of Engineers Australia" - Vol 6, No. 10, Oct. 1934, "Metropolitan and Provincial Tramways", Oct. 1934
Journal or magazine - stapled pages approx. 100 printed on semi gloss paper, with glue outside cover, titled Journal of the Institution of Engineers Australia" - Vol 6, No. 10, Oct. 1934 - Special issue - Melbourne Centenary Celebrations 1934 - 1935. Contains transactions of radio frequency, institution and related activities, and 100 years of Engineering in Victoria. These include maps of Victoria and Melbourne, Engineering Education (Kernot), Metropolitan Roads and Bridges by J. Noble Anderson City Engineer of Richmond, Country Roads and Bridges, Railway Development (VR), Metropolitan and Provincial Tramways (Strickland and Russell), Port of Melbourne, Outer ports, air transport, water supply, sewerage and drainage, gas industry, electricity supply, communications (telephone and telegraph), industrial development and mining. Has ads for British Insulated cables, Thompsons Engineer, Goodyear, GEC - British General Electric, Associated General electric, Vickers and many other companies. Photocopy of article from the Bob Lilburn collection.trams, tramways, centenary, victoria, tramways, railways, secv, mmtb, cable trams -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
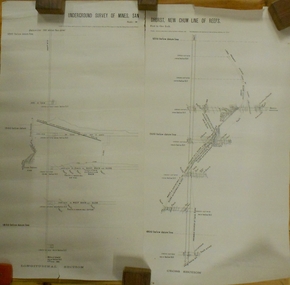
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Plan - MARKS COLLECTION: UNDERGROUND SURVEY OF MINES SANDHURST NEW CHUM LINE OF REEF
Plan, divided into two sheets, on top of sheet Underground survey of mines Sandhurst, New Chum Line of Reef. Surveyed by Caleb Thomas under the direction of Charles W. Langtree, Acting Secretary for Mines and Water Supply and Acting Chief Mining Surveyor for the Colony of Victoria. Drawn by Arthur Everett, Mining Department, Melbourne, 1884.bendigo, mining, new chum line of reef -
 Stawell Historical Society Inc
Stawell Historical Society IncPhotograph, Grampians at Halls Gap 1866
Grampians Halls Gap. Part of a collection of Photographs by Mr. O.G. Armstrong as commissioned by the Shire of Stawell for the Inter-colonial and Paris Exhibition in Melbourne in 1866. From about 1860 there was agitation for a water supply, not only for Stawell but for the Wimmer Mallee as well. In 1887 Wartook was adopted as the first reservoir for the Wimmer. Stawells water supply was designed by Mr. John D’Alton. The scheme came from Fyan’s Creek via Wooden Fluming and a Syphon and finally through the mountain in a tunnel, before being piped to a reservoir on Big Hill. The system was completed in December 1881 and although there have been modifications, basically it has not been changed to this day. The Wimmera Mallee stock and domestic system from the Grampians is the largest system of its kind in the world, the latest edition being like Belfield and piping of Wimmera channels. stawell -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTextile - Flour bag - Moran & Cato's
The flour bag is an example of packaging from the grocery store, Moran & Cato's. Moran & Cato's were a large chain of grocery stores operating from the late nineteenth century to the mid twentieth century across Victoria, Tasmania and New South Wales. The address on the flour bag is for the warehouse (wholesale depot) of the business which was a significant building in Brunswick St, Fitzroy.The flour bag provides a snapshot of packaging for a well known grocery store of the early twentieth century. The advertisement on the back for 'Cleaned Fruits' is an example of advertising that highlighted important facts relevant to that time (e.g. "latest Special Machinery" and "with running water").Small calico flour bag for self-raising flour (7lb) supplied from Moran & Cato's in Brunswick Street, Fitzroy, Melbourne. The front of the bag includes not only the detail of the business but ideas for baking, images of wheat and claims as to its excellence. The back of the bag has a written advertisement for 'Cleaned Fruits' another product of the company.Front - Wheaten Flour, Moran & Cato's, Trade mark The M & C Brand Registered, 7lbs Nett, The Highest Standard of Purity and Excellence, prepared with phosphate aerator, Self-raising Flour, For making scones bread cakes puddings & pastry, Warehouse & Office- Brunswick Street, Fitzroy, Melbourne Back - Moran & Cato's, Cleaned Fruits are Perfection, (advertising text), The Same High Quality, The Same Prices at all our Branches.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, calico, domestic object, textile, food storage, moran & cato's, flour bag, self-raising flour -
 City of Greater Bendigo - Civic Collection
City of Greater Bendigo - Civic CollectionCeremonial object - Common Seal
Bridgewater is a situated 39km northwest of Bendigo and 170 km from Melbourne. It was established as a crossing point over the Loddon River for gold diggers en route to the Inglewood gold diggings. As gold began to dry up in the district the town of Bridgewater developed due to its proximity to the river which it relied on for industries such as brewing, farming and market gardens. As demand on the water supply grew, the Water Works were established to ensure supply and manage the quality of the water for drinking. Decorated hand operated cast iron embosser with 40mm seal head attached. Gold and orange painted decorations extend from top edge of handle to sides of base. Original knob has been replace with a newer wooden knob. Well used showing all over signs of wear. Seal is for the Bridgewater Waterworks Trust 1927.Bridgewater Waterworks Trust 1927.loddon shire -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncFilm - Video (VHS), Nillumbik Shire Council, The Nillumbik Story, 1996
PART 1 – NILLUMBIK (00:00-07:17) Opening features various scenes around Nillumbik Shire. For 40,000 years Nillumbik was the home of the Wurundjeri people. Robert Hoddle gave the district its name. Jock Ryan, then president of Nillumbik Historical Society discusses the names Nillumbik and Diamond Creek. In the late 1830s white occupation began with gold found in Warrandyte in 1851 and 12 years later at Diamond Creek -the Diamond Reef which led to the Caledonian gold rush. Jock Ryan discusses the Diamond Creek mine, which was thriving until it burnt out in 1915. Large numbers of workmen moved into area in late 1870s to construct the Maroondah Aqueduct. With growing population of Melbourne, the nearby Yan Yean system had severely disrupted the flow of the Plenty River, forcing the closure of three flour mills there. The aqueduct came to the rescue carrying water 66km from Healesville to Preston. When the Diamond Creek gold mine burnt down the local economy suffered but fruit growing industry had already been established and Diamond Creek became a thriving fruit growing centre. Interview with Jack Powell, a long-time fruiterer at St Andrews market, his family had lived in the area for a hundred years, 3 to 4 generations, “a lot of hard work”. By the time the railway arrived fruit growing was no longer competitive. The railway brought the city closer and day trippers. The Green Wedge separates the shire from the more densely developed neighbours such as Whittlesea, Doncaster, Templestowe, Bulleen and Greensborough. Population at the time (1996) was 19,000 but links to the past remain strong. Mudbrick houses along the Heritage Trail The saving of Shillinglaw Cottage from demolition in 1963 and relocation brick by brick. PART 2 – ENVIRONMENT (07:18-14:44) Peter Brock (with Bev Brock in background) at St Andrews market discusses his childhood growing up in the district and the environment and the values it instilled upon him and his own family. The Brocks have been in the district since the 1860s. Nillumbik Shire responsible for managing three catchment areas; Diamond Creek, Arthurs Creek and Watsons Creek. Follows the course of the Diamond Creek commencing in Kinglake through the district to its confluence with the Yarra River at Eltham at Eltham Lower Park. Highlights Eltham Lower Park community revegetation program and the newly constructed (1996) viewing platform built of new and recycled timbers at the confluence of the Diamond Creek and Yarra River. Also featured are outdoor recreation on the river and at Eltham Lower Park including the Diamond Valley miniature railway. Sugarloaf reservoir and recreational activities and fishing. Aerial view of Memorial Park and Shire of Eltham War Memorial tower at Garden Hill, Kangaroo Ground. Significant tourism opportunities for the shire with 3 million potential day-trippers in metropolitan Melbourne. Council and community working together to find a way to promote the shires natural and artistic assets. At Arthurs Creek, the Brock family and neighbours working together to take care of their waterway. Peter Brock’s uncle, Sandy Brock talks about environmental management and the Arthurs Creek Landcare group and actions to eradicate blackberry problem. Having previously planted Cypress rows they are replacing them with indigenous species to improve the water supply, keeping cattle out of the creek bed to improve the quality downstream flowing into the Yarra. Eltham East Primary School Band playing “All things bright and beautiful” merges into scenes of the bushland sanctuary set aside by the school in 1980 with unidentified teacher discusses the sanctuary and their education program and school children’s comments. Plight of a family of Wedgetail eagles nesting in the path of a developer’s bulldozer at North Warrandyte and actions to save their nesting areas. PART 3 – ARTS (14:45-22:00) Arts and Jazz festival at Montsalvat featuring interviews with Sigmund Jorgensen discussing Montsalvat and its principles. Also Matcham Skipper. Clifton Pugh’s funeral at Montsalvat and his legacy at Dunmoochin near Cottlesbridge with artists in residence, at the time, Chicago artist Charles Reddington who discusses the benefits of the experience. An unidentified female artist also talks about the program and why people are drawn to the area. Unidentified man on street talking about the amount of talent in the area, artists, poets, musicians, authors. Artist Ming Mackay (1918-2009) interviewed talking about the people she mixes with on “the Hill”. Works of local artists are displayed Eltham Library Community Gallery and Wiregrass gallery with a new coffee shop at the Wiregrass making it an even more popular destination. Music at St Andrews Hotel (may be a little bit country) and the Saturday market where likely to hear anything. Sellers and patrons at the market asked about what attracts them to the market and where they came from. Scenes of poets/authors giving readings. CREDITS Music by John Greenfield from the CD Sweet Rain “The Snow Tree”, Uncle Music UNC 2001 Cameras - David Mirabella and Peter Farragher Editor – Olwyn Jones Written and Produced by Jason Cameron A Jason Cameron Proction for Nillumbik ShireProvides a record of the relatively newly created Shire of Nillumbik at the time and the features and attactions of the shire in its people arts, culture and environmentVHS Cassette (five copies) DVD (one copy) Converted to MP4 file format 0:22:00, 1.60GBvideo recording, arthurs creek, arthurs creek landcare group, artists, artists in residence, arts, arts festival, authors, blackberry, brock family, bulldozer, bulleen, bushland sanctuary, caledonian gold rush, charles reddington, clifton pugh, cottlesbridge, cypress rows, developer, diamond creek, diamond creek mine, diamond reef, diamond valley miniature railway, doncaster, dunmoochin, education program, eeps, eltham, eltham east primary school, eltham east primary school band, eltham library community gallery, eltham lower park, environment, fishing, flour mill, fruit growing, fruiterer, garden hill, gold mining, green wedge, greensborough, heritage trail, hurstbridge railway line, jazz festival, jock ryan, kangaroo ground, kangaroo ground tower, kinglake, maroondah aqueduct, matcham skipper, memorial park, ming mackay (1918-2009), montsalvat, mudbrick houses, music, musicians, nesting area, nillumbik historical society, nillumbik shire, north warrandyte, old timer, orchards, peter brock, plenty river, poets, population, recreation, recreational activities, revegetation, robert hoddle, sandy brock, shillinglaw cottage, shire of eltham war memorial, sigmund jorgensen, st andrews hotel, st andrews market, sugarloaf reservoir, templestowe, the hill, tourism, viewing platform, warrandyte, water catchment area, watsons creek, wedgetail eagle, whittlesea, wiregrass gallery, wurundjeri, yarra river, jack powell -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncFilm - Video (DVD), Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works, Yarra River Conference Proceedings; a Board of Works centenary event, 13-16 April 1991
Yarra River Conference History Segment [Noted on VHS tape jackets "Due to unavoidable circumstances, the quality of these tapes in some setions is less than desired."] The Yarra River Conference, organised by the Board of Works as part of the Centenary Celebrations, was held in the Board's Head Office Theatrette from 13-16 April, 1991. A segment of the Conference focussed on the role that the Yarra River has played in relation to the historical development of Melbourne. Conceived and presented by a group of prominent historians as a chronological 'trip down the river in time', and profusely illustrated with slides, this segment traced the various impacts that urban and rural growth, development of marine commerce, recreational uses, and environmental problems have had on the Yarra during a century and a half of European occupation. As no formal written paper of this combined presentation is available, these two video-tapes provide a record for anyone who has an interest in tis fascinating aspect of the Yarra's history. The speakers who combined to present this segment are identified on the cover of Tape 2. Tape 1 (2 hours) 1838-1863 Deputy ?? to Utility Early navigators of the Yarra River; developing the port of Melbourne; the gold rush and its effect on the new colony; punts and bridges; water supply; pollution of the Yarra; the discovery of gold and early settlement of the Yarra valley; floods of 1839 and 1863. 1863-1891 Formation of the Harbour Trust; Coode Canal; pollution of the Yarra by industry; aborigines, gold miners, timber getters in the Upper Yarra areas; bridges; the flood of 1891. Tape 2 ( 1 1/2 hours) 1892-1934: People Begin to See Beauty and Romance to the River Henley-on-Yarra; realignment of the Yarra; MMBW is responsible for a sewerage system; new docks to cope with increased overseas trade; development of recreational parks; new reservoirs; timber production and timber tramways; bushfire; flood of 1934. 1935-1970: The River is Neglected Still, Except When it Proves Useful Bushfirs of 1939; the end of many sawmills; birth of tourism; increased interest in conservation and preservation of land for open space; further augmentation of water supply system; birth of containerisation changes the port; environmental concerns gain momentum. Speakers Dr Tony Dingle *, Department of Economic History, Monash University Dr Carolyn Rasmussen *, History Consultant Prof. Graeme Davison, History Department, Monash University Mr. Tom Griffiths, Lecturer in Public History, Monash Uiversity Mr. Patrick Miller, History Consultant Mr. Colin Jones, Author and Historian * Co-authors of the Board's history, 'Vital Connections'.video recording, yarra river, conference proceedings -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyDocument - Land Agreement, Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works, 02/07/1951
A double sided official original page Agreement between the Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works at Spencer Street Melbourne and Maxwell Hay Proctor for the supply of water to the Queens Road Wandin property on the Second day of July 1951.A double sided official original page Agreement between the Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works at Spencer Street Melbourne and Maxwell Hay Proctor for the supply of water to the Queens Road Wandin property on the Second day of July 1951. It has The Common Seal of the Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works affixed in the presence of the Chairman, Member and Acting Secretary. It is signed Sealed and Delivered by the said Maxwell Hay Proctor in the presence of the witnesses D. Campbell and J.D.It has 'The Common Seal of the Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works affixed in the presence of the Chairman, Member and Acting Secretary. It is hand signed Sealed and Delivered by the said Maxwell Hay Proctor in the presence of the witnesses D. Campbell and J.D.'administrative records, documents, land agreements, melbourne metropolitan board of works -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Slide - DIGGERS & MINING. THE GOLD ERA, c1857
BHS CollectionDiggers & mining. The gold era. In 1857, the Yan Yean reservoir was opened, and Melbourne was ensured of a good water supply. Slide shows a good picture of the lake with a couple of people in the foreground. Markings 55 994.031 GOL:5. Used as a teaching aid.hanimounteducation, tertiary, goldfields -
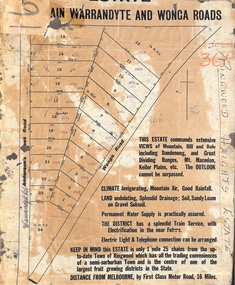 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyMap, Partially Trimmed Copy of Ringwood Heights Estate, Ringwood, Vic. - circa 1923
Clipped copy of a subdivision advertisement on cardboard backing. Sales notations on numbered allotments in Andersons's Creek Road (later Warrandyte Road) and Wonga Road, Ringwood. Handwritten title reference - LP7305. Captions - This Estate commands extensive views of mountain, hill and dale including Dandenong and Great Dividing Ranges, Mt. Macedon, Keilor Plains, etc. The outlook cannot be surpassed. Climate invigorating, mountain air, good rainfall. Land undulating, splendid drainage; soil, sandy loam on gravel subsoil. Permanent water supply is practically assured. The district has a splendid train service, with electrification in the near future. Electric light & telephone connection can be arranged. Keep in mind this estate is only 1 mile 25 chains from the up-to-date town of Ringwood which has all the trading conveniences of a semi-suburban town and is the centre of one of the largest fruit growing districts in the state. Distance from Melbourne by first class motor road, 16 miles. -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Book - Victorian Municipal Directory 1955, Arnall & Jackson, 1955
Victorian Municipal Directory, also Commonwealth and State guide and water supply Record for 1955Green book - Eighty Third Year of Publication In black writing " Victorian Municipal Directory Also Commonwealth & State Guide to Water Supply Record for 1955 T & G Mutual Life Society Head Office: Collins & Russell Street Melbourne C.I.As abovevictorian municipal directory, 1955, commonwealth & state guide, water supply record -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Codd neck bottle, E. Rowlands, 1921
The design of the bottle is called a Codd, sometimes referred to as a marble bottle or "Codd's patent bottle". During the mid-to-late 1800s, there were many inventions to keep the fizz in carbonated drinks such as ginger ale, soda water, and fruit drinks. Hiram Codd, an English engineer invented a successful process that he patented as "Codd's patented globe stopper bottle" in 1872. The Codd-neck bottle (commonly called Codd or marble bottle) is manufactured in two parts. The body of the bottle is cast in two sections. At the time of joining the sections, glass marble and rubber seal are inserted into the neck section. The lip is then applied to the top of the bottle. The Codd bottle is filled upside down as the pressure of the gas from the carbonated liquid holds the marble up and out of the way. When the bottle stands upright the gas pushes the marble up against the washer, creating a firm seal to keep the fizz inside. The bottle is opened by pushing the marble down firmly to allow some of the gas to escape. The marble drops down and is caught in a depression formed in the neck. When the bottle is tilted to pour or drink the liquid the marble rests in a dimple. Two Ballarat miners, Evan Rowland and Robert Lewis started manufacturing mineral and aerated waters, bitters, cordials, and liqueurs in 1854, in a tent on the shores of Lake Wendouree Ballarat. Another 13 firms at that time employed manual operations, whereas they introduced Taylor's No. 1 machine that speeded up the process and laid the foundation for their fortune. Evan Rowland was a pioneer in the aerated water trade in Australia. He was born on August 2, 1826, in North Wales. In 1852, during the gold rush, he emigrated to Melbourne, and in 1854 he went to Ballarat and formed a partnership with Robert Lewis, the firm being called ‘‘Rowlands & Lewis’’. Their next step was to secure a supply of pure water. Using mineral Waters that they found via a natural spring at Warrenheip, Victoria. From the outset, the beverages made from this water gained repute and were in great demand. Their business prospered so well that in 1858 they were able to build a factory at the corner of Sturt and Dawson Streets, Ballarat, and to fit with the most up-to-date machinery then in use. By 1870 their business had increased so much and demand had grown to such an extent that Mr. Rowlands erected another factory, covering over an acre of ground at the corner of Dana and Doveton Streets, costing £13,000. The factory was fitted with the most modern equipment of the time to manufacture cordials and aerated water. In 1873 Rowlands established an agency at 116 Collins St, Melbourne, because the demand for the products of the Melbourne factory became so large. The company expanded to Sydney opening a factory at the corner of Burns & Hay Streets Darling Harbour obtaining spring water to supply this plant from Katoomba in the Blue Mountains. The water was brought to Sydney by rail. In the meantime, the Melbourne concern had progressed so rapidly that in 1888 a magnificent factory embodying all the latest ideas and equipment was built in King Street Melbourne. Robert Lewis was a fellow Welshman born in 1816, and he arrived in Port Phillip in 1853 and became a partner in the early day with Evan Rowland but with lesser and shorter involvement in the firm, from which he retired in 1876. Robert Lewis was perhaps better known as Ballarat's first mayor and a Member of the Legislative Assembly. He was a strong supporter of local charities, president/treasurer of the Eisteddfod Committee, a major force in the development of the Ballarat Hospital, and he was the mayor of Ballarat five times, the first in 1863, (having been a counsellor as early as 1859) and for the last time in 1881. Lewis died in 1884 of a stroke in Ballarat. Rowlands continued in the firm and invented and patented an improved soda water bottle. The water used in Rowlands products was filtered four times but his attempts to use local corks failed on quality grounds. He was a stickler for quality, which was so good that many outside Victoria were prepared to pay the 'premium' imposed by inter-colonial customs duty payable at that time. By the 1890s, Rowlands had factories in Ballarat, Melbourne, Sydney, and Newcastle. He died in 1894 but his company continued until well after the Second World War when it was sold to Schweppes. Bottles such as this popular brand, containing soda water, were often used on paddle steamers for refreshments.An early manufacturing process producing the first mineral waters in Australia was invented and developed by an early Welsh migrant to Australia. The Evan Rowlands story gives an insight into the early development of manufacturing industries in Australia that allowed their workers and the towns they were situated in to prosper and develop into what they are today. A good example of hand blown glass.Bottle; clear glass Codd neck bottle with small marble in top. Once contained soda water or soft drink. Manufactured in 1921 by E. Rowlands of Ballarat, Melbourne, Katoomba and Sydney. The bottle is 'recyclable' - the message on the base says that it remains the property of E. Rowlands Pty Ltd. Inscriptions on three adhesive labels at time of donation"E. ROWLANDS BALLARAT MELBOURNE KATOOMBA AND SYDNEY". Imprinted into bas "1921" "THIS BOTTLE REMAINS THE PROPERTY OF E. ROWLANDS PTY LTD" On adhesive labels (3) " 1921 ON BASE (LASTED 1924) CODD PATENT 702" "SMALL SIZE. MARBLE TOP SODA WATER PAPER LABEL. USED" "ON PADDLE STEAMERS. POPULAR BRAND"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, bottle, codd bottle, hiram codd, glass marble bottle, e. rowlands bottle manufacturer, soda bottle australia, early recyclable bottle, codd's patent bottle, marble bottle, refreshments, soda water, marble top, 1920s, codd patent 702, handmade, blown -
 Ithacan Historical Society
Ithacan Historical SocietyPhotograph, Frikes, Ithaca, c1970s
As the closest port to the mainland and neighbouring island Lefkada, Frikes was historically a trading port, supplying produce and merchandise to northern Ithaca. Today it is more a quiet fishing village which comes alive during the summer months with cafes and taverns. In summer tourist yachts moor at Frikes and a ferry service operates to Lefkada. A coloured photograph of he harbour at Frikes. Thee is a stone and concrete breakwater in the foreground where three fishing boats and a yacht are moored. A sedan is parked on the breakwater. Buildings are around the water's edge in the middle distance against a backdrop of mountains. ports, frikes
