Showing 2374 items
matching irish
-
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchCoin, Royal Mint, circa 1711
Circa 1711 Queen Anne silver shilling coin Round silver coin with bust of woman - ANNA DEI GRATIA - silver chain attached Reverse side - Crowned shields - with arms of England and Scotland impaled at top and bottom, Ireland at left and France at right, forming a cross shape with the badge of the Star of the Garter at the centre; around, MAG BRI FR ET HIB REG 1711, the date being divided by a crown.coin, queen anne -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Label
Printed and used by the donor's father for labelling apple cases in his orchard.Oblong paper label, dark blue background with a red and green apple and green leaves. 'Red Moon' lettering with a red half moon. 'Fancy Apples' in green and packed by Blue Moon Fruit Co-operative Ltd, Victoria, Australia is in blue. The bottom edge of the label has Growers Count or Size Variety. The signature W. Ireland is also on the ;lower edgerural industry, orcharding -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - ALLEGRI QUARTET
The Music Advancement Society of Bendigo presents the Second Concert 1961 Series by arrangement with Musica Viva Society of Australia presenting 'Allegri Quartet'. Eli Goren - violin, James Barton - violin, Patrick Ireland - viola, William Pleeth - cello. McGillivray Hall, Bendigo. Technical College on Thursday, 1st June 1961 at 8.15 p.m. Programme 1/-. Boltons Print, Bendigo.event, entertainment, music, allegri quartet, the music advancement society of bendigo, musica viva society of australia, eli goren, james barton, partick ireland, william pleeth -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumHeadwear - HELMET - WW1 GERMAN, c. 1915
The helmet was captured by William J Hanna, Royal Irish Fusiliers. Hanna was wounded during the 1916 Battle of the Somme.World War One German Army steel helmet. The outer surface is painted. Two lugs/ventilation holes are visible on each side. Rivets securing the missing headband are also visible. The front of the helmet has an extended visor whilst the back and sides also project to cover the nape of the neck and ears. Inside on each side are attachment points for a chin strap.helmet, german army - ww1, military equipment, uniforms - army, headwear -
 Sir Reginald Ansett Transport Museum
Sir Reginald Ansett Transport MuseumUniform - Coat, 1970s
Trenchcoat belonging to the uniform designed by Irish-born Noeleen King based in Melbourne and used between 1972-1978Typical colour and design from the 1970s, this uniform demonstrates the collaboration with fashionable Melbourne-based designer Noeleen King.Long orange trenchcoat with gold belt bucklenoeleen king, stewardess, hostess, flight attendant -
 Sir Reginald Ansett Transport Museum
Sir Reginald Ansett Transport MuseumUniform - Dress and jacket, 1972 - 1977
This uniform was designed by Irish-born Noeleen King, based in 45 Flinders Lane, Melbourne, for the 1972 - 1977 period. Typical colour and design from the 1970s, this uniform demonstrates the collaboration with fashionable Melbourne-based designer Noeleen King.noeleen king, hostess, stewardess, flight attendant, orange, dress, jacket -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumPhotograph - original, 1870's
Rebecca Shanks from Poyntz Pass County Armagh, Northern Ireland who married Andrew Crawford in 1873.Original sepia portrait of lady wearing a high necked top with white collar. Cameo at neckline and locket and chain around neck.Photograph is on cardboard backing board.On back of portrait - Mrs Rebecca Crawford, Woodlands. On front: Eden Photo Studios Paris Panel Melbourne and Sydneyrebecca shanks, andrew crawford, rebecca crawford -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Furniture - Child's Cot, c1800s
Bought from Ireland by George Cox's Great Grandmother and slept in by each succeeding generation including George (Donor)Black cast iron framed child's cot with higher sides at top. Cot folds up. Childs bed.furniture, domestic-nursery -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Clare Gervasoni, Kavanagh Memorial , Warrnambool Cemetery, 27/07/2009
Daniel and Denis Kavanagh were brothers from County Carlow, Ireland. Denis Kavanagh died at Garvoc, Victoria. Kavanagh memorial in the Warrnambool Cemetery. warrnambool cemetery, denis kavanagh, daniel kavanagh, county carlow, ireland, garvoc -
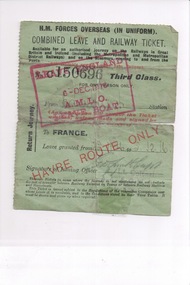 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchSouvenir - Transport Ticket, Unknown
Combined Leave and Railway Ticket No. C150696 issued to James Crawford Third class travel in Great Britain and Ireland Light green colour paper with black printed writing and red stamp front and rear. Ticket No. C150696 Havre route only. REAR - Req No. 90. Rank Sapper. Name Crawford. Unit 8 Field Co 1st Aust Div. Authority ??? ANZAC AA585 FRONT & REAR red stamp "Leave England 6 Dec 1916 AMLO LEAVE BOAT leave and railway ticket, ww1 -
![Thomas Carr: An Archbishop of Melbourne / [by] T.P. Boland](/media/collectors/550653872162f11fb04854aa/items/5ebe1cc23cafb4141cc26b19/item-media/5ebe1ddc3cafb4141cc28788/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncBook, University of Queensland Press, Thomas Carr: An Archbishop of Melbourne, 1997
Biography of Thomas Carr (1839-1917), Catholic Archbishop of Melbourne. 495 p. : ill. ; 25 cm.non-fictionthomas carr, catholic church - melbourne - victoria - bishops - biographies -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, 12 Quarry Road, Mitcham, 1998
This shed was on part of the orchard property of Mr Henry Ireland of 12 Quarry Road Mitcham. He has cleared the property and planted an apple orchard by about 1910. When he died in 1947 the orchard was cut up. Mrs Ireland lived in the house until she died. Her daughter married and rebuilt the house, but the outbuildings remained the same, at least until 1998.Coloured photograph of a path leading across a lawn to an old shed with white doors.ireland, henry, quarry road, mitcham, orchardists -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Incomplete vaginal douch apparatus set associated with midwife Mary Howlett, c. 1866 - 1920
These are parts of a vaginal douch apparatus set. The apparatus appears to be a T More-Madden model, as used at the Rotunda Hospital, Ireland.Mary Howlett (1840-1922) began practising as a country midwife in 1866 in the western district of Victoria. She qualified as a 'ladies monthly nurse' in 1887 and continued to practise as a nurse and midwife until 1920.She began her six months training at the Melbourne Lying-In Hospital. She was known by many as 'Auntie', and her career spanned more than 50 years. Mrs Howlett's midwifery box and contents were given to Dr Frank Forster, and he donated them to the museum collection in 1993.Black vulcanite bridge attachment (.1) and irrigator (.2). The bridge would attach to the rubber tubing of the set and a lead sinker, The bridge would attach to a stopcock at the proximal end of the set.midwifery -
 Buninyong & District Historical Society
Buninyong & District Historical SocietyPhotograph - Colour photograph of original Church of England and Ireland built 1857, Original Church of England and Ireland built 1857
Original Church of England and Ireland built in 1857 used as a church, then Sunday School and Common School and later a tennis pavilion.With the discovery of gold the population grew rapidly and the Rev. George Russell arrived as the first full time Anglican priest. From September 1857, services were held in the church on Sundays and school classes were taught during the week. Exterior view of the church buildingAnglican Common School Buninyong, No. 59 opened 1857church of england and ireland, church of england, common school, sunday school, rev. george russell -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, Patrick A. Collins, c1864
As a young man, Collins joined the Fenian movement (founded to overthrow British rule in Ireland). This work led him into politics. He was quickly elected a state representative and then a state senator. As a legislator, Collins worked to ease restrictions on the practice of religion for Catholics in state institutions and to earn public money for Catholic charitable institutions. With the rapidly increasing number of Irish voters in Boston in the 1870s, their vocal assertion of their rights, and strong political organization, the Irish were beginning to be recognized as a power to be reckoned with. Collins was central to these developments.(http://www.questia.com/library/journal/1P3-2036414231/young-patrick-a-collins-and-boston-politics-after, accessed 21 January 2014)Image of Patrick A. Collins, United States Congressmanballarat irish, patick collins, collins, -
 Linton and District Historical Society Inc
Linton and District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Jean Hollins
Black and white copy of original portrait of a young lady seated on an ornate chair, wearing a dark high-necked dress with decorated cuffs, collar and neckline."Jean Hollins (Hunter) b. Linton, daughter of Thomas Wilson Hunter & Harriet Walker, whose mother Bridget Murphy had come to Vic. in 1850, one of the "Irish Orphans" on the ship "Eliza Caroline". Photo taken late 1800s?".jean hollins (nee hunter) -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Colour, Barravore Ford, County Wicklow, Ireland, 2016, 09/2016
The Connor family emigrated from Barrovore Ford, Ireland, to Australia around the 1860s. Remnants of their house are still extant near the ford. barravore ford, county wicklow, ireland, creek -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1897
This Great Britain one shilling coin is dated 1897, which is during the reign of Queen Victoria. There were over 6 million of these coins minted. Queen Victoria succeeded King William IV to the British Throne in 1837 – she was only 18 years old at the time – and she ruled until 1901. British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This one shilling coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. There are three main groups of shillings produced during Queen Victoria’s reign:- - The Young Head; 1837-1887, in 8 different versions, on the obverse showing the Queen’s maturing face over 50 years. - The Junior Head; 1887-1892, minted when Queen Victoria had been reigning for 50 years. Her head was smaller on the coins minted 1887-1889 than on those shillings minted 1889-1892. - The Old Head; 1893-1901, shows the veiled head of Queen Victoria. The obverse side of the coin was designed by Thomas Brock. The inscription’s translation is “Victoria by the Grace of God, Queen of the British territories, Defender of the Faith, Empress of India”. The reverse side of the coin was designed by Edward Paynter. The inscription "HONI SOIT QUI MAL Y PENSE" translates as "Evil be to him who evil thinks". AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 Spanish dollars were imported and converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then counter-stamped and used as the official currency. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced, removing the power from the States. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. This silver shilling is also of significance to Australia as part one of the British Colonies ruled by Queen Victoria. It is part of the special silver and gold coins minted 1887-1893 to celebrate the 50 years Jubilee of Queen Victoria’s reign 1837-1887. Coin, Great Britain Shilling, 1897. Silver coin, round. Obverse; Queen Victoria head, ‘Old Head’, looking left. Reverse; 3 shields (each crowned) - 3 passant lions (England), 1 rampant lion (Scotland), golden harp (Northern Ireland) - floral symbols between them – 1 open rose, 2 thistles. Inscriptions on both sides of coin.Obverse “VICTORIA . DEI . GRA . BRITT . REGINA . FID . DEF . IND . IMP” Reverse “ONE SHILLING, 1897, Inner band, some letters hidden - HONI SO VI Y PENSE” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, british shilling 1897, thomas brock, edward paynter, great britain shilling, queen victoria currency, queen victoria 50 years golden jubilee shilling, colonial australia currency, numismatics -
 Streatham and District Historical Society
Streatham and District Historical SocietyPost Card, 1914-1918
Paper card with a picture of a house with a thatched roof. There is a stone wall and two trees that are beginning to blossom. There are four children two boys and two girls. One girl has no footwear. One boy is holding a goat. There are two goats a large pig and chicken in the picture. The words" An Irish Cabin" appears on the lower left side and a Orange ribbon has been attatched to the lower right side."Dear Bess I suppose you think I an never going to answer your pursuit but I thought I would do so while here in Belfast cause I know you have a lot of time for the Micks. How would you like a little home like this one no cows to milk only goats no horses to drive only donkies & it looks as though the girls have no boots to clean by this card but there is some first class sig hias this one has taken a purge he must be an Ulsty show. Love from Donald -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - COHN BROTHERS COLLECTION: FLOAT SEES 9% HERALD? 1958?
Newspaper cutting with the headline 'Cohn Bros. float sees 9%'. In blue ink across the top is written 'from Roy Ireland? 17-9-73. Herald 1957 1958?'. The article includes a photo of Mr F. M. W. Levy (Chairman and director of Cohns, and a director of Carlton & United Breweries). The article is about the floating of Cohn Bros. as a public company. Soft drink manufacturers.bendigo, industry, cohn bros., cohn bros. limited. cohns limited. carlton & united breweries. levy, frank m. w. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - MALE PORTRAIT - GROUP, approx. 1900
Photograph: group of seven young men seated or standing dressed in suits waitcoats , ties and hats. Shown in background a bicycle, beer bottles and 2 outbuildings. One decorated with scotch thistle, Irish shamrock, english rose and a flag of unknown origins. Photo under glass, mounted on grey card and framed with a very ornate wood and plaster moulded frame cream in colour with some gilding.W.H. Grose, Photographerperson, group, male group -
 Old Castlemaine Schoolboys Association Inc.
Old Castlemaine Schoolboys Association Inc.Photograph, Castlemaine Pipe Band 1911
19 Bandsmen Pictured: Back Row: Waggy Wilson, Bill Thompson, Mr Rackstraw, Harry McDougall, Bill McDougall, Jock Munro, Sam Laurensen, Stan McLean Second Row: Geo Sutherland, Mr Leighton, Dave Ireland, Tom Martin Snr, President, Peter Robinson, Bob McBeath Front Row: Neil McBeth, Clarrie Martin, Hughie Bell, Norm Martin -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, Charles Parnell, c1864, 1864
Parnell was an Irish nationalist and statesman who led the fight for Irish Home Rule in the 1880s. Charles Stewart Parnell was born on 27 June 1846 in County Wicklow into a family of Anglo-Irish Protestant landowners. He studied at Cambridge University and was elected to parliament in 1875 as a member of the Home Rule League (later re-named by Parnell the Irish Parliamentary Party). His abilities soon became evident. In 1878, Parnell became an active opponent of the Irish land laws, believing their reform should be the first step on the road to Home Rule. In 1879, Parnell was elected president of the newly founded National Land League and the following year he visited the United States to gain both funds and support for land reform. In the 1880 election, he supported the Liberal leader William Gladstone, but when Gladstone's Land Act of 1881 fell short of expectations, he joined the opposition. By now he had become the accepted leader of the Irish nationalist movement. Parnell now encouraged boycott as a means of influencing landlords and land agents, and as a result he was sent to jail and the Land League was suppressed. From Kilmainham prison he called on Irish peasants to stop paying rent. In March 1882, he negotiated an agreement with Gladstone - the Kilmainham Treaty - in which he urged his followers to avoid violence. But this peaceful policy was severely challenged by the murder in May 1882 of two senior British officials in Phoenix Park in Dublin by members of an Irish terrorist group. Parnell condemned the murders. In 1886, Parnell joined with the Liberals to defeat Lord Salisbury's Conservative government. Gladstone became prime minister and introduced the first Irish Home Rule Bill. Parnell believed it was flawed but said he was prepared to vote for it. The Bill split the Liberal Party and was defeated in the House of Commons. Gladstone's government fell soon afterwards.(http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/historic_figures/parnell_charles.shtml, accessed 21 January 2014) The Irish National Land League (Irish: Conradh na Talún) was an Irish political organisation of the late 19th century which sought to help poor tenant farmers. Its primary aim was to abolish landlordism in Ireland and enable tenant farmers to own the land they worked on. The period of the Land League's agitation is known as the Land War. Within decades of the league's foundation, through the efforts of William O'Brien and George Wyndham (a descendant of Lord Edward FitzGerald), the 1902 Land Conference produced the Land (Purchase) Act 1903 which allowed Irish tenant farmers buy out their freeholds with UK government loans over 68 years through the Land Commission (an arrangement that has never been possible in Britain itself). For agricultural labourers, D.D. Sheehan and the Irish Land and Labour Association secured their demands from the Liberal government elected in 1905 to pass the Labourers (Ireland) Act 1906, and the Labourers (Ireland) Act 1911, which paid County Councils to build over 40,000 new rural cottages, each on an acre of land. By 1914, 75% of occupiers were buying out their landlords, mostly under the two Acts. In all, under the pre-UK Land Acts over 316,000 tenants purchased their holdings amounting to 15 million acres (61,000 km2) out of a total of 20 million acres (81,000 km2) in the country. Sometimes the holdings were described as "uneconomic", but the overall sense of social justice was undeniable. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Irish_National_Land_League, accessed 21 January 2014) The Irish National Land League was founded at the Imperial Hotel in Castlebar, the County town of Mayo, on 21 October 1879. At that meeting Charles Stewart Parnell was elected president of the league. Andrew Kettle, Michael Davitt, and Thomas Brennan were appointed as honorary secretaries. This united practically all the different strands of land agitation and tenant rights movements under a single organisation. The two aims of the Land League, as stated in the resolutions adopted in the meeting, were: ...first, to bring out a reduction of rack-rents; second, to facilitate the obtaining of the ownership of the soil by the occupiers. That the object of the League can be best attained by promoting organisation among the tenant-farmers; by defending those who may be threatened with eviction for refusing to pay unjust rents; by facilitating the working of the Bright clauses of the Irish Land Act during the winter; and by obtaining such reforms in the laws relating to land as will enable every tenant to become owner of his holding by paying a fair rent for a limited number of years. Charles Stewart Parnell, John Dillon, Michael Davitt, and others including Cal Lynn then went to America to raise funds for the League with spectacular results. Branches were also set up in Scotland, where the Crofters Party imitated the League and secured a reforming Act in 1886. The government had introduced the first ineffective Land Act in 1870, then the equally inadequate Acts of 1880 and 1881 followed. These established a Land Commission that started to reduce some rents. Parnell together with all of his party lieutenants, including Father Eugene Sheehy known as "the Land League priest", went into a bitter verbal offensive and were imprisoned in October 1881 under the Irish Coercion Act in Kilmainham Jail for "sabotaging the Land Act", from where the No-Rent Manifesto was issued, calling for a national tenant farmer rent strike which was partially followed. Although the League discouraged violence, agrarian crimes increased widely. Typically a rent strike would be followed by evictions by the police, or those tenants paying rent would be subject to a local boycott by League members. Where cases went to court, witnesses would change their stories, resulting in an unworkable legal system. This in turn led on to stronger criminal laws being passed that were described by the League as "Coercion Acts". The bitterness that developed helped Parnell later in his Home Rule campaign. Davitt's views were much more extreme, seeking to nationalise all land, as seen in his famous slogan: "The land of Ireland for the people of Ireland". Parnell aimed to harness the emotive element, but he and his party preferred for tenant farmers to become freeholders on the land they rented, instead of land being vested in "the people".(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Irish_National_Land_League, accessed 21 January 2014)Image of bearded man known as Charles Stewart Parnellballarat irish, parnell, charles parnell, home rule -
 Lara RSL Sub Branch
Lara RSL Sub BranchBook, Holidays by LMS - 1947, 1947
This Holiday accommodation Book is the official guide to accommodation at the principal resorts in England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland, on or served by the London Midland and Scottish Railway.Printed in 1947 for London Midland And Scottish Railway.Rectangular shaped Holiday Accommodation Book.Holidays by LMS - 1947book, holiday accommodation book, lms holidays, lara r.s.l. -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumBook - Family History, Hogan Family History, 2004
Follows family of Thomas Hogan, Ireland 1788- ; Gisborne 1854- ; Tatura C 1876. Compiled for Hogan Family reunion, Gisborne, 2004.A4 size, clear plastic cover, green bound spine. 63 pages.hogan family history, hogan family, hogan family reunion -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook, Kings in grass castles
"Kings in grass castles by Mary Durack, 1968", history of the Durack family, pastoralists, from the emigration of Darby Durack from Ireland in 1949.agriculture wool - history pastoral industry - history, agriculture, wool - history, pastoral industry - history -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, 29-31 Gillies Street Mitcham, 16/12/2002 12:00:00 AM
House was built for George Ireland whose first wife died in childbirth. His sister came as housekeeper and George later married her.Coloured photograph House at 29-31 Gillies Street Mitcham to be demolished. See History.gillies street, mitcham nos. 29-31, ireland, george -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyMixed media - Video, RDHS Guest Speaker Presentation - "Hugh Mahon - Patriot, Pressman, Politician" - Dr Jeff Kildea
Digitised video (3.20GB) Duration: 63 minutes. Recorded May, 2021 (Video is available for viewing at Ringwood & District Historical Society Archives by appointment)Presenter: Dr Jeff Kildea is an Honorary Professor in Irish Studies at the University of New South Wales. In 2014 he held the Keith Cameron Chair of Australian History at University College Dublin. He is the author of numerous books and articles on the Irish in Australia including Hugh Mahon: Patriot, Pressman, Politician, Anchor Books Australia, Melbourne, 2017 (Vol 1) and 2020 (Vol 2). This talk examines the background to Mahon’s expulsion from parliament and how it led to his being ostracised by his fellow Australians including his neighbours at Ringwood. -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, Late 19th century
It is a portrait of a person assumed to be a distant relative of the Evans family. The photo has been handed down through four generations to the donor, Jane Ireland.A framed copy of an oval type photograph of a lady. The frame is made up of a brown stained timber on the outside with a gold surround in the middle and a red velvet inner surround. The head and shoulders portrait shows a lady dressed according to the fashion of the late Victorian era.evans, anne, holden, anne, emu bottom homestead, settlers, george evans collection -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, William O'Brien, c1864
William X. O'Brien (ITGWU) and William O'Brien (Home Rule/IPP) were contemporaries in Irish politics early in the 20th century, but should not be confused. Image of a bearded politician known as William O'Brien.ballarat irish, o'brien, william o'brien, home rule
