Showing 692 items
matching bowen
-
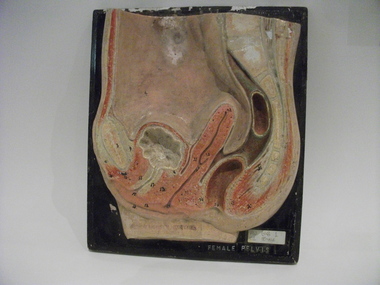 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Teaching model, female pelvis, 1940s-1950s
Originally this teaching model belonged to Prince Henry's hospital library and was transferred to the Monash Medical Centre, Clayton in the 1970s by Sister Gertrude Berger, a famous nurse-educator, who is best known for her work leading up to the transfer of nursing education in Victoria from hospitals to universities in 1986.Gerty (as she was known in the School of Nursing) bought them in Europe in the late 1940s and early 1950s.Teaching model. Female Pelvis, cross section, flat 3D panel. Painted plaster on painted timber. Originally from Prince Henry's Hospital Nurses Library [ traces of stamp "PRINCE HENRYS HOSPITAL NURSES LIBRARY" on l.l.].teaching model, anatomy, female pelvis -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Teaching model, female reproduction organs, 1940s-1950s
Originally this teaching model belonged to Prince Henry's hospital library and was transferred to the Monash Medical Centre, Clayton in the 1970s by Sister Gertrude Berger, a famous nurse-educator, who is best known for her work leading up to the transfer of nursing education in Victoria from hospitals to universities in 1986.Gerty (as she was known in the School of Nursing) bought them in Europe in the late 1940s and early 1950s.Teaching model- 3D Female Reproduction Organs on stand. Plastic. Demonstration model for the insertion of cervical diaphragm. Manufacturer: Ortho, New Jersey. Barcode label Monash Medical Centre Clayton.teaching model, anatomy, female reproduction organs -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Uterine Dilator, Bossi's, c1913
On Loan from the Otago Medical School Alumnus Association as of 18 March 2013.This loan was arranged by Dr Richard Seddon. Initially the instrument was to be donated to RANZCOG, however the Alumnus association decided on long term loan instead.Bossi's uterine dilator, for rapid dilation, four blade, manufacturer, Meyer & Meltzer, London. Stamped Meyer & Meltzer, London on central body of the instrument. Otago Medical School registration number "�M 06.18" on central body near the screw mechanism,uterine dilation -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Cranioclast, Simpson's, c1913
On Loan from the Otago Medical School Alumnus Association as of 18 March 2013.This loan was arranged by Dr Richard Seddon. Initially the instrument was to be donated to RANZCOG, however the Alumnus association decided on long term loan instead.Simpson's, cranioclast, with traction attachment,ebony handle inserts. Manufacturer unknown. Otago Medical School registration number "�M 11.211" on label.cranioclast, simpson's, destructive instrument -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Pelvimeter, Thom's
Provenance unknown, found in a box with five other pelvimeters, marked "PELVIMETERS ( not accessioned)"in the hand of the previous curator, Melissa Campbell pre 2006.Thom's pelvimeter,internal, stainless steel. Reefer to Down Bros. catalogue 939/4, page 939. Quoted from this source Thom's as used by Whitridge Wuilliams, Obstetrics", pp. 860-906. Thom, "Study of funnel pelvis,"Amereican Journal of Surgery, July 1f915.pelvimetry -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Pelvimeter, Martin's
Provenance unknown, found in a box with five other pelvimeters, marked "PELVIMETERS ( not accessioned)" in the hand of the previous curator, Melissa Campbell pre 2006.Martin's pelvimeter,external, graduated to 50cm and 20 inches. fer to Down Bros. catalogue 938/1, page 938.Manufactureer's statmp "W. & W. on arm.pelvimetry -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Pelvimeter, Martin's
Provenance unknown, found in a box with five other pelvimeters, marked "PELVIMETERS ( not accessioned)" in the hand of the previous curator, Melissa Campbell pre 2006.Martin's pelvimeter,external,nickel plated steel,l, graduated to 50cm and 20 inches. fer to Down Bros. catalogue 938/1, page 938. German manufacturer; stamped "GERMANY" on arm.pelvimetry -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Pelvimeter,Skutsch's
Provenance unknown, found in a box with five other pelvimeters, marked "PELVIMETERS ( not accessioned)" in the hand of the previous curator, Melissa Campbell pre 2006.Skutsch's's pelvimeter,external and internal, pewter with two flexible arms to attach to the pelvimeter. t, one rigid arm is missing. Refer to Down Bros. catalogue 938/4, page 938. Manufacturer's stamp "HATRICK" on arm.pelvimetry -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Commemorative Lister Memorial Oration medal presented to Dr George Rothwell Adam, 1922, Spink & Son Ltd, 1922 (approximate)
This medal was awarded to Dr George Rothwell Adam, who was a lecturer in Obstetrics at the University of Melbourne from 1899 to 1913. As part of receiving this award, Adam delivered a Listerian Oration entitled ' The influence Listerism exercises on obstetrics' at a meeting of the South Australian Branch of the British Medical Association on May 25, 1922. "This Oration and Medal was established by the South Australian Branch of the British Medical Association in 1914. The first Oration was delivered on Thursday, June 25th of that year. On that day, the new premises of the Branch was opened. Subsequently, this annual Oration became recognized as the most important scientific event in the calendar of branch Scientific Meetings. In 1948 it was delivered by one of South Australia’s famous sons, Sir Hugh Cairns. There has been no Lister Oration since 1979. The obverse of the Lister Medal shows a portrait of Lord Lister 1827-1912, and on the reverse is inscribed ‘British Medical Association, South Australian Branch, Lister Oration’. Wood Jones’ Lister Oration 1926 ‘Before a large attendance of members of the South Australian branch of the British Medical Association at Lister Hall, Hindmarsh Square [Adelaide] on Thursday evening [May 27thl Professor F. Wood-Jones, F.R.S. of the Adelaide University, was heard with close attention during his lecture on “Disease and Individuality ’ ’. ’" from Frederic Wood Jones - his academic medals and those they honoured by B. E. Christophers, Aust. N.Z. J. Surg. (1995) 65, 122-134 Bronze coloured metal medallion with presentation box. Front of medal carries a bust image of Joseph Lister, and is inscribed "LISTER 1827-/1912". Back of medal carries an image of some foliage, topped by a shield motif. The shield carries a wreath and the text "LISTER/ORATION". Back of medal also carries the text "BRITISH/MEDICAL/ASSOCIATION/SOUTH/AUSTRALIAN/BRANCH". Edge of medal is engraved with the text "G. ROTHWELL ADAM 1922". Presentation box is covered in brown leather, with gold tooling on the lid. Inside of lid covered with cream satin, and base covered with green velvet. Small length of cream ribbon sits in case under medal allowing it to be easily lifted from the depression it sits in. Text printed inside lid reads, "BY APPOINTMENT/SPINK & SON LTD./17 & 18 PICCADILLY, W.""G.ROTHWELL ADAM 1922"numismatics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Slide projector, hand held, 1970s
Belonged to Dr Geoff Bishop, used with patientsOmni Health Communicator reader with two slide cassettes [420.2, 420.3] titled "Diaphragm Insertion" and "Breast Self Exam", used in the 1970s, Dr Geoff Bishops 's rooms.teaching aid -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Pelvimeter, French model
Provenance unknown, found in a box with five other pelvimeters, marked "PELVIMETERS ( not accessioned)" in the hand of the previous curator, Melissa Campbell pre 2006.A French model of pelvimeter,external and internal,with two flexible arms, nickel plated steel, graduated 20-45 centimetres. Refer to Down Bros. catalogue 937/6/, page 9387. Manufacturer's stamp or initials of owner "M.S."pelvimetry -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Pelvimeter, French model
Provenance unknown, found in a box with five other pelvimeters, marked "PELVIMETERS ( not accessioned)" in the hand of the previous curator, Melissa Campbell pre 2006.A French model of pelvimeter,external and internal,with two flexible arms, nickel plated steel, graduated 20-45 centimetres. Refer to Down Bros. catalogue 937/6/, page 9387. Manufacturer unknown.pelvimetry -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Pelvimeter, French model
Provenance unknown, found in a box with five other pelvimeters, marked "PELVIMETERS ( not accessioned)" in the hand of the previous curator, Melissa Campbell pre 2006.A French model of pelvimeter,external and internal,with two flexible arms, nickel plated steel, graduated 20-50 centimetres. Refer to Down Bros. catalogue 937/6/, page 9387. Manufacturer unknown.pelvimetry -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Weighing scales, baby, 1970s
This item was purchased from the auction house Leski's. It was to be included in a Medical collection auction on 8 May 2013 but was left off the listing. Museum Curator made a private offer of $160 prior to the auction which the owner accepted. The weighing scales was part of a rare collection of medical, dental and pharmaceutical objects belonging to a tourism business, Kryal Castle, near Ballarat, Victoria from 1974. At some point,apparently, an officer manager discarded the museum records, so the provenance of the weighing scales, and many other items in the Leski auction, has been lost.This weighing scales is made of yellow painted metal, with a slide gauge in imperial measure. Manufacturer: Secal.Vogel & Haike, Hamburg [nameplate at front].Manufactured in the the , and such scales were widely used in Infant Welfare Centres across Victoria and possibly other states in the 1970s. A midwife/ infant welfare nurse Martine Jackson recalls seeing a weighing scales like this as a student in the 1970s in Melbourne.infant care -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Clip, Filshie, c1982
Filshie clip, titanium and silicone clip used for tubal occlusion. This clip is unused and was in the posession of the donor, Dr Ray Hyslop. Flishie clips come onto the market in 1982 and was developed by Dr Mark Filshie of Nottingham U.K.contraceptive, contraceptive, filshie clip, tubal occlusion, sterilization, female -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Forceps, Palmer's diathermy, c1969
Part of the laparoscopy equipment donated by Dr Geoff Bishop. Dr Geoffrey Bishop, whilst at the Department of O and G, University of Liverpool, UK, began laparoscopy in 1969. On returning to Australia, Bishop and Grimwade together with Mr Peter Paterson introduced gynaecological laparoscopy to Melbourne, practising at the Queen Victoria Memorial Hospital (QVMH), Melbourne in 1969. The College, through the Victorian State Committee of the Australian Council, RCOG, ran training courses in laparoscopy for local and interstate gynaecologists. These were conducted by Bishop, Grimwade and Paterson. They established protocols, with particular reference to safety, for the conduct of laparoscopy. Laparoscopy was used initially for diagnosis and for limited treatment using diathermy for conditions such as endometriosis. The real impetus came with the great upsurge of tubal sterilization in the early 1970s. Early techniques included diathermy and division of the Fallopian tubes using the Palmer forceps. [Dr Peter Renou, former honoury curator.]Palmer's diathermy forceps. It has two pronds for grasping that retracts with a screw mechanism. Purchased by Geoff Bishop as an additional part of original laparoscopy set, also included in this accession 1999005.laparoscopy, tubal ligation, infertility investigation -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Cannula, Spackman's, c1969
Part of the laparoscopy equipment donated by Dr Geoff Bishop. Dr Geoffrey Bishop, whilst at the Department of O and G, University of Liverpool, UK, began laparoscopy in 1969. On returning to Australia, Bishop and Grimwade together with Mr Peter Paterson introduced gynaecological laparoscopy to Melbourne, practising at the Queen Victoria Memorial Hospital (QVMH), Melbourne in 1969. The College, through the Victorian State Committee of the Australian Council, RCOG, ran training courses in laparoscopy for local and interstate gynaecologists. These were conducted by Bishop, Grimwade and Paterson. They established protocols, with particular reference to safety, for the conduct of laparoscopy. Laparoscopy was used initially for diagnosis and for limited treatment using diathermy for conditions such as endometriosis. The real impetus came with the great upsurge of tubal sterilization in the early 1970s. Early techniques included diathermy and division of the Fallopian tubes using the Palmer forceps. [Dr Peter Renou, former honoury curator.]This Spackman's cannula was used by Dr Geoff Bishop during gynaecological laparscopioc surgery.He used this decice as a uterine elevator. Also, for testing tubal patency by inserting dye through it. Manufacturers stamp: ANAX.laparoscopy, tubal ligation, infertility investigation -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Identification bracelet worn by F J Browne
This bracelet is possibly associated with FJ Browne's service with the Royal Army Medical Corps in World War I. Identification bracelets were worn during World War I and II in England.Francis James Browne died in Sydney 1963. He had a long career in obstetrics and gynaecology. Summary of appointments include: General Practice in Wales, Maternity Department of the Edinburgh Royal Infirmary, 1st director of obstetric unit, University College Hospital London. Retired and continued postgraduate teaching in London and NSW. Married to Grace Cuthbert, who was director of Maternal and Baby Welfare in NSW. Collection of objects transferred from the Archives to the Museum collection found amongst Professor FJ Browne's papers.Silver identification bracelet. Bracelet is engraved "FJ BROWNE/ HEATH LODGE/ WATFORD HEATH." Reverse of bracelet is engraved "SILVER". browne fj -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Cannula, infertility, c1969
Part of the laparoscopy equipment donated by Dr Geoff Bishop. Dr Geoffrey Bishop, whilst at the Department of O and G, University of Liverpool, UK, began laparoscopy in 1969. On returning to Australia, Bishop and Grimwade together with Mr Peter Paterson introduced gynaecological laparoscopy to Melbourne, practising at the Queen Victoria Memorial Hospital (QVMH), Melbourne in 1969. The College, through the Victorian State Committee of the Australian Council, RCOG, ran training courses in laparoscopy for local and interstate gynaecologists. These were conducted by Bishop, Grimwade and Paterson. They established protocols, with particular reference to safety, for the conduct of laparoscopy. Laparoscopy was used initially for diagnosis and for limited treatment using diathermy for conditions such as endometriosis. The real impetus came with the great upsurge of tubal sterilization in the early 1970s. Early techniques included diathermy and division of the Fallopian tubes using the Palmer forceps. [Dr Peter Renou, former honoury curator.]This cannula has two points for tubal attachments at one end. At yhe other end, a bell cap with a nossel.This was used by Dr Geoff Bishop during gynaecological laparscopioc surgery. This instrument is commonly used for suction. Also, for testing tubal patency by inserting dye through it. Manufacturers stamp: PRECIOUS.laparoscopy, tubal ligation, infertility investigation -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Surgical kit used by Lord Joseph Lister, Archibald Young of Edinburgh, 1870s
This surgical instrument kit, c1870s, originally belonged to Lord Joseph Lister. On his retirement in 1892, Lord Lister presented the instrument kit to his friend Dr Alexander Matthew. The donor of the surgical kit, Professor Ian Stewart Fraser, is the great grandson of Dr Alexander Matthew. The donor, Ian Fraser, checked with his mother about the inscription "Ethel Livie". There was no one of that name in his mother's family tree and the instruments were passed down from his mother's family.This surgical kit, made by Young of Edinburgh Scotland in the 1870s is significant because it belonged to and was most likely used by an internationally important figure in modern medicine, Lord Joseph Lister. Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Bt., OM, FRS, PC (5 April 1827 – 10 February 1912), known as Sir Joseph Lister, Bt., between 1883 and 1897, was a British surgeon and a pioneer of antiseptic surgery. By applying Louis Pasteur's advances in microbiology, he promoted the idea of sterile surgery while working at the Glasgow Royal Infirmary. Lister successfully introduced carbolic acid (now known as phenol) to sterilise surgical instruments and to clean wounds, which led to a reduction in post-operative infections and made surgery safer for patients. Surgical instruments in original timber case, containing two steel sharp hooks with the manufacturer's stamp,"YOUNG EDINBURGH" on the handles, five steel scalpels with ebony handles in assorted sizes. Also included separately are autopsy hooks, one metal blowpipe [commonly used with urine testing apparatus] and two dissector forceps. "YOUNG EDINBURGH"; "ETHEL LIVIE"surgery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Plaster cast of the head of the first baby to be delivered under anaesthesia by the use of ether, 1847
This a cast of the first baby to be delivered under anaesthesia, by the use of ether, in Edinburgh on 19 January 1847. The famous physician James Young Simpson, Professor of midwifery at Edinburgh University, attended this birth and wrote about it in the Monthly Journal of Medical Science 1846-7 Vol.7, p649-640. The cast of the baby's head was given to Lance Townsend, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, University of Melbourne by Robert Kellar, then Professor of Midwifery and Diseases of Women at the University of Edinburgh, when Professor Townsend was visiting Edinburgh. There is at least one other plaster copy; one is located at Wood Library-Museum of Anesthesiology, 520 North Northwest Highway, Park Ridge, IL 60068-2573, USAReplica of a new born baby's head, painted plaster, life size. The model of the head shows a large indentation of two and a half inches in the skull on the left side. The baby was delivered through a severely deformed pelvis, suffered a large indentation to the skull and did not live.obstetric delivery, anaesthesia -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Gates, Lying in Hospital, c1856
Salvaged during the building's demolition by Dr Frank Forster.Cast iron Hospital Gates from the first Lying-In hospital, a leased two storey terrace building at 41 Albert Street Eastern Hill (East Melbourne) which operated from 1856-8 before relocating to Carlton.hospital, lying-in hospital, melbourne -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Medal - Commemorative medal celebrating the centenary of the Births, Deaths and Marriages Registration Act, 1937, Royal Mint, c. 1937
The Registration Act 1836 established the General Register Office and a new system of national registration of births, marriages and deaths to take effect from 1837. There was a need to set up a system to record births, to aid with the planning of services and to record deaths to enable further study on the causes of mortality. The accurate recording of births and deaths was to be a vital tool in improving population health and would later enable systematic interventions such as vaccination, as well as aiding research and data analysis. ('1836 Registration Act')Round silver medallion with presentation case. Front of medal features portraits of King George VI and Queen Elizabeth in profile. Text encircling the portraits reads 'BIRTHS & DEATHS REGISTRATION & MARRIAGES ACTS". Back of medal carries a lit torch design at centre, encircled by the text "BIRTH . MARRIAGE . DEATH". Presentation case is a square, green, leather box with cream satin and beige velvet lining. There is a central depression within the case in which the medallion sits. Text printed on upper surface of box lid reads "B.D. and M./CENTENARY/1837-1937". Royal Mint insignia stamped in gold inside lid.numismatics -
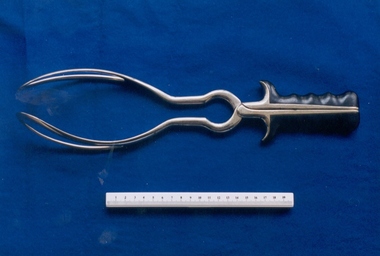 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Barnes-type obstetrical forceps with Simpson style handles, c. 1849-1962, J. Grey & Son, Sheffield, U.K
Neville Barnes obstetric forceps have a cephalic and pelvic curve and are used for delivery of babies presenting as occipitoanterior. The left blade is put on first, followed by the right blade – the baby is then pulled down until the occiput is under the symphysis, then pulled around. This particular set of Barnes forceps is unusual because it has handles/grips associated with Simpson type obstetrical forceps, making it a combination of styles. These forceps are similar in appearance to a style of 19th century forceps known as Hensoldt's forceps, made by Jetter and Scheerer, c. 1899. These are pictured as Fig. 771 in the Sir Kenardatth Das catalogue (see references). J. Gray & Son, Sheffield, were in operation from 1849 to 1962, so these forceps date from this time period.Set of obstetric forceps. Consists of a set of stainless steel blades, with black bakelite hand grip attachment. Forceps are engraved with the text 'J.GREY & SON" and "SHEFFIELD". The number '4' is engraved on the inner aspect of the blade, at the join point.'J.GREY & SON/SHEFFIELD'obstetric delivery -
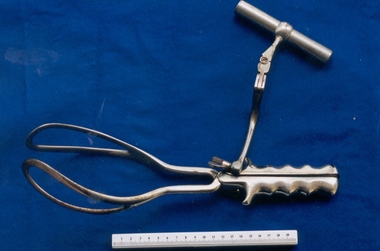 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Simpson-type obstetrical forceps with Neville traction rod used by Dr John S Green, c. 1930s
These forceps were owned by Dr John Sidney Green, who was very skilled in their use and at the peak of his career in 1936. Green was a contemporary of Arthur Wilson and Arthur Chambers [Communication from Dr Cyrus Jones, 17/7/1997]. These forceps are unusual due to the addition of the Neville traction rod attachment, which is usually associated with Barnes-Neville forceps rather than Simpson forceps. Developed by James Young Simpson in 1848, Simpson forceps have become arguably the most popular model of forceps for use, and were adapted in the creation of many later designs.Set of steel obstetric forceps, consisting of two blades and a traction rod attachment. Inscribed "J.S.G" on stem of left blade."J.S.G"obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Magic Lantern, 1927
Dr Mabel Maguire, widow of Dr Frederick Arthur Maguire (1888- 1953) donated it in 1962 along with a number of glass slides.Dr Maguire owned and used the item, giving Anatomy lessons to medocal students,. Used mostly in Sydney (University of Sydney) 1962Magic lantern or Baloptian [precursor to slide projector]. Model BC. Bausch & Lamb Optical Co, Rochester NY. Electrical, metal projector box with lens in bronze casing a timber frame for glass slides marked "(illeg.) PATENT ECLIPSE" an attached electrical lead with bakerlite plug. c1927.No slides, either missing or none received.instrument, optical -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sign, advertising, 1930s
Most likely purchased by former curator Melissa Campbell from a market or antique store.Advertising sign, enamel paint on metal, "AUSTRALIA'S/ FOSTER MOTHER/ NESTLE'S MILK". H 45..0.x w 75.4cminfant feeding -
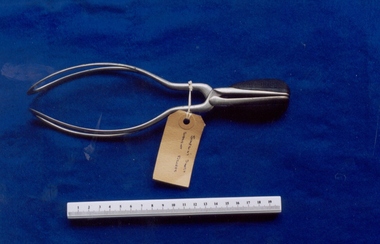 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Short handled Simpson-type obstetrical forceps, c. 1851 - 1880, W. Skidmore, Sheffield
First developed by James Young Simpson in 1848, Simpson forceps have become arguably the most popular model of forceps for use, and were adapted in the creation of many later designs.Set of small, straight metal obstetric forceps with black bakelite insertions on handles. Stamped 'W. SKIDMORE/SHEFFIELD' on inside of left handle.obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Lead nipple shields developed by Dr. Wansbrough, Dr Wansbrough, England
The changes in the metal observable on the interior of both these lead nipple shields suggests that this pair was well used. One can only imagine the long-term effects. Perhaps significantly, the lid of the box is stained with the distinctive purple of gentian violet. The underside of the lid claims “They are in no way likely to be injurious to the infant”. Allen & Hanbury’s catalogue of c1901 lists these as costing 1/- per pair.Two nipple shields, lead, moulded, 6cm diameter, with "England" impressed on inside. In original manufacturer's circular cardboard box.breast feeding -
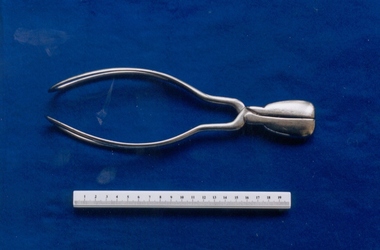 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Short handled Simpson-type obstetrical forceps, Down, London
First developed by James Young Simpson in 1848, Simpson forceps have become arguably the most popular model of forceps for use, and were adapted in the creation of many later designs.Short handled set of forceps, possibly made of stainless steel. Marked "DOWN LONDON" on inner aspect of left blade handle.'DOWN LONDON'obstetric delivery
