Showing 596 items
matching banks in warrnambool
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Money box
Metal money boxes shaped like common familiar objects became a popular from the 18th century. In the 20th century they were used to promote and advertise events and businesses. In the 1950s money boxes shaped like a bank building were given away to children by their parents' bank to encourage them to save money. This money box was possibly used in an organisation such as the Missions to Seamen as a donation box, particularly as there is no means of easily opening the box or tampering with it.The money box is an example of a way of collecting money as a donation or contribution for an organisation or charity.Money box, rectangular polished wood money box with coin slot in the top and a blue felt fabric pad on the base. The base has a purple stamped inscription which is indecipherable. There is no obvious means of opening the box. The box has contents.Stamp (indecipherable)flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, money box, money safe, vintage money box, wooden money box, savings, donations, collection, contribution -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet - English Scottish and Australian Bank Cheque Book, 1950s, English, Scottish & Australian Bank Ltd, c1950
This cheque book was found in a shop on the corner of Sturt and Camp Streets, Ballarat by a builder around 2004. The English, Scottish & Australian Bank Limited was founded in 1852 by Royal Charter in London as the English, Scottish and Australian Chartered Bank. The bank opened its first Australian branch in Sydney in 1853. Australian banknotes were printed by the bank and issued at branches in Sydney, Adelaide, Hobart and Melbourne. In 1893, the bank was renamed the English, Scottish & Australian Bank following the financial upheaval. The bank was one of 16 banks which supplied blank note forms to the Australian Government in 1911 which were superscribed as redeemable in gold and issued as the first Commonwealth notes. The bank took over the Commercial Bank of Tasmania Limited and the London Bank of Australia Limited in 1921 and the Royal Bank of Australia Limited in 1927. On 1 October 1970, the bank merged with the Australia and New Zealand Bank to form the Australia and New Zealand Banking Group Limited. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/English,_Scottish_and_Australian_Bank, accessed 27/03/2014)A half used cheque book from the English, Scottish & Australian Bank Ltd. The used cheques date from 1858 to 1860. Cheques are made out to the Old Colonists Club and Hotel Warrnambool. Notes on the inside cover are precautions against fraud.bank, banking, english scottish and australian bank, anz bank, cheque book -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Bag, 1930's
In the words of Donor, Betty Stone, "Owned by my aunt Mrs Elsie Mary (nee Dale) Towers, born 24 December 1895, daughter of Ellis and Ann Dale, of Latrigg, Wangoom, Warrnambool. This beaded bag was a personal gift from Miss Lake to Elsie Dale sometime in the early 1930s. Miss Lake was a member of a leading Warrnambool family whose property Lyndoch was situated by the banks of the Hopkins River. After completing her nursing course at Warrnambool Hospital and working there for a time, Elsie Dale was appointed Sister-in-Charge of the newly formed Baby Health Centre, which initially operated in temporary accommodation at or near the Council Chambers. In 1928 the Centre moved into new brick premises on Liebig Street. The building comprised of five rooms, a back yard and a front veranda where mothers parked their prams. The Warrnambool Standard reported in February 1928. The purpose of the Clinic is to the saving of infant's life. Many mothers attended the Clinic in the former location. They were able to acquire valuable knowledge from Sister Dale who is in charge of the Clinic and also have their infants weighed and measured each week. During the early days of the Centre Miss Lake, as a patron, took a keen interest in all aspects of the Centre and co-operated very closely with Sister Dale. Miss Lake would often call in at the centre while her uniformed chauffeur would wait beside her limousine parked in the street outside the Baby Heath Centre. I also recall my aunt driving to Lyndoch to discuss matters concerning the Centre with Miss Lake. Miss Lake purchased this evening bag in England, and upon her return from her overseas tour in the early 1930s, presented it to Sister Dale as a token of appreciation. Dedicated to her vocation, Sister Dale gave unstintingly of her effort, time and resources to create an attractive venue for mothers to visit. Her contribution to the welfare of all mothers and babies in the Warrnambool area, particularly during the Depression years, was considerable. Sister Dale, who drove a Dodge Tourer car, visited mothers in their homes when necessary and regularly visited the indigenous settlement at Framlingham. Amongst my early childhood memories are those of accompanying my aunt when she drove to the Nestles factory at Dennington to purchase large tins of dried milk baby food which she then delivered to the mothers who lived at the Framlingham settlement. Sister Elsie Dale retired in 1949 and moved to Mooroopna after her marriage to Solomon Towers. (Died aged 75 years 27 July 1971) (Note: For additional information please refer to Betty Stone’s book “Pioneers and Places - A History of three Warrnambool Pioneering Families” ie. Chamberlain, Dale and Lees Families)This item is associated with the families of Chamberlain, Dale and Lees. These families are listed in the "Pioneers' Register" for Warrnambool Township and the Shire, 1835-1900, published by A.I.G.S. Warrnambool Branch. Elsie Dale was the first Sister to work in the newly established Baby Health Centre in Warrnambool.Beaded evening bag or clutch purse. The bag was a gift to Elsie Dale from friend Miss Lake, purchased in England early 1930's. The fabric is covered in tiny white beads and features a floral design in browns and greens. The bag has two bead-covered handles and the lining includes a small pocket. Part of the 'Chamberlain Dale Lees Collection'.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, chamberlain, dale, lees, stone, betty stone, warrnambool pioneers, elsie dale, miss lake, lyndoch, handbag, purse, evening bag, beaded handbag, beaded purse, ladies' accessory, clutch purse, warrnambool baby health centre, infant welfare centre -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTimer, 1940s
Australia's first telephone exchange was opened in Melbourne in August 1880. It was operated by the Melbourne Telephone Exchange Company. Owned by W. H. Masters and T. T. Draper, the Manager of the Company was H. Byron Moore. This was only two years after the world's first exchange in the United States, and just four years after Bell first spoke on a telephone. The exchange was located in the old Stock Exchange building at 367 Collins Street, a site now occupied by the Commonwealth Bank. In 1884, the operations of the Company, by then known as the Victorian Telephone Exchange Company, had grown considerably and were transferred to Wills Street, Melbourne. Private ownership of this company continued until 1887 when it was bought out by the Victorian Colonial Government. Other colonial governments followed this example. By 1910, the growth in telephone services made additional accommodation necessary. This could not be provided in the existing building in Wills Street and arrangements were made for a new exchange in Lonsdale Street. Alexander Graham Bell visited Australia in 1910 to advise the Federal Government's Postal Commission. Telephone exchanges were established in Adelaide with (48 subscribers), Hobart (10 subscribers) and Launceston (35 subscribers). The first exchange in Western Australia was established in 1887 and located in a small three-room cottage in Wellington Street, Perth with 17 subscribers. The year 1888 marked the opening of the Fremantle exchange in a small room at the rear of the Town Hall. There were nine subscribers. Australia's first automatic exchange was installed in the GPO in Sydney, in 1911, for internal use. But the first automatic exchange for public use was opened at Geelong in Victoria in the next year July 1912 with 800 subscribers. Melbourne's first automatic exchange was opened in the suburb of Brighton in 1914; the first public automatic exchange in NSW began operating at Newtown, Sydney in 1915; and Queensland's first was installed at South Brisbane in 1925. 1929 saw the opening of Tasmania's first automatic exchange in Hobart. an automatic telephone service. In June 1977, the manual telephone exchange at Swansea was replaced with an automatic service and made Tasmania the first State in Australia to have a fully automatic net work. The half-century following Federation saw the growth of the automatic operation; a great extension of trunk line services; The automatic telephone contributed greatly to the early popularity of telephones in Australia. It was a quicker and more convenient way of communicating with another person on the same exchange — instead of having to go through tedious processes with the operator. From its introduction, the number of automatic telephones in operation grew to a remarkable extent. In 1886, the first trunk link of 16 km was connected to the exchanges of Adelaide and Port Adelaide in South Australia. Then, in 1907, the first inter-capital telephone trunk line was opened between Sydney and Melbourne. It was followed by a line between Melbourne and Adelaide in 1914. Sydney and Brisbane were linked in 1923, and Perth and Adelaide in 1930. In 1930, the first overseas calls from Australia came possible with the introduction of a radio telephone service to England, and through there to Europe and America. A similar service opened to New Zealand in the same year. Initially, trunk channels linked different manual trunk exchanges. It was necessary for a succession of trunk operators to connect the appropriate channels, one after the other until the connection was made. As trunk traffic grew. the system became increasingly unsuitable. More trunk operators had to be employed and so labour costs increased. It was a tedious and slow way of making a long-distance call, and it was sometimes hard to hear, particularly when several exchanges were linked With technical advances, trunk switching moved from manual operation through a partly automatic phase. Automatic transit switching equipment was used and only a single operator was required to connect a trunk call to a wanted automatic subscriber. Until well beyond the middle of this century, the majority of trunk traffic went through this single telephonist control. In 1953, the number of telephones in use in Australia passed the one million mark. By then, the need for improvement in the automatic exchanges was be coming well recognised. The need was for a telephone switching system which would do a better job more economically than the conventional step-by-step ex-change. This led to the adoption of the Crossbar system as the standard in automatic telephone exchanges in 1960. The introduction of Crossbar switching was a big step forward in the automation of trunk calls. It substituted automatic switching and charging equipment for the originating trunk operator, and improved the quality of the system radically. Before the introduction of the Crossbar system there were often very long delays in obtaining a booked trunk call, and the quality of sound was often very poor. With Crossbar, Subscriber Trunk Dialing (STD) became a reality. A trunk call by STD was as easy to make and almost as fast to connect as a local call.The item was made around the 1940s and used up until the 1970s in manual cord telephone exchanges as a way to time and charge users for trunk calls made over the telecom system of the time. Post Master General dept. - Trunk Call Timer.Inscribed PMG, C. of A, 37. Bell chimes at 3 min increments.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, timer, trunk call, telephone, cord exchange -
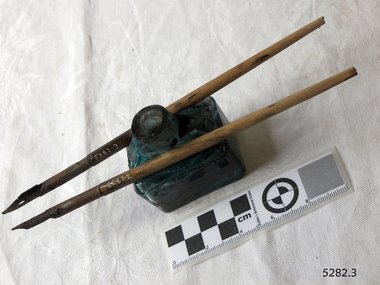 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle with pens, Early 20th century
This handmade, aqua glass ink bottle's design is sometimes called a ‘boat’ shape. The base was mouth-blown into a rectangular mould, evidenced by the lack of seams, the pontil, crease lies and the uneven thickness of the glass. The shoulder section was mouth-blown into a two-piece mould and then cut off from the blowpipe. The lip is sometimes referred to as a 'burst-lip, which was often filed to be smooth. This method of making bottles was often used in the mid-to-late 19th century. The bottle would then be filled with ink and sealed with a cork. More expensive bottles would have a lip added, which was more time-consuming and costly. The capacity for a bottle such as this was about 3 ½ oz (ounces) equal to about 100 ml. Pens are a common item for that period. Pen and ink have been used for handwriting since about the seventh century. A quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used until the mid-19th century. In the 1850s a steel point nib for the dip pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. The nis only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib into an ink well for more ink. Handwriting left wet ink on the paper, so the blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased as a ready-to-use liquid or in powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. In the 1880s a successful, portable fountain pen gave smooth-flowing ink and was easy to use. In the mid-20th century, the modern ballpoint pen was readily available and inexpensive, so the fountain pen lost its popularity. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy.The ink bottle is of interest, being made of aqua glass rather than the more common clear glass. This set of ink bottles and pens is significant because of the bottle's method of manufacture, which is representative of a 19th-century handcraft industry that has now been largely replaced by mass production. The bottle and pens are historically significant as tools used for handwritten communication until the mid-20th century when fountain pens and modern ballpoint pens became popular and convenient and mechanical typewriters became part of standard office equipment.Victorian 'Boat' ink bottle, small rectangular, aqua glass ink bottle with grooves along the long sides for pen rests. The base has a pontil, no seams, and the glass is uneven in thickness. The shoulder has two side seams and there is a ridge where it is joined onto the base; there are round indents on each of the shoulder, on the short sides, four in all. The mouth has rough edges. The neck leans to one side. The glass has impurities, crease lines and bubbles. There is dried ink in the bottle. Two pens with metal nibs are included with the ink bottle. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, ink, nib pen, writing ink, writing, copying, banks, lawyers, commerce, student, permanent ink, stationery, record keeping, handwriting, writing equipment, writing accessory, office supply, cottage bottle, boat bottle, mouth-blown bottle, two-part mould, sheer-lip bottle, burst-lip, cork seal, copy ink, aqua glass -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle and Pen, Caldwell’s Ink Factory, Early 20th century
This shaped ink bottle made by Caldwell's is called a 'boat ink bottle'. It was shaped especially to hold a nib pen when the pen was not in use. The design of the bottle is sometimes called a ‘cottage’ or ‘boat’ shape. The Caldwell’s handmade glass ink bottle was mouth-blown into a two-piece mould, a method often used in the mid-to-late 19th century. The glass blower burst the bottle off the end of his blowpipe with a tool, leaving an uneven mouth and sharp edge on the bottle, which was usually filed. The bottle was then filled with ink and sealed with a cork. More expensive bottles would have a lip added, which was more time-consuming and costly to produce. The capacity for a bottle such as this was about 3 ½ oz (ounces) equal to about 100 ml. Pen and ink have been in use for handwriting since about the seventh century. A quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used up until around the mid-19th century. In the 1850s a steel point nib for the dip pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. The nis only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib into an ink well for more ink. Handwriting left wet ink on the paper, so the blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased as a ready-to-use liquid or in powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. In the 1880s a successful, portable fountain pen gave smooth-flowing ink and was easy to use. In the mid-20th century, the modern ballpoint pen was readily available and inexpensive, so the fountain pen lost its popularity. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy. Caldwell’s Ink Co. – F.R. Caldwell established Caldwell’s Ink Company in Australia around 1902. In Victoria, he operated from a factory at Victoria Avenue, Albert Park, until about 1911, then from Yarra Bank Road in South Melbourne. Newspaper offices were appointed as agencies to sell his inks, for example, in 1904 the New Zealand Evening Star sold Caldwell’s Flo-Eesi blue black ink in various bottle sizes, and Murchison Advocate (Victoria) stocked Caldwell’s ink in crimson, green, blue black, violet, and blue. Caldwell’s ink was stated to be “non-corrosive and unaffected by steel pens”. A motto used in advertising in 1904-1908 reads ‘Makes Writing a Pleasure’. Stationers stocked Caldwell’s products and hawkers sold Caldwell’s ink stands from door to door in Sydney in the 1910s and 1920s. In 1911 Caldwell promised cash for returned ink bottles and warned of prosecution for anyone found refilling his bottles. Caldwell’s Ink Stands were given as gifts. The company encouraged all forms of writing with their Australian-made Flo-Eesi writing inks and bottles at their impressive booth in the ‘All Australian Exhibition’ in 1913. It advertised its other products, which included Caldwell’s Gum, Caldwell’s Stencil Ink (copy ink) and Caldwell’s Quicksticker as well as Caldwell’s ‘Zac’ Cough Mixture. Caldwell stated in a 1920 article that his inks were made from a formula that was over a century old, and were scientifically tested and quality controlled. The formula included gallic and tannic acids and high-quality dyes to ensure that they did not fade. They were “free from all injurious chemicals”. The permanent quality of the ink was important for legal reasons, particularly to banks, accountants, commerce, municipal councils and lawyers. The Caldwell’s Ink Company also exported crates of its ink bottles and ink stands overseas. Newspaper advertisements can be found for Caldwell’s Ink Company up until 1934 when the company said they were the Best in the business for 40 years.This pen and ink bottle set is of significance as the bottle has its original cork and retains remnants of ink, which was made from a recipe that at the time was over 100 years old, according to Caldwell.. The handmade, mould blown method of manufacture is representative of a 19th-century handcraft industry that is now been largely replaced by mass production. The bottle and its contents are of state significance for being produced by an early Melbourne industry and exported overseas. The pen and ink set is historically significant as it represents methods of handwritten communication that were still common up until the mid-20th century when fountain pens and modern ballpoint pens became popular and convenient and typewriters were becoming part of standard office equipment.Victorian boat ink bottle; small rectangular clear glass ink bottle with horizontal grooves made in the glass for resting and holding the pen. The set includes one pen and nib with the bottle and cork. The bottle is made by Caldwell's and contains its Flo-Eesi Blue Black Ink brand."Caldwell's Flo-Eesi Blue Black Ink."flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, ink, nib pen, writing ink, writing, copying, banks, lawyers, commerce, student, permanent ink, flo-eesi, blue black ink, stationery, record keeping, handwriting, writing equipment, writing accessory, office supply, cottage bottle, boat bottle, mouth-blown bottle, two-part mould, sheer-lip bottle, burst-lip, cork seal, f r caldwell, caldwell’s ink company, albert park, south melbourne, inkstands, stencil ink, copy ink, quicksticker, zac cough mixture -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Letter Scale, Philip Jakob, Maul, 1930s
Jakob Maul (1866-1953) founded a metal works factory in 1912 at Zell in Odenwald not far from Frankfurt. He was born the son of a winegrower from the Rheinhessen region of Germany that lies on the left bank of the river Rhine. At the age of 45, he started a metal works factory to produce various types of scales but during the second world war the factory was bombed and production ended. Production for the manufacture of scales resumed in 1948. In 1953 at his death Jakobs son Fritz Scharmann an engineer who had been working with his father since 1923 took over the management of the Maul companies. In 1970 the production responsibilities for Philip J Maul was taken over by Porti Office Equipment who was based in Hamburg. The company has undergone several integrations with subsidiary companies. Today the company has diversified into different areas one of which is manufacturing solar scales. An original postal scale made in Germany before the Second World War and regarded today as a collector's item. It is significant as it is a snapshot into the past and how everyday vintage items were used and interacted within society in the 1930s.Antique German Jacob Maul "Concav" brass postal or letter scale, quadrant type, with pendulum, measuring up to 9ozs. The scale has a level-adjusting screw.The balance is marked "CONCAV" and graduated in imperial ounces to 9 ozflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, scale, quadrant scale, postal weight, 9 oz, philip jakob, maul, scale manufacturer, german industry, weighing instrument, inclination scale -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDecorative object - Bookends, ca. 1930s
The pair of ornamental white resin owl bookends was likely made around the 1930s when epoxy resin became available. Bookends modelled on owls have been a popular ornament for many years, possibly because of the association between owls, books and wisdom. They are used and displayed in places where books are appreciated and valued, such as homes, libraries, educational buildings, business offices, legal institutions and banks. Bookends hold a row of upright books in place by supporting the beginning and end of the row. The books are more likely to keep their integrity when stored vertically. The first patent for a metal bookend was placed by William Stebbins Barnard in 1877. Bookends became useful and decorative items around the middle of the sixteenth century after printed books became available. At that time books were expensive and treasured possessions, treated with much respect. Even in the early nineteenth century, a Bible was often the only book in the home. It was included among the limited items brought by many immigrants to Australia. Books became more available and affordable to the public by the end of the nineteenth century and households and businesses were able to build their own libraries. Bookends were used then, and are still used now, to keep books organised, cared for, and readily accessible. Bookends, a pair of two (2) small white resin owls with clear bright red eyes standing on a stack of books, their bodies facing towards each other, chests on an upright book, heads turned towards the viewer. The ends are left and right-handed.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, ornament, bookend, bookends, pair of bookends, library, book storage, book display, room decoration, resin ornament, white bookends, owl bookends, owl ornament, white owls, resin owls, book support, bookend patent, william stebbins barnard -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Safe, W. Marr, Circa 1855
This strong, heavy bank safe was made by W. Marr in London. It was formerly owned by the ANZ Bank in Portland, Victoria. Portland’s ANZ Bank was originally a branch of the Bank of Australasia, which first came to Australia in 1835, opening in Sydney. Portland’s Bank of Australasia began in a bluestone building built on the north corner of Julia and Bentinck Streets by stonemason William Robb in 1855, around the time of Australia’s Gold Rush. Eventually, in 1951, the Bank of Australasia merged with the Union Bank to become the Australia & New Zealand Bank, known as the ANZ. Portland’s branch of the Bank of Australasia then moved into the old Union Bank building at 44 Percy Streets; both bank buildings were built around the same. The maker of this safe, W. (William) Marr, obtained a patent in 1834 for what is believed to be the first fire-retarding patent, building this into the lining of strong boxes. Others made further design improvements such as hardening the metal plates used to make the boxes. In about 1840 Thomas Milner, a Sheffield tinsmith, made the earliest safes that could safely protect their contents from a surrounding fire. This was achieved by including tubes of a substance between the inner and outer walls of the safe that would react to the heat and the contents would put the fire out. In 1851 an Exhibition at London’s Crystal Palace included fire-proof safes from different vendors. William Marr was listed under Fireproof Box Makers in the 1842 London Trades Directory, at 33 Broad Street, and 52 Cheapside. William Marr & Son were appointed to supply Her Majesty’s National Debt Office and other departments in 1860, with the address 9 Walbrook, Vulcan Safe Works, Skin Yard, Bankside, Southwark, London. 1n 1870 the address for William Marr listed under Safe Makers and Agents in the London Trades Directory was 67 Cannon Street. The manufacturer, W Marr, is significant as an inventor of a way to make a strong box fireproof, then patented his secure safe. This invention indicates that security of money was of great importance in the mid-1800s as it continues to be today. The secure safe would have given much comfort to those with investments and savings, as well as to the bank itself, the custodian of other people's money. This safe was made in London and exported to colonial Australia, giving significance to the safe as an item that was high in the list of the needs of the early Australians and their businesses. The safe has local historical significance as it was used by the original Bank of Australasia in Portland, which was built in 1855 and went on to become the ANZ Bank, still in operation today. The bank was an integral part of the establishment and growth of commerce in Colonial Victoria.Safe; heavy metal bank safe, painted green. Double doors each have top and bottom external hinges, and two front panels; the top panels are arched. The thick doors have five sliding locks. Inside is a fixed metal compartment with a locked sliding metal drawer, and several fitted shelves plus some temporary removable shelving. Both doors have a decorative brass knob near the centre opening. Left door has an oval artificial keyhole and a space where another fitting has been attached. The right door has a second brass knob and an oval keyhole. The top panels of the left door has an oval plaque with an inscription; the right door has evidence that there was an oval attachment. Made by W. Marr, London.Text embossed on plaque: "W. MARR / PATENTEE & MANUFACTURER / 52 / /CHEAPSIDE / LONDON" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, maritime museum, great ocean road, shipwreck artefact, safe, bank safe, vault, security, finances, anz bank, portland bank, w marr, william w marr, financial institution, savings, gold exchange, loans, investments, safety, safe maker, lock maker, iron box, strong-room -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph
Black And White Photograph of Loch Etive 1200 Tons. 'Outward Bound To Melbourne At The Tail of the Bank - 1896 Clyde Glasgow. 155 mm X 114 mm Sh 163.2 Ships I - Lflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, loch etive, photograph -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFurniture - Theatre Chairs, 1930's
These theatre chairs had been used in the Mozart Hall in Warrnambool for many years but are now no longer required. They were about to be offered for anyone to take but just by chance Flagstaff Hill’s Manager heard about them from a friend in Melbourne. Our Manager thought it important to keep the chairs in Warrnambool as they were significant to our local history and could be incorporated in our Museum. He made arrangements to collect and install them in Flagstaff Hill’s Theatrette. Originally these theatre chairs belonged to Warrnambool Town Hall. When The Warrnambool Baths (or Swimming Pool) in Gillies Street closed, due to the Health Act of 1958, the changing rooms were taken over by the Mozart Group. The building was modified and set up for musical concerts with the name Mozart Hall. The seats were re-covered by Miss Eva Gaspar, Director of the Warrnambool Music Society, with assistance from group members. The material was order by W.C. James (Treasurer) in 1964, at a cost of 26 pound and 10 shillings (£26-10), and supplied by Jacka-Wortley Fabrics Pty Ltd, Upholstery and Furnishing Supplies, 157-163 Pelham Street, Carlton, Melbourne, Victoria. The supplier’s telephone was “JACKAFAB” (5222 2322). The fabric was delivered to J. Hulin of 116 Belmore Rd, Warrnambool. The manufacturer of the chairs, Riddell & Preece Pty Ltd of Melbourne, also supplied theatre chairs for other public buildings including (1) the Ozone Theatre in Enfield, South Australia, in 1929, (2) the Gallery of the Horsham Town Hall in Victoria (at 26/6 each, that is 26 shillings and sixpence, approximate conversion in 2014 to $100.00au), (3) in 1927 in the Gallery of the Kyenton Mechanics’ Institute (4) in 1926, Horsham Theatre. (In May 2018 a transfer of three banks of chairs was made from Flagstaff Hill to the Australian Centre for the Moving Image in Melbourne.) The chairs are of local historical and social significance. Theatre chairs. The sixteen sets (groups or banks) of complete chairs, four seats per chair, give a total of 64 seats. Each chair has timber framed seats, with arm rests, upholstered in red vinyl. The seats are set into decorative gilt iron frames which incorporate five legs, all set into two timber floor rails. The seats are hinged to fold upwards and rest against the backrests. On ironwork "PTY. LTD"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, theatre chairs, theatre seats 1939, warrnambool town hall seats, mozart hall warrnambool, theatre furniture, mechanics’ institute chairs, j hulin warrnambool, mozart hall choral group, eva gaspar, warrnambool music society, w.c. james, jacka-wortley fabrics pty ltd -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Banknote
Legal tender £5 note. Five pound note issued by The Bank of Australasia. Serial no. A23303flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, legal tender, bank of australasia, five pound note, currency, £5, banknote -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Banknote
Legal tender £1 note. One pound note issued by The Bank of Australasia. Serial no. 03077flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, £1, one pound note, legal tender, bank of australasia, currency, banknote -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSouvenir - Money box, OXO Ltd, ca. 12-5-1937
Metal money boxes shaped like common familiar objects became popular in the 18th century. In the 20th century, they were used to promote and advertise events and businesses. In the 1950s metal money boxes shaped like a bank building were given away to children by their parents' bank to encourage them to save money. This metal money box was produced for the company of OXO Ltd of London. It was made specifically as a souvenir of the Coronation of King George VI of England, which happened on May 12, 1937. OXO Ltd. still makes OXO stock cubes, which contain a concentrated meat extract. The cubes are used to flavour soups, gravy, casseroles and other food recipes to enhance their flavour. The cubes are removed from their foil wrapper then crumbled into the dish and mixed with the ingredients. Chemist Justus von Liebig worked with engineer George Gilbert of Uruguay to produce Liebig’s Extract of Meat, the forerunner of OXO . In the late 1890s, OXO produced a liquid form of the meat extract and in 1899 registered the OXO trademark worldwide, and in 1900 in the UK. In 1910 the OXO 'penny' cube was in production and proved very popular. The money box is significant for its connection to British Monarch, King George IV, who reigned from 1932-1952. It is also significant for its connection to the OXO cube, a very well knon brand of food additive from the mid-19th century to current times.Souvenir money box, oval cylinder with domed, pull-off lid and framed coin slot, with seams on each side. It once contained six OXO Cubes. The red tin with gold tin has the Royal Insignia of King George VI and Elizabeth on one side and the Royal medallion-style portrait of King George VI and Elizabeth on the other side. There is an inscription on the base and floral decorations on the sides. It was produced for OXO Ltd, Thames House, London, England, to commemorate the coronation of King George V1 and Elizabeth on May 12th 1937.Logo, Royal Insignia: "[Crown] over "G VI R" Medallion-style Portrait image: "GEORGE VI AND ELIZABETH MAY 12TH 1937" around " (Image of King George VI and Elizabeth) " Printed on base: "CORONATION / SOUVENIR MONEY BOX / CONTAINING / 6 OXO CUBES / BRAND / OXO LTD., THAMES HOUSE, / LONDON, ENGLAND."flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, money box, money safe, commemorative money box, coronation king george iv, 1937, vintage money box, oxo cube, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle, Late-19th to early-20th century
The design of the bottle is sometimes called a ‘cottage’ or ‘boat’ shape. This handmade glass ink bottle was mouth-blown into a two-piece mould, a method often used in the mid-to-late 19th century. The glass blower burst the bottle off the end of his blowpipe with a tool, leaving an uneven mouth and sharp edge on the bottle, which was usually filed. The bottle was then filled with ink and sealed with a cork. More expensive bottles would have a lip added, which was more time-consuming and costly to produce. The capacity for a bottle such as this was about 3 ½ oz (ounces) equal to about 100 ml. Pen and ink have been in use for handwriting since about the seventh century. A quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used up until around the mid-19th century. In the 1850s a steel point nib for the dip pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. The nis only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib into an ink well for more ink. Handwriting left wet ink on the paper, so the blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased as a ready-to-use liquid or in powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. In the 1880s a successful, portable fountain pen gave smooth-flowing ink and was easy to use. In the mid-20th century, the modern ballpoint pen was readily available and inexpensive, so the fountain pen lost its popularity. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy.This ink bottle still retains its original cork. The method of manufacture is representative of a 19th-century, handcraft industry that is now largely replaced by mass production. The ink bottle is historically significant as it represents methods of handwritten personal and business communication that were still common up until the mid-20th century when fountain pens and modern ballpoint pens became popular and convenient and typewriters were becoming part of standard office equipment.Victorian 'boat' shaped ink bottle; small rectangular clear glass ink bottle with grooves in shoulders for holding pen. Bottle has side seams and a 'burst-lip'. The bottle retains its cork.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, ink, nib pen, writing ink, writing, copying, banks, lawyers, commerce, student, permanent ink, stationery, record keeping, handwriting, writing equipment, writing accessory, office supply, cottage bottle, boat bottle, mouth-blown bottle, two-part mould, sheer-lip bottle, burst-lip, cork seal, stencil ink, copy ink -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCertificate
Bank of Australasia's certificate of Court of Directors, 1835.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, bank of australasia's certificate of court of directors, bank of australasia, court of directors -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Framed Poster, Borough of Warrnambool, Victoria, Australia, after 30/06/1875
This document, also referred to as a word picture or Tablet, is framed in glass and timber with gilt trim, is handwritten with colour highlights. The penned letters rest on ruled guide lines, decorated where the lines intersect. The writing gives a description of the state of Borough of Warrnambool around 1875; its location, the area it covers, its population, Harbour and facilities, public buildings and institutions, imports and exports, financial worth, number of houses, connection with other areas of the Colony. A possible reason and origin for the document is found in an article ‘Link with US Exhibition’ from the Warrnambool Standard of December 19, 1981, written by local historian Bruce Morris. The writer mentions that the Warrnambool Borough Council met on 15th June 1875 and recorded a letter from G.C. Levey , secretary to the Melbourne group of commissioners representing the Colony, and Victoria in particular, for the Philadelphia Centennial Exhibition of 1876. The letter asks Council to provide “statistics as to the population, social condition and commercial and industrial state of the district in and around Warrnambool.” A sub committee was formed for the project. The Mayor, Cr. Thomas King, wrote and signed a Report, presented to the council on July 14, 1875, in which “The Committee … begs to recommend that a Tablet be prepared setting for the particulars respecting the following matters relating to the Borough”. The matters included area, population, annual income, churches, schools, other public buildings, societies and companies, general description of houses erected, and returns of exports and imports for 1874. The minutes note that the Report was adopted. The article above also notes the opinion of Warrnambool printers who have examined the document; it is almost certainly to be an old lithograph, which means there could be several copies. It is possible that there may be a copy in Melbourne and another in Philadelphia. It is interesting to note that (1) the quoted location co-ordinates are for an “Unnamed Road, Packsaddle NSW 2880, Australia”, and that the DMS co-ordinates for Warrnambool’s Council Offices differ, being 38.23.9.12 South, 142.28.52.887. (2) the date for “Exports and Imports for the Year Ending 30th June 1875” is different to the period mentioned by Cr. King in the sub committee’s Report of recommendation “returns of exports and imports for 1874”. The information required to have the figures for the end of June 1875 would need to have been compiled very quickly for the Tablet to be ready for the opening of the Philadelphia Exhibition on 10 May 1876. The document/certificate shows the following – - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -- - - - - - - - - - - - - - -- - - - - - - - - - - - - - -- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - “Victoria Australia, Borough of Warrnambool. Latitude, 30.24.50 South, Longitude 142.32 East The Principal Port in the Western District of the Colony and the Centre of its Choicest Agricultural Lands. Established a Municipality in 1855, and Created a Borough 1863. Population in 1875 4,500. Warrnambool is the nearest Port to Melbourne on the Western Seaboard, being about 160 miles distant. Coaches run to and from the Metropolis daily, in connexion [connection] with the Railway of Geelong and Steamers belonging to Local Companies sail between Melbourne, Warrnambool, Belfast [renamed Port Fairy], and Portland several times weekly. The Harbour is known as Lady Bay, and is partially protected by a reef of rocks stretching from the mouth of the Hopkins River. The formation of a Breakwater has been decided upon by the Government, to extend 600 yards, at an estimated cost of £100,000. There are two substantial Jetties, one of 800 and the other of 600 feet in length. The former is connected with the Town by means of a Tramroad, along which Goods, inwards & outwards, are conveyed, & the latter has been constructed solely for the purpose of facilitating the transit of material for the formation of the Breakwater. In addition to the trade of the Borough and District, the principal Townships up country receive their supplies from Melbourne and ship their exports through Warrnambool. Potatoes form the staple produce of the district, and the richness of the soil can be estimated by the fact that the Government Statistics for 1875 give as the average yield a return of Seven Tons to the acre. Several thousand acres between Warrnambool and Tower Hill are now being laid down in Potatoes by Tenants who have leased the lands at rates up to £5 per acre for the season 1875-6. Wool, Tallow, hides &c are also largely exported, while the shipments of all descriptions of Farm Produce are annually increasing. Area of Borough, 3362 Acres. Net Annual Value £27,000. Annual Revenue £5,500. Number of Houses in Borough 800. Public Buildings and Institutions Churches. Church of England, Roman Catholic, Presbyterian, Wesleyan, Congregational and Baptist. Schools. Three State Schools, average attendance nearly 1000. New Building in course of erection. Several private establishments. Banks. Bank of Australasia, Bank of Victoria, National Bank, Colonial Bank and Savings Bank. Public Buildings. Court house, Custom house, Post & Telegraph Offices, Survey & Land Offices, Shire £, Town Hall, Mechanics Institute, Volunteer Orderly Room, Odd Fellows Hall, Hospital & Benevolent Asylum, Temperance Hall &c. Companies & Societies. Steam Navigation Co, Woolen Mill Co, Gas Co, Racing Club, Amateur Turf Club, Agricultural Society, Farmers’ Club, Cricket Club, Anglers’ Society, Building Society, Freemasons Odd Fellows, Foresters, Druids, Hibernians. Protestant Alliance, Rechabites, Sons of Temperance, &c, Fire Brigade &c. --- Exports and Imports for the Year Ending 30th June 1875 –-- --Exports Total Tonnage 27,800 (Calculated at the Current Warrnambool Market Prices) Potatoes Wool Wheat Barley Hides Skins Fowls Butter Cheese Eggs Tallow Leather Ale Pigs Sheep Sundries --Imports 13,000 Tons Of the Estimated Value of £520,000 Total Tonnage of Exports and Imports 40m900 Tons, Value £806,627 Passenger Travels, to ad from Warrnambool during year, 10,000 persons Revenue from all sources paid through Warrnambool Sub Treasury From 1860 to June 1875 £1, 292, 300 Thomas King [signed] Mayor Henry T Read [signed] Town Clerk” - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -- - - - - - - - - - - - - - -- - - - - - - - - - - - - - -- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - The document is of historical, social, economic and local significance in that it summarises activities, business, community, trade, travel and government at a point in time in Warrnambool’s history – 30th June 1875.Document, also referred to as a ‘word picture’ or ‘tablet’. Document is framed in glass and timber with gilt trim, handwritten with colour highlights. The penned letters rest on ruled guide lines, decorated where the lines intersect. Document outlines the establishment of Warrnambool as a Municipality in 1855 and Borough in 1863, with a population of 4,500 in 1875. It states geographic location, public buildings and institutions, harbor facilities and imports and exports for the year ending 30th June 1875. Two signatures "Thomas King" Mayor and "Henry T Read" Town Clerk. It shows the Coat of Arms of the Borough of Warrnambool.Signatures - "Thomas King" Mayor and "Henry T Read" Town Clerk. Warrnambool Coat of Arms; “British Coat of Arms, above sailing vessel and sheaf of wheat in sun, motto “By these we flourish” and around circumference “Borough of Warrnambool 1855”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, borough of warrnambool, municipality of warrnambool, document borough of warrnambool 1875, word picture of warrnambool 1875, tablet of borough of warrnambool 1875, statistics borough of warrnambool 1875, lithograph borough of warrnambool 1875, coat of arms warrnambool, warrnambool city motto – in these we flourish, establishment of warrnambool, warrnambool history, thomas king mayor of warrnambool, henry t read town clerk of warrnambool, warrnambool breakwater, warrnambool jetty, warrnambool imports and exports 1875, warrnambool agriculture 1875, warrnambool business 1875, warrnambool population 1875, centennial exhibition philadelphia 1876, framed certificate -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook, The Logbooks of The Lady Nelson, 1915
This hardcover book, The logbooks of the 'Lady Nelson' : with the journal of her first commander, Lieutenant James Grant, R.N., by Ida Lee (Mrs Charles Bruce Marriott) was published over 100 years after the Lady Nelson arrived in Australia to navigate and survey this ‘new colony’. Included in the book are sixteen charts and illustrations from the originals in the Admiralty Library, showing the surveyed land and water. The transcribed Contents, below, summarise the trips of the Lady Nelson during this time. Book’s Content PLUS text of the Chart of ‘Part of Bass Strait’ - Chapter 1: The Lady Nelson built with centreboards. Her voyage to Sydney under James Grant. The first ship to pass through Bass Strait. - Chapter 2: Returns to explore the Strait. Her visits to Jervis Bay and to Western Port in 1801 - Chapter 3: Colonel Paterson and Lieutenant Grant survey Hunter River - Chapter 4: Murray appointed commander of the Lady Nelson. His voyage to Norfolk Island. - Chapter 5: Murray’s exploration of Bass Strait. - Chapter 6: Discovery of Port Phillip. - Chapter 7: The Lady Nelson in company with HMS Investigator examines the North-Eastern shores of Australia. - Chapter 8: The French ships in Bass Strait. The founding of Hobart. - Chapter 9: Symons succeeds Curtoys as commander of the Lady Nelson. His voyages to Tasmania, Port Phillip and New Zealand. - Chapter 10: The Lady Nelson in Tasmania. The founding of Port Dalrymple. - Chapter 11: The Estramina is brought to Sydney. The Lady Nelson visits Norfolk Island and Port Dalrymple. - Chapter 12: Tippahee and his four sons are conveyed to New Zealand in the Lady Nelson. - Chapter 13: The Lady Nelson accompanies HMS Tamar to Melville Island. - Chapter 14: The loss of the Lady Nelson Text included with the ‘Chart of Bass Strait’ … “Part of Bass Strait, including the discoveries made by Acting Lieut. J. Murray, commander of His Majesty’s armed surveying vessel Lady Nelson, between November 1801 and March 1802. By command of His Excellency Governor King.” “This chart, which bears Murray’s autograph, shows his explorations of Western Port, Port Phillip and King Island. It should be noted that Flinders Island is named Grand Capuchin. This is one of the charts referred to as "unfortunately missing” in the Historical Records of N.S. Wales, vol. iv. P. 764” The story of the Lady Nelson In 1798 the British Admiralty ordered a cutter of 60 tons to be built along the design of the armed cutter Trial that was developed by Captain John Schanck, with three sliding keels or centreboards that could be individually raised and lowered, for use on the River Thames. The new cutter was to be named Lady Nelson. Philip Gidley King, prior to taking up his appointment as third Governor of the colony of New South Wales, was in England at the time of the Lady Nelson’s fit-out and was aware of the need for such a ship for survey work in the colony in New South Wales. He convinced Captain Schanck, the Commissioner of Transport in England, to construct and rig the Lady Nelson as a brig rather than a cutter, keeping the feature of the three sliding keels, which would be very useful for mapping in shallow waters. The new Lady Nelson was launched at Deptford, England on the River Thames in November 1798, with the official commission to discover and survey the unknown parts of the coast of New Holland (Australia) and establish British sovereignty over the continent. The Lady Nelson sailed from Portsmouth, England on March 1800 under the command of Lieutenant James Grant. She carried an armament of two original and four extra brass carronade carriage guns and set sail as part of a convoy heading to Port Jackson, in New South Wales, New Holland. After a while she continued to sail on her own. Her journey was troubled with problems at times; damaged and broken keels, troublesome crew and leaking topsides between the waterline and the deck due to poor seals. She arrived at the Cape of Good Hope in July and waited for the winter to pass to avoid the strong winds of the ‘Roaring Forties’. While at the Cape, Grant received a despatch to travel to Port Jackson via the newly discovered Bass Strait, rather than the usual route via the tip of Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania). This also gave him the opportunity to survey the strait on the way. He departed the Cape in October and in December he made his first sighting of New Holland near Mount Gambier in what is now South Australia. A report by Ecclestone in 2012, ‘The Early Charting of Victoria’s Coastline’, mentions that Grant charted and named Capes Banks and Northumberland, and sighted inland hills that he named Mt Gambier and Mt Schanck, the latter after the designer of his ship. Grant then reached the south-western shores of what is now Victoria on 3-4 December 1800, and from Cape Bridgewater he examined the coast eastward to Cape Patton. Although he had not continuously sighted the coast in the vicinity of Port Fairy and Warrnambool, the western part of Victoria became known as Grant’s Land. The Lady Nelson continued eastward and passed through Bass Strait, becoming the first vessel to reach the east coast of New Holland from the west, and arrived at her destination of Port Jackson later in December 1800. Grant, in the Lady Nelson, then left Port Jackson and began survey work. He discovered Port Phillip on Victoria’s coast and explored King Island, he helped establish the first European settlement in Tasmania on the Derwent River, and Port Dalrymple, Newcastle and Port Macquarie. He made several trips from Norfolk Island to Hobart Town. Governor Macquarie sailed on with him to Van Diemen’s Land for a tour of inspection in 1811. Grant helped establish the first settlement on Melville Island in Northern Australia. The Lady Nelson was used to transport cargo, civilians and convicts and to source pigs from Timor. In February 1825 the Lady Nelson sailed again for Timor and never returned. One report said that “Every soul on board, we regret to state, was cruelly massacred, and the hull of the vessel was seen some time after with the name painted on her stern.” The hull was sighted on the island of Babar, which is almost 200 kilometres east of Timor. This particular copy of the book ... This item is from the ‘Pattison Collection’, a collection of books and records that was originally owned by the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute, which was founded in Warrnambool in 1853. By 1886 the Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute (WMI) had grown to have a Library, Museum and Fine Arts Gallery, with a collection of “… choice productions of art, and valuable specimens in almost every branch and many wonderful national curiosities are now to be seen there, including historic relics of the town and district.” It later included a School of Design. Although it was very well patronised, the lack of financial support led the WMI in 1911 to ask the City Council to take it over. In 1935 Ralph Pattison was appointed as City Librarian to establish and organise the Warrnambool Library as it was then called. When the WMI building was pulled down in 1963 a new civic building was erected on the site and the new Warrnambool Library, on behalf of the City Council, took over all the holdings of the WMI. At this time some of the items were separated and identified as the ‘Pattison Collection’, named after Ralph Pattison. Eventually the components of the WMI were distributed from the Warrnambool Library to various places, including the Art Gallery, Historical Society and Flagstaff Hill. Later some were even distributed to other regional branches of Corangamite Regional Library and passed to and fro. It is difficult now to trace just where all of the items have ended up. The books at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village generally display stamps and markings from Pattison as well as a variety of other institutions including the Mechanics’ Institute itself. RALPH ERIC PATTISON Ralph Eric Pattison was born in Rockhampton, Queensland, in 1891. He married Maude Swan from Warrnambool in 1920 and they set up home in Warrnambool. In 1935 Pattison accepted a position as City Librarian for the Warrnambool City Council. His huge challenge was to make a functional library within two rooms of the Mechanics’ Institute. He tirelessly cleaned, cleared and sorted a disarrayed collection of old books, jars of preserved specimens and other items reserved for exhibition in the city’s museum. He developed and updated the library with a wide variety of books for all tastes, including reference books for students; a difficult task to fulfil during the years following the Depression. He converted all of the lower area of the building into a library, reference room and reading room for members and the public. The books were sorted and stored using a cataloguing and card index system that he had developed himself. He also prepared the upper floor of the building and established the Art Gallery and later the Museum, a place to exhibit the many old relics that had been stored for years for this purpose. One of the treasures he found was a beautiful ancient clock, which he repaired, restored and enjoyed using in his office during the years of his service there. Ralph Pattison was described as “a meticulous gentleman whose punctuality, floorless courtesy and distinctive neat dress were hallmarks of his character, and ‘his’ clock controlled his daily routine, and his opening and closing of the library’s large heavy doors to the minute.” Pattison took leave during 1942 to 1945 to serve in the Royal Australian Navy, Volunteer Reserve as Lieutenant. A few years later he converted one of the Museum’s rooms into a Children’s Library, stocking it with suitable books for the younger generation. This was an instant success. In the 1950’s he had the honour of being appointed to the Victorian Library Board and received more inspiration from the monthly conferences in Melbourne. He was sadly retired in 1959 after over 23 years of service, due to the fact that he had gone over the working age of council officers. However he continued to take a very keen interest in the continual development of the Library until his death in 1969 This book about the logbooks of the Lady Nelson is locally significant for its association with the brig Lady Nelson, in which Lt. James Grant made the first documented European discovery of the area later known as Warrnambool in December 1800. This book is also nationally significant for its association with Grant in the Lady Nelson being the first to sail from west to east through Bass Strait, opening up a shorter, faster route to the colony of Port Jackson rather than going all the way south around Van Diemen’s Land. The book is nationally significant for its contents of the logbooks of the journeys of the Lady Nelson under various commanders and the copies of the charts created from the surveyed information and the new land of Australia was discovered. This book is also significant for its association with the full-size non-sailing replica of the Lady Nelson from Mount Gambier’s visitor centre, which was restored by Flagstaff Hill’s Master Boat Builder in Warrnambool in 2012, and with a ship mode of the Lady Nelson in our Collection The Pattison Collection, along with other items at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, was originally part of the Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s collection. The Warrnambool Mechanics’ Institute Collection is primarily significant in its totality, rather than for the individual objects it contains. Its contents are highly representative of the development of Mechanics' Institute libraries across Australia, particularly Victoria. A diversity of publications and themes has been amassed, and these provide clues to our understanding of the nature of and changes in the reading habits of Victorians from the 1850s to the middle of the 20th century. The collection also highlights the Warrnambool community’s commitment to the Mechanics’ Institute, reading, literacy and learning in the regions, and proves that access to knowledge was not impeded by distance. These items help to provide a more complete picture of our community’s ideals and aspirations. The Warrnambool Mechanics Institute book collection has historical and social significance for its strong association with the Mechanics Institute movement and the important role it played in the intellectual, cultural and social development of people throughout the latter part of the nineteenth century and the early twentieth century. The collection of books is a rare example of an early lending library and its significance is enhanced by the survival of an original collection of many volumes. The Warrnambool Mechanics' Institute’s publication collection is of both local and state significance. The Logbooks of The Lady Nelson Author: Ida Lee ( Mrs Charles Bruce Marriott) Publisher: Grafton & Co Date: 1915Label on spine with typed text RA 910.994 LEE Inside front cover has a sticker that reads Warrnambool Mechanics Institute and Free Library shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwrecked-artefact, book, warrnambool library, warrnambool mechanics’ institute, warrnambool city librarian, mechanics’ institute library, victorian library board, warrnambool books and records, warrnambool children’s library, great ocean road, the logbooks of the lady nelson, ida lee, mrs charles bruce marriott, captain john schanck, sliding keels or centreboards, lady nelson, british brig hms lady nelson, lieutennant james grant, bass strait discovery, surveying king island and port phillip bay, philip gidley king, survey map -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePlaque - Commemorative, circa August 1947
This commemorative plaque was made for the round, stained glass window titled “Christ showing the helmsman the way” that was originally installed at the St Nicholas Seamen’s Church in Williamstown. The window was donated as a memorial to the members of the Merchant Navy whose lives were lost in the Second World War, 1939-1945. The donor was the Williamstown Lightkeepers Auxiliary, an independent ladies association working with the Williamstown Missions to Seamen (re-named the Mission to Seafarers in the year 2000). The window was officially dedicated on December 14, 1947 by Geelong's Anglican Bishop, Rt. Rev. J.D. McKie. In the early months of 1948 this bronze plaque was also placed in the chapel above the altar. The Williamstown St Nicholas Seamen’s Church ceased operation in 1966. In 1979 the Victoria Missions to Seamen donated this round, stained glass window and the memorial plaque to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, along with many other items and furnishings. These items have been used to simulate the Williamstown Mission and Chapel as much as possible. THE MISSIONS TO SEAMEN The Missions to Seamen was an Anglican charity that served seafarers of the world since 1856 in Great Britain. It symbol is a Flying Angel, inspired by a Bible verse. Today there are centres in over 200 ports world-wide where seamen of all backgrounds are offered a warm welcome and provided with a wide range of facilities. In Victoria the orgainsation began in Williamstown in 1857 as a Sailors’ Church, also known as ‘Bethel’ or the ‘Floating Church’ in an old hulk floating in Hobson’s Bay, Port of Melbourne. It soon became part of the Missions to Seamen, Victoria. In the year 2000 the organisation, now named Mission to Seafarers, still operated locally in Melbourne, Portland, Geelong and Hastings. The Ladies’ Harbour Lights Guild was formed in 1906 to support the Missions to Seamen in Melbourne and other centres such as Williamstown. Two of the most significant ladies of the Guild were founder Ethel Augusta Godfrey and foundation member Alice Sibthorpe Tracy (who established a branch of the Guild in Warrnambool in 1920). The Guild continued its work until the 1960s. In 1943 a former Williamstown bank was purchased for the Missions to Seaman Club. The chapel was named St Nicholas’ Seamen’s Church and was supported by the Ladies’ Harbour Lights Guild, the Williamstown Lightkeepers’ Auxiliary and the League of Soldiers’ and Sailors’ Friends. It ceased operation in 1966. A Missions to Seamen Chapel and Recreation Room was a significant feature of ports during the late 1800s and into the 1900s. It seemed appropriate for Flagstaff Hill to include such a representation within the new Maritime Village, so the Melbourne Board of Management of Missions to Seamen Victoria gave its permission on 21st May 1979 for the entire furnishings of the Williamstown chapel to be transferred to Flagstaff Hill. The St Nicholas Seamen’s Church was officially opened on October 11, 1981 and closely resembles the Williamstown chapel. This plaque is significant for its connection with the round Sanctuary window above the altar in the chapel at Flagstaff Hill. The window was originally installed at the chapel of the St Nicholas Seamen’s Church in Williamstown in 1947, and is listed on the Victorian War Heritage Inventory No. 196973 as an object of significance. The plaque is also significant for its recognition of the members of the Merchant Navy who lost their lives in service to our country during World War II. The plaque is important for its connection with the Williamstown Lightkeepers’ Auxiliary and Missions to Seamen, which were dedicated to supporting seafarers from all over the world. The funds the group raised helped to furnish the St Nicholas Seamen’s Church in Williamstown, including the Sanctuary window, pews, carpets and hangings. These items are now part of the St Nicholas Seamen's Church Williamstown Collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Plaque: rectangular brass commemorative plaque. Each corner has a round hole. Inscription impressed into the metal and filled in with black paint. It is now part of the Williamstown Missions to Seamen Collection. “IN MEMORY OF THE MEMBERS / OF THE MERCHANT NAVY WHO WERE LOST / IN THE SECOND WORLD WAR 1939-1945 / FAITHFUL UNTO DEATH / THE WINDOW ABOVE THE ALTAR / WAS ERECTED BY THE WILLIAMSTOWN / LIGHTKEEPERS AUXILIARY / 1947.”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, mission to seamen williamstown, st nicholas seaman’s church williamstown, missions to seamen victoria, mission to seafarers, lightkeepers auxiliary, ladies harbour light guild, 139 nelson place williamstown, religion, religious service, sailors rest, bethel sailors’ church, bethel floating church, e. s. & a. bank williamstown, christ directing a sailor, christ showing the helmsman the way, quartermaster’s hand on the wheel, stained glass window, church window, religious window, sanctuary window, memorial window, war memorial window, victorian war heritage inventory, victorian heritage database, merchant navy ww2, 1939-1945, anglican church, bishop mckie, flying angel club, williamstown lightkeepers' auxiliary, ladies' harbour lights guild, commemorative window, memorial plaque, merchant navy, ww ii -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottles, Caldwell’s Ink Factory, Early 20th century
This crate of bottles may have come from a wholesaler, business, stationer or school. The design of the bottles is sometimes called a ‘cottage’ or ‘boat’ shape. Each of the 70 Caldwell’s handmade glass ink bottles was mouth-blown into a two-piece mould, a method often used in the mid-to-late 19th century. The glass blower burst the bottle off the end of his blowpipe with a tool, leaving an uneven mouth and sharp edge on the bottle, which was usually filed. The bottle was then filled with ink and sealed with a cork. More expensive bottles would have a lip added, which was more time-consuming and costly to produce. The capacity for a bottle such as this was about 3 ½ oz (ounces) equal to about 100 ml. Pen and ink have been in use for handwriting since about the seventh century. A quill pen made from a bird’s feather was used up until around the mid-19th century. In the 1850s a steel point nib for the dip pen was invented and could be manufactured on machines in large quantities. The nis only held a small amount of ink so users had to frequently dip the nib into an ink well for more ink. Handwriting left wet ink on the paper, so the blotting paper was carefully used to absorb the excess ink and prevent smudging. Ink could be purchased as a ready-to-use liquid or in powdered form, which needed to be mixed with water. In the 1880s a successful, portable fountain pen gave smooth-flowing ink and was easy to use. In the mid-20th century, the modern ballpoint pen was readily available and inexpensive, so the fountain pen lost its popularity. However, artisans continue to use nib pens to create beautiful calligraphy. Caldwell’s Ink Co. – F.R. Caldwell established Caldwell’s Ink Company in Australia around 1902. In Victoria, he operated from a factory at Victoria Avenue, Albert Park, until about 1911, then from Yarra Bank Road in South Melbourne. Newspaper offices were appointed as agencies to sell his inks, for example, in 1904 the New Zealand Evening Star sold Caldwell’s Flo-Eesi blue black ink in various bottle sizes, and Murchison Advocate (Victoria) stocked Caldwell’s ink in crimson, green, blue black, violet, and blue. Caldwell’s ink was stated to be “non-corrosive and unaffected by steel pens”. A motto used in advertising in 1904-1908 reads ‘Makes Writing a Pleasure’. Stationers stocked Caldwell’s products and hawkers sold Caldwell’s ink stands from door to door in Sydney in the 1910s and 1920s. In 1911 Caldwell promised cash for returned ink bottles and warned of prosecution for anyone found refilling his bottles. Caldwell’s Ink Stands were given as gifts. The company encouraged all forms of writing with their Australian-made Flo-Eesi writing inks and bottles at their impressive booth in the ‘All Australian Exhibition’ in 1913. It advertised its other products, which included Caldwell’s Gum, Caldwell’s Stencil Ink (copy ink) and Caldwell’s Quicksticker as well as Caldwell’s ‘Zac’ Cough Mixture. Caldwell stated in a 1920 article that his inks were made from a formula that was over a century old, and were scientifically tested and quality controlled. The formula included gallic and tannic acids and high-quality dyes to ensure that they did not fade. They were “free from all injurious chemicals”. The permanent quality of the ink was important for legal reasons, particularly to banks, accountants, commerce, municipal councils and lawyers. The Caldwell’s Ink Company also exported crates of its ink bottles and ink stands overseas. Newspaper advertisements can be found for Caldwell’s Ink Company up until 1934 when the company said they were the Best in the business for 40 years.This large collection of similar ink bottles is of particular significance as the bottles have come from the same source, most have their original corks and some retain their original labels, which is rare. The method of manufacture of these bottles is also representative of a 19th-century handcraft industry that is now been largely replaced by mass production. The bottles and their contents are of state significance for being produced by an early Melbourne industry and exported overseas. This case of ink bottles is historically significant as it represents methods of handwritten communication that were still common up until the mid-20th century when fountain pens and modern ballpoint pens became popular and convenient and typewriters were becoming part of standard office equipment.Ink bottles in a wooden crate; 70 rectangular, hand-blown clear glass ink bottles. They have side seams, uneven thickness, especially at the bases, and rough, burst-off mouths. The shoulders on the long sides have horizontal grooves used for pen rests. The bottles vary; some have labels, some contain remnants of blue-black ink, and many have their original corks. The glass has bubbles and imperfections. The remnants of printed labels are on white paper with a swirly border and black text. The bottles contained Caldwell’s blend of blue black ‘Flo-Eesi’ ink.Printed on label; “CALDWELL FLO-EESI BLUE BLACK INK” “ - - - - “ Printed script signature “F.R. Caldwell”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, ink, nib pen, writing ink, writing, copying, banks, lawyers, commerce, student, permanent ink, flo-eesi, blue black ink, stationery, record keeping, handwriting, writing equipment, writing accessory, office supply, cottage bottle, boat bottle, mouth-blown bottle, two-part mould, sheer-lip bottle, burst-lip, cork seal, f r caldwell, caldwell’s ink company, albert park, south melbourne, inkstands, stencil ink, copy ink, quicksticker, zac cough mixture -
 Victorian Interpretive Projects Inc.
Victorian Interpretive Projects Inc.Photograph - Colour, Clare Gervasoni, Koroit War Memorial, 2015, 25/12/2015
The bulk of World War One soldiers from Koroit were Protestant. It was a traumatic and divisive time for the Koroit Community based on religion, which was put behind them after the conclusion of the war. The Koroit War Memorial was not built until 1928. HONOR AVENUE AT KOROIT. Last year one side of Albert-street, Koroit was planted with plane trees, with strong guards, in honor of the men who had gone to the front from Koroit and district. The trees were planted rather late in the season, but fortunately there were only two failures, and the remainder are now higher than the guards. This year, the committee appointed decided to do the work earlier, and the King's birthday was set apart for it. On Saturday afternoon, states our correspondent; a lot of the preliminary work was done and on Monday some 30 residents assembled and went to work and by tea time the whole of the 52 trees and the guards were finished. There are 52 trees on each side of the street planted at intervals of 15 yards so that the avenue is about 800 yards long, running from the Botanical Gardens to the Lake Bank, and in a few years, when the trees are well grown, there will the a magnificent avenue. The weather was beautiful, and during the afternoon number of ladies were present. The ladies brought baskets of good things, and afternoon tea was provided at Mr. W. J. Stevenson's residence, which is situated about mid-way in the avenue. A suggestion has been made that the name of the street should be changed to "Anzac Avenue."' (Warrnambool Standard, 6 June 1918.) The Koroit War Memorial on the edge of the Koroit Botanical Gardens.world war one, world war two, world war, koroit, koroit war memorial, koroit botanical gardens, cenotaph -
 Lake Bolac & District Historical Society
Lake Bolac & District Historical SocietyColour photograph, Fiery Creek, Lake Bolac, 1997-2010 drought
Lake Bolac's eastern lake-bed and beach during the 19987-2010 drought, looking south. The lake bank exposed in this photograph is an aboriginal midden about a likometer across excavated by Dr Peter Coutts in the 1970's. Radio carbon dates of charcoal from the base levels date the midden at 12,000 years old, making this one of two middens with this very early date, the other being on the coast near Warrnambool. lake bolac, aboriginal midden, dr peter coutts -
 City of Warrnambool Rowing Club
City of Warrnambool Rowing ClubFlyer for an event, Advertisement of an event: Re dedication of a First World War plaque, 07/08/2016
The Club learnt of a memorial plaque dedicated to the to the Warrnambool Rowing Club members who enlisted for World War One, when writing the Clubs history. Every member of military age enlisted. The original plaque was unveiled in November 1916 and a Norfolk Pine planted on the Hopkins River bank - in memory of T. Redford.The tree stands however the plaque has not been found. The Club has updated the names and had a new plaque made. On 7th August 2016 - 101 years after one rower- Major Thomas Redford died - it was rededicated. The flyer is the advertisement / invitation for the day.A4 paper colored flyercity of warrnambool rowing club, warrnambool rowing club, warrnambool, world war one, first world war, rowing, memorial -
 Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and Archives
Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and ArchivesPhotograph, Alex Wilkins, c1940's
This photograph depicts Port Fairy streets in the 1940's showing Cox Street, William Street,Lower half of Bank Street River and sea. The Gas works are visible on Cox StreetThis photograph taken in the 1940's is significant because of the detail of that is shows regarding the set out of the streets and the vacant landblack and white photograph of the streets of Port Fairy2 stamps - ALEX WILKINS Photographer Warrnambool, Mrs O.G. Powell Phone 883 Port Fairy.( No 6 set over Sect 4) 4-6 streets, moyne river, port fairy, cox street, william street, gas works -
 Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and Archives
Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and ArchivesPhotograph, 1940's
This photograph shows Port Fairy from the air looking down on Douglas House across the rail lines showing Bank Street, Sackville Street, Cox street and to a lesser extent surrounding streetsThis photograph depicts the Streets and river during the 1940's and the buildings that were present at that time some no longer in existenceBlack and white PhotographALEX WILKINS PHOTOGRAPHER WARRNAMBOOL O.G.Powell Chemist Phone 88 Port Fairybank street, sackville street, railway -
 Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and Archives
Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and ArchivesPhotograph, Bennett, Richard
Richard Bennett was the first born child of Richard Bennett and Ann Isabella Kirk in February 1828 in London England. His father was a silk weaver. His family came to Sydney in 1833 but then returned to England in 1837. Richard came out himself in 1843 when he undertook a training course on the care of sheep. He first visited Belfast in January 1846 and described it as being" The centre of a large squatting district". In 1853 he married Elizabeth Nicholson Watson at St Johns Church of England Belfast Victoria. They had 11 children, 6 registered in Victoria and the other 5 born in New South Wales. Richard's aunt (or sister some sources say) Isabella married into "Belfast Royalty" by marrying Lloyd Rutledge in 1852 and they built 'Cooinda' in 1855 and lived there. However, Lloyd apparently fell down the steps drunk one night in 1858 and broke his neck. Richard's brother Ryder Bennett was Rutledge's accountant. (William or Lloyd?) Richard's sister Matilda married James Mylne knight. Richard Bennett worked on a number of properties in the district as well as heading to New South Wales in 1858 -1870 then he returned to the Port Fairy Area. He established the River Shaw Wool Scouring establishment at Yambuk in 1876 but by 1879 he had moved his business to the banks of the Merri River Dennington. He retired in 1887 and lived the rest of his life in Warrnambool. He died on 11th September 1904. Richard Bennett wrote many letters to the local newspapers regarding the early history of the district in 1984 these letters were published under the title "Richard Bennett's Early Days of Port Fairy" A book named "Richard Bennett's Early Days of Port Fairy" was edited by Jan Crichett using his letters Early settler noted for his letters regarding the Early Days of Port FairyBlack and white portrait of gentleman with a squared collarpionner, bennett, richard, dennington., early days of port fairy, river shaw wool scouring -
 Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and Archives
Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and ArchivesPhotograph
The steamer S.S.CASINO was much loved by the whole Port Fairy community- with the possible exception of some of the fishermen whose boats she ran down! Transport of the large quantities of wool, potatoes, onions, grain, sheep, cattle and other produce grown on the rich lands of the Western District Belfast was served by a plethora of shipping, both sail and steam, but only one of the steamers then in the regular trade (S.S. DAWN) would ever be able to get up the river and reap the cost savings of loading against a wharf. It was not unusual for four steamers to be anchored in the bay at once and for seven or eight different steamers to call during a week. A number of inter-colonial steamers also called to pick up produce for delivery to Melbourne, Sydney and Adelaide. Production in the Western District was increasing and virtually all of that production had to go through one of the western ports in order to reach markets. By 1882 a meeting 15ft. March, 1882, in the office of auctioneer, J.B. HoIden in Cox Street took action and it was unanimously resolved - that the Belfast & Koroit Steamship Company be formed with a capital of £20,000 in 10,000 shares of £2 each". A number of steamers were offered by letter to the fledgling company, including the new and almost sister ships, CASINO and HELEN NICHOLL. The CASINO was on her delivery voyage from England was due to arrive in Warrnambool to load potatoes for Sydney and, initially, arrangements were made for her to call into Port Fairy for inspection by the BKNS Co directors. She eventually proceeded direct to Warrnambool and the Directors inspected her there. Without hesitation they purchased her even though they had to raise a large bank loan to do so. The CASINO arrived in Port Fairy on Saturday, 29th. July, 1882, steaming triumphantly up the Moyne River, and was greeted by crowds, many of whom had driven in from the surrounding countryside, which gave her “loud ringing English cheers". By 1884 the CASINO could not carry all the cargoes available to her and in December of that year the company purchased the new steamer BELLINGER to provide additional capacity. She helped to open up the intermediate ports of Lorne, Apollo Bay and Port Campbell, but the BELLINGER was not really suitable for the trade and she was sold in 1887, leaving the CASINO to operate alone -as she was to do for almost all of the next 45 years. The opening of the railway in 1890 decreased the cargo available to the steamers and the economic depression of the early 1890's worsened the situation. The weak soon began to fall by the wayside and when the Portland & Belfast SN Co. decided to go into liquidation in April 1895, the Belfast & Koroit Company bought the Portland Company's steamer DAWN on advantageous terms, a substantial part of the payment being in BKSN Co shares. The BKNS Co and the Howard Smith Line came into direct head to head competition and nearly forced the BKNS Co out of existence. Cargo dropped to such an extent that in 1899, they reached agreement that only one ship would run and that the ship which ran would pay a weekly amount to the competitor to stay out of the trade. This controlled service ceased in1909, and competition intensified when Howard Smith placed the newly built, larger steamer EUMERALLA on the run. The BKNS Co survived this competition and even prospered during it partly by extending on a more regular basis, the CASINO'S voyages to South Australian ports Port Macdonnell, Kingston, Beachport, Robe and, on occasions Adelaide. There were setbacks when, on 20 October 1924, CASINO went ashore at the Kennett River, near Apollo Bay, and again, in February l929, when she struck a submerged object at Warrnambool and had to be beached. The railways placed great competitive pressure on the small steamship company and this pressure was intensified when the Great Depression slashed the market for Western District produce, BKNS Co struggled on, paying dividends in most years, and the company planned a big celebration for the CASINO'S fiftieth anniversary in the trade on 29th July, 1932. Disaster struck soon after 9 o'clock on the morning of Sunday I0 July, 1932 when the CASINO was lost at Apollo Bay together with the lives of 10 crew members. Black and white photograph of s.s.Casino steaming down to berth at her wharf on the left fishing boats in foregroundship, boat, industry, belfast and koroit steam navigation company, moyne river, river, s.s.casino, wharf -
 Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and Archives
Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and ArchivesPhotograph, Billing, Nathanial
Nathanial Billing was born in Brightwell Oxfordshire England on 5th May 1821. He emigrated to Australia on the ship 'Ballarat' in 1853 on arrival in Victoria he entered Government service and worked in the Warrnambool and Belfast districts until 1857. He then left the Public Service and commenced private practice. In 1850 Nathaniel and Henrietta Heybourne were married on July 17 at Hillingdon Parish, Middlesex, England. In Belfast Victoria he designed St Johns Church of England, the Bank of Australasia, and worked on St Patricks Catholic church from plans by English architect Hansom. He died on January 29 1910 in St Kilda, Victoria, Australia. Architect of 3 significant public buildings in Belfast/Port FairyBlack and white portrait of gentleman with black full beard and striped cravatpioneer, settler, portrait, people, architect, st johns church of england,, st patricks catholic church, bank of australasia, nathanial billing -
 Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and Archives
Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and ArchivesPhotograph - Panoramic Photograph, A.C. Aberline, Moyne River East Beach Port Fairy. SS Casino
The steamer S.S.CASINO was much loved by the whole Port Fairy community- with the possible exception of some of the fishermen whose boats she ran down! Transport of the large quantities of wool, potatoes, onions, grain, sheep, cattle and other produce grown on the rich lands of the Western District Belfast was served by a plethora of shipping, both sail and steam, but only one of the steamers then in the regular trade (S.S. DAWN) would ever be able to get up the river and reap the cost savings of loading against a wharf. It was not unusual for four steamers to be anchored in the bay at once and for seven or eight different steamers to call during a week. A number of inter-colonial steamers also called to pick up produce for delivery to Melbourne, Sydney and Adelaide. Production in the Western District was increasing and virtually all of that production had to go through one of the western ports in order to reach markets. By 1882 a meeting 15ft. March, 1882, in the office of auctioneer, J.B. HoIden in Cox Street took action and it was unanimously resolved - that the Belfast & Koroit Steamship Company be formed with a capital of £20,000 in 10,000 shares of £2 each". A number of steamers were offered by letter to the fledgling company, including the new and almost sister ships, CASINO and HELEN NICHOLL. The CASINO was on her delivery voyage from England was due to arrive in Warrnambool to load potatoes for Sydney and, initially, arrangements were made for her to call into Port Fairy for inspection by the BKNS Co directors. She eventually proceeded direct to Warrnambool and the Directors inspected her there. Without hesitation they purchased her even though they had to raise a large bank loan to do so. The CASINO arrived in Port Fairy on Saturday, 29th. July, 1882, steaming triumphantly up the Moyne River, and was greeted by crowds, many of whom had driven in from the surrounding countryside, which gave her “loud ringing English cheers". By 1884 the CASINO could not carry all the cargoes available to her and in December of that year the company purchased the new steamer BELLINGER to provide additional capacity. She helped to open up the intermediate ports of Lorne, Apollo Bay and Port Campbell, but the BELLINGER was not really suitable for the trade and she was sold in 1887, leaving the CASINO to operate alone -as she was to do for almost all of the next 45 years. The opening of the railway in 1890 decreased the cargo available to the steamers and the economic depression of the early 1890's worsened the situation. The weak soon began to fall by the wayside and when the Portland & Belfast SN Co. decided to go into liquidation in April 1895, the Belfast & Koroit Company bought the Portland Company's steamer DAWN on advantageous terms, a substantial part of the payment being in BKSN Co shares. The BKNS Co and the Howard Smith Line came into direct head to head competition and nearly forced the BKNS Co out of existence. Cargo dropped to such an extent that in 1899, they reached agreement that only one ship would run and that the ship which ran would pay a weekly amount to the competitor to stay out of the trade. This controlled service ceased in1909, and competition intensified when Howard Smith placed the newly built, larger steamer EUMERALLA on the run. The BKNS Co survived this competition and even prospered during it partly by extending on a more regular basis, the CASINO'S voyages to South Australian ports Port Macdonnell, Kingston, Beachport, Robe and, on occasions Adelaide. There were setbacks when, on 20 October 1924, CASINO went ashore at the Kennett River, near Apollo Bay, and again, in February l929, when she struck a submerged object at Warrnambool and had to be beached. The railways placed great competitive pressure on the small steamship company and this pressure was intensified when the Great Depression slashed the market for Western District produce, BKNS Co struggled on, paying dividends in most years, and the company planned a big celebration for the CASINO'S fiftieth anniversary in the trade on 29th July, 1932. Disaster struck soon after 9 o'clock on the morning of Sunday I0 July, 1932 when the CASINO was lost at Apollo Bay together with the lives of 10 crew members. black and white panaramic photograph mounted on cardboardMoyne River & East Beach Port Fairy- s.s.Casino-A.C.Aberline-Canterburyship, boat, sea, river, training walls, wharf, moyne river, s.s.casino, steamer -
 Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and Archives
Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and ArchivesPhotograph
S.s.Casino 1910. The people on the decks are tourists coming from Terang and surrounding areas to spend the day at the seaside. The steamer S.S.CASINO was much loved by the whole Port Fairy community- with the possible exception of some of the fishermen whose boats she ran down! Transport of the large quantities of wool, potatoes, onions, grain, sheep, cattle and other produce grown on the rich lands of the Western District Belfast was served by a plethora of shipping, both sail and steam, but only one of the steamers then in the regular trade (S.S. DAWN) would ever be able to get up the river and reap the cost savings of loading against a wharf. It was not unusual for four steamers to be anchored in the bay at once and for seven or eight different steamers to call during a week. A number of inter-colonial steamers also called to pick up produce for delivery to Melbourne, Sydney and Adelaide. Production in the Western District was increasing and virtually all of that production had to go through one of the western ports in order to reach markets. By 1882 a meeting 15ft. March, 1882, in the office of auctioneer, J.B. HoIden in Cox Street took action and it was unanimously resolved - that the Belfast & Koroit Steamship Company be formed with a capital of £20,000 in 10,000 shares of £2 each". A number of steamers were offered by letter to the fledgling company, including the new and almost sister ships, CASINO and HELEN NICHOLL. The CASINO was on her delivery voyage from England was due to arrive in Warrnambool to load potatoes for Sydney and, initially, arrangements were made for her to call into Port Fairy for inspection by the BKNS Co directors. She eventually proceeded direct to Warrnambool and the Directors inspected her there. Without hesitation they purchased her even though they had to raise a large bank loan to do so. The CASINO arrived in Port Fairy on Saturday, 29th. July, 1882, steaming triumphantly up the Moyne River, and was greeted by crowds, many of whom had driven in from the surrounding countryside, which gave her “loud ringing English cheers". By 1884 the CASINO could not carry all the cargoes available to her and in December of that year the company purchased the new steamer BELLINGER to provide additional capacity. She helped to open up the intermediate ports of Lorne, Apollo Bay and Port Campbell, but the BELLINGER was not really suitable for the trade and she was sold in 1887, leaving the CASINO to operate alone -as she was to do for almost all of the next 45 years. The opening of the railway in 1890 decreased the cargo available to the steamers and the economic depression of the early 1890's worsened the situation. The weak soon began to fall by the wayside and when the Portland & Belfast SN Co. decided to go into liquidation in April 1895, the Belfast & Koroit Company bought the Portland Company's steamer DAWN on advantageous terms, a substantial part of the payment being in BKSN Co shares. The BKNS Co and the Howard Smith Line came into direct head to head competition and nearly forced the BKNS Co out of existence. Cargo dropped to such an extent that in 1899, they reached agreement that only one ship would run and that the ship which ran would pay a weekly amount to the competitor to stay out of the trade. This controlled service ceased in1909, and competition intensified when Howard Smith placed the newly built, larger steamer EUMERALLA on the run. The BKNS Co survived this competition and even prospered during it partly by extending on a more regular basis, the CASINO'S voyages to South Australian ports Port Macdonnell, Kingston, Beachport, Robe and, on occasions Adelaide. There were setbacks when, on 20 October 1924, CASINO went ashore at the Kennett River, near Apollo Bay, and again, in February l929, when she struck a submerged object at Warrnambool and had to be beached. The railways placed great competitive pressure on the small steamship company and this pressure was intensified when the Great Depression slashed the market for Western District produce, BKNS Co struggled on, paying dividends in most years, and the company planned a big celebration for the CASINO'S fiftieth anniversary in the trade on 29th July, 1932. Disaster struck soon after 9 o'clock on the morning of Sunday I0 July, 1932 when the CASINO was lost at Apollo Bay together with the lives of 10 crew members. Black and white photograph of tourists crowded on the decks of s.s.Casino during a sail around the bay for Terang dayship, boat, sea, river, s.s.casino 1910, transport, 1910, wool, onions, grain, sheep, cattle, steam, terang day
