Showing 665 items
matching ‘the village houses’
-
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Plan - MERLE HALL COLLECTION: ROSALIND PARK CREATIVE VILLAGE BENDIGO PROJECT CONCEPT PLAN, 1993
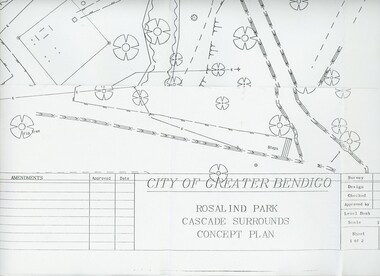
MERLE HALL COLLECTION: ROSALIND PARK CREATIVE VILLAGE BENDIGO PROJECT Concept Plan City of Greater Bendigo Rosalind Park Cascade Surrounds Concept Plan number GB095 Sheet 1 of 2 Level Book 365, Backup No Tape 01, Computer File No. ROS QEO. Large Sheet which shows the location of utilities, vegetation, drains, embankments etc. June 1993 -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Pamphlet - MERLE HALL COLLECTION: ROSALIND PARK CREATIVE VILLAGE BENDIGO PROJECT PAMPHLET, 1993
MERLE HALL COLLECTION: ROSALIND PARK CREATIVE VILLAGE BENDIGO PROJECT PAMPHLET Pathway to History Bendigo Creek Linear Park Inside pages - Graphic image of the Linear Park from Alexandra Fountain to the Botanical Gardens, includes Rosalind Park, Golden Dragon Museum, Shamrock Hotel, Bendigo Gas Works, Chinese Joss House, Chinese Tea House, Lake Weroona, Wetlands, White Hill Cemetary and mine sites. On outside pages, cover, historical notes on Bendigo and Notes on the Bendigo Creek Linear Park. Notes on the back cover: A joint project of the City of Greater Bendigo and the Department of planning and development. Production by the Publick Affairs Branch, Department of Planning and Development. Printed in Bendigo June 1993 4360/93. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - NEWSPAPER COLLECTION: TH GODEN CITY GAZETTE
The Golden City Gazette special edition Monday, March 26, 1978. Four pages special opening issue: Marong village Calder Highway, Kangaroo Flat, grand opening tomorrow Tuesday, March 27newspaper, bendigo, the golden city gazette -
 Buninyong & District Historical Society
Buninyong & District Historical SocietyPhotograph - B/W photograph, Buninyong Town Choir, winners of Provincial Choral Contest, South Street Competition, 1908, (photo) 1908
Buninyong Town Choir (aka "Ye Ancient Village Choir) winner at South Street Competitions 1908Historical record, ephemeraSmall group of documents relating to Buninyong Town Choir, copy of photograph and original (on Songbook) songbook(On songbook) stamp "YE ANCIENT VILLAGE CHOIRbuninyong, choir, south street competiton -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncJournal, Kewriosity : August 1990
Council assistance available to maintain homes / p1. Rates reminder / p1. No elections / p1. Dates for August / p2. Breast information session / p2. One act plays [Track Players] / p2. Strategies for success / p2. Rotary changeover [Kew Rotary Club] / p2. Kew's kindergartens to open doors / p3. Budget to take care of basics / p3. Urban women have a taste for country life [Kew/Balwyn Country Women's Association CWA] / p3. Your community bus needs you / p3. Recruiting drive [Meals on Wheels] / p3. Notices / p4. Major donation to St George's [Hospital] [Kew Rotary Club] / p4. Carey's new head / p4. Library corner / p4. Update on traffic / p4. Family day care / p5. Centenary celebrations for Kew East [Primary School] / p5. Courses, coffee and a chat [ Kew Community House] / p5. Govt amends Kew Planning Scheme [Willsmere] / p5. Backyard burning banned / p5. Kew Community House [courses] / p6. Clean up for Studley Park [Boroondara Bushwalkers] / p6. Council re-assesses proposal [skateboard bowl at Victoria Park] / p6. Meetings promote care giver act / p7. Council seeks community reps / p7. Kew Primary promotes its assets / p7. Recipe for success [Children's International Summer Villages] / p8. Special paper collection / p8. "Kew is for Living" [Kew Festival] / p8.Kewriosity was a local newsletter combining Kew Council and community news. It was published between November 1983 and June 1994, replacing an earlier Kewriosity [broad] Sheet (1979-84). In producing Kewriosity, Council aimed to provide a range of interesting and informative articles covering its deliberations and decision making, together with items of general interest and importance to the Kew community and information not generally available through daily media outlets.non-fictionCouncil assistance available to maintain homes / p1. Rates reminder / p1. No elections / p1. Dates for August / p2. Breast information session / p2. One act plays [Track Players] / p2. Strategies for success / p2. Rotary changeover [Kew Rotary Club] / p2. Kew's kindergartens to open doors / p3. Budget to take care of basics / p3. Urban women have a taste for country life [Kew/Balwyn Country Women's Association CWA] / p3. Your community bus needs you / p3. Recruiting drive [Meals on Wheels] / p3. Notices / p4. Major donation to St George's [Hospital] [Kew Rotary Club] / p4. Carey's new head / p4. Library corner / p4. Update on traffic / p4. Family day care / p5. Centenary celebrations for Kew East [Primary School] / p5. Courses, coffee and a chat [ Kew Community House] / p5. Govt amends Kew Planning Scheme [Willsmere] / p5. Backyard burning banned / p5. Kew Community House [courses] / p6. Clean up for Studley Park [Boroondara Bushwalkers] / p6. Council re-assesses proposal [skateboard bowl at Victoria Park] / p6. Meetings promote care giver act / p7. Council seeks community reps / p7. Kew Primary promotes its assets / p7. Recipe for success [Children's International Summer Villages] / p8. Special paper collection / p8. "Kew is for Living" [Kew Festival] / p8. publications -- city of kew (vic.), kewriosity, council newsletters, community newsletters -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncJournal, Kewriosity : December 1989
New Chief Executive for Kew / p1. Council Offices relocation [asbestos] / p1. Rates reminder / p1. Dates for December [and] January / p2. Holiday waste disposal services / p2. Christmas services / p2. Child health services / p2. Carols by candlelight / p2. Commentary / Cr Michael Montalto p3. New immunisation program / p3. Kew Junction Study / p3. Kindergarten places / p3. Kew staffer for Camberwell [Bruce Smith, Rate Collector] / p3. Meeting place suspended / p3. Notices / p4. Community grants / p4. Children's holiday program / p4. Heritage advice / p4. [Kew Community Action] Group identifies social needs / p4. Summer study for senior students / p4. Gardens project nears completion [disabled access] / p5. Local resident campaigns against drink drivers [Donald Cameron, PADD] / p5. Kew Community House / p6. [Rotaract] Club for the young / p6. New markets for Sunday shoppers / p6. Tip increase charges / p6. Did you know? [Kew Recreation Centre] / p6. MPs visit local hospice [Caritas Christi, Marie Tehan, Jan Wade, Marshall Slattery] / p7. Hole in one [Kew Festival] / p7. Occasional child care / p7. Cotham Village celebrations / p7. Boroondara Bushwalkers / p8. Hall and equipment hire / p8. Girl Guides seek leaders / p8. For dads and their children / p8. New Probus Club [Kew Ladies' Probus Club] / p8. Funny money for the young / p8.Kewriosity was a local newsletter combining Kew Council and community news. It was published between November 1983 and June 1994, replacing an earlier Kewriosity [broad] Sheet (1979-84). In producing Kewriosity, Council aimed to provide a range of interesting and informative articles covering its deliberations and decision making, together with items of general interest and importance to the Kew community and information not generally available through daily media outlets.non-fictionNew Chief Executive for Kew / p1. Council Offices relocation [asbestos] / p1. Rates reminder / p1. Dates for December [and] January / p2. Holiday waste disposal services / p2. Christmas services / p2. Child health services / p2. Carols by candlelight / p2. Commentary / Cr Michael Montalto p3. New immunisation program / p3. Kew Junction Study / p3. Kindergarten places / p3. Kew staffer for Camberwell [Bruce Smith, Rate Collector] / p3. Meeting place suspended / p3. Notices / p4. Community grants / p4. Children's holiday program / p4. Heritage advice / p4. [Kew Community Action] Group identifies social needs / p4. Summer study for senior students / p4. Gardens project nears completion [disabled access] / p5. Local resident campaigns against drink drivers [Donald Cameron, PADD] / p5. Kew Community House / p6. [Rotaract] Club for the young / p6. New markets for Sunday shoppers / p6. Tip increase charges / p6. Did you know? [Kew Recreation Centre] / p6. MPs visit local hospice [Caritas Christi, Marie Tehan, Jan Wade, Marshall Slattery] / p7. Hole in one [Kew Festival] / p7. Occasional child care / p7. Cotham Village celebrations / p7. Boroondara Bushwalkers / p8. Hall and equipment hire / p8. Girl Guides seek leaders / p8. For dads and their children / p8. New Probus Club [Kew Ladies' Probus Club] / p8. Funny money for the young / p8. publications -- city of kew (vic.), kewriosity, council newsletters, community newsletters -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncJournal, Kewriosity : December 1988 / January 1989
Household garbage collection / p1. Come and try - recreation for all [Kew Recreation Integration Group Incorporated] / p1. Rates reminder / p1. Dates for December/January / p2. Christmas Services / p2. [Kew] Conservation Study / p2&7. Carols by Candlelight [Alexandra Gardens] / p2. Commentary / Cr Allen Martin / p3. Summer holiday awareness [Kew Neighbourhood Watch] / p3. [Council] Meeting dates / p3. Christmas cards / p3. [Kew Community] Bus volunteers / p3. Christmas celebrations at Cotham Village / p4. Kew Lions [Club] News / p4. Teenage Holiday Program / p4. Music bookings [Music in the Round] / p4. 'Senior' exhibitors wanted [Senior Citizens’ Centre] / p4. Bicentennial beanstalk - and Jack [Hartwell Players] / p5. Mature aged students find TAFE supportive / p5. Bicentennial Christmas celebrations / p5. New [Kew Community] Directory for families with children / p5. Kew Community House / Judy Price p6. Children's holiday programs / p6. 25 years for local CWA / p6. Bowls notes [Kew Ladies' Bowls team] / p6. Musical comedy players wanted [Viola Musical Comedy Society] / p6. Long history for local bank [National Australia Bank, National Bank of Australasia] / p7. Special camps for young asthmatics / p7. Keeping you informed [Kew Citizens’ Advice Bureau] / p8. Music for children / p8. Better access to gardens for disabled [Alexandra Gardens] / p8. [1989] Kew Festival / p8.Kewriosity was a local newsletter combining Kew Council and community news. It was published between November 1983 and June 1994, replacing an earlier Kewriosity [broad] Sheet (1979-84). In producing Kewriosity, Council aimed to provide a range of interesting and informative articles covering its deliberations and decision making, together with items of general interest and importance to the Kew community and information not generally available through daily media outlets.non-fictionHousehold garbage collection / p1. Come and try - recreation for all [Kew Recreation Integration Group Incorporated] / p1. Rates reminder / p1. Dates for December/January / p2. Christmas Services / p2. [Kew] Conservation Study / p2&7. Carols by Candlelight [Alexandra Gardens] / p2. Commentary / Cr Allen Martin / p3. Summer holiday awareness [Kew Neighbourhood Watch] / p3. [Council] Meeting dates / p3. Christmas cards / p3. [Kew Community] Bus volunteers / p3. Christmas celebrations at Cotham Village / p4. Kew Lions [Club] News / p4. Teenage Holiday Program / p4. Music bookings [Music in the Round] / p4. 'Senior' exhibitors wanted [Senior Citizens’ Centre] / p4. Bicentennial beanstalk - and Jack [Hartwell Players] / p5. Mature aged students find TAFE supportive / p5. Bicentennial Christmas celebrations / p5. New [Kew Community] Directory for families with children / p5. Kew Community House / Judy Price p6. Children's holiday programs / p6. 25 years for local CWA / p6. Bowls notes [Kew Ladies' Bowls team] / p6. Musical comedy players wanted [Viola Musical Comedy Society] / p6. Long history for local bank [National Australia Bank, National Bank of Australasia] / p7. Special camps for young asthmatics / p7. Keeping you informed [Kew Citizens’ Advice Bureau] / p8. Music for children / p8. Better access to gardens for disabled [Alexandra Gardens] / p8. [1989] Kew Festival / p8. publications -- city of kew (vic.), kewriosity, council newsletters, community newsletters -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncDocument, Ruyton Girl's School, Ruyton Girls' Grammar School, Prospectus, 1950
Ruyton was founded in 1878 in the Bulleen Road, Kew, home of newly widowed Mrs Charlotte Anderson (now High Street South). There she hired a governess, Miss Flora Barton, to educate a small group of children, including her own, in her front parlour. Her school immediately flourished. By 1882 she was able to move it to larger premises at ‘Edgecomb’, in Studley Park Road, and name it Ruyton, after a family connection with the village of Ruyton-XI-Towns, Shropshire, England. Since that time Ruyton has continued to thrive, outgrowing its Edgecomb site, and another at A’Beckett Street, Kew, before settling into its current home in Selbourne Road in 1920. The centrepiece of this property is Henty House, now named for its original owners, Henry and Marion Henty, but once known as ‘Tarring’. The grand, polychrome brick home was built in 1872 and with nearly four acres of gardens and grounds around it, it has proved to be a place where Ruyton and its students could continue to prosper. (source: Ruyton website 2020)Prospectus provided in response to an enrolment inquiry in 1950 for Ruyton Girls' Grammar School. (See also Item 2016.0468)ruyton girls grammar school -
 Sunbury Family History and Heritage Society Inc.
Sunbury Family History and Heritage Society Inc.Photograph, c1900s
The man photograph in a garden is Joseph David Starkie, who was a Bulla Shire councillor for more than twenty years and during that time he was elected Shire President four times. He was also a member of the Sunbury Waterworks Trust and served as the chairman from 1905 - 1908. While serving on the water board he was instrumental in Sunbury gaining a permanent water supply. A drinking fountain has been erected on a reserve at the Village Green to honour the arrival of the permanent water supply to the town. The installation of a permanent water supply benefitted the town and contributed to a more reliable rail service as steam trains refilled their tanks with water at Sunbury Station. Prior to this the water was transported by horse and cart from nearby Jacksons Creek.A sepia photograph of a well-dressed man who is holding a book and is standing in a front garden of a weatherboard house.starkie, joseph daniel. -
 Falls Creek Historical Society
Falls Creek Historical SocietyJournal - Schuss Vol. 21. No. 7 September - October 1955
Schuss was advertised as Victoria’s Official Ski Journal It was issued monthly from 1935 to 1961 except during the war when summer issues covered two months. This continued after the war, but it averaged 10 issues annually over its 25 year life. Schuss was published by the Ski Club of Victoria which had a membership of 38 Ski Clubs and demanded to be recognised as the prime authority on skiing in the state. The other 30 ski clubs with 85% of the members disagreed and the politics of skiing became heated. These clubs formed the Federation of Victorian Ski Clubs with their own journal, Ski Horizon. With the establishment of the Victorian Ski Association, Ski-Horizon published its last issue in Nov - Dec. 1955 and the role of the official journal was fully taken over by “Schuss”. This item is significant because it contains stories, images and information documenting the development of the ski industry in Victoria.The journal features stories and events chronicling developments in Victoria and internationally. Page 234 - 235 featured an extensive report on developments at Falls Creek, Victoria. FALLS CREEK SKI CENTRE CONTINUES ITS STEADY ADVANCE Falls Creek skiing has continued to show markedly improved standards over this past season. Better facilities in and around the ski village itself have been accompanied by better skiing on the abundant snow covering all adjacent slopes. Just to mention a few of those facilities in the village: There have been extensions and big improvements at the Hymans Ski School, a number of excellent new club lodges have come into being, Nissen Lodge is in operation at the foot of the tow and adjacent slopes all setting new standards of ski-living that must make other resorts watch their step. While the advent of Cecil Dobson's General Store and Ski Centre, added to the service already available at the Nissen tow house, has removed all the old problems of food supply. Nissen ski-tow, the enticing face of the Frying Pan has given good service for a number of seasons now. To it has been added this year Bob Hyman's small portable tow which has worked for most of the season on the slope just in front of Skyline Lodge. The racing programme carried out at Falls Creek through this season has maintained the high standard shown in all other affairs. The main events started with the N.E.D.S.A. Championships early in August, then followed the Victorian and S.C.V. Nordic titles, and the Intermediate events.schuss journal, the ski club of victoria, developments in falls creek -
 Canterbury History Group
Canterbury History GroupEphemera - A stroll to Maling village, {2000]
Real estate advertisement for the sale of 26 Milton Street Canterbury.Includes a sketch of the house and a floor plancanterbury, milton street -
 Falls Creek Historical Society
Falls Creek Historical SocietyDocument - Hand-Written Note In Pencil - Annexe Register As Boarding House
Bob (Herman) Hymans (a former member of the Royal Netherlands Navy) was born in Bloemendaal, Holland on 30th September 1922. During World War II he fought against the Japanese in the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia) and was imprisoned in Changi and on the Burma Railway. After gaining qualifications as a Ski Instructor, Bob arrived in Falls Creek in July 1950. Working as an Instructor and Supervisor at Bogong Lodge, Bob decided his future was in accommodation. He was successful in negotiating an indenture for land from the State Electricity Commission (SEC). It took Bob two years to build his Grand Coeur Chalet but, tragically, it was burned down in August 1961. Bob also built the first Chairlift in Australia. This was a single chairlift and the structure was built from wooden electricity poles. He was constantly full of new ideas and proposals for the village. Bob Hymans die on 7th July 2007. This Collection of documents and letters tells the story of Bob's endeavours to develop Falls Creek into the ski village it is today.This item is significant because it documents proposals put forward by Bob Hymans to develop facilities in the Falls Creek Tourist Area.A note, probably a draft of a letter, discussing plans by Bob Hymans to convert his annexe to be officially registered as a boarding house. The issue has been discussed with the Health Inspector at Bright. Necessary modifications before the start of the next season. He was seeking permission to have up to 5 lodgers stay during the current year, with further changes to be made for further expansion to satisfy Health Department requirements. Mr. Hymans was asking the Management Committee for support by putting this recommendation to the State Electricity Commission.falls creek tourist area management committee, falls creek administration, bob hymans -
 Park Orchards Community House
Park Orchards Community HousePhotograph, Park Orchards Village shopping centre, Park Road
-
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBooklet - The Vanished Village - Ebden Weir / Mitta Junction, Lyn Larkin, 2004
This publication tells the story of the village of Mitta Junction which was established in about 1920 on the Victorian side of the Hume Dam construction site. The town was built to house workers and their families during the construction of the Hume Weir. It included houses, a shop, hall and school as well as tennis courts. After the completion of the weir the village and all its contents was sold at auction in June 1936 for £7000. The Mitta Junction school continued to operate until the mid 1980s. The book also documents aspects of the history of the Clark family of Bonegilla.A small publication by a local author. A4 size including photographs and a map.This publication tells the story of the village of Mitta Junction which was established in about 1920 on the Victorian side of the Hume Dam construction site. The town was built to house workers and their families during the construction of the Hume Weir. It included houses, a shop, hall and school as well as tennis courts. After the completion of the weir the village and all its contents was sold at auction in June 1936 for £7000. The Mitta Junction school continued to operate until the mid 1980s. The book also documents aspects of the history of the Clark family of Bonegilla.mitta junction township, hume weir construction, clark family bonegilla -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Mitta Junction Township
Mitta Junction which was established about 1920 on the Victorian side of the Hume Dam construction site (originally called the Mitta Junction Reservoir). The town was built to house workers and their families. It included houses, private and government boarding houses, a shop, hall and school as well as tennis courts and a cricket pitch. Mitta Junction was a thriving community with many activities, including Balls and Euchre Nights, held at the Hall which opened in February 1922. The community also fielded a very successful football team in the local competition. After the completion of the Dam, the village and all its contents were sold at auction in June 1936 for £7,000. Individual houses sold at about £40 for removal to nearby towns. The Mitta Junction School which opened in 1922 continued to operate with very small numbers after the village was moved. Its numbers were boosted in the early 1980s by the children of Army staff at the nearby Latchford Barracks Army Apprenticeship School. It finally closed in December 1985.These images are significant because they capture the history of an important vanished town whose residents played a vital role in the construction of the Hume Dam.A collection of black and white images and a sketch map featuring the village of Mitta Junction, built to house workers on the construction of the Hume Dam. Some of the photographs have been mounted on heavy card.mitta junction township, hume dam construction, hume dam history -
 City of Kingston
City of KingstonPhotograph - Digital image, Black and white, c. 1910
Black and white image of Chelsea Railway Station showing the impact of the railways on the development of the area. Shops and shoppers can be seen behind the station buildings.The extension of the railway line from Mordialloc to Frankston influenced the development of the villages along the train line. Shops and community buildings were built in proximity to the station, along with the subdivision of land for houses. Black and white image of Chelsea Railway Station showing platforms and local shopschelsea, railway station, railway, shopping strip, public transport -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyPostcard, Postcards of Egypt
Postcards were a common form of souvenirs for soldiers who were travelling either during World War 1, or just after, or while returning to Australia. These postcard scenes include the Sphinx, the Pyramids, Cairo, Alexandria, and Suez including mosques and marketplaces. The Suez Canal was used by troop ships, so this was often the first time soldiers from Australia saw Egyptians. Many troops in World War 1 were stationed first in Egypt (including near Cairo) to train before heading to Gallipoli, Turkey or on to the Western Front. These were with other World War 1 memorabilia that has come from Private John Basil McLean, 2nd Reinforcements, 37th Battalion, A.I.F. There was a large collection of postcards so he may have been collecting them as souvenirs (none of these have been written on or posted). He also had a vesta (match) case from Belfast, so it is likely he visited there. J.B. McLean (Service No. 13824) was from near Maffra, Victoria and enlisted on 22 January 1916. He embarked on 16 December 1916 for Europe. His full war record is available from AWM. He spent time with the Australian Field Artillery (Pack Section). At the end of the war he worked for a year at the A.I.F. Headquarters in London before returning to Australia on the 'Ceramic', arriving Portsea in 1920.Postcards were a very common form of communication in the first World War. Postcards as souvenirs or as correspondence would have been familiar to the first Legatees as they had served in World War 1. These places in Egypt could have been visited by the first Legatees when they were soldiers in World War 1.Postcards x 16 with images from Cairo, Alexandria and Suez in Egypt and a purple card holder that once contained 12 views of Suez (only 3 here).01137.1 Cairo - Sphinx and Pyramids 01137.2 Cairo - Arab Village near the Pyramids 01137.3 Cairo - The Citadel 01137.4 Cairo - General View of the Citadel 01137.5 Cairo - Sebil of Abbassia 01137.6 Cairo - Barrage Bridge 01137.7 Cairo - Native Woman 01137.8 Suez - Market Street 01137.9 Alexandria - San Stefano Casino 01137.10 Alexandria - Native Bazaar new Napoleon's Fort 01137.11 Alexandria - Mohamed Aly Place 01137.12 Alexandria - The Light House 01137.13 Alexandria - Column of Menasce 01137.14 Alexandria - Ramleh Boulevard 01137.15 Suez - The Port -Twefik Quay 01137.16 Suez - Railway Station Each one has the word POST CARD on the reverse with room for an address and an area for Correspondence. Different makers.souvenir, world war one -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Verses, A Book of Sea Verse, 1940s
This book was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”.The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other items and equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery.A Book of Sea Verse chosen by E C R Hadfield. 80 pages.Book title & 'Chameleon Books, Oxford'. From the W.R. Angus Collection. Print of sailing ship on the front and back covers.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, ships, poems, shipwrecks, songs -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Permit, 1940
This permit was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”.The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other items and equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery.Permit to board ships, supplied by the Commonwealth of Australia permitting the holder to board ships. Issued to Dr William Roy Angus in his capacitiy of Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. From the W.R. Angus Collection.Various: Stamped 'Warrnambool' in two places; numbered 'No. 6755'. Name etc: 'Angus, William Roy', 214 Koroit St, Warrnambool'. 'Medical Practioner'. Signature of Dr Angus. Signature of the Autorised Issuing Officer (undecipherable). Issue date: '9 Dec 1940'.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast -
 Canterbury History Group
Canterbury History GroupDocument - Comments on Boroondara Thematic Environmental History Draft document, Canterbury History Group, 1/08/2011 12:00:00 AM
... for the City of Boroondara. Canterbury Visions of a Village Education ...Comments by some concerned members of the Canterbury community regarding issues relating to Canterbury resulting from a careful study of the draft consultation document prepared for the City of Boroondara.canterbury, visions of a village, education, libraries, stationmasters house, petrol stations, canterbury road shopping centre, maling road shopping centre, theatres, police stations, canterbury gardens, railways -
 Federation University Historical Collection
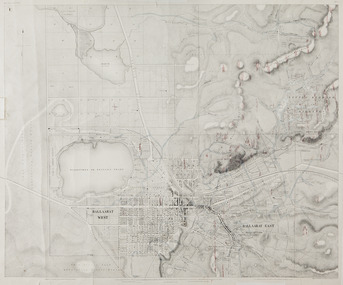
Federation University Historical CollectionMap, Ballaarat Gold Field, 1861, 1861
A party of surveyors camped by Yuille's Swamp (later Lake Wendouree) and surveyed the countryside for a map to be produced by the Geological Survey of Victoria. In November 2004 the Central Highlands Regional Library presented a special edition of 200 copies of the 1861 map reproduced from a copy in their collection. Original 1861 map of Ballarat showing streets and leads. Blue dots indicate gold leads, and red lines indicate auriferous quartz reef and outcrops of quartz veins."Compiled & Drawn from the Survey of Mining Surveyors Davidson, Fitzpatrick and Cowan & the Plans in the Surveyor General's Office by J. Brahe, 21st October 1861. R. Brough Smyth, Secretary for Mines. The Honourable J.B. Humffray, M.L.A. Commr of Mines.”ballarat, map, ballarat east, lake wendouree, survey, mines, robert davidson, ballarat gold field 1861, yuille's swamp, wendouree swamp, little bendigo diggings, gold leads, old post office hill, specimen hill, bakery hill, black hill, dead horse creek, brown hill, pennyweight hill, clayton hill, soldiers hill, golden point, gum tree flat, white flat, poverty hill, chinese village, robert brough smyth, ballarat map 1861, ballaarat vineyard, dead horse gully, deadhorse creek, invermay, black hill flat, gaelic church, police reserve, magpie range, dalton's flat, caadian lead, rifle butts, powder magazine, bathing house, government camp, gold office, chinese, llanberrris, victoria theatre, charlie napier hotel, united states hotel, grape's hoel, clayton's hill, cattleyard hill, free trade hotel, esmond lead, bakery hill, black hill lead, juvenile reformatory, ballarat orphanage, lady barkly lead, triffet's slaughter yard, little bendigo, melbourne road, t. cowan, thomas cowan -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Wooden Box, 1930s
One pharmaceutical enterprise which put greater emphasis on the manufacturing side of its business and whose successors strengthened this emphasis was Faulding's. A pharmacist, Francis H. Faulding, started his shop in Adelaide in 1841 and formed a partnership with an English physician, L. Scammel, in 1861. From its beginnings the firm showed a flare for innovation. After Simpson's discovery of the anaesthetic properties of chloroform in 1847, Francis Faulding was the first to import chloroform; in 1858 he distributed cocaine preparations; in 1864 he produced the first olive oil from South Australian olives and, after J. Lister's reports in Lancet on the reduction of mortality after surgery with the use of phenol, Faulding began production of antiseptics ('Solyptol') in 1867. Faulding was also the first to utilize the medicinal and antiseptic properties of eucalyptus oil which was obtained from distilleries on Kangaroo Island The Second World War in Europe disrupted the supply of cod liver oil, an important source of Vitamin A. Faulding chemists found an alternative source in white schnapper shark, which sustained supplies in Australia as well as generated exports to the UK . When supplies of I.G. Farben's newly discovered sulpha drugs ran out, Faulding became involved in the national program organised by the Medical Equipment Control Committee (MECC) and, jointly with universities, synthesised sulphanilamide. Following the transfer of American knowhow. Faulding's was also the first private enterprise to produce yet another life saving drug of military importance, penicillin. After the war basic synthesis of antibiotics became difficult to sustain by private enterprise because of the gigantic scale advantages of competing US producers, and competition in the synthesis of new drugs demanded huge investment in R & D; Fauldings maintained their business by a combination of marketing, wholesaling and producing consumer and medical products. In the 1970s, however, Fauldings set a remarkable precedent in research strategy and achievement in the Australian pharmaceutical business. They decided to concentrate their research on drugs which had proven efficacy, but which also suffered from certain shortcomings restricting their clinical usefulness, and to seek advances overcoming these shortcomings. This was an imaginative new strategy, a way of grafting Australian knowhow on to major products, in keeping with local resources and yet offering opportunities for sophisticated skill. At the same time it promised to open international markets, since the major producers of the basic drugs could hardly ignore significant advances. https://www.samhs.org.au/Virtual%20Museum/Medicine/drugs_nonsurg/Fauldings_drug/Fauldings_drugs.html This decorative gift box once containing Faulding’s Old English Lavender soap or powder belonged to Dr. Angus’ wife Gladys. It was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. Powder or soap in boxes such as this was perfumed and used as part of a women’s personal grooming in the early to mid 20th century. Faulding’s Company began in Adelaide, Australia, in 1845 and made a wide range of cosmetic and perfume products as well as pharmaceuticals. The company is still in operation today. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) According to Berry, her mother Gladys made a lot of their clothes. She was very talented and did some lovely embroidery including lingerie for her trousseau and beautifully handmade baby clothes. Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . Its first station was in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital (a 2 bed ward at the Nelson Street Practice) from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what previously once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr Tom and his brother had worked as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He had been House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan had gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. When Dr Angus took up practice in the Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan’s old premises he obtained their extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926. A large part of this collection is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. and an ALDI sore is on the land that was once their tennis court). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. He had an interest in people and the community They were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”.Fauldings Company is a very historical Australian company, still in operating today. The powder box is an example of fashion and grooming in the 1930's in Australia. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery.Container, wooden powder box with separate lid. Round box is made from light coloured timber and was sold containing Faulding’s Old English Lavender cosmetic powder. The wooden bowl is light in colour and the lid has a decal with text and images of two ladies facing each other, a gentleman looking over his shoulder at them, and red roses. From the W.R. Angus Collection.Faulding's Old English Lavender, and picture of old English men and women in period costume.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, shipwtreck coast, dr w r angus, faulding's, lavender, powder, cosmetic -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Weight, Thomas & James Middleton, 1840-1852
Thomas and James Middleton owned the Britannia Bedstead Works and were based at the Victoria Iron Foundry in Smethwick’s Rolfe Street Birmingham England. The Britannia Bedstead Works was not a particularly large employer by local standards in 1851 it employed 80 men but it was profitable enough to enable James Middleton and his wife Elizabeth to live in a house in New Street, North Harborne, and to employ a servant. The foundry had been in production from before 1830 or possibly earlier and had become specialist manufacturers in the Birmingham area by the 1840s making many other cast iron items at the foundry, weights being one. An item made in England around 1850-1860 by a renowned company making items various cast iron items at its foundry in Smethwick, Birmingham. Weight cast iron disc black colour4lb "Middleton"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Vanity Set, Circa late 1800s or early 1900s
The vanity set was owned by a local woman who lived in the Harbour Master's house at Warrnambool after it was decommissioned. The set was possibly a wedding gift from her mother-in-law, Caroline Edwards, a local business woman who was an importer of 'china and fancy goods' along with her husband Thomas Myers Edwards. The Edwards owned Staffordshire House, a business in Timor St (and later Liebig St) from 1876. The vanity set is an example of a valued possession of women at the time and could signify social standing. It was also a functional accessory used on a daily basis.The item is significant socially as an example of accessories available to and used by women in the late 1800s and early 1900s. Historically, it is linked to a local import business ‘Staffordshire House’ in Timor and later Liebig St Warrnambool, where it most likely came from. A pewter (or possibly silver-plated) three-piece vanity set that includes a hand mirror, hair brush and comb. All pieces feature a beautiful ornate moulded rose/flower design on the back, handles and edge of the comb. The hair brush no longer has bristles and is purely ornamental. The comb teeth and hair brush insert are most likely made of celluloid.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, vanity set, hand mirror, brush, comb, pewter, celluloid, silver plate, toilet set, harbours master's house, staffordshire house, hair brush, hairbrush -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Hand Mirror, Circa late 1800s or early 1900s
The hand mirror is part of a vanity set owned by a woman who lived in the Harbour Master's house at Warrnambool in the late 1800s and early 1900s. The set was possibly a wedding gift from her mother-in-law, Caroline Edwards, a local business woman who was an importer of 'china and fancy goods' along with her husband Thomas Myers Edwards. The Edwards owned Staffordshire House a business in Timor St (and later Liebig St) from 1876. The hand mirror is an example of a valued possession of women at the time and could signify social standing. It was also a functional accessory used on a daily basis.The item is significant socially as an example of accessories available to and used by women in the late 1800s and early 1900s. Historically, it is linked to a local import business ‘Staffordshire House’ in Liebig St Warrnambool, where it most likely came from. A pewter (or possibly silver-plated) hand mirror that is part of a vanity set. It features a beautiful ornate moulded rose/flower design on the back, handle and front edge of mirrorflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, vanity set, hand mirror, pewter, silver plate, toilet set, harbours master's house, staffordshire house -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumNewsletter, Transport Friendly Society, "Transport Friendly Society - Annual Report 1990-91" "Transport Friendly Society - Newsletter September 1991", 1991
Set of two documents issued by the Transport Friendly Society, formally the Tramways Benefit Society. .1 - Report - 36 pages, centred stapled, titled "Transport Friendly Society - Annual Report 1990-91", detailing the activities of the Society, its coat of arms, Vimy House, Nursing Home, The Mornington Retirement village, medical benefits and changes in the sector. .2 - Newsletter - folded A3 sheet, "Transport Friendly Society - Newsletter September 1991", Vimy House, Annual election, management, news and general news.trams, tramways, vimy house, benefit society, tfs, medical -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Guinea Coin, The Royal Mint, 1793 George III Spade Guinea, 1793
The coin was discovered by Julie Wilkins, a Victorian scuba diver who had already experienced more than 500 dives in Australia and overseas. She was holidaying in Peterborough, Victoria, and looking forward to discovering more about the famous Loch Ard ship, wrecked in June 1878 at Mutton Bird Island. The fast Glasgow-built clipper ship was only five years old when the tragedy occurred. There were 54 people on board the vessel and only two survived Julie's holiday photograph of Boat Bay reminds her of her most memorable dive. Submerged in the calm, flat sea, she was carefully scanning around the remains of the old wreck when, to her amazement, a gold coin and a small gold cross suddenly came up towards her. She excitedly cupped them in her hands, then stowed the treasures safely in her wetsuit and continued her dive. She soon discovered a group of brass carriage clock parts and some bottles of champagne. It was a day full of surprises. The items were easily recognisable, without any build-up of encrustations or concretion. Julie secretly enjoyed her treasures for twenty-four years then packed them up for the early morning train trip to Warrnambool. After a short walk to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village, her photograph was taken as she handed over her precious find. She told her story to a local newspaper reporter, lunched a café in town then took the late afternoon train home. Her generous donation is now part of a vast collection of Loch Ard shipwreck artefacts, including the gold watch and the Minton Majolica model peacock. The coin is a British 1793 George III Gold Spade Guinea. It was already 83 years old when the Loch Ard had set sail. The loop and ring have been added, perhaps as a pendant, pocket watch accessory or similar purpose. It may have been worn for ‘good luck’ on the long journey to Australia, where ships had to carefully navigate the treacherous Bass’s Strait before arriving at their destination of Melbourne. Sadly, many met their fate on that short stretch of ocean aptly named the Shipwreck Coast. The coin is very recognisable even though it was exposed to the wrecking of the ship, its consequent movement, and the sea's turbulence. Its bent, scratched, buckled, split, dinted and worn condition is part of its story. The red-brown-black discolouration is similar to that found on other gold coins, sometimes called the ‘corrosion phenomena’. Studies suggest the possible cause is contaminants in the minting process reacting to the coins’ environment. The GEORGE III GOLD SPADE GUINEA: - The British Guinea was introduced in 1663 and was circulated until 1814. It was made of 22 carat gold, was 25 to 26 cm in diameter and weighed 8.35 grams. It had a value of 21 British shillings. The guinea coin ceased circulation after 1816 and was replaced by the one-pound note. However, the term ‘guinea’ continued to represent 21 shillings. King George (1738-1820) had six gold guinea designs minted during his reign from 1760 and 1820. Each of the six had different obverse portraits, all facing the right. There were three different reverse sides. The Spade Guinea was the fifth issue of the coin, introduced in 1787 and produced until 1799. The reverse shows a royal crown over a flat-topped shield with the Royal Arms of Great Britain, used in Scotland between 1714 and 1800. The shield images are, from left to right, top to bottom, the Arms of England and Scotland, the Arms of France, the Arms of Ireland, and the Arms of the House of Hanover. The Gold Guinea is also part of Australia’s history. It was the first coin mentioned in the announcement of Governor King of New South Wales his Australian Proclamation of a limited variety and denomination of coins accepted for use in the Australian Colony. The historic and decorative George III Spade Guinea has been reproduced for special collections of coins. However, replicas and imitations have also been made as souvenirs for tourists, as gaming tokens and chips for gamblers, and as ‘fake’ coins for profit. These coins differ in many ways; they may be only half the weight of the genuine coin. Often have a small stamp on the obverse with “COPY” or the manufacturer’s name or initials. Some have scalloped edges, some have dates that are different to the original dates of issue, and some even have text in Latin that translates as something very different to the original coin.The King George III Guinea was only produced from 1663 to 1814 and was the first English coin to be mechanically minted. The coin is the fifth edition of the King George III Guinea, the Spade Guinea, was only produced between 1787 and 1799. It is the only edition with this portrait of King George and the only one with the Royal Coat of Arms of Great Britain in Scotland on the reverse side. This edition was also the last guinea in circulation, because the sixth edition was reserved as the Military guinea. This edition of the Guinea is unique; This coin is the only guinea in our collection. It was minted in 1793, so it is now over 230 years old. The Gold Guinea is part of Australia’s history; it was the first coin in the list of coins for use in the Australian Colonies, mentioned by Governor King of New South Wales in his Australian Proclamation speech of 1800. The George III Spade Guinea was included in the Limited Edition Sherwood 12 Coin Collection of Notable Coinage of Australia. This coin is the only known guinea coin recovered from the wreck of the Loch Ard. It was already 85 years old when the ship was wrecked.Gold coin; British. 1793, King George III of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1760-1820), Spade Guinea. Yellow gold coin with gold metal loop mount and a gold ring through the loop. The design is the fifth issue of the George III Gold Guinea. The obverse relief is a portrait of George III facing right. Reverse relief is a crown above the Coats of Arms (1801-1816) of flat top spade-shaped shield divided into four quadrants that depict crowned lions, fleur de lies, a harp. These images are identified as, from left to right, top to bottom, England and Scotland, France, Ireland and Hanover. Inscriptions are minted around the rims of each side. The coin is dated 1793. Its surface has dark areas on both sides and the reed edge and surfaces are well worn. The loop mount is bent and the ring is buckled. The coin was recovered from the wreck of the ship Loch Ard.Obverse text; 'GEORGIVS III DEI GRATIA' (translates to George the Third, by the Grace of God) Obverse relief; (King George III bust, facing right, laurel wreath on head) Reverse text; 'M.B.E.ET.H.REX.F. D.B.ET.L.D. S.R.I.A.T.ET.E' '1793' (translates to: King of Great Britain, France and Ireland, Defender of the Faith, Duke of Brunswick and Lüneburg, Arch-Treasurer and Elector of the Holy Roman Empire) Reverse relief; a spade-shaped image i.e. (Crown with fleer de lies, above Shield with crowned lions in different postures, a harp, and other details)flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, royal mint, british coin, currency, guinea, military guinea, australian currency, british guinea, gold coin, spade guinea, king george iii, george iii, fifth portrait, arms of england and scotland, arms of france, arms of ireland, arms of the house of hanover, coins, gold coins, gold medallion, georgian era, 1793, numismatics, contamination phenomena, gold corrosion, good luck, lucky charm, pendant, lucky coin, trade, loch ard, wreck of the loch ard, 1878, mutton bird island, peterborough, scuba diver, 1980s, guinea coin, gold guinea, shipwreck artefact, relic, julie wilkins -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - Loren Iron House
'Loren' (formerly James Hogg's house) is a two-storey gabled prefabricated house, constructed using broad-gauge corrugated iron and was originally erected at 60-62 Curzon Street, North Melbourne in 1853 for builder, James Hogg. By 1968 the building had deteriorated and it was dismantled and moved to Old Gippstown where it was re-erected and restored. The building's external framing system consists of exposed metal columns with Gothic panel motifs at the corners. Internally the timber framed walls have been finished with new papers over new Hessian. The corrugated iron roof has an unusual concave form and the windows, floors and doors are of moulded softwood. State historic significance as a rare type of iron prefab. house. Listed on the Victorian Heritage Register and covered by a Heritage Overlay, Latrobe City Planning Scheme. It is also listed on the Register of the National Estate.Tall square-shaped two-storey corrugated iron building with a curved corrugated iron roof with two outside brick chimneys. prefabricated iron houses, old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mine, victorian era, moe, historical village, city of melbourne, north melbourne, curzon street, james hogg, prefabricated house, two-storey gabled prefabricated house, old gippstown heritage park, latrobe valley, loren, latrobe city council -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Former home of Professor William MacMahon Ball, York Street, Eltham, 24 May 2007
Situated at the eastern end of York Street, Eltham, 'Shinrone', the former home of Professor William (Mac) MacMahon Ball was one of the first in the Shire of Eltham to incorporate mud-brick. Professor MacMahon Ball, a political scientist, writer, broadcaster and diplomat and family moved to York Street, Eltham in 1945 into a timber cottage built around the 1890s and in poor repair. Mac asked Alistair Knox to renovate the home and he expanded the living area and added verandahs. In 1948 Montsalvat artist and sculptor Sonia Skipper supervised the building of most of the mud-brick studio. Neighbour Gordon Ford made the mud-bricks. Mac also asked John Harcourt, who had worked with him as a journalist in shortwave broadcasting, to build a pise (rammed earth) and stone addition to the largely timber house. Harcourt built two bedrooms - including an attic bedroom - a balcony with a shower and toilet, a nd a fireplace and chimney of local stone. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p141 At the eastern tip of York Street, Eltham, stands Shinrone, the former home of one of Australia’s intellectual leaders. Professor William Macmahon Ball, was one of the first to bring Asia as a foreign policy issue to the Australian public.1 He was a political scientist, writer, broadcaster and diplomat. The house was one of the first in Eltham Shire to incorporate mud-brick,2 because of the acute shortage of building materials after World War Two. Its novice builders later become leaders in Eltham’s built and garden design. Mac (as he was usually called), who was the son of a Church of England minister, was born in Casterton, Victoria in 1901 and died in 1986. In 1945 he helped establish the United Nations, as political consultant to the Australian Delegation at the San Francisco Conference.3 Then in 1946 Mac was appointed British Commonwealth Representative on the Allied Council for Japan, which is recorded in detail in his diary.4 In 1948 Mac led an Australian Government Goodwill Mission to South East Asia. However, Mac was perhaps most successful as an academic and public speaker.5 He was a commentator on the Australian Broadcasting Commission, from the early 1930s to the early 1960s. He was also Controller of the Short-Wave Broadcasting Unit during World War Two, which later became Radio Australia. From 1923 he taught at The University of Melbourne, then became foundation Professor of Political Science in 1949 and was Chair until his retirement in 1968.6 In 1942, as the government expected a Japanese invasion, Mac’s wife Katrine and their only child Jenny, moved from Kew to Eltham as temporary evacuees. However Mac and Katrine lived in Eltham for almost the rest of their lives. After staying with friends, they rented a house in Reynolds Road, where, as it was wartime, they needed to keep horses for transport and a cow and poultry for milk and eggs. In 1945 the family moved to the house at York Street, which was then a timber cottage, built around the 1890s and in poor repair. The underground well, cellar and part of the garden are all that remain of what stood on the original 18 acre (7.3ha) allotment. Thanks largely to Katrine’s hard work, the house was gradually renovated and extended. The long rambling house was partially built by several young neighbours, who were inspired by the cheap mud-brick and stone building style of Montsalvat, the Eltham artists’ colony. Mac asked Alistair Knox to renovate Shinrone, named after an Irish village near Katrine’s family home. Knox later popularised the mud-brick style of house construction, for which Eltham became known. He expanded the living area and added verandas. In 1948 Montsalvat artist and sculptor Sonia Skipper supervised the building of most of the mud-brick studio. Another neighbour, Gordon Ford, who was to have a major influence on the Australian garden style, made the mud-bricks. Mac also asked John Harcourt, who had worked with him as a journalist in short-wave broadcasting, to build a pisé (rammed earth) and stone addition to the largely timber house. Harcourt built two bedrooms – including an attic bedroom – a balcony with a shower and toilet, and a fireplace and chimney of local sandstone. With pioneering work naturally came mistakes, including one particularly dramatic incident when Harcourt was building walls with unsupported sections. Jenny Ellis, Mac’s daughter, remembers being awakened from sleep by a thundering shudder. The wall of her room had fallen down – fortunately away from her! In 1950 artist Peter Glass – another neighbour and later landscape designer – built Katrine a mud-brick pottery. As a result, the house features at one end Harcourt’s characteristic steep gable roof, while at the other the flatter construction characteristic of Knox. Mac referred to the home as the Eltham ‘experimental building site’.7 Surprisingly, the combination works, perhaps partly because it has the warm inviting feel of timber, mud-brick and stone.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, eltham, alistair knox, gordon ford, john harcourt, mudbrick construction, pise construction, professor macmahon ball, shinrone, sonia skipper, york street -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Eltham Living and Learning Centre, 26 January 2008
In 1857, tanner John Pearson purchased three and a half acres of land in Little Eltham, at the western end of Pitt Street, with a 70-foot frontage to Maria Street (Main Road) and stretching down to the Diamond Creek for £100. He contracted Benjamin Oliver Wallis to build house for him. Wallis, a mason by trade who originated from the Cornish village of Newlyn, migrated to Melbourne in 1853 and was shortly engaged by Richard Warren to build the Eltham Hotel, which opened in 1854. When Warren fell into financial difficulty in 1858, Wallis purchased the hotel. That same year, Pearson constructed a tannery below the house with access to the water in the Diamond Creek. When Pearson became bankrupt in 1867, Wallis similarly acquired the house from Pearson’s creditors in 1868 and lived there until his death in 1896. For some of this time the house was in the name of Wallis’s son Richard but following his death in 1888, ownership reverted to his father. It was purchased by retired teacher Richard Gilsenen in 1899. Gilsenen was made acting head teacher at the Eltham State School in 1906 following the sudden death of head teacher John Brown. In the 1950s the house was bought by retired engineer Dr Alfred Fitzpatrick and his wife Claire who made various modifications to house goats and poultry as well as structural modifications to the house. In the early 1970s, Eltham Shire Councillors Frank Maas and Don Maling proposed an extended communities’ activities program be set up and the Commonwealth Grants Commission was approached for financial assistance. In 1974 a $50,000 Commonwealth Grant was received by the Shire Council to acquire the Fitzpatrick property as part of the planning to establish an extended communities’ activities program. The Fitzpatricks moved next door and Claire taught at the new Living and Learning Centre, which began in 1975, one of the first community education centres in Victoria. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p59 It’s a centre for sharing knowledge and friendship and it stands on the former hub of Eltham’s original township near Pitt Street. The Eltham Living and Learning Centre, with around 2000 participants a year, began in 1975 as one of the first Community Education Centres in Victoria. Classes ranging from macramé to wine making to environmental living have enriched the lives of thousands of people through the generosity of tutors sharing their skills free of charge. The centre’s heart is the brick cottage, built in 1858 by tanner John Pearson. He bought the three and a half acre (1.4ha) allotment fronting Maria Street (now Main Road) and stretching down to the Diamond Creek. The allotment formed part of a 316 acre (127.8ha) subdivision, owned by Josiah Holloway, called Little Eltham, north of the original Eltham Reserve.1 The allotment then passed through the hands of several speculators before it was sold to Pearson for £100 in 1857. Mr Pearson’s children attended the Eltham Primary School from 1864 to 1867. But creditors took possession of the property when his tannery folded in 1867. It was then sold to publican Benjamin Wallis, who owned the Eltham Hotel at the corner of Pitt Street and Main Road. In 1899 the property was bought by Richard Gilsenan, who became acting head teacher of the Eltham Primary State School in 1906. In the 1950s, retired engineer Dr Alfred Fitzpatrick and his wife Claire bought the property, and made structural changes. Claire, a journalist and community campaigner, modified and built pens for goats and poultry, a stable, a garage and planted fruit trees and a vegetable garden. In the early 1970s a young woman called Carina Hack approached Gwen Wesson at the Diamond Valley Learning Centre (Victoria’s first Community Education Centre) about starting a community centre. Following Wesson’s suggestion, Hack spoke to Shire President Alistair Knox ‘one bleak rainy afternoon, sipping hot drinks and discussing life’.2 Eltham Shire Councillors Frank Maas and Don Maling proposed a community activities program and the council received a $50,000 Commonwealth Government Grant for this venture.3 The Fitzpatricks sold their property to the council and moved next door and Claire taught at the new centre, which Hack named. Eltham obviously wanted such a centre as Hack recalls. ‘During the next two months we had about 50 volunteers working day, night and weekends, scrubbing down, plastering and painting walls, replacing floors, repairing fences, recycling furniture, sewing curtains and cushions, donating furniture, toys, equipment, clean-ing and gardening…’4 The first enrolment day saw a queue stretching up the driveway nearly to the gate and the first sessions attracted 270 people a week. Soon the outbuildings were converted into pottery studios and a large workshop. From 1979 the Eltham Art and Craft Market was held in the centre’s grounds and the Friends of the Centre ran it from 1980. A former program coordinator, Margaret Johnson, remembers enrolment day in the late 1970s and 1980s, when hundreds of people would queue – and some even camped overnight! Overnighters were greeted in the morning with fresh tea and toast. Another tradition was The Enrolment Day Cake with Recipe, given to volunteers. ‘One happy Enrolment Day fell on February 14 and let’s just say that St Valentine found some willing participants, paying $2 for a kiss.’5 Meanwhile the participants’ children could play at the Council Eltham Lower Park house in Hohnes Road, later in Susan Street. But the centre has had difficulties too. In 1990 a fire destroyed the stable and the police suspected arson. However the pavilion was built in its place.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, benjamin oliver wallis, claire fitzpatrick, don maling, dr alfred fitzpatrick, eltham living and learning centre, frank maas, john pearson, richard gilsenen, tannery
