Showing 772 items
matching john head
-
 Kilmore Historical Society
Kilmore Historical SocietyFor England's Flag, c1904
Children's book of war stories awarded to Don McDonald in 1904. Donated to Whitburgh Cottage museum c1982. Cloth- bound hardcover book with oval-shaped colour plate attached to front cover. Some wear to cover edges. Binding loose but all pages intact. Foxing and miscellaneous marks through out, yellowed pages. Faded gilt-edged pages. Black and white illustrations, colour plate opposite title page. Advertisements back & front pages. 128 pp. Fair condition.Certificate glued to inside cover, 'State School/No. 2253/Second/Prize/Awarded to Don McDonald/Class Third /for/ Year's Work/H. Worthington Head Teacher/Christmas 1904'.mcdonald, childrens literature, whitburgh cottage collection -
 Queen's College
Queen's CollegeChina plaque, c.1897
China plaque with Wesley’s head in the centre, and the words “THE BEST OF ALL GOD IS WITH US” These were Wesley’s final words from his deathbed. "The best of all God is with us The Revd John Wesley AM Wesleyan Methodist Society Established 1739"john wesley -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyBook, A.J. Downing et al, The Fruits and Fruit-Trees of America, 1890
A textbook about the Fruits and Fruit-Trees of America; The Culture, Propagation, and Management, in the Garden and Orchard, of Fruit Trees generally; with descriptions of all the finest varieties of fruit, native and foreign , cultivated in this country.A large homemade green cloth covered book, The Fruits and fruit-Trees of America by A.J. Downing, Second Edition by Charles Downing. It has diagrams and outline drawings of fruit, native and foreign cultivated in America. A section at the back is headed - Key to French Names. An Index to the Different Fruits is included along with a General Index. Appendixes I, II and III has a General Index with synonymous names in Italic. Tanning, foxing and stains are noted. 1098p. plus 193p. for Appendixes.non-fictionA textbook about the Fruits and Fruit-Trees of America; The Culture, Propagation, and Management, in the Garden and Orchard, of Fruit Trees generally; with descriptions of all the finest varieties of fruit, native and foreign , cultivated in this country.horticulture, agriculture, fruit growing -
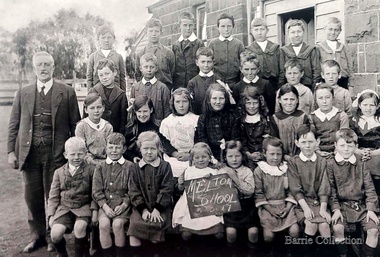 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesPhotograph, Melton State School 430 Junior Classes, 1917
Melton State School Photograph Junior Classes May 3rd 1917 Thomas Lang was the Head Teacher from 1896 - 1917 Back row: William Kilpatrick Bill D Whiting John Flynn Archibald MacDonald Arch Edward Radford Ted John Radford Jack Keith Beardemore Second Back Row: Percival Cook George Nixon Frederick Myers Bill ? Coburn Jim Coburn Bill ? Coburn [Arthur 06 Geo, William 06 Frdk Thomas 06 F James F] Second Front Row: Rita Wilson Mary Coburn Frdk Ivy Prickett - Winifred Barrie Marie Jongebloed Mary Phyllis Pearcey E. Waller Front Row: Kenneth Beaty John Parker Margaret McDonald Mary Kilpatrick Greta Jongebloed .. Norman Minns Francis Shelly Juniors classes with headmaster Thomas Lang. education, local identities -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyJug, Circa 1900
Early design ornamental earthenware jug from home of Late Mr. John Burgi.Brown earthenware jug (horn of cornucopia shape). Handle has a stylised bird's head.jugs -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBook - Rural Australia and the Great War - From Tarrawingee to Tangambalanga, John McQuilton, 2001
This publication covers common issues of life in Australia during World War 1, such as recruitment, fundraising, conscription, homecomings and the construction of memorials. However it is unique in that these aspects of war are examined through a focus on rural communities in North Eastern Victoria. The first chapter describes the region and its towns at the outbreak of war, then discusses the fracturing impact of war on different groups within these communities. It paints an interesting social history at a critical time in Australia's development. John Quilton is a native of North Eastern Victoria, having been born in Yackandandah and educated in Tangambalanga and Wodonga. He was a senior member of the Bicentennial History Project at the University of New South Wales, and head of the History and Politics Program at the University of Wollongong.This book consists of 275 pages including photos and a map, as well as an extensive bibliography. The cover depicts a soldier and his family and a country town streetscape on the back.This publication covers common issues of life in Australia during World War 1, such as recruitment, fundraising, conscription, homecomings and the construction of memorials. However it is unique in that these aspects of war are examined through a focus on rural communities in North Eastern Victoria. The first chapter describes the region and its towns at the outbreak of war, then discusses the fracturing impact of war on different groups within these communities. It paints an interesting social history at a critical time in Australia's development. John Quilton is a native of North Eastern Victoria, having been born in Yackandandah and educated in Tangambalanga and Wodonga. He was a senior member of the Bicentennial History Project at the University of New South Wales, and head of the History and Politics Program at the University of Wollongong.world war 1, rural conditions australia 1914, world war 1 social conditions australia, tangambalanga world war 1 -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Fred Rochow Railways Collection - First standard gauge passenger train from Sydney to Melbourne, 13 April 1962
The Fred Rochow Railways Collection incorporates photos related to the operation of the Wodonga Railway Station including different types of trains and railways staff C. 1930 – 1990. It was donated to the Wodonga Historical Society by Fred Rochow, a railwayman who spent many years based in Wodonga. He joined the Victorian Railways on 17th June l947 and retired in 1988. For some time, he was a member of the Australian Federated Union of Locomotive Enginemen and served a term as a member of the Trades Hall Council. He had an extensive knowledge of the struggles that took place to achieve better conditions for railway workers. Fred worked for many years as a fireman and then worked his way up the ranks to driver, experiencing many changes from the days of steam locomotives through to diesel trains, locomotives and even the modern XPT train. He worked throughout Victoria at different stages of his career, with his final working years focused on the northeast of Victoria and the Albury to Melbourne line. After his retirement, Fred continued to share his love of steam miniature trains with the community. S Class Locomotives - The eighteen members of the S Class were ordered in two batches by the Victorian Railways from Clyde Engineering for express passenger and freight workings, with the final eight locomotives ordered specifically to work the North-East standard gauge line. Many were named after prominent Victorians.This collection has local and statewide significance as it captures images of trains, locomotives and personnel who operated the railway services in Wodonga and throughout Northeast Victoria. The railways played a critical role in opening up Victoria and connecting Australia for trade, business, social communication and transport.The first standard gauge passenger train from Sydney to Melbourne pulled by Locomotive S314. This was made possible when part of Australia's gauge problem was solved with the construction of a new standard gauge line. The new line was a 317 km long line running from Albury, NSW, parallel to the existing broad gauge line to Melbourne, connecting Australia's two largest cities by standard gauge. S314 entered service on 24 April 1961 and was named after Sir John O'Shannassy who was the second Premier of Victoria. The S314 pulled the first passenger train to travel straight through from Sydney to Melbourne on 13 April 1962. On the morning of 7th February 1969, the southbound Southern Aurora collided head-on with a northbound goods train near Violet Town, Victoria. The Locomotive S314 was hauling the goods train and was destroyed by the impact of the collision. On front of locomotive "S314" On banner below Coat of Arms "FIRST STANDARD GAUGE PASSENGER TRAIN / SYDNEY - MELBOURNE/ APRIL 13 - 1962"railways wodonga, fred rochow, walker rail motor vehicles, wodonga to tallangatta rail service -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncFunctional object - Fibre glass fishing rod, John (Jack) Bowden, 1962
This fishing rod was donated to the Wodonga Historical Society by Mr. David Brown who is a retired Victorian Railways driver. It was made for him by Mr. Jack Bowden in 1962. Mr. Bowden was the driver of the Southern Aurora when it crashed with a freight train at Violet Town on 7 February 1969. The Sydney – Melbourne passenger train was bound for Melbourne. At about 7.05 a.m. the “Southern Aurora” collided head-on with the Melbourne-Albury goods train near Violet Town. 8 people lost their lives in the crash and 117 were injured. Driver John Bowden had died of cardiac arrest at some time before the collision. The driver of the goods train, Lawrence Rosevear, a good friend and workmate of Jack Bowden had tried to apply the brake when he realised the Aurora was not slowing down, but was unable to stop the impact. Lawrence also died in the crashThis was made by a local train driver who was died in the "Southern Aurora" train tragedy.A hand made fibre-glass fishing rod with wooden handle and agate runnersfishing, fishing equipment, recreational fishing, southern aurora -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncFlag - VR Flag
This flag was flying at the Wodonga Station when VR Driver John (Jack) Bowden drove past it whilst at the controls of the “Southern Aurora” on 7 February 1969. The Sydney – Melbourne passenger train was bound for Melbourne. At about 7.05 a.m. the “Southern Aurora” collided head-on with the Melbourne-Albury goods train near Violet Town. 8 people lost their lives in the crash and 117 were injured. Driver John Bowden had died of cardiac arrest at some time before the collision. The driver of the goods train, Lawrence Rosevear, a good friend and workmate of Jack Bowden had tried to apply the brake when he realised the Aurora was not slowing down, but was unable to stop the impact. Lawrence also died in the crash. A memorial is maintained at Violet Town to commemorate those who died and also recognised those who helped in the aftermath of the tragedy.This flag is connected to the "Southern Aurora" train tragedy in 1969A large blue flag bearing the gold insignia of Victorian Railways. Canvas binding and the rope is still attached on the flag pole side. There is fringing on the other side but there is some fraying due to age.victorian railways, southern aurora, john bowden -
 Falls Creek Historical Society
Falls Creek Historical SocietyUniform - Ski Patrol Star, 1960s
The Falls Creek Ski Patrol dates back to the early 60s after skiing in Falls Creek became popular. The first ski patroller in Falls Creek was Brian Caddy with two casual ski patrollers Rob Sarroff and David Crooke. Bob Howe as President of the Albury Ski Club, and a few competent skiers from his club and Myrtleford Ski Club, successfully completed the St Johns Ambulance First Aid Certificate in the hope that the Management Committee of the day would roster on two patrollers a day in return for free ski lift tickets. This plan fell through, but the year after Brian Caddy was employed as head of Ski Patrol. In 1972 the “official” Falls Creek Ski Patrol was created under the advisement of Dr Rodney Moss with the support of the Management Committee. At that time, there was one or two patrollers on staff, increasing to five members at peak times. By 1977 there were six or seven patrollers, and currently there are around 40 patrollers on the team with 13-14 rostered on each day during peak season. In 1974 the Australian Ski Patrol Association (ASPA) was formed. On the 14th of March 1975, the Falls Creek Tourist Area Management Committee applied for membership to ASPA. At that time, Falls Creek Ski Patrol was known as Falls Creek Ski Rescue. This cloth badge is in the shape of the Maltese Cross. It was the insignia of the Knights Hospitallers of St John who ministered to sick and injured pilgrims as well as fighting in the Crusades. The Maltese Cross has become a well-known symbol of protection, first-aid and assistance worldwide.A yellow cloth patch badge in the shape of the Maltese Cross. The outline of the star has been machine embroidered in yellow thread. The words "SKI PATROL" are embroidered in black thread.SKI PATROLfalls creek ski patrol, skiing safety, falls creek services -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyNewspaper - Document, article, 25,000 Returned Soldiers, Headed By Their Leader, Sir John Monash, Marched Past The Cenotaph On Anzac Day, 05/05/1928
A newspaper photo of returned servicemen and nurses marching past the original First World War memorial during an Anzac Day march in 1928. It was published as a centre page spread on 5 May 1928 in the The Weekly Times. '25,000 Returned Soldiers, Headed By Their Leader, Sir John Monash, Marched Past The Cenotaph On Anzac Day.' A war memorial to the 1914-1918 war was originally erected in Spring Street outside the Victorian Parliament Building (at that time it was the being used by the Australian Federal Parliament, from 1901-1927 when it moved to Canberra). Anzac Day services were held at this memorial in the 1920s and early 1930s. Items were in an envelope with other photos and programmes from different items relating to the Shrine of Remembrance - including discussions on its location and design. Labelled 'Shrine of Remembrance S1 - S14' it was part of an old archive numbering system (S=Shrine), that showed there has been efforts in the past to collect, order and save items of Legacy's history. From articles in Trove: The temporary cenotaph was the original first world war memorial until the Shrine of Remembrance was dedicated in 1937. The cenotaph was a half size replica of the London Symbol of Remembrance in Whitehall. It was made from timber and plaster and was initially meant to only last for the 1926 Anzac day service and be removed. With annual upkeep it remained until at least 1934 when ex-service men proceeded from the incomplete Shrine to the cenotaph on the steps of Parliament House on Anzac day.A record of an Anzac Day ceremony at the old First World War memorial in Spring Street in 1928. Not many photos are available of the original memorial. The size of the march past (reported as 25,000 soldiers) points to the enormous number of Victorians who served in the First World War. Black and white newspaper article about ANZAC Day at the old First World War memorial in Spring Street in 1928.Title: '25,000 Returned Soldiers, Headed By Their Leader, Sir John Monash, Marched Past The Cenotaph On Anzac Day.' Caption: " Scene at Parliament House, Melbourne, where the Governor, Lord Somers, took the salute, as returned Soldiers and Nurses passed, on they way to the Commemorative Service at the Exhibition.'anzac day, wreath laying ceremony -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyPhotograph, Pilgrimage to the Shrine 1991, 1991
In 1991 a relay of school children ran to the Shrine to coincide with the annual pilgrimage in 1991. A photo shows President John Sullivan holding the Legacy Torch with a group of children in yellow Legacy T shirts at the Eternal Flame at the Shrine of Remembrance on 1 September 1991. Also photos of the widows processing into the Shrine, some with wreaths to lay. From an article in Melbourne Legacy Widows' Newsletter in September 1991 it is a photo of a special torch relay. To coincide with the Annual Pilgrimage to the Shrine of Remembrance over 50 runners covered a 25 kilometre distance from War Grave Memorial in Springvale to the Shrine. President John Sullivan accepted the Legacy torch from the young runners before leading the Legacy family into the Shrine. (From the same roll of film as the event in City Square (00491) and a Legacy dinner with President Sullivan at the head table (00492). A record of children participating in a torch relay during Legacy week ending at the Eternal Flame.Colour photo x 8 of a pilgrimage to the Shrine and a torch relay in 1991. pilgrimage, wreath laying ceremony -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyDocument, Letter to Jim Gillespie, 1959
Letter dated 27 November 1959 addressed to James G. Gillespie at his place of work from D.J. Cartledge of Login Corporation Pty Ltd (North Sydney), enclosing extracts from Sydney newspapers following the publication of the Savige biography. Cartledge notes that there could have been reference to the book on television and in the Bulletin newspaper, but he has been unable to monitor them. He enclosed a cheque for one pound five shillings for a signed copy of the book.Part of the story of how the book 'There goes a Man' came to be created.Letter head quarto paper with two additional larger plain sheets, newspaper clippings pasted to them.Letter corrected and initialled in blue ink. 00929.2 handwritten in blue ink: "John, Herewith cuttings and reviews of "There goes a man", Kind Regards, Bert Scargand(?)" Annotated "D.M. 7.10.59" in blue inkstamped 7 Oct 1959. 00929.3 Annotated "D.M. 29.9.59" in blue ink, "Mrs Godfrey" in pencilsavige book, biography -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyPhotograph, Mission Matilda, 1993
Former Junior Legatee Brian Edwards set out in September 1993 to complete a flight around Australia in a tiger moth called 'Matilda' as a tribute to Legacy's 70th Anniversary. He was due to arrive at Essendon Airport on 4th October 1993 and a celebratory luncheon was held. The event was supported by Ansett Airlines and Optus Communications. The promotion in The Answer invited anyone to come to the luncheon (cost $25 a head), and greet Brian and 'Matilda'. Many school children also attended the landing. President John Stevenson and Legatee George Woodward were among those attending and are photographed greeting Brian. Brian had previously flown Matilda from the UK to Australia, covering over 12,00kms in 3 months. See also photos at 00980, 00982, 00983. A record of a former Junior Legatee making a contribution to helping Legacy raise funds.Black and white photo x 11 of a tiger moth and aviator at Essendon Airport and an article in The Answer.Printed labels from Keesing Photographic on the back of each photo.fundraising, answer -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyPhotograph - Photo, Mission Matilda, 1993
Former Junior Legatee Brian Edwards set out in September 1993 to complete a flight around Australia in a tiger moth called 'Matilda' as a tribute to Legacy's 70th Anniversary. He was due to arrive at Essendon Airport on 4th October 1993 and a celebratory luncheon was held. The event was supported by Ansett Airlines and Optus Communications. The promotion in The Answer invited anyone to come to the luncheon (cost $25 a head), and greet Brian and 'Matilda'. Many school children also attended the landing. President John Stevenson and Legatee George Woodward were among those attending and are photographed greeting Brian. Brian had previously flown Matilda from the UK to Australia, covering over 12,00kms in 3 months. See also photos at 00980, 00982, 00983. A record of a former Junior Legatee making a contribution to helping Legacy raise funds.Black and white photo x 1 and proof sheet x 3.Printed labels from Keesing Photographic on the back of each sheet. Labelled in blue text 911003/A, 911003/B and 911003/Cfundraising, answer -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyPhotograph - Photo, Mission Matilda, 1993
Former Junior Legatee Brian Edwards set out in September 1993 to complete a flight around Australia in a tiger moth called 'Matilda' as a tribute to Legacy's 70th Anniversary. He was due to arrive at Essendon Airport on 4th October 1993 and a celebratory luncheon was held. The event was supported by Ansett Airlines and Optus Communications. The promotion in The Answer invited anyone to come to the luncheon (cost $25 a head), and greet Brian and 'Matilda'. Many school children also attended the landing. President John Stevenson and Legatee George Woodward were among those attending and are photographed greeting Brian. Brian had previously flown Matilda from the UK to Australia, covering over 12,00kms in 3 months. See also photos at 00980, 00981, 00982. A record of a former Junior Legatee making a contribution to helping Legacy raise funds.Colour photo x 8 of a tiger moth and aviator at Essendon Airport and an article in The Answer.fundraising, answer, john stevenson -
 Mrs Aeneas Gunn Memorial Library
Mrs Aeneas Gunn Memorial LibraryBook, John Lane, the Bodley Head et al, Pictures of ruined Belgium, 1917
... John Lane, the Bodley Head... Ill, p.244. Pictures of ruined Belgium Book John Lane ...A photographic essay of the destruction in Belgium during World War OneIll, p.244.non-fictionA photographic essay of the destruction in Belgium during World War Oneworld war 1914-1918 - campaigns - belgium, world war - 1914-1918 - history -
 Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library Collection
Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library CollectionBook, Cabell, James Branch, Chivalry : dizain des Reines ; with an introduction by Burton Pascoe, 1928
... John Lane The Bodley Head... Branch John Lane The Bodley Head Tonbridge Printers ...281 p. fictionfiction -
 Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library Collection
Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library CollectionBook - Novel, Wherry, Edith, The Red Lantern by Edith Wherry, 1919
... John Lane The Bodley Head... Wherry Book Novel Wherry, Edith John Lane The Bodley Head Garden ...Romance novel.Hardcover book, 247 pages. Book has a green cover with black line borders. Ear of wheat in centre of cover.fictionRomance novel.edith wherry, romance, fiction -
 Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library Collection
Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library CollectionBook - Novel, Young, Florence Ethel Mills, Brief Youth by F.E. Mills Young, 1934
... John Lane The Bodley Head... Book Novel Young, Florence Ethel Mills John Lane The Bodley ...Hardcover book, 281 pages. Book has a blue cover.fictioneffie marie ford, fiction -
 Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library Collection
Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library CollectionBook - Novel, Fox, Marion, Aunt Isabel's Lover by Marion Fox, 1928
... John Lane The Bodley Head... Lover by Marion Fox Book Novel Fox, Marion John Lane The Bodley ...Hardcover book, 302 pages. Book has a dark red cover.fictionmarion fox, fiction -
 Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library Collection
Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library CollectionBook - Short stories, Leacock, Stephen, Behind the beyond : and other contributions to human knowledge, 1919
... John Lane The Bodley Head... to human knowledge Book Short stories Leacock, Stephen John Lane ...197 p. : ill. : red coverfictionfiction, short stories, stephen leacock -
 Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library Collection
Linton Mechanics Institute and Free Library CollectionBook - Novel, Cabell, James Branch, The Line of love: dizain des mariages by James Branch Cabell ; with an introduction by H. L. Mencken, 1929
... John Lane The Bodley Head... Novel Cabell, James Branch John Lane The Bodley Head Jarrold ...Romance novel.Hardcover book, 261 pages. Book has a black cover with gold embossed text.fictionRomance novel.james branch cabell, romance, fiction -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Certificate - Burwood State School Certificate, 1954
Burwood State School Mothers Club Scholarship John Davies Best General Results 1954. President R.L. Abbot. Head Teacher A.R. Donald.Framed Certificate Burwood State School Scholarship award.Burwood State School Mothers Club Scholarship -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Bookplate, 'Ex Libris Bookplate for John Gartner'
John Gartner was a fine printer and publisher, an author, a noted philatelist, and also collector of Australian banknotes and coins. He was born on 16 July 1914 and was largely self-educated, leaving school at fourteen for work following the death of his father. Gartner developed a strong interest in the history of typography and printing and was apprenticed at the Advocate where his father had been a linotype operator. Aged 17, Gartner bought a hand press and some fonts of type, and in 1937 acquired a platen press from which he set and printed his private press books, published under the imprint of The Hawthorn Press. Gartner had a strong collection of Australian bookplates. He also looked at the work of artists overseas and commissioned personal plates. He subsequently built an international collection with preference for artists who printed from wood. His initial searches were in Belgium and Holland.(http://www3.slv.vic.gov.au/latrobejournal/issue/latrobe-84/t1-g-t7.html) Oval design depicting the face of a monk, possibly St Francis, with hands showing stigmata and a dove near his headSignature bottom rightkeith wingrove memorial trust, bookplate, australian bookplate design awards -
 Barwon Estuary Heritage Centre
Barwon Estuary Heritage CentreEquipment - Anchor from the Earl of Charlemont
The Earl of Charlemont was a medium-sized, 878 ton passenger ship built at Saint John, New Brunswick, Canada, in 1849. It sailed from the Port of Liverpool on 13 March 1853 with 366 passengers plus crew, captained by William Gardner. The first port of call was to be Port Phillip, Australia, before continuing to Sydney with the majority of the passengers. After a passage of 97 days the ship reached Cape Otway on 17 June and set a course for Port Phillip some 56 miles away. At 5.15 a.m. on the 19 June 1853 the ship struck a reef (later named Charlemont Reef) about 1½ miles from Barwon Heads. The anchor was raised by Barwon Grove Skin Divers on June 25 1972. Wrought iron anchor -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Photograph, Captain John White, AATTV, arrives in Vietnam, January 1968, 1/01/1968 12:00:00 AM
Captain John E D White, Australian Army Training Team in Vietnam (AATTV) took over command of 11 Mobile Strike Force (Mike Force) Company in Da Nang, Vietnam, in February 1968. He was 26 years old. The 2 NVA Division was moving from Laos into South Vietnam and his mission was to establish contact with the division and trace its movements south. In mid-March the company was air lifted to the Special Forces camp of Kham Duc, near the Laotian border. They used an old French Foreign Legion fort as a temporary base from which patrols could be sent out. White called it Ngok Tavak after a nearby mountain. Initially, patrols failed to find the enemy, but in late April a patrol clashed with the enemy. At the same time, White received intelligence that the NVA division was closing in. At night they could hear explosions in the distance heading toward them. White decided their best chance was to leave the fort and take to the jungle to adopt guerrilla tactics. However, in the meantime a platoon of United States Marine Corps artillery arrived bringing with them two howitzers and a stockpile of ammunition. To abandon the fort was to abandon the guns. White contacted Da Nang, explaining the predicament, and was ordered to remain where he was. A Civilian Irregular Defense Group (CIDG) platoon was sent to reinforce his numbers. This was a para military force comprised mainly of indigenous highlanders, trained by United States Special Forces. They also brought with them two mortars and their crews. At 3.15am on 10 May 1968 some members of the CIDG chose to assist the NVA to attack the fort instead of supporting Mike Force, and close hand to hand fighting followed, along with grenade attacks and heavy machine gun fire. Air support offered a brief respite from the NVA attack, and some NVA forces were pushed back outside the perimeter by counter attacks, but at 9am White contacted Da Nang to advise that his position was untenable. A second attack was imminent and they could not withstand it, so they would have to withdraw. The wounded were evacuated by helicopter (under orders from Major Mai, the NVA had not attacked the previous medical helicopters that collected the wounded under the cover of air strikes) and at 1pm the rest of the force evacuated east, into the jungle. The NVA did not notice their withdrawal, and continued mortar attacks on the fort for another ninety minutes. Seven kilometres from the fort White called for a helicopter withdrawal of his forces. The force was successfully lifted to Kham Duc and then Da Nang. (Credit AWM)Coloured image of John (Jed) White, aged 26 arriving at Tan Son Nhut Airport in full uniform, bag straps over left shoulder. Close- up of chest and head with plane visible in the background.AWM - p 11058,001capt john (jed) white, aattv, battle of ngok tavak -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumBook, CAMBRIDGE PRESS, BENDIGO et al, GREATER THAN GOLD, 1985
A HISTORY OF AGRICULTURE IN THE BENDIGO DISTRICT FROM 1835 TO 1985COVER HAS GREEN BACK GROUND WITH GHOSTED POPPET HEAD IMAGE BEHIND A FULL COLOUR IMAGE OF A MECHANICAL HARVESTER IN A FIELD OF GRAINnon-fictionA HISTORY OF AGRICULTURE IN THE BENDIGO DISTRICT FROM 1835 TO 1985history of agriculture, historical field days committee -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAnimal specimen - Whale bone, Undetermined
Prior to carrying out a detailed condition report of the cetacean skeletons, it is useful to have an understanding of the materials we are likely to encounter, in terms of structure and chemistry. This entry invites you to join in learning about the composition of whale bone and oil. Whale bone (Cetacean) bone is comprised of a composite structure of both an inorganic matrix of mainly hydroxylapatite (a calcium phosphate mineral), providing strength and rigidity, as well as an organic protein ‘scaffolding’ of mainly collagen, facilitating growth and repair (O’Connor 2008, CCI 2010). Collagen is also the structural protein component in cartilage between the whale vertebrae and attached to the fins of both the Killer Whale and the Dolphin. Relative proportions in the bone composition (affecting density), are linked with the feeding habits and mechanical stresses typically endured by bones of particular whale types. A Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus Linnaeus, 1758) skeleton (toothed) thus has a higher mineral value (~67%) than a Fin Whale (Balaenoptera physalus Linnaeus, 1758) (baleen) (~60%) (Turner Walker 2012). The internal structure of bone can be divided into compact and cancellous bone. In whales, load-bearing structures such as mandibles and upper limb bones (e.g. humerus, sternum) are largely composed of compact bone (Turner Walker 2012). This consists of lamella concentrically deposited around the longitudinal axis and is permeated by fluid carrying channels (O’Connor 2008). Cancellous (spongy) bone, with a highly porous angular network of trabeculae, is less stiff and thus found in whale ribs and vertebrae (Turner Walker 2012). Whale oil Whales not only carry a thick layer of fat (blubber) in the soft tissue of their body for heat insulation and as a food store while they are alive, but also hold large oil (lipid) reserves in their porous bones. Following maceration of the whale skeleton after death to remove the soft tissue, the bones retain a high lipid content (Higgs et. al 2010). Particularly bones with a spongy (porous) structure have a high capacity to hold oil-rich marrow. Comparative data of various whale species suggests the skull, particularly the cranium and mandible bones are particularly oil rich. Along the vertebral column, the lipid content is reduced, particularly in the thoracic vertebrae (~10-25%), yet greatly increases from the lumbar to the caudal vertebrae (~40-55%). The chest area (scapula, sternum and ribs) show a mid-range lipid content (~15-30%), with vertically orientated ribs being more heavily soaked lower down (Turner Walker 2012, Higgs et. al 2010). Whale oil is largely composed of triglycerides (molecules of fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule). In Arctic whales a higher proportion of unsaturated, versus saturated fatty acids make up the lipid. Unsaturated fatty acids (with double or triple carbon bonds causing chain kinks, preventing close packing (solidifying) of molecules), are more likely to be liquid (oil), versus solid (fat) at room temperature (Smith and March 2007). Objects Made From the Whaling Industry We all know that men set forth in sailing ships and risked their lives to harpoon whales on the open seas throughout the 1800s. And while Moby Dick and other tales have made whaling stories immortal, people today generally don't appreciate that the whalers were part of a well-organized industry. The ships that set out from ports in New England roamed as far as the Pacific in hunt of specific species of whales. Adventure may have been the draw for some whalers, but for the captains who owned whaling ships, and the investors which financed voyages, there was a considerable monetary payoff. The gigantic carcasses of whales were chopped and boiled down and turned into products such as the fine oil needed to lubricate increasing advanced machine tools. And beyond the oil derived from whales, even their bones, in an era before the invention of plastic, was used to make a wide variety of consumer goods. In short, whales were a valuable natural resource the same as wood, minerals, or petroleum we now pump from the ground. Oil From Whale’s Blubber Oil was the main product sought from whales, and it was used to lubricate machinery and to provide illumination by burning it in lamps. When a whale was killed, it was towed to the ship and its blubber, the thick insulating fat under its skin, would be peeled and cut from its carcass in a process known as “flensing.” The blubber was minced into chunks and boiled in large vats on board the whaling ship, producing oil. The oil taken from whale blubber was packaged in casks and transported back to the whaling ship’s home port (such as New Bedford, Massachusetts, the busiest American whaling port in the mid-1800s). From the ports it would be sold and transported across the country and would find its way into a huge variety of products. Whale oil, in addition to be used for lubrication and illumination, was also used to manufacture soaps, paint, and varnish. Whale oil was also utilized in some processes used to manufacture textiles and rope. Spermaceti, a Highly Regarded Oil A peculiar oil found in the head of the sperm whale, spermaceti, was highly prized. The oil was waxy, and was commonly used in making candles. In fact, candles made of spermaceti were considered the best in the world, producing a bright clear flame without an excess of smoke. Spermaceti was also used, distilled in liquid form, as an oil to fuel lamps. The main American whaling port, New Bedford, Massachusetts, was thus known as "The City That Lit the World." When John Adams was the ambassador to Great Britain before serving as president he recorded in his diary a conversation about spermaceti he had with the British Prime Minister William Pitt. Adams, keen to promote the New England whaling industry, was trying to convince the British to import spermaceti sold by American whalers, which the British could use to fuel street lamps. The British were not interested. In his diary, Adams wrote that he told Pitt, “the fat of the spermaceti whale gives the clearest and most beautiful flame of any substance that is known in nature, and we are surprised you prefer darkness, and consequent robberies, burglaries, and murders in your streets to receiving as a remittance our spermaceti oil.” Despite the failed sales pitch John Adams made in the late 1700s, the American whaling industry boomed in the early to mid-1800s. And spermaceti was a major component of that success. Spermaceti could be refined into a lubricant that was ideal for precision machinery. The machine tools that made the growth of industry possible in the United States were lubricated, and essentially made possible, by oil derived from spermaceti. Baleen, or "Whalebone" The bones and teeth of various species of whales were used in a number of products, many of them common implements in a 19th century household. Whales are said to have produced “the plastic of the 1800s.” The "bone" of the whale which was most commonly used wasn’t technically a bone, it was baleen, a hard material arrayed in large plates, like gigantic combs, in the mouths of some species of whales. The purpose of the baleen is to act as a sieve, catching tiny organisms in sea water, which the whale consumes as food. As baleen was tough yet flexible, it could be used in a number of practical applications. And it became commonly known as "whalebone." Perhaps the most common use of whalebone was in the manufacture of corsets, which fashionable ladies in the 1800s wore to compress their waistlines. One typical corset advertisement from the 1800s proudly proclaims, “Real Whalebone Only Used.” Whalebone was also used for collar stays, buggy whips, and toys. Its remarkable flexibility even caused it to be used as the springs in early typewriters. The comparison to plastic is apt. Think of common items which today might be made of plastic, and it's likely that similar items in the 1800s would have been made of whalebone. Baleen whales do not have teeth. But the teeth of other whales, such as the sperm whale, would be used as ivory in such products as chess pieces, piano keys, or the handles of walking sticks. Pieces of scrimshaw, or carved whale's teeth, would probably be the best remembered use of whale's teeth. However, the carved teeth were created to pass the time on whaling voyages and were never a mass production item. Their relative rarity, of course, is why genuine pieces of 19th century scrimshaw are considered to be valuable collectibles today. Reference: McNamara, Robert. "Objects Made From the Whaling Industry." ThoughtCo, Jul. 31, 2021, thoughtco.com/products-produced-from-whales-1774070.Whale bone was an important commodity, used in corsets, collar stays, buggy whips, and toys.Whale bone vertebrae. Advanced stage of calcification as indicated by deep pitting. Off white to grey.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, whales, whale bone, corsets, toys, whips, whalebone -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAnimal specimen - Whale Vertebrae, Undetermined
Prior to carrying out a detailed condition report of the cetacean skeletons, it is useful to have an understanding of the materials we are likely to encounter, in terms of structure and chemistry. This entry invites you to join in learning about the composition of whale bone and oil. Whale bone (Cetacean) bone is comprised of a composite structure of both an inorganic matrix of mainly hydroxylapatite (a calcium phosphate mineral), providing strength and rigidity, as well as an organic protein ‘scaffolding’ of mainly collagen, facilitating growth and repair (O’Connor 2008, CCI 2010). Collagen is also the structural protein component in cartilage between the whale vertebrae and attached to the fins of both the Killer Whale and the Dolphin. Relative proportions in the bone composition (affecting density), are linked with the feeding habits and mechanical stresses typically endured by bones of particular whale types. A Sperm Whale (Physeter macrocephalus Linnaeus, 1758) skeleton (toothed) thus has a higher mineral value (~67%) than a Fin Whale (Balaenoptera physalus Linnaeus, 1758) (baleen) (~60%) (Turner Walker 2012). The internal structure of bone can be divided into compact and cancellous bone. In whales, load-bearing structures such as mandibles and upper limb bones (e.g. humerus, sternum) are largely composed of compact bone (Turner Walker 2012). This consists of lamella concentrically deposited around the longitudinal axis and is permeated by fluid carrying channels (O’Connor 2008). Cancellous (spongy) bone, with a highly porous angular network of trabeculae, is less stiff and thus found in whale ribs and vertebrae (Turner Walker 2012). Whale oil Whales not only carry a thick layer of fat (blubber) in the soft tissue of their body for heat insulation and as a food store while they are alive, but also hold large oil (lipid) reserves in their porous bones. Following maceration of the whale skeleton after death to remove the soft tissue, the bones retain a high lipid content (Higgs et. al 2010). Particularly bones with a spongy (porous) structure have a high capacity to hold oil-rich marrow. Comparative data of various whale species suggests the skull, particularly the cranium and mandible bones are particularly oil rich. Along the vertebral column, the lipid content is reduced, particularly in the thoracic vertebrae (~10-25%), yet greatly increases from the lumbar to the caudal vertebrae (~40-55%). The chest area (scapula, sternum and ribs) show a mid-range lipid content (~15-30%), with vertically orientated ribs being more heavily soaked lower down (Turner Walker 2012, Higgs et. al 2010). Whale oil is largely composed of triglycerides (molecules of fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule). In Arctic whales a higher proportion of unsaturated, versus saturated fatty acids make up the lipid. Unsaturated fatty acids (with double or triple carbon bonds causing chain kinks, preventing close packing (solidifying) of molecules), are more likely to be liquid (oil), versus solid (fat) at room temperature (Smith and March 2007). Objects Made From the Whaling Industry We all know that men set forth in sailing ships and risked their lives to harpoon whales on the open seas throughout the 1800s. And while Moby Dick and other tales have made whaling stories immortal, people today generally don't appreciate that the whalers were part of a well-organized industry. The ships that set out from ports in New England roamed as far as the Pacific in hunt of specific species of whales. Adventure may have been the draw for some whalers, but for the captains who owned whaling ships, and the investors which financed voyages, there was a considerable monetary payoff. The gigantic carcasses of whales were chopped and boiled down and turned into products such as the fine oil needed to lubricate increasing advanced machine tools. And beyond the oil derived from whales, even their bones, in an era before the invention of plastic, was used to make a wide variety of consumer goods. In short, whales were a valuable natural resource the same as wood, minerals, or petroleum we now pump from the ground. Oil From Whale’s Blubber Oil was the main product sought from whales, and it was used to lubricate machinery and to provide illumination by burning it in lamps. When a whale was killed, it was towed to the ship and its blubber, the thick insulating fat under its skin, would be peeled and cut from its carcass in a process known as “flensing.” The blubber was minced into chunks and boiled in large vats on board the whaling ship, producing oil. The oil taken from whale blubber was packaged in casks and transported back to the whaling ship’s home port (such as New Bedford, Massachusetts, the busiest American whaling port in the mid-1800s). From the ports it would be sold and transported across the country and would find its way into a huge variety of products. Whale oil, in addition to be used for lubrication and illumination, was also used to manufacture soaps, paint, and varnish. Whale oil was also utilized in some processes used to manufacture textiles and rope. Spermaceti, a Highly Regarded Oil A peculiar oil found in the head of the sperm whale, spermaceti, was highly prized. The oil was waxy, and was commonly used in making candles. In fact, candles made of spermaceti were considered the best in the world, producing a bright clear flame without an excess of smoke. Spermaceti was also used, distilled in liquid form, as an oil to fuel lamps. The main American whaling port, New Bedford, Massachusetts, was thus known as "The City That Lit the World." When John Adams was the ambassador to Great Britain before serving as president he recorded in his diary a conversation about spermaceti he had with the British Prime Minister William Pitt. Adams, keen to promote the New England whaling industry, was trying to convince the British to import spermaceti sold by American whalers, which the British could use to fuel street lamps. The British were not interested. In his diary, Adams wrote that he told Pitt, “the fat of the spermaceti whale gives the clearest and most beautiful flame of any substance that is known in nature, and we are surprised you prefer darkness, and consequent robberies, burglaries, and murders in your streets to receiving as a remittance our spermaceti oil.” Despite the failed sales pitch John Adams made in the late 1700s, the American whaling industry boomed in the early to mid-1800s. And spermaceti was a major component of that success. Spermaceti could be refined into a lubricant that was ideal for precision machinery. The machine tools that made the growth of industry possible in the United States were lubricated, and essentially made possible, by oil derived from spermaceti. Whalebone The bones and teeth of various species of whales were used in a number of products, many of them common implements in a 19th century household. Whales are said to have produced “the plastic of the 1800s.” The bone of the whale which was most commonly used wasn’t technically a bone, it was baleen, a hard material arrayed in large plates, like gigantic combs, in the mouths of some species of whales. The purpose of the baleen is to act as a sieve, catching tiny organisms in sea water, which the whale consumes as food. As baleen was tough yet flexible, it could be used in a number of practical applications. And it became commonly known as whalebone. Perhaps the most common use of whalebone was in the manufacture of corsets, which fashionable ladies in the 1800s wore to compress their waistlines. One typical corset advertisement from the 1800s proudly proclaims, “Real Whalebone Only Used.” Whalebone was also used for collar stays, buggy whips, and toys. Its remarkable flexibility even caused it to be used as the springs in early typewriters. The comparison to plastic is apt. Think of common items which today might be made of plastic, and it's likely that similar items in the 1800s would have been made of whalebone. Baleen whales do not have teeth. But the teeth of other whales, such as the sperm whale, would be used as ivory in such products as chess pieces, piano keys, or the handles of walking sticks. Pieces of scrimshaw, or carved whale's teeth, would probably be the best remembered use of whale's teeth. However, the carved teeth were created to pass the time on whaling voyages and were never a mass production item. Their relative rarity, of course, is why genuine pieces of 19th century scrimshaw are considered to be valuable collectibles today. Reference: McNamara, Robert. "Objects Made From the Whaling Industry." ThoughtCo, Jul. 31, 2021, thoughtco.com/products-produced-from-whales-1774070.Whale bone during the 17th, 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries was an important industry providing an important commodity. Whales from these times provided everything from lighting & machine oils to using the animal's bones for use in corsets, collar stays, buggy whips, and many other everyday items then in use.Whale bone Vertebrae with advanced stage of calcification as indicated by deep pitting. Off white to grey.None.warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, whale bones, whale skeleton, whales, whale bone, corsets, toys, whips, whaleling industry, maritime fishing, whalebone
