Showing 118 items
matching coal iron
-
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyFunctional object - Large Boiler, Clark and Co, early 1900's
This large 10 gallon boiler would have been used over an open fire or placed on top of coals to boil clothes clean. They were first made in England during the 1700's and onwards.They were shipped to Australia and other British Empire countries to be purchased by early settlers. A large antique black oval cast iron Boiler Pot with small curved lifting handles for holding it on both sides. There is a large cast moveable carrying iron handle with a bend at the top for hooking onto an 'S' shaped hook or rod to hang over an open fire. This handle is attached on each side to thick iron loops. The Makers name is embossed on one side.Embossed on one side is 'Clarke and Co 10.GS' inside an oval shape (for gallons) There is a diamond shape too of a blacksmith at work. cast iron, cooking, boiling utensils -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumTool - SOLDERING IRON
... (P.M.G) WHEN SOLDERING AT TOP OF POLES. IRON HEATED THEN COALS... history trades weldind SOLDERING IRON WITH WOODEN HANDLE AND METAL ...WELDER WAS USED BY EMPLOYEES [LINESMEN] OF THE P.M.G.SOLDERING IRON WITH WOODEN HANDLE AND METAL HEAD WITH RECEPTACLE FOR COALS TO KEEP HOT, WOODEN HANDLE. USED BY LINESMEN (P.M.G) WHEN SOLDERING AT TOP OF POLES. IRON HEATED THEN COALS OR COMPRESSED DISC PLACE IN HEAD TO RETAIN HEATlocal history, trades, weldind -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - Livery Stable
Used by general carriers in Warragul from the late 1880sA large, two-storey stables of timber with a corrugated iron roof. Internally there are four horse stalls on the ground floor and a loft above. The loft is accessed via steep internal stairs and a trapdoor, with an outside door and hoist point. Build in the 1880s warragul, general carriers, stables, old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mine, victorian era, moe, historical village, baw baw shire, transport, latrobe valley, old gippstown heritage park, latrobe city council -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - Bootmaker and Saddler, 1906
Built in 1906 in main street of Neerim South by Samuel Fry who established his business at that time. Exhibits include early boots and shoes, Heavy leather working machines and saddlery. Many of the tools belonged to Harry Coombs, who was Moe's first bootmaker from 1910 - 1966A small rectangular timber shop. The front has a gabled corrugated iron roof, while the workshop at the rear of the shop is not as high as the front and has a flat corrugated iron roof.Sign writing on shop frontbootmakers, neerim south, samuel fry, harry coombs, old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mine, victorian era, moe, historical village, baw baw shire, saddlery, leather work, old gippstown heritage park, latrobe valley, latrobe city council -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - Garage, 1970s
This building was constructed at Old Gippstown from materials at hand. It was named after the garage operated in Maffra by W.O. (Bill) Fulton, blacksmith, garage proprietor and later state member of parliament. A large rectangular-shaped corrugated iron shed, used as a Garage. It has a gabled roof made of corrugated iron. There is a billboard on the front of building's roof.motor garage, old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mine, victorian era, moe, historical village, petrol station, w.o. (bill) fulton, old gippstown heritage park, latrobe valley, buick hearse, chevrolet tourer, hudson hearse, stanley steamer, plume texaco, shell, cor, petrol pump -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - National Bank
Built as the Colonial Bank of Australasia in 1889 at Meeniyan, it became the National Bank in 1914. It was moved to Old Gippstown in 1968.High local historic significance on account of integrity.A large rectangular-shaped timber bank building with a gabled corrugated iron roof. The front has a mock stonework design on the timber. The ceilings inside are of pressed tin. The interior display features a collection of old National Bank furniture and banking items.bank, meeniyan, southern gippsland shire, old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mine, victorian era, moe, historical village, banking, national bank, pressed tin ceiling, old gippstown heritage park, latrobe valley, latrobe city council -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - Shelter Shed
Arrived at old Gippstown in April 1972, after having been in service at Grey Street Primary School in Traralgon.High local historic significance (Dr Linda Young significance assessment July 2009)Octagonal-shaped school shelter shed in the form of a rotunda with a cone-shaped, corrugated-iron roof, timber frame and weatherboard walls. Timber floor. Built in 1912grey street primary school traralgon, old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, goldfields, coal mine, moe, historical village, education, school shelter shed, grey street, traralgon, old gippstown heritage park, latrobe city council, latrobe valley -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - Funeral Parlour
Originally the J A & A Templeton Funeral Parlour workshop, it was built in 1930 and was situated by his house in Traralgon.A small timber shop, rectangular in shape with a gabled corrugated iron roof. It has a verandah running along the front of the building, and there is a large billboard on the roof. There is a shed fixed to one side with a corrugated iron roof.Sign writing on the outside of the buildingfuneral directors, funeral parlour, traralgon, old gippstown, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mine, victorian era, moe, historical village, j a & a templeton, old gippstown heritage park, latrobe valley, latrobe city council -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - Police Station
One-room police station was built in 1869 in Maffra and moved c.1882 to a new site in Maffra, by the new police residence office. The office was enlarged in 1936, incorporating the old police station.High local historic significance on account of age.A small timber building, rectangular in shape with a gabled corrugated iron roof. There is a small hood over the rear entrance of the station.police, maffra, old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mine, victorian era, moe, historical village, wellington shire, old gippstown heritage park, latrobe valley, law, latrobe city council -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - Shed
Built at Old Gippstown from secondhand materials during the 1970sRectangular-shaped timber shed, with a corrugated iron roof. It has a back and two side walls, while the front is open for access.shed, old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mine, victorian era, moe, historical village, bushy park, old gippstown heritage park, latrobe valley, farm shed, latrobe city council, gunaikurnai -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - Stable, 1970s
Designed and constructed by Old Gippstown from materials at hand.A small square-shaped timber stable building with a gabled corrugated iron roof.old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mine, victorian era, moe, historical village, stable, old gippstown heritage park, latrobe valley, horse drawn vehicles, latrobe city council -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Geological Gossip or Stray Chapters on Earth and Ocean, 1860, 1860
... metamorphism iron ores coal coal fields gold deposits california water ...Brown hard covered book. Chapter 16 is on gold deposits and discusses the discovery of gold in California and Australia.Brown hard covered book geology, water, rivers, the atlantic, great deep, africa, australian interior, eyre's expedition, murray river, darling river, earthqaukes, leichardt, moreton bay, volcanos, darwin's theory, evolution, egyptian race, human remains in caverns and gravel, rocks, metamorphism, iron ores, coal, coal fields, gold deposits, california, water-glass, artificial stone, porous stones, cements -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaJournal (item) - Periodicals-Annual, Shiplovers' Society of Victoria, The Annual Dog Watch
This journal provides the reader with glimpses of the adventures and hardships of a seaman's life. Many of the stories are of sailing ships.Contributes to our knowledge of the importance of shipping and places on record those stories of the sea which would otherwise be lost.Contents Joyce Lambert Memorial - - 4 Editorial - Tol. E. Goldfinch- 5 Foreword - Capt. Peter Richardson - 7 The Challenge of Change - Late Joyce M.B. Lambert - 8 Tall Ships Australia. 1988. - - 21 Why Do We Love Ships? - Pamela Eriksson - 23 Iron Pacific -- Australia's Flagship - - 26 Square Rigger -- Chip Barge - W.P. Shemmeld - 33 Diary of a Ship's Surgeon Part 1 -- Outward Bound - H.M. Lightroller M.R.C.S. -37 My Coal Burning Warship - Rev. H.W. Coffey, MBE. MA. - 49 Sage of H.M.A.V. Bounty -- New Zealand to Tahiti 1984 - Tony Crowder - 55 The Heldia Song - K. Shewan-58 The Everchanging Inside Passage -- British Columbia - B.D. Weston - 61 Longitude -- Zero - S.J.Buckland - 66 The Lost Anchor - - 73 Origin of the Sea Shanty - P.R. Swensen - 78 Port of London Recollections - - 80 Redoubtable Capt. Schutt - Late Captain F. Klebingat - 82 Capt. Frederick Klebingat Remembered - - 84 Grounding of M.V. Kanimbla - F.B. Finch - 86 "Through the Hawsepipe" - Late Capt. H.R. Watson - 91 Caribbean Capsize - Lloyd Barber - 95 Dogwatch Miscellany - - 102 Shipping Advertisements - - 105 Future Beacons - K. Shewan - 107 Williamstown -- The Destination of Many Early Arrivals - 109 Book Reviews - - 113sailing ships, steamships, shipping, seafaring life, shiplovers' society of victoria, dog watch, p.r.swensen, sea shanty -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumIron, 1940's
... Made by internee at Camp 3 Tatura and used there to iron ...Made by internee at Camp 3 Tatura and used there to iron garments.Metal laundry iron. Covered with silver paint. Hinged lid, wooden handle painted red. Vents in base and lid to allow steam from coals to escape. Handmade.iron, wied l, camp 3 -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - Slab Kitchen
A slab construction cottage built in Ripplebrook in 1880 as a home for a single female landowner by the name of Ada Donaldson, and later relocated to Labertouche. It was donated to Old Gippstown by the Mason-Brook Pastoral Co. of Labertouche. A small building of horizontal timber slabs. It has a verandah over the front entrance and the front porch, a main living area with a cast iron stove in the fireplace and a separate room (probably a bedroom). There is a stone chimney on the back wall and the roof is shingled. Originally a cottage in its own right, the slab kitchen is now a part of the Bushy Park display.Medium local historic significance.A small building of horizontal timber slabs. It has a verandah over the front entrance and the front porch. There is a stone chimney on the back wall and the roof is shingled. This building was built in 1880sout kitchen, old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mine, victorian era, moe, historical village, timber slab cottage, ripplebrook, labertouche, mason-brook pastoral co., baw baw shire, latrobe valley, old gippsland heritage park, gunaikurnai, latrobe city council -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - Loren Iron House
'Loren' (formerly James Hogg's house) is a two-storey gabled prefabricated house, constructed using broad-gauge corrugated iron and was originally erected at 60-62 Curzon Street, North Melbourne in 1853 for builder, James Hogg. By 1968 the building had deteriorated and it was dismantled and moved to Old Gippstown where it was re-erected and restored. The building's external framing system consists of exposed metal columns with Gothic panel motifs at the corners. Internally the timber framed walls have been finished with new papers over new Hessian. The corrugated iron roof has an unusual concave form and the windows, floors and doors are of moulded softwood. State historic significance as a rare type of iron prefab. house. Listed on the Victorian Heritage Register and covered by a Heritage Overlay, Latrobe City Planning Scheme. It is also listed on the Register of the National Estate.Tall square-shaped two-storey corrugated iron building with a curved corrugated iron roof with two outside brick chimneys. prefabricated iron houses, old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mine, victorian era, moe, historical village, city of melbourne, north melbourne, curzon street, james hogg, prefabricated house, two-storey gabled prefabricated house, old gippstown heritage park, latrobe valley, loren, latrobe city council -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - School
2903 SUNNY CREEK formerly YARRAGON EAST. Sunny Creek State School, first called Yarragon East, was situated on Sunny Creek Road between Yarragon and Trafalgar and was opened in 1888. It was generally served by two teachers or a Head Teacher assisted by a Sewing Mistress. Edwin Mann taught there for 35 years, with his wife, Mrs Mann, as the Sewing Mistress for some years. [Extracted from Vision and Realisation: A Centenary History of State Education in Victoria, Vol. 3, 1973. This does not contain any details of the actual construction of the school, which is a typical Education Department building, and may date from later than 1888]High local historic significance, with some social significance: reunions of old students still held. (Dr Linda Young, Deakin University, significance assessment July 2009)Single-classroom State School. It is a rectangular-shaped timber building with weatherboard walls, timber frame and corrugated iron roof. An outside verandah is situated along the side of the building. Inside there is a small entry porch, a blackboard the length of the room (with fireplace) and a small store-room/cloak room. Built in 1888Has a name board above the front window that reads " SUNNY CREEK SCHOOL SS2903".school, sunny creek, old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mines, victorian era, moe, historical village, education, sunny creek road, baw baw shire, yarragon east, latrobe valley, old gippsland heritage park, latrobe city council, board of education -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - Church
A small timber church, containing an entrance area, congregation area, vestry and a small store room. The main part of the church is rectangular, but the smaller rooms give the building a 'T' shape. The roof is 'A' framed and is corrugated iron. There are three crosses on the roof; one on the entrance and two on the main building; one on the front and one at the rear. There is a bell in the yard. Built in 1895moe, church, old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mine, victorian era, historical village, church of england, holy trinity anglican church, rev. c.j. chambers, latrobe valley, old gippsland heritage park, latrobe city council -
 Broadmeadows Historical Society & Museum
Broadmeadows Historical Society & MuseumDomestic object - Charcoal iron
This iron was used by women to press the clothes from the mid 19th century. Coal embers were put inside, heating the base of the iron. Small bellows could be used to fire up the embers in order to keep the iron hot.This item is significant as it represents the appliances used by women from the mid 19th century until the advent of electricity.Brass iron with hinged lid, curved funnel and wooden handle with asbestos standdomestic object, iron, laundry, appliance -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyDomestic object - Kitchen Stove, C. Andrews, c1900's
The cast iron combustion stove is significant as part of the evolution of domestic cooking. Previously, cooking was mostly carried out in the outdoors on open fires, and later in fireplaces indoors. The cast iron combustion stove is significant as part of the evolution of domestic cooking. Cast iron stoves burn solid fuel such as wood or coal, and are used for cooking and warmth. The stoves have a firebox with a grate where the fuel is burned. The hot air flows through flues and baffles that heat the stove top and the oven. By the 1920s gas cookers were being introduced for domestic use, and by the 1930s electric home cookers were being offered to householders. A vintage cast iron kitchen stove set in the back wall of the Mont De Lancey Slab Kitchen. It has two steel decorative hinged doors with a handle to open and close. There is one pull out metal shelf in each compartment. Between the two doors is a round door which opens to reveal the wood box with a slatted base. This allows the ash and small coals from the fire to fall though to a pull-out tray below to be emptied outside when cooled. There is another lift-out kid to clean the ash and coals underneath.On the chimney plate 'Andrews, Patent Non Pariel' On the front of the stove below the round wood box 'C Andrews Geelong'cooking equipment, cooking stoves, fuel cooking stoves, domestic ovens -
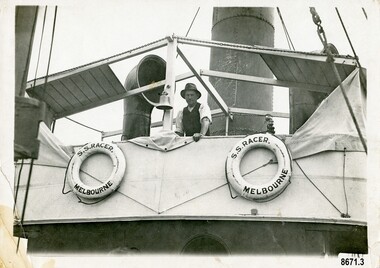 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Vessel, Steam tug "Racer", circa 1920's
The ocean Steamtug "Racer" was built in 1886 in Sunderland by "Boolds, Sharer and Company" for the "Queenstown Tug and Shipping Company". It is mentioned in several newspapers that soon afterwards it sank in Queenstown Harbour, Ireland and remained submerged for six months before being raised. It was a steel screw boat with a sluice keel, was 185 tons and 420 feet long. It was purchased around 1889 by the "Melbourne Coal, Shipping and Engineering Company Ltd" as it had sufficient power to work with the huge iron clippers that the company were dealing with. It survived several dangerous incidents on its voyage out to Melbourne. On May 28th in the middle of the night in a heavy gale, the tug was swamped by heavy seas and then several hours later was almost run down by a very large ship (the clipper Loch Vennachar) in full sail. The "Racer" (later owned by the "Melbourne Steamship Company") became one of the fastest and best-known tugs in the Port of Melbourne - working in the port until 1935. The "Racer" was involved in many rescues and dangerous incidents during its 45 years including the attempted rescue of the "Craigburn" near Cape Schanck, the rescue of the "Edina" from a reef near Williamstown and the rescue of the "Netherby" from heavy seas near Inverloch. In March 1930 she was caught by a strong wind when turning in the Yarra River and crashed into the Spencer Street Bridge - resulting in some damage to the scaffolding on the bridge and slight damage to the tug. In 1906 the "Racer" created a record for the fastest tow when it towed the 900-ton barque "Elizabeth Graham" from Sydney to Melbourne in 73 hours. In 1934 it was withdrawn from commission with plans for it to be broken up for scrap metal but was bought by a Melbourne businessman to be converted into a three masted schooner trading between Tasmania and Melbourne. George (Joe) Cunningham was born in 1892 in Geelong. His father, Alexander Cunningham was a ship builder and carpenter. George worked on oceangoing ships as a young man but after his marriage, had a twenty-six year career on Tugboats. He worked as a deckhand on the "Racer" and then worked his way up as a mate and then master on the "Maitland" and "Tooronga". Later he was in charge of two larger boats - the "Alvina" and "Helen Moore" and was engaged in salvaging the Union Steamship vessel "Karkariki" near Gellibrand Pile Light at the entrance to Hobsons Bay. George Cunningham died in 1978. This photograph was one of ten photographs donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village by Fred Trewartha. Frederick John Fox Trewartha (Fred) was a well-known Warrnambool businessman. He was born in Beeac near Geelong in 1920 and came to Warrnambool with his family as a very young child. He was apprenticed to his father John, as a saddler and later opened his own shop on Raglan Parade. He then moved into working with tarpaulins and canvases for the trucking industry. Fred was keenly interested in photography (and was a member of the Warrnambool Cine Club), yachting and boat building. He kept his yacht moored at Port Fairy for many years and participated in sailing events locally and interstate. He also built boats with his sons. He had the opportunity to meet many older sailors and it's thought this photo (and others in the set) may have been given to him by one of these men. Fred Trewartha died in 2016 in Warrnambool.This item is significant as a reminder of the important role tugboats and their crews played in the maritime history of Melbourne and the surrounding seas. This is a close-up view of a tugboat showing a man leaning against the upper deck. Two lifebuoys (with the words S. S. Racer Melbourne) are attached to the side of the deck and a funnel and an airvent are in the background. A handwritten note in pencil saying "Geo Cunningham on board Racer "is on the back of the photograph.Back - "Geo Cunningham on board Racer" Front (on lifebuoys) - S. S. RACER MELBOURNEflagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, tugboats, steamtug boats, racer, george cunningham, port of melbourne, melbourne steamship company, rescues, craigburn, steamtug, edina, elizabeth graham, netherby, yarra river, ships, historic maritime photographs, boolds sharer and company, queenstown tug and shipping company, melbourne coal shipping and engineering company limited -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Vessels at Breakwater Pier, Warrnambool, Foyle Photographic Studio, circa 1906
This photograph was one of ten photographs donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village by Fred Trewartha. Frederick John Fox Trewartha (Fred) was a well-known Warrnambool businessman. He was born in Beeac near Geelong in 1920 and came to Warrnambool with his family as a very young child. He was apprenticed to his father John, as a saddler and later opened his own shop on Raglan Parade. He then moved into working with tarpaulins and canvases for the trucking industry. Fred was keenly interested in photography (and was a member of the Warrnambool Cine Club), yachting and boat building. He kept his yacht moored at Port Fairy for many years and participated in sailing events locally and interstate. He also built boats with his sons. He had the opportunity to meet many older sailors and it's thought this photo (and others in the set) may have been given to him by one of these men. Fred Trewartha died in 2016 in Warrnambool. The three identifiable ships in this picture are the "Speculant", the "S. S. Barrabool" and the "S. S. Flinders" - coastal trading vessels that regularly came and went from Warrnambool. The steamer on the left hasn't been identified. The barquentine SPECULANT was a steel, three-masted sailing ship built in 1895 in Inverkeithing, Scotland, registered in Warrnambool, Victoria and wrecked at Cape Paton, Victoria, 10th February 1911. The SPECULANT had been involved in the timber trade between the United Kingdom and Russia, until sold to its Warrnambool owners and timber merchants Messrs. P.J. McGennan & Co. (Peter John McGennan) in 1902 for 3000 pounds and had her sailed to Warrnambool as her new port. Peter John McGennan was born in 1844 and worked as a builder and cooper in Holyhead, Anglesea, Wales. He immigrated to Australia in 1869 as a free settler and arrived in Warrnambool in 1871 and undertook management of a property in Grassmere for Mr. Palmer. Peter met his wife Emily in South Melbourne and they married in 1873. They had ten children including Harry who lived to 1965, and Andrew who lived until 1958. (The other children were their four brothers - John who was killed in the Dardenalles aged 35, Frederick who died aged 8, Peter who died aged 28, Frank who died aged 5 weeks - and four sisters - Beatrice who died age 89, Edith who died aged 49, Blanche who died aged 89 and Eveline who died aged 48.) In 1874 Peter starting a boating establishment on the Hopkins River. In 1875 he opened up a Coopers business in Kepler Street next to what was Bateman, Smith and Co., moving to Liebig Street, next to the Victoria Hotel, in 1877. In 1882 he then moved to Lava Street (which in later years was the site of Chandlers Hardware Store). He was associated with the establishment of the Butter Factory at Allansford. He started making Butter Boxes to his own design and cheese batts for the Butter Factory. In 1896 established a Box Factory in Davis Street Merrivale, employing 24 people at its peak, (it was burnt down in 1923); and in Pertobe Road from 1912 (now the Army Barracks building). Peter was a Borough Councillor for Albert Ward from 1885 to 1891, he commenced the Foreshore Trust (including the camping grounds along Pertobe Road), and he was an inaugural Director of the Woollen Mill in Harris Street, buying an extensive share-holding in 1908 from the share trader Edward Vidler. They lobbied the Town Hall to have a formal ‘Cutting’ for the waters of the Merri River to be redirected from its natural opening south of Dennington, to its existing opening near Viaduct Road, in order to have the scourings from the wool at the Woollen Mill discharged into the sea. He sold Butter Boxes around the state, and had to ship them to Melbourne by rail. Peter’s purchase of the SPECULANT in 1902 enabled him to back-load white pine from Kaipara, New Zealand to Warrnambool to make his butter boxes then, to gain profitability, buy and ship potatoes and other primary produce bound to Melbourne. (McGennan & Co. had also owned the LA BELLA, which had traded in timber as well, until she was tragically wrecked with the loss of seven lives, after missing the entrance channel to Warrnambool harbour in 1905. It appears that the SPECULANT was bought to replace the LA BELLA.) In 1911 the SPECULANT had been attempting to depart Warrnambool for almost the entire month of January to undergo docking and overhaul in Melbourne. A month of east and south-easterly winds had forced her to remain sheltered in Lady Bay, Warrnambool apart from one morning of northerlies, when an attempt was made to round Cape Otway; she had to return to shelter in Portland after failing to make any headway. With only 140 tons of sand ballast aboard, the ship would not have been easy to handle. Captain Jacobsen and his crew of nine, mainly Swedes, decided to make for Melbourne, leaving Portland Harbour on 5th February 1911. By the 9th they had reached Cape Otway, where they encountered a moonless night, constant heavy rain, and a heavy sea with a south-easterly wind blowing. After safely rounding Cape Otway the course was changed to east, then north-east to take the vessel to a point six miles off Cape Patton, following the orders of Captain Jacobsen, who told the crew to be very careful with the steering, as the wind and sea was running to leeward. The patent log (used to measure speed) had been out of order for the last four months as no-one in Warrnambool was able to fix it: it was intended to have it repaired in Melbourne. In the meantime the crew measured the vessel's speed by looking over the side and estimating wind strength. This compounded the difficulties of imprecise positioning, as the strong cross wind and sea were acting on the lightly laden vessel to steadily drive it towards the shore. At 3.30am on Friday 10 February 1911 Captain Jacobsen and the first mate were looking over the side of the vessel when they heard the sound of breakers and suddenly struck the rocks. The crew immediately knew they had no chance of getting the SPECULANT off, and attempted to rescue themselves by launching the lifeboat, which was instantly smashed to pieces. One of the crew then volunteered to take a line ashore, and the rest of the crew were all able to drag themselves to shore, some suffering hand lacerations from the rocks. Once ashore they began to walk along the coast towards Lorne, believing it was the nearest settlement. Realising their mistake as dawn broke they returned westwards to Cape Patton, and found a farm belonging to Mr C. Ramsden, who took them in and gave them a change of clothes and food. After resting for a day and returning to the wreck to salvage some of their personal possessions, at 10am on Saturday they set out for Apollo Bay, a voyage that took six hours, sometimes wading through flooded creeks up to their necks. The Age described the wreck as "listed to starboard. All the cabin is gutted and the ballast gone. There is a big rock right through the bottom of her, and there is not the slightest hope of getting her off". A Board of Marine inquiry found that Captain Jacobson was guilty of careless navigation by not taking steps to accurately verify the position of the vessel with respect to Cape Otway when the light was visible and by not setting a safe and proper course with respect to the wind and sea. It suspended his certificate for 6 months and ordered him to pay costs. The location of the wreck site was marked for a long time by two anchors on the shoreline, until in 1970 the larger of the two anchors was recovered by the Underwater Explorers' Club and mounted on the foreshore at Apollo Bay. The bell from the wreck was also donated to the Apollo Bay Surf Lifesaving Club but is recorded to have been stolen. Rusting remains of the wreck can still be found on the shoreline on the southern side of, and directly below Cape Patton. Parts of the SPECULANT site have been buried by rubble from construction and maintenance works to the Great Ocean Road, as well as by naturally occurring landslides. Peter J McGennan passed away in 1920. The Gates in the western wall of the Anglican Church in Henna Street/Koroit St are dedicated to him for his time of community work, which is matched with other prominent Warrnambool citizens; Fletcher Jones, John Younger, J.D.E (Tag) Walter, and Edward Vidler. After Peter J McGennan's death Harry, Andrew and Edith continued to operate the family business until July 11th 1923 when the company was wound up. (Andrew lived in Ryot Street Warrnambool, near Lava Street.) Harry McGennan (Peter and Emily’s son) owned the Criterion Hotel in Kepler Street Warrnambool (now demolished). His son Sid and wife Dot lived in 28 Howard Street (corner of Nelson Street) and Sid managed the Criterion until it was decided by the family to sell, and for he remained Manager for the new owners until he retired. Harry commenced the Foreshore Trust in Warrnambool around 1950. The McGennan Carpark in Pertobe Road is named after Harry and there are Memorial-Stone Gates in his memory. (The Gates were once the original entrance to the carpark but are now the exit.). The Patent Log (also called a Taffrail log) from the SPECULANT, mentioned above, and a number of photographs, are now part of the Collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village.. The S. S. Flinders was built by A. J. Inglis, Ltd, Pointhouse, Glasgow in 1878 for the "Tasmanian Steam Navigation Company', Hobart which merged with the "Union Steamship Company" of New Zealand and it was later sold to the firm "McIlwraith, McEacham and Company". It was built of iron and was 1000 tons and 227 feet, 1 inch long. It was described as "splendidly fitted up for the carriage of passengers and her cargo space was also very large". In the saloon about 130 passengers could be accommodated while the second class had sufficient room for one hundred passengers. In 1890, the S. S. Flinders would leave Melbourne on Mondays and Thursdays at 5 pm and reach Warrnambool the following morning at 8 am. On the return it would leave Warrnambool on Wednesdays and Saturdays at 5 pm and reach Melbourne the following morning. In 1896, the Weekly Times described the "steamer Flinders (otherwise known as "the Warrnambool mailboat") as "as good a sample of a seagoing steamer as there is trading on the Victorian Coast at the present time". In April 1896 newspaper reports noted the S. S. Flinders took 2915 bags of potatoes from Warrnambool to Melbourne (the largest shipment of that season) as well as 50 tons of tinned rabbits from the Hamilton Preserving Factory. It was also noted that particularly during the Christmas period, there were excessive demands for berths from holiday makers wanting to enjoy a holiday in Warrnambool. In May 1903, the S. S. Flinders narrowly escaped destruction when an explosion and subsequent fire occurred during the passage from Melbourne to Warrnambool. A drum (which apparently contained carbide of calcium) exploded and blew off a hatch cover. As the steamer got to within a mile or two of Warrnambool, smoke was seen coming out of the hold and (unknown to the passengers) flames had taken hold. The crew quickly got to work - closing down all the hatches and pumping water into the hold through a hole in the saloon floor. There were 30 or 40 cases of kerosene on board. The Flinders continued on to Warrnambool and berthed at the Breakwater. The passengers all went ashore - many unaware of the danger they had been in. A telephone message was sent to the local Fire Brigade Station however the fire was extinguished before the firemen and their equipment arrived. After the hold was checked, the Flinders was certified as seaworthy and left for Portland. The Flinders continued to transport Western District produce as well as passengers from Warrnambool to Melbourne until 1906 when (due to a decrease in shipping trade during the Winter and the availability of train services) the Flinders was replaced by the smaller steamer "Dawn" and in 1907 when it was sold to the "Adelaide Steamship Company" for use in the Western Australia coastal trade, it was replaced by the "S. S. Barrabool". The S. S. Barrabool was a coastal steamer built by "Palmer Shipbuilding and Iron Company Limited" in Jarrow, Durham in 1874. It was bought by "Howard Smith Ltd" who was a pioneer in the coal trade between Melbourne and Newcastle. Howards Smith's early fleet contained ships named after local hills and mountains -"You Yangs", "Macedon", "Dandenongs" and "Barrabool". Later they extended their fleet to include ships that were well known in Warrnambool including the "Dawn" and the "Edina". The S. S. Barrabool had a chequered start and was nicknamed the "Great Australian Ram" because of the numerous accidents it was involved in. Between 1875 and 1883 it collided with three other vessels - sinking the "Queensland" on August 3rd, 1876, near Wilson's Promontory and sinking the "Bonnie Dundee" on 10th March 1879 off Lake Macquarie, New South Wales (with the loss of five lives). In August 1884 the Barrabool collided with the steamer "Birksgate" in Port Jackson causing considerable damage to "Birksgate". However in a newspaper article published in the "Truth" in March 1899 the S. S. Barrabool was described as "one of the fine old type of vessels" and "still a stout a craft as ever". The article was describing the practice of a "two-mate" system on board many ships (the Barrabool being one) whereby the company only employs two men (a first and second mate who must alternate watches of four hours each) rather than three mates who work four hours on and eight hours off. It was suggested that ships employing the "two-mate" system may find their insurance policies "null and void" should an accident occur. However the writer did note that the Barrabool was "officered by a captain and first and second mates .. whom it would be impossible to find more capable officers amongst the maritime fleet of the colonies". Between 1900 and 1909 the Barrabool was making regular trips along the east coast of Australia, carrying coal to Hobsons Bay (Melbourne) from Newcastle, Bellambi and Sydney. In 1907 it was brought in as a temporary replacement on the Melbourne to Warrnambool route for the S.S. Flinders. In 1912 the S. S. Barrabool ran aground off the Fitzroy River in Queensland and was found to be uneconomic to repair. It was brought back to Sydney and converted into a hulk. In August 1952 it was towed 17 miles off Sydney and scuttled. “Foyle” written on the photograph is the name of Foyle’s Photographic studio - originally owned by James Charles Foyle. He owned “Foyle’s Photo Card Studios” in Liebig St, Warrnambool, which operated between 1889 – 1919 At the time of the photograph the studio was owned by both Charles and Lilian Foyle (sometimes known as Lillian or Lily), either of whom could have taken this photograph. They also worked together at a later date on the photographs, sketches and paintings of the famous and historical Pioneers’ Honour Board.This photograph is a significant record of three of the well-known coastal traders (the "Speculant", the "S. S. Barrabool" and the "S. S. Flinders") that sailed along the southwest coast of Victoria for many years - transporting goods and passengers between Melbourne and Warrnambool.A black and white photograph titled "Breakwater Pier, Warrnambool". A line of coal trucks on rails are on the Breakwater. There are three ships (one sailing ship and two steamers) moored at the pier. In the left side of the picture is another ship. The name of the photographer is printed in the lower right corner. On the back of the photograph are the handwritten names of the moored ships written in blue pen. It also has the handwritten name, town and telephone number of the donor. In the bottom right hand corner is an upside down stamped number in black ink.Front of photograph - "BREAKWATER PIER, WARRNAMBOOL." "FOYLE PHOTO" Back of photograph - "Sailing Ship" "Speculant sail ship" "Barrabool coal ship" "Flinders Passenger ship" Name of donor W'Bool (and telephone number) "K-7148 M" (stamped upside down)flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, speculant, barque speculant, p. j. mcgennan, peter john mcgennan, speculant wreck, captain jacobsen, s. s. flinders, steamer flinders, a. j. inglis ltd, tasmanian steam navigation company, mcilwraith mceacham and company, warrnambool mailboat, coastal steamer, s. s. barrabool, howard smith ltd, two-mate system, coal ship, dawn, edina, lady bay, breakwater, warrnambool breakwater, foyle, foyle photographic studio warrnambool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Steamers - Julia Percy, Dawn and Coorong, Chuck Photo Ballarat, Circa 1885
This photograph was one of ten photographs donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village by Fred Trewartha. Frederick John Fox Trewartha (Fred) was a well-known Warrnambool businessman. He was born in Beeac near Geelong in 1920 and came to Warrnambool with his family as a very young child. He was apprenticed to his father John, as a saddler and later opened his own shop on Raglan Parade. He then moved into working with tarpaulins and canvases for the trucking industry. Fred was keenly interested in photography (and was a member of the Warrnambool Cine Club), yachting and boat building. He kept his yacht moored at Port Fairy for many years and participated in sailing events locally and interstate. He also built boats with his sons. He had the opportunity to meet many older sailors and it's thought this photo (and others in the set) may have been given to him by one of these men. Fred Trewartha died in 2016 in Warrnambool. Shipping was the cheapest and most practical means of carrying produce and goods during the period 1840-1890. Regular domestic steamer services commenced in the Warrnambool district in the late 1850’s and by 1870 the passenger trade was booming. Four coastal traders made regular stops at Warrnambool in the 1880's - S. S. Julia Percy, S. S. Dawn, S. S. Nelson and S. S. Casino. The S.S. Julia Percy (later named Leeuwin) was an iron passenger-cargo steam ship built in 1876. At one point in time the Julia Percy would sail from Warrnambool to Melbourne every Friday and return from Melbourne to Warrnambool every Tuesday. The cost of a return ticket for a Saloon Fare was £1.0.0. The Julia Percy was built in Glasgow by Thomas Wingate & Company, Whiteinch, in 1876 for the Warrnambool Steam Packet Company, which commissioned it for trade in Victoria’s western district. It was first registered in Warrnambool, Victoria in 1876. Two steamships, the Julia Percy and the Nelson, collided on 25th December 1881. The Julia Percy was at that time owned by its first owners, the Warrnambool Steam Packet Company, and she sailed under the command of Captain Chapman. It had left Melbourne the evening of 24th December, with about 150 passengers, sailing in fine weather through Port Phillip Heads around 9pm. It was headed for Warrnambool, Belfast (now named Port Fairy) and Portland. The Julia Percy was off Apollo Bay when Captain Chapman was woken by the ship’s whistle after midnight, the steamer Nelson being on a collision course with the Julia Percy. The Nelson struck Julia Percy midship. Boats were lowered from the ship (apart from a damaged lifeboat) and about 30-40 of the passengers boarded the Nelson. The engine room and the forehold were checked and found clear of water. The company manager, Mr. Evans, had been on the Nelson, so he boarded and inspected the Julia Percy and the decision was made to continue on to Warrnambool with the passengers as there appeared to be no immediate danger. However, Captain Thomas Smith said the Nelson was taking on water, so Julia Percy followed it for about an hour towards Melbourne on standby in case of need. Then Julia Percy turned around towards Warrnambool again. Shortly afterwards the Nelson turned to follow her, the ships stopped and passengers were returned to Julia Percy, and three from Julia Percy boarded the Nelson. Both ships proceeded on their way. Julia Percy passed Cape Otway light afterwards, signaling that there had been a collision. It was discovered later that one of the passengers was missing, then thought to have boarded the Nelson but later thought to have fallen into the sea and drowned while trying to jump from Julia Percy to Nelson. There had been 3 tickets purchased under the same name of that passenger “Cutler”; a father, son and friend named Wordsworth, which had caused quite some confusion. No further mishap occurred to either ship and both the Julia Percy and the Nelson reached their destinations safely. An enquiry was instigated by the Victoria Steam Navigation Board regarding the cause of the accident between the two steamships, in connection with the death of Cutler who was supposed to have lost his life by the collision. The enquiry resulted in Captain Thomas Smith having his master's certificate suspended for six months. The Julia Percy changed hands several times. Its next owner was the Western Steam Navigation Co (1887), managed by Mr. T.H. Osborne (the company’s office was on the corner of Timor and Liebig Streets - its north-western wall is now part of the current Warrnambool Regional Art Gallery.) The Melbourne Steamship Co became the next owners (1890), followed by William Howard Smith and Sons (1901) for use in Queensland coastal trades and then it was bought by George Turnbull in 1903 and used for local mail contract in Western Australia. The Julia Percy was sold to the Melbourne Steamship Company Ltd. (1906) and re-named the “Leeuwin” but continued in her Western Australian coastal run. It was converted into a coal hulk in Melbourne in 1910 as a result of damaged caused when it was driven against the jetty at Dongara during a gale. The ship was eventually dismantled and scuttled off Port Phillip Heads on 28 December 1934. The steamship "Dawn" was a 522-ton coastal trader built in 1876 and the vessel operated around the Victorian west coast from 1877 until 1898 for the Portland & Belfast Steam Navigation Co. sailing between Melbourne and Portland, via Warrnambool. The vessel was then owned in October 1885 by the renamed company, Belfast & Koroit Steam Navigation Co., until March 1896 when its ownership moved to W Howard Smith & Sons Ltd. This Melbourne company used the ship to service most ports around Australia. Captain F. Chapman took over from Captain Jones and served on the SS Dawn from 1898 until 1900 when he took command of the SS Casino. On September 4th 1880, the three masted clipper ship, "Eric the Red" struck Otway Reef, near Cape Otway. The S. S. Dawn, under the command of Captain Jones, was returning to Warrnambool from Melbourne, its sailing time different to its usual schedule. The provedore of the Dawn, Benjamin Lear, heard cries of distress coming through the portholes of the saloon. He gave the alarm and the engines were stopped. Cries could be heard clearly, coming from the land. Captain Jones sent out crew in two boats, and fired off rockets and blue lights to illuminate the area. They picked up the three survivors who were in the long boat from "Eric the Red". Two men were picked up out of the water, one being the owner’s son who was clinging to floating kerosene boxes. At daylight the Dawn then rescued the 18 men from the floating portion of the deckhouse, which had drifted about 4 miles from where they’d struck the reef. Shortly after the rescue the deckhouse drifted onto breakers and was thrown onto rocks at Point Franklin, about 2 miles east of Cape Otway. Captain Jones had signalled to Cape Otway lighthouse the number of the Eric the Red and later signalled that there was a wreck at Otway Reef but there was no response from the lighthouse. The captain and crew of the Dawn spent several more hours searching unsuccessfully for more survivors, even going back as far as Apollo Bay. On board the Dawn the exhausted men received care and attention to their needs and wants, including much needed clothing. Four men (three crew and one passenger) died. A week after the shipwreck, the Australian Government had also conveyed its thanks to the Captain and crew of the S.S. Dawn - “Captain Griffith Jones, S.S. Dawn, The Hon. Mr Clark desires that the thanks of the Government should be conveyed to you for the prompt, persevering and seamanlike qualities displayed by you, your officers and crew in saving the number of lives you did on the occasion referred to. The Hon. The Commissioner has also been pleased to award you a souvenir in commemoration of the occasion, and a sum of 65 pounds to be awarded to your officers and crew according to annexed scale. I am, &c, W Collins Rees, for and in the absence of the Chief Harbour Master.” The Awards are as follows: - Crew of DAWN'S lifeboat-Chief Officer, Mr G. Peat, 15 pounds; boat's crew-G. Sterge, A.B., 5 pounds; T. Hammond, A.B., 5 pounds; J. Black, A.B., 5 pounds; H. Edwards, A.B., 5 pounds. Dinghy's Crew-Second Officer, Mr Christie, 10 pounds; boat's crew -F. Lafer, A.B., 5 pounds; W. Johnstone, A.B., 5 pounds; Mr Lear, provedore, 5 pounds; Mr Dove, purser, 5 pounds. Captain Jones receives a piece of plate. (from “Wreck of the ship Eric the Red” by Jack Loney). Medals of Bravery were awarded to the Captain and crew of the S.S. Dawn by the President of the United States, through the Consul-general (Mr Oliver M. Spencer), in July 1881 “ … in recognition of their humane efforts in rescuing the 23 survivors of the American built wooden sailing ship, the Eric the Red, on 4th September 1880.” The men were also presented with substantial monetary rewards and gifts. The city of Warrnambool’s care of the survivors was also mentioned by the President at the presentation, saying that “the city hosted and supported the crew ‘most graciously’. The Medal of Bravery awarded to Nelson Johnson is in the collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village in Warrnambool. Prior to 1882, and the arrival of the S. S. Casino, the "Dawn" was the only steamer to be able to navigate up the Moyne River at Port Fairy and unload at the wharf. The other regular steamers had to anchor in the bay instead. In February 1891 (as reported in The Age newspaper) the "Dawn" became the first vessel to berth alongside the newly completed Warrnambool Breakwater. The occasion was celebrated with a number of prominent townspeople assembling on board to "participate of a glass of wine". In 1895 the owners of the S.S. Dawn, the Portland and Belfast Steam Navigation Co., wound up and sold out to the Belfast Company who took over the Dawn for one year before selling it to Howard Smith. It took over the Melbourne to Warrnambool run in 1906 when the S. S. Flinders was sold. The S. S. Dawn was condemned and sunk in Suva in 1928. The State Library of Victoria has a lithograph in its collection depicting the steamer Dawn and the shipwrecked men, titled. "Wreck of the ship Eric the Red, Cape Otway: rescue of the crew by the Dawn". The third ship depicted in the photograph was thought to be the S. S. Coorong but there was a question mark next to its name. The photograph was thought to have been taken in 1885 and it's possible the S.S. Coorong was working in Clarence River, N. S. W. by this time. The steamer "Coorong" was built in 1862 by J. G. Lawrie of Glasgow. It was an "iron screw" steamer of 304 tons. It had many owners including Joseph Darwent of Adelaide (1863 - 1871), McMeckan Blackwood and Company, Melbourne (1871 - 1877), Mount Gambier Steamship Company Ltd. (1877 - 1881). William Whineham, Port Adelaide (1882), John See and Company, Sydney (1884 - 1892) and the North Coast Steam Navigation Company Ltd, Sydney (1892 - 1910). In 1911 it was hulked in Sydney Harbour and in 1921 it was being used as a coal hulk at Sydney. It had been originally imported into South Australia for the Port Augusta trade (primarily transporting goods needed by the early settlers) however the owners recognized that it had too much space for that purpose, so it was moved to work on the Adelaide to Melbourne line. Its passenger accommodation was enlarged and it enjoyed a "first class reputation" and by 1874 had made 313 voyages between Melbourne and Adelaide. Its captains included Captain McLean, Captain Ashton and Captain Dowell. In 1867, when 25 miles west of Cape Otway, while travelling from Adelaide to Melbourne, it came across the crew of the schooner "Black Watch" who had abandoned ship after it began quickly taking on water. The crew (six men) were able to get away in a small boat with a compass, chart and few candles. They were "excessively cold from exposure to the weather" when the S. S. Coorong picked them up. In 1877 the Coorong ran aground when entering the Outer Harbour at Adelaide (but was not damaged) and in 1882 it was stranded (for a short time) near Curdies Inlet (Victoria) with some slight damage to its bottom plates. Note - A ship with the same name "Coorong" (a coal carrying barque) was often on the Newcastle / Wollongong to Adelaide route also stopped several times in Warrnambool in the mid 1880's. The photograph has the label "Chuck Photos" printed on the front. Thomas Foster Chuck (born 1826 in London) was a photographer and entrepreneur who arrived in Victoria in 1861. The following year he produced and toured a "Grand Moving Diarama" of dramatic painted scenes from the Burke and Wills expedition. By 1866 he had established a photography studio in Daylesford and later he returned to Melbourne where he opened a studio in the Royal Arcade. In 1874 a collection of Chuck's photographs won a gold medal at the Annual International Exhibition in London. Throughout the 1870's he took over 700 individual photographs of prominent citizens for his historical photographic montage titled "Historical Pictures of the Explorers and Early Colonists of Victoria" which is now in the collection of the National Library of Australia. By 1888 he had sold his Melbourne studio and had established a studio in Ballarat (with his son Thomas Henry Chuck). In 1886 they produced an album titled "Warrnambool and District 1886, Western Hotel - J. Fox proprietor" containing over sixty large photographs of local coastal scenes and seascapes, for the use of patrons of the Western Hotel. This photo (of the three steamers in Lady Bay) was taken at this time and is in the album. Thomas Chuck died on December 7th, 1898, in Albert Park, Melbourne and his son Thomas Henry continued to operate the photography studio in Ballarat into the 1920's.This photograph is a significant record of several of the well-known coastal traders (S. S. Julia Percy, S. S. Dawn and possibly S. S. Coorong) that sailed along the southwest coast of Victoria for many years - transporting goods and passengers between Melbourne and Warrnambool in the 1880's. They are also significant in the role they played in the history of Warrnambool and the other coastal ports they visited as well as being examples of the dangers and hazards associated with navigating the waters along the southern coast of Australia. It is also a good example of a photograph taken by a well-known and significant photographer of that era.Black and white photograph of three steam ships anchored in Lady Bay, Warrnambool. They each have a funnel and two masts and are side on to the beach. A small rowboat with a crew can be seen on the far right. The words "CHUCK-PHOTO" are on the bottom left of the photograph. On the back of the photograph is the name and telephone number of the donor (handwritten in black ball point pen) and the names of the three steamships and date written in uppercase letters in dark blue ink. There is a four-figure number stamped in the centre of the back.Front - "CHUCK-PHOTO" Back - Name of donor and telephone number "6944" "JULIA PERCY, DAWN & KOORONG(?) IN LADY BAY 1885"flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, fred trewartha, s. s. julia percy, s. s. dawn, s. s. nelson, s. s. casino, leeuwin, steamer, steamship, coastal trader, warrnambool steam packet company, captain chapman, victorian steam navigation board, western steam navigation company, melbourne steamship company, william howard smith and sons, portland and belfast steam navigation company, w howard smith and sons ltd, eric the red, captain jones, medal of bravery, rescue, moyne river, warrnambool breakwater, lady bay, s. s. coorong, mount gambier steamship company, black watch, thomas foster chuck, chuck photos, chuck photography -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, The MIneral Industry its Statistics, Technology and Trade in the United States and Other Countries 1893
... , Chome iron ore, coal, copper, gold, lead, mineral industry ...This volume includes Australasia, and lists each state seperately , as well as New Zealand, It also lists Bismoth, Chome iron ore, coal, copper, gold, lead, mineral industry growth, alumite, antinomy, cobalt, coke, copper ore, gold, iron, lead, limestone flux, managanese, shale, silver, silver-lead, tin and zinc Lead production Manganese opalsRed hard cloth covered book of 115 pages. INcludes contentsnon-fictionThis volume includes Australasia, and lists each state seperately , as well as New Zealand, It also lists Bismoth, Chome iron ore, coal, copper, gold, lead, mineral industry growth, alumite, antinomy, cobalt, coke, copper ore, gold, iron, lead, limestone flux, managanese, shale, silver, silver-lead, tin and zinc Lead production Manganese opals mining, statistics, technology, trades, metal industry, minerals, united states, canada, china, france, germany, italy, japan, russia, south america, spain, sweden, united kingdom, ireland, coins, cuba, blast furnaces, gold, lead production, manganese, opals, silver, +, alumite, antinomy, cobalt, coke, copper ore, iron, lead, limestone flux, managanese, shale, silver-lead, tin, zinc -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Brass rod, Russell & Co, Circa 1886
In the 19th century, the Industrial Revolution meant that shipbuilders could build ships using iron. These iron ships could be much larger, with more space for cargo and they didn't need as much work to keep them in good condition. Isambard Kingdom Brunel's "Great Britain" built in 1843, was the first ship to be built entirely of wrought iron. In the 1880's steel began to be used instead of iron. Ships also began to be fitted with steam engines although a great deal of coal was needed to travel even short distances. For this reason, ships continued to be fitted out with sails even though some came with engines. The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. This particular artefact was one of many found by John Laidlaw (a local Warrnambool diver) when diving on the Falls of Halladale in the 1960's. In August 1973, John Laidlaw and Stan McPhee went on to discover the underwater location of the Schomberg - a passenger ship that ran aground on December 26th 1855 near Peterborough which now lies in almost 9 metres of water. When John Laidlaw died, his family donated a number of artefacts to Flagstaff Hill.This item is significant as it was recovered by a local diver from the Falls of Halladale. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).Long, slender, smooth brass rod tapering from 1.5 cm diameter at one end to .8 cm and widening back out to 1.5 cm at opposite end. One end has a smooth, rounded edge and the other end curves in and out with the end showing evidence of a piece having been broken off.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill divers, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, warrnambool, falls of halladale, falls of halladale wreck, shipwreck artefact, artefact, brass artefact, brass rod, brass fitting, diver, john laidlaw -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDecorative object - Brass Finial, Russell & Co, circa 1886
In the 19th century, the Industrial Revolution meant that shipbuilders could build ships using iron. These iron ships could be much larger, with more space for cargo, and they didn't need as much work to keep them in good condition. Isambard Kingdom Brunel's "Great Britain" built in 1843, was the first ship to be built entirely of wrought iron. In the 1880's steel began to be used instead of iron. Ships also began to be fitted with steam engines, although a great deal of coal was needed to travel even short distances. For this reason, ships continued to be fitted out with sails even though many came with engines. The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual, beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908): - Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92, Russell & Co. standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886, they introduced a 3000-ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890, they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four-masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough, south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and was able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors, and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. This particular artefact was one of many found by John Laidlaw (a local Warrnambool diver) when diving on the Falls of Halladale in the 1960's. In August 1973, John Laidlaw and Stan McPhee went on to discover the underwater location of the Schomberg - a passenger ship that ran aground on December 26th 1855 near Peterborough and which now lies in almost 9 metres of water. When John Laidlaw died, his family donated a number of artefacts to Flagstaff Hill. The brass finial may have been part of a larger decorative item such as a lamp or clock bracket.This item is significant as it was taken from the Falls of Halladale shipwreck which is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976)A brass, bell-shaped object with a body approximately 3 cm high. It has an outer lip, straight sides that taper in and a flat "cap". The inside of the object is plain with evidence of vertigris. It has a decorative topping almost 2 cm high, which has a double concave hollow neck.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill divers, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, great ocean road, warrnambool, falls of halladale, falls of halladale wreck, shipwreck artefact, artefact, brass artefact, brass finial, brass fitting, shipwreck coast, diver, john laidlaw, finial, brass decoration, handmade -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Metal ship's bolt, Russell & Co, Circa 1886
In the 19th century, the Industrial Revolution meant that shipbuilders could build ships using iron. These iron ships could be much larger, with more space for cargo and they didn't need as much work to keep them in good condition. Isambard Kingdom Brunel's "Great Britain" built in 1843, was the first ship to be built entirely of wrought iron. In the 1880's steel began to be used instead of iron. Ships also began to be fitted with steam engines although a great deal of coal was needed to travel even short distances. For this reason, ships continued to be fitted out with sails even though some came with engines. The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. This particular artefact was one of many found by John Laidlaw (a local Warrnambool diver) when diving on the Falls of Halladale in the 1960's. In August 1973, John Laidlaw and Stan McPhee went on to discover the underwater location of the Schomberg - a passenger ship sailing from Liverpool that ran aground on December 26th 1855 near Peterborough which now lies in almost 9 metres of water. When John Laidlaw died, his family donated a number of artefacts to Flagstaff Hill.This item is significant as it was recovered from the Falls of Halladale by a local diver. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).A thick metal bolt with a flattened head at one end, a smooth shaft approximately 4 cm long followed by a 6 cm long screw section - some of which is damaged and flattened. The end appears to have had a part broken off and is showing rust damage. flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill divers, flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, great ocean road, warrnambool, shipwreck coast, falls of halladale, falls of halladale wreck, shipwreck artefact, artefact, diver, john laidlaw, bolt, metal bolt, metal artefact, ship's bolt -
 Old Gippstown
Old GippstownBuilding - Coach House
Built in the 1920s on Tom Fowler's farm at Willow Grove. Used as a shed.A large square-shaped shed with walls of split timber. It has a gabled roof of corrugated iron, while the floor is made up of wooden cobbles. The roofs of the side extensions are made of wood. The floor is Red Gum blocksagriculture, old gippstown, west gippsland, gippsland, gippsland heritage park, goldfields, coal mine, victorian era, moe, historical village, baw baw shire, willow grove, latrobe valley, old gippstown heritage park, horse drawn vehicles, butchers cart, baker's cart, tanjil valley, latrobe city council
