Showing 358 items
matching processing company
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Ink Bottle, Second half of 19th Century or first half of the 20th Century
Although glass containers for wine and beer are probably 1,600 years old, much of their use began only in the late 17th century. In the United States, large-scale production of bottles was pioneered by Caspar Wistar in 1739 at his New Jersey plant. In the 1770s the carbonation process for producing soft drinks was developed, and so began an entirely new bottling industry. At the Great Exhibition of 1851 in the Crystal Palace in London, one million “pop” bottles were consumed. The first beer pasteurised in glass was produced in Copenhagen in 1870. Pasteurisation of milk followed soon after. The moulding of a screw thread on a container was invented by John Mason in 1858. The principles of the “press-and-blow” process for making wide-mouth jars were shown in the United States by Philip Arbogast in 1882, and the “blow-and-blow” process for making narrow-neck containers was demonstrated by Howard Ashley in England in 1885. These processes employed manual delivery; fully automatic jar forming by a suction-and-blow process was perfected by Michael Owens over the period 1895–1917 at the Toledo (Ohio) Glass Company, which subsequently became the Owens Bottle Machine Company. The automatic single-gob feeder was developed in 1919–22 by Karl Peiler at the Hartford-Fairmont Company in Connecticut. Fully automatic machines followed, but the true rugged survivor, utilising fully automatic gob delivery to the maximum versatility, was the Individual Section, or IS, machine invented by Henry Ingle at the Hartford Empire Company in 1925. Source: https://www.britannica.com/topic/glass-properties-composition-and-industrial-production-234890/History-of-glassmakingUnlike item 4018, this is a much smaller ink bottle, and was probably used by an individual, as against the supply of ink to pupils from a much larger bottle.Cotton Reel Ink Bottle, green glass, small, chipped around the lip, bubbles in glass.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, ink, bottle, glass -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyFunctional object - Ruler, Engineering Instruments, Inc, 10 inch slide rule model 10B and instruction booklet, 1947-1967
George Lee Lawrence (1901–1976) established a firm in Chicago to make slide rules for photography. In 1935 he moved to Wabash, Ind., renamed the company Lawrence Engineering Service, and began to manufacture general purpose slide rules. In 1938 he relocated once more to Peru, Ind., and in 1947 it was changed to Engineering Instruments, Inc., and the company remained in business until its building burned down in 1967. The model 10-B sold for 25 cents during this period. There is no record that Lawrence ever received a patent for any aspect of his design or manufacturing process.Used up to the 1960s prior to the invention of the electronic calculator.10 inch one-sided wooden slide rule painted white on the front face, which consists of two divided scales, one fixed and on movable, and a sliding window called a cursor. A, D, and K scales are on the base, and B, CI, and C scales the inside of the slide. The underside of the rule is marked with: tables for equivalents and conversions. Housed in cardboard box with instruction booklet.The top of the base is marked: MADE IN U.S.A. It is also marked ENGINEERING INSTRUMENTS, INC., PERU, INDIANA and PAT. PEND. Underside: This Famous Slide Rule... at a popular price. Solves Problems in Multiplication, Division, Proportion, Squares Roots, Cubes and Cube Roots, Reciprocals, etc., Instantly. Accurately Calibrated White Face on Well Seasoned Hardwood. Both ends of box: MODEL 10B-BK Price of 15 shillings handwritten on box.slide rule, mathematics -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Containers, Shaving cream, blue glass jar, 20thC
Shaving cream is a cream applied to the face, or wherever else hair grows, to facilitate shaving. The use of cream achieves three effects: lubricates the cutting process; swells keratin; and de-sensitizes skin. Shaving creams commonly consist of an emulsion of oils, soaps or surfactants, and water. Until the early 20th century, bars or sticks of hard shaving soap were used. Later, tubes containing compounds of oils and soft soap were sold. Newer creams introduced in the 1940s neither produced lather nor required brushes, often referred to as brushless creams. Creams that are in tubes or tubs are commonly used with a shaving brush to produce a rich lather (most often used in wet shaving). Bristol-Myers Squibb Australia Pty Ltd is a foreign owned proprietary company that obtains its revenue through the importation and distribution of pharmaceutical products. Bristol-Myers Australia is now headquartered in Mulgrave, Victoria and with an Australian presence dating back more than 80 years, Bristol-Myers Squibb Australia is a long-standing contributor to Australia’s health and economy. A blue glass jar with a screw top lid containing 'Ingrams' men’s shaving cream. Lid : Ingrams / Shaving / Cream Bottle Label : Ingrams / Concentrated / SHAVING CREAM / A LITTLE GOES A LONGER WAY / BRISTOL MEYERS CO. PTY. LTD. SYDNEY.shaving equipment, soap, safety razor, straight razor, cutthroat razors, moorabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham, early settlers, ingram pty ltd, bristol-myer squibb australia pty ltd, shaving cream, -
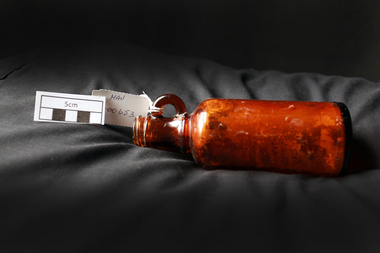 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Manufactured Glass, brown bottle, 20thC
This bottle may have held medicine used by a local early settler family. A local resident discovered it when digging his garden in McKinnon 2013. James Hardie immigrated to Australia in 1888 from Linlithgow, Scotland, and created a business importing oils and animal hides. Andrew Reid, also from Linlithgow, came to join Hardie in Melbourne, and became a full partner in 1895. When Hardie retired in 1911, he sold his half of the business to Reid. James Hardie Industries Ltd first listed on the Australian Stock Exchange in 1951 and is an industrial building materials company headquartered in Ireland which specialises in fibre cement products. James Hardie manufactures and develops technologies, materials and processes for the production of building materials. For over 20 years, Hardie has also operated a research and development facility devoted solely to fibre-cement technology. The company was a key player in asbestos mining and manufacturing in Australia through most of the twentieth century. Working with products containing asbestos - including the building material known as "Fibro" - caused people to develop various pleural abnormalities such as asbestosis and malignant mesothelioma. In December 2001, the company shareholders unanimously voted to restructure and relocate the company in the Netherlands as a parent company. This was part of a strategy to separate the company from the stigma of its asbestos liabilities. February 2010, James Hardie moved its corporate domicile from The Netherlands to Ireland, In May 2012 the High Court of Australia found that seven former James Hardie non-executive directors misled the stock exchange over the asbestos victims compensation fundA brown glass bottle, with finger grip handlearound bottom " THIS BOTTLE ALWAYS REMAINS THE PROPERTY OF JAMES HARDIE PTY. LTD. SYDNEY' on base 'IS985 / 7early settlers, pioneers, market gardeners, moorabbin, bentleigh, ormond, mvkinnon, glass bottles, medine containers, medical supplies, james hadie pty ltd. hardie -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Manufactured Glass, brown bottle, 20th C
This bottle may have held medicine used by a local early settler family. A local resident discovered it when digging his garden in McKinnon 2013. James Hardie immigrated to Australia in 1888 from Linlithgow, Scotland, and created a business importing oils and animal hides. Andrew Reid, also from Linlithgow, came to join Hardie in Melbourne, and became a full partner in 1895. When Hardie retired in 1911, he sold his half of the business to Reid. James Hardie Industries Ltd first listed on the Australian Stock Exchange in 1951 and is an industrial building materials company headquartered in Ireland which specialises in fibre cement products. James Hardie manufactures and develops technologies, materials and processes for the production of building materials. For over 20 years, Hardie has also operated a research and development facility devoted solely to fibre-cement technology. The company was a key player in asbestos mining and manufacturing in Australia through most of the twentieth century. Working with products containing asbestos - including the building material known as "Fibro" - caused people to develop various pleural abnormalities such as asbestosis and malignant mesothelioma. In December 2001, the company shareholders unanimously voted to restructure and relocate the company in the Netherlands as a parent company. This was part of a strategy to separate the company from the stigma of its asbestos liabilities. February 2010, James Hardie moved its corporate domicile from The Netherlands to Ireland, In May 2012 the High Court of Australia found that seven former James Hardie non-executive directors misled the stock exchange over the asbestos victims compensation fund' A brown glass bottle with finger ring hold at neck that may have been used by a local home owner to hold medicine c1900around base ' THIS BOTTLE ALWAYS REMAINS THE PROPERTY OF JAMES HARDIE PTY LTD SYDNEY ' on base ' IS 994 ' pioneers, market gardeners, moorabbin, bentleigh, ormond, mvkinnon, glass bottles, medine containers, medical supplies, james hadie pty ltd. hardie, early settlers -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Manufactured Glass, brown bottle 'Fauldings Aspirin', c1950
Francis Hardy Faulding 1816 – 1868 arrived in Sydney 1842. He was a Surgeon on the emigrant ship Nabob. 1845 Francis Hardy Faulding opened his first pharmacy at 5 Rundle Street in Adelaide and the business prospered. In 1867 he formed F.H Faulding & Co with Luther Scammel. as wholesale druggists and manufacturing chemists. Two of the Faulding company's major innovations were the development of a process for distillation of eucalyptus oil, and the development of the test for determining the eucalyptol content of the oil. Faulding's success was founded on eucalyptus oil, which formed the basis of an antiseptic marketed as "Solyptol" In 1868 Francis Hardy Faulding died, aged 52 at his suburban Glen Osmond home in Adelaide. Scammel’s two sons took over the business in 1888 and in 1890 the Company expanded to West Australia, then Sydney, Brisbane and finally, in 1924, Faulding began operations in Exhibition Street, Melbourne, eventually adding wholesale activities. 1986 With a presence in every city, from Darwin to Tasmania. Faulding becomes a truly national company. 2008 Zuelllig Group takes control Focusing solely on pharmaceutical wholesaling and distribution, Hong Kong based Zuelllig Group takes over control of Symbion Pharmacy Services. 2008 Symbion Pharmacy Services exceeds $3 billion with one of the country's largest networks of warehousing systems and service A brown glass, bottle with a metal screw top containing ‘Faulding's Aspirin’ tabletsFront label : FAULDINGS / ASPIRIN / GENUINE / ACETYL SALICYLIC ACID / 100 Gr 5 / for / Colds, .............. / DOSE ........... / F.H.FAULDING & CO LTD / MANUFACTURING CHEMISTS / AUSTRALIApharmacy, medicines, faulding f.h., scammell luther, faulding's aspirin, glassware, bottles, moorabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham, antiseptics, analgesics, pharmaceuticals, south australia, ss nabob, f.h.faulding & co. -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Manufactured Glass, brown bottle 'Penicillin Lozenges', 20thC
F. H. Faulding & Co was a pharmaceutical company founded in Adelaide, South Australia in 1845 by Francis Hardey Faulding 1816 – 1868, a native of Swinfleet, Yorkshire, He arrived in Sydney on the Nabob in February 1842,and travelled on the brig Dorset to Adelaide in May, where he opened a pharmacy at 5 Rundle Street in 1845.The pharmacy flourished, so he purchased a warehouse in Clarence Place in the city and transferred the manufacturing and wholesale arms of the business there. In 1861 he entered into partnership with Luther Scammell (1826–1910).a Yorkshireman, who had received medical training at Guy's Hospital, and arrived in Adelaide in 1849. Faulding died in 1868 and Scammell took over the business, however he was forced to retire in 1889 when the Bank of Adelaide threatened foreclosure after a series of failed mining and pastoral speculations. Two of his sons, Luther Robert Scammell FCS LSA ( 1858 – 1940) and William J. Scammell ( 1856 – 1928) acquired the manufacturing and wholesaling operations, and the business name, in 1888; the retail shops were sold to reduce the debt to the bank.The company expanded under the two brothers and later two sons of each became directors of the company. In June 1921 Faulding & Co. became a private company, with L.R. Scammell as chairman and managing director. He continued to run the firm's affairs until 1935.Two of the Faulding company's major innovations were the development of a process for distillation of eucalyptus oil, and the development of the test for determining the eucalyptol content of the oil. Faulding's success was founded on eucalyptus oil, which formed the basis of an antiseptic marketed as "Solyptol" (for soluble eucalyptus oil). The test became the industry standard, and the British Pharmacopoeia standard method in 1898. Other well-known products were Milk Emulsion (a pleasant alternative to cod-liver oil), Solyptol Soap, (which won a gold medal at the Franco-British Exhibition in London in 1908), Solyptol disinfectant, junket tablets, cordials, essential oils for perfumery and reagents such as Epsom salts, most produced in its factory in Thebarton The Faulding Co. built success around optimising the delivery of oral dosage form drugs. A brown glass bottle with a plastic screw top that contained 'Penicillin Lozenges' made by F.H. Faulding Co. Ltd . AustraliaFAULDING / Penicillin Lozenges / ( Troch. Penicillin B.P.) /......... / F.H.Faulding & Co. Ltd. / Adelaide, Perth, Sydney, / Melbourne, Brisbane on back DIRECTIONS......pharmacy, medicines, f.h. faulding co. ltd, penicillin lozenges, antibiotics, dentists, glassware, bottles, moorabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncNegative - Photograph, Loading fruit for market, Kinglake, c.1895
Loading buckets of fruit, probably raspberries from "The Oaks" Thomson family property, Kinglake into a covered cart hitched to a horse by four hatted farm workers. Most likely the fruit was headed to the "jam factory" at Kinglake operated by the Kinglake Fruit Growers Preserving Company which was formed about 1900. The fruit was pulped as the first step in the process by beng cooked in a steam bolier. The barrels of processed druit pulpt were then transported in barrels by horse and cart to the Whittlesea railway station.This photo forms part of a collection of photographs gathered by the Shire of Eltham for their centenary project book,"Pioneers and Painters: 100 years of the Shire of Eltham" by Alan Marshall (1971). The collection of over 500 images is held in partnership between Eltham District Historical Society and Yarra Plenty Regional Library (Eltham Library) and is now formally known as 'The Shire of Eltham Pioneers Photograph Collection.' It is significant in being the first community sourced collection representing the places and people of the Shire's first one hundred years.Digital image 4 x 5 inch B&W Neg 12.5 x 9 cm printshire of eltham pioneers photograph collection, kinglake, harvesting, pioneers and painters, fruit industry, market garden -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, early 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up to the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons) and produced. In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co. Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "clear" glass. There are other milk bottles that have a "green" tint in them.Around the bottom side of the bottle and blown into the glass "ONE PINT" and on the opposite side "MILK". Below these markings is "This BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLES RECOVERY LTD" below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION. On the base of the bottle is molded a big "M". An identification mark of "90" over "9" is beneath the "M". glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles, milk, dairy, farms, kiewa valley -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid 1800's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) to the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the large volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36"This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against sunlight penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle to contain milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle a circle within it 6/33 and next to this "ONE PINT" and under this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "4"glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, circa mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up to the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt Beauty.This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head was manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against light penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle which contained milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle a circle within it "6/18" and next to this "MILK" and opposite "ONE PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "3"glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
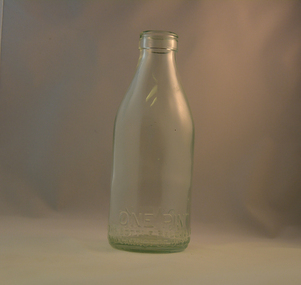 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) until the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt Beauty.This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottle along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against light penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle to contain milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle a circle within it "6/36" and next to this "MILK" and opposite "ONE PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "15" glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up until the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under the house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt BeautyThis heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against light penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle to contain milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle a circle within it "6/18" and next to this "MILK" and opposite "ONE PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "4"glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded), until the time that cheaper containers were invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under the house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt BeautyThis heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against light penetration). There are other milk bottles that do not have a "green" tint in them. This thick glass bottle, to contain milk, required its thickness because of the extensive handling (man and machine) before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the bottom end of this bottle is a circle within it "6/35" and next to this "MILK" and opposite "ONE PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base "M" underneath this "20"milk, dairy, glass bottle -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up until the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons). In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co.Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" Found under the house at 1 Beauty Ave., Mt BeautyThis heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottle along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a half pint capacity and is made from "clear" glass. There are other milk bottles that have a "green" tint in them and this tint was to protect the contents from sun damage. This thick glass bottle to contain milk required its thickness because of the extensive handling before final consumption. Milk was delivered by the "milk man" direct to the homes of consumers. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck.On the top half of this bottle is "MILK" and opposite "HALF PINT". Below this "THIS BOTTLE BELONGS TO MILK BOTTLE RECOVERY LTD" and below this "AND CANNOT BE USED WITHOUT WRITTEN PERMISSION" on the base is "2 M" underneath this "8/11" and underneath is "ISM -169"glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle - Ginger Beer, early to late 1900's
This glass ginger beer bottle was manufactured and used early to late 1900's, until the time that cheaper containers were invented(plastic bottles). This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the ginger beer processing plants from the brewing vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1990s the bottle slowly became phased out of production however boutique suppliers still preferred thick glass to contain any explosive action. Two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co. were the main suppliers for the Victorian State. In the period when this bottle was manufactured and used the major ginger beer brewing plants for the whole of Victoria were located in Melbourne because this was where its greatest consumer base was there and most rural areas were supplied by domestic sources (mother brewing ginger beer for the children). The Kiewa Valley and its region was one rural area which until road invrastructure was enhance covered the ginger beer thirst by local family production. As the population expanded considerably in the late 1940's (SECV Hydro Scheme) with a greater demand for "soft" drinks" being established supplies from larger towns and cities were call for. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents were from a reputable supplier (H Taylor) and where it originated from. These bottles were recyled by the manufacturer as a way to cut production costs. This method of recycling the bottles back to the specific manufacturer has (except for South Australia)been overtaken by a no cost recycling collection by councils (funded by their communities). This method by passes the user cost principle as the bottles are processed as non generic. The uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic containers however did not provide the keen domestic brewer of the "beer" with a reusable bottle. This heavy gauged glass ginger beer bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the filling production line. The method of pouring ginger beer into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one and a half pint capacity and is made from "light green" coloured glass(a protection against light penetration). This thick glass bottle, to contain ginger beer, required its thickness because of the extensive handling (man and machine) before final consumption. During this period delivery to homes in cities and towns was made initially by horse and cart and later by truck. Ginger beer was a "soft drink" of great demand. On the middle portion of this bottle is a large elongated circle within it and following the spherical line is "H. TAYLOR" ans a star separates this from "MELBOURNE" rounding out the bottom curviture. Within these words are the large initials "T H" . The "T" superimposed onto the "H". On the base and covering the whole bottom is the letter "T". At the opposite side to the manufacturers logo is "THIS BOTTLE CANNOT BE SOLD OR USED BY ANY OTHER PERSON & IS NOT COMPLETE WITHOUT STOPPER" glass bottle, non alcoholic drink, taylor ginger beer bottle, reuseable bottles -
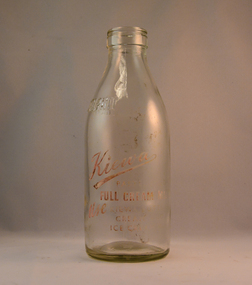 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Milk, Circa mid to late 1900's
This glass milk bottle was manufactured and used mid to late 1900's (1834 Victorian dairy industry was founded) up to the time that a cheaper container was invented(plastic bottles and polyethylene plastic lined cardboard cartons) and produced. In 1909 the supply of pure bottled milk was required for babies to overcome infant mortality due to unhygienic milk sources (unclean containers and unpasteurized milk). Due to the volume of milk being processed and hand milking could not keep up with demand, dairy farms introduced milking machines in the late 1930's. The great increases in dairy herds from the average of 18 cows per heard in 1950's to 142 cows per herd in 1996 required milk tankers to pick up the regions milk supply. This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the milk processing plants from the delivery vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1958 the milk bottle slowly became phased out of production. At this point in time Melbourne was drawing 160,000 bottles per week from the two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co. Victoria was the major state supplier of cows milk in the history of Australian milk production from the early 1800's. The Kiewa Valley and its region was a major contributor to meet that demand. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents (pasteurized milk) and where it originated from (region and supplier). This method of recycling the bottles back to specific dairy farms was a good control method but an uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic and cardboard containers. Kiewa Valley dairy herds had marked bottles bearing "90/9", "6/18", "6/33", "6/35" and "6/36" This particular one has "7/14".This heavy gauged glass milk bottle has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the milk production line. The method of pouring milk into the bottle has been part of the "production line". This bottle has a one Imperial pint capacity and is made from "clear" glass. There are other milk bottles that have a "green" tint in them. Around the bottom side of the bottle and blown into the glass "ONE IMPERIAL PINT". Below these markings and stenciled is "KIEWA" (in freehand style and underlined) underneath is "PASTEURISED FULL CREAM MILK" underneath this ,in freehand stiyle is "USE" next to this in block style "KIEWA BUTTER, CREAM, AND ICE CREAM MIX" to the left of this ,and barely readable is stenciled "THIS BOTTLE ALWAYS REMAINS/ THE PROPERTY OF/ NORTH EASTERN DAIRY Co. Ltd". On the base of the bottle is molded a big "2". with a smaller "m". An identification mark of "7" over "14" is within a circled boundary. Below this is moulded "RM - 15". glass bottles, commercial milk containers, domestic milk bottles, pasteurized milk bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle Ginger Beer, circa mid to late 1900's
This glass ginger beer bottle was manufactured and used early to late 1900's, until the time that cheaper containers were invented(plastic bottles). This bottle was so constructed to be easily moved within the ginger beer processing plants from the brewing vats/holding tanks to the final corking/sealing of the bottles for eventual distribution. From 1990s the bottle slowly became phased out of production however boutique suppliers still preferred thick glass to contain any explosive action. Two major glass bottle works companies, e.g. Australian Glass Manufacturers and the Melbourne Glass Bottle Works Co. were the main suppliers for the Victorian State.In the period when this bottle was manufactured and used the major ginger beer brewing plants for the whole of Victoria were located in Melbourne because this was where its greatest consumer base was there and most rural areas were supplied by domestic sources (mother brewing ginger beer for the children). The Kiewa Valley and its region was one rural area which until road invrastructure was enhance covered the ginger beer thirst by local family production. As the population expanded considerably in the late 1940's (SECV Hydro Scheme) with a greater demand for "soft" drinks" being established supplies from larger towns and cities were call for. Each bottle was "branded" during manufacturing to show the contents were from a reputable supplier (PHIBBS Bros) and where it originated from. These bottles were recycled by the manufacturer as a way to cut production costs. This method of recycling the bottles back to the specific manufacturer has (except for South Australia)been overtaken by a no cost recycling collection by councils (funded by their communities). This method by passes the user cost principle as the bottles are processed as non generic. The uneconomical "on cost" which was replaced by the "throw away" less costly plastic containers however did not provide the keen domestic brewer of the "beer" with a reusable bottle.This heavy gauged glass bottle (Ginger Beer) has a rim and a distinctive head at the top. This head has been manufactured to facilitate the movement of the bottled along the production line. The method of pouring ginger beer into the bottle has been part of the "production line" process of automation. This bottle has a capacity to hold 250ml of ginger beer and is made from "clear" glass. The marority of ginger beer bottles produced in this time frame where made with a "green" tint in them.This tinting helped reduce the sunlight effecting the contentsAround the bottom side of the bottle and blown into the glass is "THIS BOTTLE IS THE PROPERTY OF PHIBBS BROS, ALBURY" above this, in "running script" and sloping up from left to right is "Phibbs Bros" and underneath parallel to it "ALBURY". On the base of the bottle is molded a big "L 289" underneath this "M" and below this "AGM".ginger beer bottle, soft drink bottles, cordial bottles -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBook - Reference Printing, Charles W. Hackleman, Commercial Engraving and Printing, Circa 1921
This item relates to methods of reproducing photos on all forms of material in an era of physical offset printing.The offset method is being replaced by digital transfer direct to the final product,(paper or other porous and non porous surfaces). Newspapers and other "paper" information publications are still producing "hard copies" but these are slowly being phased out. This item was used Circa 1920s in the peek period of paper based media. From the 1940s radio and then television stepped into the mass media revolution.This book was produced when all printing, Government and private enterprise, was using the "off set" method. This method was used to a great degree in all schools within the Kiewa Valley. It was in an era before "photo-copying machines" were available. This was a period when printing inks for larger printing machines had to be purchased from specialised outlets and printing presses required to be washed after each "run" of printing before the next plate(aluminium) could be fastened onto the "off sett" machinery. Heat infusion now used in large machines and domestic printers has superseded this task. Faded green cloth covered book with green papered front and back sleeve pages.Photos and sketches are throughout the book. Gloss paper used from page 1 one to page 400. Pages 401 to page 432 are not gloss paper. The type of paper varies throughout the book until final advertisement and index pages, from page 833 to page 846, are on gloss paperThe spine cover is badly worn and wording is faded. Front cover has"Commercial Engraving And Printing" Author and publisher details written by Charles W. Hackleman. Published by Commercial Engraving Publishing Company, "A Manual of Practical Instruction and Reference Covering" Commercial Illustrating and Printing by all Processes.technical book, reference for engraving and printing -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph Tobacco selling, Tobacco sale floor, 1950 to 199
This promotional photograph by the Tobacco Growers Association was in response to a 1935 meeting of tobacco growers from Victoria, South Australia and Queensland which produced four major resolutions for the industry covering the remainder of the 1900s. These four resolutions were: (1) Adequate tariff protection (2) Control of pests and diseases (3) Orderly marketing (4) The formation of an advisory council of growers. History has produced the following results. (1) adequate tariff protection was never achieved,(2) control of disease through benzol vapour (CSIRO) breakthrough, was later identified as carcinogenic, (3) orderly marketing was achieved through (4) the establishment of the Tobacco Growers Association(19840. In October 2006, by way of Government buy back of tobacco leases from growers, resulted in the end of Tobacco farming in Australia (after 136 years of planting the first crop). It was also significant that the major tobacco companies such as Philip Morris and The British American Tobacco Australasia advised the industry that it would source its tobacco requirements overseas by 2009.This particular photograph shows prospective buyers (from the major processing firms of Philip Morris and British American Tobacco Australasia) inspecting the dried tobacco leaves at the Melbourne sales, before 2009, when they moved to overseas growers.The remnants of the Tobacco Industry can still be viewed throughout the Kiewa Valley and adjacent regions on the former tobacco farms, which still have the former tobacco drying sheds but now converted into hay sheds. The death of the tobacco industry(2006) resulted in the expansion of the dairy , sheep, beef cattle, venison and lama wool producers in the Kiewa Valley and surrounding regions. The problems from the large quantities of carcinogenic infused soil of farmlands in the region, still remains a problem now and for future generations. The tighter restrictions of where the final product can be smoked and the higher tax levied (no tariff protection) was the main contributor to this one time lucrative industry's demise.Coloured photograph pasted onto a thick wood chip backing. Two galvanised eyelets at the top of the frame, 50mm from each end, with a twine cord stretch from each, for hanging purposes. See also KVHS 0054A to KVHS 0054EA sign, which has been removed from the picture at some previous point in time is "Tobacco sale floor"tobacco, farming, rural industry, licences, ollie mould, blue mould, benzol vapour, photograph -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Document, Certificate Mr H Goodall, 1944
This certificate was awarded in appreciation of 25 years service to the Nestle Company which operated a dairy factory at Dennington in Warrnambool. The company came to Warrnambool in 1907 and purchased 17 acres at Dennington and a new dairy plant was established by 1911. At its peak it employed 600 people and processed 55000 gallons daily in the milk condensery which is a process whereby much of the water content is drawn from the milk and sugar is added making a product which has a long shelf life and because it is processed at low temperature the milk maintains much of its vitamin content.A certificate which links a local person to a long and well known industry in Warrnambool and the Western district.Cream soft card certificate with red and black text.Mr H Goodall. Nestle and Anglo Swiss Condensed Milk Co Australasia Ltd. dated 1st December 1944. The signature of the Chairman of directors is unreadable.warrnambool, nestle dennington, h goodall -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyraisin stoner, late 19th century
This item is an example of a food processing appliance used in the late 19th century long before electricity came to Orbost.A cast iron raisin stoner. It has a clamp for attachment to a bench and has a wooden handle on a turning arm.On arm-PAT.APP. Aug 20.95 Oct 5-97 On one side- WET THE RAISINS On other side-ENTERPRISE M.F.C. PHILADELPHIA. P.A. U.S.A. On chute- No. 38raisin-stoner food-preparation -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyraisin stoner, late 19th century
This domestic kitchen appliance is typical of the period when food processing was done at home. It would have been before the time of mass food processing factoriesA cast iron raisin stoner with a clamp. It has a wooden handle on a turning arm.On arm-PAT.APP. Aug 20.95 Oct 5-97 On one side- WET THE RAISINS On other side-ENTERPRISE M.F.C. PHILADELPHIA. P.A. U.S.A. On chute- No. 38raisin-stoner food-preparation -
 Cheese World Museum
Cheese World MuseumBook, Spectrum Print Solutions, Pioneering Dairy Families, May 2013
... with Victoria's oldest dairy processing manufacturer. The company ...Book developed from the Heritage Week 2011 display featuring some pioneering farming families connected with Warrnambool Cheese and Butter Factory Ltd. The book was printed and launched at the 125th Anniversary celebrations of the factory in May 2013. Families featured are Anderson, Burke, Burleigh, Chislett, Kelly, Logan, Mahony, McConnell, Rea, Taylor, Uebergang.Records the contribution of early dairy farming families connected with Victoria's oldest dairy processing manufacturer. The company was established in May 1888 and commenced commercial processing in November 1888. The company remained as an independent processor until early 2014.White cloth bound book with chrome screw binding, green and cream Warrnambool Cheese and Butter Factory Company logo and title in green print; 12 laminated pages, full colour. Book printer details on sticker on inside back cover.Spectrum Print Solutions/for all your printing needs/Shop2,377 Raglan Pde, Warrnambool/Ph 03 5561 5233 www.spectrum-oz.comdairying, dairy processors, milk, butter, cheese, families, anderson, burke, burleigh, kelly, logan, mahony, mcconnell, rea, taylor, uebergang, warrnambool cheese and butter factory company, wcb, anniversary celebrations -
 Cheese World Museum
Cheese World MuseumBooklet, The Modern Printing Company, Memorandum and Articles of Association of the Warrnambool Cheese and Butter Factory Company Ltd, 1932
The Warrnambool Cheese and Butter Factory Company Limited was established in 1888 at Allansford and remained as an independent dairy manufacturer until 2014 when it was taken over by Canadian company Saputo. The factory was burnt in 1929 and all records lost. This booklet is a reprint of the original.Warrnambool Cheese and Butter Company Ltd was the earliest dairy manufacturer registered in Victoria. Registered in May 1888, it commenced processing in November 1888. The Articles record the early rules of the company and some of those early people involved in the company.Brown soft cover 12 page booklet 'Memorandum & Articles of Association of Warrnambool Cheese & Butter Factory Company Ltd', with black border around the black text.The Companies Act 1864/ Memorandum/ and/ Articles of Association/ of/ The Warrnambool Cheese/ and/ Butter Factory Company Ltd/ Warrnambool: / The Modern Printing Company, Koroit St/ 1932allansford, warrnambool cheese and butter factory company, companies, commerce, articles of association, companies act 1864, dairy industry -
 Cheese World Museum
Cheese World MuseumDVD, A Look at our History -Vol.2, 2005
Series of interviews with former employees of Kraft (Allansford) and directors of Warrnambool Cheese and Butter Factory discussing their time and experiences as employees and directors of the factories. Warrnambool Cheese and Butter Company Ltd was established in 1888 and in 1935 developed a relationship with Kraft Foods Australia whereby Kraft leased premises from WCB. The two companies shared the milk collected to make their core products of cheese (Kraft) and butter and milk for domestic use (WCB). This arrangement continued until 1997.Gold DVD in plastic case, B&W cover with colour WCB logo.A Look at our History: Ron Campbell, Steve Heazlewood, Jim Mahony, DJ (Barney) Loganallansford, heazlewood, steve, campbell, ron, mahony, jim, logan, dj (barney), wcb, warrnambool cheese and butter factory company ltd, kraft foods ltd, dairy industry, dairy processors, factories, local history, cairns, peter, cheese manufacture -
 Cheese World Museum
Cheese World MuseumPhotograph, Warrnambool Cheese and Butter Factory Co Ltd site 2000 -aerial view, 2000
Warrnambool Cheese and Butter Factory Company was formed by a group of Warrnambool business men. The company was registered in May 1888 and commenced commercial production in November 1888. The company retained its independence for more than 125 years until acquired by Canadian firm Saputo. It has operated from the same site since its inception and also has an office in Japan. Milk processing is undertaken by Sungold. Milk powder for export is also produced on-site. Cheese World is a retail arm of the company operates on a connected site selling company products, local food products, wine and cheese tasting. Cheese World Museum operates under the Cheese World umbrella.Aerial colour photograph of Warrnambool Cheese and Butter Factory in wooden frame. Shows buildings and surrounds. Lines indicate factory boundaries, dotted lines indicate property extension. Date is recorded on the image.17.10.2000allansford, warrnambool cheese and butter factory company, saputo, dairyiing, dairy manufacturing, diary manufacturers, cheese, butter -
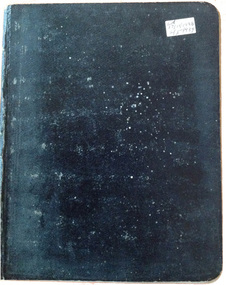 Cheese World Museum
Cheese World MuseumBook, laboratory notes
Kraft Walker commenced cheese processing at Allansford in 1935 under a lease arrangement with Warrnambool Cheese and Butter Factory. This arrangement remained in place until Kraft officially ceased bulk cheese production at Allansford in February 1993. Kraft was responsible for farm collection of milk which was then shared between the two companies -Kraft for bulk cheese manufacture and Warrnambool Cheese and Butter Factory for whole milk, milk powder and butter manufacture. Laboratory technicians tested milk and cheese during the receival and manufacturing processes to ensure a high quality product. Derek Shaw, whose notebook this is, was the first person in charge of the Kraft Allansford laboratory. He kept notes of testing undertaken and recorded results of anything considered unusual. This notebook is one in a series of 33. Les O'Callaghan commenced work in the laboratory as Derek Shaw's assistant and technician in charge following Derek's retirement. He too kept notebooks of test results.Kraft laboratory technician/bio-chemist Les O'Callaghan was responsible for the introduction of a number of quality control measures which are still in use in the dairy industry today. Les was mentored by Derek Shaw. This note book provides an insight into the dairy processing industry at this period.Black exercise book with lined pages; white sticker on front cover showing dates usedLH/ 17/11/1938 / 2/5/1939allansford, dairy industry, dairy processors, cheese making, kraft foods ltd, warrnambool cheese and butter factory company -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageNail
The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000 ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built-in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire. The Falls of Halladale shipwreck is listed on the Victorian Heritage Register (No. S255). She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).25½" of round solid copper nail. Recovered from "Falls of Halladale". Ship's nail.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, nail, copper nail, falls of halladale, ship's nail -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Anchor, Circa 1886
The anchor is one of four that were carried by the FALLS OF HALLADALE when she was wrecked near Peterborough in 1908. This Rodger’s Anchor was raised from the wreck site by Flagstaff Hill divers (Peter Ronald, Colin Goodall and Gary Hayden) in 1974 and is on permanent outdoor display at the Maritime Village. The imposing 2-tonne artefact required a raft of fourteen 44-gallon drums to raise it from the seabed before it was towed by a crayfish boat to the wharf crane at Port Campbell for loading onto land transport. Following Lieutenant William Rodger’s patent in 1831, anchor design moved away from the separate attachment of straight arms and flat flutes to each side of a long shaft. Rodger’s innovation included the forging of both arms and their flutes as a single uniformly curved piece which was then attached to the crown of the shank by a thick horizontal bolt. The two-inch diameter hole for the securing through-bolt at the crown is clearly visible in this example, the bolt dislodged by corrosion and now missing. The FALLS OF HALLADALE was a four-masted, iron-hulled barque, built by Russell and Co at Greenock in 1866 for the Falls Line of Wright & Breakenridge, Glasgow. The ship was 275 feet long, 42 feet wide, with a 24 feet draft and weighed 2,085 tonnes. She was built to carry as much cargo as possible rather than for speed. Her unmistakably square bilge earned her the title of “warehouse-type” ship and her iron masts and wire rigging enabled her to maintain full sail even in gale conditions. In 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo in her hold, the FALLS OF HALLADALE left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. 102 days later, at 3 am on the 14th of November, under full sail and in calm seas, with a six knots breeze behind and a misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a shelf of rock near Peterborough. There she stayed for nearly two months until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The iron-hulled, four-masted barque, the Falls of Halladale, was a bulk carrier of general cargo. She left New York in August 1908 on her way to Melbourne and Sydney. In her hold, along with 56,763 tiles of unusual beautiful green American slates (roofing tiles), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6500 gallons of oil, 14400 gallons of benzene, and many other manufactured items, were 117 cases of crockery and glassware. Three months later and close to her destination, a navigational error caused the Falls of Halladale to be wrecked on a reef off the Peterborough headland at 3 am on the morning of the 15th of November, 1908. The captain and 29 crew members all survived, but her valuable cargo was lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. ABOUT THE ‘FALLS OF HALLADALE’ (1886 - 1908) Built: in1886 by Russell & Co., Greenock shipyards, River Clyde, Scotland, UK. The company was founded in 1870 (or 1873) as a partnership between Joseph Russell (1834-1917), Anderson Rodger and William Todd Lithgow. During the period 1882-92 Russell & Co., standardised designs, which sped up their building process so much that they were able to build 271 ships over that time. In 1886 they introduced a 3000-ton class of sailing vessel with auxiliary engines and brace halyard winches. In 1890 they broke the world output record. Owner: Falls Line, Wright, Breakenridge & Co, 111 Union Street, Glasgow, Scotland. Configuration: Four-masted sailing ship; iron-hulled barque; iron masts, wire rigging, fore & aft lifting bridges. Size: Length 83.87m x Breadth 12.6m x Depth 7.23m, Gross tonnage 2085 ton Wrecked: the night of 14th November 1908, Curdies Inlet, Peterborough south west Victoria Crew: 29 The Falls of Halladale was a four-masted sailing ship built in 1886 in Glasgow, Scotland, for the long-distance cargo trade and was mostly used for the Pacific grain trade. She was owned by Wright, Breakenridge & Co of Glasgow and was one of several Falls Line ships, all of which were named after waterfalls in Scotland. The lines flag was of red, blue and white vertical stripes. The Falls of Halladale had a sturdy construction built to carry maximum cargo and able to maintain full sail in heavy gales, one of the last of the ‘windjammers’ that sailed the Trade Route. She and her sister ship, the Falls of Garry, were the first ships in the world to include fore and aft lifting bridges. Previous to this, heavily loaded vessels could have heavy seas break along the full length of the deck, causing serious injury or even death to those on deck. The new, raised catwalk-type decking allowed the crew to move above the deck in stormy conditions. This idea is still used today on the most modern tankers and cargo vessels and has proved to be an important step forward in the safety of men at sea. On 4th August 1908, with new sails, 29 crew, and 2800 tons of cargo, the Falls of Halladale left New York, bound for Melbourne and Sydney via the Cape of Good Hope. The cargo on board was valued at £35,000 and included 56,763 tiles of American slate roofing tiles (roof slates), 5,673 coils of barbed wire, 600 stoves, 500 sewing machines, 6,500 gallons of oil, 14,400 gallons of benzene, plumbing iron, 117 cases of crockery and glassware and many other manufactured items. The Falls of Halladale had been at sail for 102 days when, at 3 am on the night of 14th November 1908, under full sail in calm seas with a six knots breeze behind and misleading fog along the coast, the great vessel rose upon an ocean swell and settled on top of a submerged reef near Peterborough on the south-west Victoria’s coast. The ship was jammed on the rocks and began filling with water. The crew launched the two lifeboats and all 29 crew landed safely on the beach over 4 miles away at the Bay of Islands. The postmistress at Peterborough, who kept a watch for vessels in distress, saw the stranding and sent out an alert to the local people. A rescue party went to the aid of the sailors and the Port Campbell rocket crew was dispatched, but the crew had all managed to reach shore safely by the time help arrived. The ship stayed in full sail on the rocky shelf for nearly two months, attracting hundreds of sightseers who watched her slowly disintegrate until the pounding seas and dynamiting by salvagers finally broke her back, and her remains disappeared back into deeper water. The valuable cargo was largely lost, despite two salvage attempts in 1908-09 and 1910. Further salvage operations were made from 1974-1986, during which time 22,000 slate tiles were recovered with the help of 14 oil drums to float them, plus personal artefacts, ship fittings, reams of paper and other items. The Court of Marine Inquiry in Melbourne ruled that the foundering of the ship was entirely due to Captain David Wood Thomson’s navigational error, not too technical failure of the Clyde-built ship. The shipwreck is a popular site for divers, about 300m offshore and in 3 – 15m of water. Some of the original cargo can be seen at the site, including pieces of roof slate and coils of barbed wire.The shipwreck of the FALLS OF HALLADALE is of state significance – Victorian Heritage Register No. S255. She was one of the last ships to sail the Trade Routes. She is one of the first vessels to have fore and aft lifting bridges. She is an example of the remains of an International Cargo Ship and also represents aspects of Victoria’s shipping industry. The wreck is protected as a Historic Shipwreck under the Commonwealth Historic Shipwrecks Act (1976).A large iron Rodger’s anchor recovered from the wreck of the FALLS OF HALLADALE. It has a rounded crown, curved arms and moulded flutes. Heavy duty iron stock with round eyes at either end, fitted over shank and fixed into position by a wedge-shaped metal locking pin. Shackle missing but severed securing bolt remaining in shank. The presence of an empty bolthole at the crown junction of shank and arms confirms Rodger’s type. Corroded from 66 years submersion in seawater but otherwise structure is sound.warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck artefact, maritime museum, falls of halladale, rodger’s anchor, peterborough reef, 1908 shipwreck, anchor, last days of sail, great clipper ships
