Showing 538 items
matching blue water
-
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomMedal, Atlantic Star, abt 1945
The Atlantic Star was awarded to commemorate the Battle of the Atlantic between 3 September 1939 and 8 May 1945. It was designed primarily for convoys and their escorts and anti-submarine forces, as well as for crews of fast merchant ships that sailed alone. Eligibility Awarded for six months service afloat, in the Navy, the Merchant Navy and by Army and Air Force personnel serving on HM Ships, in the Atlantic and Home Waters. Awarded to aircrew who have taken part in operations against the enemy at sea within the qualifying areas for Naval personnel, subject to two months service in an operational unit after earning the 1939-1945 Star. Qualifying dates are 3 September 1939 to 8 May 1945. The Medal The Atlantic Star is a six–pointed star of yellow copper zinc alloy. The obverse has a central design of the Royal and Imperial cypher, surmounted by a crown. The cypher is surrounded by a circlet containing the words ‘The Atlantic Star'. Stars issued to Australian personnel have recipient names engraved on the plain reverse. The Ribbon The Atlantic Star ribbon has three vertical stripes of blue, white and sea green, shaded and watered. The colours represent the colours of the Atlantic Ocean. Clasps Two clasps were issued for the Atlantic Star: Air Crew Europe France and Germany Regulations only allow one clasp to be worn with the Star. When the ribbon is worn alone a silver rosette ribbon emblem is worn to denote the award of a clasp.Medal, Atlantic Star, miniature, with clasps- Air Crew Europe & France and Germanymedal, atlantic star -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomMedal, British War Medal
British War Medal 1914-20 Instituted by King George V in 1919 to mark the end of World War I and record the service given. Eligibility The British War Medal was awarded for service in a theatre of war between 5 August 1914 and 11 November 1918. Those eligible included members of women's organisations; persons on the staffs of military hospitals and members of recognised organisations who handled sick and wounded; and members of other duly recognised or other authorised organisations as specified in medal regulations. The qualification period was later extended to cover post-war mine clearance and service in Russia during 1919 and 1920. The Medal The British War Medal is cupro-nickel with the effigy of George V on the obverse. The reverse has an image of St George on horseback trampling underfoot the eagle shield of the Central Powers, and a skull and cross-bones, the emblems of death. Above this is the risen sun of victory. The years 1914 and 1918 are contained on the outside edge medal. The Ribbon The British War Medal has a wide central watered stripe of orange, flanked by two narrow white stripes, which are in turn flanked by two black pin-stripes, further flanked by two outer stripes of blue. The colours have no particular significance.british war medal -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomMedal, British War Medal 1914-18, 1919
Established on 26th July 1919. The silver or bronze medal was awarded to officers and men of the British and Imperial Forces who either entered a theatre of war or entered service overseas between 5th August 1914 and 11th November 1918 inclusive. This was later extended to services in Russia, Siberia and some other areas in 1919 and 1920. Approximately 6.5 million British War Medals were issued. Approximately 6.4 million of these were the silver versions of this medal. Around 110,000 of a bronze version were issued mainly to Chinese, Maltese and Indian Labour Corps. The front (obv or obverse) of the medal depicts the head of George V. The recipient's service number, rank, name and unit was impressed on the rim.The medal is silver and circular. A truncated bust of King George V is on the obverse, while there is a depiction of Saint George on the reverse. There is a straight clasp carrying a watered silk ribbon. This has a central band of golden yellow with three stripes of white, black and blue on both sides. The blue stripes come at the edges. 6,610,000 British War Medals were issued. The soldier's regiment and number are inscribed around the rim. Recipient: 908 DVR J E Whyte 3 LH FD AMBwar medal 1914-18 -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBook - Reference Maths, George Bell & Sons, Elementary Algebra Part 11, 1905
This item was a standard maths book used in Victoria. It would have been a continuation of the Part 1 of the same name. Elementary level would have been in the early years of secondary school. This has historic significance as it shows what Elemenetary Algebera was taught in the early - mid 20th century. This book would have been used in the Kiewa Valley schools by a local identity Wilma Davies therefore has social significance and research value. This book is now out of print and is a collectible item.A blue maths book with faded blue coth cover. It has gold lettering on the side of the book stating the name, author and publisher with their logo. It would have had its name on the cover at one stage but it no longer on it due to water damage.Cover has a triangle with Cambridge Mathematical Series enmbossed around the three sides. At the points of the triangle is the letters B D C with the letter A in the middle of the trianglebook, school, algebra, educational, math, kiewa-valley -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph Tobacco planting, Planting Tobacco seeding, Circa mid to late 1900's
This promotional photograph by the Tobacco Growers Association was in response to a 1935 meeting of tobacco growers from Victoria, South Australia and Queensland which produced four major resolutions for the industry covering the remainder of the 1900s. These four resolutions were: (1) Adequate tariff protection (2) Control of pests and diseases (3) Orderly marketing (4) The formation of an advisory council of growers. History has produced the following results. (1) adequate tariff protection was never achieved,(2) control of disease through benzol vapour (CSIRO) breakthrough, was later identified as carcinogenic, (3) orderly marketing was achieved through (4) the establishment of the Tobacco Growers Association(1984). In October 2006, by way of Government buy back of tobacco leases from growers, resulted in the end of Tobacco farming in Australia (after 136 years of planting the first crop). It was also significant that the major tobacco companies such as Philip Morris and The British American Tobacco Australasia advised the industry that it would source its tobacco requirements overseas by 2009.The remnants of the Tobacco Industry can still be viewed throughout the Kiewa Valley and adjacent regions on the former tobacco farms which still have the tobacco drying sheds and now converted into hay sheds. The problems from the large quantities of carcinogenic infused soil of farmlands in the region, still remains a problem now and for future generations. This particular photograph shows the lack of understanding by farmers and the contracted labour, at that time, and is demonstrated by the bare footed farmer walking next to the seed canister. Some workers did use protective "gum" boots but the majority of farm owners were skeptical of city scientists and their carcinogenic concerns, and it was only after the younger generation of farmers , who had attended Agricultural colleges, encompassed the scientific approach to farm management and began working closely with agricultural scientists. The "she'll be right mate" attitude of the earlier farming/rural community has since mid 1970s, been slowly dissipating. Stricter controls of herbicides and pesticides used in agriculture are now in force. The death of the tobacco industry(2006) resulted in the expansion of the dairy , sheep, beef cattle, venison and lama wool producers in the Kiewa Valley and surrounding regions.Coloured photograph pasted onto a thick wood chip backing. Two galvanised eyelets at the top of the frame, 50mm from each end, with a twine cord stretch from each, for hanging purposes. See also KVHS 0054(B) to KVHS 0054(F)A sign, which has been removed from the picture at some previous point in time is "The Tobacco seed, being so fine, is suspended in water and sown onto the seed base using a watering can [as in the photo] or similar device - August - Sept."tobacco, farming, rural industry, licences, ollie mould, blue mould, benzol vapour -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph of Lake Guy Dam, Spillway, Lake Guy Dam, c1945
In December 1939 the excavation of the diversion tunnel at the site of Junction (Lake Guy) Dam was commenced and finished in February, 1940.This allowed the stream to be diverted to facilitate the dam wall construction. This is a 'slab and buttress' dam. It is framed with timber and concrete then poured into the structure. A contract was let to Lewis Construction Co. for the construction of the dam, and the first batch of concrete was placed in September, 1940. Industrial trouble caused some delays but there was also slow progress on the part of the contractor and the work was taken over by the S.E.C., terminating the contract. The dam was completed in March, 1944. The lake is named after Mr. L.T. Guy who was the Resident Engineer, in charge of construction work and associated activities on the Kiewa area, from 1939 until November 1946. An historical pictorial record taken for the State Electricity Commission of Junction Dam (Lake Guy) on spill. Mt. Arthur is in the background and there is still evidence of the destruction of trees from the 1939 bushfires. Black and white photograph of Lake Guy Dam . The dam is spilling and Mt. Arthur is in the background. Hand written on back of photograph in blue ink " Lake Guy Dam".dam, lake, water, mr. l.t.guy -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph of Howmans Dam Camp, Howmans Dam Camp, circa 1948
... . howman's gap camp water dam Handwritten in blue ink on the back ...Howman's Gap camp was erected in 1948. The proposed dam to be built at this site was postponed in 1954 because of financial restraints imposed by the government at this time. It was to have supplied water for No. 2 Power Station at the Junction of the Pretty Valley and Rocky Valley branches of the East Kiewa River. This power station was not constructed until 2008 - 2010 and now gets it water from McKay Creek Power Station. The site of this camp is now occupied by the Howman's Gap Alpine Centre. Some of the original buildings still remain. An excellent photographic record of the type of buildings and size of the camp for accommodation of workmen during construction of the Kiewa Hydro Electric Scheme.Black and white photograph of the buildings erected at Howmans Dam site as accommodation for workmen.Handwritten in blue ink on the back of photograph "Howmans Dam Camp"howman's gap, camp, water, dam -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPolisher Floor, Hoover Appliances, Meadowbank
This appliance was a time saving method of cleaning floors. It appeared at a time (after World War II) when the domestic pressures faced by mothers and domestic staff was on the increase. The necessary "working parents" was through necessity becoming part of the "typical" family environment. It was the start of the ever increasing demand, from an economical reason, for both parents to work outside their property. Historically the period of the 1950s was one of extreme changes. It was an era where established role models were under pressure from an ever increasing demand for new and advancing consumerism. Communication levels via radio, newspapers and television was expanding at an ever increasing rate. Relatively isolated rural areas were opening up (post war) to foreign ideologies of consumerism. The basic restraints of "this will be alright mate, she'll do" was under a slow but effective take over. "I can get this done faster by this new whiz bang gadget that I saw on the TV last night!" was the new way to live by.This item is very significant in that it demonstrates the new consumerism at its infant stage of the social changes occurring due to greater communication levels between the rural Australian communities and other advancing communities world wide. The Kiewa Valley residents (mainly from the intermingling of rural and post World War II refugees working at the construction of the Victorian Hydro electricity installations, resulted in this rural area becoming integrated to new ways of living (both socially and economically). Once the attitude of "we have always done it this way mate!" was challenged and overcome, the acceptance of new time saving "gadgets" which started to pour in from foreign markets, the relative isolation of the Kiewa Valley (being mainly psychological entrenched), was over.This hoover electric floor scrubber and polisher has a main base containing two brushes (can be replaced with polishing pads). The two brushes/pads are fastened or removed from the base unit by pulling/pushing the heads from the small hexagonal shaft on the bottom of the machine motor. A pressure sensitive wire is inlaid at the brush/pad end to hold the brush/pad unit onto the shaft. The discs body and main body covering the electric motor are made from sturdy plastic. The rest of the appliance materials i.e. upright handle and the u framed attaching arm are made from lightweight powder coated steel. A small (350mm) red coloured foot switch protrudes from the back of the motor to release the the upright handle from the storage position to the action position.There are two fork shaped brackets on the rear of the handle, for securing the 6.5 metre long electrical cord and plug. There is no on/off switch on the appliance. A small stainless steel "u" framed clip (for hanging the appliance in the vertical position) for cupboard storage. Within the circle of the cleaning brush is stamped "1 above S.A.B.351" and on the opposite side P/No: 5023792". On the main plastic head of the brush discs are "TO CLEAN" and under this "USE ONLY WARM(underlined) WATER AND SOAP" on the opposite side, and within a circle is the Hoover Trademark. On the front of the blue coloured plastic dome covering the electric motor is (on a raised domed shaped plaque (on a red background) Hoover in slanted print from left to right(in a diagonal level)domestic appliances, floor cleaning, electric floor scrubbers and polishers -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph of Pretty Valley Workers Camp*, Pretty Valley Camp, circa 1949
Erection of staff quarters at Pretty Valley was completed in April, 1947 and accommodation for construction workers commenced in 1948 but suspended on 11th May for winter and resumed on 9th November. Construction of this camp was completed in 1949. A large dam was proposed at this site but was never constructed. Instead a small diversion dam was built which diverts water either to Rocky Valley Dam or to McKay Creek Power Station.An historical record of the type of accommodation provided for workmen during the construction of the Kiewa Hydro Scheme during the 1940's/50's.A black and white photograph of Pretty Valley Camp, c 1949. Dead trees are in the foreground, on both the left and right side of the photograph and a small snow gum is evident. There are camp huts and a much larger building behind these, possibly a workshop, and power poles are evident bringing electricity to the site.Handwritten in blue ink on back of photograph "Pretty Valley Camp. 5600 ft. above sea level".pretty valley, dam, water, workmen, camp -
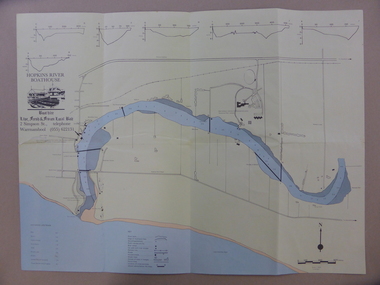 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Map - An Angler's map of the Hopkins River Estuary, Angler's map Hopkins River, 1980s
This is a map of the Hopkins River Estuary prepared by Dr John Sherwood for the benefit of anglers. The information on the sheet includes the location of sand banks, the water depths, boat ramp facilities and public access facilities. Some of the information has been gathered from aerial photographs. The map has been produced by the Warrnambool Institute of Advanced Education which was developed in the late 1960s from the tertiary section of the Warrnambool Technical College and with all its departments established by 1984 at the Sherwood Campus five kilometres from Warrnambool on the Princes Highway. Today the site is occupied by Deakin University, Warrnambool campus. The Warrnambool Anglers’ Club has its headquarters on the banks of the Hopkins River near the mouth of the river and the Lyndoch Aged Care facility.This map is of interest as a specialist one, providing fishermen with detailed information on all aspects of the Hopkins river estuary. Fishing has been both a profession and a popular recreational pursuit for Warrnambool residents since the early days of the city’s settlement. The Hopkins River Estuary has been a focal point for fishermen throughout Warrnambool’s history. This is a sheet of paper folded three times to produce a folded map. The front cover has a black and white photograph of two fishermen with a large fish. The map of the Hopkins River Estuary is in yellow, blue and black and covers the side of one sheet and three quarters of the other side. There is an advertisement for the Hopkins River Boathouse with a black and white sketch of the boathouse and notes on the map written by Dr John Sherwood. There are several diagrams showing the water depths. The map has some silverfish damage and some tearing at the folds. warrnambool anglers’ club, history of warrnambool, hopkins river, hopkins river estuary, john sherwood -
 Warrnambool RSL Sub Branch
Warrnambool RSL Sub BranchHat, Hard Yakka, 2015
This hat is part of a General Purpose Uniform issued by the Australian Airforce to Bernard Farley during service. This uniform type was developed in 2014 and replaced camouflage as the uniform worn during general base duties and in non-warlike environments. Although a camouflage pattern, this design is not intended for use as camouflage. This item has social significance, as an item of uniform worn by Warrnambool RSL community member and Secretary (2019), Bernard Farley during service with the Australian Airforce. The item is a representative example of current Airforce General Purpose Uniform and is in excellent condition. As a set, the uniform has aesthetic significance in it’s design, incorporating GPU uniform design from the Army alongside the colours and motifs of the Australian Airforce. General Purpose Uniform (GPU) hat in Airforce colours of blue and grey in camouflage pattern. Broad brim hat with black plastic cord end fastener on a blue cotton cord. Plastic tag on interior of hat lining with printed inscriptions.Inscription on tag: “Hard Yakka/AUSTRALIA/AUGUST 2015/PO No: CC2XZ8/LAY No: 10609/SQNCOR FARLEY/(broad arrow)/[Mobile Phone Number]/NSN: 8415-66-161-4051/SIZE: M 56cm/NAME:” Inscription on reverse of tag: “PM KEYS No:/75% COTTON/25% POLYESTER/CARE INSTRUCTIONS/HAND WASH IN COLD/WATER WITH MILD/DETERGENT RISE/WELL DO NOT WRING/TUMBLE DRY OR/DRYCLEAN (X)/DRIP DRY IN SHADE”camouflage, airforce, uniform, general purpose uniform, australian defence force -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Work on paper - Letter, Henry Watts, Letter written 1859
Henry Watts (1828_1889) Died at Melbourne, 16th December, 1889. He was a good microscopist. His botanical studies were chiefly devoted to algae, both fresh-water and marine, and while living for many years at Warrnambool he was a contributor of algae to Harvey, who figured Wrangelia wattsii, Harv., and Crouania wattsii, Harv., in his “Phycologia Australica " He was the author of "On the Fresh-water Algae of Victoria " (Trans. Roy. Soc. Vict., 1861-4, 67) ; .also a paper "On Fossil Polyzoa" (ib.. 82); "A Trip to Mt. Macedon in Search of Fresh-water Algae" (Wing's S. S. Record, iii., 252); "On a Species of fresh-water Algae from Victoria" (Vict. Nat., i., 21); "Some Recent Additions to our Knowledge of Microscopic Natural History" (ib., iii., I33) (includes lists of fresh-water algae and Desmidieae ), First librarian (1881-2), also a vice-president of the Field Naturalists' Club of Victoria. He is further commemorated by Acacia wattsiana. F. v. M. www.anbg.gov.au/biography/watts-henry.html . Henry Watts worked as a bootmaker in Timor and Liebig streets Warrnambool in the 1860’s but it was as an amateur scientist that Watts gained public notice.For an exhibiton in Melbourne in 1861 Henry Watts prepared a collection of over 100 different species of seaweed from the Warrnambool district. It is recorded in the Examiner in 1863 that he had been elected as an honorary member of the Bristol Microscopical Society of England He was a member of the Warrnambool Horticultural society and in 1865 he opted to become a flower distiller.At the 1866 MelbourneExhibition, Henry Watts exhibited 44 bottles of his perfumes. He had a keen interest in microscopes and microscopic organisms.He spent many hours combing the caves and examining the guano of local bats. This letter is written to Professor Quekett advising him that he has sent a collection of packets of samples of diatomaceae asking him to examine and name the same.. Professor Quekett was a famous microscopist of the Victorian era with the Quekett microscopist club one of the oldest in the world dedicated to the use of the microscope and its discoveries. Henry Watts was one of Warrnambool’s first botanists and marine scientists. He also established a flower distilling and perfume manufacturing business in Warrnambool. In 1861 he sent a collection of over 100 species of seaweed to the Melbourne Exhibition.Framed, handwritten letter, ink on blue paper. Transcript of letter is typed black on white paper. Five small numbered pieces of paper containing specimens of diatomaceae collected from marine and fresh water areas around Warrnambool.Names Henry Watts, Professor Quekett. Handwritten along the bottom of the frame, “The above was bought at a London Auction for $12-10-00 by Miss Eddey a Melbourne Book shop Proprietress and recently presented to the W.F.N. Club.: warrnambool, henry watts, watts henry, botanist,microscope, microscopic, quekett, john thomas quekett -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyfolder of documents, 1961 - 1962
The first swimming competition was conducted by the Swimming Club at the Orbost Swimming Pool not long after its construction. The results were hand-written on a cardboard sheet pinned up on a notice board. One of the events held was a crazy diving display performed by Neil Rodwell and Malcolm Corner in which they rode bikes off the diving platform.The opening of the Orbost Swimming Pool was a significant event in Orbost's development. The construction of the pool was community driven and the swimming club played a crucial role in helping young people learn about water safety away from rivers.A manila folder of documents related to the Orbost Amateur Swimming and Life Saving Club. It contains the constitution, rules of competition, competition results and a cloth badge- a white silver gull inside a pale blue circle on a darker blue background with ORBOST S & LSC below. Documents are handwritten and typed.orbost-swimming-club sport-swimming leisure-club -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical SocietyCoolgardie safe, first half 20th century
Without refrigeration, storage of meat was difficult. Flies were a problem, and it was important to keep meat cool and out of the way of pests. One way of doing this was to use a meat safe: a kind of cupboard designed to store meat and keep it fresh enough to eat. Meat safes are ventilated. They were sometimes made with sides of wire mesh or perforated metal, so that air could circulate around the meat while keeping flies and other animals out.The Coolgardie safe was invented in the late 1890s by Arthur Patrick McCormick, who used the same principle as explorers and travelers in the Outback used to cool their canvas water bags Originally they were handmade using materials to hand. In the early 20th century, Coolgardie Safes were manufactured commercially across Australia, and found their way into homes in both rural and urban areas. These safes incorporated shelving and a door, had metal or wooden frames and Hessian bodies. The feet of the safe were usually placed in a tray of water to keep ants away. (refs ABC-Home; Museum Victoria)The Coolgardie safe was an Australian invention used especially in country areas from the 1890s until the mid 20th century. It began to be replaced by ice chests from the turn of the twentieth century in cities and country towns which had ice works. This item is an example of a domestic appliance commonly used before electricity was widely available for domestic use.A cube-shaped metal Coolgardie safe painted blue. It has a triangular hook on the top for hanging or lifting. There are small feet at bottom . The sides are perforated in a Above the door; Inside a rhomboid shape "WILLOW"food-storage coolgardie-safe domestic -
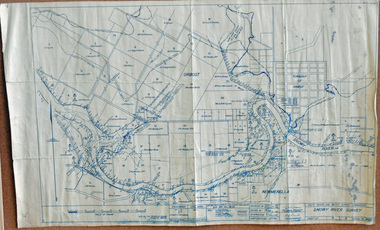 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societysurvey, 1941
this item is a useful reference tool.A survey map produced by the State Rivers and Water Supply Commission. It is on white paper with blue ink. It is a hand-drawn survey of the Snowy River in 1939-40.survey map snowy-river -
 Cheese World Museum
Cheese World MuseumManual, How to operate the ABC Spinner
Donated with the ABC Spinner washing machineBlue heavy paper cover with black lettering and an illustration of Model 60. Full title is 'How to operate the ABC Spinner -Spins Away Water -Spins Away Dirt. The Porcelain Washer -Manufactured by Altofer Bros Company Established 1909 Peoria Illinois Contents include parts price list and instructions for use'allansford, altofer brothers, abc spinner, washing machines, laundry aids -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Bowl, Late 19th or early 20th Century
The Process of Making Pottery Decorating, Firing, Glazing, Making, Technical There is a rhythm and flow to clay. It can’t be done all at once! Even the making process! It can take weeks to get everything done, especially if you can only work on your pottery once a week! Even though we have three hour classes, it’s often just not enough time! Here is an overview of some of the processes so you have a bit more grasp on some of the technical stuff! Step One – Design There are SO many ideas out there for making stuff in clay! From delicate porcelain jewellery, through to heavy sculptural work and everything in between. Deciding your direction is sometimes not that easy – when you first start, try everything, you will naturally gravitate to the style that you enjoy! The options and variations are endless and can get a wee bit overwhelming too! Check in with me before you start to ensure your ideas will work, what order you might do things, how you could achieve the look you are seeking and any other technical data required! Step Two – Making Clay is thixotropic. This means that as you work with it, the clay first gets sloppier and wetter, before is begins to dry in the atmosphere. For most things, you simply can’t do all parts of the project at once. An example of work order might look like: Get last weeks work out from the shelves Prepare clay for today’s work – roll your clay, prepare balls for throwing, make the first stage of a pinch pot) Clean up last week’s work and put it on the shelf for bisque firing Check that you have any glazing to do – and do enough of it that you will have time to finish your main project Do the next step of your next project – there might be a further step that can’t be complete immediately, in that case, wrap your work well and put onto the shelves. Letting your work rest for a while can really help keep your work clean and professional looking. Many things require bagging under plastic to keep it ready for work the next week – put your name on the outside of the bag so you can find your work easily. We have stickers and markers. Consider how you want to decorate your work – coloured slip can be applied at a fairly wet stage (remembering that it will make your work even wetter!). Trying to apply slip to dry clay won’t work! If you want to do sgraffito – you will need to keep the work leather hard (a state of dryness where you can still work the clay with a little effort and a little water and care). Step Three – Drying Most of the time your work can go into the rack uncovered to let it dry out for the following week. If you want to continue forming or shaping you will need to double bag your work – put your work on a suitable sized bat and put the bat in a bag so the base of the bag is under the bat, then put another bag over the top of the work and tuck the top of the bag under the bat. If you want to trim (or turn) your thrown work the following week, it should also be double bagged. If your work is large, delicate, or of uneven thicknesses, you should lightly cover your work for drying. When considering the drying process, bare in mind the weather, humidity and wind! The hotter and dryer, the faster things dry and work can dry unevenly in the shelves – this can lead to cracking – another time to lightly cover your work for drying. Step Four – Trimming and Cleaning Up Your work is dry! It is called greenware now and it is at it’s most fragile! Handle everything with two hands. I often refer to soft hands – keep everything gentle and with your fingers spread as much as possible. Try to not pick up things like plates too much, and always with both hands! Before your work can be bisque fired it should be “cleaned up”. You work won’t go into the kiln if it has sharp edges – when glazed, sharp edges turn into razor blades! Use a piece of fly wire to rub the work all over – this will scratch a little so be light handed. Use a knife or metal kidney to scrape any areas that require a bit more dynamic treatment than the fly wire offers! Finally, a very light wipe over with a slightly damp sponge can help soften and soothe all of your edges and dags! Trimming thrown work: If you are planning to trim (or turn) your thrown work (and you should be), make sure you bag it well – your work should be leather hard to almost dry for easiest trimming. Use this step to finish the work completely – use a metal kidney to polish the surface, or a slightly damp sponge to give a freshly thrown look. Wipe the sponge around the rim after trimming, and check the inside of the pot for dags! Trimming slip cast work: Usually I will trim the rims of your work on the wheel the following day to make that stage easier, however you will still need to check your work for lumps and bumps. Last but not least – check that your name is still clearly on the bottom of your work. Step Five – Bisque Firing When the work is completely dry it can go into the bisque kiln. The bisque kiln is fired to 1000°C. This process burns off the water in the clay as well as some of the chemically bound water. The structure of the clay is not altered that much at this temperature. Inside the bisque kiln, the work is stacked a little, small bowl inside a larger bowl and onto a heavy plate. Smaller items like decorations or drink coasters might get stacked several high. Consideration is paid to the weight of the stack and shape of the work. A bisque kiln can fire about one and a half times the amount of work that the glaze kiln can fire. The firing takes about 10 hours to complete the cycle and about two days to cool down. Once it has been emptied the work is placed in the glaze room ready for you to decorate! Step Six – Glazing Decorating your work with colour can be a lot of fun – and time consuming! There are three main options for surface treatment at this stage: Oxide Washes Underglazes Glazes Washes and underglazes do not “glaze” the work – It will still need a layer of glaze to fully seal the clay (washes don’t need glaze on surfaces not designed for food or liquid as they can gloss up a little on their own). Underglazes are stable colourants that turn out pretty much how they look in the jar. They can be mixed with each other to form other colours and can be used like water colours to paint onto your work. Mostly they should have a clear glaze on top to seal them. Oxides are a different species – the pink oxide (cobalt) wash turns out bright blue for instance. They don’t always need a glaze on top, and some glazes can change the colour of the wash! The glazes need no other “glaze” on top! Be careful of unknown glaze interactions – you can put any combination of glaze in a bowl or on a plate, but only a single glaze on the outside of any vertical surface! Glazes are a chemical reaction under heat. We don’t know the exact chemicals in the Mayco glazes we use. I can guess by the way they interact with each other, however, on the whole, you need to test every idea you have, and not run the test on a vertical surface! Simply put, glaze is a layer of glass like substance that bonds with the clay underneath. Clay is made of silica, alumina and water. Glaze is made of mostly silica. Silica has a melting point of 1700°C and we fire to 1240°C. The silica requires a “flux” to help it melt at the lower temperature. Fluxes can be all sorts of chemicals – a common one is calcium – calcium has a melting point of 2500°C, however, together they both melt at a much lower temperature! Colourants are metal oxides like cobalt (blue), chrome (green through black), copper (green, blue, even red!), manganese (black, purple and pink) iron (red brown), etc. Different chemicals in the glaze can have dramatic effects. for example, barium carbonate (which we don’t use) turns manganese bright pink! Other elements can turn manganese dioxide brown, blue, purple and reddish brown. Manganese dioxide is a flux in and of itself as well. So, glazes that get their black and purple colours, often interact with other glazes and RUN! Our mirror black is a good example – it mixes really well with many glazes because it fluxes them – causes them to melt faster. It will also bring out many beautiful colours in the glazes because it’s black colouring most definitely comes from manganese dioxide! Glaze chemistry is a whole subject on it’s own! We use commercial Mayco glazes on purpose – for their huge range of colour possibilities, stability, cool interactions, artistic freedom with the ability to easily brush the glazes on and ease of use. We currently have almost 50 glazes on hand! A major project is to test the interactions of all glazes with each other. That is 2,500 test tiles!!!! I’m going to make the wall behind the wheels the feature wall of pretty colours! Step Seven – Glaze (Gloss or sometimes called “Glost”) Firing Most of the time this is the final stage of making your creation (but not always!) The glaze kiln goes to 1240°C. This is called cone 6, or midrange. It is the low end of stoneware temperatures. Stoneware clays and glazes are typically fired at cone 8 – 10, that is 1260 – 1290°C. The energy requirement to go from 1240°C to 1280°C is almost a 30% more! Our clay is formulated to vitrify (mature, turn “glass-like”) at 1240°, as are our glazes. A glaze kiln take around 12 hours to reach temperature and two to three days to cool down. Sometimes a third firing process is required – this is for decoration that is added to work after the glaze firing. For example – adding precious metals and lustres. this firing temperature is usually around 600 – 800°C depending upon the techniques being used. There are many students interested in gold and silver trims – we will be doing this third type of firing soon! After firing your work will be in the student finished work shelves. Remember to pay for it before you head out the door! There is a small extra charge for using porcelain clay (it’s more than twice the price of regular clay), and for any third firing process! Once your work has been fired it can not turn back into clay for millennia – so don’t fire it if you don’t like it! Put it in the bucket for recycling. https://firebirdstudios.com.au/the-process-of-making-pottery/ The bowl is an example of kitchenware used in the 19th century and still in use today.Bowl white ceramic. Crack on side. Badly stained.Backstamp very faint and unable to be read.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, mixing bowl, food preparation, kitchen equipment, ceramic -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Bowl
The Process of Making Pottery Decorating, Firing, Glazing, Making, Technical There is a rhythm and flow to clay. It can’t be done all at once! Even the making process! It can take weeks to get everything done, especially if you can only work on your pottery once a week! Even though we have three hour classes, it’s often just not enough time! Here is an overview of some of the processes so you have a bit more grasp on some of the technical stuff! Step One – Design There are SO many ideas out there for making stuff in clay! From delicate porcelain jewellery, through to heavy sculptural work and everything in between. Deciding your direction is sometimes not that easy – when you first start, try everything, you will naturally gravitate to the style that you enjoy! The options and variations are endless and can get a wee bit overwhelming too! Check in with me before you start to ensure your ideas will work, what order you might do things, how you could achieve the look you are seeking and any other technical data required! Step Two – Making Clay is thixotropic. This means that as you work with it, the clay first gets sloppier and wetter, before is begins to dry in the atmosphere. For most things, you simply can’t do all parts of the project at once. An example of work order might look like: Get last weeks work out from the shelves Prepare clay for today’s work – roll your clay, prepare balls for throwing, make the first stage of a pinch pot) Clean up last week’s work and put it on the shelf for bisque firing Check that you have any glazing to do – and do enough of it that you will have time to finish your main project Do the next step of your next project – there might be a further step that can’t be complete immediately, in that case, wrap your work well and put onto the shelves. Letting your work rest for a while can really help keep your work clean and professional looking. Many things require bagging under plastic to keep it ready for work the next week – put your name on the outside of the bag so you can find your work easily. We have stickers and markers. Consider how you want to decorate your work – coloured slip can be applied at a fairly wet stage (remembering that it will make your work even wetter!). Trying to apply slip to dry clay won’t work! If you want to do sgraffito – you will need to keep the work leather hard (a state of dryness where you can still work the clay with a little effort and a little water and care). Step Three – Drying Most of the time your work can go into the rack uncovered to let it dry out for the following week. If you want to continue forming or shaping you will need to double bag your work – put your work on a suitable sized bat and put the bat in a bag so the base of the bag is under the bat, then put another bag over the top of the work and tuck the top of the bag under the bat. If you want to trim (or turn) your thrown work the following week, it should also be double bagged. If your work is large, delicate, or of uneven thicknesses, you should lightly cover your work for drying. When considering the drying process, bare in mind the weather, humidity and wind! The hotter and dryer, the faster things dry and work can dry unevenly in the shelves – this can lead to cracking – another time to lightly cover your work for drying. Step Four – Trimming and Cleaning Up Your work is dry! It is called greenware now and it is at it’s most fragile! Handle everything with two hands. I often refer to soft hands – keep everything gentle and with your fingers spread as much as possible. Try to not pick up things like plates too much, and always with both hands! Before your work can be bisque fired it should be “cleaned up”. You work won’t go into the kiln if it has sharp edges – when glazed, sharp edges turn into razor blades! Use a piece of fly wire to rub the work all over – this will scratch a little so be light handed. Use a knife or metal kidney to scrape any areas that require a bit more dynamic treatment than the fly wire offers! Finally, a very light wipe over with a slightly damp sponge can help soften and soothe all of your edges and dags! Trimming thrown work: If you are planning to trim (or turn) your thrown work (and you should be), make sure you bag it well – your work should be leather hard to almost dry for easiest trimming. Use this step to finish the work completely – use a metal kidney to polish the surface, or a slightly damp sponge to give a freshly thrown look. Wipe the sponge around the rim after trimming, and check the inside of the pot for dags! Trimming slip cast work: Usually I will trim the rims of your work on the wheel the following day to make that stage easier, however you will still need to check your work for lumps and bumps. Last but not least – check that your name is still clearly on the bottom of your work. Step Five – Bisque Firing When the work is completely dry it can go into the bisque kiln. The bisque kiln is fired to 1000°C. This process burns off the water in the clay as well as some of the chemically bound water. The structure of the clay is not altered that much at this temperature. Inside the bisque kiln, the work is stacked a little, small bowl inside a larger bowl and onto a heavy plate. Smaller items like decorations or drink coasters might get stacked several high. Consideration is paid to the weight of the stack and shape of the work. A bisque kiln can fire about one and a half times the amount of work that the glaze kiln can fire. The firing takes about 10 hours to complete the cycle and about two days to cool down. Once it has been emptied the work is placed in the glaze room ready for you to decorate! Step Six – Glazing Decorating your work with colour can be a lot of fun – and time consuming! There are three main options for surface treatment at this stage: Oxide Washes Underglazes Glazes Washes and underglazes do not “glaze” the work – It will still need a layer of glaze to fully seal the clay (washes don’t need glaze on surfaces not designed for food or liquid as they can gloss up a little on their own). Underglazes are stable colourants that turn out pretty much how they look in the jar. They can be mixed with each other to form other colours and can be used like water colours to paint onto your work. Mostly they should have a clear glaze on top to seal them. Oxides are a different species – the pink oxide (cobalt) wash turns out bright blue for instance. They don’t always need a glaze on top, and some glazes can change the colour of the wash! The glazes need no other “glaze” on top! Be careful of unknown glaze interactions – you can put any combination of glaze in a bowl or on a plate, but only a single glaze on the outside of any vertical surface! Glazes are a chemical reaction under heat. We don’t know the exact chemicals in the Mayco glazes we use. I can guess by the way they interact with each other, however, on the whole, you need to test every idea you have, and not run the test on a vertical surface! Simply put, glaze is a layer of glass like substance that bonds with the clay underneath. Clay is made of silica, alumina and water. Glaze is made of mostly silica. Silica has a melting point of 1700°C and we fire to 1240°C. The silica requires a “flux” to help it melt at the lower temperature. Fluxes can be all sorts of chemicals – a common one is calcium – calcium has a melting point of 2500°C, however, together they both melt at a much lower temperature! Colourants are metal oxides like cobalt (blue), chrome (green through black), copper (green, blue, even red!), manganese (black, purple and pink) iron (red brown), etc. Different chemicals in the glaze can have dramatic effects. for example, barium carbonate (which we don’t use) turns manganese bright pink! Other elements can turn manganese dioxide brown, blue, purple and reddish brown. Manganese dioxide is a flux in and of itself as well. So, glazes that get their black and purple colours, often interact with other glazes and RUN! Our mirror black is a good example – it mixes really well with many glazes because it fluxes them – causes them to melt faster. It will also bring out many beautiful colours in the glazes because it’s black colouring most definitely comes from manganese dioxide! Glaze chemistry is a whole subject on it’s own! We use commercial Mayco glazes on purpose – for their huge range of colour possibilities, stability, cool interactions, artistic freedom with the ability to easily brush the glazes on and ease of use. We currently have almost 50 glazes on hand! A major project is to test the interactions of all glazes with each other. That is 2,500 test tiles!!!! I’m going to make the wall behind the wheels the feature wall of pretty colours! Step Seven – Glaze (Gloss or sometimes called “Glost”) Firing Most of the time this is the final stage of making your creation (but not always!) The glaze kiln goes to 1240°C. This is called cone 6, or midrange. It is the low end of stoneware temperatures. Stoneware clays and glazes are typically fired at cone 8 – 10, that is 1260 – 1290°C. The energy requirement to go from 1240°C to 1280°C is almost a 30% more! Our clay is formulated to vitrify (mature, turn “glass-like”) at 1240°, as are our glazes. A glaze kiln take around 12 hours to reach temperature and two to three days to cool down. Sometimes a third firing process is required – this is for decoration that is added to work after the glaze firing. For example – adding precious metals and lustres. this firing temperature is usually around 600 – 800°C depending upon the techniques being used. There are many students interested in gold and silver trims – we will be doing this third type of firing soon! After firing your work will be in the student finished work shelves. Remember to pay for it before you head out the door! There is a small extra charge for using porcelain clay (it’s more than twice the price of regular clay), and for any third firing process! Once your work has been fired it can not turn back into clay for millennia – so don’t fire it if you don’t like it! Put it in the bucket for recycling. https://firebirdstudios.com.au/the-process-of-making-pottery/ This bowl is an example of kitchenware used in the 19th century and still in use today.Bowl white ceramic plain that has two sets of edging around lip. Inside bowl has plaster designed to look like cooking mixture.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, kitchen equipment, ceramic -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Bowl, J & G Meakin, Late 19th or early 20th Century
The Process of Making Pottery Decorating, Firing, Glazing, Making, Technical There is a rhythm and flow to clay. It can’t be done all at once! Even the making process! It can take weeks to get everything done, especially if you can only work on your pottery once a week! Even though we have three hour classes, it’s often just not enough time! Here is an overview of some of the processes so you have a bit more grasp on some of the technical stuff! Step One – Design There are SO many ideas out there for making stuff in clay! From delicate porcelain jewellery, through to heavy sculptural work and everything in between. Deciding your direction is sometimes not that easy – when you first start, try everything, you will naturally gravitate to the style that you enjoy! The options and variations are endless and can get a wee bit overwhelming too! Check in with me before you start to ensure your ideas will work, what order you might do things, how you could achieve the look you are seeking and any other technical data required! Step Two – Making Clay is thixotropic. This means that as you work with it, the clay first gets sloppier and wetter, before is begins to dry in the atmosphere. For most things, you simply can’t do all parts of the project at once. An example of work order might look like: Get last weeks work out from the shelves Prepare clay for today’s work – roll your clay, prepare balls for throwing, make the first stage of a pinch pot) Clean up last week’s work and put it on the shelf for bisque firing Check that you have any glazing to do – and do enough of it that you will have time to finish your main project Do the next step of your next project – there might be a further step that can’t be complete immediately, in that case, wrap your work well and put onto the shelves. Letting your work rest for a while can really help keep your work clean and professional looking. Many things require bagging under plastic to keep it ready for work the next week – put your name on the outside of the bag so you can find your work easily. We have stickers and markers. Consider how you want to decorate your work – coloured slip can be applied at a fairly wet stage (remembering that it will make your work even wetter!). Trying to apply slip to dry clay won’t work! If you want to do sgraffito – you will need to keep the work leather hard (a state of dryness where you can still work the clay with a little effort and a little water and care). Step Three – Drying Most of the time your work can go into the rack uncovered to let it dry out for the following week. If you want to continue forming or shaping you will need to double bag your work – put your work on a suitable sized bat and put the bat in a bag so the base of the bag is under the bat, then put another bag over the top of the work and tuck the top of the bag under the bat. If you want to trim (or turn) your thrown work the following week, it should also be double bagged. If your work is large, delicate, or of uneven thicknesses, you should lightly cover your work for drying. When considering the drying process, bare in mind the weather, humidity and wind! The hotter and dryer, the faster things dry and work can dry unevenly in the shelves – this can lead to cracking – another time to lightly cover your work for drying. Step Four – Trimming and Cleaning Up Your work is dry! It is called greenware now and it is at it’s most fragile! Handle everything with two hands. I often refer to soft hands – keep everything gentle and with your fingers spread as much as possible. Try to not pick up things like plates too much, and always with both hands! Before your work can be bisque fired it should be “cleaned up”. You work won’t go into the kiln if it has sharp edges – when glazed, sharp edges turn into razor blades! Use a piece of fly wire to rub the work all over – this will scratch a little so be light handed. Use a knife or metal kidney to scrape any areas that require a bit more dynamic treatment than the fly wire offers! Finally, a very light wipe over with a slightly damp sponge can help soften and soothe all of your edges and dags! Trimming thrown work: If you are planning to trim (or turn) your thrown work (and you should be), make sure you bag it well – your work should be leather hard to almost dry for easiest trimming. Use this step to finish the work completely – use a metal kidney to polish the surface, or a slightly damp sponge to give a freshly thrown look. Wipe the sponge around the rim after trimming, and check the inside of the pot for dags! Trimming slip cast work: Usually I will trim the rims of your work on the wheel the following day to make that stage easier, however you will still need to check your work for lumps and bumps. Last but not least – check that your name is still clearly on the bottom of your work. Step Five – Bisque Firing When the work is completely dry it can go into the bisque kiln. The bisque kiln is fired to 1000°C. This process burns off the water in the clay as well as some of the chemically bound water. The structure of the clay is not altered that much at this temperature. Inside the bisque kiln, the work is stacked a little, small bowl inside a larger bowl and onto a heavy plate. Smaller items like decorations or drink coasters might get stacked several high. Consideration is paid to the weight of the stack and shape of the work. A bisque kiln can fire about one and a half times the amount of work that the glaze kiln can fire. The firing takes about 10 hours to complete the cycle and about two days to cool down. Once it has been emptied the work is placed in the glaze room ready for you to decorate! Step Six – Glazing Decorating your work with colour can be a lot of fun – and time consuming! There are three main options for surface treatment at this stage: Oxide Washes Underglazes Glazes Washes and underglazes do not “glaze” the work – It will still need a layer of glaze to fully seal the clay (washes don’t need glaze on surfaces not designed for food or liquid as they can gloss up a little on their own). Underglazes are stable colourants that turn out pretty much how they look in the jar. They can be mixed with each other to form other colours and can be used like water colours to paint onto your work. Mostly they should have a clear glaze on top to seal them. Oxides are a different species – the pink oxide (cobalt) wash turns out bright blue for instance. They don’t always need a glaze on top, and some glazes can change the colour of the wash! The glazes need no other “glaze” on top! Be careful of unknown glaze interactions – you can put any combination of glaze in a bowl or on a plate, but only a single glaze on the outside of any vertical surface! Glazes are a chemical reaction under heat. We don’t know the exact chemicals in the Mayco glazes we use. I can guess by the way they interact with each other, however, on the whole, you need to test every idea you have, and not run the test on a vertical surface! Simply put, glaze is a layer of glass like substance that bonds with the clay underneath. Clay is made of silica, alumina and water. Glaze is made of mostly silica. Silica has a melting point of 1700°C and we fire to 1240°C. The silica requires a “flux” to help it melt at the lower temperature. Fluxes can be all sorts of chemicals – a common one is calcium – calcium has a melting point of 2500°C, however, together they both melt at a much lower temperature! Colourants are metal oxides like cobalt (blue), chrome (green through black), copper (green, blue, even red!), manganese (black, purple and pink) iron (red brown), etc. Different chemicals in the glaze can have dramatic effects. for example, barium carbonate (which we don’t use) turns manganese bright pink! Other elements can turn manganese dioxide brown, blue, purple and reddish brown. Manganese dioxide is a flux in and of itself as well. So, glazes that get their black and purple colours, often interact with other glazes and RUN! Our mirror black is a good example – it mixes really well with many glazes because it fluxes them – causes them to melt faster. It will also bring out many beautiful colours in the glazes because it’s black colouring most definitely comes from manganese dioxide! Glaze chemistry is a whole subject on it’s own! We use commercial Mayco glazes on purpose – for their huge range of colour possibilities, stability, cool interactions, artistic freedom with the ability to easily brush the glazes on and ease of use. We currently have almost 50 glazes on hand! A major project is to test the interactions of all glazes with each other. That is 2,500 test tiles!!!! I’m going to make the wall behind the wheels the feature wall of pretty colours! Step Seven – Glaze (Gloss or sometimes called “Glost”) Firing Most of the time this is the final stage of making your creation (but not always!) The glaze kiln goes to 1240°C. This is called cone 6, or midrange. It is the low end of stoneware temperatures. Stoneware clays and glazes are typically fired at cone 8 – 10, that is 1260 – 1290°C. The energy requirement to go from 1240°C to 1280°C is almost a 30% more! Our clay is formulated to vitrify (mature, turn “glass-like”) at 1240°, as are our glazes. A glaze kiln take around 12 hours to reach temperature and two to three days to cool down. Sometimes a third firing process is required – this is for decoration that is added to work after the glaze firing. For example – adding precious metals and lustres. this firing temperature is usually around 600 – 800°C depending upon the techniques being used. There are many students interested in gold and silver trims – we will be doing this third type of firing soon! After firing your work will be in the student finished work shelves. Remember to pay for it before you head out the door! There is a small extra charge for using porcelain clay (it’s more than twice the price of regular clay), and for any third firing process! Once your work has been fired it can not turn back into clay for millennia – so don’t fire it if you don’t like it! Put it in the bucket for recycling. https://firebirdstudios.com.au/the-process-of-making-pottery/This bowl was made by renowned pottery company J & G Meakin of England. The firm was established in the mid-1800's. The bowl is an example of kitchenware used in the 19th century and still in use today.Bowl; white ceramic, round and tapering inwards towards base. Made by J and G Meakin England.On base, 'Ironstone China Reg SOL 391413' with symbolflagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, mixing bowl, food preparation, j & g meakin, pottery, stoke-on-trent, kitchen equipment, ceramic -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Colander, Late 19th or early 20th Century
The colander is an extremely useful tool in the kitchen, as it allows food to be fully drained of liquids such as water or oil. Enamelware dates back to 1760 in Germany.This object is significant as an example of a type of item in common use in the 19th Century and that is still in use today.Mottled blue enamel colander with draining holes in the base and sides. Two thin handles on lip of bowl.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, enamel, colander, food preparation -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Water Canteen and Ladle, mid-to-late 19th century
... Water canteen and ladle; blue painted oval metal cylinder... canteen and ladle water canteen Water canteen and ladle; blue ...The horizontal water canteen has been carefully designed to fit snugly on the hip when worn with the straps diagonally across the body. The ladle allows quick and easy scooping of the contents to refresh the lifeboat and rocket launching crew, and the survivors of the disaster Saving lives in Warrnambool – The coastline of South West Victoria is the site of over 600 shipwrecks and many lost lives; even in Warrnambool’s Lady Bay there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905, with eight lives lost. Victoria’s Government responded to the need for lifesaving equipment and, in 1858, the provision of rocket and mortar apparatus was approved for the lifeboat stations. In 1859 the first Government-built lifeboat arrived at Warrnambool Harbour and a shed was soon built for it on the Tramway Jetty, followed by a rocket house in 1864 to safely store the rocket rescue equipment. In 1878 the buildings were moved to the Breakwater (constructed from 1874-1890), and in 1910 the new Lifeboat Warrnambool arrived with its ‘self-righting’ design. For almost a hundred years the lifesaving and rescue crews, mostly local volunteers, trained regularly to rehearse and maintain their rescue skills. They were summoned when needed by alarms, gunshots, ringing bells and foghorns. In July 1873 a brass bell was erected at Flagstaff Hill specifically to call the rescue crew upon news of a shipwreck. Some crew members became local heroes but all served an important role. Rocket apparatus was used as recently as the 1950s. Rocket Rescue Method - The Government of Victoria adopted lifesaving methods based on Her Majesty’s Coast Guard in Great Britain. It authorised the first line-throwing rescue system in 1858. Captain Manby’s mortar powered a projectile connected to a rope, invented in 1808. The equipment was updated to John Dennett’s 8-foot shaft and rocket method that had a longer range of about 250 yards. From the 1860s the breeches buoy apparatus was in use. The apparatus was suspended on a hawser line and manually pulled to and from the distressed vessel carrying passengers and items. In the early 1870s Colonel Boxer’s rocket carried the light line, which was faked, or coiled, in a particular way between pegs in a faking box to prevent twists and tangles when fired. The angle of firing the rocket to the vessel in distress was measured by a quadrant-type instrument on the side of the rocket machine. Decades later, in about 1920, Schermuly invented the line-throwing pistol that used a small cartridge to fire the rocket. The British Board of Trade published instructions for both the beach rescue crew and ship’s crew. It involved setting up the rocket launcher on shore at a particular angle measured by the quadrant, inserting a rocket that had a lightweight line threaded through its shaft, and then firing it across the stranded vessel, the line issuing freely from the faking board. A tally board was then sent out to the ship with instructions in four languages. The ship’s crew would haul on the line to bring out the heavier, continuous whip line, then secure the attached whip block to the mast or other sturdy part of the ship. The rescue crew on shore then hauled out a stronger hawser line, which the ship’s crew fixed above the whip block. The hawser was then tightened using the block on the shore end of the whip. The breeches buoy and endless whip are then attached to the traveller block on the hawser, allowing the shore crew to haul the breeches buoy to and from the vessel, rescuing the stranded crew one at a time. Beach apparatus equipment - In the mid-1800s the equipment could include a line throwing set, coiled line in wooden carrying case, rockets, cartridges, breeches buoy, hawser and traveller block, line-throwing pistol, beach cart, hand barrow, sand anchor, crotch pole, and tools such as spade, pick, mallet and hawser cutter. Around the 1860s Warrnambool had a Rocket House installed beside the Harbour. This water canteen is significant for its connection with local history, maritime history and marine technology. Lifesaving has been an important part of the services performed from Warrnambool's very early days, supported by State and Local Government, and based on the methods and experience of Great Britain. Hundreds of shipwrecks along the coast are evidence of the rough weather and rugged coastline. Ordinary citizens, the Harbour employees, and the volunteer boat and rescue crew, saved lives in adverse circumstances. Some were recognised as heroes, others went unrecognised. In Lady Bay, Warrnambool, there were around 16 known shipwrecks between 1850 and 1905. Many lives were saved but tragically, eight lives were lost.Water canteen and ladle; blue painted oval metal cylinder with a removable round threaded lid. Two adjustable leather shoulder straps are attached to the canteen through metal rings on the sides of the lid. A blue-painted copper ladle with a fixed, 45-degree angled handle is attached to the canteen with a length of string. The water canteen is designed to be carried horizontally.flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, warrnambool, great ocean road, lady bay, shipwreck, life-saving, lifesaving, rescue crew, rescue, rocket rescue, rocket crew, lifeboat men, beach rescue, line rescue, rescue equipment, volunteer lifesavers, volunteer crew, life saving rescue crew, lifesaving rescue crew, rocket apparatus, survival canteen, rescue canteen, dipper, cup, canteen and dipper, canteen and ladle, water canteen -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument, Zelda Martin, Central Victorian Goldmining towns - Boom Towns or Ghost Towns?, c1996
Zelda Martin was a PhD candidate at the University of Melbourne.[.1] 4th item in light blue display book titled Research Approach/Overview of Chapters/Confirmation of Canditure/Chapters1,2,3&4 of proposed thesis. *Twenty-seven page article on Victorian goldfields towns titled: Central Victorian Goldmining Towns - Boom Towns or Ghost Towns. The article was written during the author's PhD study. It outlines the context methodology, and resources and the chapters of the proposed thesis: (1) Central Victorian Goldmining Towns - The Context (2) Contemporary Views of the Factors Necessary for Town Growth (3) Outward Manifestations of Town Growth (4) The Trappings of Government (5-9) The Main Towns and Their Hinterland. [.2] 5th item in Light Blue display book as above item. *Chapter 1 of proposed thesis titled 'Pick, Shovel and Tin Dish Mining.' Covers in Section A: Central Victoria - Pre 1851: Aborigines in Central Victoria, Squatters, and Government. Section B: The years 1851-1854: The Early Gold Rushes, Government Reaction, Township Surveys, Legislation, Town Development, Local Government and Early Settlement. [.3] 6th item in Light Blue display book as above item. *2A of proposed thesis titled 'Contemporary Views of the Factors Necessary for Town Growth'. Similar information to Chapter 1 plus extra re towns and maps. Sections: Introduction, Context of Place - Geographical Towns Listed, The Context of Time - Pre1851 Aborigines, Governance of Port Phillip, The Squatters, The Villages of Central Victorian Highlands, Conclusion, Condensed Version of Chapter2B. [.4] 7th item in Light Blue display book as above item. *Chapter2B of proposed thesis. Sections: Area of Research, Schools, Banks, Newspapers, Progress Association, Town Development - Sandhurst (Bendigo), Ballarat, Castlemaine,, Maryborough, Ararat and Stawell. [.5] 8th item in Light Blue display book as above item. *Chapter 3 of proposed thesis titled 'Outward Manifestations of Town Growth'. Sections: Introduction, Contemporary Writing, Educationalists, The Bankers, The Townsfolk, Current Theory, General Theories of Urban Development, and Conclusion. [.6] 9th item in Light Blue display book as above item. *Chapter 4 of proposed thesis titled 'Trappings of Government' Sections: Introduction, Early Government Attitudes to Mining and Town Development, Law and Order, Township Surveys, Legislation, Local Government, Transport and Communication, The People and Lobbyists. [.7] 10th item in Light Blue display book as above item. *'The Rise and Fall of Central Victorian Goldmining Towns'. Includes a map showing main Goldfields, a table showing towns and villages at two points in time - 1857 and 1871; a Bibliography of Primary and Secondary Sources. [.8] Resource No1. Black display book titled Local Towns 1 : Alma: *Brief history *Directory *Maps Amphitheatre / Mountain Hut: *Brief History Post Office Directory Ararat: *Brief History *Post Office Directory 1869 - Alphabetical Listing by Occupation *Ararat - Prominent Citizens of 1858 *Langi-Morgala Museum Avoca: *Brief History *Excerpts from 'Avoca The Early Years', Margery and Betty Beavis; pg1 - Beginnings; pg11 - The Midas Touch; pg25 - Local Gold Escorts; pg27 - A Town is Born; pg51- The Administration of Justice; pg53 - The Ways of the Law; pg61 - News of the Day; pg65 - A Time to Play; pg72 - Land Ownership *Post Office Directory (Bailliere's) 1869 *Tourism Map and Information of area *Historic Avoca - A 5.5km Tour *Avoca & the Pyrenees Region - information pamphlet Ballarat: *Early History of Ballarat - Ballarat Historical Society, Publication No.1: origin of the name; Ballaarat - the Beginning; Fabulous Yields from the Ballaarat Goldfield; *Streetscape Lydiard Street. *Hand drawn map showing Leigh River, Old Portland Bay Road, plaque on road to Colac; etc. *Newspaper article re 'The Theatre Royal' ( which stood in the vicinity of the current Owen Williams store) - 'The News'15/04/1998 *Article - 'Ballarat's Mechanics' Institute Lives On' Ballarat Courier, 14/09/1985 *Article - Standing the Test of Time' The News 17/11/1993 re The Mechanics Institute & picture of the Reading Room *'Ballarat a Study of a City, Phyllis Reichl, pub. Nelson, 1968; no.3 place, time and people field studies series *Investigator Vol.33 No.2, 1998 Geelong Historical Society. Article on pg75 describes Ballarat in 1861 *Folded poster - 'Ballarat 100' a history of telegraph communication, pub. Telecom. Beaufort (Fiery Creek): *Brief history *Post Office Directory [.9] Resource No.2 Black Folder Titled Towns cont.No2 Bendigo (Sandhurst): *'Family & Local History at the Bendigo Library - 1851-2001 150 years of gold'. *Bendigo Government Camp in 1853 illustration; key to sketch and names of Government officers stationed there *Excerpts from 'Bendigo and Vicinity' Adolph Haman *The Bendigo Goldfield Registry - pgs 1-7 Introduction *Excerpt: 'Breaking the Grip' *Excerpt: The Most Go-Ahead Place *Excerpts from 'History of Bendigo' - anti license agitation; laying out of town; proposed railway; gold calls and dividends; the Sandhurst Municipality; journalism *Bibliography Blackwood: *Excerpts from 'Aspects of Early Blackwood - The Goldfield, the Landmarks, the Pioneers' Alan J Buckingham and Margaret F Hitchcock, JG Publishing,1980 Buninyong: *A Brief History *Investigator Vol1 No.2 Feb 1966 Geelong Historical Society. Pg3 - Article re gold escort route - Mt Alexander to Adelaide - (see a simple monument on the Western Highway a few miles out of Horsham. Pg 15 - Ballarat Excursion - re the finding of gold. *Three articles published by Buninyong and District Historical Society Inc: (Magpie Exploration; Finding Gold In The Green Hills; Magpie Exploration; Burnt Bridge to Cargarie to Mt Mercer) *Copies of newspaper articles/items *Buninyong Street Directory Carisbrook: *In the Beginning There Was Carisbrook *The History of the Carisbrook Racecourse Carngham / Snake Valley: *Brief History *Directory Castlemaine: *Directory 1865-1866 - Alphabetical and Street *Poster - Castlemaine A Contemporary Guide "The Great Centre" 1866 - A Contemporary Guide to the Fascinating Past *Pamphlet - Castlemaine District Community Hospital *Map - Castlemaine, Maldon & Surrounding Districts *Map and Information - The Dry Diggings Track - a 55kl walk among historic goldfields relics ( Castlemaine Fryerstown Vaughan Mt Franklin Hepburn Daylesford) *Postcard - Former Court House *Directory 1867 - Alphabetical, Trade [.10] Resource No.3 Grey folder Titled Towns 3 Creswick to Maryborough Creswick: *Brief History *Booklet - "Creswick Cemetery Walk" *Booklet - The Buried Rivers of Gold Heritage Trail Creswick *Creswick Historical Museum Information Sheet *Chronological History of Creswick *Alphabetical Directory of the Borough of Creswick *Creswick's Creek Directory 1856 *Historic Creswick Walking Tour *A Brief Account of the Schools of Creswick - Past and Present *100 Years of Railway Travel in Creswick *The Berry Deep Leads *The Spence Home at Jackass Gully in the Creswick State Forest ( William Guthrie Spence - Pioneer) *The New Australian Mine and the 1882 Disaster *Creswick District News, Issue 7, July August 1999 *The Creswick Miners Walk - Information and Map *Maps Chewton: *Brief History *Directory Clunes: *Brief History *Clunes Street Directory Daylesford: *Brief History *Notable Bushfires in Daylesford District Over More Than a Century - "Black Thursday" 1851; 1862; 1899; the Disastrous Hepburn Fire of 1906; 1939; 1944; 1969. *Post Office Directory -Daylesford and Hepburn Dunolly / Inkerman: *Brief History *Directory *Pamphlet - Goldfields Historical Museum *Pamphlet - Historic Dunolly - Victoria's Best Kept Secret *Map of Gold Workings at Dunolly Area - showing where the main gold rushes occurred *Brief History - Inglewood *Directory - Inglewood - Name Occupation, Dwelling Kingower: *Brief History *Directory - Name / Ocupation / Dwelling Linton / Happy Valley / Piggoreet: *Brief History *Directory - Lintons McIvor: *"A History of the Shire and the Township of Heathcote" by J.O. Randell Majorca: *Brief History *Official Post Office Directory 1869 - Name / Occupation/ Address Maldon (Tarrangower): *Brief History Part 1 *Brief History Part 2 *Post Office Directory *List - Alphabetical Order by Names plus Business and Trade (Tarrangower Times Oct/1858) *List - Alphabetical Order by Trade plus Name and Business *Directory - Name / Occupation / Dwelling Maryborough: *Worsley Cottage - built by Arthur Worsley, a contractor in stonework in 1894 [.11] Resource No. 4 Blue Display Book titled Towns 4 Moliagul to Stawell Moliagul: *Brief History *Moligul Legislative Assembly (Voting?) List - Names and Occupations *Moliagul Victorian Post Office Directory 1868 - Name / Ocupation / Address / Comments *"The Welcome Stranger" gold nugget *The Sunday School *The Welcome Stranger Discovery Walk - information and map Moonambel (Mountain Creek) Redbank *Brief History *List of names extracted from advertisments of the Pioneer and Mountain Creek Advertiser 16/02/1861. *Bailliere's Directory 1869 - Alphabetical List of Name / Occupation / Place St Arnaud: *Brief History Sebastapol: *Brief History *Directory 1869 - Alphabetical by Name; plus occupation and address. Browns and Scarsdale: *Brief History *Browns Street Directory - Name and Occupation Smythesdale: *Brief Description *Smythesdale Street Directory -Name and Occupation Stawell (Pleasant Creek) *Brief History *Victorian Official Post Office Directory - Name /Occupation / Dwelling *Chronology - 1841-1920 *Production of gold statistics - 1879 - 1900 *Big Hill *Extracts from "The Golden Years of Stawell". Chapt 1 - Stawell's Coming Out. Capt. 2 - The Gold Rush. Caapt.3 - Cradle of Democracy. Chapt.4 - The Reefs Becomes Stawell. Chapt. 5 - Rushing In. Chapt.6 - The Pioneers. Chapt 7 - The Decade of Optimism. [.12] Resource No. 5: Blue Display Book titled 'Towns Steiglitz to the The Golden Triangle. Steiglitz: Brief History Victorian Post Office Directory 1869 *Map of Steiglitz *List of maps relevant to Steiglitz history *Information 6 tables of data from "Reports of Mining Surveyors Talbot (Back Creek) Brief History Taradale: Post office Directory 1869 - Name/Occupation/Street. Also list in alphabetical order by Occupation Taradale *Chronological Reference to Taradale Mines *Water - The Coliban System of Waterworks *Joseph Brady *The Syphon Tarnagulla (Sandy Creek) *Brief History *Tarnagulla Businessmen Cameos to give depth to advertisments in 'The Tarnagulla Courier' various issues 1864-1871 *Directory - Name/Occupation /Address *List - Name/Business/Trade Wedderburn (Koorong) *Brief History *List - Name/Occupation The Golden Triangle: *The Early Rushes - Wedderburn / Moliagul / Sandy Creek - Tarnagulla / Jones Creek - Waanyarra / Kingower / Dunolly - Goldsborough / Inglweood *Census of 1857 - Population / Occupations *1858-1871 - A Time of Consolidation- Wedderburn / Moliagul / Sandy Creek- Tarnagulla / Arnold *Census 1871 - Population *Information gleaned from the census data - Demographics / Population / Occupations / marital / Birthplace / Religion / Literacy/ Occupation and Housing Cameos *Graphs - Birthplace of settlers /Male-Female Ratio / Married males / Children under 15 as Percentage of Population / Religion *Census 1857 - Statistical data *Maps *Bibliography [.13] Resource No. 6 - Black Display Book Information and Research in Central Victoria including: *Banking - Research from ANZ Bank Archives *Institutions - also includes articles listed from the Ballarat Times Newspaper *Australian mining History Association - A.M.H.A. Bibliography *Australia's Mining History * Bibliography - Land Surveys Victoria - *1853 Administration (Statistics and Other) includes: schools / ministers of religion / police / military / local administration / licences for sale of spirits / distances between various Victorian gold fields. * Victoria Government Gazette (Copy) - N0. 116, 12/12/1854 includes: Gold Felds Commission of Enquiry & No. 85, 15/09/1854 - Addresses presented to the Lieutenant Governor (Sir Charles Hotham) during his tour through the Gold Fields of Victoria,1854. Addresses on behalf of : the people of Bendigo; Members of the Church of England, Bendigo; Members of the Wesleyan Church on the Bendigo Gold Fields; Bendigo Gold District General Hospital; the Bendigo Prospecting Association; Committee of the Bendigo Local Exhibition; Bendigo District Medical Association; Coloured Americans Resident at Bendigo; German Inhabitants of Bendigo; Landowners, Inhabitants, and Miners of Castlemaine; Inhabitants of Forest Creek; Inhabitants of Heathcote and Gold Miners of McIvor; Residents and landholders of the District of Bacchus Marsh; Inhabitants of Kilmore and Vicinity. *Gold Fields Correspondence 1853: letter from Lieutenant Colonel Valiant, (Officer commanding the Troops in Victoria) to the Lieutenant Governor re threatened disturbance at Sandhurst (Bendigo) regarding the Gold License Fee. * Extracts from a book "Victoria" re Gold Fields Commission of Enquiry involving mainly Ballarat and Castlemaine and a chapter titled 'A Tour to the Victorian Gold-Fields' *Lists of central Victorian newspapers - listed by date published 1851to 1874; by first date available to State Library. *A list of cities and towns showing County, population in 1861 &1871, and municipal status. [.14] Resource no.7. Black display book. *Reference: Papers presented to Parliament Victoria - 1859-1860 4 volumes - relevant sections copied. Contains information on Branches of Government. General / Finance / Gold / Gazette / Commission and Warrant / Statistic. *Gold Fields Act. In accordance with the Act the gold fields are divided into six districts - Ballaarat, Castlemaine , Sandhurst, Avoca, Ararat, and Beechworth.. Official staff in each gold district consists of a Resident Warden, Wardens, Wardens' Clerks, Bailiffs, Chinese Protectors, Chinese Interpreters, and Mining Surveyors. *Gold Receiver *Gaols *Police magistrates and Clerks of Petty Sessions, etc. *Field Branch *Immigration and Emigration Overland - Chinese - 1859 *Population on the Goldfields *The Geological Survey - The Government Geologist is assisited by staff from four branches - the office Branch; the Publishing Branch; the Field Branch and the Museum Branch. *Commission to Enquire Into Sludge dated 10/02/1859 (Some sections copied) - Report to the Honorable Chief Commissioner of Public Works, Melbourne re the mode of carrying the sludge from the puddling mills in Sandhurst without interfering with the drainage of the town and the roads in the neighbourhood. [.15] Resource No.8: Camel display book titled Resource No. 8. Aborigines *Lists of book titles - +"Readings in Victorian prehistory" +"The Aborigines of Port Phillip" +Aboriginal languages and clans" +"A History of the Port Phillip District" +"Langi Ghiran 1: Aboriginal Rock...." +"Koorie History: sources for aboriginal studies in the State Library of Victoria", ed. Tom Griffiths, Melb. Friends of the State Library, 1989 +"The Public Lands of Australia Felix"; settlement and land appraisal in Victoria1834-91 with special reference to the Western Plains", J.M.Powell, Melb. Oxford University Press 1970 +*Bibliography of the Victorian Aborigines' from the earliest manuscripts to 31st December 1970, Massoa, Aldo, Melb. Hawthorn Press, 1971 +"Aborigines in Colonial Victoria, 1836-1886", M.F. Christie, Sydney University Press, 1979 +"Urban and Industrial Australia: readings in Human Geography" ed J.M. Powell, Melb. Sorrett Pub. 1974 *Extracts: -Processes of Pioneer Settlement - The Squatting Occupation of Victoria, 1834-60. J.M. Powell -Areal Variations in the Class Structure of the Central-Place Hierarchy. P. Scott - Volume1 and Volume 2: Notes Relating to the Habits of the Natives of Other Parts of Australia and Tasmania. Compiled from various sources for the Government of Victoria by R Brough Smyth. John Curry, O'Neil, Melb. 1st pub. Melb. 1876. p31-45 - Numbers and Distribution of the Aborigines in Victoria -Victorian Aborigines 1835-1901 - A Resource Guide to the Holdings of the Public Record Office, Victoria; published by the Government Information Centre 1984. *History of the Aboriginal Artefacts Displayed in the Daylesford Museum. F. G. Powell (4 page pamphlet) *Letter to Zelda Martin from Peter Lovett, Cultural Officer, Ballarat & District Aboriginal Co- Operative, 05/02/1997 *Map: Ian Clarke Victorian Tribunal Boundary Map - Clans of Central Victoria. *Victorian Rock Art and Mythology - Article about Mount Langhi Ghiran and myths of the Tjapwarong people. *Two Aboriginal myths relating to the Grampians - 'The Monster Emu' / 'The Aquisition of Fire', by the Aborigines in the Grampians Areas *Article titled (chapter 8) Ballarat - information re camping sites in the region. Lake Wendouree / Lake Burrumbeet (includes a myth) / Mt Bunninyong / Lal Lal / Pitfield / Mount Elephant / Mount Egerton / Meredith / Lake Goldsmith / Lake Learmonth / Ercildoune *Notes on the Aborigines of the Wider Ballarat Region plus European names=Aboriginal names. John Morris 26/07/1995 *Role of Aborigines in Town Development in Central Victoria. Mentions Native Police Force est. in Port Phillip 1842 and Central Board for Aborigines est. 1860 *The Grave of King Billy. (Frank Wilson) Pamphlet. *Camping Places in Central and Northern Victoria. Article re Lake Burrumbeet site. *Programme for the Unveiling of Memorial Cairn for Edward Stone Parker 1802-1865. Note portrait not accurate. Accurate portrait is available in the book "A Successful Failure A Trilogy The Aborigines and Early Settlers", Edgar Morrison, Graffiti Publications, 2002. * Large envelope addressed to Mr G Netherway containing newspaper cuttings regarding the life of Edward Stone Parker, the unveiling of the Memorial Cairn as mentioned above, articles titled 'Episodes from Our Early Days' (Edgar Morrison, Yandoit)- The Black's School, A School At Last and The Final years. Also a typed page titled 'Historical Background to E.S.Parker's Career. Includes an interesting tale titled 'When the cat lay doggo' re laying power leads for the unveiling ceremony at the memorial site. [.16] green display folder titled 'Research Aids' *List of references to Commissioners' & W'ardens' Reports (formerly held at La Trobe Library Archives, now at Public Records Office [PRO]). Indicates town referred to / date of report / name of camp if different to town. * Archive information re Anglican Records *Movement around the Goldfields - Miners and Storekeepers - usefulness of newspapers in providing information - areas covered - Castlemaine, Maldon, Ararat, Stawell, Tarnagulla, Dunolly. *Port Phillip /Victoria Directories 1839/1867 - Chronological list of Directories included in this series. *"Notes on the History of Local Government in Victoria" A.W. Greig Melb. University Press 1925 - Photo-copied extract p5-p40. (Source - Deakin University Library) - Introduction by W.Harrison Moore. Section 1 - Development in New South Wales Before Separation. Section 2 - Development in Victoria After Its Separation from New South Wales. Hand written notations: 'roads, markets, and local government 1855 on' ;'opportunity of squatters in parliament' and 'opportunities of matters in parliament p33' * Notes on the Establishment of Surveyor General's Department 1851and Commissioner of Crown Lands and Survey. * Newspaper articles from The Argus, 1849, re the discovery of gold in the Pyrenees region. * Excerpt - a report on schools - A.B.Orlebar, Inspector; re the need for permanent school buildings rather than tents. *Excerpt from - 'Approaches to Urban History', Sean Glynn: The Case for Caution * Except from - 'The Urban Sprinkle', Weston Bate: Country Towns and Australian Regional History *Reference- 'The History of Land Tenure in the Colony of Victoria', John Quick. References the Haines Land Bill, land tenure and Land Leagues. [.17] Light blue envelope folder titled 'Birtchnell's Ballarat, etc. Directory 1862 *Contains various directories for Smythesdale, Buninyong, Clunes, Brown's and Creswick. [.18] Red envelope folder no.2 titled Victorian Gazetteer *Selected pages from 1869 Victorian Gazetteer on A4 paper (with a handwritten note questioning if some pages are from 1868 Victorian Gazetteer as appears to be different sizes - A3 pages.) Information includes locations and descriptions of towns, hotels, banks, communications and populations. (Does not include names, residences and occupations) [.19] Red Envelope folder titled Bailliere's Official Post Office Directory 1868 (or1869 or a mixture of both?) *Preface *Contains a selection of pages of towns highlighted in yellow in the the index *Work on this directory was commenced in 1867. *Information includes: Municipalities - mayors and councilors; lists of towns naming male inhabitants and their occupations. [.20]Yellow manila folder titled Post Grad Seminar Presentation 1996 *Gives some background to Zelda Martin's proposed thesis and why she chose the topic Gold Mining Towns Boom or Bust [.21] A3 display book - No. 1A * A list of 'Relevant Newspapers collected: The Tarrangower Times and Maldon Advertiser (first published 1858) Includes dates 1858-1867. The Mount Alexander Mail. Includes dates 1854-1866 The Tarnagulla Courier. Includes dates from1864-1871 Dunolly and Burnt Creek Express. Includes dates from 1862-1871 * Selection of newspaper pages from The Mount Alexander Mail 1854 to 1856, mostly showing advertisements for businesses and services provided to that community. [.22] A3 display book - No. 1B * Selection of newspaper pages from The Mount Alexander Mail 1857 to 1866, mostly showing advertisements for businesses and services provided to that community. [.23] A3 display book -No. 2 * Selection of newspaper pages from The Tarnagulla Courier 1864 to 1871, mostly showing advertisements for businesses and services provided to that community. [.24] A3 display book - No. 3 *Selection of newspaper pages from The Tarrangower Times (and Maldon and Newstead) Advertiser 1858 to1867, mostly showing advertisements for businesses and services provided to that community. [.25] A3 display book - No.4 * Selection of newspaper pages from The Dunolly and Burnt Creek Express; and The Dunolly and Betbetshire Express 1862 to 1871, mostly showing advertisements for businesses and services provided for that community. [.26] A3 display book - No.5 Includes: * Bryce Ross's Diggings Directory. Includes instructions for using this directory. This directory was used by "all persons having connexion or desiring to communicate with 'working parties, private friends, or Stores at the Diggings." As a directory for each area wwas completed it was published in each month's issue of Bonwick's "Digger's Magazine." Years c1852/1853. This Directory commences first at the head of Forest Creek. Includes a directory for Bendigo and Ballarat. Of interest at the end of the Bendigo and Ballarat directory is a list of the number of storekeepers, butchers, doctors, smiths, eating houses, lemonade sellers and chapels. * The Castlemaine Directory and Book of General Information Comprehending Glass's Model Calendar for the Two Years 1862 and1863. "zelda martin, victorian goldfield towns, bendigo, castlemaine, ballarat, maldon, stawell, ararat, maryborough, creswick, avoca, heathcote, banks, bank of australasia, union bank of australia, government camp, sandhurst, water supply, tarnagulla, talbot, back creek, mountain creek, police court, carisbrook, dunolly, thompson's foundry, charles clacy, anthony trollope, robert cecil, mount alexander, urbanisation, national schools, education, govenrment, industry, railway, transport, settlement, land settlement in central victoria, steiglitz, joseph brady, the new australian mine, berry deep leads, william guthrie spence, creswick state forest, arthur worsley, worsley cottage, the welcome stranger, moliagul, moonambel, redbank, st arnaud, sebastapol, brown's, scarsdale, clunes, chewton, daylesford, bushfires, inkerman, inglewood, kingower, lintons, happy valley, piggoreet, mcivor, majorca, tarrangower, taradale, the coliban system, the syphon, sandy creek, wedderburn, koorong, arnold, jones creek, waanyarra, the golden triangle, census 1857, blackwood, buninyong, durham lead, magpie, carngham, snake valley, alma, amherst, daisy hill, amphitheatre, mountain hut, beaufort, fiery creek, counties, population, gold fields commission of enquiry1854, william westgarth, gold license fee, lieutenant colonel valiant, administration of the victorian gold fields, commission to enquire into sludge 1859, e.s. parker, edward stone parker, edgar morrison, mount franklin protectorate, dja dja wurrung, memorial cairn, franklinford, mt franklin memorial cairn, jajowurrong, dja dja wurung, tjaowarong, wothowurong, assistant protectors, daylesford museum, buluk, rock art - grampians, aboriginal mythology - grampians, aborigines, first nations people, mount franklin, aboriginal artifacts, lake burrumbeet, native police force, central board of aborigines, yandoit, commissioners' reports, wardens' reports, port phillip/victoria directories 1839-1867, local government - victoria 1853/1854, surveyor general's department - 1850's, victorian schools 1850's, a.b.orlebar, haines land bill, william charles haines, wilson gray, land tenure, land leagues, victorian gazetteer, the tarrangower times and maldon advertiser - 1858-1867, the mount alexander mail 1854-1866, the tarnagulla courier 1864, dunolly and burnt creek express 1862-1871, bryce rose's diggings directory, the castlemaine directory 1862-1863 -
 Blacksmith's Cottage and Forge
Blacksmith's Cottage and ForgeInk-well, ceramic insert, steel-nib pen
This ink-well was used in the Bacchus Marsh Court House, possibly for book-keeping and/or for court records. This type of ink-well and pen were in use everywhere in schools, businesses, courts, etc before the invention of the type-writer and the ball-point pen. Clerks were usually male and a good copperplate hand-writing was admired. Ink was often mixed by hand used a powdered ink mixed with water.Of local significance in the history of the town of Bacchus Marsh.Round pewter ink-well, with hinged lid and ceramic insert. Five round holes pierced in inner rim of metal to hold pens. Two ribbed bands around exterior of pot. Two bands indented around top of lid. Insert designed to hold ink. Pen with marbled blue handle, metal nib holder and metal nib.Indecipherable imprint on bottom of pot, possibly machine markings. Illegible written marks on side of pewter pot. Ceramic insert marked on side and bottom by red and black ink.ink, ink well, hand writing, record keeping, pens, nibs, clerical work, court records -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, McGraw-Hill Book Company, Hydraulics: A Text on Practical Fluid Mechanics, 1937
The book was used by Charles Bacon who studied at the University of Nevada in the late 1930s/early 1940s. Bacon worked at Bunker Hill Mines and Kellogg Idaho, before arriving in Australian in 1951. He worked for CN Myers, a company involved with paper converting. CN Myers was a family business (on Charles Bacon's maternal line).Blue hard-covered book of 460 pages. Chapters include Properties of Fluids, intensity of Pressure, Hydrostatic Pressure of Areas, Dams, Kinematics of fluid Flow, Dynamics of Fluid Flow, Applications of Hydrokinetics, Friction Losses in Pipes, Flow Through Pipes, Uniform Flow in Open Channels. Nonuniform Flow in Open Channels, Unsteady Flow, Dynamic Forces, Description of the Impulse Wheel, Theory of the Impulse Wheel, water Power Plants, centrifugal Pump and more.Inside Front Cover "Charles Bacon, Mackay school of Mines Reno, Nevada."charles bacon, mining engineering, metallurgy, university of nevada, mackay school of mines -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Hydraulic and Placer Mining, 1898, 1905
Blue/black hard covered book of 234 pages including index and photographic reproductions. Contents include Uses of Water in Mining; Geology of Placer Deposits; Gold Recovery; Flumes, ditches, dams, pipes; Giants, valaves, gates, weirs, miner's inch, pressure box, dams; gravel elvators; exploiting. mining, hydraulics, water, dredge, dredging, gold mining -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklets, Ballarat Historical Society, Spievogel Papers, volumes 1,2, & 3
Nathan Spielvogel was a local historian. The Spielvogel Papers consist of the articles he prepared for a series of weekly talks on Radio 3BA in 1936 and 1937. According to Alex Barnett there is a reference in the Spielvogel Papers to the moving of the bodies of diggers killed at the Eureka Stockade to the old cemetery on 26 November 1857.3 soft covered books with text relating to the history of Ballarat. .1) yellow cover .2) blue cover .3) green cover .1) includes topics such as Gold discovery, Eureka, Main Road, Ballarat Fire Brigade, Ballarat Benevolent Home, Buninyong, Burke and Wills Monument, Chinese in Ballarat, Dana Street School, Ballarat Hospital, Lost Trades of Ballarat, Ballarat Military, Mount Pleasant, Old Colonists' Club, Phoenix Foundry, Ballarat Post Office, Railways, Ballarat School of Mines, South Street Society, Martin Hosking, Charles Curnow Phillips, James Sainsbury, and William Cross Yuille. .2) includes topics such as Ballarat streets, bowls, cricket, football, hotels, Little Bendigo, Lake Wendouree, Ballarat Quartz Mines, Sebastopol, Ballarat Turf Club, Ballarat Zoo, water supply. .3) includes topics such as the Kohinoor Nugget, Eureka, Black Hill, Sebastopol, oddietown, Joe the bellman, Trades Hall, Lal Lal Iron, Ballarat Library, Yuille Creek, Martin Hosking, Stonewall Jackson, steeplechase, Lemonade Paddock, Ivey's Flour Mill, Salvation Army, Stick Jaw Davey, Unicorn Hotel, doctors, Alfred Bells, Ballarat School of Mines Museum (War Museum), Joseph Orange, Ballarat East Post Office.ballarat, speilvogel, nathan spielvogel -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, A Century of Permanent Water Supply, 1962
Blue covered book.non-fictionwater, water management, moorabool reservoir, ballarat sewerage authority, sebastopol sewerage treatment works, ballarat north sewage treatment works, sebastopol sewage treatment works -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWood Sample, about 1871
This piece of timber from the ship Eric the Red has been eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called sea worms or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by using coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch. In the 18th and 19th centuries the outside of their ships were sheathed in copper or a combination of copper and zinc (called Muntz metal) and would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. The American ship Eric the Red was a wooden, three masted clipper ship. She had 1,580 tons register and was the largest full-rigged ship built at Bath, Maine, USA in 1871. She was built and registered by Arthur Sewall, later to become the partnership E. & A. Sewall, the 51st ship built by this company. The annually-published List of Merchant Vessels of the U.S. shows Bath was still the home port of Eric the Red in 1880. The vessel was named after the Viking discoverer, Eric ‘the Red-haired’ Thorvaldsson , who was the first European to reach the shores of North America (in 980AD). The ship Eric the Red at first traded in coal between America and Britain, and later traded in guano nitrates from South America. In 1879 she was re-metalled and was in first class condition. On 10th June 1880 (some records say 12th June) Eric the Red departed New York for Melbourne and then Sydney. She had been commissioned by American trade representatives to carry a special cargo of 500 exhibits (1400 tons) – about a quarter to a third of America’s total exhibits - for the U.S.A. pavilion at Melbourne’s first International Exhibition. The exhibits included furniture, ironmongery, wines, chemicals, dental and surgical instruments, paper, cages, bronze lamp trimmings, axles, stamped ware, astronomical and time globes, samples of corn and the choicest of leaf tobacco. Other general cargo included merchandise such as cases of kerosene and turpentine, brooms, Bristol's Sarsaparilla, Wheeler and Wilson sewing machines, Wheeler’s thresher machine, axe handles and tools, cases of silver plate, toys, pianos and organs, carriages and Yankee notions. The Eric the Red left New York under the command of Captain Zaccheus Allen (or some records say Captain Jacques Allen) and 24 other crew including the owner’s son third mate Ned Sewall. There were also 2 saloon passengers on board. The ship had been sailing for an uneventful 85 days and the voyage was almost at its end. As Eric the Red approached Cape Otway there was a moderate north-west wind and hazy and overcast atmosphere. On 4th September 1880 at about 1:30am Captain Allen sighted the Cape Otway light and was keeping the ship 5-6 miles offshore to stay clear of the hazardous Otway Reef. However he had badly misjudged his position. The ship hit the Otway Reef about 2 miles out to sea, south west of the Cape Otway light station. Captain Allen ordered the wheel to be put ‘hard up’ thinking that she might float off the reef. The sea knocked the helmsman away from the wheel, broke the wheel ropes and carried away the rudder. The lifeboats were swamped, the mizzenmast fell, with all of its rigging, then the mainmast also fell and the ship broke in two. Some said that the passenger Vaughan, who was travelling for his health and not very strong, was washed overboard and never seen again. The ship started breaking up. The forward house came adrift with three of the crew on it as well as a longboat, which the men succeeded in launching and keeping afloat by continually bailing with their sea boots. The captain, the third mate (the owner’s son) and others clung to the mizzenmast in the sea. Then the owner’s son was washed away off the mast. Within 10 minutes the rest of the ship was in pieces, completely wrecked, with cargo and wreckage floating in the sea. The captain encouraged the second mate to swim with him to the deckhouse where there were other crew but the second mate wouldn’t go with him. Eventually the Captain made it to the deckhouse and the men pulled him up. At about 4:30am the group of men on the deckhouse saw the lights of a steamer and called for help. At the same time they noticed the second mate and the other man had drifted nearby, still on the spur, and pulled them both onto the wreck. The coastal steamer SS Dawn was returning to Warrnambool from Melbourne, its sailing time different to its usual schedule. She was built in 1876 and bought by the Portland and Belfast Steam Navigation Co. in 1877. At the time of this journey she was commanded by Captain Jones, and was sailing between Melbourne and Portland via Warrnambool. The provedore of the Dawn, Benjamin Lear, heard cries of distress coming through the portholes of the saloon. He gave the alarm and the engines were stopped. Cries could be heard clearly, coming from the land. Captain Jones sent out crew in two boats, and fired off rockets and blue lights to illuminate the area. They picked up the three survivors who were in the long boat from Eric the Red. Two men were picked up out of the water, one being the owner’s son who was clinging to floating kerosene boxes. At daylight the Dawn then rescued the 18 men from the floating portion of the deckhouse, which had drifted about 4 miles from where they’d struck the reef. Shortly after the rescue the deckhouse drifted onto breakers and was thrown onto rocks at Point Franklin, about 2 miles east of Cape Otway. Captain Jones had signalled to Cape Otway lighthouse the number of the Eric the Red and later signalled that there was a wreck at Otway Reef but there was no response from the lighthouse. The captain and crew of the Dawn spent several more hours searching unsuccessfully for more survivors, even going back as far as Apollo Bay. On board the Dawn the exhausted men received care and attention to their needs and wants, including much needed clothing. Captain Allen was amongst the 23 battered and injured men who were rescued and later taken to Warrnambool for care. Warrnambool’s mayor and town clerk offered them all hospitality, the three badly injured men going to the hospital for care and others to the Olive Branch Hotel, then on to Melbourne. Captain Allen’s leg injury prevented him from going ashore so he and three other men travelled on the Dawn to Portland. They were met by the mayor who also treated them all with great kindness. Captain Allen took the train back to Melbourne then returned to America. Those saved were Captain Zaccheus Allen (or Jacques Allen), J. Darcy chief mate, James F. Lawrence second mate, Ned Sewall third mate and owner’s son, John French the cook, C. Nelson sail maker, Clarence W. New passenger, and the able seamen Dickenson, J. Black, Denis White, C. Herbert, C. Thompson, A. Brooks, D. Wilson, J. Ellis, Q. Thompson, C. Newman, W. Paul, J. Davis, M. Horenleng, J. Ogduff, T. W. Drew, R. Richardson. Four men had lost their lives; three of them were crew (Gus Dahlgreen ship’s carpenter, H. Ackman steward, who drowned in his cabin, and George Silver seaman) and one a passenger (J. B. Vaughan). The body of one of them had been found washed up at Cape Otway and was later buried in the lighthouse cemetery; another body was seen on an inaccessible ledge. Twelve months later the second mate James F. Lawrence, from Nova Scotia, passed away in the Warrnambool district; an obituary was displayed in the local paper. Neither the ship, nor its cargo, was insured. The ship was worth about £15,000 and the cargo was reportedly worth £40,000; only about £2,000 worth had been recovered. Cargo and wreckage washed up at Apollo Bay, Peterborough, Port Campbell, Western Port and according to some reports, even as far away as the beaches of New Zealand. The day after the wreck the government steam ship Pharos was sent from Queenscliff to clear the shipping lanes of debris that could be a danger to ships. The large midship deckhouse of the ship was found floating in a calm sea near Henty Reef. Items such as an American chair, a ladder and a nest of boxes were all on top of the deckhouse. As it was so large and could cause danger to passing ships, Captain Payne had the deckhouse towed towards the shore just beyond Apollo Bay. Between Apollo Bay and Blanket Bay the captain and crew of Pharos collected Wheeler and Wilson sewing machines, nests of boxes, bottles of Bristol’s sarsaparilla, pieces of common American chairs, axe handles, a Wheelers’ Patent thresher and a sailor’s trunk with the words “A. James” on the front. A ship’s flag-board bearing the words “Eric the Red” was found on the deckhouse; finally those on board the Pharos had the name of the wrecked vessel. During this operation Pharos came across the government steamer Victoria and also a steamer S.S. Otway, both of which were picking up flotsam and wreckage. A whole side of the hull and three large pieces of the other side of the hull, with some of the copper sheathing stripped off, had floated on to Point Franklin. Some of the vessels yards and portions of her masts were on shore. The pieces of canvas attached to the yards and masts confirmed that the vessel had been under sail. The beach there was piled with debris several feet high. There were many cases of Diamond Oil kerosene, labelled R. W. Cameron and Company, New York. There were also many large planks of red pine, portions of a small white boat and a large, well-used oar. Other items found ashore included sewing machines (some consigned to ‘Long and Co.”) and notions, axe and scythe handles, hay forks, wooden pegs, rolls of wire (some branded “T.S” and Co, Melbourne”), kegs of nails branded “A.T. and Co.” from the factory of A. Field and Son, Taunton, Massachusetts, croquet balls and mallets, buggy fittings, rat traps, perfumery, cutlery and Douay Bibles, clocks, bicycles, chairs, a fly wheel, a cooking stove, timber, boxes, pianos, organs and a ladder. (Wooden clothes pegs drifted in for many years). There seemed to be no personal luggage or clothing. The Pharos encountered a long line, about one and a half miles, of floating wreckage about 10 miles off land, south east of Cape Otway, and in some places about 40 feet wide. It seemed that more than half of it was from Eric the Red. The ship’s crew rescued 3 cases that were for the Melbourne Exhibition and other items from amongst the debris. There were also chairs, doors, musical instruments, washing boards, nests of trunks and fly catchers floating in the sea. Most of the goods were saturated and smelt of kerosene. A section of the hull lies buried in the sand at Parker River Beach. An anchor with chain is embedded in the rocks east of Point Franklin and a second anchor, thought to be from Eric the Red, is on display at the Cape Otway light station. (There is a photograph of a life belt on the verandah of Rivernook Guest House in Princetown with the words “ERIC THE RED / BOSTON”. This is rather a mystery as the ship was registered in Bath, Maine, USA.) Parts of the ship are on display at Bimbi Park Caravan Park and at Apollo Bay Museum. Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village also has part of the helm (steering wheel), a carved wooden sword (said to be the only remaining portion of the ship’s figurehead; further research is currently being carried out), a door, a metal rod, several samples of wood and a medal for bravery, awarded to Nelson Johnson, a crew member of the S.S. Dawn by the U.S. President, for the rescue of the crew. Much of the wreckage was recovered by the local residents before police and other authorities arrived at the scene. Looters went to great effort to salvage goods, being lowered down the high cliff faces to areas with little or no beach to collect items from the wreckage, their mates above watching out for dangerous waves. A Tasmanian newspaper reports on a court case in Stawell, Victoria, noting a man who was caught 2 months later selling tobacco from the wreckage of Eric the Red. Some of the silverware is still treasured by descendants of Mr Mackenzie who was given these items by officials for his help in securing the cargo. The gifts included silver coffee and tea pots, half a dozen silver serviette rings and two sewing machines. A Mr G.W. Black has in his possession a medal and a purse that were awarded to his father, another Dawn crew member who was part of the rescue team. The medal is inscribed and named “To John Black ….” (from “Shipwrecks” by Margaret E. Mackenzie, 3rd edition, published 1964). The wreck and cargo were sold to a Melbourne man who salvaged a quantity of high quality tobacco and dental and surgical instruments. Timbers from the ship were salvaged and used in the construction of houses and sheds around Apollo Bay, including a guest house, Milford House (since burnt down in bushfires), which had furniture, fittings and timber on the dining room floor from the ship. A 39.7 foot long trading ketch, the Apollo, was also built from its timbers by Mr Burgess in 1883 and subsequently used in Tasmanian waters. It was the first attempt at ship building in Apollo bay. In 1881 a red light was installed about 300 feet above sea level at the base of the Cape Otway lighthouse to warn ships when they were too close to shore; It would not be visible unless a ship came within 3 miles from it. This has proved to be an effective warning. Nelson Johnson, recipient of the medal for bravery, married Elizabeth Howard in 1881 and they had 10 children. They lived in South Melbourne, Victoria. Nelson died in 1922 in Fitzroy Victoria, age 66. In 1895 the owners of the S.S. Dawn, the Portland and Belfast Steam Navigation Co., wound up and sold out to the Belfast Company who took over the Dawn for one year before selling her to Howard Smith. She was condemned and sunk in Suva in 1928. The State Library of Victoria has a lithograph in its collection depicting the steamer Dawn and the shipwrecked men, titled. "Wreck of the ship Eric the Red, Cape Otway: rescue of the crew by the Dawn".The wood (timber) sample is listed on the Collections Australia Database, Heritage Victoria, number 239 00010 A “The Eric the Red is historically significant as one of Victoria's major 19th century shipwrecks. (Heritage Victoria Eric the Red; HV ID 239) The wreck led to the provision of an additional warning light placed below the Cape Otway lighthouse to alert mariners to the location of Otway Reef. The site is archaeologically significant for its remains of a large and varied cargo and ship's fittings being scattered over a wide area. The site is recreationally and aesthetically significant as it is one of the few sites along this coast where tourists can visit identifiable remains of a large wooden shipwreck, and for its location set against the background of Cape Otway, Bass Strait, and the Cape Otway lighthouse.“ (Victorian Heritage Database Registration Number S239, Official Number 8745 USA) Wood sample from the wreck of the ship Eric the Red. Triangular shaped, full of sea worm (Teredo worm) holes. The wood is dark in colour and is very light in weight.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwreck-artefact, eric-the-red, zaccheus-allen, sewall, 1880, melbourne-exhibition, cape-otway, otway-reef, wood-sample, s.s.-dawn -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWood Sample, About 1871
This piece of timber from the ship Eric the Red has been eaten through by the marine animals called Teredo Worms, sometimes called sea worms or ‘termites of the sea’. The worms bore holes into wood that is immersed in sea water and bacteria inside the worms digest the wood. Shipbuilders tried to prevent this problem by using coatings of tar, wax, lead or pitch. In the 18th and 19th centuries the outside of their ships were sheathed in copper or a combination of copper and zinc (called Muntz metal) and would be re-metalled periodically to ensure the sheathing would remain effective. In more recent times the ships are protected with a toxic coating. The American ship Eric the Red was a wooden, three masted clipper ship. She had 1,580 tons register and was the largest full-rigged ship built at Bath, Maine, USA in 1871. She was built and registered by Arthur Sewall, later to become the partnership E. & A. Sewall, the 51st ship built by this company. The annually-published List of Merchant Vessels of the U.S. shows Bath was still the home port of Eric the Red in 1880. The vessel was named after the Viking discoverer, Eric ‘the Red-haired’ Thorvaldsson , who was the first European to reach the shores of North America (in 980AD). The ship Eric the Red at first traded in coal between America and Britain, and later traded in guano nitrates from South America. In 1879 she was re-metalled and was in first class condition. On 10th June 1880 (some records say 12th June) Eric the Red departed New York for Melbourne and then Sydney. She had been commissioned by American trade representatives to carry a special cargo of 500 exhibits (1400 tons) – about a quarter to a third of America’s total exhibits - for the U.S.A. pavilion at Melbourne’s first International Exhibition. The exhibits included furniture, ironmongery, wines, chemicals, dental and surgical instruments, paper, cages, bronze lamp trimmings, axles, stamped ware, astronomical and time globes, samples of corn and the choicest of leaf tobacco. Other general cargo included merchandise such as cases of kerosene and turpentine, brooms, Bristol's Sarsaparilla, Wheeler and Wilson sewing machines, Wheeler’s thresher machine, axe handles and tools, cases of silver plate, toys, pianos and organs, carriages and Yankee notions. The Eric the Red left New York under the command of Captain Zaccheus Allen (or some records say Captain Jacques Allen) and 24 other crew including the owner’s son third mate Ned Sewall. There were also 2 saloon passengers on board. The ship had been sailing for an uneventful 85 days and the voyage was almost at its end. As Eric the Red approached Cape Otway there was a moderate north-west wind and hazy and overcast atmosphere. On 4th September 1880 at about 1:30am Captain Allen sighted the Cape Otway light and was keeping the ship 5-6 miles offshore to stay clear of the hazardous Otway Reef. However he had badly misjudged his position. The ship hit the Otway Reef about 2 miles out to sea, south west of the Cape Otway light station. Captain Allen ordered the wheel to be put ‘hard up’ thinking that she might float off the reef. The sea knocked the helmsman away from the wheel, broke the wheel ropes and carried away the rudder. The lifeboats were swamped, the mizzenmast fell, with all of its rigging, then the mainmast also fell and the ship broke in two. Some said that the passenger Vaughan, who was travelling for his health and not very strong, was washed overboard and never seen again. The ship started breaking up. The forward house came adrift with three of the crew on it as well as a longboat, which the men succeeded in launching and keeping afloat by continually bailing with their sea boots. The captain, the third mate (the owner’s son) and others clung to the mizzenmast in the sea. Then the owner’s son was washed away off the mast. Within 10 minutes the rest of the ship was in pieces, completely wrecked, with cargo and wreckage floating in the sea. The captain encouraged the second mate to swim with him to the deckhouse where there were other crew but the second mate wouldn’t go with him. Eventually the Captain made it to the deckhouse and the men pulled him up. At about 4:30am the group of men on the deckhouse saw the lights of a steamer and called for help. At the same time they noticed the second mate and the other man had drifted nearby, still on the spur, and pulled them both onto the wreck. The coastal steamer SS Dawn was returning to Warrnambool from Melbourne, its sailing time different to its usual schedule. She was built in 1876 and bought by the Portland and Belfast Steam Navigation Co. in 1877. At the time of this journey she was commanded by Captain Jones, and was sailing between Melbourne and Portland via Warrnambool. The provedore of the Dawn, Benjamin Lear, heard cries of distress coming through the portholes of the saloon. He gave the alarm and the engines were stopped. Cries could be heard clearly, coming from the land. Captain Jones sent out crew in two boats, and fired off rockets and blue lights to illuminate the area. They picked up the three survivors who were in the long boat from Eric the Red. Two men were picked up out of the water, one being the owner’s son who was clinging to floating kerosene boxes. At daylight the Dawn then rescued the 18 men from the floating portion of the deckhouse, which had drifted about 4 miles from where they’d struck the reef. Shortly after the rescue the deckhouse drifted onto breakers and was thrown onto rocks at Point Franklin, about 2 miles east of Cape Otway. Captain Jones had signalled to Cape Otway lighthouse the number of the Eric the Red and later signalled that there was a wreck at Otway Reef but there was no response from the lighthouse. The captain and crew of the Dawn spent several more hours searching unsuccessfully for more survivors, even going back as far as Apollo Bay. On board the Dawn the exhausted men received care and attention to their needs and wants, including much needed clothing. Captain Allen was amongst the 23 battered and injured men who were rescued and later taken to Warrnambool for care. Warrnambool’s mayor and town clerk offered them all hospitality, the three badly injured men going to the hospital for care and others to the Olive Branch Hotel, then on to Melbourne. Captain Allen’s leg injury prevented him from going ashore so he and three other men travelled on the Dawn to Portland. They were met by the mayor who also treated them all with great kindness. Captain Allen took the train back to Melbourne then returned to America. Those saved were Captain Zaccheus Allen (or Jacques Allen), J. Darcy chief mate, James F. Lawrence second mate, Ned Sewall third mate and owner’s son, John French the cook, C. Nelson sail maker, Clarence W. New passenger, and the able seamen Dickenson, J. Black, Denis White, C. Herbert, C. Thompson, A. Brooks, D. Wilson, J. Ellis, Q. Thompson, C. Newman, W. Paul, J. Davis, M. Horenleng, J. Ogduff, T. W. Drew, R. Richardson. Four men had lost their lives; three of them were crew (Gus Dahlgreen ship’s carpenter, H. Ackman steward, who drowned in his cabin, and George Silver seaman) and one a passenger (J. B. Vaughan). The body of one of them had been found washed up at Cape Otway and was later buried in the lighthouse cemetery; another body was seen on an inaccessible ledge. Twelve months later the second mate James F. Lawrence, from Nova Scotia, passed away in the Warrnambool district; an obituary was displayed in the local paper. Neither the ship, nor its cargo, was insured. The ship was worth about £15,000 and the cargo was reportedly worth £40,000; only about £2,000 worth had been recovered. Cargo and wreckage washed up at Apollo Bay, Peterborough, Port Campbell, Western Port and according to some reports, even as far away as the beaches of New Zealand. The day after the wreck the government steam ship Pharos was sent from Queenscliff to clear the shipping lanes of debris that could be a danger to ships. The large midship deckhouse of the ship was found floating in a calm sea near Henty Reef. Items such as an American chair, a ladder and a nest of boxes were all on top of the deckhouse. As it was so large and could cause danger to passing ships, Captain Payne had the deckhouse towed towards the shore just beyond Apollo Bay. Between Apollo Bay and Blanket Bay the captain and crew of Pharos collected Wheeler and Wilson sewing machines, nests of boxes, bottles of Bristol’s sarsaparilla, pieces of common American chairs, axe handles, a Wheelers’ Patent thresher and a sailor’s trunk with the words “A. James” on the front. A ship’s flag-board bearing the words “Eric the Red” was found on the deckhouse; finally those on board the Pharos had the name of the wrecked vessel. During this operation Pharos came across the government steamer Victoria and also a steamer S.S. Otway, both of which were picking up flotsam and wreckage. A whole side of the hull and three large pieces of the other side of the hull, with some of the copper sheathing stripped off, had floated on to Point Franklin. Some of the vessels yards and portions of her masts were on shore. The pieces of canvas attached to the yards and masts confirmed that the vessel had been under sail. The beach there was piled with debris several feet high. There were many cases of Diamond Oil kerosene, labelled R. W. Cameron and Company, New York. There were also many large planks of red pine, portions of a small white boat and a large, well-used oar. Other items found ashore included sewing machines (some consigned to ‘Long and Co.”) and notions, axe and scythe handles, hay forks, wooden pegs, rolls of wire (some branded “T.S” and Co, Melbourne”), kegs of nails branded “A.T. and Co.” from the factory of A. Field and Son, Taunton, Massachusetts, croquet balls and mallets, buggy fittings, rat traps, perfumery, cutlery and Douay Bibles, clocks, bicycles, chairs, a fly wheel, a cooking stove, timber, boxes, pianos, organs and a ladder. (Wooden clothes pegs drifted in for many years). There seemed to be no personal luggage or clothing. The Pharos encountered a long line, about one and a half miles, of floating wreckage about 10 miles off land, south east of Cape Otway, and in some places about 40 feet wide. It seemed that more than half of it was from Eric the Red. The ship’s crew rescued 3 cases that were for the Melbourne Exhibition and other items from amongst the debris. There were also chairs, doors, musical instruments, washing boards, nests of trunks and fly catchers floating in the sea. Most of the goods were saturated and smelt of kerosene. A section of the hull lies buried in the sand at Parker River Beach. An anchor with chain is embedded in the rocks east of Point Franklin and a second anchor, thought to be from Eric the Red, is on display at the Cape Otway light station. (There is a photograph of a life belt on the verandah of Rivernook Guest House in Princetown with the words “ERIC THE RED / BOSTON”. This is rather a mystery as the ship was registered in Bath, Maine, USA.) Parts of the ship are on display at Bimbi Park Caravan Park and at Apollo Bay Museum. Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village also has part of the helm (steering wheel), a carved wooden sword (said to be the only remaining portion of the ship’s figurehead; further research is currently being carried out), a door, a metal rod, several samples of wood and a medal for bravery, awarded to Nelson Johnson, a crew member of the S.S. Dawn by the U.S. President, for the rescue of the crew. Much of the wreckage was recovered by the local residents before police and other authorities arrived at the scene. Looters went to great effort to salvage goods, being lowered down the high cliff faces to areas with little or no beach to collect items from the wreckage, their mates above watching out for dangerous waves. A Tasmanian newspaper reports on a court case in Stawell, Victoria, noting a man who was caught 2 months later selling tobacco from the wreckage of Eric the Red. Some of the silverware is still treasured by descendants of Mr Mackenzie who was given these items by officials for his help in securing the cargo. The gifts included silver coffee and tea pots, half a dozen silver serviette rings and two sewing machines. A Mr G.W. Black has in his possession a medal and a purse that were awarded to his father, another Dawn crew member who was part of the rescue team. The medal is inscribed and named “To John Black ….” (from “Shipwrecks” by Margaret E. Mackenzie, 3rd edition, published 1964). The wreck and cargo were sold to a Melbourne man who salvaged a quantity of high quality tobacco and dental and surgical instruments. Timbers from the ship were salvaged and used in the construction of houses and sheds around Apollo Bay, including a guest house, Milford House (since burnt down in bushfires), which had furniture, fittings and timber on the dining room floor from the ship. A 39.7 foot long trading ketch, the Apollo, was also built from its timbers by Mr Burgess in 1883 and subsequently used in Tasmanian waters. It was the first attempt at ship building in Apollo bay. In 1881 a red light was installed about 300 feet above sea level at the base of the Cape Otway lighthouse to warn ships when they were too close to shore; It would not be visible unless a ship came within 3 miles from it. This has proved to be an effective warning. Nelson Johnson, recipient of the medal for bravery, married Elizabeth Howard in 1881 and they had 10 children. They lived in South Melbourne, Victoria. Nelson died in 1922 in Fitzroy Victoria, age 66. In 1895 the owners of the S.S. Dawn, the Portland and Belfast Steam Navigation Co., wound up and sold out to the Belfast Company who took over the Dawn for one year before selling her to Howard Smith. She was condemned and sunk in Suva in 1928. The State Library of Victoria has a lithograph in its collection depicting the steamer Dawn and the shipwrecked men, titled. "Wreck of the ship Eric the Red, Cape Otway: rescue of the crew by the Dawn".The wood (timber) sample is listed on the Collections Australia Database, Heritage Victoria, number 239 00010 A “The Eric the Red is historically significant as one of Victoria's major 19th century shipwrecks. (Heritage Victoria Eric the Red; HV ID 239) The wreck led to the provision of an additional warning light placed below the Cape Otway lighthouse to alert mariners to the location of Otway Reef. The site is archaeologically significant for its remains of a large and varied cargo and ship's fittings being scattered over a wide area. The site is recreationally and aesthetically significant as it is one of the few sites along this coast where tourists can visit identifiable remains of a large wooden shipwreck, and for its location set against the background of Cape Otway, Bass Strait, and the Cape Otway lighthouse.“ (Victorian Heritage Database Registration Number S239, Official Number 8745 USA) Wood sample from the wreck of the ship Eric the Red. Oblong shaped, full of sea worm (Teredo worm) holes. The wood is dark in colour and is very light in weight. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, shipwreck-artefact, eric-the-red, zaccheus-allen, sewall, 1880, melbourne-exhibition, cape-otway, otway-reef, wood-sample, s.s.-dawn -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photographs, Richard Vincent, Washed Away Bridge at Garibaldi, c1933
Newspaper clipping documents deputations to the Minister of Public Works for grants to be made available for repairs to bridges and roads damaged by heavy flooding in 1933, in particular, the replacement of a stone and concrete bridge over the Leigh River at Garibaldi in the Buninyong Shire. The concrete slabs were still in the water in the 1960s/70s or even later. Three black and white photographs showing flood damage to the bridge over the Leigh River at Garibaldi, plus a photocopy of a newspaper clipping from The Argus December 1933 describing the extent of the flood damage. .1) shows blue stone buttress and collapsed bridge/road. .2) mirror image of above .3) unknown man waling an a girder of the Garibaldi bridge .4) photocopy of newspaper clipping about flood damage from The Argus December 1933Damage by Floods: Bridges washed away (The Argus December 1933)leigh river, garibaldi, buninyong shire, richard vincent, garibaldi bridge
