Showing 5904 items matching "1897-1966"
-
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBox Starch, Pre decimal currency date(14th February 1966)
This brand of starch was first manufactured before 1966 and covered the period when Australian made was the preferred clothing due to limited imports from England. This was a period when the demand for "home grown" produce was at its peak. This was in a time when by necessity and ease of supply and not by the "Buy Australian" campaign (of later years), was the major factor for the demand of these type of laundry goods. It was in a time when starch was used in formal clothing to put a "crisp" or fresh new appearance for clothes. This product was in the era and importantly the social more of "clothes make the person" in which starched shirts and dresses was the fashion vogue. Formality of dress was a strictly British "class" up-man-ship which from the 1950's onwards became less and less visible. The Australian "Ocker" or fair "dink'm" bloke became more entrenched after World War II. The national identity was slowly developing.This box of starch is very relevant to the Kiewa Valley because this box highlights the differences ,in this period, between city and rural social standards. Rural areas were deeply entrenched into colonial and the pioneer family structure viz- a-vie social and dress fashion standards. British values and norms lingered on well beyond the changes happening in city fashion. Tradition and English "ties" were the backbone of early colonies and it was only after World War II that these "ties" were becoming irrelevant. Early traditions lingered well past the independence sought by Federation, colony to statehood and trade with other nations eg. USA and Asia. The idea that a change in "status" would automatically change the social mores of Australians, especially in rural ares, was not fully grasped by the "law makers" and those wanting change.This box (capacity 12 ozs) has white(aged into cream) and blue printing and a "white star" on five sides, the sixth side has a laundry scene with two ladies, in early 1900's fashion. The package is made from 200 gsm thick cardboard. As manufacture was made before and during the two World Wars 1914 to 1945 the promotion was heavily focused on Australian made and Australian grown maize. One side of the box has instructions of use and all the other sides are promotional, detailing "the best in the world and won't stick to the iron""SILVER STAR", "THE BEST IN THE WORLD", "WON'T STICK TO THE IRON", "REQUIRES NO BOILING", INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE", "ROBERT HARPER AND COMPANY LIMITED", "INCORPORATED IN VICTORIA, AUSTRALIA", "NET WEIGHT 12 OUNCES", "LARGE BOX 12 OZS"domestic laundry essentials, cotton clothing preparations, household starch "crisp and neat appearances. -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaDocument - Text, Rifle Club papers, 1966-2003
A collection of papers made by Betty Williamson for a presentation at RVIB, and includes newspaper articles as well as a potted history of the Club. In the 1960's, the RVIB approached engineer George Glover to produce equipment to allow blind people to shoot, based upon that made available at St Dunstan's Hospital in the UK. The rifle range opened in February 1966 at the rear of St Kilda Road with 30 members, and soon became involved in matches with sighted rifle clubs in the area. The club had many successful years, competing against teams from Canada and New Zealand in 1968, and had the support of ICIANZ which provided them with free munitions as well as teams to compete against. In 1977, George Glover passed away and some of the skills required for maintenance of the equipment was lost, however the club continued until the late 1980's/early 1990s.1 folder of papers and pennantsrvib rifle club, george glover -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaPhotograph - Image, Man using rifle at competition, 1966-2003
An image taken of a man holding a rifle whilst two other men, one wearing a Canada Rifle Club blazer, look on. In the 1960's, the RVIB approached engineer George Glover to produce equipment to allow blind people to shoot, based upon that made available at St Dunstan's Hospital in the UK. The rifle range opened in February 1966 at the rear of St Kilda Road with 30 members, and soon became involved in matches with sighted rifle clubs in the area. The club had many successful years, competing against teams from Canada and New Zealand in 1968, and had the support of ICIANZ which provided them with free munitions as well as teams to compete against. In 1977, George Glover passed away and some of the skills required for maintenance of the equipment was lost, however the club continued until the late 1980's/early 1990s.1 Black and White image of man at shooting galleryrvib rifle club, royal victorian institute for the blind -
 Brighton Historical Society
Brighton Historical SocietyHat, 1960s
Thomas Harrison (1897-1981) was a leading Melbourne milliner from the 1930s. He began his millinery career in 1920, and by the late 1930s had a salon and workshop at 163 Collins St. He later moved the business to Toorak Road, South Yarra. He continued millinery work until 1975.Pink floral dome-shaped hat made up of silk and velvet pink hydrangea petals and mauve silk stems attached to a stiffened net base.Label, printed black on white acetate, centre back: THOMAS HARRISONthomas harrison, hats, 1960s fashion, melbourne fashion -
 Linton and District Historical Society Inc
Linton and District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Mr. and Mrs. Francis O'Beirne and Family
Annie Elizabeth O'Meara and Francis William O'Beirne were married in 1897. Their children were Maria Kathleen, b. 1898, Francis John, b. 1899, Roger Henry, b. 1901, Clement Michael, b. 1902, Gerard Vincent, 1903, Annie Agnes 1906, Mary Josephine, b. 1907.Black and white copy of original photograph which shows Francis O'Beirne, his wife Annie (née Annie O'Meara) and their family.annie elizabeth o'beirne née o'meara, francis william o'beirne, maria kathleen o'beirne, francis john o'beirne, roger henry o'beirne, clement michael o'beirne, gerard vincent o'beirne, annie agnes o'beirne, mary josephine o'beirne -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - NEWSPAPER CLIPPINGS SHAMROCK HOTEL, Unknown
(Third Newspaper Clipping )The Shamrock lights are blazing again article. Photograph of a chandelier framed in an archway in the first floor foyer. Electricity was a modern innovation when the Shamrock re-opened in 1897. Electric light lit the interior throughout and there were electric bells in every room. (The fourth Image directly underneath) depicts an invitation to the Governor of Victoria and his wife Lady Loch to a sumptuous banquet at The Shamrock in Novemebr 1886 to commemmorate their visit Sandhurst for the opening of the Juvenile and Industrial Exhibition.bendigo, history, shamrock hotel -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumDocument - MINER'S RIGHTS
.1 MINER'S RIGHT RECEIPT BOOK. NUMBER 001-250. MARCH 1910- AUGUST 1912 (2S 6D) .2 MINER'S RIGHT RECEIPT BOOK NO 86. NUMBERS 1-250. 25 MAY 1892 TO 21 DECEMBER 1894 (5/-) .3 CONSOLIDATED MINER'S RIGHTS, BOOK NO 22.. NUMBER 1 - 5. SEPTEMBER 1883 TO FEBRUARY 1884 .4 CONSOLIDATED MINER'S RIGHTS, BOOK NUMBER 1 - 18. 5 NOVEMBER 1888 TO 17 FEBRUARY 1897.1 WHITE ROUND STICKERN COVER WITH "1" .2 WHITE ROUND STICKER ON COVER "2" .3 WHITE ROUND STICKER ON COVER "4" .4 WHITE ROUND STICKER ON COVER "3"miners rights, consolidated miners rights -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumClothing - RIDING APPAREL, KINOCH CLOTHES, CIRCA 1927
LADIES RIDING OUTFIT .1 LADIES JACKET. TWEED WITH GREY SATIN LINING. 2 BUTTONS MISSING. LINING TORN. MADE BY KYNOCH CLOTHES OF SCOTLAND .2 BROWN JODHPURS. 1 BUTTON MISSING AT WAIST. LACING ON LEGS FROM BELOW KNEE TO ANKLE. .3 2 LEATHER RIDING GLOVES WITH FUR LINING AND METAL BUCKLES. THE OUTFIT BELONGED TO MRS W FAWCETT (CHRYSSIE) NEE McLENNAN. BORN 23/12/1897 DIED 29/3/1979.fawcett family, riding habit, clothing -
 Waverley RSL Sub Branch
Waverley RSL Sub BranchPlaque 4 Sqn.R.A.A.F. Hospital, R.A.A.F. Hospital
No 4 Squadron, Australian Flying Corps, formed at Point Cook, Victoria, in October 1916. After embarking for England to complete its training, the squadron deployed to France in December 1917. From the outset, No 4 Squadron aircraft regularly engaged the Red Baron's elite 'Flying Circus' and, in spite of their lack of experience, quickly gained the ascendancy over the German squadron. During its brief war service, No 4 Squadron destroyed some 128 enemy aircraft and spawned a total of eleven aces. The squadron's highest scoring airman was Captain Cobby who, in addition to shooting down 29 aircraft, also destroyed 13 observation balloons. World War II saw No 4 Squadron Wirraways deployed to Port Moresby in support of Australian troops fighting in the New Guinea jungles. In their slow and vulnerable aircraft, losses from anti-aircraft fire were high, however, this never deterred the Wirraway crews from completing their assigned tasks. This aggressive spirit was exemplified by Pilot Officer Archer and his crewman, Sergeant Coulston, who, while on a reconnaissance mission, found themselves above a Japanese Zero fighter. Despite operating a vastly inferior aircraft, Pilot Officer Archer dived to the attack and shot down the enemy aircraft. In June 1943, No 4 Squadron received its first Boomerang fighters and continued to support Allied troops during the Cape Gloucester landings before moving to Morotai. No 4 Squadron ended the war in Borneo and returned to Australia in November 1945, where it was renamed No 3 Squadron - thus closing the chapter on a very distinguished and proud unit. Summary of Unit Name(s) Start Date End Date No. 4 RAAF Hospital, Butterworth 06/06/1966 06/06/1966 No. 4 RAAF Hospital, Butterworth 03/07/1966 No. 4 RAAF Hospital, Butterworth 01/08/1966 01/08/1966 No. 4 RAAF Hospital, Butterworth 05/09/1966 No. 4 RAAF Hospital, Butterworth 29/09/1966 No. 4 RAAF Hospital, Butterworth 29/10/1966 29/10/1966 http://www.airforce.gov.au/raafmuseum/research/units/4sqn.htmWooden Plaque 15cm x 13cm with insignia of 4 Sqn.R.A.A.F. Hospital 4 Sqn R.A.A.F. Hospital r.a.a.f. 4 squadron, butterworth, r.a.a.f. hospital -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Ceremorial Object, James M. Houston
Grey coloured wooden cross with a photograph of James & his Service History.James M. Houston, 22, Walsend NSW. Station hand before enlisting, Aug 1965. Private Houston was a rifleman with 6 RAR. K.I.A. Battle of Long Tan at Phuoc Tuy 18/8/1966.houston, james m. -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaAward - Trophy, Tilbury & Lewis Pty Ltd, 1962
Stratherne Presbyterian Girls' School was founded in 1889 at the home of Miss Ethel Dare at 45 Riversdale road, Hawthorn. The final location of the school was 131 Power street, Hawthorn - a house gifted to the school by Mr and Mrs John Patterson in 1923. The Alma Pedersen Cup was awarded for best general improvement in the Junior school. The school closed in 1968.EPNS A1 trophy on a bakelite base. The trophy has two handles and engraving on both the back and front.On front: "Stratherne Presbyterian Girls' School Mrs Waters Trophy Athletics Champion House Davidson 1962" On back: "Dare 1963 Dare 1964 Dare 1965 Patterson 1966 Patterson 1967 Dare 1968"stratherne presbyterian girls' school hawthorn -
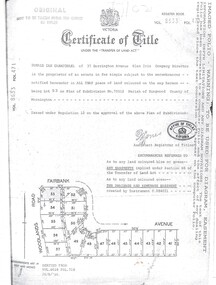 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyDocument, Certificate of Title Vol 8633 Fol 471, Plan of Subdivision No. 73512, Parish of Ringwood, County of Mornington
A4 Title Search Enquiry printout dated 2003, with Subdivision Map including Fairbank Avenue and Woodlands Road, Heathmont, Vic.Issued under Regulation 12 on the approval of the above Plan of Subdivision. Derived from Vol 8618 Fol 718, 26/8/1966. Proprietor - Donald Ian Carmichael of 37 Dorrington Avenue Glen Iris. -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Map, Aerial maps, 2/04/1966 12:00:00 AM
Melbourne 1966 project, runs 10A and 11A, lens 122 151.75 mm 9,800. Photo nos 77, 107, 109, 161, 163, 165.Melbourne 1966 project, runs 10A and 11A, lens 122 151.75 mm 9,800. Photo nos 77, 107, 109, 161, 163, 165. Areas and boundaries: Map no 77 W. Park and Cook Roads; E. Dubon Rd; N Oban Rd; S Reilly St. Map No 107. W. Indra Rd and Pakenham St; E. Rooks Rd & McLares Rd; N. Maroondah Hwy; S. Hawthorn Rd & Eley Rd. Map No 109 W. Elgar Rd. E. Blackburn Rd & McKean St; S. Eley Rd & Burwood Hwy. Map No 161. W. Elgar Rd & Huntingdale Rd; E. Blackburn Rd; N. Burwood Hwy; S. Waverley Rd. Map No 163. W. Blackburn Rd; S. Springvale Rd; N. Eley Rd & Hawthorn Rd; S. Glen Waverley Railway Line. Map No 165. W. Stanley Rd, Vermont South; E. Cathies Lane, Wantirna South; N. North of Burwood Hwy; S. High Street. Melbourne 1966 project, runs 10A and 11A, lens 122 151.75 mm 9,800. Photo nos 77, 107, 109, 161, 163, 165. aerial photographs, blackburn, blackburn south, forest hill, nunawading, box hill, burwood, burwood east, donvale, mount waverley, glen waverley, wantirna, vermont south, mitcham, ringwood north, ringwood -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyBook, Melway Street Directory of Greater Melbourne. Edition 1, 1966_
The first edition of this iconic Melbourne street directory published in 1966. The directory is accompanied by an outline of the history of the concept and publication of Melway.A surviving first edition of the Melway is rare as these directories are designed to be updated each year. Of interest in this edition is maps of the Greensborough area before large scale subdivision of the land in the late 1960s and 1970s.Soft cover street directory. Coloured maps.189 pages.melway, street directories, melbourne. -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMinutes, Victoria Institute of Colleges Minutes (selected), 1967-1969
In 1966 E.J.T. Tippett, President of the Ballarat School of Mines Council was on the interim council and committee member of the Victorian Institute of Colleges.Foolscap typed Victorian Institute of Colleges (VIC) minutes .1) Minutes of the inaugural meeting of the Victorian Institute of College held at the State Electricity Commission of Victoria, 15-23 William Street, Melbourne on 26 June 1967. This meeting followed 25 meetings of the Interim Council. The Council included E.J. Barker of the Ballarat School of Mines, representing principals of affiliated colleges outside the metropolitan area. .2) Building Committee minutes of the Victoria Institute of Colleges, 11 April 1969. These minutes mention Ballarat Institute of Advanced Education including the request for approval to purchase recording double beam spectrophotometer, Logic panel for Hitachi 505 analog computer and Nuclear-magneto-resonance gaussmeter system). The also requested approval to appoint L.H. Vernon and Associates and G.J. Harrison as joint campus planners, and outlined how water would be supplied to the Mount Helen site. The minutes outline a request for State.Commonwealth approval to purchase a concrete testing machine and an Hydraulic Flow Channel for Yallourn Technical College. The request was moved by E.J. Barker of the Ballarat School of Mines. .3) 'Colleges of Advanced Education - The Vision and the Reality' an address delivered at the Diploma Conferring Ceremony, Yallourn Technical College by R.E. Parry, registrar of the Victoria Institute of Colleges on Friday 18 April 1960. .4) Minutes of the Victoria Institute of Colleges Buildings Committee minutes, 8 November 1968. These minutes include information on the transfer of Yallourn Technical College to the new site at Churchill. .5) Minutes of the Victoria Institute of Colleges Council , 17 September 1969.victoria institute of colleges, victoria institute of colleges at ballarat, vic, vicb, jack barker, barker, e.j. tippett, tippett, victoria institute of colleges council, ll.h. vernon and associates, vernon, harrison, g.j. harrison, mount helen campus, campus development, master plan, campus master plan, water supply, mt helen campus water supply, ballarat school of mines, yallourn technical school, churchill campus, churchill, colleges of advanced education, ballarat college of advanced education, gippsland college of advanced education, parry, r.e. parry -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumManual (Item) - Master Drawing Directory Mirage Aircraft
Description: 40 pages. Published by RAAF. Published February 1966. DOC. GAMD No. 0 107 Level of Importance: World. -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Flag
It seems that the VC seamstress confused the year for 1966, as a decision to locate the new Australian base was not made until early that year.A black and gold frame of a Viet Cong flag. The flag is red and white with yellow embroidered letters. Viet Cong Flag - c1966. This viet Cong flag reads: Long Thanh-Baria's Provincial Liberation Armed force Determines/Resolves to destroy the Australian bases in Nui Dat - 1965 flag, viet cong, long thanh-baria's provincial liberation armed force, nui dat -
 Bayside Gallery - Bayside City Council Art & Heritage Collection
Bayside Gallery - Bayside City Council Art & Heritage CollectionPainting - oil on canvas, Andrew McLean, Black table still life, c. 1979
Acquired by the Sandringham City Council in 1979 as winner of the acquisitive Inez Hutchison Award, established by the Beaumaris Art Group in 1966.Andrew McLean, Black table still life c. 1979, oil on canvas, 101 x 101 cm. Bayside City Council Art and Heritage Collection. Purchased 1979.table, still life, painting, painting materials, brushes -
 Bayside Gallery - Bayside City Council Art & Heritage Collection
Bayside Gallery - Bayside City Council Art & Heritage CollectionPainting - oil on canvas, Kathleen Mitchell, Hillside, 1985
Acquired by Sandringham City Council in 1985 as winner of the acquisitive Inez Hutchison Award, established by the Beaumaris Art Group in 1966.Kathleen Mitchell, Hillside 1985, oil on canvas, 89.7 x 120 cm. Bayside City Council Art and Heritage Collection. Winner of the acquisitive Inez Hutchison Award, 1985.tree, kathleen mitchell, hillside, hill, landscape, painting, inez hutchison award, beaumaris art group -
 Beechworth RSL Sub-Branch
Beechworth RSL Sub-BranchMaxwell J Whitehead
Maxwell J Whitehead he service between 23/09/1966 22/08/1967 for a total of 334 days Photo frame is painted bronze with black engraving on it frame vietnam, 1 field squadron, royal australian engineers -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Booklet - Autographed booklet, H.M.A.S.Hobart: Australian Guided Missile Destroyer
This pamphlet was signed by actor Chips Rafferty in 1966 when on a promotional tour for the highly successful movie "They're a Weird Mob".Small cream soft-cover booklet of information about HMAS Hobart.Sincerely Chips Raffertydocument, hmas hobart, chips rafferty, vietnam -
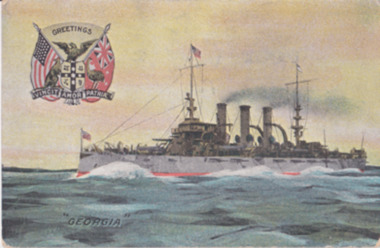 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Postcard - Post, Card Georgia, c.1910
The recipient of this card, Jessie Bonnett was born in Allansford in 1897. She spent her life on the family farm at Mepunga with her brothers Jack and George. She died in 1990 and her scrapbook came into the collection of the Warrnambool and District Historical Society through her relative, Mary O’Callaghan. Nothing is known of Ada Lawlor.This card has social significance and interest showing the communication between people in an earlier age. Postcards were commonly used to convey a short message between friends. This is a postcard with an image of the ship ‘Georgia’ on the front and a letter from Nullawarre on the back. There is a stamp from the Gray’s Colosseum Stationers and a symbol, ‘F & J’ on the back. Nullawarre, 13.10.10 Miss Jessie Bonnett, Mepunga, Dear Jessie, Just a P.C. in answer to your pretty card and for being so kind in always helping me with my sums. Please excuse this P.C. as I have no other. I remain, your affect. playmate, Ada Lawlor. Dear Jess I was not at school yesterday as I was sick with a cold.jessie bonnett, ada lawlor, the georgia -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Mia Mia, Hurstbridge, 1916
Mia Mia was a cottage on the other side of the bridge on Diamond Creek at Hurstbridge. Fred and Catherine Hurst first lived here after their marriage in 1897. For many years from at least 1916 through to 1941 it operated as the "Mia Mia" tearooms where wedding receptions and afternoon teas for convalescent soldiers were held.This photo forms part of a collection of photographs gathered by the Shire of Eltham for their centenary project book, "Pioneers and Painters: 100 years of the Shire of Eltham" by Alan Marshall (1971). The collection of over 500 images is held in partnership between Eltham District Historical Society and Yarra Plenty Regional Library (Eltham Library) and is now formally known as 'The Shire of Eltham Pioneers Photograph Collection.' It is significant in being the first community sourced collection representing the places and people of the Shire's first one hundred years.Digital imagesepp, shire of eltham pioneers photograph collection, hurstbridge, cottage -
 Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and Archives
Port Fairy Historical Society Museum and ArchivesPhotograph - Postcard
The Port Fairy rabbit factory was mooted on April 1896 by June of the same year The Port Fairy Preserving Company Limited was a registered company. Tenders were called in September and in 1897 a trial preserving run was planned. 5000 pairs of rabbits were being received each day coming by road as depicted in this photograph.Rabbit Load Jan 1908 James Stblack and white photograph on card with handwritten greetings Jan 1908 - Dad and our dear old horses Darky and Chance- x62-20-006 transport, rail, road, wagon, horses, james street, rabbits, 1908 -
 Port of Echuca
Port of EchucaFunctional object - Louvre Van (U1422)
Standard Victorian Railways Louvre Van one of 905 built. Built at Newport Workshops in February 1st1952. U1422 is one of the last batch of this design of van built at Newport between September 1951 and May 1952. The first of these vans was built in January 1908 as a lengthened of all steel louvre van was introduced in 1897. This Van is now the only surviving complete example of the long wheelbase louvre van which was a major part of the Victorian Railways from 1908 until 1988. These Louvre Vans would have been a common site at the Echuca Wharf. Although it is a relatively late example of its type.Standard Vic Railways Louvre Van U Classwharf, shire of campaspe, newport workshop, barred door, rollingstock collection, steam trains -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Ball, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A round woven cane ball, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre. The rod has a loop at each end, then a concave, octagonal metal plate that rests on the outside surface of the ball, serving as a washer. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, distant signal, signal, maritime signal, ball signal, signal shape, flagstaff signal, signal station, masthead signal, communications, marine technology, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, day shape, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Cone, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A woven cane cone, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre and two crossed metal bars at the base. The central rod has a loop at the top and passes through the bars at the base, finishing in a metal loop. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, marine navigation, marine communications, communication signal, lifesaving, ship at sea, day shape, masthead signal, day signal, day mark signals, marine technology, safety equipment, navigation equipment, marine day shape, day marker, cane day shape, signal cone, day signal cone, cone signal, cone day shape, distant signal, flagstaff signal, signal station, communications, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Ball, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A round woven cane ball, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre. The rod has a loop at each end, then a concave, octagonal metal plate that rests on the outside surface of the ball, serving as a washer. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, marine navigation, marine communications, communication signal, lifesaving, ship at sea, day shape, masthead signal, day signal, day mark signals, marine technology, safety equipment, navigation equipment, marine day shape, day marker, cane day shape, signal ball, day signal ball, ball signal, ball day shape, distant signal, flagstaff signal, signal station, communications, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Cone, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A woven cane cone, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre and two crossed metal bars at the base. The central rod has a loop at the top and passes through the bars at the base, finishing in a metal loop. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, marine navigation, marine communications, communication signal, lifesaving, ship at sea, day shape, masthead signal, day signal, day mark signals, marine technology, safety equipment, navigation equipment, marine day shape, day marker, cane day shape, signal cone, day signal cone, cone signal, cone day shape, distant signal, flagstaff signal, signal station, communications, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Ball, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A round woven cane ball, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre. The rod has a loop at each end, then a concave, octagonal metal plate that rests on the outside surface of the ball, serving as a washer. The rod has swivels at each end.distant signal, flagstaff signal, signal station, masthead signal, communications, marine technology, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, day shape, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897
