Showing 310 items
matching public institutions
-
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaAdministrative record (Series), Victorian Association of Braille Writers, 1895-1961
Victorian Association of Braille Writers, 31-51 Commercial Road, South Yarra, Victoria 3141To provide information on general information on work undertaken, financial position, income and cash flow.Single volumes created annually from 1895 until 1961.Minutes of AGM, Annual Report of Directors, President's Report, financial informationcorporation records, victorian association of braille writerscorporation records, victorian association of braille writers -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaAdministrative record (Series), Association for the Blind Annual Reports, 1955
Association for the Blind, 7 Mair Street, Brighton Beach, Victoria, Australia.To provide information on general information on work undertaken, financial position, income and cash flow.Single volumes created annually from 1955 until 1998.President's Report, Finance Report, General Overview of Services.association for the blind, corporation recordsassociation for the blind, corporation records -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaAdministrative record (Series), Royal Victorian Insitute for the Blind Annual Reports, 1892
Royal Victorian Institute for the Blind, 557-563 St Kilda Road, Melbourne, 3000.To provide information on general information on work undertaken, financial position, income and cash flow.Single volumes created annually from 1892 until 2004.President's Report, Finance Report, General Overview of Services.corporation records, royal victorian institute for the blindcorporation records, royal victorian institute for the blind -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaAdministrative record (Series), National Information Library Service annual reports, 2002-2004
NILS, 454 Glenferrie Road, Kooyong, Victoria, 3144To provide information on general information on work undertaken, financial position, income and cash flow.Single volumes created annually from 2002 until 2004.Chairman's message, CEO message, Finance Report, General Overview of Services.corporation records, national information library servicecorporation records, national information library service -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaAdministrative record (Series), Vision Australia Annual Reports, 2004
Vision Australia, 454 Glenferrie Road, Kooyong, Victoria 3144To provide information on general information on work undertaken, financial position, income and cash flow.Volumes created annually from 2004. Some years a second volume was created for the financial report.Chairman's message, CEO message, Finance Report, General Overview of Services.corporation records, vision australiacorporation records, vision australia -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaAdministrative record (Series), Royal Blind Foundation Queensland Annual Reports, 2002
Royal Blind Foundation Queensland, Kent Street, Woolloongabba, Queensland 4103To provide information on general information on work undertaken, financial position, income and cash flow.Single volumes created annually from 2002 until 2006.President's Report, Finance Report, General Overview of Services.corporation records, royal blind foundation queensland, queensland blind industrial centrecorporation records, royal blind foundation queensland, queensland blind industrial centre -
 Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)
Royal District Nursing Service (now known as Bolton Clarke)Photograph - Document/Letter, 1900
A letter dated 8th May 1973 details how the letter from Florence Nightingale was forwarded to Mrs E.G. (Janet) Wilson in 1955 by Gwendolen, Florence Nightingale's niece. The explanatory letter was forwarded by Elsa Halenstein and given to Royal District Nursing Service and remains in its Archives. From 1948 Mrs. Wilson served on the Committee of Management of Melbourne District Nursing Society (later Service), serving as President from October 1964-1967. In 1949 Mrs. Hallenstein served on the MDNS Committee of Management, becoming President of the now Royal District Nursing Service from 1967-1974. Florence Nightingale was the founder of modern nursing. Melbourne District Nursing Society (MDNS) only employed Trained nurses from its inception in 1885. They followed Florence Nightingale's basic rules of good hygiene, cleanliness, good nutrition and fresh air, which they learned during their Nursing Training at a Hospital, and taught to their patients by instruction and demonstration. In those days Trained nurses were called 'Nurse'. In 1892 MDNS employed Lucy Smith who, through the Nightingale Fund, did her nursing training at the Nightingale Training School at St. Thomas's Hospital in London. She was the first nurse from this school to work at MDNS. Florence Nightingale, born on the 12th of May 1820, was named after the place of her birth in Italy. Born into a wealthy family she was schooled at home where she excelled in her studies; spoke several languages fluently, and was taught home management. She believed she was ‘called’ to reduce human suffering and tended to ill members of her family and tenants on the family estate. She worked as a nurse at Salisbury Infirmary where she learned about nursing sanitation and hospital practice. Florence then enrolled at the Institution of Protestant Deaconesses at Kaiserswerth, Germany where she learned basic nursing skills, the importance of patient observation, and hospital organization. In 1853 she became Superintendent of the Institution for Sick Gentlewomen in Distressed Circumstances in London, where she reformed health care, working conditions, and hospital efficiency. The Crimean War broke out in late 1853 and a newspaper reported the injured and sick soldiers were being cared for by an “incompetent and ineffective medical establishment and that most basic supplies were not available for care”. After an outcry from the public, Florence was asked to lead a group of 38 nurses, whom she had trained, to Scutari where the wounded soldiers were sent. After arriving at the Barrack Hospital in October 1854, she found the soldiers were being cared for in overcrowded and filthy conditions; contaminated water, faeces on the floors and rats running freely. There were few supplies and equipment. Florence bought supplies and equipment and found help to assist in the laundry. The wards were scrubbed from floor to ceiling. Florence set a high standard of care with fresh air, hygiene, clean clothing, sufficient food and regular dressing of wounds being carried out. She realized the importance of psychological needs, and soldiers were assisted to write letters to relatives, and took part in education and recreational activities. Of a night Florence walked through the wards, carrying a lamp to light her way, to check on ill and wounded soldiers and became known as “The Lady with the Lamp”. She gained the respect of the soldiers and the establishment, and later, the public through the soldier’s letters and reports in the newspaper. After visiting Crimea she contracted ‘Crimean Fever’ from which she never really recovered. When she returned to London she was regarded a heroine. The public had given freely to buy her a gift but Florence preferred this money be used to establish a fund, which became known as the Nightingale Fund. Florence had kept excellent records on the running of the Barrack Hospital, medical and nursing staff efficiency, and the causes of illness and death. Many nurses from the training school became Matrons in many countries throughout the world. Florence pushed the Government for legislation to improve drainage and sanitation in homes and in the building of hospitals with fresh air a priority. She wrote the book ‘Notes on Nursing’ and many writings on health reform. She died, aged 90 years, in her home at 10 South Street, Park Lane on the 13th of August 1910. A handwritten letter, written in lead pencil, by Florence Nightingale. It is written to her niece Gwendolen.. The letter is on buff coloured paper and has the date 'Oct 17 1900'/ written in the top right hand corner; below this is, in capital letters, the two line black printed address - '10, South Street,/ Park Lane, W'/ is stamped. The bulk of the letter reads over eight lines: "Dearest Gwendolen",/ "Thanks for your / dear note,/ I shall gladly look / forward to seeing you, / on Friday at 5 ,/ ever your loving, / Aunt Florence./ . rdns, royal district nursing service, miss florence nightingale, mrs e.g. (janet) wilson, mrs d. (elsa) hallenstein -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncFunctional object - Victorian Railways Bowl, Grindley Hotel Ware, May 1954
... used throughout hospitality venues and public institutions ...The Grindley Hotel Ware Co Ltd was located in Stoke-on-Trent, England with its business name being registered in May 1908. The product name "Duraline" came into use c1933. From 1932 ware was marked with the month and year of manufacture. Thus the numbers 5-54 underneath this item indicate that it was manufactured in May 1954. Mr. Loftus Henry Moran, born in Winchelsea, Victoria, was well-known in the tea trade, originally working with Griffiths Bros Ltd. He started his own business, Loftus Moran Pty Ltd in 1909. Loftus Moran's company imported chinaware from Britain and sold it into the Australian market. They specialised in supplying to hotels, businesses and institutions.This item is representative of chinaware used throughout hospitality venues and public institutions throughout Australia.A white ceramic bowl bearing a red emblem of Victorian Railways. The mark of the maker Grindley Hotel Ware and the Victorian supplier, Loftus & Moran Pty, Ltd is underneath the bowl.On front: Victorian Railways On Back: "DURALINE" /SUPER VITRIFIED/ GRINDLEY HOTELWARE CO./ ENGLAND LOFTUS MORAN PTY. LTD. / MELBOURNE 5 - 54duraline, victorian railways, grindley hotel ware -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncMemorabilia - China Bowl Ronan's Coffee Palace, Grindley Hotel Ware, C.1921 - 1930
Coffee Palaces were developed throughout Australia with the backing of the Temperance Movement as an alternative venue to pubs in the late 19th century. Two Coffee Palaces identified in Wodonga in the early days were the Railway Coffee Palace and the Wodonga Coffee Palace. In 1908 Wodonga Coffee Palace was advertised for sale, having 15 rooms, a 15 stall stable and feed-room. In 1921 Wodonga Coffee Palace was taken over by Julia Ronan who had successfully conducted the dining rooms at the Wodonga Sale-yards for 15 years. The building of the Hume Weir was in progress and many of the workers boarded at the Coffee Palace. In 1936 Wodonga Coffee Palace became “Glenburnie” Guest House. Mr. Loftus Henry Moran, born in Winchelsea, Victoria, was well-known in the tea trade, originally working with Griffiths Bros Ltd. He started his own business, Loftus Moran Pty Ltd in 1909. Loftus Moran's company imported chinaware from Britain and sold it into the Australian market. They specialised in supplying to hotels, businesses and institutions.This bowl is an excellent example of earthen ware items used throughout Australia in hotels, cafes and other institutions. Loftus Moran Pty Ltd, was a major distributor and successful Melbourne Company. Mrs. Ronan's Coffee Palace was an important business in Wodonga and an alternate food and accommodation venue for those who preferred not to stay in public houses or hotels.A small white bowl bearing the logo of Ronan's Coffee Palace in Wodonga printed in green.In a scroll at the top edge "RONAN'S COFFEE PALACE" Underneath the bowl in green writing below a green crown "GRINDLEY HOTEL WARE/ENGLAND/VITRIFIED/LOFTUS, MORAN/ MELBOURNE"coffee palace, wodonga business, wodonga, mrs. ronan wodonga, 1920s wodonga -
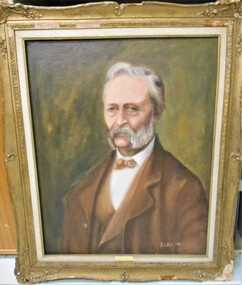 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Painting - PAINTING OF W.C. VAHLAND
William Charles Vahland (1828-1915) was born in Germany and came to Bendigo in 1854. He married Jane Barrow in 1859. He was an architect responsible for over 200 building, both public and private, in the Bendigo area. These included the Town Hall, Shamrock hotel, and Fortuna Villa. He was a director and committee member of many Bendigo institutions.Oil painting, in ornate gold frame, of W.C. Vahland. On bottom of frame is a brass plaque on which is engraved written 'W.C. Vahland, Pioneer Bendigo Architect' Painting by Ruth Ellis. Donated to BHS by Licensee of Shamrock Hotel. Given to Jim Evans. No paperwork. The painting was originally hanging in the Shamrock Hotel. Deframed -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Former Willsmere (Kew) Mental Hospital
... and opened in 1872. At various stages of the institution's history ...The former Kew Lunatic Asylum, was commenced in 1856 and opened in 1872. At various stages of the institution's history it was named the Kew Lunatic Asylum (1872-1956), Kew Mental Hospital (1956-1960s), Willsmere Mental Hospital (c.1960s-1982), and the Willsmere Unit (1982-1989). Most of the records relating to this former institution are held by the relevant Government Department or by the Public Record Office Victoria. Due to the location of this institution in Kew, the Kew Historical Society also holds an extensive photographic archive as well as significant collections of personal papers collected by staff who worked there.This photograph is one of a series donated to the Society by the photographer, taken following the closure of the Willsmere Unit, and before its redevelopment as a private residential complex. The series is historically significant in that it depicts interior and exterior views of the former institution that were subsequently altered or demolished during redevelopment. A number of the 'views' are socially significant as they allow us to examine the ways in which public institutional architecture in the 19th and 20th centuries responded to the needs of those with perceived mental health issues. Colour snapshot of a part or section of the former Willsmere (Kew) Mental Hospital, taken following its decommissioning and before its sale and redevelopment.kew lunatic asylum, kew mental hospital, willsmere mental hospital, willsmere unit, health & human services, mental health, institutional architecture -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Brown Goshawk Juvenile, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
This specimen is a Brown Goshawk juvenile. The Brown Goshawk is widely distributed across Australia, Wallacea, New Guinea, New Caledonia, Vanuatu, and Fiji. In Australia, it predominantly inhabits eucalypt forests, woodlands, farmland, and urban areas, while in the Pacific, it is primarily associated with rainforest environments. Historically, it was also present on Norfolk Island until around 1790, potentially representing an undescribed subspecies. However, the limited material available—consisting of a single historical skin and nine subfossil bones—precludes confirmation through scientific analysis. This specimen was originally identified as a Nankeen Kestral and is catalogued as such in the original Public Library and Burke Museum catalogue. The specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen exhibits distinctive plumage compared to its adult counterparts. It has a streaky appearance, with a buff to pale rufous base color on its underparts adorned with bold, dark brown streaks. The upperparts are brown, with a slightly mottled or scalloped effect due to pale feather edges. Its eyes are yellow and legs are a pale yellow. The wings are broad and rounded, and the tail is long and barred. Identification swing tag with catalogue page number reads: 4. / Nankeen Kestrel - / See Catalogue,/ Page 2. /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, birds of prey, goshawk, ornithological, nankeen kestral -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Postcard, Circa 1920's
Circa 1920's the postcard depicts a pathway and manicured lawns leading to the Beechworth Mental Asylum administration building. The asylum was constructed between 1864 and 1867 to the designs by the Public Works Department (PWD) that was renamed Mayday Hills Mental Asylum. The now decommissioned asylum was cinsidered one of the largest psychiatric hospitals in Victoria and consisted of sixty-seven buildings, one thousand two hundred patients and five hundred staff members. The asylum was one of the first asylums to focus on treatment and rehabilitation instead of institutional confinement. At the asylum active works was considered imperative and workshops were located near the male accommodations and laundries and drying yards near the female accommodation.This postcard is significant as it depicts the historical, architectural, technical and aesthetic significance of the Beechworth Mental Asylum's administration building to the State of Victoria.Black and white rectangular postcard printed on card.Obverse: Valentine Series No.1858/ The Asylum Beechworth Reverse: 1997.2464/ Valentines/ Real Photo Series Published by Valentine Publishing Co. Pty. Ltd/ Queen St.. Melbpostcard, beechworth, beechworth mental asylum, beechworth lunatic asylum, mayday hills, mayday hills mental asylum, administration building, beechworth mental asylum administration building -
 Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing Archive
Alfred Hospital Nurses League - Nursing ArchiveBook - Illustrated book, Lyndsay Gardiner, The Eye and Ear: The Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital centenary history, 1968
History of the Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital. In 1863 Dr Andrew Sexton Gray, started an institution for those suffering diseases of the eye and ear. Increased demand led to the formation of a charitable committee in 1866, and the establishment of Victoria's third public hospital. Several changes of location until the opening of the first building on the current site in 1871Hardcover illustrated book pale blue binding, title and authors name in gold on spine. Cream dustjacket title and authors name on front cover and spine. Historical illustrations of the Eye and Ear Hospiital on front and back covernon-fictionHistory of the Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital. In 1863 Dr Andrew Sexton Gray, started an institution for those suffering diseases of the eye and ear. Increased demand led to the formation of a charitable committee in 1866, and the establishment of Victoria's third public hospital. Several changes of location until the opening of the first building on the current site in 1871 royal victorian eye and ear hospital, ophthalmology-history, otolaryngology-history, hospitals-special history -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Eltham Lower Park, 20 April 2008
Originally a race course, the park has brought the community together with a variety of activities. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p45 Once used for horse racing, which attracted visitors from Melbourne, the Eltham Lower Park has brought the community together with a wide range of activities. Horse riding is now enjoyed as a recreation in the park as are other sports. The park also includes the Diamond Valley Railway miniature trains and a sanctuary for the rare and vulnerable Eltham Copper Butterfly. Eltham Lower Park, with other parks, forms an almost continuous green band from Eltham’s centre, along the Diamond Creek to the Yarra River.1 Before European settlement the Wurundjeri people met on this land, particularly at the junction of the Diamond Creek with the Yarra River, which they called Birr-arung. This is commemorated by the sculpture, Not just a Pretty Place by Aleks Danko, winner of the 2000 Nillumbik Art in Public Places Award. The first European to settle here was probably Henry Foley, who in 1841 used it as part of his pastoral run. Foley sold his leasehold to Joseph Wilson in 1845, who soon after sold it to Frederick Falkiner. During the 1840s the future park was part of a government square mile (2.6 sqkm) reserve, north of the Yarra, within the Parish of Nillumbik, later named Eltham. Soon the land was used for horse racing after nearby residents cleared ten acres (4ha) in the early 1850s. A three-quarter of a mile (1.2km) race secured the winner the £10 Publican’s Prize. In response to popular demand, the newly formed Eltham District Road Board petitioned the Surveyor General of the Colony of Victoria, in 1856, for 36 acres (14.6ha) of crown land for a racecourse and recreation. By 1858 the Eltham races had become an institution. ‘Many skirmishes occurred and the way home was paved with temptation, with sly-grog for sale.3 In the early 1870s, two jockeys were sons of the police officer in charge of the Eltham Police Station, Miles S Lyons. Another ten acres (4ha) was added to the area in 1866 and 12 acres (4.8ha) – Hohnes Hill – in 1870. In 1866, two acres (0.8ha) on the creek banks became an animal pound with William Walsh the pound keeper in 1870, but this was later incorporated into the park. By 1877 the area was called a public park but horse racing and training continued into the 1920s. In the mid-1900s trotters were trained on a circuit road. In 1953 the Eltham Pony Club was established and used a cross-country course on Hohnes Hill. From the mid 1950s the club held the Eltham Easter Fair at the park, later to include a procession along Main Road from the town centre to the park. The park also attracted picnic parties and campers from the inner suburbs as did Wingrove Park, and businesses catering for visitors, sprang up on the opposite side of Main Road. Bus-loads of school children visited the park for Gould League bird days in the 1960s. In 1979 the Eltham Shire Council bought Lenister Farm, linking the park with the Yarra River. The Lenister Farm wetland includes a bird hide, viewing platform and interpretive signs.5 Pioneer Henry Stooke, later Road Board chairman, bought the 11 acres (4.5ha) - later to become Lenister Farm - from the Crown in 1862. Stooke never lived on this site and the two houses at Lenister Farm were built in the 20th century. Since its formation in 1871, the Council has controlled this crown land, which it named Eltham Park. But in the 1920s Eltham Council bought land near the town centre for a park, which it named Eltham Central Park. To avoid confusion the Council renamed Eltham Park, Eltham Lower Park. Since 2004 the Yarra footbridge has linked the park with the Yarra Valley Metropolitan Park and the Main Yarra Trail.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, eltham lower park, eltham park -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaEquipment - Object, Harrison and Seifreid, Hall Braille writer, 1920-1940
The original Hall Braille writer was modelled on the typewriter and was the first successful mechanical point writer. Frank Haven Hall, Superintendent of the Illinois Institution for the Blind, introduced his invention to the public on 27 May, 1892 at Jacksonville, Illinois. It was manufactured by Harrison and Seifried, Chicago, ca 1892. The carriage moves one space to the left as the keys are released. The styli in the embossing heads are controlled by the keys as are the bars on a typewriter. The styli operate from the back so that letters appear in the normal position for reading. Braille writers enable all dots in a Braille cell to be created simultaneously. This model was found in the Braille and Talking Book Library in South Yarra prior to the staff departure in 2000. Presumably used by either staff or volunteers at the library.Braille writer with a key board like a piano with black wooden keys on an ivory board. The body is made from heavy cast iron with a black lacquer.Painted in gold on top of the machine: "The Hall Braille Writer / patent pendingbraille equipment, assistive devices -
 Merri-bek City Council
Merri-bek City CouncilCeramic - Ceramic, acrylic paint, gold lustre and mix media, Bundit Puangthong et al, FOOD, 2018
These captivating pieces are part of a series called "FOOD / FLESH / FAME," a collaborative effort between Melbourne-based Thai artists Bundit Puangthong and Vipoo Srivilasa. Drawing from Buddhist teachings, the series explores the three elements of attachment: Food (consumption), Flesh (sex), and Fame (power). Although these elements are known to cause suffering, they remain persistently alluring, a paradox that the artists intend to explore further in the future. In creating these pieces, Vipoo Srivilasa initiated the process by sculpting three figures with bare surfaces. Bundit Puangthong then added his artistic touch by painting each sculpture. The artists' conceptual visions harmonized perfectly, especially considering their shared commitment to Buddhist principles, which frequently inspire their respective artistic practices. After Bundit completed his painting, Vipoo enlivened the pieces by adding eyes to the figures. He also embellished the works with pom-poms, lending them a softness that makes them appear both approachable and innocent, despite the weightiness of their themes. Each sculpture embodies a specific teaching from Buddhism: "FOOD" depicts a durian, the king of fruits, painted by Bundit Puangthong. He notes, "Despite its pungent aroma, many people still love to eat it."Donated the by the artists -
 Merri-bek City Council
Merri-bek City CouncilCeramic - Ceramic, acrylic paint, gold lustre and mix media, Bundit Puangthong et al, FLESH, 2018
In creating these pieces, Vipoo Srivilasa initiated the process by sculpting three figures with bare surfaces. Bundit Puangthong then added his artistic touch by painting each sculpture. The artists' conceptual visions harmonized perfectly, especially considering their shared commitment to Buddhist principles, which frequently inspire their respective artistic practices. After Bundit completed his painting, Vipoo enlivened the pieces by adding eyes to the figures. He also embellished the works with pom-poms, lending them a softness that makes them appear both approachable and innocent, despite the weightiness of their themes. Each sculpture embodies a specific teaching from Buddhism: "FLESH" features a golden umbrella, serving as a metaphor for sex. -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Boys Exercising, Kew Cottages, c.1900
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."Kew Cottages - 1973 [sic] Boys exercising. Boys of the Cottages. The Superintendent's Office, right (until 1973). Wards 12 and 13 left."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Matron Malloy, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."Kew Cottages - Matron Malloy 19..-1944. Matron Molloy of Kew CCE until about 1944"kew cottages, matron maud molloy, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Kew Cottages, Yard
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families.Kew Cottages - Yard 1926/27. The yard of what was previously ward 26/27. New unit 7/8. kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - 12 Bed Dormitory, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families.Kew Cottages - Dormitory (12 beds). A dormitory at the Cottages.kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
![Airing Court Shed [demolished 1976], Kew Cottages](/media/collectors/550653872162f11fb04854aa/items/57a01944d0cdd121042a07ed/item-media/57a019f6d0cdd121042a4183/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Airing Court Shed, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families." Kew Cottages - Airing Court Shed demolished 1976. The building in the foreground was a so-called 'airing-court-shed'. The other building is an old Court Pell hut (ex Royal Park) transported here after World War II. There were two other such huts behind this. All these buildings were demolished in 1976 to make way for the Graham Perkins Unit."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Group of 30 Men, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."Kew Cottages - Group of 30 Men – Hospital Ward in Background. The Hospital Ward in the background."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Girls in front of Ward 25, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."Kew Cottages. Girls in front of Ward 25."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Wards 11,12,13 & Old Conference Room, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Dr Cliff Judge in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families. [Conservation note: Broken glass to be replaced]"Kew Cottages - Wards 11,12,13 & Old Conference Room. Left to right - Wards 11, 12 and 13. Old Conference Room - Wards 23, 22 and 21."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Old Ward 21 (The Nursery), Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Dr Cliff Judge in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families. [Conservation note: Glass to be replaced]"Kew Cottages - Old Ward 21 (The Nursery). Old Ward 21, previously the 'nursery', and demolished in 1973 to make way for units 4 and 5. "kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Wards 11,12,13,13A, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."Kew Cottages - Wards 11,12,13,13A. Wards 11, 12, 13 and 13A. The Hospital Ward is in the background. Ward 13A was demolished in 1966."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
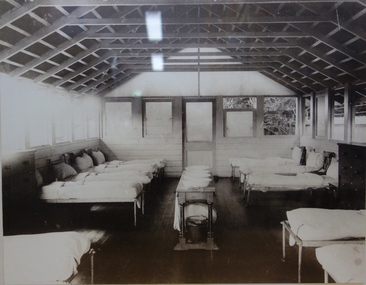 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Tent Dormitory, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by the Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."An old dormitory in the year 1973. It is still in use as a therapy room and store. Originally these buildings were called tents. Open air treatment was used to cure bad cases of insanity."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book, The History of Warrnambool by Richard Osburne, 1980
Richard Osburne (1825-1895) came to Warrnambool in 1847, a pioneer resident in the new settlement. In 1851, with John Wilkinson, he founded Warrnambool’s first newspaper, the Warrnambool Examiner, and issued it weekly for some months until he left the town for the goldfields. Returning in 1853 he resumed publication of the Examiner and continued it, intermittently in its last few years, until 1880. He was acknowledged in his day as the Father of the Warrnambool Press and was a dominant figure in Warrnambool’s early history. He was associated with the establishment of the Aboriginal Reserves, Fire Brigade, Mechanics’ Institute, Warrnambool Council, National School, Presbyterian Church, Public Wants Committee, Villiers Building Society, Fish Protection Society, Dramatic Club, Cricket Club, Otway Gold Exploration Syndicate and other institutions. In 1882 he went to live in Melbourne, returning to publish his ‘History of Warrnambool’ in 1887, a Queen’s Jubilee publication. Richard Osburne’s book is a seminal work of the 19th century history of Warrnambool and its importance cannot be over-emphasized. The original copies of this book are now hard to get and are very valuable. This facsimile is kept because the facsimiles are also now becoming rare and they are good examples of the way a facsimile is reproduced and the reason for the existence of this particular reprint– the importance and usefulness of Osburne’s history and the need to make it accessible to researchers today.This is a facsimile edition (1980) of Richard Osburne's book on the history of Warrnambool from 1847 to 1886. It is a hard cover buff-coloured book with gold lettering on the spine. The dust cover is cream-coloured paper with black writing. Inside the cover is a map of southwest Victoria (1880). There are five fold-up inserts (sketches, diagrams etc), a number of business advertisements, sepia photographs and sketches and an index. The dust cover includes information on the author. There are 25 chapters, a foreword by the Prime Minister of Australia, Malcolm Fraser and a Preface The proceeds of the book reprint went to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village.This is a facsimile edition (1980) of Richard Osburne’s book on the history of Warrnambool from 1847 to 1886. It is a hard cover buff-coloured book with gold lettering on the spine. The dust cover is cream–coloured paper with black writing. Inside the cover is a map of southwest Victoria (1880). There are five fold-up inserts (sketches, diagrams etc), a number of business advertisements, sepia photographs and sketches and an index. The dust cover includes information on the author. There are 25 chapters, a foreword by the Prime Minister of Australia, Malcolm Fraser and a Preface The proceeds of the book reprint went to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village.richard osburne, the history of warrnambool, warrnambool examiner
