Showing 3901 items matching "metalcraft-steel"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Medical container, Late 19th century or early 20th century
THE DISCOVERY OF STAINLESS STEEL Harry Brearley Since the dawn of man colonies have raced against each other to uncover new technologies, to be the first to stamp their names on a discovery, and although we’ve evolved over millions of years, the urge to be the first remains at the very core of our nature. This sense of passion and pride can lead some of the more unscrupulous humans to claim others discoveries as their own. Of course many breakthroughs are genuinely made in tandem, or are simultaneously occurring, but unless you can categorically prove that you were the pioneer of these incredible findings, then the other party involved will always dispute the fact. And so we come to stainless steel. The first point to note is that ‘inventor’ is a very ambiguous term. Is this the first person to think, to document, to patent, or to produce? The second point is that stainless steel wasn’t truly defined until 1911, so are we to cast aside those chromium-iron alloys that don’t quite meet the minimum requirement of 10.5% chromium? It seems like anyone and everyone has a different claim to being labelled the ‘inventor’ of stainless steel; from Britain, Germany, France, Poland, the U.S.A., and even Sweden. The cogs were set in motion by Englishmen Stoddart and Faraday circa 1820 and Frenchman Pierre Berthier in 1821. These scientists, among others, noted that iron-chromium alloys were more resistant to attack by certain acids, but tests were only carried out on low chromium content alloys. Attempts to produce higher chromium alloys failed primarily because of scientists not understanding the importance of low carbon content. In 1872 another pair of Englishmen, Woods and Clark, filed for patent of an acid and weather resistant iron alloy containing 30-35% chromium and 2% tungsten, effectively the first ever patent on what would now be considered a stainless steel. However, the real development came in 1875 when a Frenchman named Brustlein detailed the importance of low carbon content in successfully making stainless steel. Brustlein pointed out that in order to create an alloy with a high percentage of chromium, the carbon content must remain below around 0.15%. Thus ensued two decades of stagnation for the development of stainless steel, and while many scientists attempted to create a low carbon stainless steel, none succeeded. Hans Goldschmidt It wasn’t until 1895, when Hans Goldschmidt of Germany developed the aluminothermic reduction process for producing carbon-free chromium, that development of stainless steels became a reality. In 1904 French Scientist Leon Guillet undertook extensive research on many iron-chromium alloys. Guillet’s work included studies on the composition of what would now be known as 410, 420, 442, 446 and 440-C. In 1906 Guillet went on to analyse iron-nickel-chrome alloys, which would now be considered the basics of the 300 series. However, while noting the chemical composition of his alloys, Guillet failed to acknowledge the potential corrosion resistance of his materials. Albert Portevin In 1909 Englishman Giesen published an in-depth work regarding chromium-nickel steels, while the French national, Portevin, studied what is now regarded as 430 stainless steel. However, it wasn’t until 1911 that the importance of a minimum chromium content was discovered by Germans P. Monnartz and W. Borchers. Monnartz and Borchers discovered the correlation between chromium content and corrosion resistance, stating that there was a significant boost in corrosion resistance when at least 10.5% chromium was present. The pair also published detailed works on the effects of molybdenum on corrosion resistance. It is at this point we introduce Harry Brearley, born in Sheffield, England in 1871, he was appointed lead researcher at Brown Firth Laboratories in 1908. In 1912 Brearley was given a task by a small arms manufacturer who wished to prolong the life of their gun barrels which were eroding away too quickly. Brearley set out to create an erosion resistant steel, not a corrosion resistant one, and began experimenting with steel alloys containing chromium. During these experiments Brearley made several variations of his alloys, ranging from 6% to 15% chromium with differing levels of carbon. On the 13th August 1913 Brearley created a steel with 12.8% chromium and 0.24% carbon, argued to be the first ever stainless steel. The circumstances in which Brearley discovered stainless steel are covered in myth; some enchanted tales of Brearley recite him tossing his steel into the rubbish, only to notice later that the steel hadn’t rusted to the extent of its counterparts, much like Alexander Fleming’s experience 15 years later. Other more plausible, (but less attractive), accounts claim it was necessary for Brearley to etch his steels with nitric acid and examine them under a microscope in order to analyse their potential resistance to chemical attack. Brearley found that his new steel resisted these chemical attacks and proceeded to test the sample with other agents, including lemon juice and vinegar. Brearley was astounded to find that his alloys were still highly resistant, and immediately recognised the potential for his steel within the cutlery industry. The Half Moon Brearley struggled to win the support of his employers, instead choosing to produce his new steel at local cutler R. F. Mosley. He found difficulty producing knife blades in the new steel that did not rust or stain and turned to his old school friend, Ernest Stuart, Cutlery Manager at Mosley’s Portland Works, for help. Within 3 weeks, Stuart had perfected the hardening process for knives. Brearley had initially decided to name his invention ‘Rustless Steel’, but Stuart, dubbed it ‘Stainless Steel’ after testing the material in a vinegar solution, and the name stuck. And that’s how Harry Brearley discovered stainless steel…. well, not quite… During the 5 year period between 1908 and Brearley’s discovery in 1913 many other scientists and metallurgists have potential claims to Brearley’s title. In 1908 the Germans entered the fray, the Krupp Iron Works in Germany produced a chrome-nickel steel for the hull of the Germania yacht. The Half Moon, as the yacht is now known, has a rich history and currently lies on the seabed off the east coast of Florida. Whether the steel contains the minimum 10.5% chromium content remains inconclusive. Employees of the Krupp works, Eduard Maurer and Benno Strauss, also worked from 1912-1914 on developing austenitic steels using <1% carbon, <20% nickel and 15-40% chromium. Not happy with Europe hogging the glory, the USA got in on the act. Firstly, Elwood Haynes, after becoming disenchanted at his rusty razor, set out to create a corrosion resistant steel, which he supposedly succeeded in doing during 1911. Two other Americans, Becket and Dantsizen, worked on ferritic stainless steels, containing 14-16% chromium and 0.07-0.15% carbon, in the years 1911-1914. Elwood Haynes During 1912 Max Mauermann of Poland is rumoured to have created the first stainless steel, which he later presented to the public during the Adria exhibition in Vienna, 1913. Finally, a recently discovered article, which was published in a Swedish hunting and fishing magazine in 1913, discusses a steel used for gun barrels, (sound familiar?), which seems to resemble stainless steel. Although this is purely speculation, the Swedes have still made an audacious claim that they were in fact responsible for the first practical application for stainless steel. That concludes the shambolic discovery of stainless steel! Although there is much mystery and speculation behind the discovery of this wonderful material, there is no question that without the combined effort of all the above scientists and metallurgists, (and all the many more that were not mentioned), we would not have such a rich and versatile metal at our fingertips. https://bssa.org.uk/bssa_articles/the-discovery-of-stainless-steel/#:~:text=On%20the%2013th%20August%201913,the%20first%20ever%20stainless%20steel. This stainless steel container was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Medical box; rectangular stainless steel base and separate lid, from the W.R. Angus Collection.warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, stainless steel medical container, medical container, stainless steel -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumFunctional object - Trolley Pole Signal Skate or contactor, The Forest City Electric Co. Limited England, 1930s
Used by the Forrest City Signal system to initiate or cancel a signal indication. The trolley wheel would make contact with the steel strips which would send an electrical impulse to the control box that either would enable the signal to be shown or cancelled. There was one on the trolley wire at either end of the section. See reference for further details.Demonstrates part of the Forest City Signal system.Signal contactor mechanism comprising two brass ears, a section of copper trolley wire, two steel strips assembled onto a section of wood fitted with steel covers where the ears are fitted through. Item refurbished for display purposes by Depot staff 2023.forest city signals, tramways, overhead -
 Parks Victoria - Gabo Island Lightstation
Parks Victoria - Gabo Island LightstationHandrail
Steel hand rail from stone steps at house 3/4 recovered from grass near "Eastern Landing" in 2000.Steel tube shaped length bent at middle and curved at one end. 12 metal dowells attached to this rail, but unattached at end. Varying lengths. Rusted with some white paint residue. -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Tools, steel 'G' Clamp, early 20thC
A C-clamp or G- clamp is a type of clamp device typically used to hold a wood or metal work-piece, and often used in, but are not limited to, carpentry and welding. These clamps are called "C" clamps because of their C shaped frame, but are otherwise often called G-clamps or G-cramps because including the screw part they are shaped like an uppercase letter G. The fixed end is not adjustable so size is not variable. G-clamps are typically made of steel or cast iron, though smaller clamps may be made of pot metal. At the top of the "G" is usually a small flat edge. At the bottom is a threaded hole through which a large threaded screw protrudes. One end of this screw contains a flat edge of similar size to the one at the top of the frame, and the other end usually a small metal bar, perpendicular to the screw itself, which is used to gain leverage when tightening the clamp. When the clamp is completely closed, the flat end of the screw is in contact with the flat end on the frame When used some other object or objects will be contained between the top and bottom flat edges. A steel 'G' Clamp tools, g clamp, screws, steel, clamps, metalwork, woodwork, carpentry, early settlers, pioneers, market gardeners, moorabin, bentleigh, cheltenham -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy Railway219 NQR - Open medium truck with seats & canopy, between 1990 and 1992
219 NQR - Open medium trucks with seats & canopy (28) VR Service History Puffing Billy Service History or Notes In the 1910s some NQRs were provided with removable wood and steel framework with canvas canopies and side curtains, and seating to supplement the rest of the passenger stock during busy holiday periods. Puffing Billy recreated one of these and has built five more similarly equipped NQRs, numbered 219-223, between 1990 and 1992.Historic - Puffing Billy railway - Narrow Gauge Rolling Stock - NQR Open Medium Truck with seats & canopy219 NQR - Open medium trucks with seats & canopy made of Steel and metal219 NQR puffing billy, pbr, rolling stock , 219 nqr -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy Railway222 NQR - Open medium truck with seats & canopy, Between 1990 and 1992
222 NQR - Open medium truck with seats & canopy VR Service History Puffing Billy Service History or Notes In the 1910s some NQRs were provided with removable wood and steel framework with canvas canopies and side curtains, and seating to supplement the rest of the passenger stock during busy holiday periods. Puffing Billy recreated one of these and has built five more similarly equipped NQRs, numbered 219-223, between 1990 and 1992.Historic - Puffing Billy railway - Narrow Gauge Rolling Stock - NQR Open Medium Truck with seats & canopy222 NQR - Open medium truck with seats & canopy made of steel and metal222 NQR puffing billy railway, pbr, rolling stock , 222 nqr, open medium truck with seats & canopy -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy Railway223 NQR - Open medium truck with seats & canopy, Between 1990 and 1992
223 NQR - Open medium truck with seats & canopy Puffing Billy Service History or Notes In the 1910s some NQRs were provided with removable wood and steel framework with canvas canopies and side curtains, and seating to supplement the rest of the passenger stock during busy holiday periods. Puffing Billy recreated one of these and has built five more similarly equipped NQRs, numbered 219-223, between 1990 and 1992. Nov 2016 - Upholstery fitted Historic - Puffing Billy railway - Narrow Gauge Rolling Stock - NQR Open Medium Truck with seats & canopy223 NQR - Open medium truck with seats & canopy made of steel and metal223 NQRpuffing billy railway, pbr, rolling stock , 223 nqr, nqr open medium truck with seats & canopy -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy Railway2 NBH - Passenger Carriage - Excursion Car, 14/ 5/1900
2NBH - Excursion Car NBH SECOND-CLASS EXCURSION CAR. The H was recognising their use for "Holiday" traffic. 15 of these cars were built in 1919 and numbered 1-15. Two more were built in 1981, and numbered 16 & 17. Two extended versions for wheelchair passengers were built in 1981 & 1983. These were numbered 51 & 52 - a separate number series due to the different type of vehicle. Six, numbered 18-23, were built in 1997-98. These had steel frames, padded seats, and a wide "window sill". At first glance they look the same as the previous NBHs. There are other minor construction differences due to the use of steel framing. 18NBH entered traffic 19/4/1997; 19NBH on 5/12/1997; 20NBH on 19/12/1997, the others added in 1998. VR Service History : 14/ 5/1900 NWS Built new as 33 NQR converted & renumbered to 12/ 4/1919 - To NBH 2 VR Service History NQR 33.VA - 14/ 5/1900 NWS Built new - 12/ 4/1919 - To NBH 2.VA - *NBH 2.VA - / 4/1929 - Modified Malco BO circa 1955 - Condemned Puffing Billy Service History or Notes 12 Apr 1919 - Nos 1 to 6 NBH (new) delivered to UPPER FERN TREE GULLY after this date. Mar 2013 - In for a hot box againHistoric - Victorian Railways Narrow Gauge - Passenger Rolling Stock: Excursion Car Passenger Carriage - Excursion Car made of steel and timber2NBH puffing billy railway, pbr, rolling stock , 2nbh, victorian railways narrow gauge - passenger rolling stock,, victorian railways, nbh - excursion car, 2nbh -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy Railway8 NBH - Passenger Carriage - Excursion Car, 8/12/1919
8 NBH - Excursion Car (28) In Active Service - Belgrave Station Yard 8NBH - Excursion carriage. This car has been restored to original condition with white canvas weather blinds,Full carriage length side steps, timber tongue and groove boards,coupling centering springs and some pinch gas lighting equipment. NBH SECOND-CLASS EXCURSION CAR. The H was recognising their use for "Holiday" traffic. 15 of these cars were built in 1919 and numbered 1-15. Two more were built in 1981, and numbered 16 & 17. Two extended versions for wheelchair passengers were built in 1981 & 1983. These were numbered 51 & 52 - a separate number series due to the different type of vehicle. Six, numbered 18-23, were built in 1997-98. These had steel frames, padded seats, and a wide "window sill". At first glance they look the same as the previous NBHs. There are other minor construction differences due to the use of steel framing. 18NBH entered traffic 19/4/1997; 19NBH on 5/12/1997; 20NBH on 19/12/1997, the others added in 1998. VR Service History : *NBH 8.VA - 8/12/1919 NWS Built new - / 1/1929 - Modified AC Malco BO circa 1955 - Condemned Historic - Victorian Railways Narrow Gauge - Passenger Rolling Stock: Excursion Car 8NBH - Passenger Carriage - Excursion Car made of steel and timber8NBHpuffing billy, victorian railways, 8 nbh, passenger carriage, excursion car, narrow gauge -
 City of Ballarat
City of BallaratSculpture - Public Artwork, Inge King, Grand Arch by Inge King, 2001
Grand Arch is a five-metre by five-metre steel sculpture by Inge King placed as the centrepiece of Alfred Deakin Place, part of a redevelopment in conjunction with the State Government, City of Ballarat, University of Ballarat and Art Gallery of Ballarat. Grand Arch is representative of King's sophisticated style of abstraction that reflected animal and plant forms through to planets and the cosmos. King was a German-born Australian sculptor who created many significant public commissions including the well-loved Forward Surge (1974) at the Arts Centre, Melbourne. She was at the forefront of the development of non-figurative sculpture in Australia and held more than 26 solo exhibitions and participated in more than 60 group exhibitions in Australia, New Zealand, London and New York over almost 70 years as a practicing artist. The artwork is of artistic significance to the people of BallaratLarge steel sculpture painted matt blackgrand arch, inge king, australian modernism -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Tray, Stan Sharkey 1978-79, C 1978
Bushfield is situated on the outskirts of Warrnambool . The local Bushfield recreation reserve has been home to a number of local football and cricket clubs which play in various leagues in the Warrnambool district. Litle could be The Bushfield Cricket club has possibly been combined with another local team It is home to the Woodford Cricket Club which is the closest club to Bushfield and which uses the Bushfield oval as its home ground. It is a member of the Warrnambool and District Cricket Association. We have little information on Stan Sharkey who was obviously associated with the club in the late 1970's.Cricket is an important part of sporting life in Australia and especially in country regions where clubs often form part of the social network of the towns and districts. They rely heavily on the contributions of volunteers such as Stan Sharkey to operate. Many have recorded their histories through the years but nothing could be found on the Bushfield club.Oblong stainless steel tray with rounded corners . It has ornate handles screwed into either end , a raised lip around all sides and a circular brushed pattern on the flat surface of the tray. There is an inscription in the centre of the tray.Engraved in centre of tray," Stan Sharkey. In appreciation of servicesfor season 1978-79. From President & Players Bushfield Cricket Club."Marked stainless steel on back.warrnambool, bushfield, bushfield cricket club -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayFloodlight Projector, Tilley Model FL6, circa 1940's
Tilley Floodlight Projector - Model FL6 It stands about a metre high, and when lit, turns out about 5,000 candle power from the parabolic mirror in the back of the lamp. manufactured between the mid 1940's and early '50's It runs on kerosene that is pressurized with the integral pump, to provide a light beam from the parabolic mirror in the back of the lamp of approximately 3,000 candle power which can project over 1/4 of a mile. It features a pressure gauge, armored glass and all steel construction. Historic - Railways - Tilley Floodlight ProjectorTilley Floodlight Projector - Model FL6 made of metal, brass and glass and steelTilley Floodlight Projector - Model FL6puffing billy, tilley floodlight projector -
 City of Ballarat
City of BallaratArtwork, other - Public Artwork, Ratartat, Crossing Rubicon, 2008
“This public art project honours the people and suburb of Sebastopol, as well as providing a strong visual identity for Albert Street. It will make the street a lot more attractive and welcoming. The project is the outcome of extensive consultation with groups and individuals in the Sebastopol community, who have made suggestions both as to the nature of the project but also the aspects of life in their community they wanted to represent through the artwork.”Crossing Rubicon by Ratartat is located in Albert Street, Sebastopol, Ballarat. A row of 16 lampposts in Sebastopol’s main street are topped with large enamelled steel sculptures of trees, representing different aspects of Sebastopol’s community life and history. Ratartat is an artistic collaboration of Ballarat-based artists Geoff Bonney and Pete Widmer. The name, Crossing Rubicon, refers to Rubicon Street, the boundary between Redan and Sebastopol. The street was named after the Rubicon River, an ancient boundary between Italy and Gaul. Julius Caesar’s decision to cross the river, thereby rebelling against the Roman Senate, gave rise to the expression “crossing the Rubicon”, meaning going past the point of no return.Sixteen powder-coated steel sculptures mounted on light polesrubicon, sebastopol, ratartat -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societypair of horse hames
Hames are attached to a horse collar used to distribute the load around a horse's neck and shoulders when pulling a wagon or plough. The collar often supports and pads a pair of curved metal or wood pieces, called hames, to which the traces, which attach to the wagon or plough, of the harness are attached. The collar allows the horse to use its full strength when pulling. This pair of hames would have been used on a farm in the Orbost district. Horses were a vital part of the agricultural industry in Orbost before the mechanisation of farm machinery. This item is associated with that time.A pair of all metal horse hames, flat and angular shape. They are held together by a metal chain. Each has a hook attached and a metal ring at the end. One of the chain links has been repaired with wire.DOWNEE ALL STEELequestrian saddlery horses agriculture rural hames -
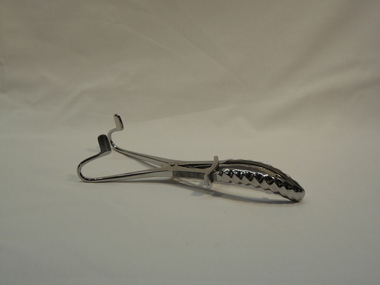 South West Healthcare
South West HealthcareMason-Ackland Mouth Gag, Medical Equipment
Metal adjustable, retractor anaesthetic instrument with sliding ring 8" (20cm)"202" "STAINLESS STEEL"gag, mouth gag -
 Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps Museum
Tatura Irrigation & Wartime Camps MuseumSpoon
Used at meal time by InterneesMetal dessert spoonAllbrite Stainless Steelspoon, metal, frank, beilharz, camp 3, tatura, war camps, domestic, cutlery -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Cooper’s Hollowing /Jigger Knife, William Greaves & Sons, 1823 -1850
William Greaves was once a prolific company that highly prospered in the 19th century during the boom of the tool and cutlery trades in Sheffield England as steel became more commercially available. William Greaves's works were situated at the Sheaf Works in the heart of Sheffield, at Maltravers Street, opening in 1823 and was known to be the largest business in this area at this time. The Sheaf Works made a range of tools and saws including cutlery, penknives and razors and also even made its steel in-house. The factory used its perfect position for water power being built on the edge of the Sheffield canal and also used the railway line nearby giving them the perfect opportunities for transporting its goods. The factory itself was also a revolution because it attempted to bring together as many cutlery manufacturing processes as possible together in one place, something that had not been attempted before. The money to build these huge works came from Greaves' trade with America, where they sent razors, table cutlery and sturdy Bowie knives. This allowed the Greaves’ to build the factory and expand their production, which made them even more money. This made William Greaves very rich indeed, and it was reported that when he died in 1830 he left each of his five surviving daughters £30,000 each, an astronomical sum at the time. In today’s money that is approximately £2.3 million. The firm finally dissolved in 1850, but Sheaf Works continued to be used by many cutlery manufacturers until the 1980s. With most of the buildings still standing today.A significant item made by a successful cutlery manufacturer in England during the first half of the 19th century. This company undertook many new processes to streamline cutlery production and introduced innervations regards working with steel that are still in use today. This item is now regarded as a collector's item given the company ceased trading in 1850. jigger/hollowing knife with internal bevel, Electro Boracic Steel. Stamped 3.1/2″ William Greaves, Sheaf Works, Sheffield flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, cooper's jigger, howeling knife, wm greaves & sons -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Tools, whetstone , 'Bridestowe' with box, 20thC
A Whetstone is a sharpening stone used for knives and other cutting tools. Sharpening stones, water stones or whetstones are used to grind and hone the edges of steel tools and implements e.g. scissors, scythes, knives, razors and tools such as chisels, hand scrapers and plane blades. Though it is sometimes mistaken as a reference to the water often used to lubricate such stones, the word "whetstone" is a compound word formed with the word "whet", which means to sharpen a blade, not the word "wet". The process of using a sharpening stone is called stoning.A square block of grey abrasive material used for sharpening steel blades , with the original boxBRIDESTOWE / Picture of ‘Kangaroo, Stag and Emu among radiating wheat stalks’ / TASMANIAwhetstones, sharpeners, steel blades, tools, cutlery, razors, moorabbin, bentleigh, cheltenham, early settlers, -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMangle, late 19th century
This mangle, sometimes referred to as a wringer, was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. The mangle was used in laundries to squeeze water from washed items and hasten the drying process. This particular wringer is larger that the usual household design and was possibly amongst the original furnishings of "Birchwood", the 1852 home of Dr Henderson when Dr. Angus purchased his home and medical practice in Koroit St, Warrnambool. The wooden rollers date the mangle to one of the earlier models manufactured. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) According to Berry, her mother Gladys made a lot of their clothes. She was very talented and did some lovely embroidery including lingerie for her trousseau and beautifully handmade baby clothes. Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . Its first station was in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital (a 2 bed ward at the Nelson Street Practice) from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what previously once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr Tom and his brother had worked as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He had been House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan had gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. When Dr Angus took up practice in the Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan’s old premises he obtained their extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926. A large part of this collection is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. and an ALDI sore is on the land that was once their tennis court). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. He had an interest in people and the community They were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Large mangle (or wringer) with wooden handle, hardwood wooden rollers and metal stand, part of the W.R. Angus Collection. Household clothes mangle with steel ball bearings, made by the American Wringer Co. New York, U.S.A. Brand and details are printed on side. Printed on side; "HOUSEHOLD / CLOTHES MANGLE / STEEL BALL BEARINGS / THE AMERICAN WRINGER Co, NEW YORK, USA” and on top "NO. HARDWOOD ROLLERS 124"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, clothes mangle, clothes wringer, laundry equipment, the american wringer company, mangle with wooden rollers, mangle with settl bearings -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyRectal Proctoscope
This medical / hospital instrument was used in the Tawonga District General Hospital which was built in the 1950s specifically for the increase in population due to the Kiewa Hydro Scheme.Historical: Shows the development of scientific hospital equipment. Provenance: Used in the Tawonga District General Hospital which was remote and therefore required good equipment.Used to look into the rectum. Part 1 fits into a hollow cylinder of part 2. 1. Plastic brown handle - round and shaped at end with 4 slices to form square shape for easy grip. attached to steel with protective plate long thin rod & then cylinder with covered shaped ends. 2. All steel - spoon shaped handle on angle to hollow cylinder wider and shaped into hollow cylinder - bottom cut cross section on angle.11AQ - on part 1. on steel between protective plate and wooden handle 11AQ - on part 2. across tip of handle DOWNS DA-001-01-Y length ways on handlemedical instrument. hospital equipment. mt beauty. tawonga. rectum. -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyFunctional object - Dressmaking Shears, 1900's
These vintage steel sewing shears were used at 'Belle's Bonnets' Milliners in Flinders lane Melbourne in the 1950's. Mrs Belle Phillpi was the Proprietor. Mrs Jill Sebire's wedding head piece was made at Belle's Bonnets.A pair of heavy vintage large hand forged steel dressmaking, tailors shears. They are joined with a pivot point screw. One finger hole is larger than the other.steel, scissors, cutting tools, dressmaking equipment, dressmaking shears, dressmaking scissors -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyDouble Ended Tonsil Dissector
This medical / hospital instrument was used in the Tawonga District General Hospital which was built in the 1950s specifically for the increase in population due to the Kiewa Hydro Scheme.Historical: Shows the development of scientific hospital equipment. Provenance: Used in the Tawonga District General Hospital which was remote and therefore required good equipment.Double ended - used to dissect tonsils Long stainless steel with curved flat end and at other end 90 degree angle hook with 3 curved points. Middle wider with etching.Etching into steel in middle, wider part - both sides. H.A.T. MELB. - next to etching at hook end. Stainless - next to etching at 'spoon' end facing other way to hook end.medical instrument. hospital equipment. tawonga. mt beauty. tonsil -
 Wangaratta High School
Wangaratta High SchoolMilitary Service Certificate, 1919
Many families at this time obtained and framed these military service certificates. This was part of the empire spirit of 1914. The prose at the top of the certificate is a quote from Act 5 scene 7 of William Shakespeare's "King John".Black and white certificate commemorating the war service of former WHS student Lt. Steel. A number of symbolic images including two men or horseback, a queen, a broken cart, a portrait surrounded by flags and lions and three rifles surround an photograph of Lt. Steel. Bordering the photograph is a modified Australian Government symbol, a laurel wreath, the Australian and British flags and two crossed rifles. Above the Portrait is a FOR KING AND EMPIRE banner and a quote from 'King John', and below is Lt. Steel's details.FOR KING & EMPIRE COME THE THREE FATHERS OF THE WORLD IN ARMS AND WE SHALL SHOCK THEM. NAUGHT SHALL MAKE US RUE IF AUSTRALIA TO ITSELF DO REST BUT TRUE NAME Liet' A. V. Steel REGIMENT 1st Battal'n COMPANY '10' RECORD OF SERVICE 1914 - 1919 -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy Railway15 NBH, Passenger Carriage - Excursion Car, July 1976
15NBH - Excursion Car Body built by Puffing Billy Preservation Society 1976. NBH - SECOND CLASS EXCURSION CAR. The H was recognising their use for "Holiday" traffic. Originally 15 of these cars were built in 1919 and numbered 1-15. Four were broken up prior to 1962, and replaced with new vehicles in 1975-76. Two more were built in 1981, and numbered 16 & 17. Two extended versions for wheelchair passengers were built in 1981 & 1983. These were numbered 51 & 52 - a separate number series due to the different type of vehicle. Six, numbered 18-23, were built in 1997-98. These had steel frames, padded seats, and a wide "window sill". At first glance they look the same as the previous NBHs. There are other minor construction differences due to the use of steel framing. 18NBH entered traffic 19/4/1997; 19NBH on 5/12/1997; 20NBH on 19/12/1997, the others added in 1998. VR Service History 8/12/1919 NWS Built new *NBH 15.VA - 8/12/1919 NWS Built new - / 3/1928 - Modified AC Malco BO circa 1955 - Condemned - 1/ 7/1962 - Scrapped. Replica body built by Puffing Billy Preservation Society 1976. Puffing Billy Service History or Notes 8 Dec 1919 - Nos 7 to 15 NBH (new) delivered to UPPER FERN TREE GULLY after this date.Historic - Victorian Railways Narrow Gauge - Passenger Rolling Stock: Excursion Car 15 NBH - Passenger Carriage - Excursion Car made of steel and timber15NBHvictorian railways, puffing billy railway -
 Waverley RSL Sub Branch
Waverley RSL Sub BranchMess kit
Probably of US origin Can , Meat (Mess Kit), M-1910, M-1918 The older style mess kits had the flat lid that could also be used as a plate. The M-1932 (not unit in our collection) unit had the plate divided into two sections so food could be separated. The folding handle, when closed, fits into the groove formed by the divider. The ring on the plate was moved to the end of the groove so the lip of the handle fits right into it. The M-1932 Meat Can was made of "corrosion resistant" galvanized steel, not aluminium. It used the same WW I style narrow profile steel handle attached by a cast hinge.Oval aluminium mess kit with steel handle which acts as a lid lock when folded. Cover has a mounted bracket for a ring fitting for attachment to belt.Nilmess kit, m-1918, m-1910 -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyCream Can - Large
Milk and cream were stored in steel cans for transportation to stores or local dairy companies.The dairy industry is and has been one of the major industries of the Kiewa Valley. This cream can was used on a dairy farm in the Kiewa Valley.Large steel dairy can used for cream or milk. The irregular shaped ring handles are welded on each side in an upright position. The lid is stuck on the can. The flat outer edge of the lid has an inscription. The centre of the lid is indented with a bar shaped handle welded across it to enable lifting.Embossed at the top of the straight sides is "Dairymaster" between the handles on each side. Lid: "B.L.Paynter" along the outer edge.dairy; cream can; kiewa valley -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyWet and Dry Bulb Thermometers - Tobacco
Tobacco farming began circa 1960 in the Kiewa Valley and consequently became one of its major industries. Many of the Italian families were involved in tobacco farming.Historical: This equipment was used on one of the first tobacco farms in the Kiewa Valley at Mongans Bridge. The frame holding the thermometers was home-made showing the resourcefulness of farmers living in the Kiewa Valley. Provenance: This tobacco farmer came from Italy and was sponsored to visit a tobacco farmer in Myrtleford to learn how to grow tobacco so that he could transfer those skills to his own farm in the Kiewa Valley.Used for monitoring the temperature and humidity in the kiln during the drying process of the tobacco leaf (the thermometer is missing the water holder) 2 thermometers attached to a steel attached to an old rusty tin frame with handle at the top enabling it to be hung, using wire, to hook on the wall. Tin frame has cap on it coming out to protect the thermometers and a base for standing the frame up. 1 thermometer has a hollow piece of material (or cord) strip (125 mm long) attached to the bottom of it.Beside the thermometers is inscribed on steel - the lines for measuring and numbers from 40, 60 (by 20s) up to 240.tobacco. kiewa valley. mongans bridge. wet and dry bulb thermometer. silvano rossaro. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Forceps, Late 19th century or early 20th century
Surgical forceps have been used in various forms from ancient times and have evolved into a indispensable instrument for modern surgeries. Forceps are surgical instruments for the practice of medicine which are used for grasping, holding, and manipulating tissues and objects during surgical procedures. Ancient Origins Surgical instruments, including forceps, have been use since man first started working with tools. Ancient civilizations, like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, had physicians who used rudimentary forceps made of bronze or iron. The forceps of the ancient world were often simple in design, with two arms that could be squeezed together to grasp objects. They were primarily used for tasks like extracting foreign bodies or handling tissues. Middle Ages and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, medical knowledge and surgical techniques experienced a decline in Europe. While the Roman empire enjoyed remarkably advanced medical care and practices, its collapse left a vacuum that led to a loss of a centralized medical knowledge and a disruption of education and trade. At the same time, religious superstitions suppressed medical inquiry. With many of the medical texts of Hippocrates and Galen and others lost, the medical practice experienced a decline. However, surgical forceps continued to be used in various forms, albeit with limited advancements. With the Renaissance period came a revival in medical knowledge and innovation. Ambroise Paré, a French surgeon of the 16th century, is credited with introducing improvements to the forceps design, making them more versatile and effective. 18th and 19th Centuries Innovators The 18th and 19th centuries marked a significant period of advancement in surgical instruments, including forceps. The famous French Surgeon Jean-Louis Petit introduced forceps with curved tips, making them more suitable for specific procedures. John Hunter, a Scottish surgeon, designed forceps with fine tips, allowing for more delicate and precise manipulation during surgeries. Joseph Lister, a pioneer of antiseptic surgery, emphasized the importance of cleanliness and sterile instruments during surgical procedures. This led to advancements in forceps sterilization techniques, which greatly improved patient outcomes. Modern Era The late 19th and early 20th centuries saw the development of a wide variety of specialized forceps for different surgical procedures. Advances in metallurgy and manufacturing techniques allowed for more intricate and delicate designs. As surgery became more specialized, forceps were tailored to suit specific procedures, such as neurosurgery, ophthalmology, and gynecology. Contemporary Advances In recent decades, surgical technology evolves continuously. Many surgical procedures are now performed using minimally invasive techniques, which require specialized instruments. Modern surgical forceps are typically made of high-quality stainless steel, stainless steel alloy, or titanium. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each suited to specific surgical tasks. Some forceps have serrated jaws for a better grip, while others have delicate tips for fine tissue manipulation. Modern Forceps The history of surgical forceps is a story of innovation, adaptation, and continuous refinement. From ancient origins to the modern era, these instruments have evolved alongside medical knowledge and surgical techniques, playing a crucial role in improving patient outcomes and advancing the field of surgery. https://www.wpiinc.com/blog/post/history-evolution-of-forceps These forceps were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Retractor forceps, from the W.R. Angus Collection. Crocodile teeth ends and locking handles.Marked 'Stainless Steel' on both parts.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, ent ear nose throat surgery, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, forceps, surgery, medical history -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Manufactured Object, Hair 'Butterfly clips' stainless steel, c1960
These are stainless steel Hair styling Clips that are used for creating definite, non permanent Waves in a lady's hair c 1920 to 1960. Ladies usually went to the hairdresser for this styling but they could do it themselves at home Gladys Reed was a member of the Ormond Choral Society c 1950. who performed plays and musicals the City of Moorabbin Finger waves were very a fashionable Hairstyle 1920 - 1960. Gladys Reed, who was a member of the Ormond Choral Society c 1950.that performed plays and musicals the City of Moorabbin used these 'butterfly clips'Steel spring 'butterfly clips' used for crimping hair to form waves. Sanitarium Health Food Company Box c 1960 used for storage.hairdressing, finger wave hairstyle, steel, fashion, theatrical props, craftwork, sequins, beading, early settlers, moorabbin shire, mechanics institute cheltenham, ormond choral society, postworld war 11 settlers, housing estates moorabbin 1950, bentleigh, ormond, moorabbin, cheltenham, drama societies, musical society cheltenham, clark judy, reed gladys, reed george, hairdressing salons -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Tools, wooden hammer with steel head, c1900
A hammer is a tool with a heavy head and a handle, often made of shock-absorbent wood or fiberglass that is used to strike an object. The most common uses for hammers are to drive nails, fit parts, forge metal, and break apart objects. Hammers vary in shape, size, and structure, depending on their uses. Hammers are basic tools in many trades. A hammer is composed of a head most often made of steel and a handle also called a helve or haft. Most hammers are hand tools. A traditional hand-held hammer consists of a separate head and a handle, fastened together by means of a special wedge made for the purpose, or by glue, or both. This two-piece design is often used, to combine a dense metallic striking head with a non-metallic mechanical-shock-absorbing handle -to reduce user fatigue from repeated strikes. If wood is used for the handle, it is often hickory or ash, which are tough and long-lasting materials that can dissipate shock waves from the hammer head. A well used hammer with wooden handle and steel headpioneers, early settlers, market gardeners, moorabbin, brighton, cheltenham, tools, craftsman, carpenters, blacksmiths, builders, woodwork,
