Showing 28 items matching " young architects"
-
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Manuscript, Robin Boyd, The New Architecture, c. 1963
... young architects... architecture Australia young architects creative architecture new ...Discusses twentieth century architecture and the evolution of modern architecture. Describes present architecture in three categories, namely vernacular, professional and creative. Examples of house designs within the new architecture are given.This manuscript was published as a book titled "The New Architecture" (The Arts in Australia Series), Longmans, Melbourne, 1963.Typewritten (c copy), pencil edits, quarto, 18 pagesmodern architecture, australia, young architects, creative architecture, new architecture, robin boyd, manuscript -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
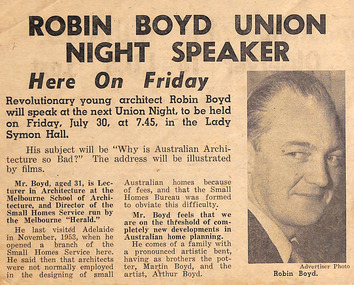
Robin Boyd FoundationNewspaper - Clipping, Robin Boyd Union Night Speaker, c. 1954
... Announcement that young architect Robin Boyd is speaking... melbourne Announcement that young architect Robin Boyd is speaking ...Announcement that young architect Robin Boyd is speaking at Union Night. The talk is titled "Why is Australian Architecture So Bad?" and will be illustrated with films.walsh st library -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Manuscript, Robin Boyd, Look Back in Apathy, 1958
... Boyd outlines reasons why architecture students and young... melbourne Boyd outlines reasons why architecture students and young ...Boyd outlines reasons why architecture students and young architects are less outspoken about the quality of architectural design in comparison to older practising architects.Original manuscript published in Meanjin, Vol.17 No.78, pp. 175-178. It was reprinted in the 'Architect' (Perth) Vol.3 No.53, pp. 26-27.Typewritten (c copy), quarto, 6 pagesarchitects, 'slate' magazine, robin boyd, manuscript -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Manuscript, Robin Boyd, What Do We Want of Architecture?, 1971
... the young architects of the period - the idea of usefulness... the young architects of the period - the idea of usefulness ...Boyd questions the current rules of architecture, as do the young architects of the period - the idea of usefulness, firmness, delight and beauty in the visual environment. He says we will only get a more exciting architecture if we ask the question posed in the title.Typewritten pencil edits, quarto, 7 pagesReferences Morris Lapidus and an exhibition at The Architectural League of New York occurring "late last year". URL reference says it occured in 1970.usefulness, firmness, architecture's purpose, role of architecture, robin boyd, manuscript -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyprogram, 1971
... in March 1931 when three young architects, looking to make... in March 1931 when three young architects, looking to make ...This program was made for the Orbost Apex Club to be used on the "change over night" of August 6th 1971. Apex Clubs were begun in March 1931 when three young architects, looking to make a contribution to their local community of Geelong Victoria, decided to create Apex. Apex is a volunteer community service organisation whose members work in local clubs across urban, regional and rural Australia to raise awareness about social justice issues, assist the needy in a practical way and contribute resources to worthwhile causes. (ref Apex website)The Apex Club of Orbost was a volunteer service club which contributed to the Orbost community. A declining population has led to the demise of many social groups in the area.A white triple fold cardboard program. It has blue print on the white background.APEX CLUB OF ORBOST 13th Change Over Nightprogram apex service-club -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, c1924
Taken in 1924, depicted are eleven young men dressed in school uniform attire standing in the playground of Beechworth State School. This group of young men were part of a farcical play titled "School Days" as part of Beechworth State School Concert series. Beechworth Primary School (formally known as Beechworth State School) was constructed in 1875 by architect Henry Bastow (1839 - 1920). Bastow was the chief architect and surveyor for the Victorian Government’s Department of Education. During his chiefship, over six-hundred schools were constructed across the state which was in response to the Victoria’s Education Act of 1872 legislating free, compulsory, and secular education. Performances such as this “School Days” play were common forms of entertainment within Beechworth up into the early twentieth century. This stems from the goldrush period in Beechworth (1852-1866) when travelling entertainers would tour the goldfields offering performances in singing, acting and circus tricks. These were usually held in a local pub or designated concert spaces, such as the Star Theatre in Beechworth. Entertainment offerings begun to slow down mid-twentieth century when the population begun to dwindle. Many locals took up this responsibility and put on their own plays and shows across the town. This photograph is historically significant as it provides insight into the types of entertainment activities held at the Beechworth School during the early twentieth century. It also demonstrates how students engaged with their school outside of their regular schoolwork. Black and white rectangular photograph printed on matte photographic paper mounted on board. Obverse: W.Howes / Beechworth Concert Party 1924 / State School / Beechworth Cyril Smith (Squidgy) / Keith Prowse / Bill Howes / J. Warde / J. Heatherly (Jumbo) / Gea Foster / B. Shallard (Shinky) / A. Foster / Ernie Smith / Jerry Burns / Ted Warden / School Master / Geo Foster in a Farscial Play “School Days” / Reverse: A03065 / 1997.2520 / 79.19.1 / school uniform, beechworth school, school days", concert series., henry bastow, beechworth primary school, victorian government’s department of education, education, victoria’s education act of 1872, beechworth state school -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyDocument - Japanese School of Melbourne
Six documents about the Japanese School: 1/The Japanese School of Melbourne Planning Brief document draft February 1984 to the City of Caulfield. Brief includes background of school, current educational standards of school and structure, future plans, including forecast of future student numbers, request to use prefabricated rooms. Also plans for new building and room alterations. Includes appendice which has current and projection graph of students attending. Period covered: January 1968-February 1984 (17 pages). 2/Fourteen page school prospectus, which includes history and location, term dates, school hours, curriculum subjects, teachers qualifications, health department approval and enrolment list. Also includes Division of School Duties, school educational aims and guidance priorities. Period covered: 07/09/1968-13/05/1986. 3/An 11/11/1988 Melbourne Development and Prospectus for the Japanese School of Melbourne, includes purpose of school, development options, planning brief, construction time, and development program. Includes seven plans and maps of school location and bus routes (14 pages). Prepared for the City of Caulfield on its request. 4/List of representatives of the Japanese School of Melbourne that met with City of Caulfield councilors on 23/11/1988. 5/Black and white photo of 'Ian Rob with Japanese students September 1991', six students included. 6/Colour photograph of 'Mayor Ed Biggs with Japanese students February 1992', thirteen adults and young people included.japanese school of melbourne limited, japanese school, caulfield, holy cross catholic, holy cross school, ellington school, keeron street, mockridge stahle and mitchell architects, architects, secondary schools, primary schools, playgrounds, hawthorn road, caulfield south, yaji hidero, japanese community, yazaki yasuo, morita hiroshi, teachers, bloink des, stokes tony, building surveyors, japanese supplementary school of melbourne, school committees, libraries, school houses, brick, bloink clarke harding consulting architects group, anthony stokes and assoc. building surveyors and town planners, rob ian, biggs ed mayor -
 Ballarat Clarendon College
Ballarat Clarendon CollegePhotograph
In August 1874 the College Trustees agreed to a loan by Mr Leckie of £1500 at 8% over three years, and the foundation stone of a new building, on the corner of Lyons and Sturt Streets in the grounds of St Andrews Kirk, was laid on 12 September by Rev Henderson, founder of the College. Designed by leading Ballarat architect Henry Caselli and built by contractors Taylor and Ellis, the building was opened for January 1875 classes. In February 1875 the original church hall was sold cheaply and moved from the site. The girls' section of the college was moved to the schoolrooms connected with the Baptist Church in Errard Street Sth. The girls school operated 1877 - 1892. Ballarat College moved to current senior campus premises at 1412 Sturt Street in 1912. A plaque commemorating the Caselli building remains on the original site. The photograph features southwest faces of building, surrounded by a picket fence; seven young boys are standing in front of the fence along the Lyons Street side. Grayscale photograph with hessian and card mountBottom right corner of photograph: ....tuhards....caselli, ballarat college, buildings -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaFilm - Documentary, Wind and Sky Productions, Harbour Lights, 2019-2020
Synopsis: “In WW1 Melbourne a pioneering network of women at the Mission to Seafarers called the Ladies Harbour Lights Guild supported sailors who risked their lives at sea. The documentary “Harbour Lights” tells the remarkable story of the Ladies Harbour Lights Guild and the lives of seafarers in early 20th century Melbourne. It focuses on Melbourne’s iconic Mission to Seafarers building, its connection to the Great War and to a unique community of ships crew and volunteers. Featuring Melbourne historians, commentators, archivists and architects and rare footage and images of sailing and social life in and around the ports of Melbourne, this film will inform and connect audiences young and old.” Commissioned by Victorian Government The movie was produced in collaboration with the Mission to Seafarers Victoria. It was directed by Jary Nemo and written and produced by Lucinda Horrocks and Jary Nemo with executive producers Sue Dight and Gordon MacMillan. The film features: Jill Garner Kate Darian-Smith Chris McConville Janet Miller (curator) Gordon MacMillan (former seafarer and board committee member) Narrated by Sharon Turley. Music by Richard Chew (professor of the Arts Academy in Ballarat) The film was presented at several festival in Australia and abroad in 2020-2021. Credits: Narrator Sharon Turley Featuring (in order of appearance) Dr Chris McConville, Gordon MacMillan, Janet Miller, Professor Kate Darian-Smith and Jill Garner With Raul S Gantalao Jr, Escoto Lemuel, Ben Schroeder, Cinda Manins And Ian Fletcher, Yuan Jia, Uma Kothari, Gordon Lansley, William Reed and Cheka Samaranayake Directed by Jary Nemo Written and Produced by Lucinda Horrocks and Jary Nemo Music by Richard Chew Executive Producers Sue Dight and Gordon MacMillan Research advisors Geraldine Brault, Maria Culka, Professor Kate Darian-Smith, Ros Fletcher, Professor Uma Kothari, Dr Barbara Lemon, Catherine McLay, Dr Chris McConville, Janet Miller, Rick Mitchell, Duncan ‘John’ Perryman, Dr Annette Sheill and Peter Taylor Archival photographs, music and footage courtesy of Australian Red Cross Society, Central Highlands Libraries, Internet Archive, National Film and Sound Archive, National Library of Australia, Mackarness Family Personal Archives, Mission to Seafarers Victoria, Public Record Office Victoria, State Library of Victoria and US National Archives Music Harbour Lights. Music by Richard Chew. Westering. Music by Richard Chew. Twilight (Crépuscule) by Jules Massenet. Performed by Amelita Galli-Curci. I Love You So, Waltz from The Merry Widow by Franz Lehár. Performed by Elise Stephenson and Harry Macdonough with Orchestra. Harbour Lights 2. Music by Richard Chew. If I Could Fly by Walking Hearts featuring Jennifer Holm. Courtesy of Epidemic Sound. With thanks to Peter Barrow, Sarah Bartak, Lin Bender AM, Patty Braumueller, Csilla Csongvay, Emer Diviney, Moira Drew, Ian Fletcher, Ajith Jayasuriya, Ben Jones, Patience Jones, Cinda Manins, Madeleine Martiniello, Georgia Melville, Elisabeth Moglia, Tara Oldfield, Lyn Pasquier, Nigel Porteous, Rev’d Onofre (Inni) Punay, Dr Rosalie Triolo, Ben Schroeder, David Simpson, Cheka Samaranayake, Daria Wray, the Helen Macpherson Smith Trust and KPMG. A special thanks to The women of the Ladies Harbour Lights Guild 1906 to 1961 Produced in collaboration with The Mission to Seafarers Victoria Created with the support of The Victorian Government Licensing This film has been released under a Creative Commons BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license Acknowledgement of country Project production and development took place on the lands of the Kulin nation. We acknowledge Traditional Owners and pay our respects to Elders past, present and future. Production company A Wind & Sky Production Copyright with © Wind & Sky Productions MMXIX The film was launched on Wednesday 26th February 2020 at the Mission. Speech by Veterans Affairs. Amongst the guests were current and former volunteers (Maria Culka, Gordon MacMillan, Elisabeth Moglia), curators (Georgia Melville, Jay Miller, Geraldine Brault)18mn documentary mixed of photographs from teh collection and interviews about the Ladies Harbour Lights Guild work during WWIladies harbour lights guild, documentary, jay miller, janet miller, geraldine brault, lucinda horrocks, gordon macmillan, jary nemo, kate darian-smith, jill garner, chris mcconville, sharon turley, richard chew, footage, archive -
 Greensborough Historical Society
Greensborough Historical SocietyCard - Postcard, Christmas card, 1925c
Albert (Gus) Lines was a local architect, councillor, and Greensborough identity in the mid 20th century. This Christmas card is from a young Albert to his teacher Mr Partington. The Partington family were Greensborough pioneers. Connects two Greensborough families in the early 20th century.Coloured postcard depicting sheep on hillside near a track.On back of card: 'To his teacher Mr Partington from Albert Lines'partington family, a k gus lines -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, The Work of Dwight James Baum, 1927 (exact)
Dwight James Baum is an American architect. He was born in 1886 in Newville, New York. As a young man, Baum moved to Syracuse. In 1909, he graduated from Syracuse University with an architecture degree. He worked for Boring and Tilton and Sanford White which are well known Architecture firms in America. Around 1912, he started his own residential design firm. During the 1920s, Baum designed a significant buildings and several houses in Sarasota, Tampa, Terrace, Temple and Florida all in the Mediterranean Revival Style such as the Ringlings dubbed Cà d'Zan, which is now known as the John and Mable Ringling Museum of Art. In 1923-1924, he also designed Sunset Hill for Mrs. Eugene D. Stocker at Warren, New York which was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2007. During the Depression Baum became involved with Good Housekeeping Magazine as consulting architect, and as designer of their building exhibit at the 1933 Chicago World's Fair. His later work includes Hendricks Memorial Chapel at Syracuse University, with John Russell Pope in 1929–1930 and the pedestal for V. Renzo Baldi's statue of Columbus in the city's Columbus Circle. Dwight James Baum died in 1939. Book with large blue hard cover. Title is written on the front cover and the spine in gold. Manufacturer's logo is written on front cover in gold. The book includes index, preface and an introduction. black and white illustrations, plates and floor planes of the architect's work such as Ca d Zan, the fantastical Venetian Gothic waterfront palace of John and Mable Ringling in Sarasota, Florida and the stately Italianate house of Anthony Campagna in Riverdale, New York and more.architecture, architectural designs, art moderne, domestic designs, ca d zan -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBook - Trade Union Rules, Shipwrights' Provident Union of the Port of London, Rules of the Shipwrights' Provident Union of the Port of London, 28-09-1895
A number of items once belonging to shipwright Norman McKenzie were donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village. They are related to Norman’s apprenticeship and certification as a Shipwright in Belfast, his Union membership and his employment as a shipwright in Melbourne. One of the items, a union Rules Book inscribed with the name H.B. Thomas and dated 1902, had within its pages Norman’s Indenture of Apprenticeship, dated 1941, Norman Desmond McKenzie was born in Belfast in 1925 and lived at 10 Pansy Street Belfast, Northern Ireland. At the age of 16 years, he began a 5-year Shipwright’s apprenticeship with Harland & Wolff Limited, Shipbuilding & Engineering Works, Belfast. He became a member of the Ship Constructors’ and Shipwrights’ Association, Belfast (B) Branch 20. His Registration Number was 38748. He completed his apprenticeship on December 16th, 1946, aged 21 years, his address was 26 Connsbrook Drive, Sydenham, N. Belfast. In October 1949 Norman received Clearance from his Union as a financial member to move to another branch. He completed his Apprenticeship on December 16th 1946. Two months later he migrated to Australia, and he arrived in Victoria, and he became a Financial Member of the Victorian branch of the Federated Shipwrights, Ship constructors, Naval Architects, Ships’ Draughtsmen and Boat Builders’ Association of Australia, Victoria branch. One of Norman’s donated books is the Rules of the Shipwrights' Provident Union of the Port of London. It is inscribed on several pages with the name H.B. Thomas and includes the year 1902 and the address of 29 Brickwood Street, Gardenvale. This is a location in Victoria, Australia. The Victoria Government Gazette, February 1959, in the section “Removal from Registration on The Architects Registration Board of Victoria, during the year ended 31st December 1956” lists “Deceased – Thomas, H.B., 29 Brickwood Street, Gardenvale”. The Architects Union includes Naval Architects and Shipwrights and other related trades came under the same union. It seems likely that when he was in Melbourne, Norman worked as a Shipwright for H.B. Thomas and was given the Rules book by Thomas, perhaps as a reference book or maybe as a gift. Around that same time, December 1949, Norman met his wife-to-be, Daphne, in Melbourne. Daphne had migrated from London with her family and her father found work with the Melbourne Harbour Trust. They married in Melbourne in 1953 and went on to have a family of five children. In 2003 Norman and Daphne moved to Warrnambool and then years later they celebrated their 60th wedding anniversary. Norman passed away on July 28th 2015 at Warrnambool’s South West Healthcare hospital. SUBJECTS Flagstaff Hill, Warrnambool, Maritime Village, Maritime Museum, Shipwreck coast, Great Ocean Road, Norman McKenzie, Norman Desmond McKenzie, Belfast shipwright, Shipwright's apprenticeship, Harland & Wolff Limited, Shipbuilding & Engineering Works, the Ship Constructors’ and Shipwrights’ Association, Registered Shipwright, Victorian branch of the Federated Shipwrights, Ship constructors, Naval Architects, Ships’ Draughtsmen and Boat Builders’ Association of Australia, Victoria branch, Shipwrights' Provident Union, H.B. Thomas, Architects Registration Board of Victoria, Naval Architect, Daphne, Norman and Daphne McKenzie, Indenture of Apprenticeship SIGNIFICANCE Norman McKenzie's Rules Book, Union Cards, Indenture of Apprenticeship, and other documents tell the story of a young Irish lad's work and qualifications to become a shipwright and his migration to Australia. The young man found a job and a wife who had also migrated, and they raised a family in Melbourne. He and his wife then retired to Warrnambool to enjoy their later years. The collection of documents relating to Norman McKenzie is significant for its connection with the shipping industry of the early 1900s, the migration of qualified tradesmen to Victoria, and their contribution to the development of Victoria. The collection also shows the role of the Union in the shipping industry. The documents link shipwright Norman McKenzie to the Shipwright's Union in London and in Australia, and to shipbuilder H B Thomas in Melbourne, most likely his employer.Norman McKenzie's Rules Book, Union Cards, Indenture of Apprenticeship, and other documents tell the story of a young Irish lad's work and qualifications to become a shipwright and his migration to Australia. The young man found a job and a wife who had also migrated, and they raised a family in Melbourne. He and his wife then retired to Warrnambool to enjoy their later years. The collection of documents relating to Norman McKenzie is significant for its connection with the shipping industry of the early 1900s, the migration of qualified tradesmen to Victoria, and their contribution to the development of Victoria. The collection also shows the role of the Union in the shipping industry. The documents link shipwright Norman McKenzie to the Shipwright's Union in London and in Australia, and to shipbuilder H B Thomas in Melbourne, most likely his employer. Book, small handbook. Rules of the Shipwrights' Provident Union of the Port of London. Rules were Registered with the Shipwrights' Provident Union of the Port of London, Register No. 527, September 28th 1895. A small book with dark blue textured fabric covers. Pages, 56, are bound with staples. The book has handwritten inscriptions dated 1902.Handwritten in black pen: Inside cover, "H.B. Thomas, 1902" Page 45 "H B Thomas, 29 Brickwood Street, Gardenvale" Page 49, handwritten in blue ink "H B Thomas, 1902"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, norman mckenzie, norman desmond mckenzie, belfast shipwright, shipwright's apprenticeship, harland & wolff limited, shipbuilding & engineering works, the ship constructors’ and shipwrights’ association, registered shipwright, victorian branch of the federated shipwrights, ship constructors, naval architects, ships’ draughtsmen and boat builders’ association of australia, victoria branch, shipwrights' provident union, h.b. thomas, architects registration board of victoria, naval architect, daphne, norman and daphne mckenzie -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Commercial, 1965
... (Handwritten) / ALLEN, JACK & COTTIER ARCHITECTS / 10 YOUNG STREET... ARCHITECTS / 10 YOUNG STREET, SYDNEY / 8 (Handwritten) Colour slide ...Colour slide in a mount. Jacobs House, Wahroonga, New South Wales, Australia, 1963. (Architects: Allen, Jack+Cottier.)Made in Australia / 31 / OCT 65M / Encircled 67 (Handwritten) / ALLEN, JACK & COTTIER ARCHITECTS / 10 YOUNG STREET, SYDNEY / 8 (Handwritten)australia, slide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Commercial, 1965
... , JACK & COTTIER ARCHITECTS / 10 YOUNG STREET, SYDNEY / 6... 65M / 9 (Handwritten) / ALLEN, JACK & COTTIER ARCHITECTS / 10 ...Colour slide in a mount. Jacobs House, Wahroonga, New South Wales, Australia, 1963. (Architects: Allen, Jack+Cottier.)Made in Australia / 20 / OCT 65M / 9 (Handwritten) / ALLEN, JACK & COTTIER ARCHITECTS / 10 YOUNG STREET, SYDNEY / 6 (Handwritten) / 9 (Handwritten)australia, slide, robin boyd -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Commercial, 1965
... , JACK & COTTIER ARCHITECTS / 10 YOUNG STREET, SYDNEY / 7... 65M / 7 (Handwritten) / ALLEN, JACK & COTTIER ARCHITECTS / 10 ...Colour slide in a mount. Jacobs House, Wahroonga, New South Wales, Australia, 1963. (Architects: Allen, Jack+Cottier.)Made in Australia / 22 / OCT 65M / 7 (Handwritten) / ALLEN, JACK & COTTIER ARCHITECTS / 10 YOUNG STREET, SYDNEY / 7 (Handwritten)australia, slide, robin boyd -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Undated
The Wesleyan Church, Denham Street in Lower Hawthorn, as the area was then called, was opened on 2 May 1886. The building was designed by Geelong architect William Henry Cleverdon and was built of brick in the Gothic style. Its dimensions were 55 x 33 ft and the façade incorporated a rose window and spire 50 ft high. A wooden vestry was placed to the rear. The building and the organ were seriously damaged by fire on 1 April 1970, started by a painter's blowtorch. The church was not rebuilt.B & W photograph of a group of young men standing and sitting with the minister outside the Methodist Church in Denham St. Hawthorn.denham street methodist church, organ, hall -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Manuscript, Robin Boyd, The Shape of Parliament House, 1964
Boyd advocates that Canberra's proposed permanent Parliament House needs to be a vital symbol and suggests an open national competition should be used to select the architect.Original manuscript of an article published as 'Young Australia in Steel and Concrete', published in 'The Australian'.Typewritten (c copy), quarto, 5 pagescanberra, parliament house, national competition, robin boyd, manuscript, national capital -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationDocument - Manuscript, Robin Boyd, The Nerve Of Our Students, 1965
... published as ‘Young architects show their nerve’ in 'The Australian ...Discusses and approves of the initiative of Australian architecture students shown by their holding their own architectural convention. The convention tackled the issues of the 'House of Tomorrow' and the types of technology that that can be manipulated and used for better design. Students also invited international guests to comment and judge the exhibition.Original manuscript published as ‘Young architects show their nerve’ in 'The Australian' on 19.06.1965. Typewritten (c copy), quarto, 4 pageseric lyons, tom marshall, john blanshard, patwant singh, robin boyd, manuscript -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photographs, L.J. Gervasoni, Boroondara General Cemetery Springthorpe Memorial, c2005-2015
The Boroondara General Cemetery is registerd by Heritage VictoriaFrom Heritage Victoria Statement of Significance Last updated on - December 15, 2005 What is significant? Boroondara Cemetery, established in 1858, is within an unusual triangular reserve bounded by High Street, Park Hill Road and Victoria Park, Kew. The caretaker's lodge and administrative office (1860 designed by Charles Vickers, additions, 1866-1899 by Albert Purchas) form a picturesque two-storey brick structure with a slate roof and clock tower. A rotunda or shelter (1890, Albert Purchas) is located in the centre of the cemetery: this has an octagonal hipped roof with fish scale slates and a decorative brick base with a tessellated floor and timber seating. The cemetery is surrounded by a 2.7 metre high ornamental red brick wall (1895-96, Albert Purchas) with some sections of vertical iron palisades between brick pillars. Albert Purchas was a prominent Melbourne architect who was the Secretary of the Melbourne General Cemetery from 1852 to 1907 and Chairman of the Boroondara Cemetery Board of Trustees from 1867 to 1909. He made a significant contribution to the design of the Boroondara Cemetery Boroondara Cemetery is an outstanding example of the Victorian Garden Cemetery movement in Victoria, retaining key elements of the style, despite overdevelopment which has obscured some of the paths and driveways. Elements of the style represented at Boroondara include an ornamental boundary fence, a system of curving paths which are kerbed and follow the site's natural contours, defined views, recreational facilities such as the rotunda, a landscaped park like setting, sectarian divisions for burials, impressive monuments, wrought and cast iron grave surrounds and exotic symbolic plantings. In the 1850s cemeteries were located on the periphery of populated areas because of concerns about diseases like cholera. They were designed to be attractive places for mourners and visitors to walk and contemplate. Typically cemeteries were arranged to keep religions separated and this tended to maintain links to places of origin, reflecting a migrant society. Other developments included cast iron entrance gates, built in 1889 to a design by Albert Purchas; a cemetery shelter or rotunda, built in 1890, which is a replica of one constructed in the Melbourne General Cemetery in the same year; an ornamental brick fence erected in 1896-99(?); the construction and operation of a terminus for a horse tram at the cemetery gates during 1887-1915; and the Springthorpe Memorial built between 1897 and 1907. A brick cremation wall and a memorial rose garden were constructed near the entrance in the mid- twentieth century(c.1955-57) and a mausoleum completed in 2001.The maintenance shed/depot close to High Street was constructed in 1987. The original entrance was altered in 2000 and the original cast iron gates moved to the eastern entrance of the Mausoleum. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522) set at the entrance to the burial ground commemorates Annie Springthorpe, and was erected between 1897 and 1907 by her husband Dr John Springthorpe. It was the work of the sculptor Bertram Mackennal, architect Harold Desbrowe Annear, landscape designer and Director of the Melbourne Bortanic Gardens, W.R. Guilfoyle, with considerable input from Dr Springthorpe The memorial is in the form of a small temple in a primitive Doric style. It was designed by Harold Desbrowe Annear and includes Bertram Mackennal sculptures in Carrara marble. Twelve columns of deep green granite from Scotland support a Harcourt granite superstructure. The roof by Brooks Robinson is a coloured glass dome, which sits within the rectangular form and behind the pediments. The sculptural group raised on a dais, consists of the deceased woman lying on a sarcophagus with an attending angel and mourner. The figure of Grief crouches at the foot of the bier and an angel places a wreath over Annie's head, symbolising the triumph of immortal life over death. The body of the deceased was placed in a vault below. The bronze work is by Marriots of Melbourne. Professor Tucker of the University of Melbourne composed appropriate inscriptions in English and archaic Greek lettering.. The floor is a geometric mosaic and the glass dome roof is of Tiffany style lead lighting in hues of reds and pinks in a radiating pattern. The memorial originally stood in a landscape triangular garden of about one acre near the entrance to the cemetery. However, after Dr Springthorpe's death in 1933 it was found that transactions for the land had not been fully completed so most of it was regained by the cemetery. A sundial and seat remain. The building is almost completely intact. The only alteration has been the removal of a glass canopy over the statuary and missing chains between posts. The Argus (26 March 1933) considered the memorial to be the most beautiful work of its kind in Australia. No comparable buildings are known. The Syme Memorial (1908) is a memorial to David Syme, political economist and publisher of the Melbourne Age newspaper. The Egyptian memorial designed by architect Arthur Peck is one of the most finely designed and executed pieces of monumental design in Melbourne. It has a temple like form with each column having a different capital detail. These support a cornice that curves both inwards and outwards. The tomb also has balustradings set between granite piers which create porch spaces leading to the entrance ways. Two variegated Port Jackson Figs are planted at either end. The Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036) was constructed in 1912-13 by Sir Leo Cussen in memory of his young son Hubert. Sir Leo Finn Bernard Cussen (1859-1933), judge and member of the Victorian Supreme Court in 1906. was buried here. The family memorial is one of the larger and more impressive memorials in the cemetery and is an interesting example of the 1930s Gothic Revival style architecture. It takes the form of a small chapel with carvings, diamond shaped roof tiles and decorated ridge embellishing the exterior. By the 1890s, the Boroondara Cemetery was a popular destination for visitors and locals admiring the beauty of the grounds and the splendid monuments. The edge of suburban settlement had reached the cemetery in the previous decade. Its Victorian garden design with sweeping curved drives, hill top views and high maintenance made it attractive. In its Victorian Garden Cemetery design, Boroondara was following an international trend. The picturesque Romanticism of the Pere la Chaise garden cemetery established in Paris in 1804 provided a prototype for great metropolitan cemeteries such as Kensal Green (1883) and Highgate (1839) in London and the Glasgow Necropolis (1831). Boroondara Cemetery was important in establishing this trend in Australia. The cemetery's beauty peaked with the progressive completion of the spectacular Springthorpe Memorial between 1899 and 1907. From about the turn of the century, the trustees encroached on the original design, having repeatedly failed in attempts to gain more land. The wide plantations around road boundaries, grassy verges around clusters of graves in each denomination, and most of the landscaped surround to the Springthorpe memorial are now gone. Some of the original road and path space were resumed for burial purposes. The post war period saw an increased use of the Cemetery by newer migrant groups. The mid- to late- twentieth century monuments were often placed on the grassed edges of the various sections and encroached on the roadways as the cemetery had reached the potential foreseen by its design. These were well tended in comparison with Victorian monuments which have generally been left to fall into a state of neglect. The Boroondara Cemetery features many plants, mostly conifers and shrubs of funerary symbolism, which line the boundaries, road and pathways, and frame the cemetery monuments or are planted on graves. The major plantings include an impressive row of Bhutan Cypress (Cupressus torulosa), interplanted with Sweet Pittosporum (Pittosporum undulatum), and a few Pittosporum crassifolium, along the High Street and Parkhill Street, where the planting is dominated by Sweet Pittosporum. Planting within the cemetery includes rows and specimen trees of Bhutan Cypress and Italian Cypress (Cupressus sempervirens), including a row with alternate plantings of both species. The planting includes an unusual "squat" form of an Italian Cypress. More of these trees probably lined the cemetery roads and paths. Also dominating the cemetery landscape near the Rotunda is a stand of 3 Canary Island Pines (Pinus canariensis), a Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii) and a Weeping Elm (Ulmus glabra 'Camperdownii') Amongst the planting are the following notable conifers: a towering Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii), a Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens), a rare Golden Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea'), two large Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris), and the only known Queensland Kauri (Agathis robusta) in a cemetery in Victoria. The Cemetery records, including historical plans of the cemetery from 1859, are held by the administration and their retention enhances the historical significance of the Cemetery. How is it significant? Boroondara Cemetery is of aesthetic, architectural, scientific (botanical) and historical significance to the State of Victoria. Why is it significant? The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical and aesthetic significance as an outstanding example of a Victorian garden cemetery. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance as a record of Victorian life from the 1850s, and the early settlement of Kew. It is also significant for its ability to demonstrate, through the design and location of the cemetery, attitudes towards burial, health concerns and the importance placed on religion, at the time of its establishment. The Boroondara Cemetery is of architectural significance for the design of the gatehouse or sexton's lodge and cemetery office (built in stages from 1860 to 1899), the ornamental brick perimeter fence and elegant cemetery shelter to the design of prominent Melbourne architects, Charles Vickers (for the original 1860 cottage) and Albert Purchas, cemetery architect and secretary from 1864 to his death in 1907. The Boroondara Cemetery has considerable aesthetic significance which is principally derived from its tranquil, picturesque setting; its impressive memorials and monuments; its landmark features such as the prominent clocktower of the sexton's lodge and office, the mature exotic plantings, the decorative brick fence and the entrance gates; its defined views; and its curving paths. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522), the Syme Memorial and the Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036), all contained within the Boroondara Cemetery, are of aesthetic and architectural significance for their creative and artistic achievement. The Boroondara Cemetery is of scientific (botanical) significance for its collection of rare mature exotic plantings. The Golden Funeral Cypress, (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea') is the only known example in Victoria. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance for the graves, monuments and epitaphs of a number of individuals whose activities have played a major part in Australia's history. They include the Henty family, artists Louis Buvelot and Charles Nuttall, businessmen John Halfey and publisher David Syme, artist and diarist Georgiana McCrae, actress Nellie Stewart and architect and designer of the Boroondara and Melbourne General Cemeteries, Albert Purchas.Digital image of the Springthorpe Memorial in the Boroondara General Cemeterycemetery, boroondara, kew, gatehouse, clock, tower, clocktower, heritage, memorial, springthorpe memorial -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photographs, Cussen Memorial in the Boroondara General Cemetery, Kew, Victoria, c2005-2015
The Boroondara General Cemetery is registerd by Heritage VictoriaFrom Heritage Victoria Statement of Significance Last updated on - December 15, 2005 What is significant? Boroondara Cemetery, established in 1858, is within an unusual triangular reserve bounded by High Street, Park Hill Road and Victoria Park, Kew. The caretaker's lodge and administrative office (1860 designed by Charles Vickers, additions, 1866-1899 by Albert Purchas) form a picturesque two-storey brick structure with a slate roof and clock tower. A rotunda or shelter (1890, Albert Purchas) is located in the centre of the cemetery: this has an octagonal hipped roof with fish scale slates and a decorative brick base with a tessellated floor and timber seating. The cemetery is surrounded by a 2.7 metre high ornamental red brick wall (1895-96, Albert Purchas) with some sections of vertical iron palisades between brick pillars. Albert Purchas was a prominent Melbourne architect who was the Secretary of the Melbourne General Cemetery from 1852 to 1907 and Chairman of the Boroondara Cemetery Board of Trustees from 1867 to 1909. He made a significant contribution to the design of the Boroondara Cemetery Boroondara Cemetery is an outstanding example of the Victorian Garden Cemetery movement in Victoria, retaining key elements of the style, despite overdevelopment which has obscured some of the paths and driveways. Elements of the style represented at Boroondara include an ornamental boundary fence, a system of curving paths which are kerbed and follow the site's natural contours, defined views, recreational facilities such as the rotunda, a landscaped park like setting, sectarian divisions for burials, impressive monuments, wrought and cast iron grave surrounds and exotic symbolic plantings. In the 1850s cemeteries were located on the periphery of populated areas because of concerns about diseases like cholera. They were designed to be attractive places for mourners and visitors to walk and contemplate. Typically cemeteries were arranged to keep religions separated and this tended to maintain links to places of origin, reflecting a migrant society. Other developments included cast iron entrance gates, built in 1889 to a design by Albert Purchas; a cemetery shelter or rotunda, built in 1890, which is a replica of one constructed in the Melbourne General Cemetery in the same year; an ornamental brick fence erected in 1896-99(?); the construction and operation of a terminus for a horse tram at the cemetery gates during 1887-1915; and the Springthorpe Memorial built between 1897 and 1907. A brick cremation wall and a memorial rose garden were constructed near the entrance in the mid- twentieth century(c.1955-57) and a mausoleum completed in 2001.The maintenance shed/depot close to High Street was constructed in 1987. The original entrance was altered in 2000 and the original cast iron gates moved to the eastern entrance of the Mausoleum. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522) set at the entrance to the burial ground commemorates Annie Springthorpe, and was erected between 1897 and 1907 by her husband Dr John Springthorpe. It was the work of the sculptor Bertram Mackennal, architect Harold Desbrowe Annear, landscape designer and Director of the Melbourne Bortanic Gardens, W.R. Guilfoyle, with considerable input from Dr Springthorpe The memorial is in the form of a small temple in a primitive Doric style. It was designed by Harold Desbrowe Annear and includes Bertram Mackennal sculptures in Carrara marble. Twelve columns of deep green granite from Scotland support a Harcourt granite superstructure. The roof by Brooks Robinson is a coloured glass dome, which sits within the rectangular form and behind the pediments. The sculptural group raised on a dais, consists of the deceased woman lying on a sarcophagus with an attending angel and mourner. The figure of Grief crouches at the foot of the bier and an angel places a wreath over Annie's head, symbolising the triumph of immortal life over death. The body of the deceased was placed in a vault below. The bronze work is by Marriots of Melbourne. Professor Tucker of the University of Melbourne composed appropriate inscriptions in English and archaic Greek lettering.. The floor is a geometric mosaic and the glass dome roof is of Tiffany style lead lighting in hues of reds and pinks in a radiating pattern. The memorial originally stood in a landscape triangular garden of about one acre near the entrance to the cemetery. However, after Dr Springthorpe's death in 1933 it was found that transactions for the land had not been fully completed so most of it was regained by the cemetery. A sundial and seat remain. The building is almost completely intact. The only alteration has been the removal of a glass canopy over the statuary and missing chains between posts. The Argus (26 March 1933) considered the memorial to be the most beautiful work of its kind in Australia. No comparable buildings are known. The Syme Memorial (1908) is a memorial to David Syme, political economist and publisher of the Melbourne Age newspaper. The Egyptian memorial designed by architect Arthur Peck is one of the most finely designed and executed pieces of monumental design in Melbourne. It has a temple like form with each column having a different capital detail. These support a cornice that curves both inwards and outwards. The tomb also has balustradings set between granite piers which create porch spaces leading to the entrance ways. Two variegated Port Jackson Figs are planted at either end. The Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036) was constructed in 1912-13 by Sir Leo Cussen in memory of his young son Hubert. Sir Leo Finn Bernard Cussen (1859-1933), judge and member of the Victorian Supreme Court in 1906. was buried here. The family memorial is one of the larger and more impressive memorials in the cemetery and is an interesting example of the 1930s Gothic Revival style architecture. It takes the form of a small chapel with carvings, diamond shaped roof tiles and decorated ridge embellishing the exterior. By the 1890s, the Boroondara Cemetery was a popular destination for visitors and locals admiring the beauty of the grounds and the splendid monuments. The edge of suburban settlement had reached the cemetery in the previous decade. Its Victorian garden design with sweeping curved drives, hill top views and high maintenance made it attractive. In its Victorian Garden Cemetery design, Boroondara was following an international trend. The picturesque Romanticism of the Pere la Chaise garden cemetery established in Paris in 1804 provided a prototype for great metropolitan cemeteries such as Kensal Green (1883) and Highgate (1839) in London and the Glasgow Necropolis (1831). Boroondara Cemetery was important in establishing this trend in Australia. The cemetery's beauty peaked with the progressive completion of the spectacular Springthorpe Memorial between 1899 and 1907. From about the turn of the century, the trustees encroached on the original design, having repeatedly failed in attempts to gain more land. The wide plantations around road boundaries, grassy verges around clusters of graves in each denomination, and most of the landscaped surround to the Springthorpe memorial are now gone. Some of the original road and path space were resumed for burial purposes. The post war period saw an increased use of the Cemetery by newer migrant groups. The mid- to late- twentieth century monuments were often placed on the grassed edges of the various sections and encroached on the roadways as the cemetery had reached the potential foreseen by its design. These were well tended in comparison with Victorian monuments which have generally been left to fall into a state of neglect. The Boroondara Cemetery features many plants, mostly conifers and shrubs of funerary symbolism, which line the boundaries, road and pathways, and frame the cemetery monuments or are planted on graves. The major plantings include an impressive row of Bhutan Cypress (Cupressus torulosa), interplanted with Sweet Pittosporum (Pittosporum undulatum), and a few Pittosporum crassifolium, along the High Street and Parkhill Street, where the planting is dominated by Sweet Pittosporum. Planting within the cemetery includes rows and specimen trees of Bhutan Cypress and Italian Cypress (Cupressus sempervirens), including a row with alternate plantings of both species. The planting includes an unusual "squat" form of an Italian Cypress. More of these trees probably lined the cemetery roads and paths. Also dominating the cemetery landscape near the Rotunda is a stand of 3 Canary Island Pines (Pinus canariensis), a Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii) and a Weeping Elm (Ulmus glabra 'Camperdownii') Amongst the planting are the following notable conifers: a towering Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii), a Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens), a rare Golden Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea'), two large Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris), and the only known Queensland Kauri (Agathis robusta) in a cemetery in Victoria. The Cemetery records, including historical plans of the cemetery from 1859, are held by the administration and their retention enhances the historical significance of the Cemetery. How is it significant? Boroondara Cemetery is of aesthetic, architectural, scientific (botanical) and historical significance to the State of Victoria. Why is it significant? The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical and aesthetic significance as an outstanding example of a Victorian garden cemetery. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance as a record of Victorian life from the 1850s, and the early settlement of Kew. It is also significant for its ability to demonstrate, through the design and location of the cemetery, attitudes towards burial, health concerns and the importance placed on religion, at the time of its establishment. The Boroondara Cemetery is of architectural significance for the design of the gatehouse or sexton's lodge and cemetery office (built in stages from 1860 to 1899), the ornamental brick perimeter fence and elegant cemetery shelter to the design of prominent Melbourne architects, Charles Vickers (for the original 1860 cottage) and Albert Purchas, cemetery architect and secretary from 1864 to his death in 1907. The Boroondara Cemetery has considerable aesthetic significance which is principally derived from its tranquil, picturesque setting; its impressive memorials and monuments; its landmark features such as the prominent clocktower of the sexton's lodge and office, the mature exotic plantings, the decorative brick fence and the entrance gates; its defined views; and its curving paths. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522), the Syme Memorial and the Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036), all contained within the Boroondara Cemetery, are of aesthetic and architectural significance for their creative and artistic achievement. The Boroondara Cemetery is of scientific (botanical) significance for its collection of rare mature exotic plantings. The Golden Funeral Cypress, (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea') is the only known example in Victoria. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance for the graves, monuments and epitaphs of a number of individuals whose activities have played a major part in Australia's history. They include the Henty family, artists Louis Buvelot and Charles Nuttall, businessmen John Halfey and publisher David Syme, artist and diarist Georgiana McCrae, actress Nellie Stewart and architect and designer of the Boroondara and Melbourne General Cemeteries, Albert Purchas.Digital imagescemetery, boroondara, kew, gatehouse, clock, tower, clocktower, heritage, memorial, cussen -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Black and White, Chinese Sunday School, Main Road, Ballarat East, 2003
The Chinese School was attached/run by the Town Mission. "THE CHINESE SUNDAY SCHOOL . The opening services of the newly erected Chinese Sunday school building in connection with the Town Mission, were brought to a close on Monday night by a tea and public meeting, held in the Mission Hall. The now building, which presents a very nice appearance, and is an improvement to that part of the Main road, was erected at a cost of £95 ; Mr H. R. Caselli acting as honorary architect, kindly prepared plans, etc. A new front fence was erected at a cost of £l6, which, with all other expenses, amounted to £126 3s 6d. Previously to the present effort collections and subscriptions were obtained as follow; —Mr Burnett's service, £l8 11s 5d; Chinese Sunday school anniversary, £9 16s 10d; concert on Easter Monday, £8 15s; Phoenix Foundry, per Mr Pethard, £7; sub scriptions, £23 8s 6d, leaving a debtor balance of £57 7s 9d. The. collections on Sunday were good. Mr Lee Young, of the Chinese store, Main road, kindly gave the tea, whioh was a valuable donation. The proceeds of the tea meeting will be about £l0. The building was prettily decorated by Mr Chessell, Mrs King Hook, and the gir!s.connected with the sohool. Mr Moorshead, the caterer, gave all the school children tea gratis- Mrs Lee Young, Miss Emma Lee Young. Miss G. Kay, Miss J. Hong Gong, Mrs King Hook, Mrs Stoneman, and Mrs Pethard waited at tables. Mr M. D. Morgan presided at the public meeting in the Mission Hall, and was supported platform by the Mayor of Ballarat East, the Revs. J. White, J. J. Perrin, and E. Turner, who delivered excellent and suitable speeches; but previously, however, offers of donations - to clear off the debt were made by Mr D. Ham, £10; the chairman, £5; Mr and Mrs Whitrick, £2 17s; a number of donors of £1 each, and less sums, which, with the collec tions, amounted to £58 16s 7d. This sum, with the sale of the cottage.on the ground, clears the debt, and leaves the com mittee a few pounds in hand towards lining and seating the building. A pleas ing feature in the meeting was the hearty giving of several Chinese Christians, including Mr Le Young; also singing by the Chinese chil dren, led by Mr Pethard. When the result was made known tbe whole, meeting stood and sang —“ Praise God from whom all blessings flow," for the success in having the place opened free of debt. Votes of thanks were passed to Mr Caselli, and all who took part in the effort: and one of the happiest meetings ever hold by the mission was brought to a close by again singing the doxology and the benediction." Ballarat Star, 27 February 1885)Black and white image of a weather board school known as the Chinese School, Ballarat.chinese school, ballarat, ballarat town and city mission, chinese, education, school, chinese sunday school -
 Robin Boyd Foundation
Robin Boyd FoundationSlide, Commercial, 1964
Colour slide in a mount. Jacobs House, Wahroonga, New South Wales, Australia, 1963. (Architects: Allen, Jack+Cottier.)Made in Australia / 25 / OCT 64M / ALLEN, JACK & COTTIER ARCHTECTS. / TEL. 27-7981 / 10 YOUNG STREET, SYDNEYaustralia, slide, robin boyd -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncClothing - Pink Cotton Dress, Norma Tullo, c.1965
Norma Tullo began her dressmaking business in 1956. At the age of 20, she rented a small shop in the Metropole Arcade, initiating a career that included manufacturing, designing and retailing. In 1965, she became the first Australian to be selected by Butterick Company Inclusive to join their pattern making company. The stylish Tullo ‘look’ in the first half of the 1960s was young, colourful, feminine and most importantly had a strong American appeal. The patterns were distributed worldwide except to Russia and Germany. At this time, she had a collection of 300 garments. This dress is one of a number of items donated to the Fashion Collection by Dione McIntyre.The McIntyre Collection of clothing and clothing accessories forms one of the largest single donations to our Fashion & Design collection. It includes clothing and clothing accessories worn by four women in the Cohen and McIntyre families across three generations. The items worn by Melbourne architect, and Kew resident, Dione McIntyre date from the 1960s and 1970s, and include evening wear, day wear, hats and shoes. As Dione McIntyre often accompanied her husband, fellow architect Peter McIntyre, to formal events, there are a number of pieces of evening wear among the items. The McIntyre Collection also includes items worn by women of an earlier generation: by Lilian Cohen, Dione McIntyre's mother, and by her mother-in-law, the wife of the architect Robert McIntyre. At the other end of the chronological spectrum are a number of outfits belonging to, worn and donated by Annie McIntyre. These include outfits created by notable late 20th century Australian and/or international fashion designers. The McIntyre Collection is significant historically and artistically as it includes examples of design that demonstrate changing tastes in fashion over an 80-year period. The collection is also significant in that it includes the work of a large number of Melbourne designers from the 1960s to the 1990s. Long sleeved, pale pink cotton mini dress designed by Norma Tullo with ruffled trims on the bodice and the hem of the skirtLabel: TULLOnorma tullo, australian fashion - 1960s, mcintyre collection, mini-dresses, day dresses -
 Surrey Hills Historical Society Collection
Surrey Hills Historical Society CollectionWork on paper - Newsletter, Holy Redeemer - St Joseph's Weekly Notice Sheet, c 14 December 1967
In 1901, Fr George Robinson, Parish Priest of Camberwell purchased the present site of Our Holy Redeemer Church, Surrey Hills, which at the time came within the Camberwell Parish. The owner of the land was reluctant to sell to the Catholic Church, but Miss Amy Castles, a noted singer and friend of Fr Robinson, purchased the land in her own name and then transferred it to the church. On 11 May 1902, the Church of the Most Holy Redeemer (the original title of the church) was blessed and opened by Archbishop Thomas Carr, Archbishop of Melbourne. The architect was A. A. Fritsch. The cost was £3,500. In 1904, Fr. Robinson constructed a weatherboard school-hall (later replaced by a brick hall). Archbishop Mannix opened and blessed the new brick school on 10 November 1918. Fr Tim Fitzpatrick was the third parish priest and served from 1941-1972. A slightly yellowed foolscap sheet printed on both sides detailing the activities of the Surrey Hills parish around Easter in April 1972.st joseph's convent, holy redeemer, catholic church, fr tim fitzpatrick, fr n mackay, b mcdonald, j moloney, k lourey, r kennedy, francis baker, mary gertrude mier, veronica fitton, dorothy erwin, terry young, carmel young, junior youth club, joan murphy, mr hurley, mrs kit o'neil, pat galletti, mothers' club, ed curmi, peter burns, angela lamaro, mary owen, helen buckley, p heffernan, n griffith, g mooney, a dignam, e rankin, d mooney, sister margarida -
 Vision Australia
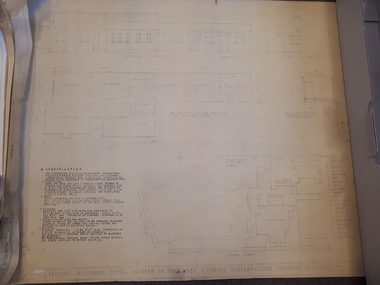
Vision AustraliaPlan - Image, Proposed additional nurses bedroom to "Myer Home" existing nursery, Blind Institute, St Kilda Rd, 23/8/1949
In 1949 an architect produced this plan to detail the addition of a bedroom for the nursing staff, who looked after children in the Blind Babies nursery. The plan shows a layout of the RVIB site, including the 'Myers Home' (the name of the nursery) where young children were cared for. The south and eastern elevations are detailed, as well as a plan of the nursery, which had 4 bedrooms, a living room, a dinning room , bathroom, 2 kitchen areas and the proposed additional nurses bedroom next to Bedroom 4.1 architectural plan of Myer House and proposed extensionPercy E Everett, Chief Architectroyal victorian institute for the blind, rvib nursery, plans, myer house -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaImage, 2001 Vision Australia Library Awards, 2001
To encourage the development of audio books, a series of awards were established by the National Library of Australia in 1988, and sponsored by TDK from 1991 until their demise in 2000. Open to both commercial and non-commercial publishers, it aimed to recognise the quality achievements by individuals and publishing houses and to promote the inclusion of audio books into the mainstream market. After the conclusion, Vision Australia Foundation decided to continue the awards in-house.1 digital imageVision Australia Library Awards 2001 2001 Braille Book of the Year: The Shark Net by Robert Drewe 2001 Sanderson Young Adult Narrator of the Year: David Tredinnick for Max 2001 Sanderson Young Adult Audio Book of the Year: Whistle Man by Brian Ridden 2001 Adult Narrator of the Year: Deidre Rubenstein and James Wright for The Architect 2001 Adult Audio Book of the Year: Conditions of Faith by Alex Millervision australia foundation -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Digital photographs, L.J. Gervasoni, Henty Memorial in Boroondara General Cemetery, c2005-2015
The Boroondara General Cemetery is registered by Heritage Victoria. The Henty's were some of the earliest settlers in Victoria.From Heritage Victoria Statement of Significance Last updated on - December 15, 2005 What is significant? Boroondara Cemetery, established in 1858, is within an unusual triangular reserve bounded by High Street, Park Hill Road and Victoria Park, Kew. The caretaker's lodge and administrative office (1860 designed by Charles Vickers, additions, 1866-1899 by Albert Purchas) form a picturesque two-storey brick structure with a slate roof and clock tower. A rotunda or shelter (1890, Albert Purchas) is located in the centre of the cemetery: this has an octagonal hipped roof with fish scale slates and a decorative brick base with a tessellated floor and timber seating. The cemetery is surrounded by a 2.7 metre high ornamental red brick wall (1895-96, Albert Purchas) with some sections of vertical iron palisades between brick pillars. Albert Purchas was a prominent Melbourne architect who was the Secretary of the Melbourne General Cemetery from 1852 to 1907 and Chairman of the Boroondara Cemetery Board of Trustees from 1867 to 1909. He made a significant contribution to the design of the Boroondara Cemetery Boroondara Cemetery is an outstanding example of the Victorian Garden Cemetery movement in Victoria, retaining key elements of the style, despite overdevelopment which has obscured some of the paths and driveways. Elements of the style represented at Boroondara include an ornamental boundary fence, a system of curving paths which are kerbed and follow the site's natural contours, defined views, recreational facilities such as the rotunda, a landscaped park like setting, sectarian divisions for burials, impressive monuments, wrought and cast iron grave surrounds and exotic symbolic plantings. In the 1850s cemeteries were located on the periphery of populated areas because of concerns about diseases like cholera. They were designed to be attractive places for mourners and visitors to walk and contemplate. Typically cemeteries were arranged to keep religions separated and this tended to maintain links to places of origin, reflecting a migrant society. Other developments included cast iron entrance gates, built in 1889 to a design by Albert Purchas; a cemetery shelter or rotunda, built in 1890, which is a replica of one constructed in the Melbourne General Cemetery in the same year; an ornamental brick fence erected in 1896-99(?); the construction and operation of a terminus for a horse tram at the cemetery gates during 1887-1915; and the Springthorpe Memorial built between 1897 and 1907. A brick cremation wall and a memorial rose garden were constructed near the entrance in the mid- twentieth century(c.1955-57) and a mausoleum completed in 2001.The maintenance shed/depot close to High Street was constructed in 1987. The original entrance was altered in 2000 and the original cast iron gates moved to the eastern entrance of the Mausoleum. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522) set at the entrance to the burial ground commemorates Annie Springthorpe, and was erected between 1897 and 1907 by her husband Dr John Springthorpe. It was the work of the sculptor Bertram Mackennal, architect Harold Desbrowe Annear, landscape designer and Director of the Melbourne Bortanic Gardens, W.R. Guilfoyle, with considerable input from Dr Springthorpe The memorial is in the form of a small temple in a primitive Doric style. It was designed by Harold Desbrowe Annear and includes Bertram Mackennal sculptures in Carrara marble. Twelve columns of deep green granite from Scotland support a Harcourt granite superstructure. The roof by Brooks Robinson is a coloured glass dome, which sits within the rectangular form and behind the pediments. The sculptural group raised on a dais, consists of the deceased woman lying on a sarcophagus with an attending angel and mourner. The figure of Grief crouches at the foot of the bier and an angel places a wreath over Annie's head, symbolising the triumph of immortal life over death. The body of the deceased was placed in a vault below. The bronze work is by Marriots of Melbourne. Professor Tucker of the University of Melbourne composed appropriate inscriptions in English and archaic Greek lettering.. The floor is a geometric mosaic and the glass dome roof is of Tiffany style lead lighting in hues of reds and pinks in a radiating pattern. The memorial originally stood in a landscape triangular garden of about one acre near the entrance to the cemetery. However, after Dr Springthorpe's death in 1933 it was found that transactions for the land had not been fully completed so most of it was regained by the cemetery. A sundial and seat remain. The building is almost completely intact. The only alteration has been the removal of a glass canopy over the statuary and missing chains between posts. The Argus (26 March 1933) considered the memorial to be the most beautiful work of its kind in Australia. No comparable buildings are known. The Syme Memorial (1908) is a memorial to David Syme, political economist and publisher of the Melbourne Age newspaper. The Egyptian memorial designed by architect Arthur Peck is one of the most finely designed and executed pieces of monumental design in Melbourne. It has a temple like form with each column having a different capital detail. These support a cornice that curves both inwards and outwards. The tomb also has balustradings set between granite piers which create porch spaces leading to the entrance ways. Two variegated Port Jackson Figs are planted at either end. The Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036) was constructed in 1912-13 by Sir Leo Cussen in memory of his young son Hubert. Sir Leo Finn Bernard Cussen (1859-1933), judge and member of the Victorian Supreme Court in 1906. was buried here. The family memorial is one of the larger and more impressive memorials in the cemetery and is an interesting example of the 1930s Gothic Revival style architecture. It takes the form of a small chapel with carvings, diamond shaped roof tiles and decorated ridge embellishing the exterior. By the 1890s, the Boroondara Cemetery was a popular destination for visitors and locals admiring the beauty of the grounds and the splendid monuments. The edge of suburban settlement had reached the cemetery in the previous decade. Its Victorian garden design with sweeping curved drives, hill top views and high maintenance made it attractive. In its Victorian Garden Cemetery design, Boroondara was following an international trend. The picturesque Romanticism of the Pere la Chaise garden cemetery established in Paris in 1804 provided a prototype for great metropolitan cemeteries such as Kensal Green (1883) and Highgate (1839) in London and the Glasgow Necropolis (1831). Boroondara Cemetery was important in establishing this trend in Australia. The cemetery's beauty peaked with the progressive completion of the spectacular Springthorpe Memorial between 1899 and 1907. From about the turn of the century, the trustees encroached on the original design, having repeatedly failed in attempts to gain more land. The wide plantations around road boundaries, grassy verges around clusters of graves in each denomination, and most of the landscaped surround to the Springthorpe memorial are now gone. Some of the original road and path space were resumed for burial purposes. The post war period saw an increased use of the Cemetery by newer migrant groups. The mid- to late- twentieth century monuments were often placed on the grassed edges of the various sections and encroached on the roadways as the cemetery had reached the potential foreseen by its design. These were well tended in comparison with Victorian monuments which have generally been left to fall into a state of neglect. The Boroondara Cemetery features many plants, mostly conifers and shrubs of funerary symbolism, which line the boundaries, road and pathways, and frame the cemetery monuments or are planted on graves. The major plantings include an impressive row of Bhutan Cypress (Cupressus torulosa), interplanted with Sweet Pittosporum (Pittosporum undulatum), and a few Pittosporum crassifolium, along the High Street and Parkhill Street, where the planting is dominated by Sweet Pittosporum. Planting within the cemetery includes rows and specimen trees of Bhutan Cypress and Italian Cypress (Cupressus sempervirens), including a row with alternate plantings of both species. The planting includes an unusual "squat" form of an Italian Cypress. More of these trees probably lined the cemetery roads and paths. Also dominating the cemetery landscape near the Rotunda is a stand of 3 Canary Island Pines (Pinus canariensis), a Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii) and a Weeping Elm (Ulmus glabra 'Camperdownii') Amongst the planting are the following notable conifers: a towering Bunya Bunya Pine (Araucaria bidwillii), a Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens), a rare Golden Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea'), two large Funeral Cypress (Chamaecyparis funebris), and the only known Queensland Kauri (Agathis robusta) in a cemetery in Victoria. The Cemetery records, including historical plans of the cemetery from 1859, are held by the administration and their retention enhances the historical significance of the Cemetery. How is it significant? Boroondara Cemetery is of aesthetic, architectural, scientific (botanical) and historical significance to the State of Victoria. Why is it significant? The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical and aesthetic significance as an outstanding example of a Victorian garden cemetery. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance as a record of Victorian life from the 1850s, and the early settlement of Kew. It is also significant for its ability to demonstrate, through the design and location of the cemetery, attitudes towards burial, health concerns and the importance placed on religion, at the time of its establishment. The Boroondara Cemetery is of architectural significance for the design of the gatehouse or sexton's lodge and cemetery office (built in stages from 1860 to 1899), the ornamental brick perimeter fence and elegant cemetery shelter to the design of prominent Melbourne architects, Charles Vickers (for the original 1860 cottage) and Albert Purchas, cemetery architect and secretary from 1864 to his death in 1907. The Boroondara Cemetery has considerable aesthetic significance which is principally derived from its tranquil, picturesque setting; its impressive memorials and monuments; its landmark features such as the prominent clocktower of the sexton's lodge and office, the mature exotic plantings, the decorative brick fence and the entrance gates; its defined views; and its curving paths. The Springthorpe Memorial (VHR 522), the Syme Memorial and the Cussen Memorial (VHR 2036), all contained within the Boroondara Cemetery, are of aesthetic and architectural significance for their creative and artistic achievement. The Boroondara Cemetery is of scientific (botanical) significance for its collection of rare mature exotic plantings. The Golden Funeral Cypress, (Chamaecyparis funebris 'Aurea') is the only known example in Victoria. The Boroondara Cemetery is of historical significance for the graves, monuments and epitaphs of a number of individuals whose activities have played a major part in Australia's history. They include the Henty family, artists Louis Buvelot and Charles Nuttall, businessmen John Halfey and publisher David Syme, artist and diarist Georgiana McCrae, actress Nellie Stewart and architect and designer of the Boroondara and Melbourne General Cemeteries, Albert Purchas.Digital imagescemetery, boroondara, kew, gatehouse, clock, tower, clocktower, heritage, memorial, henty, james henty -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyArticle - South Caulfield Hebrew Congregation
Four articles about the South Caulfield Hebrew Congregation from the Australian Jewish Newspaper: 1/ An article dated 15/09/1961 about the appointment of Rabbi Rudzki to the South Caulfield Hebrew Congregation and celebration for that. The president and chairman welcomed various Jewish congregations presidents and rabbis, also a brief about Rabbi Rudzki plus new architect plans were announced for a new synagogue. 2/ An article dated 06/09/1963 about the opening of new synagogue in Leopold Street. It also gave a brief overview on who attended, who the speakers were and the procession of the Sifrei Torah, this being the gift of Nossbaum Family. 3/ An article dated 08/08/1969 on the 20 year history of South Caulfield Hebrew Congregation 4/ An article dated 10/12/1976 on the committee of South Caulfield Young Married Group and forthcoming functions for the congregation of South Caulfield synagogue.duffield w, prawer d, slonim jacob, roth s, bruce e mrs, slonim yaakov, jedwab i. h, rudzki mrs, waysman joseph, goldsmith m, nossbaum r, gescheit rev, rudzki s rabbi, goldenburg p, bricker e. e, cohen s. h, fox c, lamm e, super n, kaplinski l, groner i, nossbaum family, herz s mr, herz s mrs, sussman geoffrey, levy manfred, slonim mordie, enker moshe, kehilla kedosha tiferes yeshurun, goldfarb mr, lasky l mr, lasky l mrs, duffield w mrs, rathner k, slonim yankel, bruce harvey, goldsmith rebecca, leopold street, south caulfield, religious groups, ladies auxiliary, south caulfield hebrew congregation
