Showing 57 items matching "blacksmith warrnambool"
-
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMemorabilia - Horseshoe Case, 1906 – 1907
... blacksmith warrnambool..., and in Warrnambool he owned a blacksmith business at the Warrnambool... a blacksmith business at the Warrnambool Racecourse Grounds. Brian ...The horseshoes in this purpose-built display case were made by Thomas Alfred Chapman in 1906-1907. Chapman operated a blacksmith’s shop in Mortlake Rd, Purnim, about 15 mins drive from Warrnambool. Chapman made this horseshoe case especially for the 3rd Exhibition of Australian Manufacturers and Products, held in the Exhibition Building in Melbourne, which was organised and promoted by the Australian Natives Association (ANA). Reference is made to the horseshoe case in the Exhibition’s Souvenir Catalogue of 1907 on page 85, under the heading 'In the Machinery Section the following exhibits are also shown … 'CHAPMAN, T.A. , Woolsthorpe, via Warrnambool, Case of Horseshoes'. The Australian Natives’ Association (ANA) were a non-partisan and non-sectarian, friendly society founded in Melbourne, Australia in April 1871. It was set-up for the benefit of Australian-born white men, and membership was restricted exclusively to that group. Men of other races including the Chinese and Indigenous people were not allowed to join. The ANA had relatively progressive views on women (for the time) and attracted suffragists seeking support for their cause, and in 1894, the ANA advocated for women’s enfranchisement. Although, white women were only admitted as members from 1964. The organisation was most prominent in Victoria and sought to shape Australia’s national identity and was a training ground for businessmen, trade unionists and politicians including many of Australia’s early prime ministers such as Edmund Barton, Alfred Deakin, James Scullin and Francis Forde, and the first Australian-born governor-general, Isaac Isaacs, was a member. By 1910 it had developed into a nationwide association with real political and social influence, and members would participate in many activities. The ANA lobbied strongly for anti-Chinese legislation and were an ardent believer of colonial unification. Its mission and efforts are largely credited for the successful referendums that resulted in Federation of the six Australian colonies into a new nation, the association’s most important legacy. The ANA was also a supporter of trade protection, and were a staunch advocate of the first act of Australia's new parliament, the Immigration Restriction Act 1901 (cth) or commonly known as the White Australia Policy, which became one of the central pillars of Australian nationalism in the 20th-century. The ANA campaigned against the Australian Federal Government's new immigration policy after the Second World War (non-British immigration from southern and central Europe) in order to maintain a 'white Australia', and resisted changes when the Labor government during the 1970s fully dismantled and abandoned the White Australia Policy. The ANA merged with Manchester Unity Independent Order of Oddfellows, in 1993 to become Australian Unity Ltd. The display case of horseshoes changed hands several times, going from its maker Thomas Chapman to his mother then various other members of his family. The case was also displayed at the Lee Family’s butcher shop at 188 Liebig St Warrnambool, and in the Purnim Hotel during the Warrnambool May Races. In the late 1950s the horseshoe case went to Thomas’s son, Brian. He was a Master Farrier and completed his apprenticeship at Flemington Racecourse, and in Warrnambool he owned a blacksmith business at the Warrnambool Racecourse Grounds. Brian later operated a blacksmith’s at Flagstaff Hill, where his customers would bring their horses to be shod. Brian passed away in August 2017. The horseshoe case is significant as an example of trades in the early 20th century in Western Victoria, Australia. It is also significant as an example of horseshoes from the early 20th century. The horseshoe display case is also significant for its association with the Australian Exhibition of 1907, showcasing Australian produce and manufacturing to the world. The horseshoe display case is locally significant for its association with local families, essential businesses and community events. Display case of homemade horseshoes. Wooden case with glass front containing 16 horse shoes grouped in sets, each set with a label: Made 1906-1907 for Australian Exhibition of 1907 by Thomas Alfred Chapman of Warrnambool. The case contains (a) complete chrome set each of Trotting Shoes, Hunting Shoes and Racing Plates, and (b) one pair of Hind Polo Shoes and one pair of Front Aluminium Shoes. The wooden frame has gold lettering on each side proclaiming “Australian Natives Association, T.A. Chapman, horse shoer, Warrnambool” and is topped by a painted Australian coat of arms. Gold lettering on frame, in the order of top/bottom/ left/right “AUSTRALIAN.NATIVES.ASSOCIATION / T.A. CHAPMAN / Horse Shoer / Warrnambool”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, horseshoe display case 1906-1907, chromed set of trotting shoes 1906-1907, chrome set of hunting shoes 1906-1907, chrome set of racing plates 1906-1907, pair of hind polo shoes 1906-1907, pair of front aluminium shoes 1906-1907, australian exhibition 1907, australian natives association (ana), t.a. chapman horse shoer warrnambool, thomas alfred chapman, brian chapman, brian “snacks” chapman, blacksmith warrnambool, warrnambool may races, warrnambool racecourse, purnim hotel, lee family’s butcher shop warrnambool -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book, The Horse and Dog, C 1880
... trainer, Professor Sample.. horse training blacksmith warrnambool ...This book belonged to Joseph Conn who was a blacksmith at Conn's Corner in Dennington. The author of the book was H Sample, an American professor who was a horse trainer. In 1884 he was in Warrnambool giving a demonstration of his system of horse training. It is conjectured that Joseph Conn attended the demonstration and bought the book.This book is of some some interest because of its association with a local blacksmith, Joseph Conn and an American horse trainer, Professor Sample..This is a hard covered book with gold printing on the front cover and spine and an image in gold of a horse and a dog in a horse shoe.There are 284 pages. It contains printed material and illustrations. Some pages are torn and the binding is loose. There are three hand written signatures inside a front cover. Joseph Conn ( Three times)horse training, blacksmith, warrnambool, joseph conn -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Leg Vice, Mid 19th Century
The blacksmith leg vise is also called the "solid box vise" and is one of the most important tools in the blacksmith's shop. It firmly holds hot iron while it is hammered, chiseled, or twisted. These are the only vises that are designed to take this kind of use day in and day out. A small 30-pound blacksmith's vise can survive pounding that would wreck a much heavier cast iron bench model. Three things make a blacksmith's vice special. One is that they are forgings, not cast iron or ductile iron. The second is the leg that provides support to the floor or from a sunken post. The last is the hinge, while not a perfect way to construct a vice the pin joint is durable and can take a considerable beating. If sheared it is easy to replace. These things all combine into a tool that can take decades of heavy use and abuse. Most in use is one to two hundred years old.Some of these vises were made by specialists such as Atwood of Stourbridge England, Steel City and Columbian in the U.S. and others were made in anvil manufacturing plants such as "Mousehole Forge" and "Peter Wright" in England and "Fisher-Norris" and others in North America. The design of these vises right down to the last chamfer seems to have been perfected in the 1600s and remained more or less the same until the 20th century. The bodies are forged wrought iron or mild steel and they have hard steel surfaces welded into the jaws. The jaws have little or very shallow serrations which are generally worn off.Around the turn of the 20th Century during the hey-day of the blacksmith shop in North America, these tools were considered so standard a commodity that they were sold without reference to the manufacturer. Very few were even marked with the maker's name. Size is best defined by weight as there is some variation in jaw size from manufacturer to manufacturer. They were sold by the pound and are still best judged by the pound.A vintage tool used in a Blacksmiths shop during the early 19th century to the beginning of the 20th century. Regarded as a significant into social history of the time.Leg Vice attached with screws to bench via a block of wood. Has large metal pole which practically reaches the floor. Also has a metal device to either tighten or slacken vice.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDrill Press, early to mid-20th century
This post drill press has been made by Melbourne business, Dawn Manufacturing Company. It can be operated manually or by a pulley driven flywheel, with the aid of an engine connected to a power supply. In the late 1800s early 1900s a drill press like this would have been driven by steam from a boiler, the main power source for manufacturer’s power at that time. Dawn’s Golden Anniversary 1917-1967 Catalogue describes this model 611 drill as … “Ruggedly constructed with accurately reamed bearings. The coupling between the main spindle and feed screw engages the full circumference of the spindle, and embraces a ball-bearing thrust race. The pillar, as in all “Dawn Drilling Machines” is a solid bright steel bar, in place of the usual light tubing. Adjustable automatic feed.” And “F. & l. Pulleys extra, if required”. DAWN MANUFACTURING CO. The Dawn Manufacturing Co. was founded in Coburg, Melbourne, in 1917 by the four Blake brothers, who were all engineers. After World War I Dawn was supplying drills Australia wide and the company was growing at a healthy rate. During the depression they remained busy, with employees working 60-80 hour weeks. Dawn was contracted to supply vices and clamps to the Australian Defence Department and munitions factory during the World War II. - 1959 the company was taken over by G.N. Raymond Group. - 1967 the Dawn Manufacturing Co. had distributors in Australia and overseas, including USA, Canada, New Zealand, Asia and the Middle East. - 1973 the Siddons Ramset Limited acquired Dawn. - December 1991, Dawn became a unit of the United States owned Stanley Works Pty. Ltd. - November 1998 Dawn became 100 per cent Australian owned. The drill is a typical tool of a blacksmith, cart wright, wheelwright and garage business. It is an example of the tools of the blacksmiths’ trade in Victoria in the early to mid-20th century.Post type drill press machine with gear driven flywheel. Drill press is attached to a post and is fitted with a pulley belt and will run at a speed of maxim 200 r.p.m. The machine can also be manually operated. It has an aperture in the centre, a chuck, for the drill bit and has two metal handles at the centre, on the right hand side. Gear ratio 2:1 main drive, 6" diam, 3:1 reduction gear. Made by Dawn of Melbourne, Australia. Model No. 611, Code No. 9157"DAWN MFG COY”, “MELB. AUSTRALIA", " 611"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, blacksmiths, blacksmith’s drill, blacksmith tools, dawn drill model no. 611, dawn drill code no. 9157, dawn manufacturing coy melbourne, dawn manufacturing coy coburg, dawn post drill, drilling machine, drill with gear driven flywheel, forging tool, metal working tool, post drill, steam powered drill, trade tool, warrnambool district 1900s -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Compass, late 19th to early 20th century
This large compass is well made. It is now pitted and scratched, indication much use. Compasses were used to measure and mark out the head of the barrel by coopers. Very large compasses were used by block, spar and pump makers to help shave off angles left by axes and other tools on mast sides. Also they were used by blacksmiths in their work draftsmen, carpenters, engineers and navigators.This compass is an example of a drawing instrument that could have been used in the 19th and early 20th century by coopers and blacksmiths as well as navigators and ship smiths.Compass; large metal compass, 90-degree angle, two pointed arms hinged at the top. Inscription on the top of one arm.Stamped into the metal " J J E " ( or J J F )flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, compass, drawing instrument, measuring instrument, scientific instrument, draftsman, technical drawing, navigation, engineering, blacksmith, cooper, plumber -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLeg Vice, c. early 1900s
This leg (post) vice once belonged to Goodall and Sons, who were blacksmiths in Terang. The leg vice is a common tool of the ‘smithies’ (blacksmiths). It is also an engineer's tool but in the early 1900s the smith was often the nearest approach to an engineer’s services for many miles around. The smith was called upon to do a variety of work. The leg vice is used to hold hot iron while the metal is pounded, heated and beaten again and again until it is the required shape. Henry Goodall (1870-1936) Henry Goodall was the proprietor of garages as H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd., at both Terang (McKinnon and High Streets) and Mortlake (Dunlop Street). His business was in operation in at least in 1916 and perhaps well before, considering the date of the tyre bender and its use for wagons with wooden wheels. It was still in operation in 1953, chasing up debtors in Mount Gambier Court. Amongst the employees of H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd. was Ernie Entwistle, a blacksmith (a soldier who died in 1916 ) and Alfred Hodgetts, radio expert (killed in a fatal accident in 1943, when he was in his early 30s ). Henry Goodall was involved in the community as a Justice of Peace, a deputy coroner, President of the Mortlake Hospital, trustee of the Soldiers’ Memorial Hall, and as a prominent Freemason. He and his wife had two sons (Charles and John) and one daughter (Mrs. Chas. Newton, of Skipton). The leg vice is locally significant as it was used by a local company in Terang and Mortlake in their blacksmith, wheelwright and garage business. It is an example of the tools of the blacksmiths’ trade in Victoria in the early to mid-1900s.Leg vice, also called a post vice. The large iron vice stands on a post on the floor and post brackets attach it firmly to a solid object such as a workbench. The sliding metal handle winds the screw spindle in and out to change the grip of the jaws that hold the workpiece. This leg vice once belonged to Harry Goodall & Sons, blacksmiths of Terang.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, h. goodall & sons of terang, terang blacksmith, h. goodall & sons pty ltd, mortlake, ernie entwistle blacksmith, alfred hodgetts radio expert, charles goodall, john goodall, mrs. chas. newton nee goodall, trade tools, blacksmith tools, leg vice, leg vise, pose vice, post vise, terang 1900s, warrnambool district 1900s -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAnvil, early to mid-1900s
... Warrnambool district 1900s Anvil Blacksmith’s anvil Single horn anvil ...This anvil once belonged to Goodall and Sons, who were blacksmiths in Terang. The smith was called upon to do a variety of work. In the early 1900s he was often the nearest person to be able to perform an engineer’s services for many miles around. An anvil is used by blacksmiths to forge and shape his work pieces. The conical horn is used for hammering curved work pieces. The anvil is a common tool of the blacksmiths (‘smithies’) and other metalworkers. There has been very little change in the basic design of the anvil since Greek and Roman times. Henry Goodall (1870-1936) Henry Goodall was proprietor of garages as H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd., at both Terang (McKinnon and High Streets) and Mortlake (Dunlop Street). His business was in operation in at least in 1916 and perhaps well before, considering the date of the tyre bender and its use for wagons with wooden wheels. It was still in operation in 1953, chasing up debtors in Mount Gambier Court. Amongst the employees of H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd. was Ernie Entwistle, a blacksmith (a soldier who died in 1916 ) and Alfred Hodgetts, radio expert (killed in a fatal accident in 1943, when he was in his early 30s ). Henry Goodall was involved in the community as a Justice of Peace, a deputy coroner, President of the Mortlake Hospital, trustee of the Soldiers’ Memorial Hall, and as a prominent Freemason. He and his wife had two sons (Charles and John) and one daughter (Mrs. Chas. Newton, of Skipton). The anvil is locally significant as it was used by a local company in Terang and Mortlake in their blacksmith, wheelwright and garage business. It is an example of the tools of the blacksmiths’ trade in Victoria in the early to mid-1900s. Anvil, single horn, used as a tool by blacksmiths and metalworkers. Large block of metal with a flat top face, a conical horn on one side and a ‘v’ shape on the other. The anvil’s base has a squat stand and sides that are a variety of shapes. This anvil once belonged to Harry Goodall & Sons, blacksmiths of Terang. C. early to mid-1900s.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, h. goodall & sons of terang, terang blacksmith, h. goodall & sons pty ltd, mortlake, ernie entwistle blacksmith, alfred hodgetts radio expert, charles goodall, john goodall, mrs. chas. newton nee goodall, trade tools, blacksmith tools, metalworking tool, forging tool, terang 1900s, warrnambool district 1900s, anvil, blacksmith’s anvil, single horn anvil -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAnvil
... -village anvil blacksmiths tinsmith tools trades Warrnambool Ports ...This anvil was once the property of Warrnambool Ports and Harbours. It is associated with the shipping trade and wold have been used by a blacksmith or tinsmith for forging and shaping metal. According to Pliny, the anvil is supposed to be invented by Cinyra of Cyprus, but it was probably much older. There has been very little change in the basic design of the anvil since Greek and Roman times. This anvil is significant for its association with the local government body of Warrnambool Ports and Harbours, which is of local historic significance. It is also significant for its association with blacksmiths and tinsmiths, which are rare trades today.Anvil, small, for use by blacksmiths and tinsmiths.It was once the property of the Warrnambool Ports and Harbours.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, anvil, blacksmiths, tinsmith, tools, trades, warrnambool ports and harbours -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSwage Block
Swage block, an iron block having various indentations and holes intended for use in forming hot metal. Used in blacksmithing. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, swage block, blacksmith -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDrill Press, 1920s-1950s
This drill once belonged to Goodall and Sons, who were blacksmiths in Terang. The smith was called upon to do a variety of work. In the early 1900s he was often the nearest person to be able to perform an engineer’s services for many miles around. The Dawn Ball-bearing Post Drill no. 611 is described in McPherson’s Catalogue as a “drilling machine with adjustable automatic feed, with improved Dawn coupler and ball-bearing thrust’. The heavy design of the flywheel enables it to maintain momentum” and is “fitted with pulleys for belt drive if desired” The hand crank drives an automatic feed to work off a cam-follow system opposite a large wheel. Made by Dawn Manufacturing Co. Australia 1920-1950. DAWN MANUFACTURING CO. Dawn Manufacturing Co. was founded in Coburg, Melbourne, in 1917 by the four Blake brothers, who were all engineers. After World War I Dawn was supplying drills Australia wide and the company was growing at a healthy rate. During the depression they remained busy, with employees working 60-80 hour weeks. Dawn was contracted to supply vices and clamps to the Australian Defence Department and munitions factory during the World War II. In 1959 the company was taken over by G.N. Raymond Group, then in 1973 the Siddons Ramset Limited acquired Dawn. In December 1991, Dawn became a unit of the United States owned Stanley Works Pty. Ltd. In November 1998 Dawn became 100 per cent Australian owned. HENRY GOODALL & SONS Henry Goodall (1870-1936) was proprietor of garages as H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd., at both Terang (McKinnon and High Streets) and Mortlake (Dunlop Street). His business was in operation in at least in 1916 and perhaps well before, considering the date of the tyre bender and its use for wagons with wooden wheels. It was still in operation in 1953, chasing up debtors in Mount Gambier Court. Amongst the employees of H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd. was Ernie Entwistle, a blacksmith (a soldier who died in 1916 ) and Alfred Hodgetts, radio expert (killed in a fatal accident in 1943, when he was in his early 30s ). Henry Goodall was involved in the community as a Justice of Peace, a deputy coroner, President of the Mortlake Hospital, trustee of the Soldiers’ Memorial Hall, and as a prominent Freemason. He and his wife had two sons (Charles and John) and one daughter (Mrs. Chas. Newton, of Skipton). The drill is locally significant as it was used by a local company in Terang and Mortlake in their blacksmith, wheelwright and garage business. It is an example of the tools of the blacksmiths’ trade in Victoria in the 1920s-1950s.Dawn Ball-bearing Post Drill no. 611, made by Dawn of Melbourne, model no 611. Hand operated drill press. Self-feeding blacksmiths’ drill-press. This drill once belonged to Harry Goodall & Sons, blacksmiths of Terang. Dated 1920s-1950s. Gear ratio 2:1 main drive, 6" diam, 3:1 reduction gear. "Dawn", "Melbourne"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, h. goodall & sons of terang, terang blacksmith, h. goodall & sons pty ltd, mortlake, ernie entwistle blacksmith, alfred hodgetts radio expert, charles goodall, john goodall, mrs. chas. newton nee goodall, terang 1900s, warrnambool district 1900s, post drill, blacksmith’s drill, dawn post drill, dawn ball-bearing post drill no. 611, blacksmiths, dawn of melbourne -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTyre Bender, 1884
A tyre bender is used to bend and shape metal rims for wooden wagon wheels. This tyre bender’s model first appeared in the Day Bros catalogue in 1884 as the “Giant” model. The catalogue of 1883 only showed a lighter duty model called the “Lion”. It can be assumed that this later “Giant” model was a heavy duty improvement over the 1883 "Lion" and other smaller models which were still being advertised for sale in 1884. The Day Bros foundry, makers of this tyre bender, was operating as the manufacture of wheel right and blacksmith tools and general machinery in the 19th century in the USA and successfully exported their goods all over the world. Wagon tyre benders would have been very common circa 1850-1920, so there were probably many makers over the years. Early on, it would have become clear to the blacksmiths about which designs worked best so, eventually, the various makers would have made similar products to each other. This tyre bender was once used by Harry Goodall of H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd. corner of McKinnon and High Streets, Terang. Victoria. Henry Goodall & Sons Henry Goodall (1870-1936) was proprietor of garages as H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd., at both Terang (McKinnon and High Streets) and Mortlake (Dunlop Street). His business was in operation in at least in 1916 and perhaps well before, considering the date of the tyre bender and its use for wagons with wooden wheels. It was still in operation in 1953, chasing up debtors in Mount Gambier Court. Amongst the employees of H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd. was Ernie Entwistle, a blacksmith (a soldier who died in 1916 ) and Alfred Hodgetts, radio expert (killed in a fatal accident in 1943, when he was in his early 30s ). Henry Goodall was involved in the community as a Justice of Peace, a deputy coroner, President of the Mortlake Hospital, trustee of the Soldiers’ Memorial Hall, and as a prominent Freemason. He and his wife had two sons (Charles and John) and one daughter (Mrs. Chas. Newton, of Skipton). The tyre bender is significant as it demonstrates how blacksmiths or wheelwrights could make new metal rims for wagon wheels for carts, wagons, stage coaches and carriages over a 135 years ago. The machine is a part of our social history as it demonstrates part of the process of making wagon wheels, which played an important part in aiding the continuation of daily transport needs that people had at the time, such as farming, personal transport and commercial activities. The machine or tool is locally significant as it was used by a local company in Terang and Mortlake in their blacksmith, wheelwright and garage business. Steel tyre bender mounted on timber base, used for wagon wheel steel rims. Made from cast iron and steel, double geared with four cogs to unite the upper and lower steel rollers. There are adjustable guide collars to keep the iron in line while it is being bent. It can also be used with two cranks for heavy duty work utilising the use to two operators. It is the Giant model, made in 1884 by Day Bros. of Philadelphia. This tyre bender once belonged to Harry Goodall & Sons, blacksmith's of Terang. Victoria. “DAY BROS. PHILAP. PA” cast into the side of machineflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, machinery, wagon wheel, wheelwrights, blacksmith, steel rim wheels, tyre bender, tire bender, the giant tyre bender, henry goodall (1870-1936), terang, wheelwright tool, blacksmith trade, blacksmithing equipment and supplies, wagon tyre bender, day bros. philadelphia pennsylvania, h. goodall & sons of terang, terang blacksmith, h. goodall & sons pty ltd, mortlake, ernie entwistle blacksmith, alfred hodgetts radio expert, charles goodall, john goodall, mrs. chas. newton nee goodall -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageVice, 1800s
A wheelwright’s spoke vice was used to hold the wheel hub firmly while the spokes were hammered into the wheel hub, then the spokes would be joined to the wooden wheel felloe before finally the metal flat tyre, or later the rubber tyre, would be attached to the felloe. A wheelwright’s spoke vice would have been very necessary for blacksmiths circa 1800s-1920s as it would have been used in the manufacture and repair of carts, wagons, coaches and other horse-drawn vehicles. This wheelwright’s spoke vice was once used by Harry Goodall of H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd. corner of McKinnon and High Streets, Terang. Victoria. Henry Goodall & Sons Henry Goodall (1870-1936) was proprietor of garages as H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd., at both Terang (McKinnon and High Streets) and Mortlake (Dunlop Street). His business was in operation in at least in 1916 and perhaps well before, considering the date of the tyre bender and its use for wagons with wooden wheels. It was still in operation in 1953, chasing up debtors in Mount Gambier Court. Amongst the employees of H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd. was Ernie Entwistle, a blacksmith (a soldier who died in 1916) and Alfred Hodgetts, radio expert (killed in a fatal accident in 1943, when he was in his early 30s). Henry Goodall was involved in the community as a Justice of Peace, a deputy coroner, President of the Mortlake Hospital, trustee of the Soldiers’ Memorial Hall, and as a prominent Freemason. He and his wife had two sons (Charles and John) and one daughter (Mrs. Chas. Newton, of Skipton). The wheelwright’s spoke vice is significant as it demonstrates how blacksmiths or wheelwrights could make new metal rims for wagon wheels for carts, wagons, stage coaches and carriages over a 135 years ago. The machine is a part of our social history as it demonstrates part of the process of making wagon wheels, which played an important part in aiding the continuation of daily transport needs that people had at the time, such as farming, personal transport and commercial activities. The tool is locally significant as it was used by a local company in Terang and Mortlake in their blacksmith, wheelwright and garage business. Vice; wheelwright’s wheel spoke vice. Manufactured in 1800s. This was once belonged to Harry Goodall & Sons, blacksmith's of Terang. Victoria.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, machinery, wagon wheel, steel rim wheels, henry goodall (1870-1936), terang, wheelwright tool, blacksmith trade, blacksmithing equipment and supplies, h. goodall & sons of terang, terang blacksmith, h. goodall & sons pty ltd, mortlake, ernie entwistle blacksmith, alfred hodgetts radio expert, charles goodall, john goodall, wheel hub, wheel spoke, wheel felloe, wheel tyre, wheel tire -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDrawer Cabinet, 1920-1950
This blacksmith’s drawer cabinet once belonged to Goodall and Sons, who were blacksmiths in Terang. The drilled holes in the drawers may have once had knotted rope handles. Some of the drawer fronts have been split, on broken, in the area of the holes, indicating that they drawers have had heavy use. The stencilled numbers could have been used for sorting different blacksmith items such as tools, scraps of materials, fasteners and horse shoes. The smith was called upon to do a variety of work. In the early 1900s he was often the nearest person to be able to perform an engineer’s services for many miles around. HENRY GOODALL & SONS Henry Goodall (1870-1936) was proprietor of garages as H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd., at both Terang (McKinnon and High Streets) and Mortlake (Dunlop Street). His business was in operation in at least in 1916 and perhaps well before, considering the date of the tyre bender and its use for wagons with wooden wheels. It was still in operation in 1953, chasing up debtors in Mount Gambier Court. Amongst the employees of H. Goodall & Sons Pty. Ltd. was Ernie Entwistle, a blacksmith (a soldier who died in 1916 ) and Alfred Hodgetts, radio expert (killed in a fatal accident in 1943, when he was in his early 30s ). Henry Goodall was involved in the community as a Justice of Peace, a deputy coroner, President of the Mortlake Hospital, trustee of the Soldiers’ Memorial Hall, and as a prominent Freemason. He and his wife had two sons (Charles and John) and one daughter (Mrs. Chas. Newton, of Skipton). The drawer cabinet is locally significant as it was used by a local company in Terang and Mortlake in their blacksmith, wheelwright and garage business. It is an example of the furniture of the blacksmiths’ trade in Victoria in the early to mid-1900sBlacksmith's drawer cabinet with 8 compartments and 7 drawers (the 8th drawer is missing). The drawers each have two drilled holes. Both top and base of the cupboard extend past the sides, the base further than the top to give it stability. The cupboard once belonged to Harry Goodall & Sons, blacksmiths of Terang. Dated early to mid-1900s.Stencil or hand painted on drawers “5” “3” “12” “11” “4” “4P”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, h. goodall & sons of terang, terang blacksmith, h. goodall & sons pty ltd, mortlake, ernie entwistle blacksmith, alfred hodgetts radio expert, charles goodall, john goodall, mrs. chas. newton nee goodall, terang 1900s, warrnambool district 1900s, box cupboard, drawer cabinet, drawer storage unit, blacksmith’s furniture -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Flat Iron, circa 1900
... Warrnambool great-ocean-road Blacksmiths started forging simple flat ...Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top. An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today. Iron; small flat domestic iron.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, iron, flat iron, domestic iron, laundery, ironing equipment, sad iron -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTongs
Blacksmiths Round Nose Tongs, metal, Forged steel, Length 33cm.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, tongs -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Ledger, Hugh McCullough, Circa 1900
This ledger contains entries from 1894 until 1910 which relate to the farrier business of Hugh Mc Cullough. Accompanying the ledger is an index of names which contain the following J W Adams, J H Allan, J Beattie Batterbee, Rev Grey Dixon, Duirs and Warrell, Wm Houston, Dr G Wilson, Warrnambool Rabbit Factory, Western Stage Co, Spalding & Fletcher, Stevens Hay & corn store, Hugh Mc Cullough was a blacksmith. He was born in County Down, Ireland on 13 March, 1848 and died in Warrnambool, Victoria, 10 september, 1905. He married Margaret Lutton Mayne, born Caramut, Victoria, 15 October, 1856, died 28 February, 1928, Warrnambool, Victoria. Hugh and Margaret had 11 children.This ledger is linked historically and socially to Warrnambool, containing a large number of local names.Dark green cloth over card with leather spine binding and corners. 527 pages with alphabetical index at the front Green and maroon patterned pages inside front and back covers.Hugh McCullough printed inside front page. Stamp inside back cover, “G U Petterd Bookseller and stationer Warrnambool”warrnambool, mccullough, mccullough farriers, farriers warrnambool,, hugh mccullough -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Pamphlet, Owens of Warrnambool
This is a brochure produced for the Owens of Warrnambool Farm and Workshop Expo. The story of Owens of Warrnambool began in the 1880s when Flett and Hopkins began a plumbing and blacksmith business in Lava Street. In the early 1900s the business was taken over by Bruce and McClure who added a foundry and produced and serviced farm equipment. In 1945 the business was purchased by four Owen brothers. In 1953 the business became known as Owens of Warrnambool. In 1987 the business was purchased by Alan Lane and following his death in 1995 the business became part of the Alan Lane Foundation. In 2000 the business was transferred to Caramut Road. This brochure is of some interest as it contains information on Owens of Warrnambool, a prominent business in Warrnambool today and one with a significant history in the city. This is an Owens of Warrnambool A4- size fold-out brochure of three pages, printed back to back. There is information on the history of Owens of Warrnambool, Owens Water Industries, Owens Rural and Industrial Supplies and associated firms with their logos. There are black and white and colour photographs and the front page features the Owens logo and a photograph of the shop front in Caramut Road, Warrnamboolowens of warrnambool, warrnambool -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Lead shot mould, Early 20th century
This lead shot mould would have been used by those people wanting ammunition for shotguns. The moulds were probably originally used in a blacksmith’s forge. Although it has no known local provenance, this lead shot mould is of interest as an example of an early tool. This is a metal tool with handles in the shape of calipers with a rounded ball of metal at one end. The ball is split in the middle to allow molten material to be inserted for casting into lead shot. The object is heavily rusted.‘16’history of warrnambool, vintage tools -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Harness, C late 19th century
Horse harness is composed of a number of items some leather and other pieces are metal such as these particular ones. The loose attachments allow for the movement of the horse without its muscles being impinged or hampered. There are a number of different types of harness which relate to the type of work or recreation being engaged at the time and for different breeds of horse. Many of the leather straps were also adaptable allowing for different sized horses to use the same set of harness. These items are quite heavy are were possibly used by work horses of an earlier era. They were possibly made locally at one of the many blacksmiths in the town.Parts of a common item from earlier times and as such has historic significance. It opens the discussion of the use of horses in everyday life and work.Three similar oval shaped items with a wider flatter section at one end and a thicker heavier section on the other end. They are made of iron and heavily rusted.history of warrnambool, horse harness -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Clothes Iron, last quarter of the 19th century
... Warrnambool great-ocean-road Blacksmiths started forging simple flat ...Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today.Clothes Iron, wedge shaped, cast iron painted black with cylindrical handle small funnel through centre of handle.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry equipment, sad iron, domestic object -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Clothes Iron, last quarter of the 19th century
... Warrnambool great-ocean-road Blacksmiths started forging simple flat ...Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today.Clothes Iron, wedge shaped, cast iron painted black with cylindrical handle small funnel through centre of handle.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry equipment, sad iron, domestic object -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Fuller, Grooving iron
This hand groover is sometimes called a seamer, grooving iron, punch or fuller. It would have been used by a metal smith, such as a blacksmith, tinsmith or sheet metal worker. It is used to join two edges of metal. The smith overlaps the edges of the metal, then places the tool on top and beats it with a hammer on the top, forcing the metal into the tool's groove, which joins the metal. The device would be moved along the edges to complete the seam. The same tool could give a decorative finish to an artisan's work.This hand groover is sometimes called a seamer, grooving iron, punch or fuller. It would have been used by a metal smith, such as a blacksmith, tinsmith or sheet metal worker. It is used to join two edges of metal. The smith overlaps the edges of the metal, then places the tool on top and beats it with a hammer on the top, forcing the metal into the tool's groove, which joins the metal. The device would be moved along the edges to complete the seam. The same tool could give a decorative finish to an artisan's work.Tool: a fuller, used to form a groove in heated iron. It is also referred to as a groover, seamer or fuller punch. Hand tool with round handle, flat round top and indented rectangular base. Base has grooves on long edges. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, blacksmith tool, vintage tool, sheet metal fabrication, groover, seamer, hand tool, tinsmth, metalsmith, seaming tool, sheet metal worker, manual tool, smith's tool, fuller, grooving iron, punch -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Bellows, Late 19th to Early 20th century
The fireplace was the main heating source for small houses before 1900, so a bellows to coax a flame from a dying fire was important. Early bellows were a bag made from the skin of a small animal and a piece of metal, usually brass, to direct the gust of air created by squeezing the bellows to fan the flames. Such bellows existed in China at least since the 5th century BC, when it was invented, and had reached Europe by the 16th century. In 240 BC, The ancient Greek inventor Ctesibius of Alexandria independently invented a double-action piston bellow used to lift water from one level to another.An item in domestic use in homes to coax a domestic fire into flame, the subject item was probably used in the late 19th to early 20th century home with open fireplaces as a domestic object. It gives a snapshot into how domestic heating was provided using wood or coal before electricity or gas came into regularly used.Bellows wood, leather and metal, parts Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, bellows, blacksmith bellows, fire bellows -
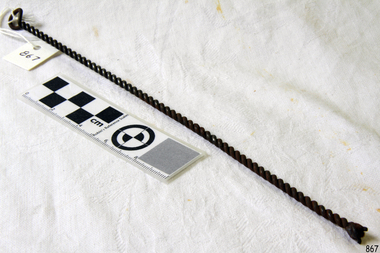 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Stretching Hook
Hand forged metal tool, possibly a sailmaker's hook with the hook broken. It may be a fire iron. The twisted metal is a skill learned by a blacksmith.The item is a handmade tool, an example of the work of a blacksmith. Smiths were sought after in colonial Australia. Their trade allowed them to custom make work for the different industries necessary for survival in a new land.Sailmaker's stretching tool; long thin metal rod bent in half, with centre forming a handle or loop, and long ends twisted together to form a stem. The loose ends are formed together but appear broken.warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, tool, sailmaker's tool, fire iron, blacksmith, twisted rod, twisted wire, sailmaker's hook -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Clothes Iron, last quarter of the 19th century
... Warrnambool great-ocean-road Blacksmiths started forging simple flat ...Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today.Clothes Iron, wedge shaped, cast iron painted black with cylindrical handle small funnel through centre of handle.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry equipment, sad iron, domestic object -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Flat Iron, 1890-1935
... Warrnambool great-ocean-road Blacksmiths started forging simple flat ...Blacksmiths started forging simple flat irons in the late Middle Ages. Plain metal irons were heated by a fire or on a stove. Some were made of stone. Earthenware and terracotta were also used, from the Middle East to France and the Netherlands. Flat irons were also called sad irons or smoothing irons. Metal handles had to be gripped in a pad or thick rag. Some irons had cool wooden handles and in 1870 a detachable handle was patented in the US. This stayed cool while the metal bases were heated and the idea was widely imitated. Cool handles stayed even cooler in "asbestos sad irons". The sad in sad iron (or sadiron) is an old word for solid, and in some contexts this name suggests something bigger and heavier than a flat iron. Goose or tailor's goose was another iron name, and this came from the goose-neck curve in some handles. In Scotland people spoke of gusing (goosing) irons. At least two irons were needed on the go together for an effective system, one would be in use, and the other re-heating. Large households with servants had a special ironing-stove for this purpose. Some were fitted with slots for several irons, and a water-jug on top.An early domestic object that gives an insight into how the ironing of clothes was done before the electric type irons we use and take for granted today. Flat iron cast iron with traces of original black finish on handle. Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, iron, flat iron, laundry, clothes ironing, sad iron, tailors goose -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Fire Tongs
Fireplace tongs were used to add wood to the fireplace as well as break down the crackling wood to add more oxygen to growing flames. Of the four tools that were usually found in an upright fireplace set, tongs had the biggest design variation. Some tongs looked like medical calipers that were rounded at the bottom, while others were almost like metronomes with their rectangular shapes. https://www.lovetoknow.com/home/antiques-collectibles/vintage-antique-fireplace-tools Tongs are tools used to handle items, and generally move the item from one place to another, or turn things, like a piece of meat on a barbecue. Tongs usually have flat ends to pick up items without damaging them and to grip onto the items easily, however, some tongs have claws or toothed ends to grab more bulky and slippery items. Tongs are used mainly for handling food or hot items. Modern tongs are usually made from plastic, metal, stainless steel, or other material, depending on their purpose. Originally, tongs were probably wood sticks that eventually became metal sticks around 3000 BC to handle hot items in a fire Tongs are used to extend the hand or as a replacement handler for potentially dangerous items. Tongs usually have a sprung end so that the operator is required to squeeze the middle of the tongs to grab hold of an item, or they have a pivot which requires the user to squeeze the handles at the end to grip onto items, these being more effective at holding heavy items due to the extra force able to be applied. There are many types of tongs including barbecue tongs, salad tongs, blacksmith tongs, crucible tongs, ice cube tongs, sugar cube tongs and fire tongs. Tongs are often called ‘a pair of tongs’ and the word comes from the Old English, ‘tange’ or ‘tang’, meaning ‘that which bites’. There is evidence of Egyptians using metal rods and tong like tools to hold objects over fire, in around 1450 BC. https://tenrandomfacts.com/tongs/Fire tongs are still used with most open fires in homes.Brass fire tongs with holding clip and flat rounded handle at the end.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, fireplace tools, tongs -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Coopered Bucket, 1960 to 1980
This bucket was made from vertical planks of wood with bands of metal around it for strength. Buckets such as this were made by coopers, who had expertise in making wooden barrels. Wood or animal skin was used to make buckets in colonial times when other materials were unavailable. Buckets had many uses in domestic and agricultural life including carrying, measuring and storing. Cooper tradesmen used carpentry and blacksmithing skills to make a wide range of wooden containers and other objects. They sometimes used water or steam to bend and mould the timber.The bucket is an example of a product made from wood and iron by an experienced Cooper. In early colonial timeswhen ready-made products were scarce so the trades of coopers, blacksmiths, metal smiths, carpenters, builders and others were necessary for domestic, commercial and industrial establishment.Wooden coopered bucket; three metal bands around vertical wooden planks that form the body of the bucket. Two lugs extend higher than the planks and have a rope joined between them.warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime village, bucket, wooden bucket, container, domestic bucket, cooper, cooper trade, coopered bucket -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageClock, 1867-1870
Chauncey Jerome (1793–1868) was an American clock maker in the early to mid 19th century. He made a fortune selling his clocks, and his business grew quickly. Jerome was born in Canaan USA in 1793 son of a blacksmith and nail-maker. He began his career in Plymouth, making dials for long-case clocks where he learned all he could about clocks, particularly clock cases, and then went to New Jersey to make seven-foot cases for clocks mechanisms. In 1816 he went to work for Eli Terry making "Patent Shelf Clocks," learning how to make previously handmade cases using machinery. Deciding to go into business for himself, Jerome began to make cases, trading them to Terry for wooden movements. In 1822 Jerome moved his business to Bristol New Haven, opening a small shop with his brother Noble and began to produce a 30-hour and eight-day wooden clocks. By 1837 Jerome's company was selling more clocks than any of his competitors. A one-day wood-cased clock, which sold for six dollars had helped put the company on the map. A year later his company was selling that same clock for four dollars. The company also sold one line of clocks at a wholesale price of 75 cents and by 1841 the company was showing an annual profit of a whopping $35,000, primarily from the sale of its brass movements. In 1842 Jerome moved his clock-case manufacturing operation to St. John Street in New Haven. Three years later, following a fire that destroyed the Bristol plant, Jerome relocated the entire operation to Elm City factory. Enlarging the plant, the company soon became the largest industrial employer in the city, producing 150,000 clocks annually. In 1850 Jerome formed the Jerome Manufacturing Co. as a joint-stock company with Benedict & Burnham, brass manufacturers of Waterbury. In 1853 the company then became known as the New Haven Clock Co, producing 444,000 clocks and timepieces annually, then the largest clock maker in the world. Jerome's future should have been secure but in 1855 he bought out a failed Bridgeport clock company controlled by P.T. Barnum, which wiped him out financially, leaving the Jerome Manufacturing Co. bankrupt. Jerome never recovered from the loss. By his admission, he was a better inventor than a businessman. When Jerome went bankrupt in 1856 the New Haven Clock Company purchased the company. One of the primary benefits of Jerome purchasing New Haven in the first place was the good reputation of the Jerome brand and the network of companies that remained interested in selling its clocks. In England, Jerome & Co. Ltd. sold Jerome clocks for the New Haven company until 1904, when New Haven purchased the English firm outright. After his involvement with the New Haven Company in 1856, Jerome traveled from town to town, taking jobs where he could, often working for clock companies that had learned the business of clock making using Jerome's inventions. On returning to New Haven near the end of his life, he died, penniless, in 1868 at the age of 74. The company struggled on after Jerome's bankruptcy until after World War II, when the company endeavored to continue through disruptions caused by a takeover along with poor sales, finally having to fold its operations in 1960 a little more than 100 years after it had been founded. The item is significant as it is associated with Chauncey Jerome who had made a historic contribution to the clock making industry during the 19th century when he began to substitute brass mechanisms for wooden mechanisms in his clocks. This was said to be the greatest and most far-reaching contribution to the clock industry. Because of his discovery of stamping out clockwork gears rather than using castings, Jerome was producing the lowest-priced clocks in the world. That can only add to his significance as the major clock manufacture of the 19th century. Jerome may have made and lost, a fortune selling his clocks but was perhaps the most influential and creative person associated with the American clock business during the mid-19th century. Also, he had served his community as a legislator in 1834, a Presidential elector in 1852 and mayor of New Haven, Connecticut from 1854 to 1855.Eight day movement wall clock with Roman numerals, octagonal shaped rosewood veneered casing, hinged face with locking clip. Wound from front. Face has adjustment for Fast-to-Slow.Part paper label on back of case can just make out "Jerome" and "ight and One" probable meaning is "Eight and One Day" describing the movements operational time between winding the mechanism.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, clock maker, jerome & co, new haven, chauncey jerome, canaan -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Nail, circa 1825
Nails such as this solid copper nail were forged by blacksmiths. A nail of this length could have been used for the ship's decking. It was recovered from the shipwreck of the barque Children. The Children wrecking: The barque Children was one of the first vessels to be lost in the Western District the vessel was wrecked to the east of Warrnambool on 14th January 1838. When it ran ashore in hurricane-force winds, 22 passengers and crew were fortunate to escape being battered to death on the rocks. The Children broke up within 20 minutes, sweeping sixteen of those on board to their deaths. After eleven days, the survivors, all of whom were injured, were rescued and taken to Portland. According to Lloyd's Shipping Register 1837-1839, the Children was built in 1825 at Liverpool and operated by owners Gordon & Co, of London. Registration number 123/1837, James Henty then bought her in 1837 as a three-masted barque of 254 tons, with a hull of “part pitch pine, felt sheathed” and “coppered in 1837” at Launceston registered number 6/1837. In 1838 the Children, under her master Captain H. Browne, completed a successful round trip from Launceston to London (carrying wool and whale oil loaded in Portland), returning in late November of that year carrying a general cargo including house bricks used for ballast. On the 11th of January 1839, the Children sailed from Launceston for Adelaide, with 24 passengers, 14 crew, and an awkward mixed cargo, including 1500 sheep, 8 bullocks, 7 horses, and farming implements, and six whaleboats with associated whaling gear. One account states that when the Children were “put out from port she was light and badly ballasted”. The vessel immediately encountered four days of hurricane-force storms, eventually clearing on the early morning of the 14th. However, it was too late to take accurate measurements of the sun or stars to establish their position relative to the coast. The Children collided with a limestone stack at the entrance of Childers Cove, and the seas smashed her into pieces within half an hour. All the cargo and 16 lives were lost including 8 children. The Henty brothers contributed £150 towards a fund for the 22 survivors at a memorial service held in Launceston later that year. It was a major financial setback for James Henty and his brothers, but one from which they recovered. In a submission to the Governor of New South Wales dated 24 March 1840, the Henty’s summarised their work over the previous six years of establishing the Portland settlement stating. “Six stations have been occupied, one at Portland Bay three at the open country about 60 miles inland called ‘Merino Downs’ They have erected two houses at Portland Bay and two others at Merino Downs”.This nail is significant as part of the vessels original fixtures. The Children was delivering cargo intended for the Portland Bay settlement of her owners the James Henty brothers The wreck is also significant as one of the first vessels to have been lost in the Western District of Warrnambool. As a result the shipwreck of the Children is registered with the Victorian Heritage Register S116. Ship's nail, copper, with a washer attached. The nail has a round head, solid round shank and a flat end. It is bent, twisted and has indentations in the centre section. The nail was recovered from the wreck of the CHILDREN.warrnambool, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, shipwreck artefact, the children, nail, copper nail, ship's nail, children shipwreck
