Showing 126 items matching "code one"
-
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncNewspaper, Eltham Festival, November 11-14, 1993: "flowers, fur & feathers" celebrating the nature of Eltham; Special Cover Wrap, Diamond Valley News, 1993
... code one... of chaos classic fireplaces & bbqs code one comfyhome dauphine ...12 page newspaper cover wrap of news, events and information concerning the 1993 Eltham Festival including advertisementsNewsprint1993, 1993 eltham fun run, alistair knox park, australian automotive paint supplies pty ltd, body glove, cathy poussard, circus of chaos, classic fireplaces & bbqs, code one, comfyhome, dauphine, diamond valley and eltham community orchestra, diamond valley community hospital, diamond valley news, diamond valley nursery, doncal heating & cooling, eltham and district woodworkers association, eltham arts council, eltham bookshop, eltham circus of chaos, eltham community centre, eltham festival, eltham health foods, eltham high school, eltham hotel, eltham motor inn, eltham town park, eltham wildcats basketball club, eltham wiregrass gallery, forward auto salvage, gibson's menswear, hanglider lounge, inside out, integrity paint company, kristina jenkins, lancome beauty therapy, leo scott, lizzy tumbri, lower plenty hotel, mgs eltham, montsalvat garden nursery, mr milky's, murrundindi, naomi crowe, north riding living and learning centre, pam sladden, papua new guinean cultural promotion dance group, peter glass, senior citizen's hall, shire of eltham, shire president, shoestring youth theatre, sonya's health foods, steam train, the dancing bares, the eltham bookshop, the landscape factory, the ridge healthclub, the year of indigineous people, tony hicks trio, tony hicks, valley engineering, valley vision, victoria police rock band, vox bandicoot conservation theatre company, yarra yarra aboriginal dancers -
 Marysville & District Historical Society
Marysville & District Historical SocietyTHE TRIANGLE NEWS-VOL 24 NO 6-14 FEBRUARY 1997
... code one concert... herb farm code one concert the keppel name landmarks community ...marysville, victoria, australia, humans vs country, taggerty herb farm, code one concert, the keppel name landmarks, community news, reflections on history, marysville & district historical society, community health services, mystic mountain tourism cocktail party, mops, church news, marsysville bowls club, golf club news, mid goulburn water, marysville cricket club, for sale, commissioner's column, public notices, marysville village, gilberts restaurant, fruit salad farm, st john ambulance, emergency first aid level 2, phelps bakery, marysville tattslotto, lions club, buxton primary school, trades directory, triangle real estate -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook - Music, 'Manual of Orchestration' by Hamilton Clarke, 1888
... Percy Code was the elder son of Edward Thomas Code, one...Percy Code was the elder son of Edward Thomas Code, one ...Percy Code was the elder son of Edward Thomas Code, one of Australia's foremost bandmasters of the early 1900s. This book was part of Frank Wrigth's collection. Red hard covered book, 100 pages, with gold lettering title on coverEdwd. Code Elsternwick 1891 (left hand side front end paper) 15 27 9 14 33 (right hand front end paper), Some pencil markings inside near textmusic, wright, curwen, orchestration, code, edward code, 1891, percy code, frank wright -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchPhotograph, c1945
... objective for the Allied attack on Tarakan (code-named "Oboe One.... The primary objective for the Allied attack on Tarakan (code-named ...Prior to the Second World War Tarakan Island was part of the Dutch East Indies and an important oil-producing centre. In early 1942 it was occupied by the Japanese. The primary objective for the Allied attack on Tarakan (code-named "Oboe One") was to secure and develop the island's airstrip so that it could be used to provide air cover for subsequent landings in Brunei, Labuan and Balikpapan. The secondary objective for the operation was to secure Tarakan's oilfields and bring them into operation as a source of oil for the Allied forces. As part of the 26th Brigade the 2/24 Battalion landed at Tarakan on May1 1945. The task of capturing Tarakan's airstrip was assigned to the 2/24th Battalion. The Battalion's initial attack on the airstrip on the night of 2 May was delayed when the Japanese set off large explosive charges, and the airstrip was not secured until 5 MayThe 2/24th Battalion was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army, which served during World War II .A unit of all-volunteers, it was formed in July 1940 from primarily Victorian volunteers and was known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. It served in North Africa in 1941–1942 as part of the 26th Brigade, which was assigned to the 7th Division, before being reassigned to the 9th Division. In early 1943, the battalion returned to Australia and later took part in campaigns against the Japanese in New Guinea in 1943–1944 and Borneo in 1945, before being disbanded in 1946. The 2/24th suffered the highest number of casualties of any 2nd AIF infantry battalion. The Unit was granted the Freedom of the City by the Rural City of Wangaratta in 1996 and one of the first, if not the first, to receive this type of honour. Reproduced black and white photograph of metal pylon structures with man standing in bombed foreground Handwritten on rear - Oil wells on Tarakan2/24th battalion, tarakan, ww2 -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchPhotograph
... forces on 1 May, code-named Operation Oboe One. While the battle... by Australian forces on 1 May, code-named Operation Oboe One. While ...The Battle of Tarakan was the first stage in the Borneo campaign of 1945. It began with an amphibious landing by Australian forces on 1 May, code-named Operation Oboe One. While the battle ended with success for the Allied forces over the Japanese defenders, this victory is generally regarded as having not justified its costs. 225 Australian soldiers of the 26th Brigade, 9th Division, 2nd Australian Imperial Force were once buried here. They were killed in the Battle of Tarakan (1 May - 21 June 1945) or died due to their wounds until 15 August 1945.The 2/24th Battalion was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army, which served during World War II .A unit of all-volunteers, it was formed in July 1940 from primarily Victorian volunteers and was known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. It served in North Africa in 1941–1942 as part of the 26th Brigade, which was assigned to the 7th Division, before being reassigned to the 9th Division. In early 1943, the battalion returned to Australia and later took part in campaigns against the Japanese in New Guinea in 1943–1944 and Borneo in 1945, before being disbanded in 1946. The 2/24th suffered the highest number of casualties of any 2nd AIF infantry battalion. The Unit was granted the Freedom of the City by the Rural City of Wangaratta in 1996 and one of the first, if not the first, to receive this type of honour. Reproduced black and white photograph of a monument/cenotaph and lawn grave sites with white crosses.Handwritten on rear - Tarakan Cemetery2/24th battalion, wangaratta, tarakan -
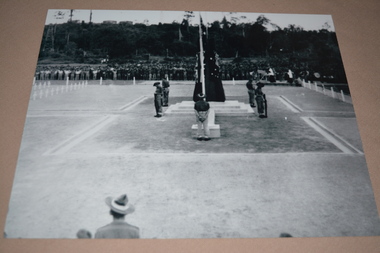 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchPhotograph
... , code-named Operation Oboe One. While the battle ended... on 1 May, code-named Operation Oboe One. While the battle ended ...September 30,1945 - The official dedication service and unveiling of the Cenotaph at Tarakan War Cemetery The Battle of Tarakan was the first stage in the Borneo campaign of 1945. It began with an amphibious landing by Australian forces on 1 May, code-named Operation Oboe One. While the battle ended with success for the Allied forces over the Japanese defenders, this victory is generally regarded as having not justified its costs. 225 Australian soldiers of the 26th Brigade, 9th Division, 2nd Australian Imperial Force were once buried here. They were killed in the Battle of Tarakan (1 May - 21 June 1945) or died due to their wounds until 15 August 1945.The 2/24th Battalion was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army, which served during World War II .A unit of all-volunteers, it was formed in July 1940 from primarily Victorian volunteers and was known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. It served in North Africa in 1941–1942 as part of the 26th Brigade, which was assigned to the 7th Division, before being reassigned to the 9th Division. In early 1943, the battalion returned to Australia and later took part in campaigns against the Japanese in New Guinea in 1943–1944 and Borneo in 1945, before being disbanded in 1946. The 2/24th suffered the highest number of casualties of any 2nd AIF infantry battalion. The Unit was granted the Freedom of the City by the Rural City of Wangaratta in 1996 and one of the first, if not the first, to receive this type of honour. Reproduced black and white photograph of monument/cenotaph and catafalque party2/24th battalion, tarakan, cenotaph -
 Lara RSL Sub Branch
Lara RSL Sub BranchCigarette case, Circa1942
... by the Japanese. The battle, code named Operation Oboe One, began when.... The battle, code named Operation Oboe One, began when Australian ...This cigarette case was made from the plexiglass windscreen of a Japanese Mitsubishi Zero aircraft. Whilst its maker is unknown, its inscription, “Tarakan May 1st 1945” suggests that it was created during the Battle of Tarakan. Tarakan was a small, oil-rich island off the coast of Borneo which in 1945 was held by the Japanese. The battle, code named Operation Oboe One, began when Australian forces landed on May 1st 1945, and continued until June 21st. 240 Australians died during the conflict. The term ‘Trench art’ describes objects made from the debris and by-products of warfare. Reasons for making trench art varied, from creating mementos of battles to passing time or mitigating the effects of warfare. This object has historic significance at a national level due to its association with World War Two. As an example of trench art, it makes an important contribution to our understanding of Australian soldiers’ experience of the war. This object is an example of skilled craftsmanship and has artistic and aesthetic significance due to its detailed engraving of a beach scene. Unlike the majority of trench art, which was made from used ordnance, it is made from the windscreen of a Mitsubishi Zero aircraft and therefore is comparatively rare.Cigarette Case made from the windscreen of a Japanese Zero aircraft"Tarakan May 1st 1945" "A-F-B" Engraved beachcigarette, tarakan, windscreen, japan, australia, united states, netherlands, beach -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMagazine, The Radio Press, Popular Radio Weekly, 1925, 1925
... , Morse Code, An Efficient one-valver, A Simple Crystal Circuit... 1925. (Purchasing a receiver, eliminating static, Morse Code ...Five 'Popular Radio Weekly Magazines. .1) Vol. 1, No. 1, 25 February 1925. (Purchasing a receiver, eliminating static, Morse Code, An Efficient one-valver, A Simple Crystal Circuit, Combining Valve and Crystle, the Alfred Hospital, Frank Tate on Radio. Images of Josie Melville, Alberto Zelmanm circuits) .2) Vo. 1, No. 14, 27 May 1925. (Purity amplifier, Popular Wireless, Oscillations, Marconi's Wireless Beam Transmitter, Resistance coupled Amplifiers, Condenser Losses) .3) Vol. 1, No. 2, 04 March 1925. (A Crystal Receiver, Medium Wave Four-Valver, The Harkness Circuit, A One-Valve Super, The Aerial Mast, The Police Patrol, C Batteries, A Two Crysal set, La Bela Lingvo, Plain Aerial. Images - Transmitting Aeroplace, A. Nicholson - Chief Commissioner of Police) .4) Vol. 1, No 15, 03 June 1925. (The Ham and Radiophone, A Good Circuit, How the Microphone Transmitter Works, A Reflex Circuit, A Millionaire's Radio Installation, Teh Deresnadyne, Crystal Detectors, Hints an Accumulators, 3LO, Selection Radio Parts) .5) Vol 1, No. 6, 01 April 1925. (The Renartz Tuner, A 600 foot aerial, Measuring your Receiver, Doctoring Your Set, Understanding What You Read, The Vernier Condenser, Radio and Railways, Who Can Build the Smallest Set.)radio, valve, electrical engineering, frank tate, alberto zelman -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
... but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code... but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code ...This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Ball, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A round woven cane ball, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre. The rod has a loop at each end, then a concave, octagonal metal plate that rests on the outside surface of the ball, serving as a washer. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, distant signal, signal, maritime signal, ball signal, signal shape, flagstaff signal, signal station, masthead signal, communications, marine technology, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, day shape, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
... but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code... but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code ...This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Cone, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A woven cane cone, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre and two crossed metal bars at the base. The central rod has a loop at the top and passes through the bars at the base, finishing in a metal loop. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, marine navigation, marine communications, communication signal, lifesaving, ship at sea, day shape, masthead signal, day signal, day mark signals, marine technology, safety equipment, navigation equipment, marine day shape, day marker, cane day shape, signal cone, day signal cone, cone signal, cone day shape, distant signal, flagstaff signal, signal station, communications, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
... but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code... but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code ...This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Ball, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A round woven cane ball, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre. The rod has a loop at each end, then a concave, octagonal metal plate that rests on the outside surface of the ball, serving as a washer. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, marine navigation, marine communications, communication signal, lifesaving, ship at sea, day shape, masthead signal, day signal, day mark signals, marine technology, safety equipment, navigation equipment, marine day shape, day marker, cane day shape, signal ball, day signal ball, ball signal, ball day shape, distant signal, flagstaff signal, signal station, communications, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
... but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code... but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code ...This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Cone, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A woven cane cone, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre and two crossed metal bars at the base. The central rod has a loop at the top and passes through the bars at the base, finishing in a metal loop. The rod has swivels at each end.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, shipwreck coast, marine navigation, marine communications, communication signal, lifesaving, ship at sea, day shape, masthead signal, day signal, day mark signals, marine technology, safety equipment, navigation equipment, marine day shape, day marker, cane day shape, signal cone, day signal cone, cone signal, cone day shape, distant signal, flagstaff signal, signal station, communications, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Distant Signal, 1897-1931
... but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code... but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code ...This three-dimensional Distant Signal is part of a Flagstaff Signal set of ball, cone and drum shapes. It has been woven and then fabricated with strong metal swivel fittings and loops for suspending from a high point on a flagstaff at a signal station or on a ship’s masthead. The cane signal was constructed to withstand all weather and to be visible from a long distance. The gaps between the woven cane allow air to pass through, minimising possible swaying. Similar sets were made from rope or fabric. Warrnambool's Flagstaff was erected in 1854. Its primary use was to display visual signals that could convey messages between land and sea. It was also used to notify the local population of the approach of ships. One of the popular signalling codes in use in the early-to-mid 1800s was the Marryat’s Code but there were others in use as well; there was no one standard code. In 1857 the International Marine Conference adopted an International Code of Signals as a standard communications system for all vessels that could be understood in many different languages. The Normanby Advertiser reported on June 5th 1857 a query from the Post Master General as to whether the request of the Chief Harbour Master would be carried out, in that Warrnambool would receive a new flagstaff and a set of Marryatt’s signal flags. The Table of Codes was published, showing how to use combinations of these flags to send messages. The Code was revised in 1887 to cover situations where distance, light, wind and weather conditions affected the visibility of the flags and prevented clear communication. The first report of the International Code of Signals Committee of 1897 warned signalmen not to rely on ordinary semaphore flags and introduced a Distant Signal Code using either particular semaphore flags or the three-dimensional shapes of a ball, cone and drum that aligned with the semaphore flag shapes of a circle, pennant and square. International Code of Signals In 1931, after World War I’s experiences in using signal codes, the International Code of Signals conference in Washington revised and published the rules for the conduct of signalling. One of the changes was that “the use of the Distant Signals and of fixed semaphore was abandoned”. It is of interest to know that modern marine law in many countries insists that a set of Day Shapes must be carried onboard vessels of a certain size. These highly visible geometric shapes are used at sea in daylight to communicate messages between vessels. They are used in a similar way to the Distant Signals, in that different combinations of shapes represent different messages. The set of shapes includes a ball, cylinder, cone and diamond. The shapes are hung between the top of the vessel’s foremast and the front of the vessel. They are only coloured black and are about 1.5 metres high. The vertical line of shapes can mean messages such as Boat not under command, Fishing, and Under sail and power.Distant Signals were an important means of marine communication from the late 1880s to the early 1930s, including during World War I. They were an advancement to the International Shipping Codes and safety. The cane signals’ shapes appear to be the same from whatever direction they are viewed, removing confusion about the message they convey. The same shapes continue to be used today for the sets of Day Shapes used as marine navigational signals that are mandatory on certain-sized vessels.Distant Signal Ball, part of a Flagstaff signal set. A round woven cane ball, painted black, with a metal rod passing through the centre. The rod has a loop at each end, then a concave, octagonal metal plate that rests on the outside surface of the ball, serving as a washer. The rod has swivels at each end.distant signal, flagstaff signal, signal station, masthead signal, communications, marine technology, signals, marine signals, flaghoists, international marine conference, international code of signals, signal codes, marine safety, signal flags, day shape, daymark, day symbol, navigation, warrnambool flagstaff, 1854, 1857 1931, 1887, 1897 -
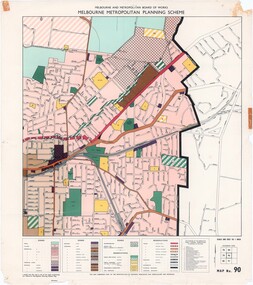 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyMap - Melbourne Metropolitan Planning Scheme, Municipality of Ringwood area - circa 1970
Colour-coded map marking proposed and existing business, industrial, transportation, public reservation, etc. planning zones within the City of Ringwood. Includes (undated) certification that this map is one of the maps constituting the Melbourne Metropolitan Planning Scheme Map.Scale: 800 feet to 1 inch. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Portrait, about 1930
This photograph is of Angela Elizabeth Pearce, granddaughter of Tom Pearce - one of only 2 survivors from the shipwreck LOCH ARD. Angela Elizabeth Pearce had written in her grandfather’s Bible in childish handwriting the words “This Bible belongs to Angela E. Pearce”. Angela was born in England in 1925 and died in Woollahra N.S.W. in 1944, aged 19. She was one of Tom Pearce’s granddaughters. Her father, Robert Pearce was Tom’s second son. Tom Pearce is a famous hero, the rescuer of Eva Carmichael, the only other survivor from the 1878 shipwreck of the LOCH ARD. The Bible was given to Tom Pearce in recognition of his bravery at the wreck of the LOCH ARD. It is on loan to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village from Parks Victoria. The ‘official’ inscription in the Bible reads, “Presented to Mr Thomas Pearce, In recognition of invaluable service performed in saving life when the Loch Ard was wrecked off the coast of Australia., by the Loyal Orange Institution of Victoria, Protestant Hall, Melbourne, August 1878” The photograph is accompanied by a letter, dated 4th May 2010, and is written by Angela’s cousin, Pamela Dormer of Devon, U.K. Her letter includes the words “Dear Mr Abbott, re Tom Pearce’s Bible, As you know, I have been in contact with Mr Peter Yarnis about means by which my grandfather’s presentation Bible can be released to be exhibited with his other effects, like the binoculars at Flagstaff Hill Museum. In the event that it will be, I have enclosed a photograph to join it. When my son Bill Dormer was at Port Campbell he was about to handle his great grandfather’s Bible and was surprised by a childish inscription opposite that of his presentation, which reads (I think this is the way it goes), THIS BIBLE IS THE PROPERTY OF ANGELA ELIZABETH PEARCE. Angela is my late cousin. Her father was Tom Pearce’s second son Robert Strasenburgh Pearce. I and my brother Raymond Simpson are the surviving grandchildren of Tom, by my mother Edith May Pearce, his only daughter. Angela and her mother, at the beginning of W.W.2, evacuated from England to Sydney, N.S.W. but sadly both were dead by early in the 60’s. Robert (my uncle Bobby) went down with his ship on the Malta Convoy, code named PEDESTAL, escorting with other ships the vital oil tanker OHIO to the island. (signed) Pamela Dormer” THE LOCH ARD’S STORY The sailing ship LOCH ARD was built in Glasgow in 1873 and belonged to the famous Loch Line. She made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage which ended in tragedy near Port Campbell. The LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. The ship carried a general cargo which reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. LOCH ARD also had a crew of 37, and 17 passengers. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the boat out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers, and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef running out from Mutton Bird Island. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. It took time to free the lifeboats and when one was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "if you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open a case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance, upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. The media of the time had created one of Australia's first media celebrities. Everyone followed the story of Tom Pearce and Eva Carmichael with great interest and were disappointed when the two went their separate ways. It was felt by many that Tom should have proposed to Eva - given they had spent an evening together unsupervised in the cave and had drunk brandy to keep warm. Coleman Jacobs composed the music “The Young Hero Schottische” and dedicated it, by permission, to Mr. Thomas R. (Tom) Pearce. The sheet music was published in 1878 by the Messieurs Roberts, professors of dancing etc. Melbourne. It was on sale for 3/- (3 shillings) and in aid of the “LOCH ARD” fund. [This is Coleman Jacobs’ only surviving musical work Coleman Jacobs, accomplished pianist, musical performer, singer, composer, professor of music and music teacher, was born in 1827 and died on 4 July 1885, aged 58 years. Coleman Jacobs was buried in the Melbourne Cemetery (grave 461, Church of England section).] The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island and much of the cargo has been salvaged. Some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge following the shipwreck. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. The photographic is of significance because of Tom Pearce and his association with the disaster of the LOCH ARD shipwreck, which is of State significance ― Victorian Heritage Register S417 Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. Photograph, sepia coloured, with accompanying letter. The photograph is a portrait of a young girl in a short sleeved top with a flower on her left shoulder. The girl is "Angela Elizabeth Pearce, granddaughter of Tom Pearce" as inscribed on back of photograph. Tom Pearce was one of two survivors of the 1878 shipwreck LOCH ARD. Included with the photograph is a letter from its donor, Pamela Joan Dormer, other granddaughter of Tom Pearce. The letter dated 4th May 2010 explains the connection between Angela Pearce and Tom Pearce's Bible.Back of photograph, written in blue pen “ANGELA ELIZABETH PEARCE / TOM PEARCE’S GRANDAUGHTER / PHOTO PRESENTED BY / HIS OTHER GRANDAUGHTER / PAMELA JOAN DORMER / 2010” Letter from Pamela Dormer verifying the connection between Angela Pearce and Tom Pearce’s Bible.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, angela pearce, tom pearce, thomas r pearce, eva carmichael, loch ard shipwreck, tom pearce bible, loch ard presentation bible, hero tom pearce, loyal orange institution of victoria, royal humane society of victoria, mutton bird island, coleman jacobs, the young hero schottische -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Postcard, Co-op Card, Early 21st Century
These cards were for use in connection with the Warrnambool Co-Op store. The Warrnambool Co-operative Society Limited was established in 1960 as the Allansford and District Artificial Breeders Co-operative Society Limited to provide herd improvement service to district farmers. In the mid 1970s the Co-Op opened a retail store in Warrnambool in Timor Street and gradually expanded, so that by the late 1990s they had 8000 members and employed 84 full time and 120 casual staff. The Co-Card enabled members to have trading arrangements with 200 other businesses. The Warrnambool Co-Op ceased operations in 2007.These cards are of interest as mementoes of the Warrnambool Co-Op, an important business concern in Warrnambool for over 40 years. The owner of the co-cards was Ronald Cumming. He and his wife. Leonie were members of the Historical Society for many years.These are two plasticised cards associated with the Warrnambool Co-Op. One is a Co-Card and the other is a Co-Op Charge Card used to receive discounts at other businesses. Both cards have bar codes. The larger card has a silver-coloured background with green printing and the smaller card is yellow with blue, black and yellow printing. Larger card - The Co-Op Co Card, 1204 B, Cumming Ronald J and ML (signed by Leonie Cumming on the back) Smaller card – The Co-Op Charge Card, 1204AA warrnambool co-operative society limited, co-card, warrnambool -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Amateur Radio Card, A 3AJ, 1920's
The Wireless Institute of Victoria was established in 1910 and amateur radio operators (called hams) in Victoria were issued with licences by this institute. Cards such as this one were exchanged by operators to confirm a contact between two amateur radio operators anywhere in the world (called QSL cards). The cards contained information regarding the radio contact made, the strength of the signal, the type of transmitter etc and the words, codes and abbreviations used were known internationally. This card, which is an unused one, belonged to Ted Salamy who had the call sign A 3AJ. This licence was issued in 1924 and was the 35th amateur radio licence issued in Victoria. It is believed that this was the first amateur radio station established in Warrnambool. Ted Salamy (1903-1977) was the son of Michael Salamy who established jewellery shops in Timor Street and in Liebig Street in Warrnambool in the 20th century. Ted Salamy was later the proprietor of these stores up to the 1960s when he retiredThis card has considerable local significance as an early Warrnambool amateur radio card and as one belonging to a prominent 20th century Warrnambool businessman, Ted Salamy. This is a card with a buff-coloured background and black and red printing on one side of the card and handwritten information in blue ink on the other side. The remains of adhesive tape applied to the edges of the card are still visible. ‘Timor Street Warrnambool Vic. Australia A 3AJ, E. Salamy Op.’ amateur (ham) radio, victoria, ted salamy -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Morse key, C 1930
The Morse telegraph system had its beginnings in 1836 when Samuel Morse, Alfred Vail and Joseph Henry developed an early model of the system. There are a number of variations on the machine but the operating system is very similar in all and the language is a standardised international code which has been in operation since the 1860's. Morse code consists of five elements, dots, dashes, and gaps of one , three and seven units in length. It is still in use to this day and has been applied to other systems of communication such as amateur radio, mobile phones and communication systems for disabled people. This particular telegraph key possibly has post office or naval origins.Morse code was an important invention in world communication systems and this machine therefore has important social and research significance. It is useful as an interpretive item.This instrument sits on a black rectangular base of black bakelite. The mechanism ids held in place by three larger metal screws and two smaller ones on the upright section from the base.The movable part is metal with the attached handle a similar black material as the base.ADMY.PATT No 7681 KEY MORSE SERN PL 23780 Rocker Front contact. Lift @ turn on one of the screws on the bar.history of warrnambool, rocker telegraph, telegraph key, morse code -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Morse code key, Mid 20th century
... knob at one end. Morse code key ...This is a Morse Code key. Morse Code is a method of transmitting text information using short and long signals (‘dots and dashes’). It is named after Samuel Morse, the inventor of the telegraph and was developed in the 1860s. It was used extensively in the 1890s for early radio communication before it was possible to transmit voice and continued to be used in the 20th century along with voice transmission , especially by amateur radio persons. It was also used in military and naval communication but not so much today. It is believed that this Morse Code key belonged to Ted Salamy, a jeweller and the first person in Warrnambool to hold an amateur radio licence (1924 Call Sign A3AJ, the 35th licence issued in Victoria).This Morse Code key is of interest as an object more used in the past, especially by amateur radio persons. It is believed to have been the property of Ted Salamy, the first person in Warrnambool to hold an amateur radio licence. This is a metal Morse Code key with an oval metal base. It has three screws inserted in the base and two more screws attached to the sides of the base. There is a key lever on top of the base and this is adjustable. The hinge on which the key lever sits is missing. The lever has a round black knob at one end. ‘Made in U.S.A. H15.682’ Wm.M. Nye Co Inc. Bellevue W.A.’ morse code key, ted salamy,, history of warrnambool -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Labels x 2, Evans & Co, Early 20th century
The saddler and harness business of E.D. Evans and Co. in Liebig Street was prominent in Warrnambool from the 1870s to the early decades of the 20th century. Edward Evans came to Warrnambool in the 1850s, was a Warrnambool Councillor from 1875 to 1878 and from 1884 to 1888 and was prominent in racing circles in the town,These labels are of interest as E.D. Evans was a well known saddle and harness maker in Warrnambool's history..1 Light brown cardboard label, primarily rectangular with mitred corners at one end, a hole with a red reinforce sticker surrounding it. The label has black printed text and several parallel lines. Also there is a pencilled code. .2 Identical to .1 but smaller.1 FROM E. D. EVANS & CO. SADDLE & HARNESS MAKERS, WARRNAMBBO, PORT FAIRY, AND TERANG. C 1900 ( In pencil) .2 Identical to .1 edward evans, saddler, warrnambool councillor, warrnambool racing -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Notebook, Telephone Code Dialling & Change Book, Mid 20th century
This notebook has been used in the Nullawarre Post Office in the mid 1900s. It lists the telephone exchange codes of places in Victoria and also the code for the telephone charges to those places. Charles and Vida Williams were the Post Master and Post Mistress at Nullawarre Post Office during the mid 20th century years. Nullawarre is a small settlement 25 kilometres south east of Warrnambool and is mainly an agricultural area. European settlement first occurred in the late 1860s. This notebook is of some interest as one used in the day-to-day business of the Nullawarre Post Office in the mid 20th century.This is a notebook which was originally set up as a Postman’s Redirection Book but has been used to list alphabetically telephone exchange areas and their codes. The book has an alphabetical index on the side of the pages and printed black lines and hand-ruled lines on the pages. The cover is light brown with blue binding on the spine and the binding is partly giving way. There is black printing and handwritten writing on the front cover. The material on the pages is handwritten in blue ink and pencil. There is a blue stamp and some pieces of paper pasted into some pages. ‘Postman’s Redirection Book’ ‘Telephone Code Dialling & Charge Book’ ‘Nullawarre’ -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Tool - Hedgetrimmer, 1949
This is a manual hedge trimmer which has a push pull action. It is not a very common garden tool possibly a lot slower to use than clippers. It dates from mid 20th century.This is quite a rare tool.This tool is consists of a metal bar with a row of prongs attached . A blade on one end is moved along the length of the metal bar thereby trimming the bush. There is a wooden handle attached to the metal bar and a wooden ball and spring on the righthand side.Code Half Time. Made in England Pat App No 16418/49warrnambool, tool, hedgetrimmer, code halftime -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument - Document - Student Information, VIOSH: Graduate Diploma in Occupational Hazard Management; Names and Information for Students, 1978 for First Intake 1979
Victorian Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (VIOSH) Australia is the Asia-Pacific centre for teaching and research in occupational health and safety (OHS) and is known as one of Australia's leaders on the field. VIOSH has a global reputation for its innovative approach within the field of OHS management. VIOSH had its first intake of students in 1979. At that time the Institution was known as the Ballarat College of Advanced Education. In 1990 it became known as Ballarat University College, then in 1994 as University of Ballarat. It was 2014 that it became Federation University. VIOSH Australia students are safety managers, senior advisors and experienced OHS professionals. They come from all over Australia and industry. Students are taught active research and enquiry; rather than textbook learning and a one-size fits all approach. VIOSH accepts people into the Graduate Diploma of Occupational Hazard Management who have no undergraduate degree - on the basis of extensive work experience and knowledge. Information from Ken Clements, Academic Registrar, to Derek Viner re Course codes for three Graduate Diploma Courses. One of these courses is in Occupational Hazard Management (ES4F/ES4P). The other two courses are Graduate Diploma in Management and Graduate Diploma in Music. There are four pages of names and addresses of the applicants for all courses. Those applying for Occupational Hazard Management to begin in 1979 are: Alistair Allan - Western Australia, Graham Suckling - New South Wales, Noel Arnold - Victoria, Allen Pang - Victoria, Bill Embling - South Australia, John Moroney - South Australia, John Florence - Queensland, Gwyn Griffiths - Victoria. Two applicants began in the Second Intake in 1980; Roy Hegney - Western Australia and Andrew Barnard - Victoria. Applicants were sent information regarding their application form - what was required and information on the residence at Mount Helen Campus - conditions and amenities.Six foolscap sheets, typed. First four are names and addressesviosh, victorian institute of occupational safety and health, ken clements, derek viner, academic registrar, graduate diploma in occupational hazard management, application information, residence information, mount helen campus, ballarat college of advanced education, alistair allan, graham suckling, noel arnold, allen pang, bill embling, john moroney, john florence, gwyn griffiths, western australia, new south wales, victoria, south australia, roy hegney, andrew barnard -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - PHOTOGRAPH NAVAL, MOUNTED, Exchange Studios, C.1900
The Steamer ASCANIUS became a troop Ship for the 1st AIF with the code name “HMAT A11”Photo B & W on light cream cardboard backing, photo is a 2 master, one funnel ship at sea, at the base is a Coat of Arms surrounded by the makers details in a circle. The rear has written details.On the rear in ink, “ ASCANIUS A11, Dear Exie, this is the old boat I am on, this photo was taken before she joined the Army”. On rear in pencil,” 9034. 1026 ........ 9 7/8. 6 3/4 .........”ascanius, troopships, aif -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumEquipment - WIRELESS SET 1944, 1944
This is a 6 valve portable transceiver, made in Australia from a British design. It was only used for C.W. (morse code). Its frequency was in the range of 2.5-3.5MHz. Output power 0.5-5 watts. Use was for commando and infantry patrols up to battalion level. It had an external battery pack for low and high voltage supply. 1 man operation in Tropics. An image of this type of wireless set in operation can be found in the AWM Collection: P02952.012 081815 Aluminium box, cover missing. The top has various dials, jacks and one gauge. There is a small length of cable coming from the control panel to a 4 pin plug. On the outside of case is the phrase D (arrow up)D 208 MKIIPlaque on control panel "WIRELESS SET - ZAA 2088 SERIAL NUMBER 168 DATE = 1944"wireless, wwii -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet - Booklet - Standards Association, Standards Association of Australia: .1 Welding Code, .2 Structural Steel
Two booklets produced by the Standards Association of Australia - established under the aegis of the Commonwealth and State Governments for the promotion of standardisation and simplified practice. .1 is on Welding Code. It was first issued on 1933 and revised in 1939. Cost One Shilling and Sixpence. .2 is the code for Structural Steel. It was first issued in 1928, amended in 1931 and revised in 1940. Cost Two Shillings and Sixpence. Both published by The Association, Science House, Gloucester and Essex Streets, Sydney..1 Folded green cover, 28 pages, stapled .2 Folded light brown cover, 30 pages, stapled.1 T R Gordon in blue pencil on cover .2 E J Barker in blue pen on cover.standards association of australia, commonwealth government, state governments, welding code, structural steel code, 1933, 1939, 1928, 1940, science house sydney -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaSouvenir - Cup, Margaret Woodward, 2015
Margaret Woodward is a an artist and an an associate professor of design at Charles Sturt University. Artist statement: "The Sea is All Around us is a multi-layered event which creates a memorable experience for those visiting the Dome Gallery and the Mission to Seafarers in Melbourne’s Docklands. The event acknowledges and raises awareness of the often difficult and dangerous working lives and journeys of seafarers by making visible their role in transporting commodities, materials and objects to and from Australia’s shores. This installation at the Dome Gallery in the Mission to Seafarers in Melbourne’s Docklands marks the third stage of an ongoing research project which seeks to reveal the ‘social life’ of souvenirs. Beyond their representational role souvenirs also trigger intangible, affective qualities – reminders of journeys and places, new associations with tastes, sounds and people, and thereby becoming objects which focus and hold memories. This installation invites seafarers and visitors to participate in a global project which aims to witness sea journeys and trace the mobile life of seafarers and souvenirs. For a fortnight in May 2015, the Dome Gallery became an architectural large scale compass, with the circular floor marking the intersection of its latitude and longitude (37 º 49'21" S 144º 57'03"E). Over these two weeks the Dome Gallery was inscribed with marks recording journeys made by seafarers, recording destination and departure ports, home lands and waterways, and in doing so making visible a small segment of the global patterns of seafaring. Custom-made souvenirs designed for the installation are given to seafarers as gestures of welcome and a memento of their visit. The souvenirs originating in Poland continue their journey by sea, to destinations beyond the Dome becoming part of the global network of seafaring, with an invitation for seafarers to record their future journeys using QR code scanning technologies. It is hoped that by releasing the 200 limited edition souvenirs accompanying the seafarers the mobile life of souvenirs and seafarers will also become visible. Like messages in bottles they leave our shores, becoming ambassadors, representing the Dome Gallery at the Mission to Seafarers, the waters of Port Phillip Bay, Australia’s red soil and vegetation, and carrying memories of visiting Melbourne." The Mission has always been open to the community and has a tradition of hosting cultural events: shows, concerts, exhibitions, festivals.Orange enamel and teal mug created for the art installation by artist Margaret Woodward at the Mission to Seafarers. On one side it is decorated with a compass and a latitude and longitude; on the opposite side, a leaf, a QR code on the bottom takes you to the website.Written at the bottom of the mug: Please scan to map the journey of this souvenir * www.sensingtheremote.net *2015cultural events, norla dome, mso, 2015, art installation, margaret woodward -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaPhotograph - Photographs, Serie, Mission to Seafarers Victoria, The sea is all around us, 29 May 2015
EXHIBITION in the DOME The Sea is All Around Us - Margaret Woodward 11-21 May 2015 Dome Gallery – Mission to Seafarers, 717 Flinders Street, Melbourne, Australia. 37 º 49'21" S 144º 57'03"E Hours: Daily 11.00am - 4.00pm The sea is all around us is a multi-layered event which will create a memorable experience for those visiting the Dome Gallery and the Mission to Seafarers in Melbourne’s Docklands. The event will acknowledge and raise awareness of the working lives and journeys of seafarers by making visible their role in transporting commodities, materials and objects to and from Australia’s shores. This installation invites seafarers and visitors to participate in a global project which aims to witness sea journeys and trace the mobile life of seafarers and souvenirs. For a fortnight in May 2015, the Dome Gallery will become an architectural large scale compass, with the circular floor marking the intersection of its latitude and longitude (37 º 49'21" S 144º 57'03"E). Over these two weeks the Dome Gallery will be inscribed with marks recording journeys made by seafarers, recording destination and departure ports, home lands and waterways, and in doing so making visible a small segment of the global patterns of seafaring. Custom-made souvenirs designed for the installation will be given to seafarers as gestures of welcome and a memento of their visit. The souvenirs originating in Poland will continue their journey by sea, to destinations beyond the Dome becoming part of the global network of seafaring, with an invitation for seafarers to record their future journeys using QR code scanning technologies. It is hoped that by releasing the 200 limited edition souvenirs accompanying the seafarers the mobile life of souvenirs and seafarers will also become visible. For more information visit the website: sensingtheremote.net Margaret Woodward is Associate Professor of Design at Charles Sturt University For a fortnight in May 2015, Margaret Woodward was ‘in residence’ at the Mission to Seafarers Norla Dome Gallery with her participatory installation project "The Sea is All Around Us". The floor of the gallery became a large scale compass. Seafarers were welcomed to the gallery their ships, journeys and destinations were recorded and mapped on the floor drawing. Seafarers were welcomed with cake and souvenir mugs of tea. These mugs, a momento for the seafarers, were inscribed with a scannable QR code and an invitation for seafarers to record their journeys on a dedicated project website. Around 120 souvenirs are now continuing their journey by sea and seafarers have scanned the mugs from locations including Singapore, Brisbane, Fremantle, Adelaide, Busan and Johor! After the exhibition Margaret Woodward was able to follow the seafarers' whereabout: ""The Sea is all Around Us". I am in awe of where this project might go, well done Margaret. One week has passed since finishing up at the Mission to Seafarers Victoria. Today I check my website and can see that the cup-carrying seafarers are reaching warmer climates, they tell me it’s getting hot as some are already in Suva and Port Lautoka. I’ve watched the souvenirs travel and fan out from Melbourne, some West to Adelaide and Fremantle, others going north to Sydney Brisbane, Singapore and Busan. Another seafarer scans in from Changi Airport, excited to be going home for some time with his family in the Phillipines. I keep an eye on my ‘fleet’ of 22 ships that visited the Dome Gallery, and see where they are on the Live Shipping website, watch some of them sail up the coast of Western Australia and marvel at the steady pace this journey takes. I am so used to flying over coastlines and countries in a matter of hours, impatiently watching the tracking screen from my airline seat, this shipping pace seems so much more real, so much more of a passage. I feel connected to these ships, to the people on board, to know that an object has passed from my hands to theirs, now holding in it my cargo of concern."margaret woodward, installation, exhibition, norla dome, 2015, sea voyage, sea journey, cultural events -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomBooklet, Field Engineering & Mine Warfare Pam 8 Assault River Crossing, 1951
Soft covered booklet providing the necessary information to enable instructors of Royal Engineers and Assault Pioneers to train their men in methods of getting supporting weapons and some vehicles across water obstacles. 2 copies. One copy has amendments Nos 4 & 5WO Code No 8668. Part II Rafting and Watermanship (RE and Aslt Pnrs) 1951military engineering, river crossings -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomBooklet, GS Training Publications, Command & Organization of a Corps Headquarters in War, 1950
A soft covered booklet indicating one way of operating a corps HQ that evolved from four years of active warfare in the desert, Sicily and NW EuropeWO Code No 8618corps hq operations
