Showing 92 items
matching violence
-
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Whitehorse Emergency Relief Network
The Nunawading Ladies Benevolent Society became the Whitehorse Emergency Relief Network in 1999, when a number of local organizations were encouraged to form a network by Betty and Keith Rooney. The object was to collect domestic items of good quality to assist people in need, especially women who have been the victims of domestic violence.Coloured photograph of the interior of the Whitehorse Emergency Relief Network 10-12, Thornton Crescent, Nunawading. Domestic goods showneastern emergency relief centre, thornton crescent mitcham nos 10-12 -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Photograph, Eastern Emergency Relief Network
The Nunawading Ladies Benevolent Society became the Whitehorse Emergency Relief Network in 1999 when a number of community organizations were encouraged to form a network by Betty and Keith Rooney. The object is to collect domestic items of good quality to assist people in need, especially women who have been the victims of domestic violence.Coloured photograph of the opening of the Eastern Emergency Relief Network, 10-12 Thornton Crescent, Mitcham on April 13 1999. Photograph shows people viewing donated goods.whitehorse emergency relief network, mitcham, thornton crescent no 10-12 -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratRobyn Mason: collected memorabilia and press cuttings, 1993-2015
Robyn Mason was a member of the ALP and unsuccessfully contested the seat of Ballarat West in 1996. She was a feminist, teacher and a social worker who fought hard for those affected by sexual abuse and violence. Robyn Mason passed away in 2016. This large collection was donated after her passing; it is a reflection of the vastness of Robyn's contribution to the Ballarat community. Politics, government, advocacy, education - Ballarat region. News articles, correspondence and other memorabilia.btlc, ballarat trades hall, ballarat trades and labour council, politics and government, alp, australian labor party, brumby, john, mason, robyn, kirner, joan, beacham, jenny, howe, brian, elections - state - victoria, sheehan, frank, laffey, catherine, thwaites, john, keating, paul, cain, john, kennett, jeffrey, state premiers, advocacy - sexual abuse, advocacy - violence -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaPhotograph, Peter Storey: President-elect of the Methodist Conference of South Africa, 1984
The World Alliance of Reforned Churches had declared the South African Dutch Reformed churches heretical because of their doctrinal advocacy of apartheid. Storey spoke about the situation in South Africa - "Speaking from his non-violence Christian viewpoint, he said that violence was counter-productive. 'When an organisation uses these methods it loses something of its moral case. I understand why people such as the ANC turn to those methods. I will never agree with them.' He saw four main taks for the church in South Africa - to continue to tell the truth in a propagandised society, to continue to bind up the wounds of people who are victims in that society—in this area the church's record is a good one, to demonstrate in its own life an alternative to apartheid, and to try to fashion strategies which would bring about change, in harmony with the teachings of Christ."Storey is shown sitting at a table addressing a meeting.C&N identification.apartheid, storey, peter, south african churches -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratRobyn Mason: scrapbook, 1993-1995
Robyn Mason was a member of the ALP and unsuccessfully contested the seat of Ballarat West in 1996. She was a feminist, teacher and a social worker who fought hard for those affected by sexual abuse and violence. Robyn Mason passed away in 2016. This large collection of correspondence, photographs and other memorabilia, was donated after her passing; it is a reflection of the vastness of Robyn's contribution to the Ballarat community. Politics, government, advocacy, education. Standard scrapbook containing news articles, photos, and other.btlc, ballarat trades hall, ballarat trades and labour council, politics and government, alp, australian labor party, brumby, john, mason, robyn, kirner, joan, beacham, jenny, howe, brian, elections - state - victoria, sheehan, frank, laffey, catherine, thwaites, john, keating, paul, cain, john, kennett, jeffrey, state premiers, advocacy - sexual abuse, advocacy - violence -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Slide - DIGGERS & MINING. THE GOLD LICENCE, 1850s
Diggers & Mining. The gold licence. The Government Camp. Many of the goldfields police were men of poor character, who carried out their duties with blustering arrogance, demanding the production of the licence with threatening language, and sometimes open violence; and hauling off as common criminals men who, by some mischance, did not have their licences on their persons, when, given a few minutes, they could have shown they had complied with the law. Markings: 35 994.LIF. 4. Used as a teaching aid.hanimounteducation, tertiary, goldfields -
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyNewspaper - Yorston, J.S., Councillor
Photocopy of page three of CAULFIELD ADVERTISER (17th April 1947) carrying potted biography and photograph of Councillor J.S. Yorston, Father of the Council, which was number two in the newspaper’s KNOW YOUR COUNCIL series. Filed also includes the entire issue (eight pages) of the same ADVERTISER, on the front page of which is a report of a domestic violence charge proven at Caulfield Court of Petty Sessions against Herbert Charles Woodbridge, who assaulted his wife and daughter.yorston j.s., caulfield council, woodbridge herbert charles, domestic violence, dickson and yorston, lempriere avenue, building and construction company, victorian scottish union -
 Nillumbik Shire Council
Nillumbik Shire CouncilMixed media: Liz NETTLETON, Liz Nettleton, Respite and Repose, 2010
Nettleton creates an image of peace and tranquility after the violence felt from the 2009 Black Saturday bush fires / At the Arthurs Creek cemetery Nettleton found the grave of Reg Evans and Angela Brunton, friends who had perished in the fires / Nettleton sat on the edge of their joint grave and photographed their view / It was only after examining the photos more closely that she realized Mount Sugarloaf had burnt almost to the valley / Sugarloaf is always in an indigo haze. This work is by a local contemporary artist and encompasses themes dealing with the 2009 Black Saturday bushfires. Mixed media (acrylic paint, acrylic ink and indian ink) on board / Landscape painting of Mount Sugarloaf and green pastures after the 2009 Black Saturday bushfires / Mount Sugarloaf is depicted in an indigo haze in the background / A line of trees bathed in light border the mountain's edge / Lines of trees parallel to each other jut out diagonally in the foreground / Framing this view of the landscape is a pattern (topographical maps of the Nillumbik area), which suggest the vast extent of the devastated area of landscape. In black marker 'LIZ NETTLETON' + artist signature '2011' on back - middle right side nettleton, respite and repose, landscape, painting, mixed media, black saturday, mount sugarloaf -
 Australian National Surfing Museum
Australian National Surfing MuseumBook, Surf Rage, 2000 (exact)
This book is a direct result of an incident on 16 March 2000 when Australian surfing champion Nat Young was physically assaulted at Angourie Beach after an altercation in the water. The book contains a series of eleven articles exploring the issue of aggression (rage) in the surfing community. The book features a forward by Drew Kampion and articles by a number of surfers including Nat Young, Derek Reilly, Nick Carroll, Fred Pawle and Torquay local, Gordon Stammers. This book is significant in that it was the first Australian publication to formally address the issue of surf rage on Australian beaches.SURF RAGE by Nat Young (a surfers guide to turning negatives into positives). Full colour, soft colour book with a photo of a tubing wave on the coverISBN 0-9585750-1-0surfing, nat young, surf rage, nick carroll, gordon stammers, tribal law, surfers, violence, anger -
 Women's Art Register
Women's Art RegisterBook, Oxford University Press, Idols of perversity. Fantasies of Feminine evil in Fin-de-Siecle Culture, 1989
Analysis of late 19th century American and European writing, art, science and philosophy exploring cultural misogyny. Discusses the attitude to women as having only sexual and reproductive roles and being depicted as symbols of evil, passivity and sensuality, and ever dependent, while men were free to follow financially independent public and intellectual lives.Booknon-fictionAnalysis of late 19th century American and European writing, art, science and philosophy exploring cultural misogyny. Discusses the attitude to women as having only sexual and reproductive roles and being depicted as symbols of evil, passivity and sensuality, and ever dependent, while men were free to follow financially independent public and intellectual lives. painting, feminism, sexuality, violence, symbolism, mythology, motherhood, darwinism, pre-raphaelites -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncDocument - Folder, Nichols, Alan
Montmorency resident, Rev Alan Nichols worked as a crime reporter then as a priest n Burma, Papua New Guinea, Thailand, the Gaza Strip, Lebanon, South Africa and Kenya; he was deputy chairman of the Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre board and writing a book on the West Papuan refugees who came to Australia by canoe in January 2006. Contents Newspaper article: "A life close to violence," Diamond Valley Leader, 21 March 2007. Outlines Rev Alan Nichols past work and current activities.Newspaper clippings, A4 photocopies, etcalan nichols, west papuan refugees 2006 -
 Women's Art Register
Women's Art RegisterBook, Judy Chicago, Through the Flower. My struggle as a women artist
BookBooknon-fictionBookfeminism, feminist art, exhibition, abstraction, art education -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Diploma of Applied Science Nursing: NB311 Psycosocial Processes III, 1998
The University of Ballarat was a predecessor Institution of Federation University AustraliaBlue paper covered report nursing, healthcare, diploma of applied science nursing, psychosocial processes, course readings, cognitive behavior modification, behavioural techniques, carers, violence, behaviour control -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratPower and terror : post 9/11 talks and interviews, Junkerman, John, 2003
The book comes from public talks given by Chomsky in 2002 (as a follow up to 9/11) and a previously unpublished interview. Chomsky reflects upon terrorism, US foreign policy and offers different non-violent solutions. Contents: Part I: Interview with Noam Chomsky for the film Power and Terror Part II: U.S. arms, human rights, and social health Part III: Talks and conversations "Why do they hate us, when we're so good?" Visiting the West Bank with Azmi Bishara Media bias and Palenstine How should we respond? The United States and the world Part IV: More information Further reading: a selection of books by Noam Chomsky About the film Power and Terror: Noam Chomsky in our times About the author About the editor About the publishers. Relevant to 9/11 and to US foreign policy and terrorism.Paper; book. Front cover: colour photograph of a military officer with gun and children looking on; black and red lettering. Front cover: author's name and title.btlc, ballarat trades hall, ballarat trades and labour council, 9/11, terrorism, foreign policy - united states, chomsky, noam, interviews, violence, government -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Jarrod Watt, Seven police officers stand guard in front of Hong Kong's main police headquarters on Arsenal Street in Wan Chai, 2019, 21/06/2019
Carrie Lam, Hong Kong’s chief executive, had plenty of political support in the territory’s pro-Beijing legislature to pass a bill that would allow extraditions to mainland China. The legislators were set to begin discussing the bill in early June, and intended to vote on it just weeks later. A series of protests took place, and after a June 16 protest saw the largest turnout yet, Ms. Lam made a major concession: She postponed the bill, at least temporarily. It was an undeniable victory for the protesters — but it did little to quell the unrest. Since the bill could later be reintroduced, protesters felt they remained in danger. The police tactics to break up the demonstrations on June 12, including the use of more than 150 tear gas canisters to push protesters far away from the government office, created a new set of demands from the protesters. Now, instead of just calling for the withdrawal of the bill and Ms. Lam’s resignation, they said they wouldn’t be content unless there was an independent investigation of officers’ conduct. They also wanted the release of protesters arrested on June 12, and for the government to rescind its description of the demonstrations as a “riot,” a designation that carries legal significance. None of that has happened. Many analysts say Ms. Lam is unlikely to step down, nor would Beijing accept her resignation if she offered it. She has more wiggle room on the other demands, but has not indicated any willingness to budge. The Hong Kong Protests are a leaderless, digital movement.There is no single leader or group deciding on or steering the strategy, tactics and goals of the movement. Instead, protesters have used forums and messaging apps to decide next steps. Anyone can suggest a course of action, and others then vote on whether they support it. The most popular ideas rise to the top, and then people rally to make them happen. At its best, this structure has empowered many people to participate and have their voices heard. Protesters say it keeps them all safe by not allowing the government to target specific leaders. Their success in halting the extradition bill, which was shelved by the territory’s chief executive, speaks to the movement’s power. Despite the lack of a clear leader, protesters have shown extensive coordination at the demonstrations, having planned the specifics online beforehand. Supply stations are set up to distribute water, snacks, gloves, umbrellas and shields made of cardboard. Volunteer first aid workers wear brightly colored vests. People form assembly lines to pass supplies across long distances, with protesters communicating what they need through a series of predetermined hand signals. Anyone walking in dangerous areas without a helmet or a mask is quickly offered one. No individual can speak on behalf of the protesters, which makes negotiations difficult, if not impossible. (https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/02/world/asia/hong-kong-protest-explained.html, accessed 07/07/2019) Hong Kong’s amended extradition law would allow the extradition of suspects to mainland China for the first time. Supporters say the amendments are key to ensuring the city does not become a criminal refuge, but critics worry Beijing will use the law to extradite political opponents and others to China where their legal protections cannot be guaranteed. The government claims the push to change the law, which would also apply to Taiwan and Macau, stems from the killing last year of a Hong Kong woman while she was in Taiwan with her boyfriend. Authorities in Taiwan suspect the woman’s boyfriend, who remains in Hong Kong, but cannot try him because no extradition agreement is in place. Under the amended law, those accused of offences punishable by seven years or more in prison could be extradited. The new legislation would give Hong Kong’s leader, known as the chief executive, authority to approve extradition requests, after review by the courts. Hong Kong’s legislature, the legislative council, would not have any oversight over the extradition process. Many Hong Kongers fear the proposed extradition law will be used by authorities to target political enemies. They worry the new legislation spells the end of the “one country, two systems” policy, eroding the civil rights enjoyed by Hong Kong residents since the handover of sovereignty from the UK to China in 1997. Many attending the protests on Sunday said they could not trust China as it had often used non-political crimes to target government critics, and said they also feared Hong Kong officials would not be able to reject Beijing’s requests. Legal professionals have also expressed concern over the rights of those sent across the border to be tried. The conviction rate in Chinese courts is as high as 99%. Arbitrary detentions, torture and denial of legal representation of one’s choosing are also common. Many in the protests on Sunday 09 June 2019 said they felt overwhelmed by a sense of helplessness in the face of mainland China’s increasing political, economic and cultural influence in Hong Kong. Hong Kong’s top political leader is not elected by ordinary voters but by a 1,200-strong election committee accountable to Beijing. Half of its legislature are chosen through indirect electoral systems that favour pro-Beijing figures. Many Hong Kongers also cited the jailing of leaders and activists from the 2014 Occupy Central movement– a 79-day mass civil disobedience movement – as well as the disqualification of young localist lawmakers as signs of the erosion of civil freedoms. Resentment towards China has been intensified by soaring property prices – with increasing numbers of mainland Chinese buying properties in the city – as well as the government’s “patriotic education” drive, and the large numbers of mainland tourists who flock to Hong Kong. Many Hong Kongers are also concerned about China’s growing control over the city’s news media, as they increasingly self-censor and follow Beijing’s tacit orders. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/jun/10/what-are-the-hong-kong-protests-about-explainerSeven police officers stand guard in front of Hong Kong's main police headquarters on Arsenal Street in Wan Chai as an estimated one thousand protestors surround on 26 June 2019. Protestors take turns to step up and hurl abuse at the officers, in a protest lasting 6 hours before peacefully dispersing. The protesters chanted 'Release the martyrs' and 'Stop police violence' in reference to violent clashes with police in the days previous. ( https://www.scmp.com/news/hong-kong/politics/article/3016238/hong-kong-police-under-siege-again-protesters-surround)carrie lam, hong kong protests, extraditions, protest, protestors, police, wan chai -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - HEALTH ON THE BENDIGO DIGGINGS: 1852 TO 1858
''Health on the Bendigo Diggings - The Early Years 1852 - 1858'' (Patricia Worsley- Bendigo Technical College , Mature Age Students, 1982, 8-paged Australian History paper). Broad scope with references to : Diseases (typhoid, dysentery, 'dandy blight') sanitation and water supply; violence, Publican's licence; suicide; medical 'qualifications'; compulsory registration of legally qualified medical practitioners; inquests, Dr Richard Tracy; Bendigo Waterworks Company; Bendigo Hospital; 'Hospital Hill' ; Bendigo Goldfields Hospital; Benevolent Asylum; Sir John O'Shanassy. Bibliography.Patricia Worsleybendigo, mining, miners health, typhoid, dysentery, dandy blight sanitation, bendigo water supply, hospital hill, benevolent, sir john o'shanassy, dr richard tracy -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratPhotograph: John Thwaites, John Brumby, Robyn Mason and Steve Bracks, October 1994
Picture is of John Thwaites, John Brumby, Steve Bracks and Robyn Mason at Lake Wendouree. John Thwaites was Mayor of South Melbourne and subsequently served in the Victorian Parliament from 1992-2007, filling the position of Deputy Premier from 1999 – 2007. Steve Bracks was the 44th Premier of Victoria from 1999-2007. He was born in Ballarat. John Brumby was the 45th Premier of Victoria from 2007-2010. Robyn Mason was a member of the ALP and unsuccessfully contested the seat of Ballarat West in 1996. She was a feminist and a social worker who fought hard for those affected by sexual abuse and violence. Robyn Mason passed away in 2016.Photographs.Described on label as, "the three handsomest men in Victorian parliament."btlc, ballarat trades hall, ballarat trades and labour council, mason, robyn, thwaites, john, brumby, john, bracks, steve, politicians, social workers, advocacy - sexual abuse, advocacy - violence, australian labor party, alp, premier - victoria -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratRobyn Mason: collected photographs, 1993-2000
Robyn Mason was a member of the ALP and unsuccessfully contested the seat of Ballarat West in 1996. She was a feminist, teacher and a social worker who fought hard for those affected by sexual abuse and violence. Robyn Mason passed away in 2016. This large collection of photographs was donated after her passing; the collection reflects the vastness of Robyn's contribution to the Ballarat community. Photographs here include the following persons: Batchelor, Peter Beacham, Jenny Borchers, Betty Borchers, Norm Bracks, Steve Breen, Barry Brumby, John Garbutt, Sherryl Keating, Paul Knight, Sharon Laffey, Catherine Mason, Robyn Rootes, Jeff Sheehan, Frank Thomson, Hedley Thwaites, John Politics, government, advocacy, education - Ballarat region. Photographs.btlc, ballarat trades hall, ballarat trades and labour council, politics and government, alp, australian labor party, brumby, john, mason, robyn, beacham, jenny, elections - state - victoria, sheehan, frank, laffey, catherine, thwaites, john, keating, paul, kennett, jeffrey, state premiers, batchelor, peter, borchers, betty, borchers, norm, bracks, steve, breen, barry, keating, paul, knight, sharon, rootes, jeff, thomson, hedley -
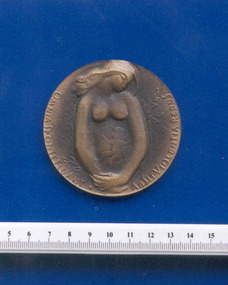 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Commemorative Alfred Kotasek medal associated with Frank Forster, 1974, 1974 (approximate)
According to a typed note with the object, this medal came from Czechoslovakia in 1974. It belonged to Frank Forster. Alfred Kotasek (1911-1991) was a Czech professor of obstetrics and gynaecology. The date featured on this medal is the date of his birth, and 'MUDr' is a Master of General Medicine qualification. The Latin motto featured on this medal is strongly associated with the 17th century Czech (Moravian) author and pedagogue Jan Amos Komensky, who allegedly took this phrase as his motto and featured it in one of his most famous works, 'Orbis sensualium pictus' (The World in Pictures) [1658]. Loosely translated, the meaning of the motto approximates 'Let everything flow freely, without violence to things.' 'Orbis sensualium pictus' has been described as the first true illustrated book for children, and Komensky is considered by some to be the father of modern education.Round bronze coloured medallion. Front of medal features a profile portrait of Professor Alfred Kotasek and is inscribed "19.12.1911/PROF.MUDR/ALFRED/KOTASEK". Back of medal features a raised image of a woman with a child in utero and is inscribed "OMNIA SPONTE FLUANT ABSIT VIOLENTIA REBUS".numismatics -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumTextile - Quilt, Lois Densham, Anzac Anniversary, 1985
This quilt is called "Anzac Anniversary" and was made by Lois Densham in Melbourne in 1985. Lois Densham was a member of the Running Stitch group of quilters. This quilt was displayed in "Wool Quilts Old and New", a touring exhibition presented by the Running Stitch quilters group in 31 Jan. 1986 to Feb. 1987. It was catalogue entry no. 3. The artist's statement reads: "A veil of violence over a calm surface. Violent angles of the tartans and plaids with elongated curved segments which bring to mind Scottish warfare and Australians with Scottish forefathers. I began this quilt because of Anzac Day and the 70th anniversary of the First World War. Anzacs rededicate themselves yearly to peace within their circle of family and friends." This quilt was later exhibited in an identically titled exhibition held at the National Wool Museum in 1989.Quilt - "Anzac Anniversay" by Lois Densham, Melbourne, 1985anzac day, handicrafts quilting, running stitch group, running stitch collection, masters of technique: creators on cloth - exhibition (15/06/2001 - 22/07/2001) highlights of the national wool museum: from waggas to the wool quilt prize - exhibition (22/09/2001 - 02/12/2001), densham, ms lois, handicrafts, quilting -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratStrange Birds in Paradise : A West Papuan Story, Nicolai, Jamie, 2009
Blurb from the back: While the Indonesian army continues to dominate the indigenous inhabitants of West Papua, Hill-Smith records the fate of West Papuans trying to maintain village life against a backdrop of covert military violence. In the West Papuan highlands, Hill-Smith - an Australian writer, cartoonist and comedian - hears stories of escape, oppression and exile and listens to the defiant songs of murdered musician and independence hero Arnold Ap. Together with friends Donny Roem, a recent exile, and Jacob Rumbiak, a child soldier in the West Papuan resistance movement, Hill-Smith returns to Melbourne to record outlawed folk songs with renowned Australian rock musicologist David Bridie. An extraordinary story of an imaginative, adaptable culture confronting tyranny with the joyful power of art, music and self-expression.Relevant to the history of West Papua and the Indonesian military presence and violence. Use of music to draw attention to the issues faced by West Papua.DVDFront cover: Title, rating (M), picture of winged West Papuan Man with guitar, "Winner Best Doco SBS IF award 2010". Back cover: Precis of content, website for producer company, names of contributors, directors, editors, etc.btlc, ballarat trades and labour council, ballarat trades hall, west papua, indonesia, war, songs, animations, military violence -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratPhotograph: Robyn Mason, Frank Sheehan, Jenny Beacham, Hon Justice Kerr and John Brumby, 1996
Photograph: from left, Robyn Mason, Frank Sheehan, Jenny Beacham, Justice Kerr, John Brumby. The photograph was taken to launch the ALP Victorian Federal campaign in Ballarat in 1996 outside of the ALP campaign office. Robyn Mason was a member of the ALP and unsuccessfully contested the seat of Ballarat West in 1996. She was a feminist and a social worker who fought hard for those affected by sexual abuse and violence. Robyn Mason passed away in 2016. Frank Sheehan was the state member for Ballarat South from 1982 to 1992. Jenny Beacham is a former Labor state secretary and was an ALP candidate for Ballarat in 1996. Justice Kerr served in federal parliament as the member for Denison for 23 years (1987–2010). He was Attorney-General (1993) and Minister for Justice (1993–1996) in the Keating Government and Parliamentary Secretary for Pacific Island Affairs (2007–2009) in the Rudd Government. John Brumby was the 45th Premier of Victoria from 2007-2010. At the time of the photo, he was leader of the opposition.Photograph.btlc, ballarat trades and labour council;, ballarat trades hall, mason, robyn, sheehan, frank, beacham, jenny, kerr, justice duncan -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Document, Nurse A Watt , Cheltenham Nursing Home c1900, c1900
Nurse A. Watt was a registered Nurse who owned the Cheltenham Nursing Home, located up on the hill, at 200 Charman Road Cheltenham c1900. With Dr. Fleming Joyce, she brought many local identities into the world. Len Allnutt recalls that his brother, Ray, was born there in 1924. Nurse Watt had an excellent reputation for her care and ability in the local area. One recorded event was when in November 1910 Constable Edwards was shot by his son David, at his police house, after an episode of domestic violence involving Constable Edwards long suffering wife - the mother of David. Const. Edwards was first taken to the Police Station, but later taken by Shire ambulance to Nurse Watt's Cheltenham Nursing Home. At 8pm, Edwards was operated on by Dr. Joyce and Dr. Weigall. Despite the surgery, Edwards died the next day of haemorrhage and shock. David was convicted of manslaughter. Dr A Fleming Joyce was the Shire Medical Officer c1914 - 1930. Nurse Watt bequeathed her Estate to the Methodist Church. ( H. Stanley CMHS)c1900 Nurse A Watt had an excellent reputation for her care and ability in the Cheltenham area where Medical, Surgical and Midwifery Cases were received at her Nursing Home in Charman Road. She also accommodated convalescent cases. She worked with Dr A.Fleming Joyce and Dr Weigall.a) Advertisement / Leaflet for Nurse A.Watt c1900 b) Black & White photograph of the Cheltenham Nursing Home, 200 Charman Road Cheltenham c1900watts nurse a, joyce dr. a f., cheltenham nursing home c1910, charman road cheltenham, nursing, medicine, midwifery, victoria police force, smith j l; smith mary ann, stanley helen,, horse drawn carts, toll gates brighton, motor cars 1900, steam engines, early settlers, bentleigh, mckinnon, parish of moorabbin, city of moorabbin, county of bourke, moorabbin roads board, shire of moorabbin, henry dendy's special survey 1841, were j.b.; bent thomas, o'shannassy john, king richard, charman stephen, highett william, ormond francis, maynard dennis, market gardeners, vineyards, orchards -
 Unions Ballarat
Unions BallaratPhotograph: John Brumby, Frank Sheehan, Robyn Mason, Norm Borchers - ALP state campaign 1996, 1996
Photograph: from left, John Brumby, Frank Sheehan, Robyn Mason and Norm Borchers. Launch of the ALP state campaign in 1996 at Begonia House, Ballarat Botanical Gardens. Ballarat Botanical Gardens is located near Lake Wendouree, Ballarat. John Brumby was the 45th Premier of Victoria from 2007-2010. At the time of the photo, he was leader of the opposition. Frank Sheehan was the state member for Ballarat South, serving from 1982-1992. Robyn Mason was a member of the ALP and unsuccessfully contested the seat of Ballarat West in 1996. She was a feminist and a social worker who fought hard for those affected by sexual abuse and violence. Robyn Mason passed away in 2016. Norm Borchers passed away in 2008. Borchers was a Club President of the Sebastopol Lions Club (1975-76). He worked for the railways as an engineering employee and was long-term trade unionist (Amalgamated Engineering Union and the Australian Railways Union) and ALP member; he lived and worked in the Ballarat area. Norm was active in workplace disputes during the ALP split in 1955. He was a long time supporter of Ballarat Trades Hall.Photograph.btlc, ballarat trades hall, ballarat trades and labour council;, mason, robyn, borchers, norm, brumby, john, politicians, sheehan, frank, elections, alp, australian labor party, begonia house, ballarat botanical gardens -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour, Jarrod Watt, A thousand protestors surround Hong Kong's main police headquarters on Arsenal Street in Wan Chai on June 26th 2019, 21/06/2019
Carrie Lam, Hong Kong’s chief executive, had plenty of political support in the territory’s pro-Beijing legislature to pass a bill that would allow extraditions to mainland China. The legislators were set to begin discussing the bill in early June, and intended to vote on it just weeks later. A series of protests took place, and after a June 16 protest saw the largest turnout yet, Ms. Lam made a major concession: She postponed the bill, at least temporarily. It was an undeniable victory for the protesters — but it did little to quell the unrest. Since the bill could later be reintroduced, protesters felt they remained in danger. The police tactics to break up the demonstrations on June 12, including the use of more than 150 tear gas canisters to push protesters far away from the government office, created a new set of demands from the protesters. Now, instead of just calling for the withdrawal of the bill and Ms. Lam’s resignation, they said they wouldn’t be content unless there was an independent investigation of officers’ conduct. They also wanted the release of protesters arrested on June 12, and for the government to rescind its description of the demonstrations as a “riot,” a designation that carries legal significance. None of that has happened. Many analysts say Ms. Lam is unlikely to step down, nor would Beijing accept her resignation if she offered it. She has more wiggle room on the other demands, but has not indicated any willingness to budge. The Hong Kong Protests are a leaderless, digital movement.There is no single leader or group deciding on or steering the strategy, tactics and goals of the movement. Instead, protesters have used forums and messaging apps to decide next steps. Anyone can suggest a course of action, and others then vote on whether they support it. The most popular ideas rise to the top, and then people rally to make them happen. At its best, this structure has empowered many people to participate and have their voices heard. Protesters say it keeps them all safe by not allowing the government to target specific leaders. Their success in halting the extradition bill, which was shelved by the territory’s chief executive, speaks to the movement’s power. Despite the lack of a clear leader, protesters have shown extensive coordination at the demonstrations, having planned the specifics online beforehand. Supply stations are set up to distribute water, snacks, gloves, umbrellas and shields made of cardboard. Volunteer first aid workers wear brightly colored vests. People form assembly lines to pass supplies across long distances, with protesters communicating what they need through a series of predetermined hand signals. Anyone walking in dangerous areas without a helmet or a mask is quickly offered one. No individual can speak on behalf of the protesters, which makes negotiations difficult, if not impossible. (https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/02/world/asia/hong-kong-protest-explained.html, accessed 07/07/2019) Hong Kong’s amended extradition law would allow the extradition of suspects to mainland China for the first time. Supporters say the amendments are key to ensuring the city does not become a criminal refuge, but critics worry Beijing will use the law to extradite political opponents and others to China where their legal protections cannot be guaranteed. The government claims the push to change the law, which would also apply to Taiwan and Macau, stems from the killing last year of a Hong Kong woman while she was in Taiwan with her boyfriend. Authorities in Taiwan suspect the woman’s boyfriend, who remains in Hong Kong, but cannot try him because no extradition agreement is in place. Under the amended law, those accused of offences punishable by seven years or more in prison could be extradited. The new legislation would give Hong Kong’s leader, known as the chief executive, authority to approve extradition requests, after review by the courts. Hong Kong’s legislature, the legislative council, would not have any oversight over the extradition process. Many Hong Kongers fear the proposed extradition law will be used by authorities to target political enemies. They worry the new legislation spells the end of the “one country, two systems” policy, eroding the civil rights enjoyed by Hong Kong residents since the handover of sovereignty from the UK to China in 1997. Many attending the protests on Sunday said they could not trust China as it had often used non-political crimes to target government critics, and said they also feared Hong Kong officials would not be able to reject Beijing’s requests. Legal professionals have also expressed concern over the rights of those sent across the border to be tried. The conviction rate in Chinese courts is as high as 99%. Arbitrary detentions, torture and denial of legal representation of one’s choosing are also common. Many in the protests on Sunday 09 June 2019 said they felt overwhelmed by a sense of helplessness in the face of mainland China’s increasing political, economic and cultural influence in Hong Kong. Hong Kong’s top political leader is not elected by ordinary voters but by a 1,200-strong election committee accountable to Beijing. Half of its legislature are chosen through indirect electoral systems that favour pro-Beijing figures. Many Hong Kongers also cited the jailing of leaders and activists from the 2014 Occupy Central movement– a 79-day mass civil disobedience movement – as well as the disqualification of young localist lawmakers as signs of the erosion of civil freedoms. Resentment towards China has been intensified by soaring property prices – with increasing numbers of mainland Chinese buying properties in the city – as well as the government’s “patriotic education” drive, and the large numbers of mainland tourists who flock to Hong Kong. Many Hong Kongers are also concerned about China’s growing control over the city’s news media, as they increasingly self-censor and follow Beijing’s tacit orders. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/jun/10/what-are-the-hong-kong-protests-about-explainerMore than a thousand protestors surround Hong Kong's main police headquarters on Arsenal Street in Wan Chai on June 26th following a peaceful rally at Edinburgh Place in Central. Doors to the complex were barricaded by protestors, who left after a six hour siege in protest at police violence at a prtest held earlier on 12 June 2019. Protesters ended a six-hour siege of Hong Kong’s police headquarters – their second in a week over the now-suspended extradition bill – early on Thursday morning. More than 1,000 were involved at the height of the protest, which began after 10pm on Wednesday. Around 100 were left at the end and dispersed without a fight when officers with riot shields emerged from the building in Wan Chai at 4am on Thursday. After a peaceful rally attended by thousands earlier at Edinburgh Place in the Central business district, hundreds descended on Arsenal Street, blocking the junction with Lockhart Road to all traffic and sealing the entrances to the police base. (https://www.scmp.com/news/hong-kong/politics/article/3016238/hong-kong-police-under-siege-again-protesters-surround )carrie lam, hong kong protests, extraditions, protest, protestors -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph - Colour Photograph, Street Protests in Hong Kong against proposed extradition laws, 2019, 17/06/2019
Carrie Lam, Hong Kong’s chief executive, had plenty of political support in the territory’s pro-Beijing legislature to pass a bill that would allow extraditions to mainland China. The legislators were set to begin discussing the bill in early June, and intended to vote on it just weeks later. A series of protests took place, and after a June 16 protest saw the largest turnout yet, Ms. Lam made a major concession: She postponed the bill, at least temporarily. It was an undeniable victory for the protesters — but it did little to quell the unrest. Since the bill could later be reintroduced, protesters felt they remained in danger. The police tactics to break up the demonstrations on June 12, including the use of more than 150 tear gas canisters to push protesters far away from the government office, created a new set of demands from the protesters. Now, instead of just calling for the withdrawal of the bill and Ms. Lam’s resignation, they said they wouldn’t be content unless there was an independent investigation of officers’ conduct. They also wanted the release of protesters arrested on June 12, and for the government to rescind its description of the demonstrations as a “riot,” a designation that carries legal significance. None of that has happened. Many analysts say Ms. Lam is unlikely to step down, nor would Beijing accept her resignation if she offered it. She has more wiggle room on the other demands, but has not indicated any willingness to budge. The Hong Kong Protests are a leaderless, digital movement.There is no single leader or group deciding on or steering the strategy, tactics and goals of the movement. Instead, protesters have used forums and messaging apps to decide next steps. Anyone can suggest a course of action, and others then vote on whether they support it. The most popular ideas rise to the top, and then people rally to make them happen. At its best, this structure has empowered many people to participate and have their voices heard. Protesters say it keeps them all safe by not allowing the government to target specific leaders. Their success in halting the extradition bill, which was shelved by the territory’s chief executive, speaks to the movement’s power. Despite the lack of a clear leader, protesters have shown extensive coordination at the demonstrations, having planned the specifics online beforehand. Supply stations are set up to distribute water, snacks, gloves, umbrellas and shields made of cardboard. Volunteer first aid workers wear brightly colored vests. People form assembly lines to pass supplies across long distances, with protesters communicating what they need through a series of predetermined hand signals. Anyone walking in dangerous areas without a helmet or a mask is quickly offered one. No individual can speak on behalf of the protesters, which makes negotiations difficult, if not impossible. (https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/02/world/asia/hong-kong-protest-explained.html, accessed 07/07/2019) Hong Kong’s amended extradition law would allow the extradition of suspects to mainland China for the first time. Supporters say the amendments are key to ensuring the city does not become a criminal refuge, but critics worry Beijing will use the law to extradite political opponents and others to China where their legal protections cannot be guaranteed. The government claims the push to change the law, which would also apply to Taiwan and Macau, stems from the killing last year of a Hong Kong woman while she was in Taiwan with her boyfriend. Authorities in Taiwan suspect the woman’s boyfriend, who remains in Hong Kong, but cannot try him because no extradition agreement is in place. Under the amended law, those accused of offences punishable by seven years or more in prison could be extradited. The new legislation would give Hong Kong’s leader, known as the chief executive, authority to approve extradition requests, after review by the courts. Hong Kong’s legislature, the legislative council, would not have any oversight over the extradition process. Many Hong Kongers fear the proposed extradition law will be used by authorities to target political enemies. They worry the new legislation spells the end of the “one country, two systems” policy, eroding the civil rights enjoyed by Hong Kong residents since the handover of sovereignty from the UK to China in 1997. Many attending the protests on Sunday said they could not trust China as it had often used non-political crimes to target government critics, and said they also feared Hong Kong officials would not be able to reject Beijing’s requests. Legal professionals have also expressed concern over the rights of those sent across the border to be tried. The conviction rate in Chinese courts is as high as 99%. Arbitrary detentions, torture and denial of legal representation of one’s choosing are also common. Many in the protests on Sunday 09 June 2019 said they felt overwhelmed by a sense of helplessness in the face of mainland China’s increasing political, economic and cultural influence in Hong Kong. Hong Kong’s top political leader is not elected by ordinary voters but by a 1,200-strong election committee accountable to Beijing. Half of its legislature are chosen through indirect electoral systems that favour pro-Beijing figures. Many Hong Kongers also cited the jailing of leaders and activists from the 2014 Occupy Central movement– a 79-day mass civil disobedience movement – as well as the disqualification of young localist lawmakers as signs of the erosion of civil freedoms. Resentment towards China has been intensified by soaring property prices – with increasing numbers of mainland Chinese buying properties in the city – as well as the government’s “patriotic education” drive, and the large numbers of mainland tourists who flock to Hong Kong. Many Hong Kongers are also concerned about China’s growing control over the city’s news media, as they increasingly self-censor and follow Beijing’s tacit orders. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2019/jun/10/what-are-the-hong-kong-protests-about-explainerCrowds mass on Queens Way in Hong Kong as an estimated 2 million people march in protest at the government's refusal to withdraw a controverisal law allowing people to be extradited to mainland China. Chants demanded the chief executive apologise and the legislation be withdrawn, while many held signs protesting police violence. Nearly 2 million protesters flooded the streets of Hong Kong on Sunday, organisers claimed, delivering a stunning repudiation of Chief Executive Carrie Lam Cheng Yuet-ngor’s governance and forcing a public apology out of the city’s leader over her campaign to bulldoze a controversial extradition bill through the legislature. A day after Lam suspended her push for the bill, expecting it to defuse a crisis that has seen violent clashes between mostly young protesters and police, the centre of Hong Kong was brought to a complete standstill as the masses marched to chastise her for refusing to withdraw the bill or apologise when first asked to, and declaring that nothing short of her resignation would satisfy them now. (https://www.scmp.com/news/hong-kong/politics/article/3014737/nearly-2-million-people-take-streets-forcing-public-apology ) carrie lam, hong kong protests, extraditions, protest, protestors, admiralty -
 Ballarat and District Irish Association
Ballarat and District Irish AssociationImage, Daniel O'Connell, the Great Irish Agitator, c1864, c1864
Daniel O’Connell was born near Cahirciveen, Co. Kerry, on 6 August 1775. His wealthy childless uncle adopted him at an early age and brought him up at Derrynane. He spoke Irish and was interested in the traditional culture of song and story still strong in Kerry at the time. He also understood how the rural mind worked which served him well in later years. In 1791 he was sent to school at St. Omer and Douai and what he saw there of the French Revolution left him with a life-long hatred of violence. He read law at Lincoln’s Inn (1794 -96) and continued his studies in Dublin where he was called to bar in 1798. He had soon built up an enormous practice. The 1798 rising and the terrible butchery that followed it confirmed his horror of violence. While he approved of the principles of the United Irishmen, their call for reform and for Catholic Emancipation, he disagreed with their methods. In 1815 O’Connell criticised harshly the Dublin corporation. O’Connell was challenged to a duel by one member D’Esterre. In the exchange of shots D’Esterre was killed and O’Connell vowed never to fight again. O’Connell was soon drawn into political action. Hopes of Catholic emancipation had been raised by promises given while the act of union was being passed. In 1823, O’Connell founded the Catholic Association. The aim of the organisation was to use all the legal means available to secure emancipation. It turned into a mass crusade with the support of the Catholic clergy. All members of the association paid a membership of a penny a month (the Catholic rent). This helped to raise a large fund. The Clare election in 1828 was a turning point. O’Connell, with the support of the forty-shilling freeholders, managed a huge victory against the government candidate. He was well supported by the clergy whose influence on the poor uneducated peasant class was enormous. The polling took place in Ennis at the old courthouse where the O’Connell monument now stands. At the final count, O’Connell was elected by a majority of about eleven hundred votes. The ascendancy party had suffered its first big knock since 1798. The whole country was aflame. The British Government feared a rising and granted Catholic emancipation in April 1829. The franchise was, however, raised to 10 pounds which excluded the forty-shilling freeholders. O’Connell was now the undisputed leader in Ireland and he gave up his practice at the bar to devote his time entirely to politics. At the King’s insistence, O’Connell was not allowed to take his seat until he had been re-elected for Clare. In February 1830, O’Connell became the first Catholic in modern history to sit in the House of Commons. For the rest of his life, he was supported by “The O’Connell Tribute”, a public collection out of which O’Connell paid all his expenses. O’Connell now decided to concentrate on winning repeal of the act of union and getting an Irish parliament for the Irish people. British political leaders feared repeal as they did not fear emancipation. They saw repeal of the Act of Union as the first step in the break-up of the act of union, as the spirit of the repeal movement was revived when the young Ireland writers wrote about it in the Nation. In 1841, O’Connell was elected Lord Mayor of Dublin and in 1843 the subscriptions to his Repeal Association, the Repeal “Rent” came to 48,400 pounds. He now began to organise monster meetings throughout the country. It is thought that three-quarters of a million people gathered on the hill of Tara to hear the man they called the “Liberator”. The government became alarmed at the strength of the Repeal Movement and a meeting which O’Connell had planned for 8 October 1843 in Clontarf, Dublin was banned. Huge crowds were already on their way when O’Connell called off the meeting to avoid the risk of violence and bloodshed. He was charged with conspiracy, arrested and sentenced to a year in jail and a fine of 2,000 pounds. The sentence was set aside after O’Connell had been three months in prison. When he was released he continued with his campaign for repeal. However, a turning point had been reached. The tactics that had won emancipation had failed. O’Connell was now almost seventy, his health failing and he had no clear plan for future action. There was discontent within the Repeal Association and the Young Irelanders withdrew. There was also some failure in the potato crop in the 1840’s, a sign of things to come in the Great Famine of 1845-1847. Aware of the fact that he had failed with his great goal, (the Repeal Movement), O’Connell left Ireland for the last time in January 1847. He made a touching speech in the House of Commons in which he appealed for aid for his country. In March, acting on the advice of his doctor, he set out to Italy. Following his death in Genoa on 15 May 1847, his body was returned to Ireland and buried in Glasnevin Cemetery. [http://www.clarelibrary.ie/eolas/coclare/people/daniel.htm, accessed 13/12/2013]Portrait of a man known as Daniel O'Connell.ballarat irish, daniel o'connell, o'connell -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionWork on paper - Artwork - Printmaking, Juli Haas, "Nutone Ball" by Juli Haas, 1992
Juli HAAS (26 April 1952- 02 March 2014) Born Melbourne Juli HAAS (1952-2013) Born Melbourne Juli Haas mainly produced watercolours, artist’s books and limited edition prints using the printmaking technique of Drypoint. She often explores the lives of everyday people with her work often portraying the darker side of human nature in an interior world filled with fantasy and absurdity. Themes throughout her work incorporate the use of childhood memory, place and a sense of personal history. Inspiration is derived from observing her own environment, which is then developed into a portrayal of the absurdity and drama of everyday human situations. Haas applies layers of intense and vibrant colour, which also serves to reinforce the narrative element that runs through the work. The psychological drama that informs this narrative exposes the darker side of life, expressing elements of anger, violence and isolation. Juli Haas obtained the following qualifications: * 1994-95 Master of Arts (Research). Monash University, Victoria * 1989-90 Graduate Diploma of Arts (Visual Arts), Monash University, Victoria * 1987-89 Bachelor Of Arts (Visual Arts), Gippsland Institute of Advanced Education, Victoria (now Federation University Australia) * 1971-74 Fine Arts, Caulfield Institute Of Technology, Victoria. Haas exhibited in most states of Australia and participated in numerous group shows. She is represented in most major Australian collections including the National Gallery of Australia. Career highlights include winning the Sir John Sulman prize in 1995 at the Art Gallery of NSW and in 1994 and 1997 the Martin Hanson Memorial Works on Paper Prize. In 2008 her artist’s book A Wife Of Silver was acquired for the Public Art Collection of the Arts Centre Melbourne as part of the Maxwell and Merle Silver Bequest. Career highlights include winning the Sir John Sulman prize in 1995; and in 1994 and 1997 the Martin Hanson Memorial Works on Paper Prize. Framed limited etching by Julie Haas. juli haas, gippsland campus, churchill, gippsland institute of advanced education, alumni -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Nola Purdie, Working Together: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Mental Health and Wellbeing Principles and Practice, 2010
Pt 1 History and contexts: 1. Australian Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander mental health: an overview 2. A history of psychology in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander mental health 3. The social, cultural and historical context of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians 4. The policy context of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander mental health Pt 2 Issues of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander mental health and wellbeing: 5. Mental illness in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples 6. Social determinants of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander social and emotional wellbeing 7. Preventing suicide among Indigenous Australians 8. Anxiety and Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander young people 9. Substance misuse and mental health among Aboriginal Australians 10. Trauma, transgenerational transfer and effects on community wellbeing 11. Indigenous family violence: pathways forward Pt 3 Mental health practice: 12. Working as a culturally competent mental health practitioner 13. Communication and engagement: urban diversity 14. Issues in mental health assessment with Indigenous Australians 15. Reviewing psychiatric assessment in remote Aboriginal communities 16. Promoting perinatal mental health wellness in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities Pt 4 Working with specific groups: models, programs and services: 17. Ngarlu: a cultural and spiritual strengthening model 18. Principled engagement: Gelganyem youth and community well being program 19. Dealing with loss, grief and trauma: seven phases to healing 20. The Marumali program: an Aboriginal model of healing 21. Mental health programs and services.colour photographs, tablesmental health -
 Uniting Church Archives - Synod of Victoria
Uniting Church Archives - Synod of VictoriaEngraving from photograph, Undated
James Watkin (1805–86), Pioneer Missionary. James Watkin was born in Manchester in 1805. While still young he felt the call to preach and in 1830 was accepted as a candidate for the Wesleyan Ministry. In the same year he married Hannah Entwistle and they sailed with a missionary party to Tonga. The work of the mission was jeopardised by prolonged and involved struggles between Christian and non-Christian Tongan chiefs; Watkin faced alone the danger of tribal warfare, but the experience left him depressed and exhausted. On his removal with his family to Sydney in September 1837 he prayed for a return home to England. Instead, when John Jones offered a free passage for a missionary appointed to Waikouaiti, where Jones had a whaling station, Watkin was selected for the post and arrived there in May 1840. Here he established the first mission station in the South Island. Watkin found the whaling settlement of Waikouaiti a centre of violence, licentiousness, and drunken depravity. Thoroughly disliking the corrupted Maoris and convinced that they were doomed to extinction, and disgusted by the brutality and vices of his fellow Europeans, Watkin laboured without hope, in the bitterness of exile and with deepening depression and distress. In spite of an abhorrence for his situation he established schools at Waikouaiti and Matanaka, and stationed partly trained Maori teachers at Stewart Island and at Moeraki. He had a natural flair for languages, preached in Maori four months after his arrival, and compiled an elementary reading book to be printed in Ngai Tahu. In November 1840 Watkin was greatly disturbed by Bishop Pompallier's visit to Otago. When, however, this was followed by Anglican intrusion – for Bishop Selwyn visited Otago in January 1844 – Watkin thought of withdrawing his own Maori teachers and abandoning the field. Never reconciled to his position at Waikouaiti, Watkin was relieved by Charles Creed and in June 1844 he sailed for Wellington, leaving 227 church members in Otago. In 1855 Watkin settled in New South Wales, and was president of the National Methodist Conference at Adelaide in 1862. He retired in 1869 and died on 14 May 1886, at Ashfield, New South Wales. 'WATKIN, James', from An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand, edited by A. H. McLintock, originally published in 1966. Te Ara - the Encyclopedia of New Zealand URL: http://www.TeAra.govt.nz/en/1966/watkin-james (accessed 30 Apr 2018) B & W engraving from a photograph of the Rev. James Watkin.Revd. James Watkin, Australia Engraved by J. Cochran from a Photograph.
