Showing 3959 items matching "machine"
-
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumWeights
A six piece set of cast iron weights, associated with the Wertheim "Preciosa" knitting machine.A six piece set of cast iron weights, associated with the Wertheim "Preciosa" knitting machine.knitting, jepson, mr keith -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Washing Machine
Patented RapidWash plunger design with attached wringer. These machines significantly reduced the effort required to launder heavy items compared with hand-washing in a tub.A metal tub 44 centimetres diameter and 50 high supported by three legs that are 24 centimetres long. A metal bar extends 27 centimetres above the tub and has a 66 centimetre long metal bar attached by a hinge, above the middle of the tub this bar has a hinged attachment with a 24 centimetre long metal bar on ii which has a 38 centimetre wide and 24 centimetre high metal conical plunger with a fluted apron on the end of it. The plunger is forced up and down the tub by the lever action of the 66 centimetre bar. A water outlet is in the bottom of the tub. There is a piece of wood six and a half centimetres by two centimetres by 45 centimetres attached to the tub which would have supported a ringer.THE LEHMANN COMPRESSED AIR AND VACUME WASHING MACHINE PAT No 30614/30lehmann, washiing machine, laundry equipmenr -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - PHOTOGRAPH, MACHINE GUN
Photo of Vickers Machine Gun Training. Used by British and Australian troops.Black and white photo of soldiers being trained in use of a machine gun - Vickers .303 inch.passchendaele barracks trust, vickers machine gun training -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyAdding Machine - Addmaster
An adding machine is like a calculator enabling the user to do addition and subtraction and multiplication and division by repetition. Adding machines provided a printed receipt for each entry and calculators display information on a screen.Adding machines were used in the office and were replaced by calculators and comptometers.Used by a resident of the Kiewa Valley and possibly in the SECV office.Formerly UKV 242 or Contex UKV 253 - Electric (no cord). Beige and grey plastic covered adding machine with blue numbers and black function keys. Paper roll winder and dispenser at the top of the machine. Charcoal coloured plastic base with label and patent information. A blue handle for carrying. 2 small grooved wheels on the base.Left hand front: Addmaster label and logo Base: Label on base - "Addmaster Corp. Made in USA serial number 175614". Patent information labeladding machine, addmaster, mathematics -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaEquipment - Object, Alfred Wayne & Co, The Visible, circa 1900
Alfred Wayne & Co. produced a number of braille writers over the years, including The Visible. Alfred Wayne (1854-1926) was listed as a 'manufacturer of small novelties in metal and steel' in the 1901, however by the 1911 census he had turned his company into a 'manufacturer of apparatus for use of the blind'. Together with Henry Stainsbury, they produced a number of braille typewriters as well as the more well know crab design of the Stainsby-Wayne brailler.Cast iron Brailler. The body of the Braille writer is painted in black with silver and gold painted inscriptions. Seven metal oval keys are situated at the front of the machine. The roller for turning the paper is made from turned wood.Marked: Painted on front of machine: "The visible/manufactured by/Alfred Wayne/Handsworth/Brimingham. Englandbraille equipment, assistive devices -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumSouvenir - CERAMIC MODEL, C. Arnold, The Bridge
Item in the collection of "Frederick Baxter MC". Refer Cat No. 4219 for his service history.White porcelain model of soldier firing a Vickers Machine gun. On front the shield of the town of Welwyn. Shield has image of red deer and at top a picture of a cathedral. Base has gold rim around edge.On bottom is written "Model of Tommy and His Machine Gun RTN7657214" On shield on front "WELWYN".baxter collection, souvenir, ceramic model, baxter mc -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBooklet, Why Not...?
"Why Not Help the Country in its Economy Campaign by Economising Yourself and thus Increase Your Profits ?" - James Bailey, Textile Machine Maker, Huddersfield, c. 1926. Promotes the advantages of buying a new scouring machine.Booklet, c.1926. Produced by James Bailey, textile machinery manufacturer, Huddersfield, to promote a new scouring machine.textile machinery textile finishing, james bailey, textile machine maker, scouring, textile machinery, textile finishing -
 Shepparton RSL Sub Branch
Shepparton RSL Sub BranchVickers Machine Gun ammunition belt, 1940
Standard .303 Vickers Machine Gun Belt from ww2250 round Vickers Machine Gun Ammunition Belt MK III 1940 Brass loading tabTF&S Ltd .303 250 M/C PATd APP 40 III to brass tabvickers machine gun -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societywheel
Many of the early sewing machines were powered by a treadle mechanism. The treadle was operated by pressing down on it with a foot, or both feet, to cause a rocking movement. This movement spins a large wheel on the treadle frame, connected by a thin leather belt to a smaller driving wheels on the sewing machine.A treadle sewing machine flywheel mad of cast iron. It is three tangent circles within a larger circle.3treadle sewing-machine flywheel -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumNeedles
A block of wax into which have been pressed four needles for the "Behiive" sock knitting machine.A block of wax into which have been pressed four needles for the "Behiive" sock knitting machine.knitting textile machinery machine knitting, hosiery, knitting, textile machinery, machine knitting -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumPhotograph, Scouring Machines, Unknown
Photographs were most likely used for promotional purposes. Room filled with wool scouring machines in an unknown textile mill.Sepia photo of a room filled with Scouring Machines in landscape format, located a textile mill.textile machinery, wool manufacture, wool, scouring -
 Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub Branch
Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub BranchWeapon - Owen Gun (replica)
The first prototype of the Owen Gun was first developed by Evelyn Owen in 1931 and finalised the design in 1938. The Owen was the only entirely Australian - designed and constructed service sub-machine gun of World War11 and was used by Australian Army from 1942 until 1971. It was manufactured at Lysaght's works who built 45,000 units. The cartridge was the 9x19 Parabellum - fired 700 rounds per minute and had an effective range of 125 yards.The Owen was of significant advantage to the Australian Army in the jungles of Vietnam.Owen Gun - sub-machine gun also known as the (Owen machine carbine). Steel body and timber grip and butt.WFM 0067 on top of barrel. -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumFolder, Burgon, Burgon & Ball, Ronaldson & Tippett, Munro, sheep shearing machines
Part of Ken Galloways research material associated with his career as a woolclasser. "Burgon, Burgon & Ball, Ronaldson & Tippett, Munro, sheep shearing machines"Burgon, Burgon & Ball, Ronaldson & Tippett, Munro, sheep shearing machines 2woolclassing shearing machinery, wool press, burgon, ronaldson, galloway, mr ken, woolclassing, shearing machinery -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societysewing machine, C 1920's
This machine was given to Ada Healey as a child. Ada Healey was for 20 years a volunteer and organizer at the Orbost Slab Hut (Orbost Information Centre). She was known for her craft skills and was a particularly fine knitter. Ada was the only child of Tom & Queenie Warne, born in Bombala/Delrgate. She was married to Keith Healey. The Healey family were early settlers in Marlo.This is an example of a toy given as a "teaching" toy. It was used by its owner to practise sewing before graduating to an adult type machine.A small hand-operated sewing machine. The body of the sewing machine is painted black. The top arm appears to have been painted in a white/cream colour. The machine could have been used to make small articles. There is no bobbin.On the stand- A.L.L.sewing handcraft toy toy-sewing-machine -
 Montmorency–Eltham RSL Sub Branch
Montmorency–Eltham RSL Sub BranchEquipment - Pouch, Leather, for Slide Rule Mk III, Vickers Machine Gun, 1940
To hold Slide rule MK III for Vickers Machine Gun. Leather pouch for Slide Rule Mk III for Vickers Machine Gun. Flap with stud closure and belt loop.slide rule, vickers mg -
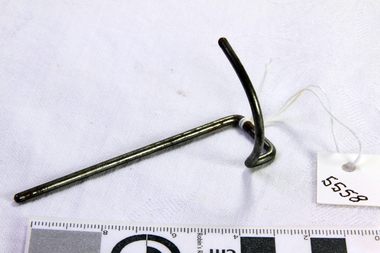 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Hook, ca. 1891
This sewing machine accessory was donated with our collection's Wertheim sewing machine accessory box. The box contains twelve accessories, the instruction book and the receipt for the purchase of a Wertheim sewing machine. The receipt was written on July 23rd 1891 by the Wertheim distributor in Melbourne, Hugo Wertheim. His business was the Wertheim Sewing Machine and Hapsburg Piano Depot, trading at 173 Williams Street, Melbourne. The purchaser was Mrs Burrowes from Burrumbeet, Victoria, a district northwest of Ballarat. She paid £6-6 (six pounds and six shillings) in cash. The receipt was signed by H. Wertheim and the other signatory looks like John A. Cherry. Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919) was an agent for his father’s cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established sewing machine manufacturer in Germany. He was born in Lispenhausen, Germany, and migrated to Melbourne in October 1875, where he opened a merchandising business at 39 Flinders Lane East. He returned to Germany in 1885 to marry Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie. The couple came back to Melbourne, and Hugo quickly established a substantial business selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He exhibited at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. One of his staff was O. C. Beale, who later set up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Hugo Wertheim opened a piano factory in Richmond, Melbourne, aiming to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos a year, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis in 1919 at his home in South Yarra. His eldest son, Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), continued the business. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices. The Wertheim Sewing Machine Company – Joseph Wertheim (1804–1899) founded the company in 1868 in Frankfurt, Germany. At this time Joseph was the Frankfurt city delegate for the Democratic Party. At its height, the Wertheim factory employed approximately 650 workers. The company used a trademark of a dwarf holding a hammer which is known to have been used until at least 1925, however in 1909 a Star of David was also registered. In 1870 a Wertheim subsidiary was formed in Barcelona, Spain. The business imported and sold complete machines, including the English Jones machine. Locals began calling the sewing machines “las rapidas”, and the business became known as “las casa de las rapidas”. In 1915 production began of a totally manufactured Spanish Wertheim machine. Wertheim in Germany continued manufacturing machines until 1932 when the Wertheim family fled to Spain. Despite converting to Christianity from Judaism, they feared the political unrest in Germany during that time. Wertheim Spain became Rapida SA and was then the sole manufacturer of the Wertheim machines. The factory was managed by Karl Wertheim under the alias Carlos Vallin. The sewing machine accessory is part of a donation that connected to domestic life in 1891 during the Victorian era. It is significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor of Wertheim sewing machines, Hugo Wertheim, to Victoria’s northwest district where the purchaser lived. It is also significant for connecting the Melbourne distributor to the importing of goods from the well-known German manufacturer of early domestic sewing machines, Joseph Wertheim. Hook; thin metal rod bent at one end into a curved upward arc. Thais sewing machine part was made for a Wertheim sewing machine by Joseph Wertheim, Germany, and distributed by Hugo Wertheim, William Street Melbourne. Circa 1891.flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, wertheim, sewing machine, victorian era, sewing machine accessory, wertheim sewing machine and hapsburg piano depot, wertheim sewing machines, domestic machines, dressmaking, home industry, fashion -
 Lakes Entrance Historical Society
Lakes Entrance Historical SocietyEquipment - Paper
Stencil paper used for duplicating machine during 1960's and 1970's at Waters Edge Caravan ParkPlastic bag containing sheets of duplicating paper for use in Roneo machine. VTMH Cat no 10194commerce, office equipment, stationery -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionRaindance Aerial Incendiary Machine R2
Alan McArthur from the CSIRO began his experimental burning program in the late 1950s near Canberra and published his landmark paper in 1962, “Controlled burning in eucalypt forests”. Leaflet No. 80, as it was known, proved a turning point for forest and fire managers across Australia. It led to the McArthur Forest Fire Danger Meter (FFDM) which first appeared in operational use in 1967 as the Mk 4. The CSIRO had developed its semi-automatic aerial incendiary machine dropping small capsules, with the first trial from a fixed-wing Cessna 337 at Manjimup in December 1965. Many technological and safety improvements followed including the Raindance machineAerial Incendiary Machine developed in Western Australia Rather than "ping pong balls" it uses a belt of incendiary "caplets" which are injected inside the machine before being ejected Raindance Systems R2forests commission victoria (fcv), planned burning, bushfire aviation, bushfire -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageGestetner Machine, c. 1922 - 1929
This Gestetner Cyclostyle duplicating machine was invented and manufactured by David Gestetner. He claimed in 1922, once he had released several models, that if a Gestetner Durotype stencil was used together with his Cyclostyle machine, then 10,000 copies could be made from the one Durotype stencil, an amazing claim for office technology of that era. David Gestetner (1854-1939), was born in Csoma, Hungary. He has been called the “founder of the worldwide office copying and duplicator industry.). He moved to London and in 1879 filed his first copying patent. In 1881 he patented the Cyclostyle stylus (or pen), which was used in conjunction with his Cyclograph device for copying text and images, He established the Gestetner Cyclograph Company in England at this time (1881) to protect his inventions and to produce his products; stencils, stylos (stylus or pen) and ink rollers. HIs inventions included nail-clipper and the ball-point pen (although the latter is more commonly associated with Laszlo Biro). Gestetner’s patented Cyclograph duplicator was used with his Cyclostyle Stylus or pen to write or draw on special thin wax-coated stencil paper (originally used for kite making paper) in the following way; 1. The Cyclostyle stencil was placed on a lower, framed metal plate of the Cyclograph 2. An upper frame was clipped over the top 3. The Cyclostyle pen, with its tip being a small metal-spiked or toothed wheel, was used to write or draw on the stencil, punched small holes into the paper and removed the wax coating in those places 4. The upper frame and stencil was then removed and a piece of blank paper was placed onto the metal plate in the lower frame and the upper frame with stencil was replaced 5. A roller was given an even distribution of Cyclostyle ink and rolled by hand over the stencil in the frame. This forced the ink through the holes in the stencil to and made a copy of the stencil on the paper 6. The upper frame was raised, the printed paper removed and another blank sheet was put into place. The whole process was repeated until enough copies were made. Gestetner’s invention developed further in 1894, with a stencil that could be placed on a screen on a revolving drum. The drum was manually rotated, the stencil then wrapped around another drum and was fed between cloth-covered rollers on which ink was evenly spread. Each revolution of the drum forced ink through the holes in the stencil and transferred the ink onto paper that had been fed between rollers and pressed against the drum. The process was repeated for each page. The paper was still fed and removed manually in this earlier invention but became more automatic in later models. In 1902 Gestetner duplicator model 6 was put onto the market. This model included the improvement of an automatic paper feed that synchronised with the rotation of the stencil. The Gestetner machine was the first office printing machine. It was easily installed and it made exact copies of the sane document quickly, effectively and inexpensively. This changed the way offices operated, making information easily available to many more users. The machines were commonly used in small businesses, schools, churches, clubs and other organisations for the wide distribution of a wide variety of information in the form of worksheets, newsletters and more. In 1906 the Gestetner Works were opened in Tottenham Hale, North London, and thousands of people were employed there up until the 1970’s. Due to the fast growing success of the Gestetner Duplicator machines many international branches for sales and service centres were established. David Gestetner was succeeded by his son Sigmund, followed by his grandson’s David and Jonathan. Further advancement was made by using a manual typewriter with specifically designed stencils. The end product was a printed, typewritten copy similar to the print from newspapers and booklets. In the next few years there were further developments of this revolutionary invention. The Gestetner Cyclostyle duplicator in our Collection is dated c.1922 - 1929 and it uses Gestetner Durotype stencils The 1922 British Industries Fair’s catalogue contained advertising for the Gestetner Rotary Cyclostyle “The World’s Premier Duplicator”, demonstrated at Stand K 86.” A Notice at the foot of the advertisement’s page boasts "Important - D Gestetner's latest invention, the "Durotype" Stencil, enables you to obtain 10,000 copies from one original if desired. It contains no wax of any description, is indestructible, can be stored indefinitely and printed from as required” In 1929 the look of the Gestetner machines changed; American designer Raymond Loewy was invited by Gestetner to improve the look of his duplicators, resulting in a very streamlined appearance. Eventually, around 1960’s, offices replaced their Gestetner with small photocopying machines and printers. Gestetner took over ownership of other office machine companies over time, including Nashua, Rex Rotary, Hanimex and Savin and eventually all came under the holding company name of NRG (Nashuatech, Rex Rotary and Gestetner). In 1996 Ricoh acquired the Gestetner Company, and it was renamed the NRG Group. REFERENCES Cyclostyle, Stencil Duplicating Machines, antique Copying Machines, Early Office Museum, http://www.officemuseum.com/copy_machines.htm Duplicating machines, Wikipedia Duplicator, Collection online, Canada Science and Technology Museums Corporation http://techno-science.ca/en/collection-research/collection-item.php?id=1989.0229.001 Gestetner duplicators, Totterham-Summerhillroad.com http://tottenham-summerhillroad.com/gestetner_duplicators_tottenham.htm Gestetner Duplicator, V&A Museum http://collections.vam.ac.uk/item/O322014/gestetner-duplicator-duplicator-loewy-raymond-fernand/ Gestetner, Grace’s Guide to British Industrial History, http://www.gracesguide.co.uk/Gestetner Duplicating machines such as this one revolutionalised access to copies of printed material, changing the way that educational bodies, offices, small businesses and community clubs and charities operated.Duplicating machine, Gestetner Cyclostyle Durotype, a stencil-method duplicating machine with two rotating drums plus rollers. Hand operated, tabletop office machine. Front has folding Bakelite handle, oil filling hole, calibrating gauge with scale, and copy counting meter. Right side has printed manufacturer’s plate that slides out as a paper output tray. Left side has metal plate with protrusions and perforations, plus another similar plate that is detached. It also has a metal frame attached [that would have been used to hold a paper input board, adjusted for various sizes of paper]. Cover, metal, with folding wooden handle on top, attaches to base with metal clips. Inscriptions printed on machine, mostly in gold-coloured paint. Round metal manufacturing plate is stamped with Serial Number 95759. Made by D. Gestetner, London, c.1922-1929Maker’s plate “MANUFACTURED / BY / D. GESTETNER LTD, / No. 95759 / CYCLOSTYLE WORKS / TOTTENHAM HALE / LONDON, N” Copy counting meter shows “1 4 6 4 8 [space]“ copies. Calibrating gauge has divisions with numbers “0 1 2“, labelled “← [left arrow] “TO PRINT LOWER” and “→ [right arrow], TO PRINT HIGHER”. “The Gestetner”, “Cyclostyle”, “Gestetner” (Trade Mark), Right side print of manufacturing details includes “The / Gestetner / TRADE MARK” And “THE FOLLOWING TRAFE MARKS / - - - OF INK, STENCILS / - - - AND GUARANTEE OF PERFECT / - - - BOTH - - - AND MACHINE” and “CYCLOSTYLE / DUROTYPE / GESTETNER” and “D. Gestetner” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, office machine, copying machine, gestetner machine, duplicating machine, duplicator, stencil machine, gestetner cyclograph company, cyclograph, cyclostyle, d. gestetner ltd, gestetner durotype stencils, gestetner cyclostyle, printing machine, office technology, durotype stencils, david gestetner, raymond loewy, roneo, rotary duplicatorten, mimeo, mimeograph machine, roneograph copier -
 Maldon Vintage Machinery Museum Inc
Maldon Vintage Machinery Museum IncSewing Machine, 1883 - 1885
Treadle sewing machine with metal base, wooden table and leather drive belt. The base plate is decorated with a rural scene featuring a 3 storey house, male & female figures in Victorian dress, horse and buggy painted in colour.Name printed on arm of machine, hard to decipher - appears to be "New Home Treadle Serial No 404879"dometsic items sewing machinery -
 Learmonth and District Historical Society Inc.
Learmonth and District Historical Society Inc.Washing Machine, Circa 1876
This is an early example of a mechanical device for the washing of clothes.It worked on a rocking motion making the chore of washday easier for the housewife.This is an early example of a mechanical device for washing of clothes.This Washing Machine is made of wood and the main barrel part is a rectangular shaped box with slopping sides.On the top is the lid and a handle.It is set on a stand which allowes it to be used with a rocking motion.F.WOLTER & ECHBERG"S PATENT WASHING MACHINE .NO 2955. 6 RUSSELL STREET MELBOURNE.ROYAL LETTERS PATENT GRANTED 1876.washing machine 1876.household appliance -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumPhotograph
Photograph of a Tentering machine, as produced by H. Krantz Soehne (manufacturers of finishing machinery) of Aachen, Germany.Photograph of a Tentering machine, as produced by H. Krantz Soehne (manufacturers of finishing machinery) of Aachen, Germany, c.1930.H. KRANTZ SOEHNE / AACHEN. 853textile machinery textile finishing, h. krantz s??, tentering, textile machinery, textile finishing -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Docket machine, Lamson Paragon, 1930s
This 20th century business machine was used by the firm of D.H.Wood Motors of 169 Koroit Street Warrnambool. This firm advertised that it sold mainly Peugeot and Studebaker cars and Hillman and Humber cars and commercial trucks. This machine has local provenance as it came from the 20th century business of D.H.Wood Motors. It also has some historical interest as an example of a business or office machine used in the early to mid 20th century before the general use of computers. This is a grey rectangular-shaped metal box with rounded edges. The box has four metal studs on the base to keep the box stable. The box has a hinged section for the insertion of the paper dockets and a turning mechanism for removing the dockets, one at a time from a slot at the top of the machine. The dockets have a white (customer's) copy and a pink duplicate copy for the business to file. Two of the dockets have been removed from the machine to show the contents. The number of dockets in the machine is unknown. The metal surface of the machine is rubbed and rusty and the paper is stained. 'Paragon' 'D.H.Wood Motors, 169 Koroit Street, Warrnambool' 'Lamson Paragon Limited Wiz Register' vintage business machines, warrnambool -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumBadge - VICKERS BADGES, 1914-1919
Items were in the collection relating to Carl Ernest Moller No 1242 AIF, DOW’s. Refer Cat No 1803.4 for his service details. The badges were worn on the sleeve of a uniform to denote that you had passed a Vickers machine Gun course..1)& .2) Brass badge s, crossed Vickers machine guns.numismatics-badges, military, metalcraft, vickers -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumEphemera - Roll of Ultimate ticket machine tickets, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), 1980s
This type of ticket was issued by "safety zone sellers" at the busy city stops to relieve the work on tram conductors. The tram conductor would punch the ticket to cancel it. Has the issuer "MMTB" printed on the ticket and ticket number, Issued using Ultimate ticket machines. See item 7003 for an example.Demonstrates a roll of tickets of the type that would be issued to ticket sellers.Roll of Ultimate ticket machine paper tickets commencing 04099.tramways, mmtb, tickets, ultimate, machine issued tickets -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumQuilt, Floral chintz quilt
Quilt made from pink patchwork curtain cloth, machine stitched and patched at a later date by hand. Part of the Wagga collection.Quilt made from pink patchwork curtain cloth, machine stitched and patched at a later date by hand.quilting history, patchwork history, running stitch group, running stitch collection, quilting - history, patchwork - history -
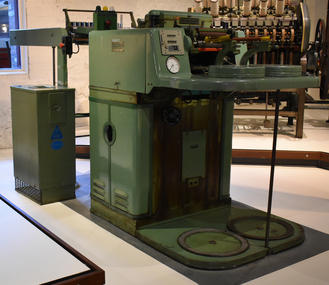 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumMachine - Gill Box, Deutscher Spinnereimaschinenbau Ingolstadt, 1963
This machine uses a series of combs attached to bars that move with increasing speed away from a starting point. This draws-out and aligns the wool fibres to produce a gilled top. The gilling process is also used in other positions along the worsted production line. A gill box draws and combs the fibres prior to spinning. Gold plaque on display with machine until 2018 read: G.H. Mitchell & Son, Adelaide have celebrated 125 Years of involvement with the Australian Wool Processing Industry by contributing the funds necessary to restore The Carding Machine, Noble Comb & The Gill Box.Gill box. Green painted steel.Deutscher / Spinnereimaschinenbau / Ingolstadt / 1963deutscher spinnereimaschinenbau ingolstadt, gilling, gill box, textile industry, wool processing, factory, machine, mills, spinning, fibre, comb -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionIncendiary machine
The Canadians developed a machine that used "ping pong balls" instead of cylindrical incendiary capsules and, in 1977, the FCV purchased a Premo machine for evaluation. The 32mm-diameter balls were made from high impact polystyrene and contained 3.5g of potassium permanganate. They were injected with 1ml of glycol which would ignite after a short delay The first Premo machine used four slipper blocks, which were loaded via a hand-operated hopper which, when rotated forward, the balls would be fed into four feed chutes to individual slipper blocks. Each slipper block has an opening allowing individual balls to enter and exit once injected. The original design of the machine was not suitable to meet the burning objectives and a number of modification were necessary. Following close inspection and field testing it was clear that utilising four slipper blocks was excessive and would generate too much fire. It was acknowledged that satisfactory spacing could be achieved by using just one slipper block. Selective spacing could be achieved by the speeding up or slowing down of the slipper block transferring the capsules during the injection process. Regulating the speed that the injected capsules were being dropped controlled the amount of fire created on the ground. This machine was the result of many years of experimentation at AltonaSignificant development of aerial incendiary machines enabled expansion of the fuel reduction burning program across Victoria.Aerial Incendiary machine for use in helicopters Modification at the Altona workshops over many years by Barry Marsden forests commission victoria (fcv), planned burning, bushfire, bushfire aviation -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMachine - Guillotine, c. 1880's
This guillotine is a hand operated machine specifically designed to cut through multiple sheets of paper or card. It has a very heavy and sharp single blade knife mounted between vertical guides or runners. The main users of a machine like this is in by the printing and publication binding industry. Book binding companies use a guillotine to evenly trim the pages of a book after it has been bound. The way the guillotine is used is - paper or card is stacked squarely on the flat table and pushed firmly against the back guide - the handle below the table at the front of the machine is wound around, which brings the back guide forward, pushing the paper stack forward and positioning the centre of the stack below the vertical frame - the upper wheel is wound around, which brings the clamp and firmly in position on top of the paper, to hold it very firmly - the large wheel on the side of the machine is turned around to lower the long sharp blade down onto the pages and cut them through. The sharp edge of the blade is protected somewhat from becoming blunt; a block of wood sits in the table under the stack of paper An early model of a guillotine was patented in 1837 by Thirault, who built a model with a fixed blade. Guillotines similar in principal to this one were patented by Guillaume Massiquot in 1844 and 1852. Over the years many improvements have been made and operation has moved from man power to electricity. Oscar Friedheim Ltd. was the importer and wholesaler of a large range of machinery and equipment for the printing and bookbinding industry. He sold most of his equipment under his own name. On this guillotine or paper cutter he refers to the origin of the guillotine’s manufacture only as “German Manufacrure”. A reference book “Commercial Bookbinding: a description of the processes and the various machines used" by Geo. Stephen, 1910, recommends Oscar Friedheim, amongst others, for the supply of “reliable cutting machines for hand or power”. It also recommends Oscar Friedheim’s for a wide range of other printing machinery and processes. OSCAR FRIEDHEIM LIMITED, LONDON Oscar Friedheim Ltd. was established in 1884 and operated from Ludgate in London. The company was an importer and wholesale supplier in the 1880’s, offering machinery and equipment for the printing and packaging industry for the UK and Ireland. The company became incorporated in 1913. An advertisement of 1913 includes a telegraphic code plus two telephone numbers for Oscar Friedheim Ltd and invites readers to call at the Ludgate, London, showrooms to see the machines working. The company later became Friedheim International Ltd. The book titled “Friedheim, A Century of Service 1884-1984 by Roy Brewer, celebrates Oscar Friedheim’s achievements. Friedheim International currently operates from Hemel Hempstead, on the northern outskirts of London UK. It promotes itself as “… the leading supplier of finishing, converting and packaging machinery to the printing, graphic arts, and highly varied packaging industries in the UK and Ireland. The company’s policy is simple – “employ the best people, work with the best equipment manufacturers in the world, and treat our customers as partners!” The company still sells guillotines. The guillotine is significant for its ability to represent aspects of the printing trade in Warrnambool and in a typical port town circa 1850 to 1910. It represents communication methods and processes used in the time before electrically powered equipment became common in industry.Guillotine (or paper cutter), hand operated. Metal framework with vertical guides, stand and metal mechanical parts including wheels and gears. Table with back guide; handle below front of table winds to move the back guide. A wheel at top of machine winds to adjust pressure of the clamp on the work on the table below it. The cutting blade fits between vertical guides; a timber insert in the table below the blade helps minimise the loss of sharpness of the blade. A handle on the side of the machine turns a large spoked wheel, which rotates a large gear, causing the blade to move up and down. Makers details are on a small oval plaque with embossed maker’s details is screwed onto main body. Maker is O Friedheim, London, and the machine is of German manufacture, circa late 1880’s.Maker’s plaque inscribed "O. FRIEDHEIM / London / German Manufacture"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, printing machinery, printer’s guillotine, paper guillotine, paper cutter machine, oscar friedheim ltd london, friedheim international ltd, bookbinding industry, printing industry -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumEphemera - MMTB Ticket - Ultimate machine - street seller, Bell Punch Co, 1970s
Type of ticket issued by street sellers, at City tram stops or safety zones for use in Ultimate ticket machines, from the Bell Punch Company. Made in rolls. See 1028 for other examples.Illustrates the type of ticket sold at Safety Zones to give some relief to Conductors at busy times,Paper ticket - 35c - Ultimate machine type Bc76617, printed on light grey paper.tramways, tickets, mmtb, ultimate, machine issued tickets, safety zones, bell punch co.
