Showing 430 items
matching george long
-
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumWeapon - SHELL CASES, c.1914 - 1945; .3) 3.1916; .4) 1940
Names re 59th Light Aid Detachment. Brain, Henry Baker VX47758, Patterson, Clive Douglas VX17382, Gaston, Stanley William VX18709, Dawson, VX36870, Tonkin, Archibald William VX20511, Kilburn, Douglas Barry VX18171, Long, Michael Roderick VX26974, Boyle, Allan Lemnos VX48814, Schmidt, Bruno Alexander VX43575, Bennett, Walter George VX44891, Hardstaff, John Robert NX5930. Milgate is the only name not readily identifiable. Hardstaff enlisted in 1939, all the rest enlisted in 1940..1) Dark metal slim line shell casing. .2) Dark metal shell casing. Dented at top. .3) Brass shell casing. .4) Brass shell casing..4) Etched on outside of shell: “59LAD 21 INF BDE HQ” “CAPT H B BRAIN, WOII C D PATTERSON, CPL S W GASTON, CPL A C DAWSON, PRIVATES: A W TONKIN, D B KILBURN, M R LONG, A L BOYLE, S H MILGATE, B SCHMIDT, W G BENNETT, J R HARDSTAFF”weapon, shell cases -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumBook, Claim for Special Allowance to Ex-Prisoners of War 1939-45
The book belonged to George Llewellyn Thomas VX58918 2nd AIF, POW. Refer 1075 for service history also 1073.2, 1074P. Soft cover book. Cover is cardboard. Book binding brown ..cloth tape with staples. Covers fawn coloured.Black printing on front cover. 131 pages, paper cut, plain & off white Inside cover on first page handwritten blue ink " G.L.Thomas./7 Creeth St./Long Gully,/Bendigo" book, history -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph, Happy Valley State School No.376 Honor Roll, c1920
World War One honor roll of former students of the Happy Valley State School No 376 who enlisted. The original honor roll no longer exists. There is a framed photograph of it in the current Happy Valley School building now used for community events. This honor roll would appear to be made before the end of WW1 as Ernest Alfred Yung died in September 1917 at Ypres. His brother George Alfred Yung returned who was also in the same battle returned to Australia. Honour rolls were also made to encourage more men to enlist. Margaret Young studied at Ballarat West Art School in 1894. This was one of Ballarat's Art schools. In 1907 they merged and became Ballarat Technical Art School (BTAS). Margaret became a teacher and taught for many years at BTAS, specialising in woodcarving. At the end of the First World War, Honour Boards were requested to be made to honour the men who had served. Ballarat was the main provider of these boards. Margaret Young was one of the people responsible for the carvings and specially mentioned for her work by the Caulfield School in Melbourne. On her resignation, Margaret moved to Adelaide. At the past students Reunion Celebrations in 1930, Margaret Young was to be the Guest of Honour. Unfortunately she was unable to attend due to ill health. Sepia photograph of honor roll board for World War One with white background mounted on grey cardboardReverse lhs upper - inked words 'Photo only'; centre - 'Mrs J Garvey, Happy Valley'; rhs upper - two stamps, 1 penny and a half penny franked with Ballarat; pencilled writing 'Mrs Garvey Happy Valleyhappy valley, happy valley state school, honor roll, honour roll, o. brough, e. daniels, g. daniels, philately, j. dial, g. dial, a. gradnor, w. gradnor, g. kiely, a. kerr, w. lowe, l. martinez, h. martinez, j. milburn, c. milburn, a. may, e. morgan, f. opie, a. paterson, n. reid, f. rankin, h. smith, t. thomas, l. thomas, e. yung, a. yung, a. bromley, j. blundell, h. barraclough, j. crommie, g. darling, j. darling, w. w. groves, j. gardiner, a. keys, j. keys, p. kelly, s. kelly, m. morgan, w. montgomery, j. rutherford, r. rutherford, p. smith, w. wishart, h. wark, s. ronald, k.n. mcnamee, p. bennington, sister m.j. thomas, d.l. thomas, w.e. thomas, j.s. gower, f.h. gower, s. gower, s.t.m. gower, happy valley school honor roll, a.a. louden -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Horse trough, Annis & George Bills, circa Dec. 1932
This horse trough is the only survivor of the two troughs originally installed in Raglan Parade, Warrnambool, in 1932. It was later moved to the Pony Club at Albert Part, near the north corner of Coulstock and Craig Streets. Over the time there its purpose was changed from a horse watering trough to a colourful garden bed of agapanthus plants. By February 2013 the horse trough had been transferred to Flagstaff Hill for display in the Maritime Village’s grounds. This trough is one of hundreds provided by the Annis and George Bills Estate Trust since 1927 for the welfare of working horses and dogs. The original concrete cap over the small compartment is still retained. There are also markings on the right side of the trough where it probably had a birdbath, tap or a dish for the horseman’s dog, similar to other troughs donated elsewhere by the Trust. Less than half of the troughs produced for the Annis and George Bills Trust still survive. In 2017 Felicity Watson, National Trust Victoria’s advocacy manager, said that the troughs were treasures and becoming rare, with more than a dozen across Victoria now being heritage protected. ABOUT ANNIS AND GEORGE BILLS The 1927 Will of George Bills included setting up the Annis and George Bills Estate Trust, which provided for hundreds of horse troughs to be supplied and installed throughout Australia, Britain, USA and other parts of the world for the welfare of horses. Town and city councils could apply to the Trustees for a horse trough for their communities. George “Joe” Bills was born in Brighton, England, in 1859. The family migrated first to New Zealand then to Australia in 1873, settling in the Echuca-Moama district. George moved to Brisbane in 1882 where he met Annis Swann, formerly from Sheffield. Both were animal lovers. George and Annis married 1885 and moved to Sydney to join George’s brother Henry in his mattress wire weaving business, later known as the Bills Brothers. They patented their own machine in 1893 and the business became very profitable. George was able to donate to charities that supported his passion to improve animal welfare. He and Annis joined the Victorian Society for the Protection of Animals and in 1924 George received a Life Membership with the RSPCA. George retired in 1908. The couple moved to Hawthorn, Victoria, in 1910, where they donated troughs for the work horses of Melbourne. During a visit to England Annis passed away. In 1927 George moved from Hawthorn to Camberwell, where he passed away at the end of that year. George had requested in his Will that a trust fund be set up from his estate "…construct and erect and pay for horse troughs wherever they may be of the opinion that such horse troughs are desirable for the relief of horses and other dumb animals either in Australasia, in the British Islands or in any other part of the world subject to the consent of the proper authorities being obtained." The troughs were to bear a plaque inscribed “Donated by Annis and George Bills, Australia”. In 1927 the cost to make a trough was about £13 (which converts to about $1079 in 2020 ), plus transport and installation costs. Most of the troughs were installed between 1930 and 1939 in Victoria and New South Wales. It is estimated that over that time around 500-700 Bills Horse Troughs were installed in Australia and another 50 overseas. Most of the troughs made in Victoria had three moulded front panels like this trough, and no panels moulded on the rear, whereas troughs made in NSW had four panels on the front and five on the back. Victorian troughs were made by a Bills’ relative, J H Phillips. Later, other manufactures for the Trust’s troughs included Rocla Concrete Pipes Ltd, in Auburn Road, Hawthorn, Victoria, who produced to the same original design. No further troughs produced after the end of World War II. A memorial to Annis and George Bills was first erected in Hawthorn in 1929. It included a drinking fountain and a dog dish. Its current location is unknown. In 1964 the George Bills RSPCA Resource Centre opened in Burwood East. This Bills horse trough is nationally significant as one of the surviving examples of the standard Bills memorial horse troughs that still has its compartment cap and evidence of it once having had attached fittings, possibly for a birdbath or dog dish. This trough has State historical significance for being produced in the early 1930s by a business in Hawthorn, Victoria. This example of a Bills horse trough is significant for being in comparatively good condition. The trough is locally significant for being the sole survivor of the two Bills horse troughs installed in the City of Warrnambool in 1932, originally installed on Raglan Parade and continued to be used in the community at the Pony Club, then finally transferred to its current location at Flagstaff Hill by early 2013. It is culturally significant as it represents the community’s dependence on horses for travel and transportation previous to motorised vehicles. It is morally significant as a generous gift from a couple concerned with the welfare of animals.Horse trough; a long narrow rectangular container used for storing water. Trough is made from pre-cast concrete with one large open compartment and a small covered compartment. The base of the small compartment is raised slightly above the base of the trough and is covered by a removable concrete cap. The design of the front of the trough includes three panels moulded into it that align with the shape of the back pediment (panel). The pediment is shaped with side arcs that step up to a wide centre arc. A rectangular concrete plaque is cast into the centre of the pediment and is engraved with the names of the original donors, Annis and George Bills. The trough was made in Hawthorn, Victoria, by J H Phillips circa 1932. “DONATED BY / ANNIS & GEORGE BILLS / AUSTRALIA”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, annis and george bills, bills trust, j h phillips, rocla concrete pipes ltd, hawthorn, water trough, watering trough, horse trough, animal welfare, bills horse trough -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1819
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1819, the year before King George III died. There were over 7 million of these coins minted. King George III succeeded his grandfather, King George II, on the throne in 1760. He reigned until his death on 29th January 1820. The shield in the centre of the reverse of the coin is the Hanoverian Shield, showing that the House of Hanover was elected to the crown rather than taking the crown as a victory. This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - The 6 pence coin is 19mm - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) - The Half Crown is 32mm British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George III by the Grace of God, King of the British territories, Defender of the Faith”. The engraver of the obverse image was Benedetto Pistrucci. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated "Evil to him who evil thinks” The engraver of the reverse image was Thomas Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time Australia became a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation, the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling, 1819. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George III head, looking right. Reverse; crown on top of quartered shield, 2 diagonally opposite quarters both show 3 lions, another quarter has a rampant lion, another quarter has a harp; in the centre of the shield is a small crowned shield with 3 symbols that appear to be lions. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEOR . III D . G . BRITT . REX F . D .” and “1819” Reverse “HONI . SOIT . Q [UI obscured] . MAL . Y . PENSE” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1819, king george iii currency, colonial australia currency, benedetto pistrucci, thomas wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1819
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1819, the year before King George III died. There were over 7 million of these coins minted. King George III succeeded his grandfather, King George II, on the throne in 1760. He reigned until his death on 29th January 1820. The shield in the centre of the reverse of the coin is the Hanoverian Shield, showing that the House of Hanover was elected to the crown rather than taking the crown as a victory. This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - The 6 pence coin is 19mm - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) - The Half Crown is 32mm British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George III by the Grace of God, King of the British territories, Defender of the Faith”. The engraver of the obverse image was Benedetto Pistrucci. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated "Evil to him who evil thinks” The engraver of the reverse image was Thomas Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling, 1819. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George III head, looking right. Reverse; crown on top of quartered shield, 2 diagonally opposite quarters each show 3 lions, another quarter has a rampant lion, another quarter has a harp; in the centre of the shield is a small crowned shield with 3 symbols that appear to be lions. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEOR . III D . G . BRITT . REX F . D .” and “1819” Reverse “HONI . SOIT . Q [UI obscured] . MAL . Y . PENSE” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1819, king george iii currency, colonial australia currency, benedetto pistrucci, thomas wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCurrency - Coin, 1826
This Great Britain shilling is dated 1826. There were over 6 million of these coins minted during the reign of King George IV, 1820-1830 This coin’s denomination is not inscribed on the coin but it has been identified as a shilling from information about the King George III currency 1816-1820. - This Shilling is 24mm (the same size as this coin) British coins such as this one shilling were in circulation in the colony of Australia until 1910, when the Commonwealth of Australia began producing its own coinage. This coin was minted by the Royal Mint at Royal Mint Court, in Little Tower Hill, London, England. Coins for circulation in the Kingdom of England, Great Britain and most of the British Empire were produced here until the 1960’s when the Royal Mint shifted location to Wales. The obverse side of the coin’s inscription translation is “George IV by the Grace of God”. The engraver of the obverse image was William Wyon. The reverse side’s inscription on the coin is translated " King of The British territories, Defender of the Faith” The engraver of the reverse image was William Wyon. AUSTRALIAN CURRENCY The early settlers of Australia brought their own currency with them so a wide variety of coins, tokens and even ‘promissory’ notes (often called IOU’s) were used in the exchange of goods and services. In 1813 40,000 silver Spanish dollars, purchased by the English government, were delivered to Sydney to help resolve the currency problem reported by Governor Macquarie. The coins were converted for use by punching a hole in the centre of the coin. Both the outer ring, called the holey dollar, and the punched out ‘hole’, called the dump, were then used as the official currency. The holey dollars hold the place of being the first distinctively Australian coins. In 1825 the British Government passed the Sterling Silver Currency Act, making the British Pound the only legal form of currency in the Australian colonies. Not enough British currency was imported into the colony so other forms of currency were still used. In the mid 1800’s Australia entered the Gold Rush period when many made their fortunes. Gold was used for trading, often shaped into ingots, stamped with their weight and purity, and one pound tokens. In 1852 the Adelaide Assay Office, without British approval, made Australia’s first gold coin to meet the need for currency in South Australia after the Gold Rush began. In 1855 the official Australian Mint opened in Sydney, operating as a branch of the Royal Mint in London, and the gold was turned into coins called ‘sovereigns’. Other branches also opened in Melbourne and Perth. Up to the time of Australia becoming a federation in 1901 its currency included British copper and silver coins, Australian gold sovereigns, locally minted copper trade tokens, private banknotes, New South Wales and Queensland government treasury notes and Queensland government banknotes. After Federation the Australian government began to overwrite privately issued notes and prepared for the introduction of its own currency. In 1910 a National Australian Currency was formed, based on the British currency of ‘pounds, shillings and pence’ and the first Commonwealth coining was produced. In 1966, on February 14th, Australia changed over to the decimal currency system of dollars and cents. Australia did not have its own currency in the colonial times. Settlers brought money from other countries and they also traded goods such as grain when currency was scarce. For a long time there was no standardised value for the different currencies. In 1825 British currency became the only official currency in the colony of Australia and coins such as this silver shilling were imported into Australia to replace the mixture of foreign currency. Australia became a Federated nation on 1st January 1901. In 1910 National Australian Currency was formed and Australia produced its own currency, based on the British ‘pounds, shillings and pence’. The British currency was no longer valid. This silver shilling is of national significance as it represents the British currency used in Australia from 1825-1910. Coin, Great Britain shilling. 1826. Silver coin, round. Obverse; King George IV bare head, looking left. Reverse; crowned lion; below, a large crown; below are a shamrock, rose and thistle united. Inscriptions on both sides of coin (denomination not inscribed).Obverse “GEORGIUS IV DEI GRATIA” and “1826” Reverse “BRITANNIARUM REX FIDEI DEFENSOR” flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, coin, currency, money, legal tender, australian currency history, royal mint, great britain shilling 1826, king george iv currency, colonial australia currency, william wyon, numismatics -
 Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.
Phillip Island and District Historical Society Inc.Photographs, Fuji Film, Re-enactment of the Landing of George Bass, 01/1998
A Plaque was erected on the occassion of the re-enactment. The wording is as follows: "In Recognition of a brave adventure on January 5 1998. Five men: Bern Cuthbertson (skipper), Tom O'Byrne (first mate), Craig Dixon, Rick McMahon and Geoff Zwan, landed in Flinders after 4 weeks at sea having rowed and sailed from Darling Harbour Sydney in the 'Elizabeth', a nine metre whale boat. This voyage re-enacted the discovery and naming of Western Port by Royal Navy Surgeon George Bass and his crew of five in 1798." They rowed an 8.7m long open whale boat some 1930 km from Port Jackson (Sydney).A collection of colour photographs taken at the re-enactment of the landing of George Bass. Showing "Sailors", a Canon, inside the boat, boats on the water and spectators on the foreshore.bass landing re-enactment 1998, george bass, san remo, p & e king -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers Victoriaadministrative record (item) - Letter book, W.H.C. Darvall, The Victorian Seamens' Mission, Institutes and Rests: No 1 Letter Book, late 19th Century
One of 2 volumes of late 19th early 20th Century letter books. Each volume provides us with extensive listings of correspondence with supporters, fundraisers, patrons, architects, Mission staff and business transactions carried out by the Honorary Secretary Mr WHC Darvall over the period of a decade. Queen Victoria, Governors of Victoria: Earl of Hopetoun, Lord Brassey, Sir George Sydenham Clark, Lord Talbot and Governors General: Baron Northcote, performers such as Nellie Melba, Kitty Grindley, Sir Samuel Gllott president of the Law Institute, Hugh Reid, Crawford Pasco R.N. FRGS are just a few. The late 19th C - early 20th C period covered by the 2 vol collection of correspondence records together with annual reports and minutes documents a significant transition period not only across centuries but also towards a new framework of operations for the original mid 19th C founded Mission to seamen. The death of a long-standing Chaplain, Wesleyan, Ebenezer James in 1901 eventually led to a proposed merger in 1905 which resulted in the amalgamation of the Victorian Mission with the Anglican based Mission to Seafarers under the leadership of Rev'd Gurney Goldsmith who arrived in 1905. The new Mission was launched in 1906 with a long planned and much needed new central building opened in 1907 on the Australian Wharf. Mr Darvall, in his time produced a handwritten 40 page epitomised history, drawn from annual reports and was exceptionally meticulous in his efforts to cross reference related correspondence, press clippings, report material and documents. He was a strong supporter of Libraries and first town clerk of Beechworth.Primary inscription on title page ( see title field this record) also: "Commencing on Sunday 1st of February , 1895. / Ending on Saturday 18th December , 1902 / Indexed to / Page 18,22,29,32,34,35,44,45,48,53,63,75,80,82, 90, 112, 120, 121,136,151,167,171,173,174, 185, 200, 212, 216, 218, 232, 233, 241, 361, 362, 373, 375, 378, 428, 455, 477, 508, 509, 516, 520, 521, 543, 562, 607, 657, 658, 667, 669, 706, 718, 724, 732, 735, 738, 741, 745 748, 749 ./ WHC Darvall / Hon'y Secretary. "correspondence records, seafarer advocacy, seafarer shore facilities, ship to shore, index, missions to seamen, seamen's missions, mission to seafarers, correspondance, letters, letter book, welfare, nellie melba, kitty grindley, crawford pasco, lord thomas brassey, william henry charles darvall (1830-1906) -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers Victoriaadministrative record (item) - Letter book, W.H.C. Darvall, The Victorian Seamens' Mission, Institutes and Rests: No 2 Letter Book, c. 1890
One of 2 volumes of late 19th early 20th Century letter books. Each volume provides us with extensive listings of correspondence with supporters, fundraisers, patrons, architects, Mission staff and business transactions carried out by the Honorary Secretary Mr WHC Darvall over the period of a decade. Queen Victoria, Governors of Victoria: Earl of Hopetoun, Lord Brassey, Sir George Sydenham Clark, Lord Talbot and Governors General: Baron Northcote, performers such as Nellie Melba, Kitty Grindley, Sir Samuel Gllott president of the Law Institute, Hugh Reid, Crawford Pasco R.N. FRGS are just a few. The late 19th C - early 20th C period covered by the 2 vol collection of correspondence records together with annual reports and minutes documents a significant transition period not only across centuries but also towards a new framework of operations for the original mid 19th C founded Mission to seamen. The death of a long-standing Chaplain, Wesleyan, Ebenezer James in 1901 eventually led to a proposed merger in 1905 which resulted in the amalgamation of the Victorian Mission with the Anglican based Mission to Seafarers under the leadership of Rev'd Gurney Goldsmith who arrived in 1905. The new Mission was launched in 1906 with a long planned and much needed new central building opened in 1907 on the Australian Wharf. Mr Darvall, in his time produced a handwritten 40 page epitomised history, drawn from annual reports and was exceptionally meticulous in his efforts to cross reference related correspondence, press clippings, report material and documents. He was a strong supporter of public Libraries and first town clerk of Beechworth.In handwritten black ink primary inscription on title page (see title field this record...) also: "Commencing on 19th October 1902 Ending ...1905 / Indexed to:.../ WHC Darvall / Hon'y Secretary. "correspondence records, seafarer advocacy, seafarer shore facilities, ship to shore, william henry charles darvall (1830-1906), letters, sailors' rest, welfare, seamen's mission, mission to seamen, mission to seafarers, correspondence, letter book, nellie melba, kitty grindley, lord thomas brassey, crawford pasco -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaLetter - Correspondence, 14/02/1952
Allan describes London following the death of King George VI. He witnessed the Proclamation of the Queen at the Royal Exchange. He writes "The Proclamation was read in four different parts of the city and about a hundred Lifeguards escorted the Royal carriages through the city." And ....."I also saw the procession from Kings Cross station to Westminister Hall when they brought the King back to London." He would have liked to walk past the coffin lying in state at Westminister Hall but the queue was three miles long and it took seven hours to get into the hall.Quinn CollectionA pale blue self-folding letter (0894.a1) headed 37 Elsham Road, London W 14 and dated 14/02/52. Letter is typed using a very small font. The print is faint and difficult to read. It is addressed to Mrs K Hayes, 14 Fitzroy Street, St Kilda, Victoria, Australia. There is no postmark. The return address is Allan Quinn, 37 Elsham Road, London W14.letters-from-abroad, allan quinn, alette andersen, death of king george vi, proclamation of queen elizabeth ii, london 1952 -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaMagazine (sub-item) - Newsletter, The Victoria Missions to Seamen, Jottings From Our Log, Number 4 - Michaelmas 1906, 1906
Content: WHC Darvall's death Mission's motor boat New central mission Institute Williamstown Rest condition LHLG and their work Thanks Opening hours AdvertisingPublished for some 30 years by the Victorian Missions to Seamen issued to supporters the series contributes to the history of the organisation. It is a key cross reference supplying many details and dates of Chaplain and LHLG activities in both Melbourne, Port Phillip and other States where Missions were gradually established and information not able to be included in Annual Reports. It is also a source of images.newsletter, victorian seamen's mission, melbourne misson to seamen, jottings from our log, lhlg, rope, flying angel, seagull, advertising, port melbourne, williamstown, sailors' home, australian wharf, seamen's institute, sailors' rest, services, concerts, events, socials, deaths, captain press, w.h.c. darvall, motor boat, geelong, boat builder, manx king, glenlui, dovenby, marion woodside, ainsdale, robert reid, bagatelle board, billiard table, sir wilmot fawkes, lady fawkes, book bags, woolies, michaelmas, 1906, ladies harbour lights guild, captain strickland, quarterly, patron, sir reginald talbot, president, archbishop of melbourne, vice president, f.t. derham, w.h. allard, frederick thomas derham (1844-1922), william henry allard (1860-1927), committee membres, archdeacon hindley, archdeacon crossley, william george hindley, owen thomas lloyd crossley, mary danne, mrs e.w. underwood, captain parsons, captain creswell, captain j.h.fearon, ethel augusta godfrey, hugh r. reid, charles blunt, ditty bags, donachy and sons, rope manufacturers, robur tea, mackenzie mustard, excelsior baking powder, admiral wilmot fawkes, bobs, games -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaPhotograph, Mr David Conolly and Ms Marjorie Stafford Debutante Ball at St Kilda Town Hall, 1957
Taken at a Debutante Ball 1957 St Kilda Town Hall. David Canolly was a lay reader and Marjorie Stafford, the daughter of George Stafford, a policeman who was involved in the Mission helping during the 1950s. (Conolly interview in 2016)Subjects LHLG member MS and Lay Reader DC had a long standing connection with the Mission Black and White Gloss print photograph of a couple in evening dress, both are standing.Hand written in black texta; l Circa 1957 Marjorie Stafford daughter of George Stafford, & D C at Debutante Ball for Robert Burns Lodge at Stkilda TRown Hall lay reader, david conolly, marjorie stafford, lhlg, st kilda town hall, george stafford -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaPhotograph - Photograph, Black and white, Bill Doyle (Reverend C.J. Eldridge-Doyle), c. 1950
The Mission to Seafarers held many social functions to raise funds for the work of the organisation and to benefit visiting seafarers. Many dances were held on a Saturday with good attendance. On the pillar on the left of the stage there is a photograph of a monarch, possibly King George VI, thereby dating the photograph at pre-1953.The Mission to Seafarers as an organisation is dedicated to not only providing spiritual and practical support to seafarers, but has long found it important to provide social opportunities as well. In the past there have been many dances, concerts and other social events that have been designed to cater for visiting seafarers.Small black and white photograph of people dancing in the Flying Angel Club at Mission to Seafarers Melbourne. There is a band on the stage in the background of the photograph and several couples dancing.photograph, flying angel club, monarch, band, floorboards, stage, dance, king george vi, lhlg, seamen, orchestra, mission to seamen, melbourne, seamen mission, mission to seafarers, entertainment, music, musicians, drums, piano, saxophone -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaPhotograph - Photograph, Sepia, Just married, Harry and Dora, 14 February 1928
The Marriage Register lists Harold Priestley Simpson and Amy Dora Walker as the bride and groom, and the wedding date as 14th of February 1928. The photograph uses the personal Harry and Dora, instead of the formal Harold and Amy. In the Register, Amy started signing her name as Dora. before correcting it. The photograph shows that weddings took place at the Chapel during the late 1920's, and the style of weddings at the time. This includes the type of outfits worn, such as the length of the veil and the type of bouquet carried. Dora's Bridesmaids are depicted in 2 other images in the MTSV collection also an image of the chapel decked with flowers for the occasion. The article in the Herald of the day describes the event: "WEDDING AT SEAMEN'S CHAPEL Reception at Hotel Windsor The pretty little chapel at the Sea men's Institute was packed with interested friends this afternoon, when Miss Dora Walker, one of the Mission's most enthusiastic and efficient voluntary helpers, chose it as the setting for her marriage with Mr H. P. Simpson, son of Mr and Mrs J. H. Simpson, of Mornington. A group of her fellow workers decorated the chapel with lovely pink and white gladioli, carnations and roses. The ceremony was performed by the Rev. J. R. Weller, chaplain of the Mission, and the bride was given away by her father, Mr A. W. Walker, of Manning road, East Malvern. She wore a lovely ivory georgette frock, the finely tucked skirt being fashioned with a deep transparent hem of Chantilly lace. Over it fell a beautiful Honiton lace veil mounted on tulle and arranged to give the ef fect of a train. Fragrant white roses composed her bouquet. Two attendants followed her down the aisle — her sister, Miss Molly Walker, and Miss Ella Kendall — both wearing dainty shrimp pink georgette frocks and large crinoline straw hats in the same shade with a dainty edging of tulle. They carried bouquets of pink cactus dahlias nnd delphiniums. Mr Louis Buscombe was best man, and Mr George Thompson grooms man. After the ceremony Mr and Mrs Walker entertained about 50 guests at the Hotel Windsor."The photograph shows St. Peter chapel was being used for weddings in 1928. The Anglican church has been used for weddings since being finished in 1917. The Marriage Register shows that these weddings were legal in the Commonwealth of Australia, and lists Church of England as the denomination for this wedding. Miss Amy Dora Simpson (nee Walker) had a long association with the Mission, first as a young Volunteer with the Ladies Harbour Light Guild circa WW1, and through to her wedding in early 1928 and beyond. Square sepia, glossy photograph of a bride and groom, taken as they leave a building. Guests are throwing rice at the newlywed. The groom is turned towards the camera, while the bride is looking ahead, carrying a bouquet. There is a white border around top, bottom and left edges, the photograph seems to have been cut in half along the right edge.On the reverse: handwritten in blue pen JUST MARRIED!/DORA & HARRY/28/2/28. 618 is stamped in blue ink . (date is incorrect as wedding took place on 14/2/28)bride, wedding, groom, 1928, dora simpson, dora walker, st peter chapel, harry simpson, lhlg, flinders street, harold priestley simpson, valentine's day, amy dora walker, ladies harbour lights guild, mr and mrs a.w. walker, malvern, manning road, reverend j.r weller, molly walker, ella kendall, david simpson -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionBook, George Alfred Henty, Dorothy's Double, 1894
Dorothy Hawtrey's life is turned topsy turvy by a rogue enemy who cultivates a poor girl who resembles Dorothy and uses her to impersonate Dorothy. The tale expands to the California gold fields where the double and her captor are eventually discovered. The double turns out to be a long lost sister, the rogue is killed, and all ends well.Dark brown leather bound spine and cover corners. Green cloth-covered board covers. Gold text on spine.fictionDorothy Hawtrey's life is turned topsy turvy by a rogue enemy who cultivates a poor girl who resembles Dorothy and uses her to impersonate Dorothy. The tale expands to the California gold fields where the double and her captor are eventually discovered. The double turns out to be a long lost sister, the rogue is killed, and all ends well.fiction, historical fiction, thriller -
 Blackburn Cricket Club
Blackburn Cricket ClubPremiers 1961-62 1st XI A Grade, 1961-62 1st XI A Grade Premiers
How many matches did these men play? Away games, home games? Any remarkable runs or scores? How long had each been playing? Were they professionals or amateurs? 1961-62 brought the Blackburn Cricket Club a triple premiership winning the A Grade, C Grade and D Grade flags in addition to the Under 16s. Team Standing (L-R): George Allerton, Keith Sturgeon, George Stone, Brian Pickett, Keith Blackley, Jim Robertson, Peter Grant. Sitting: Alan Taylor, Les Reed (President), Neveille Jacobs (vc), Don Meehan (c), Stuart Walker, Allan Berry (Sec), Ken Henwood.Black and white portrait of the cricket team anf officials. cricket, a grade, blackburn, blackburn cricket club, cricket whites, 1961-62, a grade premiers, george allerton, keith sturgeon, george stone, brian pickett, keith blackley, jim robertson, peter grant, alan taylor, les reed, neveille jacobs, don meehan, stuart walker, allan berry, ken henwood -
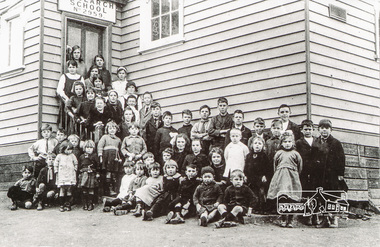 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Class of 1922, Research State School No. 2959
The Children of Research State School in 1922 Photo and list of children provided by Ivy Reynolds to Ross McDonald. Ross has supplemented and filled in some blanks, from the children names in Andrew Lemons book 'Return to Research. A centenary of Research Primary School, 1989 ' page 103. Additional commentary provided by Ivy Reynolds in 2006. 1. Winnie La Frenz - a great friend of the Reynolds 2. Ruth Thompson - Wally Buttwell's niece 3. Bertha Wiltshire 4. Ivy Dickson (who grew up to be a good-looking woman) 5. May Norman - a cousin to the Reynolds through Ernest Reynolds 6. Elsie Shaw 7. Veenie Turner (Ivy was not 100% sure of her surname, but said she was not related to Hazel Turner) 8 Lil La Frenz (Lilian) - a bright spark and a lively tennis player 9 Lily Wilson (looks like a boy) - had red hair 10 Hazel Turner - a cousin of the Reynolds who lost her mother very early in life. Her father remarried and the family then became Roman Catholics, which in those days, caused them to become distant with the Anglican Reynolds family 11 Lila Dickson (Lyla) 12. Jack Wilson - a red-head like his sister 13. Len Blashick 14. Marjory Palmer 15 ? Burgoyne 16 Lance Doney and 17 Bill Doney. Cleaver boys who went to Ivanhoe Grammar. Both caught TB from their mother and died young. 17. Bill Doney - The Doneys were clever boys. They went to Ivanhoe Grammar after Research Primary and this educational advantage caused them to grow apart from the local boys. Both caught tuberculosis from their mother and didn't live long. Lance died first, but Bill survived long enough to join the Merchant Navy. He eventually entered the Mont Park Sanatorium where Ernest Reynolds used to visit him every Sunday. The Doney boys were keen on Margaret and Ivy Reynolds at one stage (probably before they became seriously ill) and Bill gave Ivy a macrame belt he'd made. 18 ? Burgoyne 19 ? Messen (Frank or Alex Masson) 20 Neville West 21 ? Shaw 22 ? Shaw 23 Neil Palmer 24 George Shaw or his brother Bertie 25 George Shaw or his brother Bertie 26 Eva Kilson 27 Lorna Turner 28 ? Henry Fox (or possibly Eric?) 29 Nancy Storey (adopted) 30 Mona Fox 31. Nell Storey (also adopted) She married Sam Howard and they had 2 daughters. One went to Queensland, the other lived locally and helped at the Research Anglican Church. 32 Victor Davey 33 Margaret Reynolds 34 Ethel Davey - cousin of the Reynolds through Ernest Reynolds 35 ? Randall (Freddie) 36 ? Randall (Kitty) -Their father was a builder who made toys for every child at the school one Christmas 37 Ronnie Turner 38 ? Ivy couldn't remember his name, but thought he lived at the Research Hotel 39 John Reynolds 40 Jim Davey 41 Unknown 42 Ivy Reynolds 43. Unknown - one of the unknown boys is Jimmy Storey 44. Unknown 45. Unknown 46. Dorothy La Frenz 47. Eric Fox 48. Unknown 49. Possibly Bert Shaw One of the boys in the photograph is Jimmy Storey The Reynolds family were early settlers in Research. The Reynolds/ Prior collection of photographs were taken by Tom Prior, the maternal uncle of Ivy Reynolds, around 1900 and the 60 photos in the album give a fine overview of many of the landmarks of Research and Eltham over 100 years ago. lvy lived in the family home for many years at 106 Thompson Cres Research. Ivy's father, Ernst Richard Reynolds and grandfather, Richard Reynolds, lived at the same address. Ivy's father Richard worked for Mr. Trail on his property in Research. Reynolds Road is named after the family. Mr Tom Prior (wife Eva) worked at the Melbourne zoo. He was very innovative and made his own camera, using the black cloth hood to exclude the light. The photographs are a reminder of the rural nature of Research and Eltham and its rich heritage. Black and white photograph mounted in an album, the Reynolds/Prior Photograph Collection, this being one of 53 reproduced black and white images of early Eltham.The Reynolds/Prior Photograph Collection, Presented to the Eltham District Historical Society, 14 June 2006 by Ross McDonald. A second copy was also presented to the Andrew Ross Museum, Kangaroo Groundreynolds prior collection, research (vic.), research school, schools, school children, state school no. 2959, winnie la frenz, ruth thompson, bertha wilshire, ivy dickson, may norman, elsie shaw, veenie, lil la frenz (lilian), lily wilson, hazel turner, lila dickson (lyla), jack wilson, len blashick, margery palmer, burgoyne, lance doney, bill doney, frank messen, alex masson, neville west, shaw, neil palmer, george shaw, bertie shaw, eva kilson, lorna turner, henry fox, eric fox, nancy storey, mona fox, nell storey, victor davey, margaret reynolds, ethel davey, freddie randall, kitty randall, ronnie turner, john reynolds, jim davey, ivy reynolds, dorothy la frenz, bert shaw, jimmy storey -
 Trinity College Cultural Collections
Trinity College Cultural CollectionsSovereign balance, c.1850
Sovereigns are no longer used as currency in Australia. Brass balance for weighing one soveriegn and half sovereigns. Contained in a small orange coloured cardboard box which opens in half.A 'crown' etched on the left of the fulcrum and 'sovereign' and 'warranted' etched in the first circle and 'sovereign' '1/2' ( half) on the second circle. Box has writing " Improved sovereign balance\To weigh and gauge soveriegns and half sovereigns\Being so exact that no conterfeit can possibly go through the gauge\of sufficient weight to turn the balance."sovereign, sovereigns, half sovereigns, george w rusden -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBook - Reference Maths, George Bell & Sons, Elementary Algebra Part 11, 1905
This item was a standard maths book used in Victoria. It would have been a continuation of the Part 1 of the same name. Elementary level would have been in the early years of secondary school. This has historic significance as it shows what Elemenetary Algebera was taught in the early - mid 20th century. This book would have been used in the Kiewa Valley schools by a local identity Wilma Davies therefore has social significance and research value. This book is now out of print and is a collectible item.A blue maths book with faded blue coth cover. It has gold lettering on the side of the book stating the name, author and publisher with their logo. It would have had its name on the cover at one stage but it no longer on it due to water damage.Cover has a triangle with Cambridge Mathematical Series enmbossed around the three sides. At the points of the triangle is the letters B D C with the letter A in the middle of the trianglebook, school, algebra, educational, math, kiewa-valley -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book, The Federal Arithmetic, Early 20th century
This is a Grade V Arithmetic book used by George Bonnett at Allans Forest School. The Bonnett family farmed in the Mepunga area on the Childers Cove Road. The Allans Forest State School, number 1086, was established in 1871 and closed in 1993. The first Head Teacher was Mr Bradhurst. The school closed in 1903 and re-opened in 1905 as a half-time school with Mepunga East and in 1908 it resumed as a full time school. This book is significant because it was used by George Bonnett at the Allans Forest State School and is a memento of both the Bonnett family of Mepunga and the Allans Forest State School, a school no longer existing. It is also of antiquarian interest as an example of arithmetic school text books used early in the 20th century. This is soft cover book of 128 pages. The cover is grey with black print and black lines around the edges of the front cover. The book has a prefatory note, arithmetical exercises and advertisements for other school text books published by Whitcombe and Tombs. The cover is torn and soiled and partly ripped away. There is handwriting in black ink on the first page.‘George H. Bonnett, Allans Forest State School’bonnett family, mepunga allans forest state school history of warrnambool -
 Victoria Police Museum
Victoria Police MuseumPhotograph (Victoria Police Group Photo), Police Officers group photo, 1920s
Black and white photograph mounted on grey frame. 17men pose for photograph in forma suits in 3 row structure (front ones hold hats on their laps). *Most of them wear Freemansonry waistcoast chain. Photograph was taken during King George time - VPRG They stand in terrace of open brick building (on the back), with large windows and some plants.Printed above photograph: POLICE COLLEGE << Course No.1 -- November, 1958 - June 1959 >> Printed bellow photograph: Left to Right, Back Row: Stn. Officer Mooney, Sgt. Sheather, Det-Sgt. Carter, Sgt. Poulter, Sgt. Mooring, Sgt. Pearson, Sgt. Comrie, Sgt. Sharkey, Det.Sgt. McKnight. Centre Row: Sgt. Scotney, Insp. Hynes, Sgt. Long, Sgt. Payne, Insp. Houghton, Sgt. Peach, Sgt. Moore, Sgt. Heath, Sgt. Rose. Front Row (Directing Staff): Mr. C. H. Smith, Det-Sgt. Warne, Insp. Quill, Insp. DeLany, Insp. Milner, Det-Sgt. Braybrook, Mr. R. Crowling.victoria police museum, police officers, police academy, police force, freemasonry, masons, free masons -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book - Book: The Puzzle Picture Book, Ernest Nister, The Puzzle Picture Book, 1900
The book, awarded to Ethel Henderson in 1903, from Christ Church, Warrnambool is an example of a Sunday School prize given to children attending Sunday School at the time. Christ Church Anglican Church was one of the early churches in Warrnambool.The Puzzle Picture Book is a rare 'movable' children's book from 1900. It contains 6 chromolithic dissolving scenes (also called slats/transformations). It is unusual due to its educational content. It was published by Ernest Nister in London, E F Dutton & Co in USA and is also thought to have been published in German under the title 'Ueberraschungen Aller Art'. [source: The Little Book Store]Child's picture book with full colour cover depicting a mother dressed in long white spotted dress, white apron, white bonnett and black button-up shoes, sitting on a wooden armchair while dressing a young girl's hair with pink flowers. The girl is dressed in a pink frock with puffed sleeves and frill around the hem, and cream apron. She is looking in a brown wooden-backed hand mirror. A woven straw basket with pink roses sits on the floor. A framed silhouette picture is on the wall. The title is in a display typeface mimicking rose stems; a swag of pink roses decorates the top right hand corner. The publishers' names are printed on the bottom left and right hand corners at the bottom, and the printer in the centre. The inside cover has a book plate. The title page shows two boys arguing over the book. The verses are by Clifton Bingham, the pen and ink illustrations by Hilda K. Robinson. The story has a monochrome page with rhymes opposite a colour page with cut-out boxes showing four small pictures, each with a question. By pulling the tab at the bottom of the page the answer to the questions is revealed. There are six chromolithic 'dissolving scenes'.Book plate: Christ Church. Sunday School, Warrnambool. 1st Prize Girls Class II. Awarded to Ethel Henderson. S M George Vicar. Warrnambool, May 1903children's picture books, ethel henderson, children's picture books, puzzle books, christ church anglican church, sunday school prizes, ernest nister london, warrnambool, ethel henderson, e f dutton &amp;amp; co new york -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Functional object - G.S. Mackay company seal, Late 19th century
George Sutherland Mackay came to Warrnambool in 1891 and in 1893 joined his practice with that of James Fletcher and the firm became known as Mackay and Fletcher later changed to Mackay and Taylor. G S Mackay served for a long time on the Warrnambool City Council including 4 terms as Mayor. He was also an active member of the Presbyterian Church and worked to establish the Warrnambool Agricultural High School. He built the offices which still stand at 131 Kepler Street. He died in 1926. The firm celebrated its centenary in 1993.A commonly used office item which is well linked to both a long established business in Warrnambool and G. S. Mackay who contributed greatly to the community of Warrnambool and district. Cast iron painted black with rounded rectangular base. Circular seal and shaped handle which moves down 45 degrees. Trimmed with worn gold paint. Excelsior in gold on the front. The oval seal reads G. S. Mackay Warrnambool solicitor.warrnambool, g s mackay, mackay & taylor, mackay solicitor, company seal -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph, "Beaumont", Cherry Tree Road, Panton Hill, (built 1874). Mr. and Mrs. Edwin Smith and Family, 1894
L-R: Florry (Mrs. Scarce), Alice (Mrs. Cracknell), Mr. Smith and Victor, Edwin Jnr., Rose (Mrs. D. White), Mrs. Smith, at back May (Mrs. Jones) and Bert, Will, George and Alfred. Source: Mrs. E.W. Motschall (nee Marjorie Smith), Long Gully Road, Panton HillThis photo forms part of a collection of photographs gathered by the Shire of Eltham for their centenary project book,"Pioneers and Painters: 100 years of the Shire of Eltham" by Alan Marshall (1971). The collection of over 500 images is held in partnership between Eltham District Historical Society and Yarra Plenty Regional Library (Eltham Library) and is now formally known as the 'The Shire of Eltham Pioneers Photograph Collection.' It is significant in being the first community sourced collection representing the places and people of the Shire's first one hundred years.Digital imagesepp, shire of eltham pioneers photograph collection, panton hill, alfred jones, alice cracknell, bert jones, edwin simth, edwin smith jnr., florry scarce, george jones, may jones, mrs smith, rose white, victor smith, will jones -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybeading
These items are from the Temple estate. George Temple (1832-1916) started Temple's store opposite Post Office. Packed stores to Bendoc area gold fields.One long rope of jet beads and a pair of bobble jet beads. One jet bead applique piece.beading jet-beads costume-accessories haberdashery
