Showing 176 items matching "obstetric"
-
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Badge - Royal Army Medical Corps cap badge worn by F J Browne, World War I, 1915 (approximate)
Issued to Royal Army Medical Corps soldiers, this cap badge would have been worn by Francis Browne during World War I. Francis James Browne died in Sydney 1963. He had a long career in obstetrics and gynaecology. Summary of appointments include: General Practice in Wales, Maternity Department of the Edinburgh Royal Infirmary, 1st director of obstetric unit, University College Hospital London. Retired and continued postgraduate teaching in London and NSW. Married to Grace Cuthbert, who was director of Maternal and Baby Welfare in NSW. Collection of objects transferred from the Archives to the Museum collection found amongst Professor FJ Browne's papers.Dark brown metal cap badge. Design features a crown sitting atop a laurel wreath, which surrounds a representation of the Rod of Asclepius (serpent wrapped around a rod). A scroll is affixed below the wreath which is inscribed 'ROYAL ARMY MEDICAL CORPS'.world war i, numismatics, browne fj -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
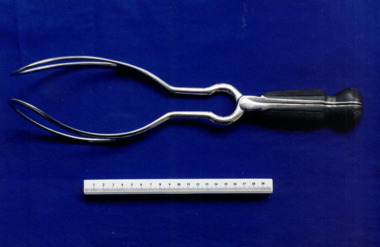
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Barnes-type obstetrical forceps, Evans & Co., London
The '24' inscribed on the handle is a theatre number for instrument identification. Invented by British obstetrician Robert Barnes (1817-1907), these forceps were designed to "enable delivery from the superior strait and from above the brim in cephalo-pelvic disproportion." One of Barnes' aims with this design "was to reduce the incidence of craniotomy, because the Caesarean operation was at this time a desperate last resort." (Source: Forster, F M C. (1971), Robert Barnes and His Obstetric Forceps. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, 11: 139-147.) With the addition of William Neville's axis-traction handle (invented in 1886), a variation of these forceps known as the Neville-Barnes forceps gained widespread popularity.Set of metal forceps, consisting of two nickel plated blades with bakelite handles. Inscribed 'EVANS & CO./LONDON'.Theatre mark "24" inscribed on handle of both blades.obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Document - Two Day Diary associated with F.J. Browne, 1940, John Walker & Co Ltd, Farrington House, Warwick Lane EC4, 1939
Personal diary of Dr F.J Browne. Donated by Grace Cuthbert Browne, wife of Dr Brown. The original diary would have had a small pencil attached. Francis James Browne died in Sydney 1963. He had a long career in obstetrics and gynaecology. Summary of appointments include: General Practice in Wales, Maternity Department of the Edinburgh Royal Infirmary, 1st director of obstetric unit, University College Hospital London. Retired and continued postgraduate teaching in London and NSW. Married to Grace Cuthbert, who was director of Maternal and Baby Welfare in NSW. A collection of objects found amongst Professor FJ Browne's papers were transferred from the Archives to the Museum collections in January 1994.Personal diary. Small navy blue hard cover bound diary with "1940" in gold lettering on front cover. Inscription on front page, "F.J. Browne/ 8 Downing Street/ Cambridge". Pencil/loop holder attached to back cover. Entries in diary are written in pencil - only partially used as a diary. The diary entries finish on 6 June 1940. browne fj -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Instrument - Dührssen-style 8 bladed dilator, Unknown
Alfred Dührssen (23 March 1862 – 11 October 1933) was a German gynecologist and obstetrician born in Heide, Schleswig-Holstein, at the time part of Denmark. He studied medicine at the University of Marburg, as well as the Kaiser-Wilhelm-Akademie für das militärärztliche Bildungswesen (Kaiser-Wilhelm-Academy for Military Physicians). In 1886, he became an obstetrical assistant to Adolf Gusserow (1836-1906) in Berlin, and in 1888 he began work as a lecturer at the University of Berlin. In 1892 he opened a private clinic for obstetrics and gynecological diseases. Dührssen was a prominent figure in modern German gynecology, being remembered for his pioneer work in surgical practices such as vaginal Caesarean section (vaginalen Kaiserschnitt). He was an advocate of institutional births for all pregnancies, and proposed that pregnant women undergo screening processes to uncover possible difficulties prior to giving birth. (Wikipedia) Metal uterine dilator consisting of a handle, a short shaft, and eight prongs. The prongs each have a bump/curve in the prong towards the top, to allow them to bend around the shaft of the instrument and meet at their tips. There is a second 'bump' in the prongs just before the tips. The tip of each prong has five ridges to assist with grip. The handle of the device is a flat, rounded handle, which is turned to open the prongs and set them at various degrees of diameter. There is a gauge on the shaft of the instrument which ranges from 0-12, showing the current setting of the instrument. There is also a pin and T-shaped slot arrangement located just above the start of the prongs, which has been engraved '8' on the left hand side, and '1' on the right hand side. Each prong is also engraved with a number at the base of the prong, reading '1' to '8'. gynaecology -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Print - Reproduction print, Carl William Weisbrod (active 1770s) et al, Vue de la Place Publique de Cos, c. late 18th century
This is an image of a public square on the island of Kos in Greece. Kos was the home of Hippocrates, and the tree in this image is reputedly the plane tree under which Hippocrates sat as he taught his pupils medicine. Hippocrates is known as the "Father of Medicine" for his revolutionary impact on the field of medicine. The letters 'A.P.D.R' printed below the title on this artwork refer to the copyright granted to engravers in France.Black and white engraving of a market square scene on the island of Kos in Greece. A large tree dominates the scene. Below the tree sits a roofed structure with a series of small steps. Water appears to be coming out of a channel of each of the visible sides of the structure, suggesting a fountain. To the left, an array of human figures, horses and a dog sit or stand beneath the tree and on the steps of the fountain. To the right, there are shaded platforms on which people are sitting in groups. There are three dogs in front of the group sitting on a platform at bottom right. Text printed below image reads 'VUE DE LA PLACE PUBLIQUE DE COS/A.P.D.R.' Small printed text below bottom left corner of image is partly illegible, but references the original creator of the artwork, Jean-Baptiste Hilair. Small printed text below bottom right corner of image reads ' Gravé à l'eau forte par C. Weisbrod/ el terminé au burin par J. Aliamet'. Small printed text above top left hand corner of image reads 'Pl. 59.' The print has been framed in a brown wooden frame with gold trim. An old display label is affixed to the back of the object. A card from Professor Franco Crainz is affixed to the back of the object, thanking the unnamed receiver for a reprint of their "interesting paper on D.D.Davis' Obstetric Atlas". The front of the card carries a print of the Temple of Esculapia, located in the Villa Borghese in Rome. A wire and two hooks have been attached to the rear of the work for hanging. -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
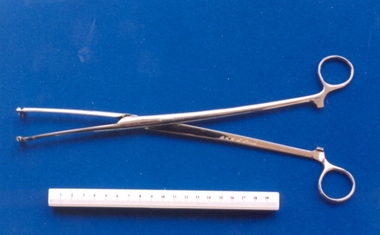
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Placenta praevia forceps used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward, Ramsay
Similar to Willett's placenta praevia forceps [see Down Bros Catalogue of Surgical Instruments and Appliances, c1930, p 940]. John Abernethy Willett (1872 -1932) modified an existing pair of surgical scalp forceps for use in bringing down the head of a foetus in the case of placenta praevia. As the safety of c-sections increased and fetal viability became a dominant consideration, these were used only for the dead/pre-viable foetus. (Source: Baskett, Thomas. 'On the Shoulders of Giants - Eponyms & Names in O&G'.) This was included with other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, from Box Hill Hospital labour ward given to RANZCOG in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill hospital combined with St Geroge's Hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett.Pair of long handled forceps, placenta praevia style. Inscribed "B.H.H.L Ward" inner handle."B.H.H.L Ward"destructive instruments -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Medal - French World War I military service awarded to FJ Browne, c.1914-1918, A. Mayeur, 1918
This French Service medal was awarded to F.J. Browne for service in the First World War tending to the wounded soldiers evacuated from France on hospital ships. The places inscribed on the medal are all in the Communaupole (Urban Area) of Lens-Liévin in the Pas de Calais where the broad plain and low hills of Artois saw some of the most savage and bloody fighting of World War I.Francis James Browne died in Sydney 1963. He had a long career in obstetrics and gynaecology. Summary of appointments include: General Practice in Wales, Maternity Department of the Edinburgh Royal Infirmary, 1st director of obstetric unit, University College Hospital London. Retired and continued postgraduate teaching in London and NSW. Married to Grace Cuthbert, who was director of Maternal and Baby Welfare in NSW. A collection of objects found amongst Professor FJ Browne's papers were transferred from the Archives to the Museum collection in January 1994. A small round gold medal (.1) with presentation case (.2). The scene on the front of the medal depicts an ancient castle & surrounds with the rising sun in the background, and is inscribed "SUNT LACRYMAE RERUM". On the reverse is a figure of a winged woman against a cross, and the inscription "AUX HEROS", above a list of inscribed place names: "DE GARENCY, VIMY, ABLAIN, AVION, SOUCHEL, LENS, LORETTE, LOOS". The outside of the presentation case is maroon leather. There is a cream velvet mount for the medal and the inside of the lid of the case is lined with cream satin. "A. MAYEUR" is inscribed on both sides of the medal. "SUNT LACRYMAE RERUM", "AUX HEROS", "DE GARENCY, VIMY, ABLAIN, AVION, SOUCHEL, LENS, LORETTE, LOOS", "A.MAYEUR"numismatics, world war i, france, browne fj -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
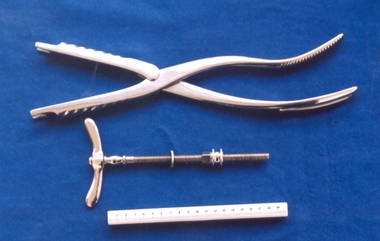
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Set of Braun's craniotomy forceps used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward, Allen & Hanburys, England
Carl Rudolph Braun (1823-1891) was the inventor of this instrument, as well as a type of decapitation hook. Braun was born and practiced in Austria, and followed Semmelweis as assistant to Klein at the Vienna Maternity Clinic in 1847, before becoming its head in 1856. Braud added a gynaecology section to the clinic in 1858, being convinced that obstetrics and gynaecology should be together. (Source: Baskett, Thomas. 'On the Shoulders of Giants: Eponyms and Names in Obstetrics and Gynaecology'). This device was included with a range of other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, given to RANZCOG from Box Hill Hospital labour ward in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill Hospital combined with St George's hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett.Craniotomy forceps, Braun's. Stainless steel forceps, with wingnut. Upper blade has open oval section and ridged grip section on the handle. Lower blade has serrated inner edge and ridged grip section on the handle. Wingnut is used for attaching the upper and lower blades of the forceps. Inscribed "B.H.H.L Ward" on forceps."B.H.H.L Ward"destructive instruments -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
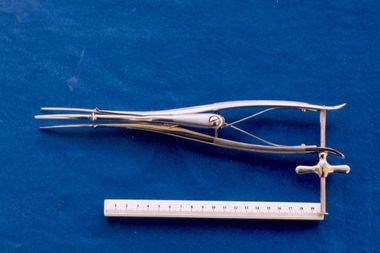
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Sims-type uterine dilator used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward
Used for probing a woman's uterus through the cervix, to measure the length and direction of the cervical canal and uterus. Dilators are primarily used to open and dilate the cervix to gain access to the uterine cavity but can also be used as sounds. This device was included with other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, given to RANZCOG from Box Hill Hospital labour ward in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill Hospital combined with St George's Hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett.Three bladed Sims uterine dilator, consisting of upper blade, lower blade, bridge, and wingnut. Blades are polished stainless steel with matte steel handles. Upper surface inscribed, (trademark) MADE IN GERMANY INOXIDABLE", "21"."21"box hill hospital -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
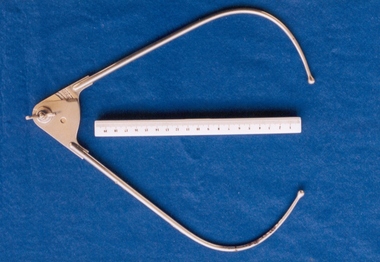
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Pelvimeter used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward
A pelvimeter is used in obstetrics for measurement of the female pelvis, with the aim of attempting to determine whether there will be any potential issues with a vaginal birth. The style of this pelvimeter is similar to Collyer's pelvimeter as depicted in Aesculapius Surgical Instruments p. 2195. This instrument was included with other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, given to RANZCOG from Box Hill Hospital labour ward in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill Hospital combined with St George's Hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett.Pelvimeter. Similar in style to Collyer's pelvimeter. Has adjustable arms hinged with a wingnut, and a scale graduated in inches and centimetres.obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
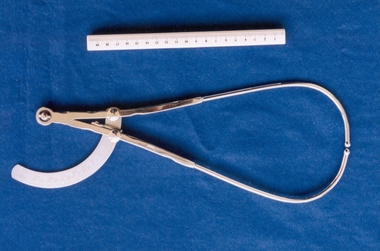
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - 'Ramsay' pelvimeter used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward, Ramsay
A pelvimeter is used in obstetrics for measurement of the female pelvis, with the aim of attempting to determine whether there will be any potential issues with a vaginal birth. This pelvimeter is similar in style to Martin's pelvimeter (see Aesculapius). This instrument was included with other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, given to RANZCOG from Box Hill Hospital labour ward in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill Hospital combined with St Geroge's Hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett.Pelvimeter, manufactured by Ramsay. Metal device with calibrator graduated to 18 inches/ 45 cms. Inscribed " Ramsay" upper arm."Ramsay"obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
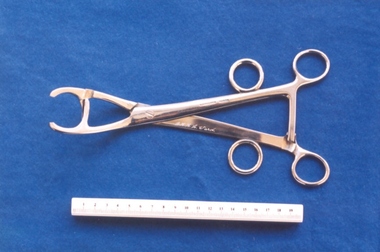
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Bonney's myomectomy clamp used by Box Hill Hospital labour ward, Down Bros., London
Victor Bonney (1872- 1953) was a gifted and innovative surgeon. One of Bonney’s most notable achievements was his development of a successful procedure for myomectomy. After his wife developed fibroids and had her uterus removed early in their marriage, Bonney took a great interest in the practice of conservatism in surgery. Prior to Bonney, myomectomy “had fallen into disuse because of excessive blood loss during the operating and the infections that commonly followed” (Chamberlain, 'The master of myomectomy') , but Bonney saw an opportunity to revolutionise this practice. In his words: “I set myself to make myomectomy so feasible, successful and safe as to render it a fair alternative to hysterectomy in every case… Excepting only in a very few instances… I have succeeded, and now enter the operating theatre free of the trammels which at one time too often compelled my hand against my heart.” (Bonney, 'The fruits of conversatism') Bonney’s crucial innovation was the development of a new surgical clamp, an instrument which is now referred to as Bonney’s myomectomy clamp. The clamp was ingeniously designed to cut off blood supply to the uterus by compressing the uterine arteries, immediately reducing the excessive blood loss which had previously been associated with the procedure. Although technological advances mean that these are now seldom used, Bonney’s success with this procedure was such that his clamps were regularly used for myomectomy procedures for decades after his death. This instrument was included with other obstetric instruments, mostly destructive instruments, given to RANZCOG from Box Hill Hospital labour ward in February- March 1998. The maternity service at Box Hill Hospital combined with St George's Hospital in Kew to be known as Birralee Maternity Service. These instruments were collected by Julie Collette, Unit Manager, St George's Kew and given to RANZCOG Museum Curator, Susan Barnett. Stainless steel clamp. Scissor type instrument with two sets of finger grips and a locking ratchet mechanism. The blades close to form two apertures which can be selectively decreased in size."DOWN BROS LONDON STAINLESS" upper surface of RH handle; "B.H.H.L. WARD" inner surface of LH handle.surgery, obstetrics -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
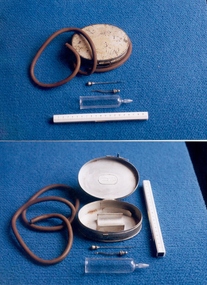
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)'Horrocks' saline infusion apparatus used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, Down Bros., London
Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated the obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period. 'Horrocks' saline infusion apparatus. Consists of white, metal lidded oval shaped case [169.1], containing a gauze insert, a glass intravenous drip chamber [169.2], straight intravenous needle [169.3], wire insert for the needle [169.4] and rubber tubing [169.5]. Inscribed inside box, "Down Bros., St Thomas Street, Borough of London."hydration -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
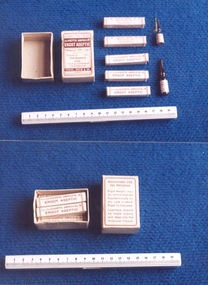
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Box of ampoules used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, Parke, Davis and Co, c. 1952
Ergot aseptic was used to stimulate uterine contractions after labour to expel the placenta. Pitocin was also used for this but could also be used during labour to quicken and stimulate the labour process. Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated the obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period. Box, with lid, labelled "CLASEPTIC AMPOULES/ERGOT ASEPTIC", Parke, Davis & Co, Sydney, manufactured February 1952. Within the box are three smaller boxes containing glass ampoules of "Ergot Aseptic" and two boxes containing ampoules of Pitocin.obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Weighing scales used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
Scales like these were used to weigh babies.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated the obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The gladstone bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period. Set of small, portable spring balance scales. With case/enclosure.infant care -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
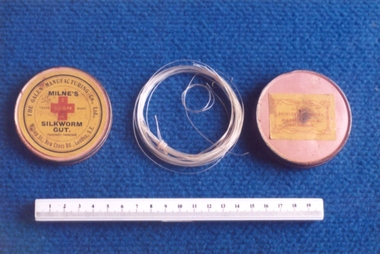
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tin of silkworm gut used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, Galen Manufacturing Co. Ltd, c.1871-1930
Used in surgery. Made from silkworms.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated the obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The gladstone bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Round metal tin containing silkworm gut. Tin is painted pink, with a yellow label affixed to the lid bearing a central image of a red cross. Tin is labelled 'MILNE'S/SILKWORM/GUT.' Tin contains a ring of eighteen strands of silkworm gut tied with fine hat elastic, and one additional ring of silkworm gut. surgery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
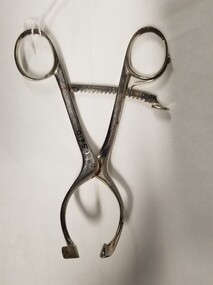
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Doyen's mouth gag used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
A mouth gag was used when required to assist in the administration of anaesthesia to a patient. It is used to keep the patient's mouth open, and could also be used for oral surgery or airway management. This particular mouth gag is known as a Doyen's type.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated the obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The gladstone bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Stainless steel mouth gag. Design of item resembles a pair of scissors, but with a foot at the end of each blade and a ratchet attached to keep the device open.anaesthesia -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Instrument steriliser used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, c. 1907
This type of steriliser was in use from approximately 1907 onward. Designed for surgeons who frequently moved from hospital to hospital. The body and lid of the steriliser were made from one continuous piece of metal to produce a germ-free surface. Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Metal instrument steriliser. Consists of a rectangular metal container with lid, an internal metal tray, and two spirit burners. The lid has a small wire handle at either end. The internal tray also had two handles and in perforated with holes to allow for drainage. The upper edge of each burner has a series of eighteen holes in the rim. disinfection -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Surgical scrub brush with storage box used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Wooden handled brush with pig hair bristles. With oval shaped metal case consisting of lid and base.disinfection -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)String used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
This type of string, or twine, was frequently used by obstetricians to tie the umbilical cord after the delivery of a baby. Thicker string was favoured because there was less chance of cutting through the soft cord tissue surrounding the umbilical vein. Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Brown string, possibly made of hemp, in two separate lengths. obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
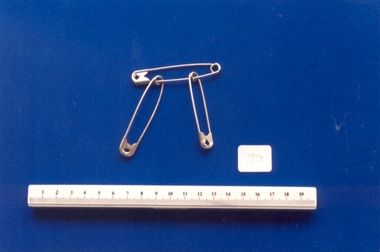
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Domestic object - Safety pins used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, c. 1930-1960
These type of safety pins were commonly used in hospitals between 1930- 1960. Pins such as these were advertised for sale as "Hospital and Sick Room Sundries" and were generally supplied in boxes of 12 dozen (144). The pins were supplied in sizes ranging from 0 to 6 - the pins catalogued here are sizes 4,5, and 6. Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Three nickel plated safety pins (.1 - .3) of differing sizes. .1 is size 4, .2 is size 5, and .3 is size 6. -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Tool - Metal clamps used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
The provenance and use of these items is uncertain, but they are possibly part of portable steriliser or could have been used as abdominal binder holders.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Two metal clamps. Each clamp consists of a central metal stem, with oval shaped handles at each end of the clamp. One clamp is slightly longer than the other. -
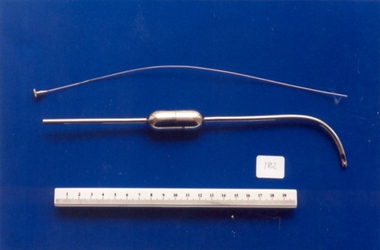 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Carton's mucus evacuator, and introducer, used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
Used for the removal of mucus, chiefly, from newborn infants. The top section of the chamber in the evacuator acted as a receptacle for wool to absorb any excess overflow of fluid/mucus. The lower section of the chamber collected the aspirated fluid. Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Metal evacuator with wire introducer. Evacuator has a rounded middle chamber, which is divided into two sections. Proximal end of evacuator is curved to approximately 60 degrees and has two small holes in the end. Introducer is a straight piece of wire attached to a flanged head, with a small, serrated edge. obstetric delivery -
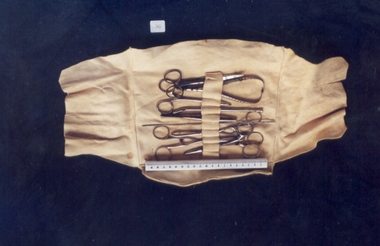 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Pocket dressing case containing surgical tools used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
The metal probe in this set (.6) was used to puncture superficial skin blisters or eruptions and to probe suspected pus filled wounds. The Mayo scissors (.7) was (and still is) part of all major and minor suturing sets. It is also used in general theatres.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Pocket dressing case containing surgical tools. Case [185.1] is made of cream household chamois, with two end flaps and small overlapping front piece to indicate the front of the case. Middle of the case has a strip of chamois divided into nine sections to hold the instruments. Tools contained in the case are: straight Spencer Wells artery forceps x2 [185.2,185.3], Allis box jointed tissue forceps x2 [185.4,185.5], straight probe [185.6], curved Mayo scissors [185.7], straight dissecting forceps [185.8], catheter (female) [185.9], straight McPhail needle holder [185.10]. Artery forceps 185.2 are stamped with '19' on both inner arms. Tissue forceps 185.4 are stamped with "2" on inner arm. Tissue forceps 185.5 are stamped with "8" on inner arm. Mayo scissors 185.7 are marked with '"1". Dissecting forceps 185.8 are marked with "1".surgery -
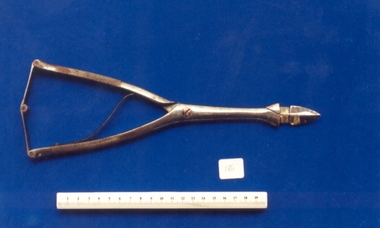 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Simpson's perforator used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
Perforators were used to pierce and empty the skull in craniotomy.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Simpson's perforator. Instrument consists of two straight, pointed blades with screw joint, and a spring loaded insert. Also includes a connecting spring bar at top of handle with three hinge joints. Handles are textured for grip.destructive instruments -
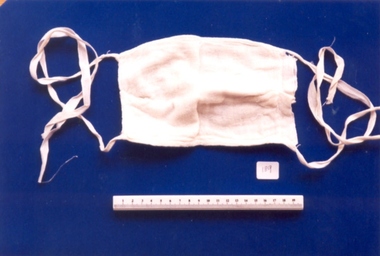 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Surgical gauze mask used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Mask is made up of several layers of muslin gauze sewn together with cotton tape. The ends of the tape were used to tie the mask to the doctor's face covering the nose and mouth.surgery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Iodine bottle used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan
Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Small amber coloured glass bottle used to store iodine. Bottle has a clear glass stopper.antiseptic -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Chloroform bottle used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, W.J. Bush & Co
The use of chloroform as an anaesthetic for humans was first demonstrated by Edinburgh surgeon James Young Simpson in 1847. It was used as an anaesthetic in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Amber glass bottle (empty) with clear glass stopper. Bottle carries its original label which "W.J. Bush & Co. Ltd. London ... Chloroform.."". On the base is the number "12" and "AS 9A"anaesthesia -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Silk umbilical tape in glass vial used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, Allen & Hanburys, England
To use this tape, the tube would be broken in half using cat-gut breakers.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Glass vial, containing silk umbilical tape [193.2] in sterile solution. The tape is wound around a flat spool.obstetric delivery -
 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)
Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists (RANZCOG)Two glass vials of 'Ethicon' catgut #3 used by Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan, Ethicon
Tanned or chronic catgut came from top quality catgut (fat free). A hardening process was then applied to the muscle durations. The process was introduced and perfected by the firm of Mersons of Edinburgh, makers of sterile surgical ligatures in the early 1930s. Once processed the catgut was preserved in an iod-asceptic preserving spirit and hermetically sealed in glass tubes. It was completely sterile and ready for immediate use. The length of the catgut in each tube was five feet, or 2.5m, and could be wound onto glass winders in assorted colours.Dr Mitchell Henry O'Sullivan worked in the Victorian country town of Casterton as a general practitioner from 1919 until his death in 1977. He also practiced obstetrics. His son, Dr David More O'Sullivan donated his obstetric bag and its contents to the College in 1999. The bag and contents are a unique time capsule of the type of instruments and pharmaceuticals used in the inter-war period.Two glass vials [195.1,.3] with catgut number three "Ethicon" [195.2,.4] in sterile solution. Vials are moulded and sealed at both ends.obstetric delivery
