Showing 1122 items matching "warrnambool business"
-
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Equipment - money ball, Wooden Money Ball Cramond & Dickson, Late 19th century/Early 20th century
... important businesses in Warrnambool’s retail history ...This wooden cash ball came from the retail business of Cramond and Dickson. It was part of the mechanism for sending money and change to and from the customer to a shop assistant dealing with the finances. The ball ran along sloping rails in the shop. John Cramond and James Dickson, both from Scotland, established a general store in Warrnambool in 1855 in Timor Street. The business was later transferred to the corner of Liebig and Timor Streets and became a well-known landmark in Warrnambool, closing in 1973. This item is significant as it came from one of the most important businesses in Warrnambool’s retail history – that of Cramond and Dickson. It also is an important example of retail store practice in the late 19th century and early 20th century. This is a cylindrical wooden ball which separates into two parts to allow the insertion of money in the middle. There is a round metal disc which is housed in the centre of the wooden ball.It has a circle marked on the outer surface of both semi circles of the ball. It is brown in colour. On both halves of the ball on the outside – ‘D 4’cramond and dickson, warrnambool, money ball -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Memorabilia - Newspaper cuttings scrapbook, Martin Carter, Saddler, Warrnambool, late 19th century (1887-1894)
This scrapbook contains newspaper cuttings, mainly about football, and other written material from the late 19th century. It belonged to Martin Carter ((1870-1943), a Warrnambool saddler who worked for many years in the saddlery business established by his father, Samuel. Martin Carter was very active in community affairs - President of the Warrnambool Bowling Club, a member of the local Volunteer Militia, Secretary of the Progress Association, a football player and umpire and a local cricketer. He was the Secretary of the Warrnambool Town (later City) Band for fifty years and a memorial plaque in his honour was erected at the Band headquarters in Warrnambool. He was also a Warrnambool Councillor (1917-1925) and Warrnambool Mayor (1922-24). His interest in football can be seen from the great number of football newspaper cuttings in this notebook.This little notebook is most interesting as it provides us with details on football in the Warrnambool district in the late 19th century and gives us an indication of the popularity of the game at that time. It is a valuable research tool.This is a small notebook with a black cover. The pages contain ruled red lines over which have been pasted newspaper cuttings. Some pages have handwritten material and some pages are blank. There are also several loose cuttings. The notebook has been stapled but the staples have been removed.M.L.Carter Warrnambool June 13th 1887 S.Carter Saddler Warrnambool (stamp)warrnambool town band, martin carter warrnambool, football in the warrnambool district, sydney giddings warrnambool saddler -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Instrument - Decimal Currency Converter, Ultra Publicity Pty Ltd, C 1966
This decimal currency converter was produced about 1966 when the Australian currency was changed from the imperial system to the decimal system. It has been used by a Warrnambool businessman, Alan Lane to promote one of his businesses, Lane’s Motors and would have been given to business clients. Alan Lane (d.1995) was prominent in Warrnambool as a businessman man, community leader and philanthropist. His businesses included a bus company, a taxi company and a travel agency. His community services included involvement in the St. John Ambulance Brigade, the Rotary Club, the local Football League, the Warrnambool Art Gallery, the Performing Arts Centre, the Warrnambool Chamber of Commerce and the Warrnambool Council. The A.L. Lane Foundation was established with funds from his estate and continues to assist local projects and charitable causes. This item is of interest as a memento of the time when the Australian currency was converted to the decimal system and as a memento of the prominent Warrnambool community worker, Alan Lane. This is a card consisting of four circles of paper of different sizes joined in the centre with a metal clip. The smallest central piece of paper has advertising material and the other three pieces have red and black numbers, some of decimal currency notations and some of imperial currency notationsDecimal Currency Computer Instructions for Use See Back Lane’s Motors alan l. lane, warrnambool, a.l. lane foundation -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Audio - Video, Bruce Chamberlain. Warrnambool, A conversation with Mrs Reta Brauer, 26/09/2002
Mrs Rita Brauer, widow of the Dr Alfred Brauer Warrnambool doctorVoice recording & CD recording of interview by Bruce Chamberlain and Rita Brauer widow of Dr Alfred Brauer W'bool doctor, giving a small part of Mrs Brauer's contribution to life in Warrnambool.Slip cover Sony Super DX 180 - card (red, yellow, blue & white) Front of slip case has business card. The Hon Bruce Chamberlain. Video black plastic case with video tape A conversation with Mrs Rita Brauer and Bruce Chamberlain 26/9/2002.video, dvd, conversation, video, dvd, conversation, brauer reta, chamberlain bruce, oral histories -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Financial record - Ledger, Cash Book Swinton's Store, Early 20th century
... Swinton business in Timor Street Warrnambool is the oldest family ...This is a cash book from the business of William Swinton and Sons. The entries list stock, financial assets, deeds and insurance policies from 1902 to 1911. William and Ann Swinton migrated to Australia in 1854 and for a decade William Swinton worked as a builder and carpenter in the Warrnambool area, erecting many buildings, including the Wangoom Presbyterian Church. In 1865 he opened a store in Timor Street, Warrnambool, selling groceries, china, glassware and hardware. By 1888 the business was known as William Swinton and Sons. Branch stores were opened in Cudgee, Nullawarre, Wangoom, South Warrnambool and West Warrnambool. After William died his son Robert became the first managing director in 1913 of Swintons Pty Ltd. In 1934 the business split, with George Swinton and Sons selling furnishings, clothing and glassware and Swintons Pty Ltd selling seeds, hardware and produce. Today the Swinton family still operates a furniture and bedding shop in Timor Street. This cash book is of considerable interest as a business document of William Swinton and Sons. The entries for the early 20th century give details of business stock and finances and will be very useful to researchers. The current Swinton business in Timor Street Warrnambool is the oldest family business in Warrnambool and, with the Swinton name associated with businesses in Timor Street for 152 years, it is one of the oldest family businesses in Australia.This is a hard cover book of 96 pages with a dark green cover and red leather trimmings on the spine and cover corners. There is gold lettering on the spine. The insides of the cover have a green and brown mottled patterning and the page edges have a multi-coloured mottled patterning. The pages have printed ruled red lines. The entries are handwritten in black ink. There are five loose sheets. ‘Cash Book’ swinton family warrnambool, history of warrnambool -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Medals, Stokes Melbourne, Industrial & Art Exhibition 1886-7, 1896
These are souvenir medals of the Warrnambool Industrial and Art Exhibition of 1896-7. This exhibition organised by a local committee under the chairmanship of the Mayor, Walter Hickford was one of the most important events in Warrnambool's history. It ran for three months and was said to have attracted 70000 visitors. It was held in Liebig Street and utilised both the civic centre buildings and temporary buildings erected for the event. It had several exhibition courts featuring art worksand business exhibition stands, competitions,entertainments and visiting experts in various fields. These medals were made at the exhibition at the stand of Stokes and Son. Visitors to the exhibition were able to get a gold silver or bronze medal made while they watched and the medal was then perforated ready to put on a watch chain or pendant. Thomas Stokes came to Australia in the 1850's and established a successful business in Melbourne manufacturing buttons, medals and tokens. The business was called Stokes and Son following a fire in 1893.These medals are of great significance as a memento of an important event in Warrnambool -The Warrnambool Industrial and Art Exhibition of 1896-7. Medals such as these would have been in the homes of many residents of Warrnambool and district and beyond after 1896..1 This silver circular medal has text around the outer rim and an image of Queen Victoria on the reverse. On the obverse is text and an image of the Warrnambool Exhibition building erected for the occasion. The medal is secured by a red thread , button and clear tape to a piece of card. On the card is a hand drawn sketch the Warrnambool Exhibition building and a hand drawn sketch of a profile of Queen Victoria . .2This silver circular medal has text around the rim and an image Warrnambool Exhibition building on the reverse and on the obverse a stylised coat of arms topped by the rising sun . Inside the field is a sailing ship, a pick and shovel , a sheep and sheaf of wheat .1 on the Reverse : around the rim, Struck at the Exhibition mint. On the obverse : Industrial exhibition 1896 Warrnambool. .2 On the obverse : Industrial exhibition 1896 Warrnambool.warrnambool, great exhibition of warrnambool, 1896 exhibition warrnambool, warrnambool exhibition medal -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAudio - Gramophone Cylinder, B & H Jack, 1907
Edison Records was one of the early record labels that pioneered sound recording and reproduction, and was an important player in the early recording industry. The first phonograph cylinders were manufactured in 1888, followed by Edison's foundation of the Edison Phonograph Company in the same year. The recorded wax cylinders, later replaced by Blue Amberol cylinders, and vertical-cut Diamond Discs, were manufactured by Edison's National Phonograph Company from 1896 on, reorganized as Thomas A. Edison, Inc. in 1911. Until 1910 the recordings did not carry the names of the artists. The company began to lag behind its rivals in the 1920s, both technically and in the popularity of its artists, and halted production of recordings in 1929. Thomas A. Edison invented the phonograph, the first device for recording and playing back sound, in 1877. After patenting the invention and benefiting from the publicity and acclaim it received, Edison and his laboratory turned their attention to the commercial development of electric lighting, playing no further role in the development of the phonograph for nearly a decade. Start of the Recording Industry: In 1887, Edison turned his attention back to improving the phonograph and the phonograph cylinder. The following year, the Edison company introduced the ”Perfected Phonograph”. Edison introduced wax cylinders approximately 4+1⁄4 inches (11 cm) long and 2+1⁄4 inches (5.7 cm) in external diameter, which became the industry standard. They had a maximum playing time of about 3 minutes at 120 RPM, but around the turn of the century the standard speed was increased to (first 144) and then 160 RPM to improve clarity and volume, reducing the maximum to about 2 minutes and 15 seconds. Several experimental wax cylinder recordings of music and speech made in 1888 still exist. The wax entertainment cylinder made its commercial debut in 1889 at first, the only customers were entrepreneurs who installed nickel-in-the-slot phonographs in amusement arcades, saloons and other public places. At that time, a phonograph cost the equivalent of several months' wages for the average worker and was driven by an electric motor powered by hazardous, high-maintenance wet cell batteries. After more affordable spring-motor-driven phonographs designed for home use were introduced in 1895, the industry of producing recorded entertainment cylinders for sale to the general public began in earnest. Blank records were an important part of the business early on. Most phonographs had or could be fitted with attachments for the users to make their own recordings. One important early use, in line with the original term for a phonograph as a "talking machine", was in business for recording dictation. Attachments were added to facilitate starting, stopping, and skipping back the recording for dictation and playback by stenographers. The business phonograph eventually evolved into a separate device from the home entertainment phonograph. Edison's brand of business phonograph was called the Ediphone. The collection of three phonograph cylinders are an example of early recorded music use for domestic entertainment. They are significant as they represent the beginnings of the modern recording industry.Cardboard tube-shaped gramophone cylinder box with lid. The printed label on the outside of the box advertises the maker and patent details. The Catalogue Number and Title are either printed or hand written on the cylinder’s lid. This cylinder contained Record no. 49, “B & H Jack” and was made at the Edison Laboratory USA. C. 1905On lid “Edison Record No. 49”, written in pencil “B & H Jack” (it looks like this) On cylinder “EDISON GOLD MOULDED RECORDS ECHO ALL OVER THE WORLD” Patents listed for 1904 & 1905warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, gramophone record, gramophone cylinder, edison cylinder, edison record, home entertainment, music recording, edison laboratory orange nj, usa, national phonograph company of australia ltd sydney, thomas a. edison -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAudio - Gramophone Cylinder, National Phonograph Co, Poor old England, 1908
Edison Records was one of the early record labels that pioneered sound recording and reproduction, and was an important player in the early recording industry. The first phonograph cylinders were manufactured in 1888, followed by Edison's foundation of the Edison Phonograph Company in the same year. The recorded wax cylinders, later replaced by Blue Amberol cylinders, and vertical-cut Diamond Discs, were manufactured by Edison's National Phonograph Company from 1896 on, reorganized as Thomas A. Edison, Inc. in 1911. Until 1910 the recordings did not carry the names of the artists. The company began to lag behind its rivals in the 1920s, both technically and in the popularity of its artists, and halted production of recordings in 1929. Thomas A. Edison invented the phonograph, the first device for recording and playing back sound, in 1877. After patenting the invention and benefiting from the publicity and acclaim it received, Edison and his laboratory turned their attention to the commercial development of electric lighting, playing no further role in the development of the phonograph for nearly a decade. Start of the Recording Industry: In 1887, Edison turned his attention back to improving the phonograph and the phonograph cylinder. The following year, the Edison company introduced the ”Perfected Phonograph”. Edison introduced wax cylinders approximately 4+1⁄4 inches (11 cm) long and 2+1⁄4 inches (5.7 cm) in external diameter, which became the industry standard. They had a maximum playing time of about 3 minutes at 120 RPM, but around the turn of the century the standard speed was increased to (first 144) and then 160 RPM to improve clarity and volume, reducing the maximum to about 2 minutes and 15 seconds. Several experimental wax cylinder recordings of music and speech made in 1888 still exist. The wax entertainment cylinder made its commercial debut in 1889 at first, the only customers were entrepreneurs who installed nickel-in-the-slot phonographs in amusement arcades, saloons and other public places. At that time, a phonograph cost the equivalent of several months' wages for the average worker and was driven by an electric motor powered by hazardous, high-maintenance wet cell batteries. After more affordable spring-motor-driven phonographs designed for home use were introduced in 1895, the industry of producing recorded entertainment cylinders for sale to the general public began in earnest. Blank records were an important part of the business early on. Most phonographs had or could be fitted with attachments for the users to make their own recordings. One important early use, in line with the original term for a phonograph as a "talking machine", was in business for recording dictation. Attachments were added to facilitate starting, stopping, and skipping back the recording for dictation and playback by stenographers. The business phonograph eventually evolved into a separate device from the home entertainment phonograph. Edison's brand of business phonograph was called the Ediphone. The collection of three phonograph cylinders are an example of early recorded music use for domestic entertainment. They are significant as they represent the beginnings of the modern recording industry.Cardboard tube-shaped gramophone cylinder box with lid. The printed label on the outside of the box advertises the maker and patent details. The Catalogue Number and Title are either printed or hand written on the cylinder’s lid. This cylinder contained Record no. 13619, the recording “Poor old England” published by Castling and Godfrey, sung by Billy Williams. Made by National Phonograph Company USA. C.1907On lid “Edison Record” and “This record should turn at 160 revolutions per minute, no faster” Written on lid in blue pen “Trumpet”, “EDISON AMBEROL RECORD / FOUR MINUTE”warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, gramophone record, gramophone cylinder, edison cylinder, edison record, home entertainment, music recording, edison laboratory orange nj, usa, national phonograph company of australia ltd sydney, thomas a. edison -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAudio - Gramophone Cylinder, Sandy McNab, 1908
Edison Records was one of the early record labels that pioneered sound recording and reproduction, and was an important player in the early recording industry. The first phonograph cylinders were manufactured in 1888, followed by Edison's foundation of the Edison Phonograph Company in the same year. The recorded wax cylinders, later replaced by Blue Amberol cylinders, and vertical-cut Diamond Discs, were manufactured by Edison's National Phonograph Company from 1896 on, reorganized as Thomas A. Edison, Inc. in 1911. Until 1910 the recordings did not carry the names of the artists. The company began to lag behind its rivals in the 1920s, both technically and in the popularity of its artists, and halted production of recordings in 1929. Thomas A. Edison invented the phonograph, the first device for recording and playing back sound, in 1877. After patenting the invention and benefiting from the publicity and acclaim it received, Edison and his laboratory turned their attention to the commercial development of electric lighting, playing no further role in the development of the phonograph for nearly a decade. Start of the Recording Industry: In 1887, Edison turned his attention back to improving the phonograph and the phonograph cylinder. The following year, the Edison company introduced the ”Perfected Phonograph”. Edison introduced wax cylinders approximately 4+1⁄4 inches (11 cm) long and 2+1⁄4 inches (5.7 cm) in external diameter, which became the industry standard. They had a maximum playing time of about 3 minutes at 120 RPM, but around the turn of the century the standard speed was increased to (first 144) and then 160 RPM to improve clarity and volume, reducing the maximum to about 2 minutes and 15 seconds. Several experimental wax cylinder recordings of music and speech made in 1888 still exist. The wax entertainment cylinder made its commercial debut in 1889 at first, the only customers were entrepreneurs who installed nickel-in-the-slot phonographs in amusement arcades, saloons and other public places. At that time, a phonograph cost the equivalent of several months' wages for the average worker and was driven by an electric motor powered by hazardous, high-maintenance wet cell batteries. After more affordable spring-motor-driven phonographs designed for home use were introduced in 1895, the industry of producing recorded entertainment cylinders for sale to the general public began in earnest. Blank records were an important part of the business early on. Most phonographs had or could be fitted with attachments for the users to make their own recordings. One important early use, in line with the original term for a phonograph as a "talking machine", was in business for recording dictation. Attachments were added to facilitate starting, stopping, and skipping back the recording for dictation and playback by stenographers. The business phonograph eventually evolved into a separate device from the home entertainment phonograph. Edison's brand of business phonograph was called the Ediphone. The collection of three phonograph cylinders are an example of early recorded music use for domestic entertainment. They are significant as they represent the beginnings of the modern recording industry.Cardboard tube-shaped gramophone cylinder box with lid. The printed label on the outside of the box advertises the maker and patent details. The Catalogue Number and Title are either printed or hand written on the cylinder’s lid. This cylinder was made by Edison 1908 and contains Record number 53 by Sandy McNab. c. 1908On label “Edison Record No. 53, Sandy McNab" and "Form no. 1130, April 1908. Patented December 6 1904, No. 2109, and December 6 1904 No. 2110. “This record is sold by the National Phonograph Company of Australia Ltd, at Sydney Australia.” Trade Mark Thomas A. Edison warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, gramophone record, gramophone cylinder, edison cylinder, edison record, home entertainment, music recording, edison laboratory orange nj, usa, national phonograph company of australia ltd sydney, thomas a. edison -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Box, Dentist, 1940s
Pat King was a surgeon dentist in Warrnambool from the late 1920s through to the 1940s. In 1929 the King family owned the stone building in Liebig Street next to the old Tattersalls Hotel (now McDonalds fast food outlet). The King family remodelled the building and turned it into shops with living quarters upstairs. Pat King had his dental business in the centre of the building and his brother had a produce store at the northern end of the building. It was known at that time as Kings building. By the early fifties, at the time of his death, Pat King had been living at 32 Howard Street. Kings building was auctioned in 1953.This little box is of some interest as it came from the dental business of Pat King, a prominent dentist in Warrnambool in the 1930s and 40s. This is a small buff-coloured cardboard box with a lid. The four corners of the box and the lid have metal rivet reinforcements and a semi-circular cardboard inset has been stapled into the box. The box was used by the dentist Pat King of Warrnambool and the box appears to have been made to hold dentures. Lid of box: ‘P. V. King, L.D.S, B.D.Sc., Dental Surgeon, 187 Liebig Street, Warrnambool, Phone 451’. kings building,, warrnambool, pat king, dentist, history -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Booklet, Warrnambool Woollen Mill 1951-53, 1953
In 1869, the Warrnambool Meat Preserving Company commenced their business on the site, where it operated until 1875 when it was sold to the directors of the Warrnambool Woolen Mill Company. After being destroyed by fire in 1882 it wasn’t until 1910 that the Warrnambool Chamber of Commerce was approached by Marcus Saltau and Peter McGennan to invest in a new mill. The original directors were James Dickson, P J McGennan, Robert Swinton, M Saltau, and J W Younger. In 1955 the Warrnambool Woollen Mill formed a partnership with the Wangaratta Woollen Mills. Dunlop bought the mill in 1968. From that time until its closure in 2000 it had a number of different owners, the last being the Smith Family Industries. This report contains the financial reports for the three years from 1951-1953.This report shows records of the Woollen Mill which was one of the most important industries in Warrnambool for nearly 100 years. As such it has links to many local families and organisations.Light brown paper cover with black text underlined in red. Bound in black tape. Accountants’ name along bottom of cover in black.warrnambool, warrnambool woollen mill, warrnambool woolen mill, -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Cutlery, George Rolfe, Mid to late 19th century
In 1854 in Melbourne George Rolfe Senior established an import business dealing in groceries, wines and spirits and tea. His son George, born in England, took over the business of Rolfe and Co in 1871. A keen sportsman, George Rolfe’s love of fishing led him to take frequent holidays in Warrnambool. He began buying blocks of land near the mouth of the Hopkins River in Warrnambool in the 1870s. By the 1880s Rolfe owned 50 acres in the Hopkins River area and named the property, Lyndoch. He built stables, chaff and bone sheds, a jetty, a boatshed, a water well, a windmill, a reservoir and extensive gardens. He also bought the nearby properties of Shipley and Fairy Hill, establishing a stud farm and breeding cattle. In 1891 he married Jane Ann Lake, the widow of his property manager, and when he died in 1919 his step-daughters, Florence and Annie Lake, inherited Lyndoch. The property was sold and became an aged care facility in 1952. The cutlery items were in use in the building erected by Florence Lake in 1920 and known today as Lyndoch but the ‘R’ monogram on the items suggest that they belonged to George Rolfe or even his father before him.These cutlery items are of considerable importance as mementoes of George Rolfe and his family. They were prominent in Warrnambool’s history in the late 19th and early 20th centuries with the establishment and development of the property, Lyndoch, near the mouth of the Hopkins River. These are 17 pieces from a silver cutlery set that belonged to the Rolfe family (one tablespoon, six large forks, five smaller forks, four small spoons and one mustard spoon.) All the pieces of cutlery have a monogrammed ‘R’ at the end of the handles. Twelve of the items are tarnished and one small spoon is very worn. All the items have six hallmarks. ‘R’george rolfe, lyndoch, warrnambool, rolfe & co. melbourne, florence lake, lyndoch warrnambool., history of warrnambool -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Bat, Cricket bat, 1870s
This bat was awarded to Thomas William Southcombe in 1876 for the best batting average during the 1875-6 season at Warrnambool Cricket Club. Thomas William Southcombe was the son of Thomas and Mary Southcombe of Port Fairy. With his parents, Thomas and Mary, he arrived in Port Fairy in 1854. Thomas Senior was a carpenter who established several businesses in Port Fairy and served on the local Council for many years as a Councillor and Mayor. Thomas Junior appears to have migrated to U.S.A. and died there in 1904. The cricket bat was manufactured by the British firm of James Lillywhite, Frowd & Co. James Lillywhite was an English cricketer whose uncle had originally established the sports store and manufacturing business which lasted under various names until the 21st century. A cricketer named Lillywhite played in Warrnambool in 1874 with an All England Team under the captaincy of W.G.Grace. It is not known whether this was James Lillywhite or another member of the Liilywhite family as several of them played first class cricket.. The impression of the signature of W.H.Ponsford on the bat is an intriguing one. W.H. (Bill) Ponsford was a famous Australian cricketer who retired in the late 1930s. The Southcombe cricket bat was given by Mary Southcombe (Thomas’ sister) to the old Warrnambool Museum in 1923 and it is surmised that Bill Ponsford visited Warrnambool in 1957 (tthis appears to be the date under the signature imprint) and was shown the bat. It is then surmised that he rested a piece of paper or an album page on the bat while he signed his name and the impression of the signature has come through onto the bat. The old Museum closed in the 1960s and the bat was then passed on to the Warrnambool and District Historical Society from the Warrnambool City Council collection of items from the Museum. This bat is of considerable importance because of its provenance and its connection with the Warrnambool Cricket Club, the Southcombe family of Port Fairy, the Lillywhite manufacturers, the old Warrnambool Museum and Bill Ponsford. It is also a good example of the type of cricket bat used in Australia in the 1870s. This is a wooden cricket bat (light colour wood, presumably willow) with a handle covered in oiled thread. It has an etched inscription on one side of the bat and the names of the manufacturer and distributor on the other side. There is also a faint impression of another signature. The blade of the bat is slightly curved. ‘W.C.C. Season 1875-6 Presented to T.W. Southcombe, for Best Batting Average’ ‘James Lillywhite Frowd & Co., Manufacturers, Borough, England’ ‘Made for George Marsh, Melbourne’ ‘W.H.Ponsford, -/1/1957’ warrnambool cricket club, thomas william southcombe, w.h.ponsford, warrnambool’s old museum -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Pants, Fletcher Jones, Mid 20th century
... of a Warrnambool business that was nationally and internationally known ...These trousers have been made by Fletcher Jones and Staff. This business was established by David Fletcher Jones (1895-1977) in 1924 when he leased three shops in Liebig Street, Warrnambool. In 1928 he moved his business to the main retailing area near the Liebig Street/Koroit Street intersection. In 1931 a shop built to Fletcher Jones’ requirements was erected and by 1938 he had a staff of 40. By 1945 FJ trousers were sold in 123 stores in Victoria and in 1948 the Fletcher Jones factory was established in Flaxman Street Warrnambool, officially named Pleasant Hill. In 1951 the company became Fletcher Jones and Staff and by the mid 1970s the staff had 75% ownership. By this time FJ and Staff had become one of the largest clothing manufacturers in Australia with 55 shops and almost 3000 employees. The range of clothing was enlarged to include both men’s and women’s wear. In the 1980s, after the death of Fletcher Jones, the abolition of import tariffs and the availability of cheap imported clothing caused the Fletcher Jones Company to decline and to be sold to a Geelong company. By 2011 all Fletcher Jones shops had closed. These trousers are of great interest as they are a product of a Warrnambool business that was nationally and internationally known in the 20th century for its quality men’s wear, especially the Coverdine brand trousers. The Fletcher Jones business remains one of the most important businesses, (if not the most important), that ever existed in Warrnambool. It employed a great number of local people in the second half of the 20th century, and is remembered with great fondness by many people in the city and surrounds today. The Fletcher Jones Gardens at the Factory site are still maintained today and are a tourist attraction in the city. These are a pair of brown Fletcher Jones trousers made of Coverdine material (87.5% wool with nylon). There is some lining around the waist area and the legs are turned up at the end with some leather binding inside the bottom legs. The waist band is stiffened and is fastened with a metal clip and two buttons. The waist band has two adjustable areas using tabs and two buttons each side. The back pockets also have buttons.fletcher jones and staff, coverdine fletcher jones trousers, history of warrnambool, david fletcher jones -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Work on paper - Document, Victorian Saddle & Harness Warehouse, C 1900
... in Warrnambool but he also had a similar business in Lonsdale Street... in Warrnambool but he also had a similar business in Lonsdale Street ...This is an advertising card for the business of E.D.Evans & Co., the Victoria Saddle and Harness Warehouse situated in Liebig Street Warrnambool next to the Victoria Hotel. This business operated in Liebig Street from 1872 to the last known date of 1911. Edward David Evan's saddlery business was prominent in Warrnambool but he also had a similar business in Lonsdale Street, Melbourne. He was a Warrnambool Councillor from 1875 to 1878 and from 1884 to 1888. He was also heavily involved with the Warrnambool Racing Club being President for some time. This is an interesting card because it comes from the saddlery business of E.D. Evans and Co., a prominent business in Warrnambool in the 19th and early 20th Centuries . A white card with black printing on both sides.The card is stained particularly around the edges.VICTORIA SADDLE AND HARNESS WAREHOUSE E.D. EVANS & CO.e.d.evans, saddler of warrnambool, saddlery in warrnambool, edward david evans -
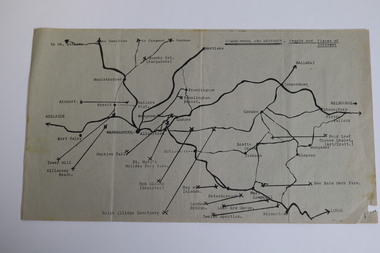 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Map - Tourist Map Collection: Warrnambool & District Tourist Maps, Philprint, Warrnambool
... attractions. warrnambool tourist maps warrnambool businesses ...This is a diverse collection of Tourist Maps for the Warrnambool & District area. [.1] From information on this guide it dates from the mid 1970's. It appears to not have been commercially printed and includes details of attractions no longer operating in Warrnambool such as Warrnambool Aquarium and the Oasis Reptile Park and Zoo. [.2] Commercially printed Warrnambool tourist map (c mid 1980's) surrounded by advertisements for local businesses. [.3] Commercial printed December 1991 tourist map of Warrnambool and District includes a competition entry form [.4] Commercially printed tourist map aimed at children [.5] Walking map of Warrnambool and District [.6] Commercially printed Warrnambool tourist map (c mid 1980's) surrounded by advertisements for local businesses. This collection of maps from the mid 1970's to early 1990's gives an insight into what was available to assist tourists find their way around Warrnambool and District. They include advertisements for business operating during this period and include lists of available accommodation, eateries, and tourist attractions.[.1] Tourist Attractions In and Around Warrnambool two foolscap pages with two sides of type written information of local and district attractions. There is a Warrnambool City map with points of interest marked and a hand drawn district map; [.2]Commercially printed grid map of Warrnambool City surrounded by advertisements from local businesses. Reverse side has a district map and a map of the Warrnambool CBD surrounded by advertising. [.3] Brochure including small grid maps of Warrnambool and district listing accommodation providers and places of interest. Stylised blue & bright green design of Norfolk pines and sea. [.4] Children's treasure hunt map to Warrnambool There are two examples, one with blue edging (Jan 1986) and one with red edging (Aug 1993) Both have a circular logo with a stylised whale and lighthouse [.5] Walking maps of Warrnambool blue printed photo of four tourists walking coastline on the front cover. [.6] Commercially printed grid map of Warrnambool with a bright yellow inset of Warrnambool CBD main shopping centre. The map is surrounded by advertising for local businesses.warrnambool, tourist maps, warrnambool businesses, warrnambool accommodation -
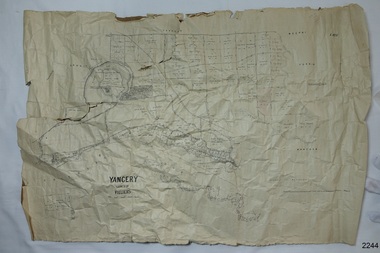 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageMap - Survey Map, F.F. McGovern, Yangery - County of Villiers, 1884
A surveyor was employed to measure the land designated as Yangery, County of Villiers, in the Borough of Warrnambool. The area on the map is similar to the earlier Farnham Survey undertaken by William Rutledge in the 1850's. Warrnambool was a Borough between 1863-1883. Coutours, waterways, sea and other significant points are shown. The distances are accurately measured. This survey map was used for planning future land sales, recreation areas and roads. WILLIAM RUTLEDGE (1806-1876) William Rutledge surveyed the land known as Farnham in southwest Victoria in 1843. His tenants made him a profitable business from working the land there. In 1863 Rutledge moved from nearby Port Fairy to Farnham and became very successful in breeding sheep, which he imported from J.R. Kirkham of Lincolnshire, England. He also bred horses on his land. The survey map of Yangery is important for its connection with renowned surveyor William Rutledge. The map shows the growth of landholders in the district when compared to the original Rutledge survey of the 1850's.Survey map of Yangery, titled "Yangery - County of Villiers". Printed on white paper, mounted on brown paper. c. 1863-1876. Comments printed on the Map include; Special Survey by William Rutledge, Photo-lithographed at the Department of Lands and Survey, Melbourne by W.J. Burson, Price 1/- [one shilling]. Scale is in Chains. Map has boundaries of Koroit Borough, Meerai, Purnim, Wangoom, Borough of Warrnambool, Mentions the Proposal of Tower HIll for Public Recreation. The map names the owners of the land at that time. Hand written pencil marks and figures and "Sauls fence" drawn on map. Hand written pencil markes and figures and "Sauls fence" drawn onto map. "For Department Use only". "Scale: 8 chains to 1 inch" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, county of villiers map, yangery district, w.j. burson, borough of warrnambool, koroit, purnim, meerai, wangoom, proposal of tower hill for public recreation, special survey by william rutledge, william rutledge, farnham, lincolnshire sheep, clydesdale -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Souvenir - Book Clip T.H. Easson Tea & Coffee Merchant
... for the Warrnambool Tea & Coffee merchant, T. H. Easson. T. H. Easson ...This is an example of an early merchandising item for the Warrnambool Tea & Coffee merchant, T. H. Easson.T. H. Easson was an early tea & coffee merchant in Warrnambool (1898-1973). The business was located at 125-127 Liebig Street and later at 103A Liebig Street. The business was also known at various times as Easson's "The Tea & Coffee Shop" and as Easson's Tea Rooms.A heart shaped, thin, soft metal book clip with a floral decoration pressed into the metal outer edge. The top of the heart has a small hole and a bow, ribbon and floral decoration pressed into the metal below it. There is a floral design at the base of the heart above the word Warrnambool. T.H. EASSON TEA & COFFEE MERCHANT WARRNAMBOOLt.h. easson, tea & coffee merchants, warrnambool, liebig street -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Booklet - Booklet Collection: City of Warrnambool Tourist Guides, Collett, Bain and Gaspar, Warrnambool
This is a collection of sixteen tourist guides dating from the mid 1970's to 2013. These contain listings of businesses, accommodation, eateries and events in Warrnambool and district. They also include maps of Warrnambool and surrounds, advertising and photographs of various attractions. While mainly covering Warrnambool a small number of the guides cover the South West Region. These directories have mainly been published by the Warrnambool City Council and are a selection of the types of information provided to visitors at the Tourist information centre during this time period.These tourist guides give snapshots of the City of Warrnambool for the years covered and will be useful for research.[.1] An 8 page paper booklet with black printing and a black & white photo of the pond at the Botanical Gardens on the front cover. [.2] two photocopied A4 black and white pages from the book "On the Trail" K Winser 1956 (Main Roads of Australia) [.3] A trifold colour brochure with a stylised map of the coast on the yellow and blue front cover. The inside has stylised colour drawings on Warrnambool attractions. The rear cover has coloured photographs of bush, Liebig Street and Fletcher Jones gardens [.4] A trifold black and white brochure with a black line drawing of a whale on the front cover. [.5] A trifold white card with mauve printing. The front cover has a line drawing of the former Timor Street post office and a map of businesses and landmarks in Timor Street. The reverse side contains a brief history of Warrnambool. [.6] A 98 page stapled booklet with a foreword by Vanda Savill. There are 4 pages of coloured photographs. The remainder are black and white photographs. The front cover is purple with white writing in the lower third. There is an outline of the coast and five colour photographs of district attractions. The inside middle page has a map of the Western wonderland region. The content covers towns in this area. Content relating to Warrnambool is in the last six pages. [.7] Twelve loose photocopied black and white pages. The front cover has the Warrnambool Premier Town 1988-1991 logo and a photo of a Southern Right Whale and calf. The bottom right hand corner has a Standard Warrnambool logo. [.8] 44 page booklet printed with blue ink. The staples have been removed. The glossy front cover has blue printing with a coloured photo of Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village pond. The centre pages has a fold out map of the City of Warrnambool. The rear cover has photos of The Twelve Apostles and Hopkins Falls. [.9] 4 loose photocopied pages with Warrnambool Library and Corangamite Regional Library Service Warrnambool City Library black ink stamps. The front page line drawing illustrations of Warrnambool attractions [.10] A single sheet of glossy white paper folded in half to make four pages. The front page has a Warrnambool premier town logo 1979-1982 and blue printing and a visitor survey. [.11] A conference pack of light card folded to make a pocket containing three brochures, a shipwreck coast tourist directory and a Australian Heritage Parks Association conference program dated 24 to 27 May 1992. The front cover of the pack has green writing over a stylised upward arrow. There is a City of Warrnambool logo in the top right hand corner and two film strips diagonally across the cover containing photographs of Warrnambool. The rear cover has a coloured Warrnambool Premier Town logo. [.12] A 63 page stapled booklet with coloured photographs of Warrnambool. The front cover has black writing on white background. There is a coloured photograph of Flagstaff Hill in the middle of the cover and a Warrnambool City and Visit Victoria logos on the lower edge. The middle pages has a coloured of the city of Warrnambool with an inset map of Allansford. [.13] A single large sheet of white paper folded in ten to make a brochure. The front cover has black printing. The rear cover has a purple ink stamp for the City of Warrnambool Tourist Information Centre. When folded out the reverse side has a green, grey and white map of the South West Region of Victoria. [.14] A 48 page colour booklet on glossy paper. The front cover has white writing on a blue background and includes photographs of the Twelve Apostles, the Promenade walk, Flagstaff Hill and a southern right whale's tail. The rear cover has photographs of The Twelve apostles, a passenger train from Melbourne passing the Lake Pertobe playground, and a rural scene. There is white writing and a white Warrnambool City logo on a blue background. The centre pages have a stylised green and blue map of the city of Warrnambool. [.15] A 48 page colour booklet on glossy paper. The front cover has white writing over colour photographs of two people at a lookout, Flagstaff Hill, three southern right whales and a child at the Lake Pertobe playground. The lower edge has blue upper case writing on a white background. The rear cover has a colour photograph of the Twelve Apostles. The lower white border on the rear covers has a a blue and green City of Warrnambool logo and blue writing. The centre pages have a stylised green and blue map of the city of Warrnambool. [.16] A 64 page colour booklet on glossy paper. The front cover has black writing on a black background and there is a photograph of a southern right whale's tail. The lower edge has the Warrnambool City and Visit Victoria Logos. The centre pages have maps of Warrnambool and surrounds. [.1] This week in Warrnambool Vol 2 No. 5 Thurs 1st Feb. For the time of your life [.2] Warrnambool Way [.3] Warrnambool The Holiday Host on the South West Coast with compliments City of Warrnambool and Warrnambool Chamber of Commerce [.4] MMI Insurance presents Whales Giants of the Deep Whale Watcher's Logbook Warrnambool [.5] Warrnambool History began in Timor Street [.6] Western Wonderland Tourist Association [.7] A Premier Arrow Tour of Warrnambool Victoria's Premier Town Australia's Southern Right Whale Nursery [.8] Warrnambool The Heart of Victoria's Great Southwest Visitor's Handbook [.9] What to see in Warrnambool Victoria's Premier City 1979-1982 [.10] Win a Free Holiday & $200 Cash in Victoria's Premier Town [.11] Advancing Warrnambool together! [.12] Great Ocean Road Warrnambool Official Visitor Guide [.13] Tourist guide to the South West Region Victoria All it needs is you [.14] Warrnambool visitor guide 2005 the great ocean road experience attractions accommodation entertainment dining [.15] Warrnambool Visitor Guide 2006 the great ocean road experience Attractions Accommodation Entertainment Dining [.16] Official Visitors' Guide Warrnambool Victoria Australia Discover the Great Ocean Road warrnambool, warrnambool tourist guides -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Document - Ledger, Cash Book, Circa 1917
This cash book contains entries relating to the farrier business of W M McCullough in Fairy St Warrnambool. It lists names and numbers of shoes replaced. It dates from January 1917 to march 1919 and contains many local names such as Sheldrick, Selby, Skuse, Horne and Saltau, to name a few.Listing many local people and being associated with a local business, it has social and historical significance. Green cloth covered card cover with maroon binding. Blue, maroon and white patterned inside covers. White paper label edged in floral design, pasted to front cover. 92 pages double numbered to page opening. Hand written entries to page 32 warrnambool farriers, w mccullough warrnambool, farriers of warrnambool, 1915 farriers -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book, The History of Warrnambool by Richard Osburne, 1980
Richard Osburne (1825-1895) came to Warrnambool in 1847, a pioneer resident in the new settlement. In 1851, with John Wilkinson, he founded Warrnambool’s first newspaper, the Warrnambool Examiner, and issued it weekly for some months until he left the town for the goldfields. Returning in 1853 he resumed publication of the Examiner and continued it, intermittently in its last few years, until 1880. He was acknowledged in his day as the Father of the Warrnambool Press and was a dominant figure in Warrnambool’s early history. He was associated with the establishment of the Aboriginal Reserves, Fire Brigade, Mechanics’ Institute, Warrnambool Council, National School, Presbyterian Church, Public Wants Committee, Villiers Building Society, Fish Protection Society, Dramatic Club, Cricket Club, Otway Gold Exploration Syndicate and other institutions. In 1882 he went to live in Melbourne, returning to publish his ‘History of Warrnambool’ in 1887, a Queen’s Jubilee publication. Richard Osburne’s book is a seminal work of the 19th century history of Warrnambool and its importance cannot be over-emphasized. The original copies of this book are now hard to get and are very valuable. This facsimile is kept because the facsimiles are also now becoming rare and they are good examples of the way a facsimile is reproduced and the reason for the existence of this particular reprint– the importance and usefulness of Osburne’s history and the need to make it accessible to researchers today.This is a facsimile edition (1980) of Richard Osburne's book on the history of Warrnambool from 1847 to 1886. It is a hard cover buff-coloured book with gold lettering on the spine. The dust cover is cream-coloured paper with black writing. Inside the cover is a map of southwest Victoria (1880). There are five fold-up inserts (sketches, diagrams etc), a number of business advertisements, sepia photographs and sketches and an index. The dust cover includes information on the author. There are 25 chapters, a foreword by the Prime Minister of Australia, Malcolm Fraser and a Preface The proceeds of the book reprint went to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village.This is a facsimile edition (1980) of Richard Osburne’s book on the history of Warrnambool from 1847 to 1886. It is a hard cover buff-coloured book with gold lettering on the spine. The dust cover is cream–coloured paper with black writing. Inside the cover is a map of southwest Victoria (1880). There are five fold-up inserts (sketches, diagrams etc), a number of business advertisements, sepia photographs and sketches and an index. The dust cover includes information on the author. There are 25 chapters, a foreword by the Prime Minister of Australia, Malcolm Fraser and a Preface The proceeds of the book reprint went to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village.richard osburne, the history of warrnambool, warrnambool examiner -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Yard ruler, J Russell Pty Ltd, Mid 20th century
... business. r J russell warrnambool Newcombe Pty Ltd Warrnambool ...R J Russell operated a timber and hardware store in Koroit Street Warrnambool around the 1950’s. He succeeded from Newcombe Pty Ltd which had operated a timber and hardware store on the site (the present Target store) from the 1870’s. The business continued to trade under the Newcombe name after the death of Newcombe around 1900.A common well used item with links to a local business.Wooden yard ruler with markings in one eigthth inch measurements and numbered in inches. Text written in black on both sides.On front side: J Russell Pty Ltd. Timber and hardware merchants 148 Koroit Street Warrnambool. Phone 22. On reverse: Fencing materials, general hardware, paints, oils , Glass. Contractors or builders. Phone 22r j russell warrnambool, newcombe pty ltd warrnambool, timber yards warrnambool -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Booklet - Deakin University Warrnambool Graduation Ceremonies 2015, 2015
Deakin University was established in 1974 as the fourth university in Victoria. It has a number of campuses around the state including Warrnambool where it merged with The Warrnambool Institute of Advanced Education in 1990. The university was named after Alfred Deakin, three times Prime Minister of Australia and leading figure in the process of Federation in Australia. Each year a number of students graduate from the Warrnambool Campus which is located on the Eastern edge of Warrnambool on the banks of the Hopkins River. In 2015, there were graduands from the faculties of Arts and Education, Business and Law, Science and health. Deakin University occupies an important educational position In Warrnambool and district. This program contains the names of the many people associated with the university and the graduating students for the year 2015. Photograph of two students sitting on lawn in front of grey building. Text in white at top of cover.Back cover green with white text. "Phillpot OAM" on sticker on front cover. Deakin logo on bottom right corner of front cover.deakin university warrnambool, deakin university graduation 2015 -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Pamphlet (Collection) - Warrnambool Tourist Maps, Warrnambool City Council, 1975 to 2002
Warrnambool Tourist Maps collected over the years by Warrnambool Historical Society membersPreservation of local maps for historical purposesEnclosed in A4 size plastic envelopes in an A4 size archival box and numbered and catalogued according to the date of acquisition.This collection has 16 pamphlets containing maps of Warrnambool and district and some accompanying printed materialwarrnambool tourism, city of warrnambool, shipwreck coast tourismwarrnambool tourism, city of warrnambool, shipwreck coast tourism -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Administrative record - Rent Ledger, 1910 to 1925
The name of the business that produced the contents of this ledger is unknown. It is a record of rents paid by tenants to the property owners in Warrnambool and district from 1910 to 1925 and includes the rents paid and the dates. It probably belonged to a real estate firm or an accountancy or law firm dealing in property, mortgages and financial investments. Many of the names contained in the ledger are well-known (Coakley, Alston, Gleeson, McGennan etc) and the ones that are not so well known are mostly those with only one or two rental properties. This ledger is of some interest as a research tool giving information on property owners and renters in Warrnambool from 1910 to 1925. It will be of greater value if the name of the ledger owner can be found. This is a ledger with a cover made of wood and covered with a light brown material. It has a heavy metal insert inside to hold the pages. There are heavy card pages and white pages ruled with red and blue lines. The page entries are handwritten in ink. warrnambool renters 1910-1925, warrnambool property owners 1910-1925 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Vanity Set, Circa late 1800s or early 1900s
The vanity set was owned by a local woman who lived in the Harbour Master's house at Warrnambool after it was decommissioned. The set was possibly a wedding gift from her mother-in-law, Caroline Edwards, a local business woman who was an importer of 'china and fancy goods' along with her husband Thomas Myers Edwards. The Edwards owned Staffordshire House, a business in Timor St (and later Liebig St) from 1876. The vanity set is an example of a valued possession of women at the time and could signify social standing. It was also a functional accessory used on a daily basis.The item is significant socially as an example of accessories available to and used by women in the late 1800s and early 1900s. Historically, it is linked to a local import business ‘Staffordshire House’ in Timor and later Liebig St Warrnambool, where it most likely came from. A pewter (or possibly silver-plated) three-piece vanity set that includes a hand mirror, hair brush and comb. All pieces feature a beautiful ornate moulded rose/flower design on the back, handles and edge of the comb. The hair brush no longer has bristles and is purely ornamental. The comb teeth and hair brush insert are most likely made of celluloid.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, vanity set, hand mirror, brush, comb, pewter, celluloid, silver plate, toilet set, harbours master's house, staffordshire house, hair brush, hairbrush -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageAccessory - Hand Mirror, Circa late 1800s or early 1900s
The hand mirror is part of a vanity set owned by a woman who lived in the Harbour Master's house at Warrnambool in the late 1800s and early 1900s. The set was possibly a wedding gift from her mother-in-law, Caroline Edwards, a local business woman who was an importer of 'china and fancy goods' along with her husband Thomas Myers Edwards. The Edwards owned Staffordshire House a business in Timor St (and later Liebig St) from 1876. The hand mirror is an example of a valued possession of women at the time and could signify social standing. It was also a functional accessory used on a daily basis.The item is significant socially as an example of accessories available to and used by women in the late 1800s and early 1900s. Historically, it is linked to a local import business ‘Staffordshire House’ in Liebig St Warrnambool, where it most likely came from. A pewter (or possibly silver-plated) hand mirror that is part of a vanity set. It features a beautiful ornate moulded rose/flower design on the back, handle and front edge of mirrorflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, maritime village, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, vanity set, hand mirror, pewter, silver plate, toilet set, harbours master's house, staffordshire house -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillagePhotograph - Vessels Speculant and S. S. Flinders, Between 1902 and 1907
This photograph was one of ten photographs donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village by Fred Trewartha. Frederick John Fox Trewartha (Fred) was a well-known Warrnambool businessman. He was born in Beeac near Geelong in 1920 and came to Warrnambool with his family as a very young child. He was apprenticed to his father John, as a saddler and later opened his own shop on Raglan Parade. He then moved into working with tarpaulins and canvases for the trucking industry. Fred was keenly interested in photography (and was a member of the Warrnambool Cine Club), yachting and boat building. He kept his yacht moored at Port Fairy for many years and participated in sailing events locally and interstate. He also built boats with his sons. He had the opportunity to meet many older sailors and it's thought this photo (and others in the set) may have been given to him by one of these men. Fred Trewartha died in 2016 in Warrnambool. The two identifiable ships in this picture are the "Speculant" and the "S. S. Flinders" - both coastal trading vessels that regularly came and went from Warrnambool. The third steamer on the left hasn't been identified The barquentine SPECULANT was a steel, three-masted sailing ship built in 1895 in Inverkeithing, Scotland, registered in Warrnambool, Victoria and wrecked at Cape Paton, Victoria, 10th February 1911. The SPECULANT had been involved in the timber trade between the United Kingdom and Russia, until sold to its Warrnambool owners and timber merchants Messrs. P.J. McGennan & Co. (Peter John McGennan) in 1902 for 3000 pounds and had her sailed to Warrnambool as her new port. Peter John McGennan was born in 1844 and worked as a builder and cooper in Holyhead, Anglesea, Wales. He immigrated to Australia in 1869 as a free settler and arrived in Warrnambool in 1871 and undertook management of a property in Grassmere for Mr. Palmer. Peter met his wife Emily in South Melbourne and they married in 1873. They had ten children including Harry who lived to 1965, and Andrew who lived until 1958. (The other children were their four brothers - John who was killed in the Dardenalles aged 35, Frederick who died aged 8, Peter who died aged 28, Frank who died aged 5 weeks - and four sisters - Beatrice who died age 89, Edith who died aged 49, Blanche who died aged 89 and Eveline who died aged 48.) In 1874 Peter starting a boating establishment on the Hopkins River. In 1875 he opened up a Coopers business in Kepler Street next to what was Bateman, Smith and Co., moving to Liebig Street, next to the Victoria Hotel, in 1877. In 1882 he then moved to Lava Street (which in later years was the site of Chandlers Hardware Store). He was associated with the establishment of the Butter Factory at Allansford. He started making Butter Boxes to his own design and cheese batts for the Butter Factory. In 1896 established a Box Factory in Davis Street Merrivale, employing 24 people at its peak, (it was burnt down in 1923); and in Pertobe Road from 1912 (now the Army Barracks building). Peter was a Borough Councillor for Albert Ward from 1885 to 1891, he commenced the Foreshore Trust (including the camping grounds along Pertobe Road), and he was an inaugural Director of the Woollen Mill in Harris Street, buying an extensive share-holding in 1908 from the share trader Edward Vidler. They lobbied the Town Hall to have a formal ‘Cutting’ for the waters of the Merri River to be redirected from its natural opening south of Dennington, to its existing opening near Viaduct Road, in order to have the scourings from the wool at the Woollen Mill discharged into the sea. He sold Butter Boxes around the state, and had to ship them to Melbourne by rail. Peter’s purchase of the SPECULANT in 1902 enabled him to back-load white pine from Kaipara, New Zealand to Warrnambool to make his butter boxes then, to gain profitability, buy and ship potatoes and other primary produce bound to Melbourne. (McGennan & Co. had also owned the LA BELLA, which had traded in timber as well, until she was tragically wrecked with the loss of seven lives, after missing the entrance channel to Warrnambool harbour in 1905. It appears that the SPECULANT was bought to replace the LA BELLA.) In 1911 the SPECULANT had been attempting to depart Warrnambool for almost the entire month of January to undergo docking and overhaul in Melbourne. A month of east and south-easterly winds had forced her to remain sheltered in Lady Bay, Warrnambool apart from one morning of northerlies, when an attempt was made to round Cape Otway; she had to return to shelter in Portland after failing to make any headway. With only 140 tons of sand ballast aboard, the ship would not have been easy to handle. Captain Jacobsen and his crew of nine, mainly Swedes, decided to make for Melbourne, leaving Portland Harbour on 5th February 1911. By the 9th they had reached Cape Otway, where they encountered a moonless night, constant heavy rain, and a heavy sea with a south-easterly wind blowing. After safely rounding Cape Otway the course was changed to east, then north-east to take the vessel to a point six miles off Cape Patton, following the orders of Captain Jacobsen, who told the crew to be very careful with the steering, as the wind and sea was running to leeward. The patent log (used to measure speed) had been out of order for the last four months as no-one in Warrnambool was able to fix it: it was intended to have it repaired in Melbourne. In the meantime the crew measured the vessel's speed by looking over the side and estimating wind strength. This compounded the difficulties of imprecise positioning, as the strong cross wind and sea were acting on the lightly laden vessel to steadily drive it towards the shore. At 3.30am on Friday 10 February 1911 Captain Jacobsen and the first mate were looking over the side of the vessel when they heard the sound of breakers and suddenly struck the rocks. The crew immediately knew they had no chance of getting the SPECULANT off, and attempted to rescue themselves by launching the lifeboat, which was instantly smashed to pieces. One of the crew then volunteered to take a line ashore, and the rest of the crew were all able to drag themselves to shore, some suffering hand lacerations from the rocks. Once ashore they began to walk along the coast towards Lorne, believing it was the nearest settlement. Realising their mistake as dawn broke they returned westwards to Cape Patton, and found a farm belonging to Mr C. Ramsden, who took them in and gave them a change of clothes and food. After resting for a day and returning to the wreck to salvage some of their personal possessions, at 10am on Saturday they set out for Apollo Bay, a voyage that took six hours, sometimes wading through flooded creeks up to their necks. The Age described the wreck as "listed to starboard. All the cabin is gutted and the ballast gone. There is a big rock right through the bottom of her, and there is not the slightest hope of getting her off". A Board of Marine inquiry found that Captain Jacobson was guilty of careless navigation by not taking steps to accurately verify the position of the vessel with respect to Cape Otway when the light was visible and by not setting a safe and proper course with respect to the wind and sea. It suspended his certificate for 6 months and ordered him to pay costs. The location of the wreck site was marked for a long time by two anchors on the shoreline, until in 1970 the larger of the two anchors was recovered by the Underwater Explorers' Club and mounted on the foreshore at Apollo Bay. The bell from the wreck was also donated to the Apollo Bay Surf Lifesaving Club but is recorded to have been stolen. Rusting remains of the wreck can still be found on the shoreline on the southern side of, and directly below Cape Patton. Parts of the SPECULANT site have been buried by rubble from construction and maintenance works to the Great Ocean Road, as well as by naturally occurring landslides. Peter J McGennan passed away in 1920. The Gates in the western wall of the Anglican Church in Henna Street/Koroit St are dedicated to him for his time of community work, which is matched with other prominent Warrnambool citizens; Fletcher Jones, John Younger, J.D.E (Tag) Walter, and Edward Vidler. After Peter J McGennan's death Harry, Andrew and Edith continued to operate the family business until July 11th 1923 when the company was wound up. (Andrew lived in Ryot Street Warrnambool, near Lava Street.) Harry McGennan (Peter and Emily’s son) owned the Criterion Hotel in Kepler Street Warrnambool (now demolished). His son Sid and wife Dot lived in 28 Howard Street (corner of Nelson Street) and Sid managed the Criterion until it was decided by the family to sell, and for he remained Manager for the new owners until he retired. Harry commenced the Foreshore Trust in Warrnambool around 1950. The McGennan Carpark in Pertobe Road is named after Harry and there are Memorial-Stone Gates in his memory. (The Gates were once the original entrance to the carpark but are now the exit.). The Patent Log (also called a Taffrail log) from the SPECULANT, mentioned above, and a number of photographs, are now part of the Collection at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village.. The S. S. Flinders was built by A. J. Inglis, Ltd, Pointhouse, Glasgow in 1878 for the "Tasmanian Steam Navigation Company', Hobart which merged with the "Union Steamship Company" of New Zealand and it was later sold to the firm "McIlwraith, McEacham and Company". It was built of iron and was 1000 tons and 227 feet, 1 inch long. It was described as "splendidly fitted up for the carriage of passengers and her cargo space was also very large". In the saloon about 130 passengers could be accommodated while the second class had sufficient room for one hundred passengers. In 1890, the S. S. Flinders would leave Melbourne on Mondays and Thursdays at 5 pm and reach Warrnambool the following morning at 8 am. On the return it would leave Warrnambool on Wednesdays and Saturdays at 5 pm and reach Melbourne the following morning. In 1896, the Weekly Times described the "steamer Flinders (otherwise known as "the Warrnambool mailboat") as "as good a sample of a seagoing steamer as there is trading on the Victorian Coast at the present time". In April 1896 newspaper reports noted the S. S. Flinders took 2915 bags of potatoes from Warrnambool to Melbourne (the largest shipment of that season) as well as 50 tons of tinned rabbits from the Hamilton Preserving Factory. It was also noted that particularly during the Christmas period, there were excessive demands for berths from holiday makers wanting to enjoy a holiday in Warrnambool. In May 1903, the S. S. Flinders narrowly escaped destruction when an explosion and subsequent fire occurred during the passage from Melbourne to Warrnambool. A drum (which apparently contained carbide of calcium) exploded and blew off a hatch cover. As the steamer got to within a mile or two of Warrnambool, smoke was seen coming out of the hold and (unknown to the passengers) flames had taken hold. The crew quickly got to work - closing down all the hatches and pumping water into the hold through a hole in the saloon floor. There were 30 or 40 cases of kerosene on board. The Flinders continued on to Warrnambool and berthed at the Breakwater. The passengers all went ashore - many unaware of the danger they had been in. A telephone message was sent to the local Fire Brigade Station however the fire was extinguished before the firemen and their equipment arrived. After the hold was checked, the Flinders was certified as seaworthy and left for Portland. The Flinders continued to transport Western District produce as well as passengers from Warrnambool to Melbourne until 1906 when (due to a decrease in shipping trade during the Winter and the availability of train services) the Flinders was replaced by the smaller steamer "Dawn" and in 1907 when it was sold to the "Adelaide Steamship Company" for use in the Western Australia coastal trade, it was replaced by the "S. S. Barrabool".This photograph is a significant record of two of the well known coastal traders (the "Speculant" and the "Flinders") that sailed along the south west coast of Victoria for many years - transporting goods and passengers between Melbourne and Warrnambool.Black and white photograph of the Breakwater in Warrnambool with two ships docked and another in the bay. On the front boat (the Speculant), men can be seen at the wheel, on the deck and on the bottom two booms where they appear to be furling the sails. The sails of the top booms are already furled. A small boy can be seen on the deck and a young girl, two women and a dog are on the Breakwater. There is a steam ship (the S. S. Flinders) tied up behind the "Speculant" and an unidentified steam ship (with smoke coming from its smokestack) in the bay. There is a blue and black handwritten label on the back of the photo - naming the ships and the owner of the photo.Speculant and Flinders / Passenger ship in / Lady Bay / name of donor and phone numberflagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, speculant, barque speculant, flinders, s. s. finders, steamship flinders, coastal trader, passenger ship, goods, steamer, breakwater, lady bay, warrnambool mailboat, p. j. mcgennan, peter john mcgennan, butter boxes, captain jacobsen, cape patton, tasmanian steam navigation company -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageLegal record - Charter, Copy of Charter of Bank of Australasia, 01-10-1867
This Copy of the Charter of the Bank of Australasia originated from the Bank of Australasia. The bank of Australasia was incorporated by Royal Charter of England in March 1834. It had its Australian beginning on 14th December 1835, opening in Sydney. The Acting Superintendent of the bank at that time was David Charters McArthur. He was Superintendent from 1867-to 1876. The Melbourne branch opened on 28th August 1838 in a two-roomed brick cottage on the north side of Little Collins Street, where two huge mastiff dogs were used at night to guard the bank. The government also provided an armed military sentinel. Due to the bank's rapid growth, a new building for the Melbourne branch was opened in 1840 at 75 Collins Street West. By 1879 the bank had been upgraded to a magnificent two-storey building on the corners of Collins and Queens Streets, with the entry on Collins Street. In 1951 the Bank of Australasia amalgamated with the Union Bank to form the Australia and New Zealand Bank, now known as the ANZ. Then in 1970, the ANZ merged with both the ES&A and the London Bank of Australia to form the ANZ Banking Group Limited. The ANZ Banking Group Ltd kindly donated a variety of historic items from the Bank of Australasia. BANK of AUSTRALASIA, WARRNAMBOOL – In 1854 Warrnambool had two banks, the Union Bank and the Bank of Australasia. Later, completely different bank businesses opened; in 1867 the National Bank of Australasia, then in 1875 the Colonial Bank of Australasia. The original Warrnambool branch of the Bank of Australasia was established in July 1854, and operated from a leased cottage on Merri Street, close to Liebig Street. The bank next bought a stone building previously erected by drapers Cramond & Dickson on the corner of Timor and Gibson Streets. Samuel Hannaford was a teller and then Manager at the Warrnambool branch from 1855 to 1856 and the Warrnambool Council chose that bank for its dealings during 1856-57. In 1859 Roberts & Co. was awarded the contract to build the new Bank of Australasia branch for the sum of £3,000; the firm built the Warrnambool Post Office in 1856 and purchased land in Timor Street in 1858. The land was on a sand hill on the northeast corner of Timor and Kepler Streets and had been bought in 1855 from investor James Cust. The new building opened on May 21, 1860. The bank continued to operate there until 1951 when it merged with the Union Bank to form the ANZ Bank, which continued operating from its Liebig Street building. Warrnambool City Council purchased the former Bank of Australasia building in 1971 and renovated it, then on 3rd December 1973 it was officially opened as the Art Gallery by Cr. Harold Stephenson and Gallery Director John Welsh. The Gallery transferred to the purpose-built building in Liebig Street in 1986 and the old bank building is now the Gallery club. Staff at the Bank of Australasia in Warrnambool included the following men but others were also involved: Samuel Hannaford, Teller then Manager from 1855-1856; Hawkins, Manager in 1856, W H Palmer, Manager from January 1857 until November 1869 when the Teller Basil Spence was promoted to Manager; H B Chomley, Manager from April 1873 and still there in 1886; A Butt, Manager in 1895-1904; J R McCleary Accountant and Acting Manager for 12 months, until 1900; A Kirk, Manager 1904; J Moore, staff until his transfer to Bendigo in December 1908; J S Bath was Manager until 1915; C C Cox, Manager until April 1923; Richard C Stanley, Manager 1923 to April 1928. The Copy of the Charter of the Bank of Australasia has significance through its association with the Bank of Australasia. The early Australian bank was established in 1834 by Royal Charter and opened in Sydney, Australia, in Sydney in 1835. The bank had many Australian offices in November 1877, particularly on the east and south coasts. Victoria had 45 per cent of all Offices. The Charter is locally significant for its association with the Warrnambool Bank of Australasia, which was established in 1854. It was Warrnambool Council’s first bank. The bank continued to operate until the organisation's merger in 1951 when it became the ANZ Bank Group today. The Bank was an integral part of the growth of local commerce and the community. Record book, hard cover, tan black and beige pebble-pattern on front and back, and tan reinforced strip on spine with decorative embossing. Handwritten title on cream paper is attached in centre of front cover. Cream paper pages are lined and have watermarks on each one. Pages are numbered up to the last written page, number 35. The last page is sealed in red with an official stamp and dated 1st October 1867. Inscriptions are on three labels. and on front end page, and red oval stamp inside front cover. It is an official copy of the Charter of the Bank of Australasia.Label with title, handwritten in pen "Copy / Charter / of / The Bank of Australasia" Label on spine, typewritten "COPY / CHARTER" Label on front cover, handwritten in pen "A G / 28" Front inside cover, red oval stamp "AUSTRALIA AND NEW ZEALAND BANK LIMITED - ARCHIVES - " and in the oval, in pen "A G / 28" Front end page, handwritten in pencil "Normal Copy 5 Dec No. 74" Front end page, in pencil "L 28"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, bank of australasia, boa, union bank, australia & new zealand bank, anz bank, david charters mcarthur, d c mcarthur, sydney, new south wales, currency, banknote, legal tender, commerce, banking, roberts & co., james cust, heraldic shield, insignia, samuel hannaford, w h palmer, basil spence, h b chomley, a butt, j r mccleary, a kirk, j moore, j s bath, c c cox, richard c stanley, charter of the bank of australasia -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDocument - Ticket, voyage, P & O Branch Service, P & O, Australia via The Cape Service, Bef.3rd June 1929
The bearer of this ticket was George Thomas Henry Phillpot, who was only 17 years old when he sailed on the S.S. Ballarat (II), built in 1921. (The first S.S. Ballarat was built in 1911 and sunk after being hit by a torpedo in 1917 while serving during WWI). George relates his trip from England to Australia, summarised as follows: He caught a bus from Bolton to Manchester, in the north west U.K., then the train from Manchester to London and the boat train to Tilbury Docks (near Gravesend). On the morning of June 7th 1929, the ship S.S. Ballarat sailed down the Thames estuary and into the English Channel. The next port of call was Southampton, UK, to take on board some technical equipment. The S.S. Ballarat then sailed through the Bay of Biscay. Instead of taking the customary route around the Cape of Good Hope, this trip, on her maiden voyage, was through the Suez Canal. She sailed through the Straits of Gibraltar, into the Mediterranean Sea and on to Malta, where George and others paid a local boat owner to take them ashore for a short time. They then sailed to Port Said, stopping to load cargo, then at night through the Suez Canal. They woke up early the next morning to watch the locals working on the banks of the canal. The excessive heat on board the ship caused much illness. As they travelled through the Red Sea, the heat and the smell of oil also caused sickness. On they went through the Arabian Sea to Colombo, the capital of Sri Lanka (which at that time was called Ceylon). A Navigation Slip, donated together with this ticket, shows the coordinates for a location 16 miles from Colombo. They again went ashore for a meal at four-pence a head and a bottle of lemonade for a penny. George and another passenger walked to the slums area and were shocked at the state of it compared to Britain’s slums. They then sailed via the Indian Ocean to Fremantle, stopping again for goods to be unloaded. While ashore, they played a game of soccer against the ship’s crew. Then on to Port Adelaide via the Great Australian Bight. Here they shopped for suitable clothing under the advice of some Australian passengers. They then arrived at Port of Melbourne on July 20th 1929, and two days later (on George’s mother’s birthday). George left for Warrnambool. He received his Citizenship Award in 1971. He conducted an electrical retail business in Liebig Street for many years. His son William became principal of the accounting business Sinclair and Wilson, on the retirement of Bill Sinclair, and was actively involved in support of many community organisations. His daughter-in-law, Glenys Phillpot, is actively involved in the Warrnambool community and local government. George was one of 3 orphans on the S.S. Ballarat. (The daughter and son-in-law of one of the other orphans also live in Warrnambool.) Herbert B.G. Larkin, whose rubber-stamped name appears on the ticket, later migrated to Australia and passed away in NSW in 1944. Of Historical Significance, this ticket is for the ship’s maiden voyage via the Suez Canal route (previously the ship travelled via the Cape of Good Hope). It is also the only existing ticket for the "S.S. Ballarat"(3rd) in our collection. Socially, it shows the fare, luggage restrictions, conditions and weekly provisions for a third-class passenger’s voyage from London to Melbourne, which has research potential. This ticket is also of significance to the Local Community, giving the background of the ancestor of a local family. It was also of Personal Significance to the bearer as he kept and preserved it in his possession for at least 46 years before donating it to our museum, together with a Navigation Slip, a map and a summary of his journey to Australia.Third Class steerage Passenger’s Contract Ticket, accompanied by the Navigation Slip, for passage on board the P & O line’s steamer, S.S. Ballarat, to Australia via the Cape Service, from Port of London to Port of Melbourne. The ticket contract is printed on both sides of a thin paper page. The documents have been completed by hand, and the pages have creases as though they have been folded. Details include the date of sailing, amount paid, and the signature of the P & O Branch Service’s representative. The contract ticket lists weekly provisions for the voyage, a disclaimer of the shipping company, a list of dangerous goods not to be carried on board, and fines. The page has straight edges, top and bottom, and perforated edges on the sides; some perforation holes are complete. A small fleur de lies is printed along the inside of each perforation, forming a decorative left and right border. Stamps and inscriptions are on the contract ticket and navigation slip, which also has a black and white photo of a steam ship.The ticket has been stamped in black, No. ‘1040’. Handwritten details are in black pen and ink. Date of departure: ‘Seventh June [192]9’ for the cost of,’33’ [poind], and the sum of ‘33’ pounds is acknowledged as received. ‘Mr George T.H. PHILLPOT’, the age is written as ‘17’, equal to the status of ‘1’ adult, the total number of persons is ‘One’. The fare is handwritten in pen £’33’ and the total £’33’. It has a purple stamp ‘HERBT. B G LARKIN’ and a crossed out stamp ‘FREDERICK WHITE, A handwritten signature ‘_Seymore’. Under the signature, the date is stamped ‘3 JUNE 1929’.warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, s.s.ballarat, phillpot, 7 june 1929, george phillpot, george t.h. phillpot, third class passenger, steerage passenger, herbert b g larkin, ticket, voyage, p & o, australia via the cape, cape of good hope, suez canal, passengers’ contract ticket, navigation slip, s.s. ballarat, steamship, 1929, 3-6-1929, 7-6-1929, third-class, steerage, port of london, port of melboune, 33 pounds, george thomas henry phillpot, herbt. b g larkin, _seymore, bolton, manchester, english channel, southampton, bay of biscay, straits of gibraltar, maritia, port said, arabian sea, colombo, sri lanka, ceylon, indian ocean, fremantle, port adelaide, citizenship, 1971, herbert b.g. larkin, s.s. ballarat ii,
