Showing 1523 items matching " weight"
-
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyrabbit trap, first half 20th century
During the Great Depression from 1929 to 1932, rabbit trapping was a means of survival for many people. Rabbits provided meat and pelts which were sold for making felt hats such as the Akubra. Rabbit populations are controlled in the 21st century by poisoning, destroying or 'ripping' burrows (warrens), biological control with rabbit haemorrhagic disease and myxomatosis, and by shooting. Rabbit-proof fences also prevent the spread of rabbits into some areas. (ref. Powerhouse Museum) This trap was used in the Orbost district. Steel-jawed rabbit traps were widely used in urban and rural Australia from 1880 to 1980. This trap is symbolic of the battle that Australians have waged against burgeoning rabbit populations for over a century. Rabbits cause enormous damage to Australian soils and biodiversity. The introduction of rabbits to this country was an environmental disaster.A rusted iron rabbit trap which consists of a pair of jaws held closed by spring tension and a triggering mechanism. When the trap is triggered the jaws close over the top of the bridge, plate and tongue mechanism that is designed to trigger the trap. A chain is attached by a hook on the bent end of the trap's spring with a long steel spike looped over the last link of the other end of the chain. The trap is designed so that the metal jaws snap shut against each other when the trap is activated by the application of weight to the pressure plate. In use, traps are set with open jaws, buried lightly just below the surface of the earth. When an animal steps on the pressure plate, the jagged teeth of the jaws snap around the animal's leg, usually breaking bone and sinew. Thus the animal is immobilised. rabbit-trap rural -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Cannon, 1813
This 1813 cannon is classified as a carronade, having been made by the Carron Ironworks foundry in Stirling, Scotland in 1813. It is a large calibre, short range, gun mainly used on ships. The carronade model of cannon was first used when introduced into the British Royal Navy in the American War of the Revolution (1775-1883). This cannon was originally a 28pdr, 48cwt, 8ft gun. The date ‘1837’ on the barrel probably indicates the date that the Board of Ordinance accepted the change in size to a 32pdr. It may originally have been a naval gun and the conversion undertaken when it was brought ashore. It is very probably one of the 15 guns that are known to have constituted the defences of Victoria in 1860. This group of 32pdrs was the shorter model of the 4800width and 8ft length cannon and as such are different from the 32pdrs found in NSW. It was originally located on Cannon Hill in Warrnambool when it was the site of the Warrnambool Battery Western Artillery, formed in 1866. It was obsolete by the time of the 1887 fortifications, and was moved from the Warrnambool Fortifications to the Botanic Gardens in 1910, when the Fortifications were declared obsolete. HISTORIC INFORMATION ABOUT THE CANNON IN THE WARRNAMBOOL AREA In the years following the Crimean War (1854-1857J) there was a great concern in the Colony that Imperial Russia would attempt an invasion. Coastal defences in the colony of Victoria were greatly strengthened by the Government as a result. Warrnambool was originally protected by cannons at Cannon Hill, approximately 1 kilometer west of the Flagstaff Hill Fortifications. The cannons included two 1866 guns, both 80 Pound Rifled Muzzle Loaders (RML) purchased by Victoria’s Colonial Government. They were part of a shipment of 26 such guns sent from England in December 1866. They are registered as No. 23 (80cwt-2qr-0lbs) - Gun 1, and No.13 (81cwt-1qr-12lbs) - Gun 2. They were cast at the Royal Gun Factory, Woolwich Arsenal, in 1866 and have a 6.3 inch bore. Both barrels carry the Royal Cypher of Queen Victoria, Insignia of the Royal Engineers, within the Garter and Motto surmounted by the Crown, with the Royal Cypher of Queen Victoria within the Garter (letters in centre “VR”, motto “HONI SOIT QUI MAL Y PENSE”, "Shame be to him who thinks evil of it."). The guns were originally supplied with wooden carriages. (The Royal Arsenal at Woolwich, England, was established eleven years after the Restoration of King Charles II. It was the principal supplier of armaments to the British and Empire Governments. At the height of its operations during World War One the factory covered 1300 acres and employed very nearly 80,000 workers. Woolwich was the Headquarters of the Royal Artillery since the raising of that Regiment in 1716. The Arsenal was closed in the late 1960’s.) The two 80pdr cannons were transferred to the Warrnambool Garrison Artillery Battery Fortifications erected at Flagstaff Hill in 1887 as part of Victoria’s Coastal Defences. The original wooden carriages were subsequently replaced with the present iron garrison carriages in 1888. They are a “C” pivot. The ‘racers’ or curved track set into the floor of the gun emplacement (which enabled the guns to be traversed more quickly) are as specified for guns up to 10 inch, being of wrought iron 2.78 inches wide. A temporary third gun, now no longer on Flagstaff Hill’s site, was a 5 inch Rifled Breech Loading (BL) Armstrong gun mounted on an Elswick hydro pneumatic disappearing carriage It was faster to load and fire than the 80 pound RMLs and its arrival spelt the end of the older 80 pound guns’ useful life, apart from being used for practice sessions. The 5 inch BL gun was the main defensive weapon of the Warrnambool Battery until the Battery was downgraded in importance and the gun was recalled to Melbourne in 1910. The gun emplacement still remains in place set between the 2 80pdr cannon. The State of Victoria took over the ownership of the guns at the time of Australian Federation in 1901. In about 1901/1902 the Garrison Battery was converted to the Warrnambool Battery of the Australian Field Artillery (No 4 Field Battery). It was equipped with 4.7 inch naval guns mounted on field carriages. They were now a mobile unit but continued to use the Warrnambool Garrison area at Flagstaff Hill for practice. When the Fortifications were declared obsolete the two 80 Pounder RML were relocated to Cannon Hill in 1910. On the outbreak of World War 1 the 4.7 inch guns were recalled to Melbourne, and the Battery was disbanded. Most of the personnel probably re-enlisted in the local 4th Australian Light Horse Regiment. The two 80 Pounder RML were moved back to the Fortifications in 1973. They were both fully restored by Army First Year Apprentices at the Ordinance Factory in Bendigo in time for the centenary year of the fortifications in 1987. The guns are capable of firing 80 pound (32.3kg) armour piercing exploding shells 3.65kms out to sea. They were original manned by volunteers before a paid Garrison was established. Now the Guns are again fired by volunteers on Special Event days. Since restoration the Gun Number 1 had been fired on a regular basis but Gun Number 2 hadn’t been fired since the mid 1990’s. In April 2015 Gun Number 2 was serviced in preparation for the firing of both cannons on the ANZAC Centenary commemorations on April 25th 2015. Other guns from the original Cannon Hill location were obsolete by the time the 1887 Warrnambool Garrison Artillery Battery was built. These guns are (1) a 32 Pounder Muzzle Loading Smooth Bore (SB) cast in 1813 at the famous Carron Foundry, number 80837 and now located in the Warrnambool Botanic Gardens. It is now mounted on a replica carriage due to the original carriage being in a fragile condition (the original carriage stored under cover at Flagstaff Hill). (2) a 68 Pounder Muzzle Loading Smooth Bore cast in 1861 at the equally august Low Moor Foundry, number 10310 and now located on the lawn area at the entrance to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. It is still mounted on its original wooden garrison carriage. Its wooden slide compressor mechanism is fragile and now kept in Flagstaff Hill’s storage. There are only seven 32 Pounder SB made by Carron and fifteen 68 Pounder SB made at Low Moor known to exist in the State of Victoria Plaque attached to the carriage “This replica carriage was constructed by the Warrnambool Tritan Woodworkers club in conjunction with the generosity of local businesses and the Warrnambool community. The original carriage (circa 1860) was removed for restoration and is now located at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The timber used for the replica carriage is Monterey Cypress, which was an early planting in the gardens. 2010 marked the centenary of the cannon’s relocation in the Warrnambool Botanic Gardens.” (Reference; Victorian Guns and Cannons, South Western Victoria Assessment, May 2008, item W/B/01; Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village datasheets and archives). There are only seven 32 Pounder SB made by Carron known to exist in the State of Victoria and this is one of them. On a world level, this cannon represents a high level of rarity. Further, as it has been modified (bored up) it is representative of the historical process of amending artillery in order to ensure a longer usefulness of each piece despite rapidly advancing artillery technology. The number of surviving carriages with traversing slides in this group in South Western Victoria is unique in Australia and probably in the World. Out of 10 such platforms surviving in Australia, the South Western Victorian group has half. Several survive around the world but probably not in such a large group. The wooden sliding compressor mechanism belonging to this cannon is extremely rare, and the only one in this South Western Victorian group of Guns and Cannons. As a whole, this cannon has undergone very little restoration or modification, giving it a high level of integrity. The City of Warrnambool is one of several custodians of a collection of artillery pieces of heritage significance at a state, national and international level. These pieces are directly related to the defence of south-west Victoria in the 19th century. The care and preservation come under the Heritage Act 1995. (Reference; Victorian Guns and Cannons, South Western Victoria Assessment, May 2008).Cannon, or carronade, 32pdr with wheels. Muzzle loading smooth bore (SB) cannon. Cannon has original wooden Burmese Teak carriage and slide with wrought iron fittings and iron wheels. Manufactured by Carron in Scotland, in 1813. It has been converted from a 28pdr. There is a loop for a rope on the cascabel, which was part of the original casting. Re-bored in 1837. Marks include Serial Number, Royal Cypher of King George III, broad arrow of proofing, and numbers to represent the weight. NOTE: The cannon is displayed in the Warrnambool Botanic Gardens and is mounted on a replica wooden carriage; the original wooden carriage is now stored under cover at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. This carriage has 4 wheels on swivel attachments and a central gear that allows the wheels to turn on rails. Pressed into left trunnion “80837 / CARRON / 1813”, cast on barrel“symbol (Royal Cypher of King George III”, “symbol (broad arrow of proofing)” and numbers “45-3-24 / 1837” . Cascable “CV” and marks with gradations from nought to three in quarters on each side, On the carriage the end of one of the main slide members carries the mark “W symbol (broad arrow) D” incised into the timber. Plaque attached to the carriage by the Warrnambool Tritan Woodworkers club, 2010, marking the centenary of the cannon’s relocation in the Warrnambool Botanic Gardens and the addition of the replica carriage. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, victoria’s coastal defences, warrnambool fortification, warrnambool garrison battery, ordinance, armaments, cannon hill fortifications, victorian colonial government, carron ironwroks foundary, 32pdr smooth bore cannon, 28pdr smooth bore cannon, 1813 cannon, carronade -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumCeremonial object - SHIPS BELL, HMAS BENDIGO 1941, 1941
HMAS BENDIGO (J187) was an Australian made "Corvette" which served throughout WW2 until 'paid off' on 27 September 1946. The Bendigo Military Museum also holds the last ensign of HMAS BENDIGO, it has a large number of auto graphs. We also hold the wooden crest and Battle Honours Board, this is on loan for 5 years. Refer to Cat 4546 Ensign.1. This is a medium size ships bell. It is cast from Brass. It has a protrusion on the top with a hole in it, used for mounting. The words HMAS BENDIGO 1941 are engraved into the side and painted black. The exterior surface has a few pits, but has been polished numerous times. The interior surface is rough cast, with a large quantity of dints, where it has been struck by the clapper. 2. This is the clapper. There is a steel hook under which is a weight of steel. Under that is a ring. Suspended from the bottom ring is the rope handle. This is an excellent example of navy rope work. At the top of it is a metal ring. Under that is a white and red stylised crown. Under the 'headband' of the crown is a white rope handle with blue inserts. At the bottom is a large rope "Ball" with numerous rope threads of about 180mm length.ww2, ran, hmas bendigo -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumUniform - UNIFORM, ARMY, C.1941 - 44
Items issued or made for Henry T RIDGE V57996 & VX148845 CMF & 2nd AIF. Refer Cat No 475.10 for service details..1) Coat, Service Dress, Kahki, winter, 2 x Rising Sun Epaulettes badges, 2 x Australia badges, 2 x colour patches, rectangular white over red with grey surround, Lieut rank badges, 2 on one side, one on the other (missing one), metal buttons. .2) Belt-cloth, Kahki, metal buckle, leather adjustment straps on inside, for .1) .3) Coat, Service Dress, summer, light Kahki, 1 x Rising Sun lapel badge (one missing), 2 x combined cloth Australia and Lieut shoulder badges, 4 pockets, plastic buttons. .4) Shirt, light weight, Kahki, Service Dress summer style, short sleeve, plastic buttons..1) “Wilkes Todhunter, Civil and Military Tailors”, “H.T.Ridge 9/7/41” .3) “Wilkes Todhunter, Civil and Military Tailors”, “H.T.Ridge 3072, 15/7/1941” .4) “Wilkes Todhunter, Civil and Military Tailors”, “H.T.Ridge 7976, 14/1/44uniform ww2, army, officer -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyMeter AVO, circa 1930 to 1951
When this AVOMETER was being utilised in the early 1950's it was at the "leading" edge of electrical measuring instrumentation.The first meter was produced by Automatic Coil Winder and Electrical Equipment Co. in 1923. This model was produced in the time from 1933 to 1951 when it was superseded by the most popular model, Model 8 (1951 to 2008).This AVO meter brought the measuring of three electrical power indicators i.e., amps, volts and ohms into one measuring unit. By using a "one fits all" unit, the carrying of separate measuring devices was reduced considerably. The need for a mountainous and a large area of operational requirements, such as the SEC Vic Kiewa Hydro Electricity Scheme, to minimise the weight of equipment carried by electricians and technicians was of the utmost relevance. The significance of this meter to the Kiewa Valley region relates to the impact of modern technology (at that time) upon a mainly rural environment. This equipment shows how the boost of "modern" equipment into the area because of the "Hydro Scheme" was facilitated a lot faster than would have taken under "normal" evolutionary time. The speed of information on all "new technology" had a relatively slow assimilation rate to those living in rural communities. This AVOMETER is a Model 7 MKII, production pre 1951. This meter measures electrical Amps, Volts and Ohms and has two internal batteries for its power. The main casing is made from aluminium with a bake-lite front. The front has a "window" detailing, with a needle pointer, the amount of electrical power being tested. There are two big dial switches, detailing Direct Current(DC) and Alternating Current(AC) when reading measurements of Ampere, Voltage and Ohms for power. This meter took the place of three or four meters used earlier. Modern meters (2000 onwards) have become digilised and are considerably lighter in weight and smaller. There are two electrical connection leads (one black and one red) each has a removable clasp and is 125cm long.Molded on the front centre panel " UNIVERSAL AVOMETER". Below this and above the left hand dial "D.C. SWITCH" .Above the right hand switch the right "A.C. SWITCH". On the left of each switch is an arrow pointing to it.The left switch is marked with a "+" and the right one with a "-". There is a "divisional 2" mark. Between and below the dials is "CUT OUT" plunger.electrical meters, electrical equipment, sec vic., state electricity commission of victoria, mt beauty, bogong village -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Textile - FLOUR BAG COLLECTION: ROBERT HARPER AND COMPANY, 1900-1950
Textiles. Calico flour bag printed on one side in red and blue''EMPIRE SELF RAISING FLOUR 25 lbs nett weight. Contains phosphate Baking Powder. Robert Harper & Company Incorporated Victoria, Australia''. In the background is a lighthouse with three beams of light extending from each side. Printed on the light beams- ''LIGHT BREAD, LIGHT PASTRY, LIGHT PUDDINGS, LIGHT LABOUR, LIGHT HEARTS, LIGHT HOMES''. Robert Harper (1842-1919), businessman and politician, was born in Scotland. He migrated to Melbourne with his family in August 1856. He worked for J.F.McKenzie & Co., roasting and grinding millers. In 1865 he established Robert Harper & Co., trading in tea, coffee and spices from the East Indies and later in oatmeal and flour.textiles, domestic, robert harper & co flour bag -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumEphemera - Ticket/s, J.J. Miller, ESCo Morning and Evening Weekly Ticket, 1/6, early to mid 1920's to 1930's
Ticket contained within Reg. Item 2488, page 31, ESCo, Ballarat Tramways, Morning and Evening Weekly Ticket, price 1/6, printed for Week 2, that is not available for Sundays or Holidays. Ticket printed on light weight card, in two colours, off white and teal, numbered 7743 available only between the City and Macarthur St. Notes the conditions of use, the time available for which the ticket may be used and where. Ticket has been punched or nipped a number of times. Printed by J.J. Miller, Melbourne. Note Item Not formally Numbered. Image btm2494i2 shows position on page relative to items 2494 to 2504. See Reg Item 2948 for circular detailing their use at the commencement of the issue of this style of Weekly Tickets - some detail differences in the style and colours later on.Some inscriptions about the ticket in pencil.trams, tramways, tickets, weekly tickets, esco -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Black & White Photograph/s, 1887
Black and white photograph contained within Reg. Item 2526, page 3 of the pattern Ballaarat Tramway Co. Ltd outside the Duncan & Fraser's Carriage Works in Adelaide. Has a Australian 2d stamp (1936 South Australian Centenary) over the top right hand corner. Has been cut from a larger photograph. Handwritten notes in pencil noting the time of the photograph, the tram weight, couplings, lamp brackets, the possible purpose of the photograph, the incompleteness of the tram when compared to actual running condition. Dated 7/1/1940. Also notes on the 3 legged stool used by the horse tram drivers and the double decked buses operating then in Melbourne ( Bourke St.). Has sketch of the stool in ink. Note Item Not formally Numbered.tramways, trams, horse trams, duncan & fraser, adelaide, double deck buses -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumLeisure object - Jigsaw, Resort Puzzles Pty Ltd, c1988
BTPS Postcard, featuring No. 27 and 38 in Wendouree Parade (Reg. Item 1781) that has been manufactured or stamped into a 24 piece jigsaw by Resort Puzzles Pty Ltd. of Lithgow, c1988. Card after stamping has been mounted onto a sheet of brown cardboard then enveloped with a sheet of clear light weight plastic and onto the rear, a printed white sheet of paper has been glued or fixed onto it. The pre-printed sheet of paper acts as the rear of the postcard for mailing purposes, providing a stamp location, address and writing area. The printed details give information about the manufacturer, phone number and on the top left hand corner has the words "Greetings from Australia" and has been translated under that into oriental characters.trams, tramways, btps, jigsaw, postcard, wendouree parade -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumLeisure object - Jigsaw, Resort Puzzles Pty Ltd, c1988
BTPS Postcard, featuring trams No. 26, 27 and 33 over three separate images Wendouree Parade (Reg. Item 1657) that has been manufactured or stamped into a 24 piece jigsaw by Resort Puzzles Pty Ltd. of Lithgow, c1990 Card after stamping has been mounted onto a sheet of brown cardboard then enveloped with a sheet of clear light weight plastic and onto the rear, a printed white sheet of paper has been glued or fixed onto it. The pre-printed sheet of paper acts as the rear of the postcard for mailing purposes, providing a stamp location, address and writing area. The printed details give information about the manufacturer, phone number and on the top left hand corner has the words "Greetings from Australia" and has been translated under that into oriental characters.trams, tramways, btps, jigsaw, postcard, wendouree parade -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumEphemera - Ticket/s, J.J. Miller, ESCo Morning and Evening Weekly Ticket, 1/3, c1927
Demonstrates how ESCo managed Weekly tickets during the late 1920's and yields information about the way the system was arranged. The source of the ticket, NSW tramways is significant in that it was obtained by them as a sample. Morning and Evening Weekly Ticket, price 1/3, printed for Week 1, that is not available for Sundays or Holidays. Ticket printed on light weight card, in two diagonally, light green and teal, numbered 0076 available only between Queen St and Doveton St. Notes the conditions of use, the time available for which the ticket may be used and where. Printed by J.J. Miller, Melbourne. In the bottom right hand corner has a perforated triangular section which could be removed. Has the words "P.M. Friday" printed on it. Ticket has been removed from a block - has staple hole at the top. See Reg Item 2948 for circular detailing their use at the commencement of the issue of this style of Weekly Tickets - some detail differences in the style and colours later on.trams, tramways, tickets, weekly tickets, esco -
 Beechworth RSL Sub-Branch
Beechworth RSL Sub-BranchJumper, Square rig, 2001
This style of jumper has a long history in the Royal Australian Navy, descending from the uniform style of the 19th century Royal Navy.Navy blue long sleeved, heavy-weight jumper with square rig collar. On left sleeve is an embroidered patch with the word "AUSTRALIA," underneath which is an anchor insignia and three downward pointing chevrons in gold embroidery thread. On right sleeve is an embroidered patch with the word "AUSTRALIA" on the upper shoulder, underneath which is an embroidered gold wheel on a semi-circle shaped patch. The jumper has a deep neckline, tied with a cotton navy tie. Accompanying collar (0036.2) attaches to the jumper via three navy blue plastic buttons at the back of the neck, and three navy blue plastic buttons running down both left and right interior neckline. The jumper has a zip on the left hand side which runs from the hem to the waist.On patches "AUSTRALIA" Interior label at back of neck reads "ADA/2001/[broad arrow]/NSN: 8405 66 132 2508/SIZE: 111 L/NO/NAME/WOOL/POLYESTER/DRY CLEAN ONLY"royal australian navy, uniform, marine, shirt, australian defence apparel, ratings -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyDecorative object - Horse Dairy Buggy Model, Chas W Davis
The collection of thirteen model horse drawn vehicles were carefully handmade by Mr Chas W Davis 1925 - 2002. He was a talented artist and saw doctor. This model of a horse drawn Dairy Cart replicates the vehicle that enjoyed respect from the public during the 1880 and early 1900's. A model of a horse drawn black open Davis Dairy Buggy or Cart which is a lightweight two wheeled one passenger open horse drawn carriage where the driver sits behind. It has two large gold painted spoked wheels with black rims and mudguards, blue painted seating and gold painted armrests, two gold coach lamps and gold patterned footrest in front of the driver. At the rear are three silver milk cans with two taps to dispense the milk. There are two long brown wooden shafts on each side to surround the horse. It has a model of a brown coloured horse with a black tail and mane, which has the necessary horse tack for carriage use to help the driver communicate with the horse. These carrier carts or vans were two wheeled medium weight Commercial Vehicles.DAVIS DAIRY painted in white lettering on each side of the cart.replicas, models, scale models, vehicles, carriages, horse drawn vehicles, toy horses, early commercial vehicles, milk cart -
 Falls Creek Historical Society
Falls Creek Historical SocietyJournal - Schuss Vol. 18. No. 3 May 1952
Schuss was advertised as Victoria’s Official Ski Journal It was issued monthly from 1935 to 1961 except during the war when summer issues covered two months. This continued after the war, but it averaged 10 issues annually over its 25 year life. Schuss was published by the Ski Club of Victoria which had a membership of 38 Ski Clubs and demanded to be recognised as the prime authority on skiing in the state. The other 30 ski clubs with 85% of the members disagreed and the politics of skiing became heated. These clubs formed the Federation of Victorian Ski Clubs with their own journal, Ski Horizon. With the establishment of the Victorian Ski Association, Ski-Horizon published its last issue in Nov - Dec. 1955 and the role of the official journal was fully taken over by “Schuss”. This item is significant because it contains stories, images and information documenting the development of the ski industry in Victoria.The journal features stories and events chronicling developments in Victoria and internationally. Items related to the Falls Creek Area in this issue include:- Cover - Australian Olympic Skiers Return Left to Right: Bill Day, Bob Arnott, Gordon Day. Page 111 - FRONT-SPRING CABLE BINDINGS - A note from Bob Hymans advises that he has for sale a number of Front- Spring Cable Bindings made by Ramy, the well-known French maker. In This pattern the spring is attached to the ski in front of the toe-irons and eliminates the weight of the spring around the heel fitted to most cables. It is very popular with ski-racers in Europe for its comfort and control. Bob also advises that his Ski School at Fails Creek will be open during the weekends of June, and from June 30 onwards till the end of the season. schuss journal, bob hymans, front-spring cable bindings -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumPicker
Wool picking machine designed to separate locks of wool before it is carded and spun. The picker opens the wool’s locks which makes it easier to send the fleece through a carding machine. It does this by teasing the fibres (which can also be done by hand just by pulling the lock structure apart), but a picker does this in bulk and much quicker than what can be done by hand. It is possible to spin fibres directly after the picking stage; however, it is usually more desirable to card and blend them with other fibres. Typically, at a textile mill, a picking machine can separate enough lengths of fibre for a full day’s work after just a single hour. It will also help to remove any vegetation matter or other any unwanted elements that may be present in the wool. The quality of the casting on this machine suggest that it was made locally, either in Australia or New Zealand. Mike Leggett, the donor of the machine, acquired it from New Zealand where the seller said it had been used by his father to pick wool to make hand stuffed horse saddles. Mike attempted to used it a couple of times to pick alpaca hair, but the speed of the attached motor caused damage to the fibres. The motor is thought to be an added attachment, sometime around the 1960s judging by its age, while the machine itself is thought to be dated around the 1920s. The machine works by inserting wool through the rollers. Initially there was a conveyor belt feeder system which was powered by the handle on the side. This conveyor belt has been removed however, most likely due to age and deterioration. Wool is now fed through the initial teeth and is met by a spiked rotating drum which works to separate the fibres. The separated fibres would then complete a loop of the drum before being dispatched somewhere below, around where the motor presently sits, at a rapid rate of speed. Typically this wool will be collected in a closet or large catchment area, as can be seen from the 8:47 minute marker in the linked video (link - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kMjx-t3tH3A). It is not apparent how the wool is collected with this machine. Red and green machine with four green legs currently attached to a wooden pallet with wheels for easy movement. The green legs lead up to a red central circular barrel from which many attachments are present. Also present on the wooden pallet is a small black motor which is attached by a rubber belt to the central drum inside the red barrel. The belt spins the wooden drum via a dark red circular plate attached to the side of the drum. On the other side of the red barrel, a green handle extends for turning the picker’s conveyor belt feeder system. Two green walls extend forward from the central red barrel, guarding either side of where the conveyor belt would have been. At the start of these walls is a wooden cylinder, which the conveyor belt would have wrapped around, followed by two interlocking gears which rotate and accept the fed wool. The red roof extends over the central cylinder from here, securing the wool inside and protecting hands from the heavily spiked internal wooden cylinder which rotates and separates (picks) the wool. Extending over the top of this red roof is a green handle which reaches to the back of the machine (not pictured). Here it accepts a weight to ensure pressure is always present for the initial feeder interlocked gear teeth. There are two large gear cogs on the rubber belt side of the machine and 3 small gear cogs on the handle side of the machine, all coloured green. A green handle is also present at the rear of the machine, below the location from which the weight is hanging. A power cable extends from the motor and there are two adjustable metal rods on the top of the machine, the purpose of these rods is presently unknown. Black texter. On top of drum. Wording: HG3707 Wording. Imprint: BRACEWIND BLYN On motor. Wording AEIwool picking, textile manufacturing, wool processing -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPamphlet, Rail Projects Victoria, "MetroTunnel Newsletter", May. 2018
Pamphlet Series of 8 printed and digital documents - titled "MetroTunnel Newsletter issued by Rail Projects Victoria (formally Melbourne Metro Rail Authority). Reports on the changes to the Domain Intersection tram stops, track relocation during Easter 2018 and that the Tunnel boring machines are on the way. The machines are compared to the length and weight of E class trams. Includes station names Anzac Station. Has the logos of the State of Victoria and Rail Projects Victoria. Previous issues: down loaded from the Metro Tunnel website 22-10-2018 Issue 01 - June 2015 - i1.pdf 02 - December 2015 - i2.pdf 03 - May 2016 - i3.pdf 04 - May 2017 - i4.pdf 05 - October 2017 - i5.pdf 06 - May 2018 - i6.pdf - folded A3 sheet - Reports on the changes to the Domain Intersection tram stops, track relocation during Easter 2018 and that the Tunnel boring machines are on the way. The machines are compared to the length and weight of E class trams. Includes station names Anzac Station. 07 - October 2018 - i7.pdf - folded A3 sheets - reporting on work at Federation square and the station locations, some before and after photos and archaeological digs. 08 - September 2019 - i8.pdf - folded A3 sheet - report on traffic changes in Flinders St, the Tunnel boring machines, North Melbourne Station, progress at various sites. 09 - February 2021 - i0.pdf - folded A3 sheet, report on the tunnelling machine progress and a list of dates during 2020 along with notes on the Airport rail line.trams, tramways, metro tunnel, e class, domain interchange, domain junction, anzac station -
 Anglesea and District Historical Society
Anglesea and District Historical SocietyTobacco Tin, J.G. Dill's Best Cut Tobacco, Estimated date: 1890
Tobacco tin, badly rusted of J.G. Dill's Best Cut Plug. J.G. was once a great Virginian tobacco company, known worldwide for its Dill's Best Pipe tobacco.Lady with arms above head. DILL'S / BEST. J.G. DILL'S / BEST / CUT PLUG / RICHMOND VA USA / On sticker - red writing: 1.8.oz Net Factory Weight when packed Sides of tin: (1 & 2) DILL'S BEST CUT PLUG x 2. (3) THE BEST CUT PLUG. Celebrated for its smoking quality. (4) Notice - The manufacturer of this tobacco has complied with all requirements of law. Every person is cautioned under penalties of law not to use this package for tobacco again. smoking, j.g. dills, pipe tobacco -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - Photographic Technicians operating the KLIMSCH Camera at the Army Survey Regiment, Fortuna, c1980s
These four photographs were most likely taken in the mid-1980s in Lithographic Squadron at the Army Survey Regiment, Fortuna, Bendigo. The equipment operated by the technicians is the KLIMSCH camera. The main tasks undertaken by the technicians were most likely enlargements and reductions of map reproduction material. The KLIMSCH Commodore camera was introduced in 1953 and was the largest in the Southern Hemisphere. It was replaced with a new model of the same size in 1979. The new model with its computer-based interface provided productivity gains with improved speed and its consistent results led to less wastage in time and materials. Its variomat lens system provided improved retention of map feature linear weights during the camera reduction process. The camera which was specially made for the Army in Germany was fully automatic and power operated. It was claimed to be one of the biggest automatic cameras of its type in the world. It was made to the specifications of the Royal Australian Army Survey Corps to assist in the production of the very high standard maps for the Army. This is a set of four photographs of technicians operating the KLIMSCH Camera at the Army Headquarters Survey Regiment, Bendigo c1985. The photographs were on 35mm negative film and scanned at 96 dpi. They are part of the Army Survey Regiment’s Collection. .1) Photo, black & white, c1985, Frank Lenane operating the KLIMSCH Camera. .2) - Photo, black & white, c1985, KLIMSCH Camera. .3) to .4) - Photo, black & white, c1985, John Whaling operating the KLIMSCH Camera..1P to .4P – no annotationroyal australian survey corps, rasvy, army survey regiment, army svy regt, fortuna, asr, litho -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument - Document - Design, E J Barker: University of Melbourne: Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering; Civil Engineering 1 and 1A; Design of Welded Plate Girder, 1946
Assessment No 2 Project was to design a welded plate girder required in a building to span between two steel columns which have to be spaced 60 feet centre to centre. It needs to carry its own weight plus specified loads. This was part of Civil Engineering 1A . Jack chose to do Engineering while still at Footscray Technical School as it gave access to Diploma Courses and tertiary studies. This enabled him to enter the University of Melbourne and do a Bachelor in Mechanical Engineering - 1945, 1946, and 1947. In 1948 he did a Diploma in Education at Melbourne University. From this path he was able to follow a career in teaching and his first appointment was at the School of Mines in Ballarat, (SMB) 1949. He became the first Vice Principal of SMB in 1960 and then Principal in 1964 to 1976. From 1976 to his retirement in 1987, he was the Foundation Director of Ballarat College of Advanced Education (BCAE). The Library building at Mount Helen Campus is named after him.Manila folder with design assessment. Written descriptions and detailed drawings.e j barker, jack barker, melbourne university, engineering, diploma of mechanical engineering, diploma of electrical engineering, school of mines ballarat, smb, diploma in education, vice principal, principal, foundation director, ballarat college of advanced education, bcae, bachelor of mechanical engineering, library, mount helen campus, engineering drawing, design, specifications, manufacture, civil engineering, welded plate girder, 60 feet, steel columns -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBelt Linesman Pole, circa mid to late 1900's
This linesman belt was used under the 1947 Electricity Regulations and before tighter Occupation and Health regulations (late 1990's early 2000's) were introduced that mechanical lifting platforms(wherever possible) replaced the belt up the pole method.The safety concern was that it required that tools needed by the linesman had to be placed in a large canvas bag and attached to the belt (extra weight) then the linesman had to climb the ladder. Ladders had to be at the correct angle and not able to "slip" from their initial footings. A full harness and a secondary fall belt is now mandatory for pole linesmen. The safety of fellow workers could be compromised if they were required to assist or recover the first linesman if needed. In 2006 an additional 269 registered lineworkers were employed. Please note that the terminology of linesman has become unisex. The linesman's belt enabled the linesman to place his feet against the pole adjust the belt (if needed) and lean back securely allowing both hands to be free to work with. This linesman belt is very significant to the Kiewa Valley due to the numerous poles and high voltage overhead power structures that needed maintenance for the extensive "mushroom" installation of electrical power polls(wood and metal). On high poles (steel) climbing pegs were welded on, however in the Alpine areas snow in winter caused an OH&S problem which were hard to overcome. The safety of a linesman when maintenance of electricity line on poles can be highlighted by the New Zealand linesman who survived an 11,000 volt shock when carrying out maintenance. For the record 11,000 volts is four times more powerful than execution by "the electric chair". The maintenance of the linesman's belt was his responsibility (keeping it clean and in "good" condition). Labour laws change this initial responsibility, from the linesman, to the employer. Climbing pegs were installed on higher poles that extended beyond the reach of ladders.This thick leather linesman belt is made from two lengths of heavy lengths of leather straps sewn together to make up 80% of the belt. The remaining 20% is "the belt tonge" which has eleven holes for three (solid steel tang) buckle connections.kiewa hydro electricity scheme, victorian state electricity commission, relays, generators, electrical pole maintenance -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageContainer - Collar Box, Rexbilt Leather Company, 1924-1930
The evolution of the stiff shirt collar occurred in the 1830s when the detachable collar was "invented." At this time, the detachable collars were simply normal shirt collars like you’d see today, but sold separately from the shirt itself and needed to be kept in a container to keep them clean and accessible. The detachable collars were a way to avoid the weekly laundry. Because collars and cuffs were both the most visible parts of shirts and the parts most likely to get dirty, separating them allowed people to do the shirt equivalent of only washing your armpits after you go to the gym. That meant that the main body of the shirt could remain soft while the collar and cuffs that were visible could be starched and shaped. The popularity of detachable collars and starched collars, in general, began to fade in the 1920s and 30s. As shirt styles began to change. The advent of central heating, lighter weight fabrics, and a more relaxed social attitude to fashion all contributed to making men’s clothes more comfortable and less formal.An item that was used to store detachable men’s shirt collars from the early 20th century at a time when men's fashion was more formal and how a person dressed especially for formal occasions dictated a person's social standing. The subject item comes from a time that gives a snapshot into the past at the social norms of the time.Collar box, leather, cylindrical, includes strap, buckle, stitching and cardboard lining and man's white collarCollar inside box marked "CF652 Rexbilt Size 16 1/2 x 1 3/4" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, collar box, men's collar box, men's collar, leather collar box -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumEphemera - Ticket, State Electricity Commission of Victoria (SECV), Block of SEC 1/6 weekly tickets
Each ticket medium weight card, on manila coloured (210gsm) card and printed on black ink to give day numbers, monthly, week number, transfers and day of week, excluding Sunday. Numbered on right end of ticket. Static number (1 - 7) on left indicate it may be the day of issue. Each ticket has been stamped "CANCELLED" On the rear of the ticket is the details of the ticket use, allowing the passenger one return journey between City and section 2-3 or 3, or between 2-3 and 4. Not available on Sundays. Form Number TYE 2-12. Note: See Reg. Item 230 on the page dated Feb. 22 for another two weekly tickets, c1950, price 2/6. Printed in off-white card in red ink. Available for travel between city and section 3 or 4. See also Reg. Item 2103, 2104, 2105, and 2106. Not known when these tickets were used, possibly before the 1950's.Demonstrates a SEC Weekly ticket.Block of SEC 1/6 weekly tickets, ticket numbers A124165 to A124179. Printed and stapled into a blocks of 20 tickets. trams, tramways, tickets, weekly tickets -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumEphemera - Ticket, State Electricity Commission of Victoria (SECV), Block of SEC 2/- weekly tickets
Each ticket medium weight card, on 210gsm manila coloured card and printed on black ink to give day numbers, monthly, week number, transfers and day of week, excluding Sunday. Numbered on right end of ticket. Stapled with heavy brown cardboard backing strip. Static number (1 - 7) on left indicate it may be the day of issue. On rear of ticket is the details of the ticket use, allowed passenger one return journey between City and section r 3, or between 3 and 6. Not available on Sundays. Form Number TYE 3-11. Note: 1. See Reg. Item 230 on the page dated Feb. 22 for another two weekly tickets, c1950, price 2/6. Printed in off white card in red ink. Available for travel between city and section 3 or 4. See also Reg. item 2102, 2104, 2105 and 2106 Not known when these tickets used, possibly prior to 1950's.Demonstrates SEC Weekly tickets.Block of SEC 2/- weekly tickets, ticket numbers B 89023 - 89039. Printed and stapled into a blocks of 20 tickets. trams, tramways, tickets, weekly tickets -
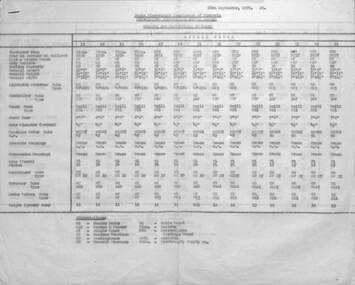 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumDocument - List, State Electricity Commission of Victoria (SECV), "Numbers and Particulars of Trams" - Ballarat, 28/9/1970
List titled "Numbers and Particulars of Trams", dated 28/9/1970, split into separate sheets for single truck and bogie trams which includes the Scrubber tram. Tram 20 has been deleted following its demolition on 17/9/1970 (see item 1088). Gives details of where purchased from, date of purchase, type, body builder, seating capacity, overall length, overall height, overall width, Lightning arrester, controller make and type, Truck Maker and type, type of truck, axle type, wheelbase, axle diameter, motors type and maker, Motor horsepower, Armature bearings, suspension bearings, gear teeth, Air compressor make and type, Brake Valves make and type, Governor make and type, Weight in tons. Has a list of abbreviations on the base of each sheet. See also 8721 and 8722 for other versions - different dates and 8690 for a Bendigo list. Note: Framed copies of both Ballarat and Bendigo are held in the depot. Yields information about the dimensions and equiipment on Ballarat Tramcars operated by the SEC.Typed List of tramcars and their details for Ballarat - carbon copy two double foolscap sheets.tramcars, ballarat, equipment, lists, data -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumBook - Notebook, Collins Textile Diary - 1958, 1958
Nino Corda was a Geelong based textile designer who worked at various textile mills between 1957 & 2003. He travelled the world in search of the latest fashions and techniques and developed timeless designs that were much loved by Australians. These items are on rotational display at the National Wool Museum’s ‘In the Factory’ exhibition. For many years, Nino also worked as part of the Honorary Staff of the National Wool Museum. His passion for the world of textiles provided energy and knowledge to the visitors and staff of the museum. Although Nino has now retired from his honorary position and has hung up his Australian Tartan vest, these items will continue to serve the community in sharing the stories of Australian Textile design. This notebook contains information on how to calculate and enlarge a small sample pattern into a larger textile. The equations would provide answers to the required length of thread (often measured in weight as opposed to distance) of a selected textile. The sample and appropriate thread would be needed for mass production at a commercial mill.Blue textured vinyl forms the covers of this notebook. On the front of the inscription is visible in gold text. Internally, small font black writing on yellowing pages forms most of this notebook. Pp.128 published pages with calendar and spare pages for notes forming the second half of this notebook. Front Cover. Words, printed. WITH THE COMPLIMENTS OF / NOEL P. HUNT & CO. PTY. LTD.textile design, textile calculations -
 Trafalgar Holden Museum
Trafalgar Holden MuseumVehicle - Holden model FB sedan, 1960 - 1961
The FB was promoted as being longer, lower, more spacious and more powerful than the FC model, but in reality it was only slightly so on each count overerall length was 5.5 inches (140 mm) greater, although the wheelbase remained the same. The engine bore was still 3 inches (76 mm), the last model with that specification. Engine capacity was 138 cubic inches (2.16 L) but the compression ratio was raised. However, the resulting extra 4 brake horsepower (3 kW) of power did not compensate for the greater weight of the FB, so performance was inferior to that of its predecessor. Changes were also made to the brakes, front coil springs, air cleaner and clutch. Obvious styling differences were the lower bonnet, finned rear mudguards with new taillights (on the sedans and wagons only) and a wrap-around windscreen. Seating was improved, as was the instrument panel. A refinement of the FC model but appearance significantly changed with a wraparound windscreen, lower bonnet and finned rear guards.. This vehicle was purchased in NSW The interior was in excellent condition bur required extensive exterior work to bring it back to its original condition, It had a mileage of 8500. A refinement of the FC model but appearance significantly changed with a wraparound windscreen, lower bonnet and finned rear guards. It was the first Holden with acrylic paintwork.Two tone grey body , four door FB Holden sedan. Finned rear mudguard,. Holden Special Registered number 63452-Hholden, automobile, 1960, car -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaFunctional object - Object, Cane basket on wheels
Basket weaving and brush making was a source of income for those who worked in the workshops at RVIB and other institutions in New South Wales and Queensland. A diverse range products could be produced with cane, such as cane chairs, cots, washing baskets and trolleys, and the Institution sought to highlight these in the annual report. Over time the demand for, and supply of, cane changed - particularly during World War 2 when Asian sources were under attack or destroyed. At home, other materials such as plastics as well as the ability to import cheaper pre-produced products further reduced the demand for workshop pieces. This cane basket was used at QBIC for transporting heavy items. The side has been reinforced with wood and four metal bands to help the cane keep it's shape and take the weight of heavy items. The base has two pieces of board and rotating wheels are attached to the middle of the lower board which allows it to sit above ground level and be wheeled over flat surfaces. A rope handle is attached to two sides as well.1 deep cane basket with two wheelsQBIC Industries - Asset Number: 1430-1 Description: Push Trolley 7 Location: 18R Block Cane Shop employment, qbic industries -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyTin Tobacco, Mid to late 1900s
The British Australasian Tobacco Co. (based in Melbourne and Sydney. The parent company was founded in England, circa 1902). This item "HAVELOCK" is one of many ready rubbed tobacco tins produced by the British Australasian Tobacco Company.The ready rubbed tobacco held within the tin was mainly used by those smokers who rolled their own cigarettes. These smokers would have mainly used their palm and formed a cup then placing their choice of the amount of tobacco to be rolled. This would then be placed on the fine cigarette paper and rolled and sealed (using saliva in the mouth) into the required shape. There were mechanical "roll you own" gadgets on the market but most rural users, especially males used their palms. The quantity of tobacco used to make up the cigarette was up to the individual user. The thinner that the cigarette was rolled the longer and more economical did the supply last. The by -products of this method were nicotine stained fingers and hands. "Chain" smokers were easily identified and could therefore be discriminated against obtaining smoke sensitive employment. The two world wars (1914-18 and1939-45) produced a significant rise in the consumption of cigarette use by men and the eventual overflow to women. Cigarette smoking before the 1900s was seen as rough and uncouth (socially frowned upon), however after the introduction of overseas films (U.K. and U.S.A.) and film stars presenting smoking as socially acceptable, the rise of smoking cigarettes, especially roll you own (American western movies) in rural areas was an accepted way of life. Things however started to change in the mid 1900s when medical evidence pointed to the health problems of regular smokers. Governments were now implementing non smoking education material. Restrictions on where and when smoking was permitted and acceptable started to creep into all areas of society whether city or rural. This was the era that highlighted the use of roll your own cigarettes, especially when the costs of "tailor made" cigarettes were taxed at an increasing amount. Roll your own cigarettes also provided an avenue for the consumption of illicit drug use.The significance of this ready rubbed tobacco tin to this rural region is, stems from how much influence that the Western novels and overseas films (portraying rural lifestyles) played in shaping the rural social and working mores of the Kiewa Valley. The post war depression (financially) resulted in more smokers turning away from expensive machine (tailor) made cigarettes to the roll your own, using ready rubbed tobacco. This tobacco tin relays a long ago era, when personal contact, and not something that has been written down by some "unknown", was valued as the true appraisal of a member of the community. This was especially relevant in a small regional area such as the Kiewa Valley. Although social networking was not as fast then as the internet provides now, appearances, manners, fashion and etiquette with first impressions high on the order of evaluating someone in the community. Pointer such as the brand of tobacco smoked was part of the rural assessment method. Up until the demise of the Australian Tobacco Industry, circa 2004, the Kiewa Valley and surrounding district was part of a vibrant producer of tobacco leaves. The remnants of this industry still remain today but the drying sheds (for tobacco leaves) are now used to store hay for the valley's dairy and beef cattle industries.This tobacco tin is constructed from tin plated thin rolled steel. The lid is attached by two pressed and formed (from the main frame) hinges using the nip and tuck construction method.The lid and outside frame have had a green "weave" pattern anodised to the metal.On the outside of the lid and at the top left is stamped, in gold coloured letters "HAVELOCK". The bottom of the lid is stamped (in smaller script) "READY RUBBED TOBACCO" and below this in smaller lettering "2oz NET WEIGHT WHEN PACKED". On the rim of the lid is "THE BRITISH AUSTRALASIAN TOBACCO CO. PTY. LTD." Inside of the lid and stamped in black print on a gold anodised lid is "Every tin of genuine HAVELOCK Ready Rubbed Tobacco has the mane Havelock printed on the paper lining, and also on the band or wrapping sealing the tin. On the hinge side of the lid is "HAVELOCK READY RUBBED"roll your own, cigarette tins, smoking accessories, personal effects, tobacco containers -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDiathermy Equipment, c. 1926
This Diathermy Equipment set once belonged to Dr T.F. Ryan of Nhill and was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s T.S.S. Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Diathermy Equipment once belonging to Dr T.F. Ryan, from the W.R. Angus Collection. The equipment is stored in 2 boxes. A long box contains llight weight wooden pieces that make up a Diathermy Clamp (2 extension arms and 2 cross bars). A short deep box contains Diathermy Electrodes; metal (2), metal mesh (2), rubber sponges (2 melded into 1 by perishing), Large Diathermy Pad with cable and connector attached "DIATHERMY PAD" hand written on back. Also, documents (6); receipt to "Dr Ryan, Nhill", from Stamford X-Ray & Radium Co 8/2/1926, instructions (2), notes written on back of eye Field of Vision charts (3). Both boxes have the maker's name on the label "Liebel-Flarsheim Co., Cincinnati, Ohio."Stamped onto the label on the Clamp bos "4 1/2 x 5" and (Cat. No.) "2028" Hand written in black on back of diathermy pad "DIATHERMY PAD" Receipt made to "Dr Ryan, Nhill"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, dr w r angus, dr ryan, surgical instrument, t.s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, mira hospital, flying doctor, medical treatment, medical history, diathermy treatment, stamford x-ray and radium co, l-f diathermy clamp, both boxes have maker's label liebel-flarsheim co., cincinnati, ohio. -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyScoop metal, no makers identification, circa mid to late 1900's
This scoop was professionally made and well before plastics and aluminium scoops were manufactured. It was in a period when mass production and cheap imports where not common. This item would have been produced well after World War II and before the cheap Asian imports. It was a period in time(the last years) when items such as this scoop were made to last and consumerism was not at the "throw away" mass consumption time of the late 1900's. The rural sector in the Kiewa Valley used this type of "made to last" domestic implement when home made cakes and pastries were commonly made in the household kitchen. Because of the relatively isolation of the valley, bulk supplies of flour, sugar and other cooking ingredients were the required quantity for both domestic household and farm use. Local general stores also had these scoops to provide clients with their required flour, sugar and other bulk loose grains (processed or unprocessed) This lite galvanised rolled steel flour/sugar scoop has a tapered handle extruding from a small cone shaped base. It has a half circle scoop extending from a full circular base which has a small containment ridge which acts as a collection rim. The collection scoop has its front shovel end tapered and rolled edge (outwards) presenting a barrier and air relief when thrust into the flour/sugar. All the edges are rolled and connection links have been soldered. The handle is not of solid steel which accounts for the light weight. The base of the "shovel" is slightly concave to allow gravitational forces to keep the flour centre of mass. The handle has a ridge pressed in the sheet metal at about two thirds up the shaft All metal to metal joins have been pressed and soldered together.loose grains, sugar, millet, nus, nails, loose grocery items.
