Showing 1289 items matching "open family"
-
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Documents, Atlas Automatic Fire Services Pty Ltd, Woollen Mill, late 20th century
These items are from the Warrnambool Woollen Mill and relate to the fire protection services operating at the factory in the late 20th century. The Warrnambool Woollen Mill was commenced as a local public company and opened in 1910 in South Warrnambool with the first manager, John Bennett. During World War Two there were 700 employees at the mill due to wartime demand. In 1958 the factory became the first in Australia to manufacture electric blankets. In 1968 the mill was purchased by the Dunlop company and in 1982 Dunlop sold out to Onkaparinga Woollen Company which was taken over by Macquarie Worsteds and became known as Warrnambool Textiles. When Macquarie Worsteds ceased operations in Warrnambool the Smith Family managed the factory on behalf of the owners, the Warrnambool City Council. In 2000 the Woollen Mill closed and the site has been sold and developed as a housing estate.These items are of minor interest as mementoes of the Warrnambool Woollen Mill and will be added to the Woollen Mill collection in the Historical Society archives. .1 A sheet of white paper showing a sketch plan in black of the Warrnambool Woollen Mill with three areas coloured pink, yellow and blue .2 the same as .1 except that there are no shaded areas. .3 A sheet of lightweight card with black and yellow printing and a diagram of a machine Fire Plan For Insurance Purposes Atlas Automatic Fire Services Pty Ltd warrnambool woollen mill, history of warrnambool, onkaparinga woollen company, dunlop company -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Busst House, cnr Silver Street and Kerrie Crescent, Eltham, 2 February 2008
Considered the best of the early mud-brick houses built by Alistair Knox. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p143 The Busst house hidden by trees at the corner of Silver Street and Kerrie Crescent is considered the best of the early mud-brick houses built by Eltham architect, Alistair Knox. Knox himself said, that the Busst house was the most mature mud-brick house designed at that period. ‘It related with true understanding to its steep site and expressed the flexibility of earth building ………to develop a new sense of flowing form and shape’. Built in 1948 for artist Phyl Busst, a former art student at Montsalvat, the house helped usher in Eltham Shire’s distinctive mud-brick residential character. Knox was the pivotal figure of the style developed from the 1950s to the 1970s. Scarcity of building materials after World War Two encouraged mud-brick building because earth was a cheap and plentiful building medium. But when Knox began building in mud-brick in 1947, no council in Victoria knew anything of this ancient art and he needed a permit. Fortunately the Commonwealth Experimental Building Station at Ryde in NSW, had been experimenting with earth construction to help overcome the shortages of that time. They published a pamphlet that became available in Melbourne on the same day the Eltham Council was to consider whether the earth building should be allowed. Knox caught one of the three morning trains to the city in those days and bought several copies of the pamphlet to give to each councillor. On his return he found the councillors standing on the steps of the shire offices after lunch at the local hotel. He heard that earth building had been discussed before lunch and that they were not in favor of it. Knox gave each councillor a pamphlet. They passed that plan and by doing so, opened the door for all future earth building in Victoria and by default, in Australia. Mud-brick houses attracted artists to Eltham, for their aesthetic appeal and because they were cheap. Those who built their own houses, included film maker Tim Burstall, artists Peter Glass, Clifton Pugh, Matcham Skipper, Sonia Skipper and husband Jo Hannan. For Knox, mud-brick building was more than just a cheap building medium. He saw it as harmonising with the surrounding bush and as a way of counteracting the growing materialism of the age. He wrote of its impact on ‘ 20th century man. It should counteract the confusion that the perpetual flow of high technology products have upon him ..’ Building the Busst house on a steep site was difficult because most earth-moving equipment was then in its infancy. For instance drilling for explosives was done by hand, which was a slow and painful process. Knox, assisted by his foreman Horrie Judd and Gordon Ford (who was to become a famous landscape designer), built two large main rooms - a living room/ kitchen downstairs - and upstairs, a studio/bedroom. The studio/bedroom opens onto the balcony, which covers the living area. The bath made of solid concrete by stonemason Jack Fabro, is particularly deep. Sunshine pours through the three French windows of the north-east facing kitchen/living area, which is lined with timber. The large hearth can fit a family around the fire while the timber floors and solomite (compressed straw) ceilings add to the cosy atmosphere. The garden is thick with trees, and in the late 1990s, Ford put in a pool near the original dry wall he had built as a young man.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, alistair knox, alistair knox design, busst house, kerrie crescent, mudbrick construction, mudbrick houses, silver street -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Blue Lake, Plenty Gorge Park, 2008
A quarry was transformed into the Blue Lake. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p179 The dramatic steep-sided Plenty Gorge lies along the divide of two geological areas, and separates the Nillumbik Shire and the City of Whittlesea. On the Nillumbik side are undulating hills and sedimentary rock, and in Whittlesea, lies a basalt plain formed by volcanic action up to two million years ago. This provides the Plenty Gorge Park with diverse vegetation and habitats, making it one of Greater Melbourne’s most important refuges for threatened and significant species. The park, established in 1986, consists of around 1350 hectares, and extends 11 kilometres along the Plenty River, from Greensborough to Mernda. It provides a wildlife corridor for around 500 native plant and 280 animal species. The area’s plentiful food and water attracted the Wurundjeri Aboriginal people and then European settlers. By 1837 squatters had claimed large runs of land for their sheep and cattle. The Plenty Valley was among the first in the Port Phillip District to be settled - mainly in the less heavily timbered west - and was proclaimed a settled district in 1841.But by the late 1880s, the settlers’ extensive land clearing for animal grazing, then agriculture, depleted the Wurundjeri’s traditional food sources, which helped to drive them away. Many Wurundjeri artefacts remain (now government protected), and so far 57 sites have been identified in the park, including scarred trees, burial areas and stone artefacts. Pioneer life could be very hard because of isolation, flooding, bushfires and bushrangers. Following the Black Thursday bushfires of 1851, basalt was quarried to build more fire-resistant homes. Gold discoveries in the early 1850s swelled the population, particularly around Smugglers Gully; but food production made more of an impact. In the late 1850s wheat production supplanted grazing. In the 1860s the government made small holdings available to poorer settlers. These had the greatest effect on the district, particularly in Doreen and Yarrambat, where orchards were established from the 1880s to 1914. Links with a prominent early family are the remains of Stuchbery Farm, by the river’s edge bounded by Smugglers Gully to the north and La Trobe Road, Yarrambat, to the east. The Stuchberys moved to the valley in 1890, and the family still lives in the area. In 1890, Alfred and Ada first lived in a tent where four children were born, then Alfred built the house and outbuildings around 1896. They planted an orchard, then a market garden, and developed a dairy. The family belonged to the local Methodist and tennis communities. Their grandson Walter, opened the Flying Scotsman Model Railway Museum in Yarrambat, which his widow, Vi, continues to run. Wal was also the Yarrambat CFA Captain for 22 years until 1987. Walter sold 24 hectares in 1976 for development - now Vista Court - and in 1990, the remaining 22.6 hectares for the park. Remaining are an early stone dairy and remnants of a stone barn, a pig sty and a well. Until it was destroyed by fire in 2003, a slab hut stood on the Happy Hollow Farm site, at the southern end of the park. The hut is thought to have been built in the Depression around 1893. This was a rare and late example of a slab hut with a domestic orchard close to Melbourne. Emmet Watmough and his family first occupied the hut, followed by a succession of families, until the Bell family bought it around 1948. There they led a subsistence lifestyle for 50 years, despite encroaching Melbourne suburbia. The Yellow Gum Recreation Area includes the Blue Lake, coloured turquoise at certain times of the year. Following the 1957 bushfires, this area was quarried by Reid Quarries Pty Ltd for Melbourne’s first skyscrapers, then by Boral Australia. However in the early 1970s water began seeping into the quarry forming the Blue Lake and the quarry was closed. The State Government bought the site in 1997 and opened it as a park in 1999.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, blue lake, plenty gorge park -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Stuchbery Farm dairy, 14 March 2008
Stuchbery Farm was situated on the Plenty River bounded by Smugglers Gully to the north and La trobe Road, Yarrambat, to the east. Alan and Ada Stutchbery moved to the valley in 1890, first living in a tent where four children were born. Alfred built a home and outbuildings around 1896. They planted an orchard, then a market garden and developed a dairy. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p179 The dramatic steep-sided Plenty Gorge lies along the divide of two geological areas, and separates the Nillumbik Shire and the City of Whittlesea. On the Nillumbik side are undulating hills and sedimentary rock, and in Whittlesea, lies a basalt plain formed by volcanic action up to two million years ago. This provides the Plenty Gorge Park with diverse vegetation and habitats, making it one of Greater Melbourne’s most important refuges for threatened and significant species. The park, established in 1986, consists of around 1350 hectares, and extends 11 kilometres along the Plenty River, from Greensborough to Mernda. It provides a wildlife corridor for around 500 native plant and 280 animal species. The area’s plentiful food and water attracted the Wurundjeri Aboriginal people and then European settlers. By 1837 squatters had claimed large runs of land for their sheep and cattle. The Plenty Valley was among the first in the Port Phillip District to be settled - mainly in the less heavily timbered west - and was proclaimed a settled district in 1841. But by the late 1880s, the settlers’ extensive land clearing for animal grazing, then agriculture, depleted the Wurundjeri’s traditional food sources, which helped to drive them away. Many Wurundjeri artefacts remain (now government protected), and so far 57 sites have been identified in the park, including scarred trees, burial areas and stone artefacts. Pioneer life could be very hard because of isolation, flooding, bushfires and bushrangers. Following the Black Thursday bushfires of 1851, basalt was quarried to build more fire-resistant homes. Gold discoveries in the early 1850s swelled the population, particularly around Smugglers Gully; but food production made more of an impact. In the late 1850s wheat production supplanted grazing. In the 1860s the government made small holdings available to poorer settlers. These had the greatest effect on the district, particularly in Doreen and Yarrambat, where orchards were established from the 1880s to 1914. Links with a prominent early family are the remains of Stuchbery Farm, by the river’s edge bounded by Smugglers Gully to the north and La Trobe Road, Yarrambat, to the east. The Stuchberys moved to the valley in 1890, and the family still lives in the area. In 1890, Alfred and Ada first lived in a tent where four children were born, then Alfred built the house and outbuildings around 1896. They planted an orchard, then a market garden, and developed a dairy. The family belonged to the local Methodist and tennis communities. Their grandson Walter, opened the Flying Scotsman Model Railway Museum in Yarrambat, which his widow, Vi, continues to run. Wal was also the Yarrambat CFA Captain for 22 years until 1987. Walter sold 24 hectares in 1976 for development - now Vista Court - and in 1990, the remaining 22.6 hectares for the park. Remaining are an early stone dairy and remnants of a stone barn, a pig sty and a well. Until it was destroyed by fire in 2003, a slab hut stood on the Happy Hollow Farm site, at the southern end of the park. The hut is thought to have been built in the Depression around 1893. This was a rare and late example of a slab hut with a domestic orchard close to Melbourne. Emmet Watmough and his family first occupied the hut, followed by a succession of families, until the Bell family bought it around 1948. There they led a subsistence lifestyle for 50 years, despite encroaching Melbourne suburbia. The Yellow Gum Recreation Area includes the Blue Lake, coloured turquoise at certain times of the year. Following the 1957 bushfires, this area was quarried by Reid Quarries Pty Ltd for Melbourne’s first skyscrapers, then by Boral Australia. However in the early 1970s water began seeping into the quarry forming the Blue Lake and the quarry was closed. The State Government bought the site in 1997 and opened it as a park in 1999.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, ada stuchbery, alan stuchbery, dairy, stuchbery farm, farm buildings, yarrambat, plenty gorge park -
 Falls Creek Historical Society
Falls Creek Historical SocietyLift and Ski School Lesson tickets 1985, Falls Creek Alpine Enterprises
SKI TICKETS Before tows and lifts were introduced at Falls Creek, it could take skiers 20 minutes to climb to the Summit … but only TWO minutes to go back to the bottom. The arrival of tows, then chairlifts and T-bars changed the face of skiing forever. The first rope tow was constructed by Toni St. Elmo for the 1951 winter season. Bob Hymans installed a smaller tow for his guests at Skyline Lodge. Tows were still quite slow, so in 1956 Bob Hymans created his single chairlift. In 1958 the Village rope tow, designed by Albury engineer Jock Wilson, opened. It was financed by shareholders including Bill Griffith (Bowna Ski Club) and the Bridgford family (St. Trinian’s Ski Club). Several other tows followed including the Summit T-bar in 1961, built by Ron McCallum and operated by Alpine Developments Pty. Ltd. which was a company formed by C. H. (Bill) Bridgford. By 1982 Falls Creek was served by 16 different lifts or T-bars, all owned and operated by Alpine Developments (Holdings) Pty. Ltd. During the development of Falls Creek, different methods have been used to pay for the use of tows, lifts and T-bars … including metal tokens, single tickets, strips of tickets and season passes. The Falls Creek Historical Society Collection includes many examples of these items.These tickets are significant because they represent a stage in the progression of chair lifts and management at Falls Creek Tourist Village.A collection of tickets issued for entry to Falls Creek, lift passes and lessons at Falls Creek Ski School for 1984. The tickets include adult and child passes and range from a single lesson passes up to booklets for seven lessons. They also cover the low, shoulder and high season.ski tickets falls creek, falls creek management, falls creek ski school -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Clothing - Fletcher Jones Man's Sports Coat, 1970s
This sports coat was made at a Fletcher Jones factory about the 1970s. David Fletcher Jones (1895-1977) served in World War One and in the 1920s set up as a travelling hawker selling drapery in Western Victoria. In 1924 he leased three shops in Liebig Street, Warrnambool and in 1928 opened his Man's Shop at the intersection of Koroit/Liebig Streets. He manufactured men's clothing on site in a new building erected in 1931. In 1946 a Fletcher Jones shop was opened in Melbourne and in 1948 a factory was established in Warrnambool with a new company Fletcher Jones and Staff established in 1951.This company then operated in other States and known Australia-wide firstly for its production of men's trousers and later for men's and women's clothing. By 2011 the Warrnambool factory was closed and the company dissolved. This coat was bought by Lew Officer, a member of a family with pastoral interests in the Western District.This item is of considerable historical interest as an example of the high quality work produced by the Fletcher Jones and Staff Clothing Stores. This company was a key industry in Warrnambool in the 20th centuryThis is a man's sports coat made of Harris tweed hand woven in the Outer Hebrides made from Scottish-grown wool. The checked material is in brown tonings. The coat has a brown material lining and there are two brown buttons down the front and two on each sleeve. The collar has a grey felt lining.fletcher jones clothing stores, warrnambool, harris tweed jacket, lew officer -
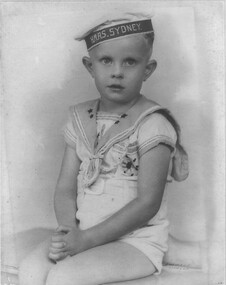 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Photograph, Denis Gibbons 7
Denis Gibbons (1937 – 2011) Trained with the Australian Army, before travelling to Vietnam in January 1966, Denis stayed with the 1st Australian Task Force in Nui Dat working as a photographer. For almost five years Gibbons toured with nine Australian infantry battalions, posting compelling war images from within many combat zones before being flown out in late November 1970 after sustaining injuries. The images held within the National Vietnam Veterans Museum make up the Gibbons Collection.A black and white photograph of Denis Stanley Gibbons in 1940, aged three years. This family portrait was taken at Lithgow prior to going to Sydney to visit HMAS Sydney during an 'open day' prior to her sailing off to war. During the vist to Garden Island, I managed somehow to become disengaged from my mother and father each thinking the other had me with them. When they finally met up and no Denis in sight, panic became the order of the day. I was finally found below deck where some of the sailors had taken me and were giving me a grand time. They informed my mum and dad that had I not been found they were going to make me the Sydney's mascot. To this day when I recall this story l think of all those fine young sailors who lost their lives when Sydney was sunk by the German raider off the coast of Western Australia.photograph, hmas sydney, gibbons collection catalogue, denis gibbons, photographer, vietnam war -
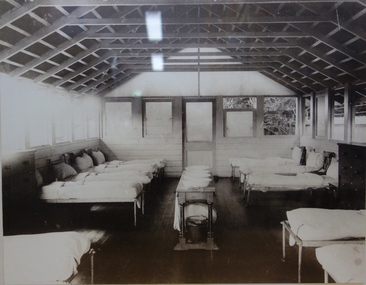 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncPhotograph - Tent Dormitory, Kew Cottages
The Children's Cottages at Kew were first opened in 1887 as the "Idiot Ward" of Kew Asylum. Located on the asylum's grounds, the children's cottages were established to provide separate accommodation for child inmates who had previously been housed with adult patients. Although the Cottages only admitted children as patients, many of those children remained in residence at the Cottages as adults. The function of the institution was to provide accommodation and educational instruction for intellectually disabled children. Some Wards of the State and other various "difficult" children were also admitted.Shortly after opening, the Idiot Ward began functioning separately from the Kew Lunatic Asylum, and became known as the Kew Idiot Asylum from 1887 until c.1929. From 1929 they have been known as the "Children's Cottages, Kew" or alternatively "Kew Cottages Training Centre". The institution was finally closed in July 2008. [Source: Wikipedia, 2016]One of a series of framed historical photographs of the Kew Cottages that once formed part of the collection of the Kew Cottages Historical Society, founded by Dr. Cliff Judge and Fran Van Brummelen in the 1980s. The set contains both copies of originals in other collections such as the Public Record Office Victoria and photographs taken by Dr Judge for his books on intellectual disability in Victoria. The significance of the set of framed photographs is that they provide a curated collection of images of the development of the Cottages over a one hundred year period.Framed photograph, forming part of the Kew Cottages collection, donated by the Kew Cottages Historical Society 1987-1993 in 1993. Dr. Judge was a consultant psychiatrist at the cottages for 14 years, as well as an author and vocal advocate for the intellectually disabled and their families."An old dormitory in the year 1973. It is still in use as a therapy room and store. Originally these buildings were called tents. Open air treatment was used to cure bad cases of insanity."kew cottages, dr cliff judge, kew cottages historical society 1987-1993 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Sewing Machine and case, Joseph Wertheim, late 19th century
Hugo Wertheim (1854-1919), was a merchant and manufacturer and was born on the 12th July 1854 at Lispenhausen, in the German electorate of Hesse-Kassel, son of Meyer Wertheim and his wife Minna, née Heinemann. Hugo reached Melbourne in October 1875. He soon began advertising, from premises at 39 Flinders Lane East, as agent for his father's cousin Joseph Wertheim, a well-established manufacturer of sewing machines. Hugo returned to Germany where he married Joseph Wertheim's daughter Sophie Emilie (1864-1953) on 30 August 1885 at Frankfurt. the couple then came to Melbourne. In a short time, with extensive advertising, Hugo established a substantial business, selling sewing machines, bicycles, pianos and other mechanical devices, under brands such as Wertheim, Electra, Planet, Griffin and Hapsburg. He also mounted elaborate displays at agricultural shows and in 1901 at the Pan American Exposition, Buffalo, United States of America. O. C. Beale worked with him before setting up his own piano business in New South Wales. Hugo continued to own 25 per cent of one of Beale's companies, which became Wertheim's Queensland business. In 1908 Wertheim opened a large, innovative piano factory at Richmond, Melbourne, intending to produce 2000 pianos and player pianos annually, predominantly using Australian materials. In laying the foundation stone, Prime Minister Alfred Deakin observed that “few men with such opportunities for a life of ease would have embarked on such an enterprise” Hugo died of chronic hepatitis on 11 July 1919 at his home at South Yarra, his wife, two daughters and three sons survived him; Herbert Joseph (1886-1972), the eldest, continued the business. Rupert became a share broker and went on to represent Victoria in inter-State tennis in 1913-27 and Australia in Davis Cup matches against Czechoslovakia in 1922. The piano factory closed in 1935, becoming a Heinz food processing plant and in 1955, GTV Channel 9 studios and offices.Early Australians had to be self-reliant in regards to making and mending their clothes and utensils. This sewing machine was one of many items used that exhibit the skill and craftsmanship of the women in these early families. A sewing machine was a necessary part of each home and this item demonstrates how women of the time managed had to become self-reliant in the repair and making of their families clothes to make their household budgets go further.Sewing machine, Wertheim brand “ Syst 182” hand crank operated machine with folding handle, timber case and carry handle. Metal machine is painted black, with remnants of gold, red and green scrolls and floral decoration. Machine has base with inlaid measuring rule across front and 2 holes drilled through the base (perhaps for mounting machine to a bench). Machine tilts open, hinged on one side, after thumb screw is unwound, revealing machine’s workings and serial number. Base has a fitted round, concave, silver metal pin holder with lid that hinges open, and symbol pressed into lid; several pins are inside. Body of machine has brand name transfer across front and oval metal trademark disc on front. Metal sliding covers over footplates have stamped lettering. Timber machine case or cover includes an accessory box with sliding cover and metal hook and eye latch, and inside the box are 23 metal sewing attachments, a disc and a stick of black crayon with maker’s trademark on it paper cover. Workings of machine have seized up. The crayon wrapper has printed on it “For the wonderful Wertheim new family machine made in Germany ‘Syst. 182’”, and the maker’s symbol with “Trademark” beside it. Made for Hugo Wertheim.“WERTHEIM” transfer across front and back of machine body. Cover of pin holder has symbol ‘Wings above a shield’. Maker’s trademark on gold oval disc, “WERTHEIM / FRANCFURT” and picture of a dwarf with a hammer. Left footplate has script “Syst 182”, right footplate has stamp in oval shape “MANUFACTURED IN - - /SPECIALLY FOR / HUGO WERTHEIM” Serial Number “7501”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, sewing machine, hand crank sewing machine, hugo wertheim, wertheim, clothing manufacturer, sewing, syst 182 -
 Bacchus Marsh & District Historical Society
Bacchus Marsh & District Historical SocietyPhotograph, Border Inn, Main Street Bacchus Marsh 1883
The Border Inn located on the corner of Main Street and Graham Street Bacchus Marsh opened in 1851 making it a very early hotel in Victoria. It was built and owned by John Pilmer. The first licensee was James Watt. The building has been added to and changed many times. It was originally a single storey building. A second storey was added in 1863 by John Pilmer. In 1866 the hotel was purchased by Edward Jones. The Jones family owned and operated the hotel until 1939. Additional second storey sections were added in 1883, 1904 and 1936. For a number of years the Border Inn was a stopping post for coaching services between Melbourne and Ballarat. The first licensee of the hotel James Watt was among the first in Victoria to offer a regular coaching service and his hotel was used for overnight accommodation by coach travellers. At the time this picture was taken coach services were still operating between Bacchus Marsh and other locations. The coach in this picture is possibly one of those coaches.This building has been documented as of state significance by Richard Peterson and Daniel Catrice in their 1995 heritage study for the then Shire of Bacchus Marsh. Their assessment of the heritage significance of the building was: "The Border Inn is of state historical significance as a pioneering pre-gold rush building, on the route to the Ballarat goldfields. It is the representative-embodiment of several historical periods and their way of life. It demonstrates a complex changing sequence of patterns of occupancy and architectural styles. Its development at this location, demonstrates the effect of a social movement, the gold rush, as a transport stopover.It is also historically significant for its association with the first rural public transport in Victoria. Locally, the hotel is significance for its association with the first meeting of municipal government, and also for its social significance as a traditional community, visitor focus and meeting place".Small sepia unframed photograph on card with gold border framing photograph. Housed in the album, 'Photographs of Bacchus Marsh and District in 1883 by Stevenson and McNicoll'. The image shows the Border Inn Hotel at an angle depicting the front of the building facing directly to the camera. It is a two storey brick building, with one-story additions at either end. Five chimneys can be seen extending from the building. The bottom storey has a verandah extending onto the footpath. A covered wagon, probably a coach, with four horses in harness is in front of the building. There are several people in the image. Two people are sitting on the driver’s seat of the wagon. Another man is standing holding the reins of the horses. At his feet is a dog. Behind them are two male adults. One is holding a small child. A young boy stands beside him.On the front: Stevenson & McNicoll. Photo. 108 Elizabeth St. Melbourne. COPIES CAN BE OBTAINED AT ANY TIME. On the back: LIGHT & TRUTH inscribed on a banner surmounted by a representation of the rising sun. Copies of this Portrait can be had at any time by sending the Name and Post Office Money Order or Stamps for the amount of order to STEVENSON & McNICOLL LATE BENSON & STEVENSON, Photographers. 108 Elizabeth Street, MELBOURNE. stevenson and mcnicoll 1883 photographs of bacchus marsh and district, hotels bacchus marsh, border inn hotel bacchus marsh, carriages and coaches, stagecoaches, james watt bacchus marsh, john pilmer bacchus marsh, edward jones family bacchus marsh -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPhotograph - Black and White photograph, Jan. 1937
Black and white photograph of a lightly loaded cable car set, trailer 415, eastbound in Bourke St, nearing Russell St. Set has destination of Nicholson St. The Conductor and Gripman are both on the grip car - "gossiping". In the background are signs for Sharpe's store, Parers Hotel, Lewis's and Normans. On the underside of the photograph written in black ink "Cable Tram in Bourke St Jan 1937" Noelle Jones - 24/5/2021 It is no later than 1946, as Maples purchased the Love & Lewis business (194-6 Bourke St) in that year (the business was being sold by the executors of the owner). Note also that Parer's (not Parkers) Hotel, at 200 Bourke Street, was established in the 1880s by the Parer Brothers, originally from Spain. The most famous member of the family was Damien Parer, the WWII photographer. The building was demolished in 1960, and is the site of the Midcity Arcade. Sharpes bought the property on the left (202-4 Bourke St) in 1954, after being tenants for 20 years. Normans Corner Stores opened in 1932.trams, tramways, bourke st, nicholson st, cable trams, crews, tram 415 -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumMagazine, Metropolitan Transit Authority (MTA), "Met Lines", September 1984 to June 1985
Magazine, published by the Metropolitan Transit Authority of Victoria "Met Lines" (Metlines) - A3 when folded, printed on white gloss paper, with the MTA logo or symbol. Issued under the name of L. A. Strouse as Chairman. Continues from Reg Item 1040 - "Headway News" Major tram and bus items listed. Tramway and bus names only listed, not railway. .1 - Vol 1 No. 1 - September 1984 - 8 pages - 130 years of rail service. Has note about former name, station revitalisation, Met Miles achieved, travel club, Centre page spread of photos of Preston workshop activities, names in Key Associations, repainting of Scrubber 8W, 8, 745, Vic Tramways Bowls Association, Alan Edwards retirement, item on Hawthorn Clothing Workshop (with photo), Munitions bus 301 - Geoff Foster, John Weighman and Daryl Mead and sporting news, - Preston Workshops Soccer team. .2 - Vol 1 No. 2 - 8 pages - Christmas Issue 1984 - Intermodal - Box Hill, Royal Show, A class tram introduced - Driver Don Everard, new tourist guide, Neighbourhood bus revamp in Ringwood, Westona station, Bundoora extension, Transit brass band, Beppie Hedditch - Occupational Welfare Service at Hawthorn, B class trams, sporting news and restored Tacit train. .3 - Vol 1 No. 3, March 1985 - 8 pages - introduction of AVM, bus driver Geoff Neicno, Communications Technician Bruce Smith with MTA Posters or advertisements, Bundoora extension opened, exporting tramway expertise, bus neighboured planning, English on the Job, Met card travel competition, 130 new B class trams and auction sale of Tait Trains. .4 - Vol 1 No. 4 June 1985 - 8 pages - Flagstaff opened, Men at Work band, investigation Officers, library moves to Queen St, first annual report, families on the job - Kimber, Sutton and Luciews, AVM at Nicholson St Engine house. The magazine continues to an A4 version ,see Reg item 1059 and onwards.trams, tramways, mta, preston workshops, hawthorn, buses, sports, box hill, a class, tramway band, welfare, b class, posters, advertisements, metcard, competition, new trams, flagstaff station, nicholson st, tram 8, tram 745, tram 8w -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaPlaque - Opus sectile tablet, In grateful Memory of Alfred Michael Nicholas Esq, (1881-1937), 1937
This plaque was made to commemorate the generous funds donated Mr A.M Nicholas in 1936 almost entirely funding the building of the new Mission to Seamen at Port Melbourne opened in 1937. Mr Nicholas died in Feb 1937. The new building was opened on the 4th of December 1937 by Lord Huntingfield, the plaque was dedicated and unveiled the same by his nephew Mr Nicholas Lightfoot. The plaque was removed from the building which ws demolished in 1995. The plaque is really similar to the memorial plaque made in memory of Ethel Godfrey (see item 2053).Mr Nicholas together with Mr HW Shmith organised rights to produce Aspirin aka ASPRO in Australia in 1915 during WW1. The Nicholas Family were significant philanthropists in Melbourne and Victoria and this plaque commemorates his gift to the Mission for visiting seamen between 1937 and late 20th C. The story of the donation is told in an unpublished autobiography by the then Rev'd Frank Oliver, based at 717 Flinders st. as senior Mission Chaplain 1930-1960.A heavy ceramic plaque with moulded metal alloy frame, polychrome glazed irregular ceramic tesserae design and memorial text in Gothic script in central lozenge set into a rectangular clay base.in each corner design features initials: "ihs" / IN central lozenge of design text reads: " To the Glory of God/ and in grateful memory of/ ALFRED MICHAEL NICHOLAS Esq / through whose generous gift/ the whole of this Institute / and Chapel were built./ Died February 26th 1937"1908, plaque, alfred m. nicholas, memorial, alfred michael nicholas, port melbourne, 1937, aspro -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageVehicle - Murweh Carriage, c.1874
This private late-nineteenth-century four-wheeled carriage has been built to transport a family or group of passengers with a coachman in the front seat. It can be pulled by one horse, or by two horses if the T-pole is attached. The button fittings along each side of the carriage indicate that a folding roof or hood was once attached. The frame across the front of the carriagewas likely to have been a ‘dashboard’ with a leather or wood covering to prevent water, mud and other particles from splashing onto the passengers. The rear step between the two side-facing bench seats is adjustable to allow for ladies’ long skirts. These rear seats appear to be removable, in which case the carriage could be converted to a wagon to transport goods and equipment. The carriage could have been illuminated by oil or carbide lamps placed into the lamp holders on the sides. The carriage was kept under cover for many years in an open-front sandstone building that also included living quarters and an area that may have been stable. It was at ‘Murweh’ a Warrnambool property at 203 Liebig Street. The home is now Heritage and National Trust Listed and described as a ‘gentleman’s residence’. It was built by James Wotton Shevill in the 1860s. Shevill was a councillor from 1875 to 1878, serving in 1878 as Mayor of the Borough of Warrnambool. Jeremiah Wade lived at Murweh there from 1879-1880. By 1915 F.B. Whitehead and his family were living there, and by 1930 the address was used by Mr T.J. Rome and his family. Thomas James Rome was still using that address in September 1973 after his 100th birthday. It is believed that one of the property’s owners had been an Obstetrician in Warrnambool. The current owner re-told the story that children used to hide in the back section of the carriage and smoke, hidden from the sight of onlookers. He had heard the story from a previous owner.The well-appointed horse-drawn four-wheeled carriage is likely to have first belonged to a local councillor and past Mayor of the town of Warrnambool, J.W. Shervill, whose 1860s city property was the carriage location for many years. The carriage is a rare local example of a town-based lifestyle befitting a prosperous personality of the late 19th century. It adds to the story of Warrnambool's development as a town influenced by the port, wealth gained from shipping and the home place of prominent local people such as the Councillor and later Mayor. The side-facing rear seating is unusual for a passenger carriage. It has the feature of removable rear bench seats, allowing for the dual purpose of a carriage or wagon.Carriage; the Victorian-era horse-drawn four-wheeled open carriage has a coachman’s bench seat across the front and two side-facing bench seats in the rear. There are steps at the front on each side and a centre adjustable step and the back. It has a hinged shaft, two lamp holders and a separate T-pole. The bench seats have padded backrests upholstered in green leather and each has padded armrests at the ends. A rectangular metal frame, likely to have been a dashboard, is mounted across the front of the carriage. It has two inner vertical bars. The carriage's body is painted dark green with crimson highlights on some of the panelling. Decorative oval panels with hand-painted motifs are mounted along the sides. The side panels of the carriage have metal fastener buttons attached. The iron-rimmed wheels have sixteen wooden spokes and copper cuffs on the outside of the hubs, and the rear wheels are higher than the front wheels. Wooden brake blocks are mounted onto the back wheels and are active by a metal lever at the front right side of the carriage. The undercarriage is fitted with leaf springs on each side, mounted from front to back axles. Included are: (1) The separate T-pole that allows two horses to be harnessed to the carriage (2) Leather horse winkers with metal hardware and oval brass plate on the side of each winkerMotif painted on an oval panel [a musical lyre within a blue floral wreath flanked by scrolls] flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, murweh, buggy, cart, carriage, wagon, horse-drawn vehicle, victorian buggy, four-wheeled carriage, coachman’s seat, bench seat, side-facing benches, upholstered seats, victorian decals, heritage vehicle decoration, antique hand painting, hand painted decals, motifs, iron-rimmed wheels, wooden brake blocks, leaf springs, t-pole shaft, rear step, equine carriage, 19th century vehicle, victorian transport, transport, gentleman’s vehicle, james wotton shevill, councillor, mayor, jeremiah wade, f.b. whitehead, thomas james rome, warrnambool obstruction, warrnambool genealogy, warrnambool pioneers, victorian carriage, one horse carriage, two horse carriage, horse drawn carriage -
 Falls Creek Historical Society
Falls Creek Historical SocietyCard - Membership Cards - Falls Creek Tennis Club
These items are from the private collection of George Shirling of Red Onion, Falls Creek. They document the involvement of the Shirling Family in the Falls Creek Tennis Club over a long period. The first tennis court in the Falls Creek area was cleared on a flattened area of ground between Wallace's and Wilkinson's huts prior to World War II. George Shirling arrived in Falls Creek in 1962. He engaged Phil Nowell to build the original Koki Alpine Lodge which opened in 1965 with 14 beds. George operated the lodge with Michael “Baldy” Blackwell as manager. He also graduated in sport psychology in 1981 and was invited to become team psychologist for the Australian Winter Olympic team which went to Albertville, France, in 1992. He later owned the Red Onion Chalet. George credited the success of Koki to “Baldy” Blackwell. “Baldy” and Phil Nowell started the Trackers Mountain Lodge in partnership during the 1980s. In 1971 George sold Koki Lodge to Sigi Doerr. In 2024 the renamed Koki Alpine resort remains a highly popular destination in Falls Creek. George Shirling passed away on 27th February 2023. He had remained actively involved in Falls Creek and was generous with his time and knowledge, always an amazing supporter of The Falls Creek Museum and Falls Creek Village.This item is significant because it is evidence of other links George Shirling had in Falls Creek.A large collection of Falls Creek Tennis Club Membership cards and receipts for the Shirling Family ranging from 1983 until 1997. Various names and dates on ticketsgeorge shirling, falls creek, falls creek tennis club -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyDomestic object - Cutlery Tray, Unknown
This antique wooden cutlery tray was used to store every day cutlery such as knives, forks and spoons used by the family. It's practical use was for ease of storage and carrying.A handmade brown wooden cutlery tray with two separate compartments. The divider also serves as a handle as it has a curved open shape in the middle to lift it with.trays, cutlery trays, wooden trays, storage trays, cutlery, kitchenware -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Document - Copy of Aerial photo, The Allen Findlay family and Heatherdale Reserve, unknown
Shows the location of trees planted by the Findlay family at their farm prior to it becoming part of Heatherdale Reserve.Shows the location of trees planted by the Findlay family at their farm prior to it becoming part of Heatherdale Reserve.non-fictionShows the location of trees planted by the Findlay family at their farm prior to it becoming part of Heatherdale Reserve.findlay family, findlay wilma, scoble wilma, heatherdale reserve -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncFunctional object - Reeves' "Greyhound" Pastels
This box of pastels was donated to the Wodonga & District Historical Society by Betty L. Barberis (nee Barton), a prominent artist. They were given to her by Mr Colin Findlay, the teacher at Upper Gundowring Primary School from 1930 to 1939. His students at that school and many others used these pastels each day. Reeves’ “Greyhound” business was originally established by William Reeves who opened his first shop near St Paul’s Cathedral in London, England in 1766. The greyhound crest was later adopted as their emblem, taken from the coat-of-arms of the extinct Ryves family of Dorset. It consisted of a black-seated greyhound spotted with gold. After William’s death, the business was carried out by his brother, in partnership with various businessmen. They sold a wide range of art supplies in England and their trade extended to supplying drawing instruments and stationery products to the East India Company in the early 1800s. In the 1920s the Greyhound Colour Works at Enfield became known especially for its famous Greyhound pastels. Reeves Greyhound products were also being made in Melbourne, Australia. They were marketed widely through schools in all States from the 1920s onwards. Reeves continues to be a huge brand both in the United Kingdom and internationally, placed in over 70 countries worldwide including America, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, South Africa and Australia.These pastels are significant because they were widely used in Victorian Schools and were donated to our Collection by a prominent local artist.A cardboard box with a corrugated cardboard to store 12 pastels. The pastels are held in a cardboard tray insert.REEVES' 'GREYHOUND" PASTELS (REGISTERED) Directions for use Non-INJURIOUS Made in Australia On each pastel: REEVES GREYHOUND reeves greyhound pastels, primary school art supplies, education 1930s, upper gundowring primary school, betty l. barberis -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - Army Survey Regiment – Presentation to Charity Organisation, 1984
These photographs of a presentation to a charity organisation were taken in the grounds of Fortuna Villa, Army Survey Regiment in 1984. SPR Tracy (Parker) Ash was the unit’s Miss Golden North section entrant in the Miss Australia Quest. MAJ Bob Roche, RSM Bob Mason and SPR Parker presented a fundraising cheque to the unidentified representative from the Spastic Society. The the newspaper article is from the Bendigo Advertiser. The following wording is taken from the article: ‘Tracy Parker is a sapper in the Army, and a cartographic technician stationed at Fortuna, Bendigo. Originally from Melbourne, Tracy, 23, is the latest entrant in the Miss Golden North segment of the Miss Australia Quest. The highlight of Tracy’s quest will be an open day at Fortuna, once the magnificent home of Bendigo’s Quartz King, George Lansell. This open day at Fortuna, on Sunday, August 26, between 10 am and 4 pm, will give district residents a rare opportunity of inspecting this magnificent building and its gardens. Tracy said there will be handicrafts, rides, competitions and refreshments available at the open day. The main attraction, apart from the building and gardens, would be a hot air balloon. Admission to the open day would be: Adults $2, children and pensioners $1, family party $5. All proceeds from the open day at Fortuna will go to the Spastic Society. Tracy, like all other Miss Australia candidates work hard for the Spastic Society in fundraising activities. Getting further involved in fundraising, Tracy and her strong committee have organised a 6km fun run for Sunday August 19. Entry forms are available at Bendigo sports stores, and at the end of the fun run will be a barbecue. Apart from her vocation in the Army, and fundraising for the Spastic Society, Tracy Parker has a great love of horses, and associated activities of riding, jumping and showing her horses. Tracy is keen to do well in her fundraising, and with the Australian Army, or more particularly, the ranks of Fortuna behind her, Tracy looks like succeeding.’The first three items are photographs of a presentation to a charity organisation at the Army Survey Regiment, Bendigo in 1984. The fourth item is an article from the Bendigo Advertiser describing Army Survey Regiment’s fund-raising activities. The photographs were printed on photographic paper and are part of the Army Survey Regiment’s Collection. The photographic proof prints were scanned at 600 dpi. Photos .1P and .2P were scanned at 300 dpi. The newspaper article was scanned at 762 dpi. .1) to .3P) - Photo, black & white, 1984, L to R: MAJ Bob Roche, Regional Coordinator Mrs Jan Lamborn, SPR Tracy (Parker) Ash, RSM WO1 Bob Mason. .4) – Bendigo Advertiser newspaper article with photo, black & white, 1984, SPR Tracy (Parker) Ash. .1P to .2P – ‘Presentation of Certificate of Appreciation from Spastic Society. Presented by Regional Coordinator Mrs Jan Lamborn to MAJ Roche, SPR Tracy Ash (entrant in Miss Australia Quest (1984) and WO1 Mason.' .3P – No personnel identified. .4P – SPR Tracy Parker named in newspaper article.royal australian survey corps, rasvy, army survey regiment, army svy regt, fortuna, asr -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumMagazine, Yarra Trams, "Yarra Connections", Dec. 2003
Demonstrates a Yarra Trams staff newsletter..1 - Magazine - 8 pages, full colour, centre stapled, printed on recycled paper, titled "Yarra Connections Issue 12, December 2003", published by Yarra Trams. Notes the launch of the "Wheelchair users guide" for tram passenger, Yarra Trams support for Wheelchair Rugby, planning for Vermont South extension, French award for CEO, Hubert Guyot, photo exhibition featuring employees by Georgia Metaxas, Boroondara residents and Travelsmart, Metlink Team Tigers Basketball, Ikea store in Richmond, pram friendly trams, feedback and return of W class trams to route 30. New track maintenance vehicle -"scrubber truck". .2 - Letter on Yarra Trams letterhead, addressed to Ron Wilson of Orange Grove Bayswater, signed by Paul Matthews Marketing Manager forwarding a copy of the magazine to Ron, noting highlights. Gives address details. .3 - Magazine - as for .1 - issue 1 dated October 1999 with a forward by the CEO Steve Macdonald , Camberwell depot, Deputy CEO Hubert Guyot, new logo designs, reduction in tram stops, tennis trams, family day, Docklands route 70 extension and competition. .4 - magazine - 3 fold A4 - issue 9, dated Nov. 2002, Notes the construction of Route 109, W class, St Vincent's Plaza, Gordon Atkins, Docklands tram services, explorer program, Feedback, Line Officers, Corporate Report and Melbourne Museum tram. .5 - magazine - issue 11 - August 2003 - 8 pages - opening of Box Hill line, Harry the Wombat, trams in the press, Welcome to Dennis Cliche, B class seating trial, Metlink, Docklands, trial information at tram stops (early TramTracker) project and route 75. .6 - magazine issue 13 - April 2004 - Australian Open tram service, Collins and Spencer Superstop, tram services, feedback, Metlink, Channel 10 - The Secret life of us, PTC Cricket Squad. .7 - issue 8 - April 2002 - Grand Prix, Box Hill update, Citadis update, Collins and Spring superstop, Australia Open, Fare Evastion and track joints. 8 - issue 10, undated - Australian Open tennis, Eurotram comes to Melbourne, Docklands joins the City Circle, route 109, Box Hill extension and what is a substation.trams, tramways, yarra trams, w class, disability services, vermont south, awards, metlink, route 30, camberwell depot, docklands, route 70, st vincent's plaza, line officers, box hill, route 109, b class, superstops, cricket, tennis, tramtracker, route 75, city circle -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncDomestic object - Small Butter Churn, E. Cherry & Sons, c1880 - 1920
North east Victoria was a major dairy producing region in the late nineteenth century. The Wodonga Butter Factory Ltd was established in 1892. Many families living in the town or on farms also owned their own cow for family needs and produced their milk and butter. This churn is representative of the equipment they used to process their own dairy products at home. This churn was made by E. Cherry & Sons which was established in Gisborne, Victoria in 1858. Edward Cherry (1830-1910) arrived in Australia from Hertfordshire, England, in 1855. The business manufactured churns and in 1875 opened a larger factory. On his death, the business was taken over by his son and continued to operate until the 1970s.This item has strong links to the history of Wodonga and north east Victoria. It has interpretative potential in the areas of local agricultural history, and the social history of food and farming.A wooden butter churn with metal turning handle and removable lid. The wooden paddle inside is attached to the turning handle which rotates to churn the butter. The model number is T1. It was probably made by E Cherry & Sons of Gisborne although the brand is blurred.On one side in black: "T 1"butter churns, dairying industry, domestic appliances, e. cherry churns -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageEquipment - Surgical silks and sutures, Teleflex (manufacturers of Deknatel), Early 1900s
Through many millennia, various suture materials were used or proposed. Needles were made of bone or metals such as silver, copper, and aluminium bronze wire. Sutures were made of plant materials (flax, hemp and cotton) or animal material (hair, tendons, arteries, muscle strips and nerves, silk, and catgut).[citation needed] The earliest reports of surgical suture date to 3000 BC in ancient Egypt, and the oldest known suture is in a mummy from 1100 BC. A detailed description of a wound suture and the suture materials used in it is by the Indian sage and physician Sushruta, written in 500 BC. The Greek father of medicine, Hippocrates, described suture techniques, as did the later Roman Aulus Cornelius Celsus. The 2nd-century Roman physician Galen described sutures made of surgical gut or catgut. In the 10th century, the catgut suture along with the surgery needle were used in operations by Abulcasis. The gut suture was similar to that of strings for violins, guitars, and tennis racquets and it involved harvesting sheep or cow intestines. Catgut sometimes led to infection due to a lack of disinfection and sterilization of the material. Joseph Lister endorsed the routine sterilization of all suture threads. He first attempted sterilization with the 1860s "carbolic catgut," and chromic catgut followed two decades later. Sterile catgut was finally achieved in 1906 with iodine treatment. The next great leap came in the twentieth century. The chemical industry drove production of the first synthetic thread in the early 1930s, which exploded into production of numerous absorbable and non-absorbable synthetics. The first synthetic absorbable was based on polyvinyl alcohol in 1931. Polyesters were developed in the 1950s, and later the process of radiation sterilization was established for catgut and polyester. Polyglycolic acid was discovered in the 1960s and implemented in the 1970s. Today, most sutures are made of synthetic polymer fibers. Silk and, rarely, gut sutures are the only materials still in use from ancient times. In fact, gut sutures have been banned in Europe and Japan owing to concerns regarding bovine spongiform encephalopathy. Silk suture is still used today, mainly to secure surgical drains. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Surgical_suture#:~:text=Sutures%20were%20made%20of%20plant,a%20mummy%20from%201100%20BC. This tin contains a variety of surgical threads and accessories that were used by Dr W.R.Angus. It was donated to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village by the family of Doctor William Roy Angus, Surgeon and Oculist. It is part of the “W.R. Angus Collection” that includes historical medical equipment, surgical instruments and material once belonging to Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Thomas Francis Ryan, (both of Nhill, Victoria) as well as Dr Angus’ own belongings. The Collection’s history spans the medical practices of the two Doctors Ryan, from 1885-1926 plus that of Dr Angus, up until 1969. ABOUT THE “W.R.ANGUS COLLECTION” Doctor William Roy Angus M.B., B.S., Adel., 1923, F.R.C.S. Edin.,1928 (also known as Dr Roy Angus) was born in Murrumbeena, Victoria in 1901 and lived until 1970. He qualified as a doctor in 1923 at University of Adelaide, was Resident Medical Officer at the Royal Adelaide Hospital in 1924 and for a period was house surgeon to Sir (then Mr.) Henry Simpson Newland. Dr Angus was briefly an Assistant to Dr Riddell of Kapunda, then commenced private practice at Curramulka, Yorke Peninsula, SA, where he was physician, surgeon and chemist. In 1926, he was appointed as new Medical Assistant to Dr Thomas Francis Ryan (T.F. Ryan, or Tom), in Nhill, Victoria, where his experiences included radiology and pharmacy. In 1927 he was Acting House Surgeon in Dr Tom Ryan’s absence. Dr Angus had become engaged to Gladys Forsyth and they decided he would take time to further his studies overseas in the UK in 1927. He studied at London University College Hospital and at Edinburgh Royal Infirmary and in 1928, was awarded FRCS (Fellow from the Royal College of Surgeons), Edinburgh. He worked his passage back to Australia as a Ship’s Surgeon on the on the Australian Commonwealth Line’s SS Largs Bay. Dr Angus married Gladys in 1929, in Ballarat. (They went on to have one son (Graham 1932, born in SA) and two daughters (Helen (died 12/07/1996) and Berenice (Berry), both born at Mira, Nhill ) Dr Angus was a ‘flying doctor’ for the A.I.M. (Australian Inland Ministry) Aerial Medical Service in 1928 . The organisation began in South Australia through the Presbyterian Church in that year, with its first station being in the remote town of Oodnadatta, where Dr Angus was stationed. He was locum tenens there on North-South Railway at 21 Mile Camp. He took up this ‘flying doctor’ position in response to a call from Dr John Flynn; the organisation was later known as the Flying Doctor Service, then the Royal Flying Doctor Service. A lot of his work during this time involved dental surgery also. Between 1928-1932 he was surgeon at the Curramulka Hospital, Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. In 1933 Dr Angus returned to Nhill where he’d previously worked as Medical Assistant and purchased a share of the Nelson Street practice and Mira hospital from Dr Les Middleton one of the Middleton Brothers, the current owners of what was once Dr Tom Ryan’s practice. Dr L Middleton was House Surgeon to the Nhill Hospital 1926-1933, when he resigned. [Dr Tom Ryan’s practice had originally belonged to his older brother Dr Edward Ryan, who came to Nhill in 1885. Dr Edward saw patients at his rooms, firstly in Victoria Street and in 1886 in Nelson Street, until 1901. The Nelson Street practice also had a 2 bed ward, called Mira Private Hospital ). Dr Edward Ryan was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1884-1902 . He also had occasions where he successfully performed veterinary surgery for the local farmers too. Dr Tom Ryan then purchased the practice from his brother in 1901. Both Dr Edward and Dr Tom Ryan work as surgeons included eye surgery. Dr Tom Ryan performed many of his operations in the Mira private hospital on his premises. He too was House Surgeon at the Nhill Hospital 1902-1926. Dr Tom Ryan had one of the only two pieces of radiology equipment in Victoria during his practicing years – The Royal Melbourne Hospital had the other one. Over the years Dr Tom Ryan gradually set up what was effectively a training school for country general-practitioner-surgeons. Each patient was carefully examined, including using the X-ray machine, and any surgery was discussed and planned with Dr Ryan’s assistants several days in advance. Dr Angus gained experience in using the X-ray machine there during his time as assistant to Dr Ryan. Dr Tom Ryan moved from Nhill in 1926. He became a Fellow of the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons in 1927, soon after its formation, a rare accolade for a doctor outside any of the major cities. He remained a bachelor and died suddenly on 7th Dec 1955, aged 91, at his home in Ararat. Scholarships and prizes are still awarded to medical students in the honour of Dr T.F. Ryan and his father, Dr Michael Ryan, and brother, John Patrick Ryan. ] When Dr Angus bought into the Nelson Street premises in Nhill he was also appointed as the Nhill Hospital’s Honorary House Surgeon 1933-1938. His practitioner’s plate from his Nhill surgery states “HOURS Daily, except Tuesdays, Fridays and Saturday afternoons, 9-10am, 2-4pm, 7-8pm. Sundays by appointment”. This plate is now mounted on the doorway to the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, Warrnambool. Dr Edward Ryan and Dr Tom Ryan had an extensive collection of historical medical equipment and materials spanning 1884-1926 and when Dr Angus took up practice in their old premises he obtained this collection, a large part of which is now on display at the Port Medical Office at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in Warrnambool. During his time in Nhill Dr Angus was involved in the merging of the Mira Hospital and Nhill Public Hospital into one public hospital and the property titles passed on to Nhill Hospital in 1939. In 1939 Dr Angus and his family moved to Warrnambool where he purchased “Birchwood,” the 1852 home and medical practice of Dr John Hunter Henderson, at 214 Koroit Street. (This property was sold in1965 to the State Government and is now the site of the Warrnambool Police Station. ). The Angus family was able to afford gardeners, cooks and maids; their home was a popular place for visiting dignitaries to stay whilst visiting Warrnambool. Dr Angus had his own silk worm farm at home in a Mulberry tree. His young daughter used his centrifuge for spinning the silk. Dr Angus was appointed on a part-time basis as Port Medical Officer (Health Officer) in Warrnambool and held this position until the 1940’s when the government no longer required the service of a Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool; he was thus Warrnambool’s last serving Port Medical Officer. (The duties of a Port Medical Officer were outlined by the Colonial Secretary on 21st June, 1839 under the terms of the Quarantine Act. Masters of immigrant ships arriving in port reported incidents of diseases, illness and death and the Port Medical Officer made a decision on whether the ship required Quarantine and for how long, in this way preventing contagious illness from spreading from new immigrants to the residents already in the colony.) Dr Angus was a member of the Australian Medical Association, for 35 years and surgeon at the Warrnambool Base Hospital 1939-1942, He served as a Surgeon Captain during WWII1942-45, in Ballarat, Victoria, and in Bonegilla, N.S.W., completing his service just before the end of the war due to suffering from a heart attack. During his convalescence he carved an intricate and ‘most artistic’ chess set from the material that dentures were made from. He then studied ophthalmology at the Royal Melbourne Eye and Ear Hospital and created cosmetically superior artificial eyes by pioneering using the intrascleral cartilage. Angus received accolades from the Ophthalmological Society of Australasia for this work. He returned to Warrnambool to commence practice as an ophthalmologist, pioneering in artificial eye improvements. He was Honorary Consultant Ophthalmologist to Warrnambool Base Hospital for 31 years. He made monthly visits to Portland as a visiting surgeon, to perform eye surgery. He represented the Victorian South-West subdivision of the Australian Medical Association as its secretary between 1949 and 1956 and as chairman from 1956 to 1958. In 1968 Dr Angus was elected member of Spain’s Barraquer Institute of Barcelona after his research work in Intrasclearal cartilage grafting, becoming one of the few Australian ophthalmologists to receive this honour, and in the following year presented his final paper on Living Intrasclearal Cartilage Implants at the Inaugural Meeting of the Australian College of Ophthalmologists in Melbourne In his personal life Dr Angus was a Presbyterian and treated Sunday as a Sabbath, a day of rest. He would visit 3 or 4 country patients on a Sunday, taking his children along ‘for the ride’ and to visit with him. Sunday evenings he would play the pianola and sing Scottish songs to his family. One of Dr Angus’ patients was Margaret MacKenzie, author of a book on local shipwrecks that she’d seen as an eye witness from the late 1880’s in Peterborough, Victoria. In the early 1950’s Dr Angus, painted a picture of a shipwreck for the cover jacket of Margaret’s book, Shipwrecks and More Shipwrecks. She was blind in later life and her daughter wrote the actual book for her. Dr Angus and his wife Gladys were very involved in Warrnambool’s society with a strong interest in civic affairs. Their interests included organisations such as Red Cross, Rostrum, Warrnambool and District Historical Society (founding members), Wine and Food Society, Steering Committee for Tertiary Education in Warrnambool, Local National Trust, Good Neighbour Council, Housing Commission Advisory Board, United Services Institute, Legion of Ex-Servicemen, Olympic Pool Committee, Food for Britain Organisation, Warrnambool Hospital, Anti-Cancer Council, Boys’ Club, Charitable Council, National Fitness Council and Air Raid Precautions Group. He was also a member of the Steam Preservation Society and derived much pleasure from a steam traction engine on his farm. He had an interest in people and the community He and his wife Gladys were both involved in the creation of Flagstaff Hill, including the layout of the gardens. After his death (28th March 1970) his family requested his practitioner’s plate, medical instruments and some personal belongings be displayed in the Port Medical Office surgery at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village, and be called the “W. R. Angus Collection”. The repair of open wounds is essential to prevent infection and death. The W.R. Angus Collection is significant for still being located at the site it is connected with, Doctor Angus being the last Port Medical Officer in Warrnambool. The collection of medical instruments and other equipment is culturally significant, being an historical example of medicine from late 19th to mid-20th century. Dr Angus assisted Dr Tom Ryan, a pioneer in the use of X-rays and in ocular surgery. Black tin with hinged lid, containing reels and packets of surgical silk, gut and metal suture threads, scalpel blades, chamois and metal blade holder with tensioned chamois piece across top. (W.R. Angus Collection)‘MEDRAFIL, Dr MULLER- MEERNACH, Nr O, MADE IN GERMANY.’ printed on one of the paper bags in the box containing a suture bobbin. 'PEARSALL'S LONDON' printed on some bobbins. 'J A DEKNATEL & SON INC, QUEENS VILLAGE, LONG ISLAND NEW YORK' printed on others.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, surgical silks and sutures, dr w r angus, medical equipment, surgical instrument, dr ryan, ophthalmology, s.s. largs bay, warrnambool base hospital, nhill base hospital, flying doctor, medical history, medical treatment, mira hospital, medical education, sutures, surgical silk -
 Hymettus Cottage & Garden Ballarat
Hymettus Cottage & Garden BallaratWork on paper - Horticultural award certificate, Ballarat Horticultural Society Amateur {Small Gardens) Class First Prize
non-fictionballarat, horticulture, art nouveau, ballarat horticultural society, pansies -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Photograph, South Warrnambool School, framed
The South Warrnambool Primary school No 1902 was opened in 1877 by the mayor at the time Cr J Cramond. The first teacher was Mrs Eliza Clarke. It catered for the children of the strong and closely knit community of South Warrnambool. The Mc Donald family was one of these families. A clear photograph of a school with which many past students would have fond memories. A contribution over 25 years to a primary school in this case by W D McDonald is a story of personal endeavour. It therefore has historical and social significance.Coloured photograph of the South Warrnambool State School framed with inscription written in black ink at bottom of coffee coloured mount.Presented to Mr W D McDonald by the residents of South Warrnambool as a token of appreciation for services rendered as a member of the School Committee (1912-1937) A Wilkins Photo. Stuart Mc Donald and Shirley written on back of frame mounting board.south warrnambool primary school, school number 1902, warrnambool history -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - VICTORIA HILL - THE RICH VICTORIA HILL AND IT'S HISTORICAL ASSOCIATION
Two copies of document : nineteen handwritten pages of notes on 'The Rich Victoria Hill and Its Historical Association' Signed by A Richardson and dated 30 - 8 - 1971. and a typed copy of same. Notes include: Introduction, Hotels, Mines, Mining History and descriptions of features where the signposts are. Mines mentioned in the text are: North Old Chum. Ballerstedt's first open cut, Lansell's Big 180. 20 head stamper, Lansell's Cleopatra Needle, Victoria Quartz Mine. Cleopatra's Needle was a square sectioned brick chimney with this four sided pyramidal chimney top with four vents to allow the smoke to escape whatever the direction of the wind. It was demolished in the 1950's as it had a bend in it and it was considered unsafe. Lansell had two other mines with similar chimneys, the '222' in Chum Street and his 'Sandhurst' or 'Needle' mine near the Bendigo, Eaglehawk boundary. Notes prepared by Albert Richardson.mine, gold, victoria hill, victoria hill, the rich victoria hill and it's historical association, j. n. macartney, quartz miner's arms hotel, ironbark methodist church, greek orthodox church, john brown knitwear factory, little 180 mine, geo lansell, conrad heinz, british & american hotel, victoria reef gold mining coy, manchester arms hotel, housing commission homes, ironbark (victoria reef gold mines, hercules and energetic, midway, wittscheibe, gt central victoria, wm rae, mr & mrs conroy, wm rae jr, central nell gwynne, moorhead's shop, gill family, gold mines hotel, david chaplin sterry, pioneer, new chum and victoria, burrowes and sterry, new chum and victoria tribute, rotary club of bendigo south, big 180, victoria quartz mines, jeweller's shop, bendigo and district tourist association, north old chum mine, john wybrandt, ballerstedt's first open-cut, j c t christopher ballerstedt, ballerstedt's mine, bendigo cemetry, lansell's 'cleopatra nedle' type chimney, 222 mine, sandhurst or 'needle' mine, victoria quartz mine, victoria reef quartz company, mr e j dunn, eureka ext'd, new chum railway, pearl, bendigo advertiser 16 june 1910, victoria consols, shamrock, shenandoah, victoria quartz dams, rae's open cut, prospecting tunnels, floyd's small 5 head crushing battery, gt central victoria (midway) shaft, midway no 2, midway north, ballerstedt's small 24 yard claim, the humboldt, the tribute coy, advance, luffsman and sterry's claim, a round shaft, chinese joss house, lansell's fortuna, p m g repeater station, a richardson -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
Sent to Mrs M MacDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia from V129537 ACI Gilbert A V Group 436 RAAF Flinders Island during World War 2 Victoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with coloured drawing of path leading to three mountains.top left corner - Air Mail/ACF in red star right top corner - postage stamp left side - AIF censor stamp right side - Mrs M Mac Donald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia rear - V129537 ACI Gilbert A V Group 436 RAAF Flinders Islandenvelope art, ww2, aci gilbert a v -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
One of a series of illustrated envelopes which once contained letters drawn by a soldier/s and sent to Mrs MacDonald of 32 Grey Street Wangaratta.Victoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with drawing of war scene - cannon in front of hut and palm trees, ambulance in centre and bomb exploding below aircraft in sky.Top left - AIR MAIL Top right - postage stamp Left side - AIF Censor stamp Right side Mrs M MacDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia ww2, envelope art -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
Envelope Art made during WW2 Victoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with coloured picture of sun setting over water with palm trees in foregroundTop left - ACF in red star / AIR MAIL Top right - postage stamp Right side Mrs M MacDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australiaenvelope art, ww2 -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
Sent to Mrs MacDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta by soldier during second world war.Victoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with hand drawn scroll with stick figure either side Top left - AIR MAIL Top right - postage stamp Left side - AIF Censor stamp Right side Mrs M MacDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australiaww2, envelope art -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchWork on paper - Envelope Art
One of several illustrated envelopes, without letter, sketched by soldier/s during the second world war and sent to Mrs MacDonald of WangarattaVictoria's 2/24th Infantry Battalion was raised in Wangaratta in July 1940. They were welcomed with open arms by the local community as they rapidly built up their numbers. The people of Wangaratta adopted the Battalion and they became known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. Many of the soldiers maintained life long friendships with the people of Wangaratta. Even though the Battation was disbanded in 1946 members and their families return each year, in November, for a commemorative service at the 2/24th Battalion Memorial Wall at the Wangaratta Cemetery.Cream paper envelope with coloured sketch of soldier running away from aircraft dropping bombs. Box and bottles in foreground.Top left - AIR MAIL Top right - postage stamp Left side - AIF Censor stamp Right side Mrs M MacDonald "Monald" 32 Grey Street Wangaratta Victoria Australia Bottom left- "Fair Dinkum Wouldn't it!" Box - "Jungle Juice 100% OP' ww2, envelope art
