Showing 3147 items matching "any"
-
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photo, Former Oddfellows Hall, Albert Street, Ballarat, 2004, 2004
"MR JOHN WHYKES AT THE ODD FELLOWS’ HALL. Mr John Whykes addressed an enthusi astic meeting of the ratepayers of the South Ward last evening, at the Oddfellows’ Hall, Albert street. Mr C. A. Welch was voted to the chair. The candidate, who was well received, explained his views on municipal matters. His remarks were received with favor, and were frequently applauded. Several questions were put and answered to the satisfaction of the meeting. A vote of cofidencc was passed, on the motion of Mr A. Reynolds, seconded by Mr Bromley. The meeting terminated with a vote of thanks to the chair. To-night Mr Whykes will not address any meeting, being desirous of meeting the central committee, but tomorrow evening will address the ratepayers at half-past 8, at All Saints’ schoolroom, Drummond street.(Ballarat Star, 04 August 1887) The hall was demolished 2004-5.Six colour photographs of a weatherboard hall at 125 Albert Street, Ballarat. The hall was demolished soon after the photographs were taken.albert street ballarat, oddfellows hall, oddfellows' hall -
 Otway Districts Historical Society
Otway Districts Historical SocietyPoster, Colac Herald, Otway Ratepayers' Poll Flyer, 1963, 1963
On 15 January 1964 the Shire of Otway was going to poll its ratepayers about a loan required to build temporary municipal workshops and a Shire Engineer's office in the Apollo Bay Riding. This led to a number of objections at public meetings in the west and central ridings, such that a Committee of protest was formed, with a nominated Chairman, Secretary and members, to put to ratepayers their considered point-of-view of disapproval. After drafts the Committee produced a printed flyer for distribution to ratepayers summarising the Committee's position. The Committee knew and agreed with a Council Sub-Committee's recommendation to Council of a new, adequate building on one site of suitable size. However, this did not happen. Instead Council moved for loans for temporary renovations of existing buildings. This the Committee objected to believing that Council must decide on a final location before any consideration is given to borrowing money for temporary repairs. This was the opinion the Committee put to ratepayers.B/W Flyer. Otway Ratepayers' Poll on January 15. This concerns YOU. To the Ratepayer as addressed. Details on Ballot Paper.ratepayers; shire of otway; -
 Bayside Gallery - Bayside City Council Art & Heritage Collection
Bayside Gallery - Bayside City Council Art & Heritage CollectionWork on paper - watercolour, John C. Paul, St. Andrew's Brighton, 1971
St Andrew’s Anglican Church, located at 228 New St, Brighton, is the oldest continuous Anglican Church in Victoria. Opened on St Andrews day in 1842, it was one of the earliest Christian churches established in the Port Phillip District. A second church building was erected on the site in 1851, followed by a third building and schoolhouse in 1857 which was enlarged in 1886. A fire in 1961 engulfed the building and renowned Australian church architect Louis Williams was appointed to be the architect of the new building. The present church complex is amongst the largest church buildings in Australasia. Using over 500,000 bricks and over 16,000 roof tiles, this space consisted of three areas: the main church building, the Pioneer chapel and the Lady chapel. The large arcaded cloister, seen in this painting, with an internal cloister garden, is extremely rare in any church in Australasia, and links the Pioneer Chapel to the narthex of the new building.John C. Paul, St. Andrew's Brighton 1971, watercolour, 44 x 30.5 cm. Bayside City Council Art and Heritage Collection. Purchased 1974.brighton, john c paul, st andrews, church, anglican, cloister, arcade -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaAdministrative record - Text, RVIB Geelong Auxiliary papers, 1933 - [1998?]
The Geelong RVIB Auxiliary was formed on February 13, 1933 by Mr Birtchnell. This collection of papers includes the minute books from 1944 until 1998. It was noted in correspondence that Geelong and surrounds had been the most outstanding financial contributor to RVIB's revenue. Collections from the Geelong community had provided high donations every year. The Geelong Auxiliary posted 301 pounds on their first return in 1934, easily topping any of the other 200 auxiliaries in the state at that time. The Annual Report from July 31, 1995 noted that with regret due to health reasons and the passing of many members The Geelong RVIB Auxiliary had no option but to go into recess. The certificate reads: Centenary Certificate of Appreciation presented to Geelong Auxiliary for outstanding service. Royal Victorian Institute for the Blind babies, children and adults. (Signed by) President (Charles Bennett) Executive Director (F.G. Turley).5 minute books -- 2 accounts books -- 1 book of newspaper clippings --various loose papers and letters -- 1 certificate of appreciation Certificate: white paper with light turquoise thick border and gold and blue thin borders. The RVIB official seal is at the base of the right hand side and a coloured image of the RVIB logo, with the words 'Centenary year 100 1866/1966' in the bottom left corner.royal victorian institute for the blind, auxiliaries -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaDecorative object - Object, Presentation envelope from Takeo Iwahashi Award, 1988
Takeo Iwahashi was the founder of the Nippon Lighhouse for the Blind in Japan. He made an enormous contribution to the lives and progress of blind people around the world, and was a great friend of Helen Keller. The annual Takeo Iwahashi Award was founded in his memory and is awarded to a "worker for the blind whose contribution to work for the blind in the fields of education, training, rehabilitation, placement, prevention and cure of blindness, administration of services for the welfare of the blind or any other program related to the welfare of the blind has been outstanding." Hugh Jeffrey won this award in 1988. This intricate and delicate presentation envelope is made from a heavy guage paper/fabric blend. It features a small addition of origami on the front, as well as Japanese calligraphy and a gold and silver knotted ribbon holding it closed. Originally the envelope unfolded to a large size with a red liner, and contained the Award certificate and cheque for the prize money.Handmade paper envelope with red edging and gold and silver ribbonshugh jeffrey, awards -
 City of Greater Bendigo - Civic Collection
City of Greater Bendigo - Civic CollectionEquipment - Y2K Hard drive, Australian Government, 1999
Y2K / the year 2000 / The millennium bug / was commonly used to refer to a widespread computer programming shortcut that was expected to cause extensive havoc as the year changed from 1999 to 2000. Instead of allowing four digits for the year, many computer programs only allowed two digits (e.g., 99 instead of 1999). As a result, there was immense panic that computers would be unable to operate at the turn of the millennium when the date descended from "99" to "00". The Bug presented a formidable challenge to the problem-solving skills of local government officials. Lacking a cure-all that will work for every municipality, local officials must develop their own solutions to meet their community's unique needs. At the same time, the Y2K bug provided a once-in-a-millennium leadership opportunity for local officials who understood that they are the key to preparing their communities for any issues.Hard drive mounted in an alaminium case with glass window front and back.Presented to Greater Bendigo City Council / by Hon, Roger Hallam. MLC / Minister for Finance / and / Hon, Robert Maclellan. MLA / Minister for Planning and Local Government / on 21 June. 1999 / In recognition of being the first Victorian Council / to be Y2k compliantmillennium bug -
 Melbourne Legacy
Melbourne LegacyDocument - Minutes, Minutes of Meeting of Board of Management (H49)
Records an extended Board Meeting which took place from 7.30-11.30 p.m on Thursday 16 July 1928 at the office of the Hon Sec in Collins Street , adjourning until 1.00-8.15 pm on Monday 20 August 1928 at the Alcazar Cafe, and then from 1.00-2.15 pm on Wednesday 22 August 1928, also at the Alcazar Cafe. No mention is made of any meals, but it can be assumed that such a long meeting included both food and drink. 56 items were discussed including membership, Junior Legatee activities and supervision, non-attendance by rostered Legatees and conference matters. Mention was made of the stewardship of the Club origin and history; unfortunately despite this promising start much has been lost over the years since. After this epic meeting, the next one was scheduled for 13 September, 1928.Not only do the minutes record the work done by Legacy in the early days, but illustrates the different style of governance in more leisurely times.White foolscap copy sheets x 8 pages of a board of management meeting"H49" (see Item 00937) in blue ballpoint.board of management, founding legatee -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaFunctional object - Object, Cane basket with handle
Basket weaving and brush making was a source of income for those who worked in the workshops at RVIB and other institutions in New South Wales and Queensland. A diverse range products could be produced with cane, such as cane chairs, cots, washing baskets and trolleys, and the Institution sought to highlight these in the annual report. Over time the demand for, and supply of, cane changed - particularly during World War 2 when Asian sources were under attack or destroyed. At home, other materials such as plastics as well as the ability to import cheaper pre-produced products further reduced the demand for workshop pieces. Generic style basket that would have been used for shopping or any household task requiring movement of multiple items. Cane baskets were the original green alternative to plastic shopping bags. Note that the handle is deliberately askew, for easier carrying against the hip.1 cane basket with askew handleemployment, royal victorian institute for the blind -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Wood Sample, Before 1878
On a piece of paper subsequently glued near one end of its curved upper face, this length of planed and polished hardwood timber bears the inscription: “A [p]iece of w[r]ec[k] of the Loch Ard wrecked near Sherbroke River”. The timber is carefully worked with rich dark colouring and a uniformly moulded design, suggesting that it was part of a fitting or furnishing that was publicly visible and prominent. If the artefact is what it is declared to be, then it is possible that it formed part of the ship’s railings or companionway stairs. The LOCH ARD was a 1,693 ton, 3 masted barque, built on the Clyde in 1873. In an age of increasing competition for the emigrant passenger trade from steam-driven vessels, special attention was paid to her wooden furnishings and fittings. The Loch Line owners prided themselves on their attractive, distinctively painted, sailing ships. Below decks, where cargo and third class passengers were stowed, was made of iron. But everything above deck, and on show to the saloon and second class passengers, was carved and varnished timber. Captain Daish’s 1878 report for the ship’s underwriters notes “a quantity of general Cargo washed up in a confused mass” in the cove and “a number of Cases, Casks and Bales; also deals and boards floating about in some of the gorges” further west of the shipwreck. Contemporary newspaper accounts also reported a large quantity of cargo and timber washed ashore in the days following the LOCH ARD shipwreck, adding “but those were speedily removed by persons who came down from Port Campbell, Scott’s Creek and other places with carts and pack horses”. The appearance and good condition of this wood artefact, and the aged patina and dated hand-writing style of its pasted on inscription, support the suggestion that it was ‘souvenired’ from the floating debris of the LOCH ARD at or near the 1878 date of its foundering off Mutton Bird Island. HISTORY OF THE LOCH ARD The LOCH ARD belonged to the famous Loch Line which sailed many ships from England to Australia. Built in Glasgow by Barclay, Curdle and Co. in 1873, the LOCH ARD was a three-masted square rigged iron sailing ship. The ship measured 262ft 7" (79.87m) in length, 38ft (11.58m) in width, 23ft (7m) in depth and had a gross tonnage of 1693 tons. The LOCH ARD's main mast measured a massive 150ft (45.7m) in height. LOCH ARD made three trips to Australia and one trip to Calcutta before its final voyage. LOCH ARD left England on March 2, 1878, under the command of Captain Gibbs, a newly married, 29 year old. She was bound for Melbourne with a crew of 37, plus 17 passengers and a load of cargo. The general cargo reflected the affluence of Melbourne at the time. On board were straw hats, umbrella, perfumes, clay pipes, pianos, clocks, confectionary, linen and candles, as well as a heavier load of railway irons, cement, lead and copper. There were items included that intended for display in the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. The voyage to Port Phillip was long but uneventful. At 3am on June 1, 1878, Captain Gibbs was expecting to see land and the passengers were becoming excited as they prepared to view their new homeland in the early morning. But LOCH ARD was running into a fog which greatly reduced visibility. Captain Gibbs was becoming anxious as there was no sign of land or the Cape Otway lighthouse. At 4am the fog lifted. A man aloft announced that he could see breakers. The sheer cliffs of Victoria's west coast came into view, and Captain Gibbs realised that the ship was much closer to them than expected. He ordered as much sail to be set as time would permit and then attempted to steer the vessel out to sea. On coming head on into the wind, the ship lost momentum, the sails fell limp and LOCH ARD's bow swung back. Gibbs then ordered the anchors to be released in an attempt to hold its position. The anchors sank some 50 fathoms - but did not hold. By this time LOCH ARD was among the breakers and the tall cliffs of Mutton Bird Island rose behind the ship. Just half a mile from the coast, the ship's bow was suddenly pulled around by the anchor. The captain tried to tack out to sea, but the ship struck a reef at the base of Mutton Bird Island, near Port Campbell. Waves broke over the ship and the top deck was loosened from the hull. The masts and rigging came crashing down knocking passengers and crew overboard. When a lifeboat was finally launched, it crashed into the side of LOCH ARD and capsized. Tom Pearce, who had launched the boat, managed to cling to its overturned hull and shelter beneath it. He drifted out to sea and then on the flood tide came into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. He swam to shore, bruised and dazed, and found a cave in which to shelter. Some of the crew stayed below deck to shelter from the falling rigging but drowned when the ship slipped off the reef into deeper water. Eva Carmichael had raced onto deck to find out what was happening only to be confronted by towering cliffs looming above the stricken ship. In all the chaos, Captain Gibbs grabbed Eva and said, "If you are saved Eva, let my dear wife know that I died like a sailor". That was the last Eva Carmichael saw of the captain. She was swept off the ship by a huge wave. Eva saw Tom Pearce on a small rocky beach and yelled to attract his attention. He dived in and swam to the exhausted woman and dragged her to shore. He took her to the cave and broke open case of brandy which had washed up on the beach. He opened a bottle to revive the unconscious woman. A few hours later Tom scaled a cliff in search of help. He followed hoof prints and came by chance upon two men from nearby Glenample Station three and a half miles away. In a state of exhaustion, he told the men of the tragedy. Tom returned to the gorge while the two men rode back to the station to get help. By the time they reached LOCH ARD Gorge, it was cold and dark. The two shipwreck survivors were taken to Glenample Station to recover. Eva stayed at the station for six weeks before returning to Ireland, this time by steamship. In Melbourne, Tom Pearce received a hero's welcome. He was presented with the first gold medal of the Royal Humane Society of Victoria and a £1000 cheque from the Victorian Government. Concerts were performed to honour the young man's bravery and to raise money for those who lost family in the LOCH ARD disaster. Of the 54 crew members and passengers on board, only two survived: the apprentice, Tom Pearce and the young woman passenger, Eva Carmichael, who lost all of her family in the tragedy. Ten days after the LOCH ARD tragedy, salvage rights to the wreck were sold at auction for £2,120. Cargo valued at £3,000 was salvaged and placed on the beach, but most washed back into the sea when another storm developed. The wreck of LOCH ARD still lies at the base of Mutton Bird Island. Much of the cargo has now been salvaged and some was washed up into what is now known as LOCH ARD Gorge. Cargo and artefacts have also been illegally salvaged over many years before protective legislation was introduced. One of the most unlikely pieces of cargo to have survived the shipwreck was a Minton porcelain peacock - one of only nine in the world. The peacock was destined for the Melbourne International Exhibition in 1880. It had been well packed, which gave it adequate protection during the violent storm. Today, the Minton peacock can be seen at the Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum in Warrnambool. From Australia's most dramatic shipwreck it has now become Australia's most valuable shipwreck artefact and is one of very few 'objects' on the Victorian State Heritage Register. The Loch Ard wreck is of state significance – Victorian Heritage Register S417. However there is a lack of documented provenance that limits the interpretive value of this piece of timber (for example, its potential to interpret nineteenth century souveniring and scavenging from shipwrecks along the south west coast of Victoria). Flagstaff Hill’s collection of artefacts from LOCH ARD is significant for being one of the largest collections of artefacts from this shipwreck in Victoria. It is significant for its association with the shipwreck, which is on the Victorian Heritage Register (VHR S417). The collection is significant because of the relationship between the objects, as together they have a high potential to interpret the story of the LOCH ARD. The LOCH ARD collection is archaeologically significant as the remains of a large international passenger and cargo ship. The LOCH ARD collection is historically significant for representing aspects of Victoria’s shipping history and its potential to interpret sub-theme 1.5 of Victoria’s Framework of Historical Themes (living with natural processes). The collection is also historically significant for its association with the LOCH ARD, which was one of the worst and best known shipwrecks in Victoria’s history. A length of hardwood timber, planed and varnished to smooth finish on three sides, with two unfinished tongues protruding from each end (one broken off), possibly from the wreck of the LOCH ARD. The front or upper face is moulded and routed to a regular, linear (skirting board type) design along its entire length, the two sides flat planed. One side contains two inserted dowel rods that have been broken off. The bottom face has not been finished to the same standard. The sample is good quality wood that has retained its density and weight and shows no evidence of having been submerged in seawater for any length of time. Glued on to the upper face of the length of timber near the right hand end is a deteriorated square of paper bearing an inscription. The paper, peeling back and with torn edges, is stuck over an original wood stain but under a subsequent layer of varnish. The faded ink words are indecipherable where paper is missing, but written carefully in an old fashioned cursive script.The inscription on the paper reads: “A [p]iece of w[r]ec[k] of the Loch Ard wrecked near Sherbroke River”. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, nineteenth-century souveniring, shipwreck scavenging, loch line sailing ships, wood sample -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Postcard - PETHARD COLLECTION: F. LISZT POSTCARD
Black and white photo: Head and shoulders image of F. Liszt He is wearing a three piece suit, waistcoat buttoned up to neck, stiff white collar. Long white hair, profile image. Generic letter from F. Liszt is printed on rear of postcard. The letter reads; mason & Hamlin Co. Boston - Letter from Franz Liszt to Mason & Hamlin Co.. Highly esteemed Sirs; - What a magnificent organ for which I have to thank you! It is a marvel, and really praiseworthy! Even players of moderate ability will be able to create much admiration in its use. I shall have this summer, in all probability, a call from Dr. Naumann, of Jena, Walter Bache, of London, and St. Saens, who, in my opinion, is the most eminent and greatest master of the organ. I shall not fail to induce these artists to become acquainted with your instrument. There need not be any fear of its being misused; it will remain closed to the ordinary player. Accept, dear sirs, the sentiment of my deep esteem and gratitude. Weimer, June 12, 1883. F. Liszt.Mason & Hamlin Co., Bostonperson, individual, f. liszt, sandhurst, bendigo, pethard, f. liszt -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumNewspaper, State Electricity Commission of Victoria (SEC) and The Courier Ballarat, SEC Spring Song, Feb. 1962
Yields information about the views of various letter writers, views of the Courier, union views, rehabilitation costs and employment.Foolscap sheet of plain paper, with rounded corners, with 4 newspaper cuttings, concerning the mooted closure of the Ballarat Tram system 28 Feb and 2 March 1962. All from The Courier, unless noted otherwise. 1 - "SEC Spring Song" - 23/2/62 - Editorial - about the SEC actions to desert Ballarat, Council meeting with Parliamentary representatives, cost of new cars and always a second-hand place. 2 - "Tramways" - 24-2-62 - letter by R. Courtney, Union Secretary, re use of new trams, one-man cars and Mr. Mawby's jet propelled buses. 2nd letter, written by a car driver, lamenting the closure, employment of trammies and SEC 3 - Untitled article - 27/2/62 - cost of rehabilitating the system given compared to buses, cost estimate from TRB, concessions (not to Pensioners), bus routes in Geelong, people preferred any replacement bus service to be run by a public authority. 4 - "Tram Employees" - 24-2-1962 - SEC would find alternative employment for the displaced tramway workers.closure, letter to the editor, editorial, sec, rehabilitation, staff, buses, concession fares -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumBook, Committee of the Ballarat Tramways and SEC Benefit Fund, "The Objects, Rules and Regulations of 'The Ballarat Tramways and SEC Benefit Fund.'", 1963
Yields information about a social welfare or friendly society part of the Ballarat Tramways - group who looked after their fellow workers through contributions. Gives the rules of the 'The Ballarat Tramways and SEC Benefit Fund'Sixteen page with light brown light weight card covers, centre stapled book titled "The Objects, Rules and Regulations of 'The Ballarat Tramways and SEC Benefit Fund." Details the committee, that it was approved by the Department of Social Services, name, objects, constitution, trustees, executive, collectors, meeting of members, members qualifications, benefits (in pounds), claims, unfinancial members, payment of claims, the Secretary, alteration to constitution and Order of business. Note the membership allowed for any SEC employee in the district. President J. Tucker Secretary and Treasurer - W. Cross Vice President L.Hoare and H. Gilbert Committee - R. Parrot, P.Egan, V.McCartin, B. Browne, S. Stevenson, T. Tonkin, J.Megee. Later version of Reg Item 3658, benefits similar, but contribution 1/6 - instead of 1/- per week. Noted on page 1 as being revised on 29/6/1963. Additional copy added 6/8/2016 from donation of T. Jeffreys. See also Reg Item 7134 for another version. Full scan of document added as a pdf file 5/6/2019.On front cover in ink "H.Knight", copy 2 - On top right hand corner of cover "A. Jeffreys" in blue ink.trams, tramways, social welfare, sickness, sec, ballarat -
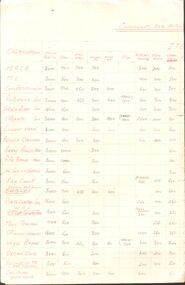 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - MERLE HALL COLLECTION: COMMUNITY ARTS CENTRE SPACE REQUIREMENTS
Community Arts Centre - a. Space Requirements: 'Spreadsheet' - single page ruled up with horizontal rows listing 21 Bendigo arts organizations and vertical columns inserting 20 varied space requirements (e.g. main auditorium; stage; back stage; wings; etc) + Total space requirement for each organization. No date or author provided; b. Same 'spreadsheet' but specified as space in square feet. Attached is a handwritten note (no stated author) entitled ''Plaza Proposal'' (19/1/77) stating that the schedule is for the area requirements of local groups with information as to spending money of architectural surveys of existing buildings and time constraints on putting forward any proposition. List of Community Arts organisations; M.A.S.B.,M.L., Competitions society, Repertory society, Shakespeare Society, Operatic Society, concert Orchestra, Benola Choristers, Brass Bands Association, Pipe Bands Association, Victorian Society of Organ's, Film Group, Bendigo Arts Council, Photographic Society, W.E.L., Music Teachers, Spinners & Weavers, Wyse Players, Organ Club, Friends of the Art Gallery, California Gully Youth Club. -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumFunctional Object - Ticket Wallet with 9 blocks of tickets, State Electricity Commission of Victoria (SECV), late 1960's
Demonstrates the method of dispensing tickets by conductors, how the tickets could be arranged, although the arrangement may not exactly represent the 1958-1963 arrangements of a ticket wallet. Yields information about the style and printing of tickets used in Ballarat and Bendigo tramways and how they were presented. Has a strong association with Travis Jeffery.Ticket wallet with a set of nine 1950-60's Ballarat tram tickets set up to represent a typical conductor's set of tickets by Travis Jeffrey, though these may not exactly line up with the fares at any one period - 1958 to 1963 following the introduction of concession tickets. Does not have a 3d City Section Ticket. 4000 - Sheet of leather, approx. 2mm thick, stained brown with four pockets formed on each side with another sheet of leather, stitched on all sides to form pockets to hold eight blocks of tickets. Stitching is a light cream or white colour cotton. The stitching on one side that forms the pockets has been removed, possibly by Travis, to present the tickets. 3992 - 7d black 3993 - 6d teal 3994 - 5d green 3995 - 4d brown 3996 - 4d Parcel check 3997 - 2d Red 3998 - 3d orange 3999 - 2d concession - red 4001 - 3d concession - orange 4002 - 2d City Section - red See Alan Bradley's notes "Fares in Ballarat"trams, tramways, secv, tickets, conductors -
 Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub Branch
Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub BranchEmergency Ration Tin, WWII era
VX 27898 Corporal Thomas John Morris Thomas (Tom Thomas) donated several items to Cranbourne RSL. He served in the Australian Corp Signals in WWII both in Australia and overseas. He was born at Womerah on 9/11/1906 and died at Koo Wee Rup 16/06/1984. He enlisted at Yarram on 1/7/1940 and was discharged at Royal Park on 9/3/1945.Rectangular painted metal tin for holding emergency rations. Green paint with canvas tape along sides. Hinged lid. Silver inside.Lid: "MADE IN AUSTRALIA / EMERGENCY RATION / To be consumed only when no other rations of any kind are procurable. Consumption of this ration must be reported at first opportunity. / Instructions for use are printed INSIDE the lid. / KEEP PACK INTACT / D (ARROW) D" Inside lid: ' INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE / FRUIT RATION & MILK TABLETS: / To be consumed as found. / MEAT & VEG. RATION: / 1. May be eaten as packed / 2. A more palatable meal results by cooking in orheating with four times its bulk of boiling water. / 3. Moistened with water it can be fried as a Rissole without added fat."ration tin, emergency rations, rissole, fruit ration, veg ration, milk tablets -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - PETER ELLIS COLLECTION: LETTER TO PETER ELLIS
Letter written to Peter Ellis from Stephen Brady Official Secretary to the Governor-General and Secretary of the Order of Australia. Dated 4 October 2011. Honours-in-Confidence. Mr Peter Nicolaus Ellis 5 Flora Lane Flora Hill Vic 3550. Dear Mr Ellis I am writing on behalf of the Governor-General to inform you that you are being considered for the award of the Medal of the Order of Australia in the General Division within the Australian Honours System. The Order of Australia is the pre-eminent means by which Australia recognises the outstanding and meritorious service of its citizens. Awards are publicly announced on Australia Day and The Queen's Birthday. It is proposed that your award be announced in the Australia Day Honours List on Thursday 26 January 2012, and the proposed citation for the honour would be: 'For service to the arts through the collection and preservation of Australian folk history and heritage'. Please find enclosed an acceptance and privacy form and information concerning your award, which is intended for release to the media. If you wish to accept the proposed award, please complete and sign both sides of the form and return it to me in the envelope provided, together with any amendments you may suggest regarding the media information. I need to receive your reply by 22 October 2011 please. If you feel unable to accept the proposed award, I ask that you please confirm this in writing. After the Governor-General has considered all the proposed awards, I shall advise you of the outcome prior to the announcement date. Finally, I ask that you keep the contents of this letter strictly confidential until you receive confirmation of the honour, and the subsequent announcement of the award is made in the Commonwealth of Australia Gazette. In the event that you decline the award, I would ask that you maintain the confidential status of the proposal. If you have any queries please contact the Australian Honours Secretariat on 02 6283 3604. Yours sincerely Stephen Brady Official Secretary to the Governor-General and Secretary of the Order of Australia. Government House Canberra, ACT 2600 Australia telephone (02) 6283 3533 Facsimile (02) 62833620 Email [email protected] Honours-in-confidenceperson, individual, peter ellis oam -
 4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History Room
4th/19th Prince of Wales's Light Horse Regiment Unit History RoomPhotograph, Sydney Whillams, Silver Trophies, Est mid 20th Century
Lloyd Lindsay Competition In 1873 Colonel Loyd Lindsay introduced a prize for mounted riflemen. The initial experimental competition was a great success and it was for many years a feature of the various shooting programs. The conditions in 1873 required that sections of four mounted men were to ride about three quarters of a mile, taking two flights of hurdles in the course, and were, while dismounted and their horses either linked or held by alternate files, each to fire five shots at 200 yards standing, and the same number at 400 yards in any position. There was a time limit of twelve minutes, and the rifle, of any Government pattern, had to be carried on the back or slung to the saddle. 13TH GIPPSLAND LIGHT HORSE HANDSOME TROPHIES ON VIEW Thery are on view in the window of Mr. A. W. Bennett, Jeweller, some handsome trophies which were pre sented to the 13th (Gippsland) Light Horse, and which are worthy of the admiration they have elicited. A handsome pair of solid silver candal abra, presented to the officers mess of the Regiment by Mrs. Norman Mc Lean in memory of her husband, the late Lieut. Norman McLean, who for many years was a member of the re giment, are a fine piece of workman ship and valued at £200. The silver cup donated by the same lady for competition amongst the Regimental troops, is also very handsome. The late* Hon. .William - Pearson, M.L.C., who was Honorary Colonel of the 13th (Gippsland) Light Horse Re giment, presented a handsome silver cup. for competition amongst the' troops of the 'regiment, Iand teams will compete 'for it annually at the camp of continuous training. The ar ray of trophies is a most interesting one. Gippsland Times 19 Jan 1925 HUTTON SHIELD Stratford Troop Beaten After winning the Hutton Shield for four years in succession, the Stratford Troop of the 13th. (Gipps land) Light Horse was defeated in this year's competition last week, Scottsdale Troop (Tasmania) beating Stratford by 17 points. Gippsland Times 22 May 1933 Black & white photo of 17 silver Light Horse trophies on a British flag draped display stand. Trophies include: Lloyd Lindsay Competition for best section & lance and sword events, Foster Cup for best troop in Australia, Machine Gun Troop, Pearson Cup, Digger Trophy for best Regiment in Australia, McClean Cup and donated candelabra, Hutton Shield for best Light Horse Troop in Australia, Brigade Cup for sports in annual camp.Sydney Whillams. Sketch on back identifying objectslight horse, trophies, photo -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumBottle, glass, Post 1916 - c.1939
TROVE : Port Philip Gazette and Settler's Journal (Vic. : 1845 - 1850) Saturday 21 April 1849 p 3 Advertising 'On MONDAY, 23RD INSTANT, (WITHOUT RESERVE,) at 12 o'clock, AN INVOICE of Drawings, Prints, Crayons, Portraits, coloured Figures II M. Ships '"Vindictive," "Victory," "Pomona," ''Vanguard," " Carysfoot," " Magicienne," &c., coloured ; the Channel Fleet, Jenny Lind, and a large quantity of Engravings. Three hundred volumes Books, comprising Novels, History, Poetry, School Books, &c., &c., &c. A large quantity of assorted stationery consisting of boxes of India rubber bands, pens, show cases, fancy wafers, satin note paper. One cask Stephen's Fluid Ink, in pints and half-pints. Terms— Cash'. TROVE : The Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 - 1957) Tuesday 27 March 1956 p 2 Advertising 'PUBLIC NOTICE TO BOTTLERS, BOTTLE DEALERS. Etc., RE PROPERTY BRANDED BOTTLES WHICH ARE NOT SOLD The undermentioned Firms and Companies,' carrying on businesses at Sydney and elsewhere, HEREBY GIVE NOTICE that all Bottles delivered by them to their customers having: a notification moulded thereon (including bottom) that they are, or remain the property of. the Firms and Companies mentioned below ARE NOT SOLD WITH THE CONTENTS THEREOF BUT REMAIN THE PROPERTY OF SUCH FIRMS AND COMPANIES. Such Bottles are loaned solely for the purpose of enabling the contents to be delivered to purchasers from the said Firms and 'Companies and to all subsequent purchasers of the contents. As soon as the Bottles are emptied of their contents they must not be refilled destroyed, damaged, or used again for any purpose, but must, on demand be delivered up to the Companies or Firms whose names are moulded thereon or to their Accredited Agents: BUTLER & NORMAN PTY. LTD., MANDIBLE STREET. ALEXANDRIA, N.S.W. The remuneration received by Collectors, Dealers, etc.,- is simply an allowance for the safe custody and collection of the Bottles LEGAL ACTION WILL BE TAKEN AGAINST ANY PERSON OR COMPANY VIOLATING THE PROPERTY RIGHTS OF THESE FIRMS OR COMPANIES' BRANDED BOTTLES. ABC Mop Co.......................Stephens Ink (Australia) Pty Ltd.......................'.Squat round clear glass ink bottle with embossed text on heel at base and monogram on base'PROPERTY OF STEPHENS INKS AUSTRALIA LTD' on heel of base. Austrralian Glass Manufacturers monogram on base with embossed illustration of a feather quill.ink bottle -
 Coal Creek Community Park & Museum
Coal Creek Community Park & MuseumBottle, glass, c. 1859 - c.1941
TROVE : Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 - 1957), Monday 17 January 1859, page 7 TO the PHYSICIANS of AUSTRALIA -WOLFE'S SCHIEDAM AROMATIC SCHNAPPS, A superlative Tonic, Diuretlc, Anti-Dyspepsic and invi-gorating Cordial,-This medical diet-drink is manufactured soley by the proprietor at his distillery, in Schiedam, in Holland, expressly for medicinal purposes. It Is the pure tincture of junlper, distilled from the best barley that can be selected in Europe at any cost. It is flavored and medicated, not by the common harsh berry, but by the choice botanical variety of tho aromatic Italian juniper berry, whose more vinous ex-tract is distilled and rectified with its spirituous sol-vent. and thus it becomes a concentrated tincture of exquisite flavor and aroma, altogether transcendant in Its cordial and medicinal properties to any alcoholic stimulant now in use In the world. It has been submitted to all the first chemists and physicians in the United States, who endorse it over their own signatures as one of tho great essentials of the materia medica. It is now proscribed with great success In gravel, grout, rheumatism, obstruction of the bladder and kidneys, dyspepsia, whether acute or chronic, in general debility, sluggish circulation of the blood, inadequate assimilation of food, and exhausted energy, are acknowledged by the whole medical faculty and attested in their highest written authorities. Put up in quart and pint bottles, enveloped In yellow paper, with tho proprietor's name on tho bottle-, cork, and label. For sale by all the respectable druggists and merchants. UDOLPHO WOLFE WILKINSON BROTHERS and Co., sole agents for Australia. Depots at Melbourne and Sydney. TROVE : Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 - 1954), Wednesday 19 November 1941, page 4 WOLFE'S Aromatic SCHNAPPS Wolfe's Schnapps is now distilled in Australia from the original formula of Udolpho Wolfe. It remains, as before, a beverage of unique medicinal properties — Appetising, Re-freshing, , Stimulat-ing — as good for women as for men. -Wolfe's 'Schnapps for j your health's sake FOR VICTORY-buy War Bonds Now . W.B.157.13 Olive green glass bottle, square in section, slightly tapering toward the base, text embossed on three sides, circular ring embossed in shallow pontil shaped impression on base.Side 1 : UDOLPHO WOLFE'S'. Side 2 : 'SCHIEDAM'. Side 3 : 'AROMATIC SCHNAPPS'.schnapps, schiedam, gin -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayFunctional object - Billabong Ram Pump Size #5, Unknown
Pump - Billabong Ram Pump Size #5 Based on available historical data, the Australian-made Billabong Hydraulic Ram is one of the oldest rams produced anywhere in the world The Billabong Hydraulic Ram was first introduced into Australia in 1855 by John Danks and Son Limited, John Danks & Son Pty Ltd began as a plumbing business in 1859, established by brothers John and Samuel. It occupied a prominent site in Bourke Street, Melbourne, for 100 years. The business quickly grew to include factories in Melbourne and Sydney which manufactured and supplied a variety of plumbing and engineering products such as brassware, pumps, windmills and bells. The company was registered in Victoria on 25 January 1889 to continue the hardware manufacturing and supply business founded by brothers John and Samuel Danks in 1859. The head office was based in Bourke Street, Melbourne while another branch was established in Sydney in the 1880s. The company had factories in Melbourne and Sydney. The John Danks and Son Limited catalogue published in 1890, listing Billabong Hydraulic Rams as one of its major machinery products. The catalogue also provides reference to the company’s ram experience and manufacture, beginning by stating that in 1890 they already had 35 years of experience with Billabong Hydraulic Rams. The Hydraulic Ram has stood the test of time and it remains one of the few really practical and efficient uses of natural energy today. It operates without almost any cost, will last indefinitely and, with only two moving parts, is simplicity itself. It requires minimum maintenance and minimum replacement of parts. It is not uncommon to find rams working continuously for many years without any attention. • The Rams do not require electricity, fuel or steam to operate. • They possess simplicity of construction and operation – only 2 moving parts. • Powered only by running water. • Require very minimal or almost no maintenance. • Heavy duty cast Iron base and Dome. This Pump recovered from the Clematis Creek in the Mid 1970's Used to pump water from the creek to the Paradise (Clematis) Hotel. Historic - Farm Equipment - Used to pump water from the creek to the Paradise (Clematis) Hotel.Cast Iron Bronze valveBillabong 5billabong, puffing billy, ram pump -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaDocument - Image, 1934 - 1954 - 50 Years of Talking Book Service, 1984
The Talking Book Library of the Royal Victorian Institute for the Blind is celebrating its 50th anniversary during 1984. This service began in 1934 with 78 rpm records. These were later superceded by 33rpm records which remained in use until 1960. The first cassettes were imported from England and weighed 7 lb. along with the player which weighed 28 lb. These 18 track cassettes usually contained one whole book. In the early 1970's a change was made to smaller cassettes containing 12 hours of recorded material on 6 tracks. The latest system currently being introduced is the Library of Congress 4 Track System utilising cassettes which play for 6 hours and machinery which is adaptable to the conventional 2 track system cassette. The Talking Book Library today provides services to 2500 readers as opposed to only 500 in 1964. The service is free of charge to anyone who is visually handicapped and includes talking books, talking book machines, mail service, servicing of machines at regular intervals and any modifications that may be required. Over 1600 cassettes are handled daily. The library currently holds over 3500 individual titles. Catalogues are available in print, audio and braille format. Once selection is made, borrowers may receive at least 3 books at any one time. Other services include current magazines, foreign language books, newspapers and magazines and regional country newspapers. Many books are recorded at the R.V.I.B. by our volunteer readers while others are bought from similar agencies in Australia and overseas. The department of the R.V.I.B. relies almost entirely on voluntary donations from the public. Other services provided by the Royal Victorian Institute for the Blind Community Resources Section, Aids & Equipment Shop, Tertiary Resource Service, Industrial Department, Retired Personnel Allowance, Children's Services, Social Services, Housing Loans, Vocational Development1 digital image of typewritten pageroyal victorian institute for the blind, talking books -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesNewspaper, Historic Homestead Vandalised, 1990
Edna Barrie describes the Darlingsford property. C.E. Barrrie Land developers bought the property from my husband’s brother. It was one big farm and they were a big family. When the father died he left it to be cut up for the family. The youngest son had to reach age 21 before the property could be divided and portioned out to the mother and children, but it was deferred until Jim returned from the war. Eventually it was cut up into two parts, we were married by then and so was Edgar. Part of the land included the block on the other side of Ferris road, which became the quarry, Edgar’s section was on the Toolern Creek end, he was the last one married and lived in the old bluestone house until 1974. The developers bought this section but they could not get permits due to the state of the old bridge due to the cost. Barries had built the bridge across the creek [1926]. It took the big loads of hay and the family kept it maintained. Once the Barries had gone it did not get any upkeep. The developers found the cost of replacing the bridge and developing site with sewerage and drainage power before they sell. The rural land itself is not worth much as the developer has to complete the subdivision before any blocks can be sold. The developer from Sydney had a man living in the house, who let it go the rack and ruin. He managed to buy from the developer 25 acres with the bluestone house. Bernard Coburn had it for a while but is was well out of our hands by then. There were various people who have bought into and tried to develop and have given up. There was a project sometime ago to save the buildings from ruin but nothing has happened as yet, they are six or seven years to late. The buildings continue to deteriorate and were badly damaged vandals and fire. The Shire bought all the rest of it from the developer, where the tip is now, that was also part of Edgars land. Article about a fire at Darlingsford Estate featured in the Telegraphlocal architecture, local identities, emergency services -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Fob Watch, ca 1878
The story behind this little gold watch is intriguing. The condition of the watch certainly shows the effects of time in the sea. Some inner workings can be seen through broken encrustations and missing sections of the watch’s case. The winding knob on the top is recognisable even though it is covered by sand and other adhesions from the sea. The manufacturer of this dainty watch may have made it for a female, and the value of the gold metal case shows that it would be marketed for a person with wealth. The watch was donated along with a letter, an envelope and a newspaper cutting, all neatly folded and tucked with the watch into a small, strong cardboard box with metal reinforcing on the corners and a fitted lid. The letter is dated March 6, 1905, and its sender writes about the ‘souvenir’ lady’s gold watch found in Loch Ard Gorge at Port Campbell, though the finder remains unnamed. The letter’s date is also uncertain, as there are only 27 years, not 28, between its date and the date the Loch Ard was wrecked (1905-1878 = 27). The signature on the letter appears to be ‘Wyon’, which is the name of a creek in NSW, and also the name of the renowned William Wyon, medallist and engraver of British coins, medals and stamps; and continued as Wyon and Sons, London. The envelope has a postmark for Florence (Firenze), Italy. It is stamped October 12th, 1911 (12.10.11). It is addressed to an illegible name, then Glencove, Portsea, Victoria, Australia: 'Glencove, Portsea' is referred to in newspapers between 1927 and 1949. The newspaper cutting puts the watch into its context, telling the story of the wreck of the Loch Ard, the survival of only two of the 54 people onboard, and a little of the survivors’ future events. It doesn’t single out the watch in any way. Any one of the 17 passengers sailing on the Loch Ard could have owned the watch, including Dr. Carmichael, his wife, Eva, their other three daughters, and two of their sons. Instead of belonging to anyone onboard, it may have been amongst the cargo, as the ship’s manifest includes ‘clocks and watches £25’. The donated watch was carefully packaged with related documents, showing respect for this small shipwreck artefact, which is nearing 150 years of age at the time of writing (2025). The watch’s connection to the sands of Loch Ard Gorge also connects it to the ship Loch Ard, contributing to our knowledge of personal items brought to Australia in 1878, whether as the belongings of a passenger or as cargo; a gold watch would be intended for a wealthy buyer. Although many people would have visited the shipwreck site, it was revealed over 25 years after the Loch Ard was wrecked; this length of time helps us understand the effects of the sea on shipwreck objects. The watch is significant for its connection to the infamous Loch Ard, where only two of the 54 people on board survived.Ladies' fob watch, thought to be gold. It is now covered in encrustation. A bump on the edge would be the winding mechanism for the watch. A small section of the back of the case has broken away, and an engraved surface can be seen. Face and hands are missing, revealing the spring workings inside. Donated with the watch were two documents and a newspaper cutting about the story of the shipwreck of the Loch Ard. They are all in a strong cardboard box with reinforced corners on the base and lid. Found at Loch Ard Gorge and said to have been from the Loch Ard. The three donated documents are: - 1. A rectangular envelope made of cream waxy paper lined with black and white diagonally striped paper. The top right corner, usually meant for a postage stamp, has been torn off, partly exposing text on a rectangular printed logo. A round black postmark stamp near the top centre shows the post office location and date. The address on the front is handwritten in black ink. The creases on the envelope suggest it has been folded three times. 2. A letter on cream rectangular paper features clear, handwritten script in black ink. The unevenly cut bottom edge has two short black vertical lines, possibly the tops of tall written letters. There are creases where the page has been folded three times. 3. A newspaper clipping featuring text, an illustration, and handwritten details of the newspaper’s source.1. Envelope: - Address: ”Australia (per Postage) / (illegible) / Glencove, (Portsea) / Victoria” Postmark: “FIRENZE” 12 10 11” “ - - - -PORTEN – (illegible)” Logo inside envelope: “BUSTA BRE--- / Earliera Lialia” [Italian; Busta = envelope, Earliera == earlier] 2. Letter: - “I am sending you a ‘souvenir’ from the wreck of the Loch Ard 28 years ago at Port Campbell. It is the remains of a lady’s gold watch found in the gorge where Miss Carmichael & Tom Pearce (the only two saved) were washed up. This souvenir was lying there ever since. I went down into the awful gorge & saw the cave where these two unfortunates (or fortunate perhaps, as they were saved) lived until rescued. I also saw the graves of those who were washed up from the wreck. One grave contains Dr and Mrs Carmichael & six of their children. Later on, when I can get some good views of that wild coast I will send them. [signed] Wyon. 6/3/05.” 3. Newspaper cutting: - History of the Lochard. Refer to the Sydney Morning Herald, Nov. 28th, 1971: “Loch Ard: the wreck that became a legend”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, loch line, loch ard, captain gibbs, eva carmichael, tom pearce, glenample station, mutton bird island, loch ard gorge, ladies fob watch, gold watch, fob watch, pocket watch, horology, accessory, time keeping, scientific instrument, ladies' watch, ladies' pocket watch, diagonally striped envelope lining, glencove, portsea victoria, firenze, busta, earliera, souvenir watch, loch ard souvenir, lady's watch, port campbell, tom pearch, survivor, miss carmichael, mrs carmichael, dr carmichael, wyon, 1878, 1905, 1911, loch ard: the wreck that became a legend, florence, clocks and watches -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageToy Gun, 1911
This cap gun was found by a local Warrnambool resident in about 1971. Cap guns first appeared following the end of the American Civil War in the mid-1860s, when firearms companies experimented with toy guns to stay in business. Cap guns became especially popular when the heroes of cinema and television rode through the West ridding the territories of villains. Many cap guns were named after or endorsed by leading matinee idols like Roy Rogers, Gene Autry, Hopalong Cassidy, The Lone Ranger, Tonto, Dale Evans, Marshal Matt Dillon, or any of countless others. Cap guns became popular after the second world war and children all over the world emulated their heroes and collected and played with these toy guns. Eventually all of the famous cap gun manufacturers either sold out to other toy companies or started manufacturing other types of toys. Before it was deemed dangerous or politically incorrect for young children to point pistols at each other and fire at will, cap guns were a staple of toy chests. The item demonstrates how society has changed its attitudes and now regard these types of toys as morally unacceptable as they tend to promote violent attitudes towards others. The item demonstrates significantly how our societies social attitudes have changed since world war two from general societal acceptance of such toys to one of distaste.Toy gun; cap gun. Cast iron toy pistol with metal trigger. Name "National" in raised embossing in the casting on the handle on both sides of the gun. Made in 1911."National" flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, toys, cap gun, national fireworks distrubuting company, toy guns, toy pistol -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageTool - Barrel bung hole reamer, 1851 - 1872
R Timmins & Sons were makers of heavy steel 'toys' - toy in this context means any small metal object, including hand tools. The company was founded in 1790 by Richard Timmins and was situated in Hurst St, and later in Pershore Street, Birmingham. In 1850 Richard Timmins died aged 60 and the company continued with his wife Ann and their son Henry who were the executors of his will. In 1889 they were taken over by another Birmingham maker, W & C Wynn of Suffolk Street also edge tool makers and the business moved to Commercial Street Birmingham in 1872. For a few years, both companies continued to operate under their original names. In 1892 they were incorporated as Wynn, Timmins & Co, and in 1897 the premises in Commercial St were renamed Century Works. The company survived until 1969 when they were taken over by Balfour Dawins Ltd of Sheffield, and the works in Birmingham then closed.A significant item given its age having the probability of having been made after Richard Timmins had died and before the take over in 1872 during the time the company was being run by his wife Ann and son Henry. Given the inscription on the item is "A Timmins & Sons". The items significance is social given it was used to clean bungholes in barrels and was possibly used in the early cooperage industries of the early Australian colony. Bung reamer metal with wooden handle. A Timmins & Sons stamped on blade.warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, coopers tools, bung hole reamer, barrels, barrel making -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book, African trader, Late 19th Century
This is a book prize given to Bessie Mackay some time in the 1890s. Unfortunately neither the book nor the book plate has any date. Bessie Mackay is probably Marie Elizabeth Mackay, born to Thomas and Marie Mackay in 1883. Thomas Mackay was an auctioneer and commission agent in Warrnambool in the later decades of the 19th century. Ellerslie College was an important private school in Warrnambool and the building still stands (Koroit Street). It was a purpose-built school, initially for girls and it was erected in 1889 for Bella Davidson. Miss Davidson conducted this school until 1891 when it was taken over by William Lawson. He had had a school for boys and girls in King Street and when he moved his school to Ellerslie College he was employing three lady teachers as well as his male staff. It is not known whether Bessie Mackay was a pupil at Miss Davidson’s school or Lawson’s school or both. This book is of great interest as a memento of Ellerslie College, a well-known private school in Warrnambool in the late 19th century and early 20th century. At that time, most pupils in Warrnambool wishing to go on to higher education attended private schools. This is a hard cover book of 128 pages. The cover is dark green with an image of a bunch of flowers in silver, red and black colouring on the front cover and on the spine. The printing is in black lettering on the front cover and in silver colouring on the spine. The book has eight chapters with a full page colour sketch at the front of the book. The cover is slightly frayed and a little stained. The book plate has black printing on a white background and handwriting in black ink. ‘Ellerslie College, Warrnambool, Non Scholae Sed Vitae Discimus, Name. Miss Bessie Mackay, Class V, For Geography’. ellerslie college, warrnambool, history of warrnambool, bella davidson, william lawson, bessie mackay -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Documents – Art Gallery, Chief Secretary’s Office, Melbourne, 1886-1911
All but two of these letters came from the office of the Chief Secretary of the Government of Victoria and concern the grants allocated to the Warrnambool Art Gallery from 1886 to 1911. At that time the Art Gallery was under the control of the Warrnambool Mechanics Institute Committee and managed by the Secretary/Treasurer of that group. The Government funding for the Art Gallery at the time represented a sum of money equal to the value of the works of art donated locally to the Art Gallery in any given year and frequently the estimated value of these art works were queried by the Warrnambool Secretary of the time. Two notable Secretaries of the Mechanics Institutes during this time were Walter Cockman (1880-1892) and George Lance (1892-1901). The correspondence under review here was retained by George Lance and his family and came into the possession of Lance’s grandson, Bruce Morris who was the editor of the Warrnambool Standard newspaper from 1946 to 1968 and was a well-known local historian. These letters are of considerable importance as they are original and document the struggle of the Warrnambool Art Gallery over the years 1886 to 1911 to secure funding from the Victorian Government.These are 19 pieces of correspondence relating to Warrnmbool Art Gallery grants and purchases from 1886 to 1911. The letters are written on different size pieces of paper (mostly foolscap size), with thirteen of them being handwritten and six being typed. All letters have original signatures. The earliest letter (1886) is very tattered. warrnambool art gallery, history of warrnambool -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFurniture - Chair, Late 19th to early 20th century
Originally the Bow Chair started off life with the name of the ‘Smoker’s Bow Chair’ where originally, it wasn’t designed for grandeur like many chairs of the time, but instead was designed for practicality and comfort. The original Smoker’s Bow Chair was a simple chunkier version of the Windsor Chair design which first appeared in the 1820’s. Although it lacked the high back found on any Windsor Chair of the time, it maintained a heavier, sturdier appearance. The main feature was a hoop or bow which was fashioned from steamed wood. This was then curved to make both the back support and arms. The chair also consisted of a wide seat, supported by 4 splayed, spindle legs. In its original form it was found in many country kitchens of the day as well as in many inns and public houses throughout the United Kingdom. Its name of the "Smoker’s Bow Chair" because the sweeping armrests were the perfect height to support a smokers arm when smoking a pipe.A significant piece of furniture from the late 19th century designed for a specific purpose, smoking. These chairs are now highly collectable and valuable today and avidly sought by collectors of antique furniture.Chair wooden dark brown "Smoker's Bow" chair, with wide and deep seat with broad arms, turned spindles and thick turned legs joined by a double stretcher.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, chair, furniture, smokers chair, bow chair -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFurniture - Chair, Late 19th to early 20th century
Originally the Bow Chair started off life with the name of the ‘Smoker’s Bow Chair’ where originally, it wasn’t designed for grandeur like many chairs of the time, but instead was designed for practicality and comfort. The original Smoker’s Bow Chair was a simple chunkier version of the Windsor Chair design which first appeared in the 1820’s. Although it lacked the high back found on any Windsor Chair of the time, it maintained a heavier, sturdier appearance. The main feature was a hoop or bow which was fashioned from steamed wood. This was then curved to make both the back support and arms. The chair also consisted of a wide seat, supported by 4 splayed, spindle legs. In its original form it was found in many country kitchens of the day as well as in many inns and public houses throughout the United Kingdom. Its name of the "Smoker’s Bow Chair" because the sweeping armrests were the perfect height to support a smokers arm when smoking a pipe.A significant piece of furniture from the late 19th century designed for a specific purpose, smoking. These chairs are now highly collectable and valuable today and avidly sought by collectors of antique furniture.Chair wooden dark brown "Smoker's Bow" chair, with wide and deep seat with broad arms, turned spindles and thick turned legs joined by a double stretcher.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, chair, furniture, smokers chair, bow chair -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFurniture - Chair, Late 19th to early 20th century
Originally the Bow Chair started off life with the name of the ‘Smoker’s Bow Chair’ where originally, it wasn’t designed for grandeur like many chairs of the time, but instead was designed for practicality and comfort. The original Smoker’s Bow Chair was a simple chunkier version of the Windsor Chair design which first appeared in the 1820’s. Although it lacked the high back found on any Windsor Chair of the time, it maintained a heavier, sturdier appearance. The main feature was a hoop or bow which was fashioned from steamed wood. This was then curved to make both the back support and arms. The chair also consisted of a wide seat, supported by 4 splayed, spindle legs. In its original form it was found in many country kitchens of the day as well as in many inns and public houses throughout the United Kingdom. Its name of the "Smoker’s Bow Chair" because the sweeping armrests were the perfect height to support a smokers arm when smoking a pipe.A significant piece of furniture from the late 19th century designed for a specific purpose, smoking. These chairs are now highly collectable and valuable today and avidly sought by collectors of antique furniture.Chair wooden dark brown "Smoker's Bow" chair, with wide and deep seat with broad arms, turned spindles and thick turned legs joined by a double stretcher.Noneflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, chair, furniture, smokers chair, bow chair
