Showing 148 items
matching industrial development.
-
 Kew Historical Society Inc
Kew Historical Society IncBooklet, Duncan & Weller Pty Ltd, Old Kew Golf Links Estate, 1927, 1927
... for industrial development and the building of a new Kodak factory ...The booklet advertises the third sale within the Old Golf Links Estate which was a major subdivision of farmland in North Kew in the 1920sThe subdivision of the Kew Golf Links Estate was a major subdivision of farmland in Kew. The site was at one stage designated for industrial development and the building of a new Kodak factory. The decision by Council to oppose the redevelopment makes the beginning of the period when all industrial development was banned in Kew.6 page illustrated brochure advertising the third section of a major subdivision in Kew in 1927 including 75 charming home allotments and 7 valuable building sites. The brochure includes the subdivision plan. The front cover includes a colour illustration of the almost completed houses in Woolcock Avenue. Streets named include: Kilby Road, Kodak Avenue, Baker Avenue, Mathers Avenue, Coleman Avenue, White Avenue and Belford Road. Lots for sale are numbered. Existing buildings are designated with a square.subdivisions - kew (vic), kew golf links estate -
 Kew Historical Society Inc
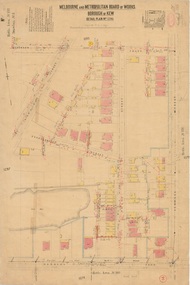
Kew Historical Society IncPlan, Melbourne & Metropolitan Board of Works : Borough of Kew : Detail Plan No.1296, 1904
The Melbourne and Metropolitan Board of Works (MMBW) plans were produced from the 1890s to the 1950s. They were crucial to the design and development of Melbourne's sewerage and drainage system. The plans, at a scale of 40 feet to 1 inch (1:480), provide a detailed historical record of Melbourne streetscapes and environmental features. Each plan covers one or two street blocks (roughly six streets), showing details of buildings, including garden layouts and ownership boundaries, and features such as laneways, drains, bridges, parks, municipal boundaries and other prominent landmarks as they existed at the time each plan was produced. (Source: State Library of Victoria)This plan forms part of a large group of MMBW plans and maps that was donated to the Society by the Mr Poulter, City Engineer of the City of Kew in 1989. Within this collection, thirty-five hand-coloured plans, backed with linen, are of statewide significance as they include annotations that provide details of construction materials used in buildings in the first decade of the 20th century as well as additional information about land ownership and usage. The copies in the Public Record Office Victoria and the State Library of Victoria are monochrome versions which do not denote building materials so that the maps in this collection are invaluable and unique tools for researchers and heritage consultants. A number of the plans are not held in the collection of the State Library of Victoria so they have the additional attribute of rarity.Original survey plan, issued by the MMBW to a contractor with responsibility for constructing sewers in the area identified on the plan within the Borough of Kew. The plan was at some stage hand-coloured, possibly by the contractor, but more likely by officers working in the Engineering Department of the Borough and later Town, then City of Kew. The hand-coloured sections of buildings on the plan were used to denote masonry or brick constructions (pink), weatherboard constructions (yellow), and public buildings (grey). This area was once known as O’Shaughnessy’s Paddock. O’Shaughnessy was the licensee of the Kew Hotel. The ‘Paddock’ or farm was for many years the closest farm to Melbourne. By 1903, when this plan was surveyed and lithographed, little of the farm remained. The area is dominated by a ‘clay hole’, on the site of the current Foley Reserve. It was used by Smart’s Brickyard from the 1880s until 1911, when the Council purchased it for a rubbish dump. It is notable as the site is one of the few industrial operations to have existed in Kew. By 1903, urban development was characterised by larger houses fronting Barkers Road and brick and weatherboard villas in Foley Street. Nearer the pit, weatherboard houses predominated. Foley Street bisected the triangular block and continued right to Denmark Street. At this stage, a house impeded the through road, only allowing access via a right of way to High Street.melbourne and metropolitan board of works, detail plans, mmbw 1296, cartography -
 Sunbury Family History and Heritage Society Inc.
Sunbury Family History and Heritage Society Inc.Photograph, Sunbury Asylum, c1920s
The brick buildings in the photograph are of the former Sunbury Asylum and F3 Ward is in the foreground. Initially the site on Jackson Hill also known as She0ak Hill opened as an Industrial School for orphaned or neglected children and in 1879 it became an asylum where it continued to function as an asylum until the Victorian Government closed it on 20th November 1992.The Sunbury Asylum played an important part in Sunbury and wider community's development over 150 years. throughout its existence there was much interaction between the residents, staff and local community, many of whom were employed at 'The Hill' as it was known locally. A sepia non-digital photograph of a large brick hospital building with three nurses standing outside it on a narrow pathway edging a garden bed. A picket fence is at the rear of the building enclosing a small yard where washing is drying on the line.sunbury asylum, jackson hill, caloola, sheoak hill, ward f3 -
 National Wool Museum
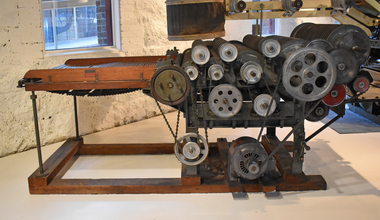
National Wool MuseumMachine - Carding Machine, CSIRO, 1960s
After scouring, the wool fibres are still tangled together. Carding untangles the fibres by brushing and straightening. The wool moves through a series of wire brush rollers that revolve at different speeds and in different directions to tease apart the wool. The fibres emerge from the machine as a continuous filmy web - called a sliver. The sliver must be thinned and divided into strands before the next process. Carding machines constantly require tuning. A highly skilled technician maintained and adjusted the speed of the rollers on the machine. This machine was developed by the CSIRO in the 1960s as a small-scale experimental machine. Industrial carding machines were four times the size of this one. Gold plaque on display with machine until 2018 read: G.H. Mitchell & Son, Adelaide have celebrated 125 Years of involvement with the Australian Wool Processing Industry by contributing the funds necessary to restore The Carding Machine, Noble Comb & The Gill Box. Also another gold plaque read: Experimental Carding Machine donated to The National Wool Museum by C.S.I.R.O Ryde has been rebuilt by Nick Sokolov of Comb Research & Development with the help of Bernard Tolan.Carder with small roller missing at coiling end. Driven by three horse power motor. Wooden slated feed table synchronised to overall gearing.carding machine, machines, wool industry, manufacturing, wool processing -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaDocument - Image, 1934 - 1954 - 50 Years of Talking Book Service, 1984
The Talking Book Library of the Royal Victorian Institute for the Blind is celebrating its 50th anniversary during 1984. This service began in 1934 with 78 rpm records. These were later superceded by 33rpm records which remained in use until 1960. The first cassettes were imported from England and weighed 7 lb. along with the player which weighed 28 lb. These 18 track cassettes usually contained one whole book. In the early 1970's a change was made to smaller cassettes containing 12 hours of recorded material on 6 tracks. The latest system currently being introduced is the Library of Congress 4 Track System utilising cassettes which play for 6 hours and machinery which is adaptable to the conventional 2 track system cassette. The Talking Book Library today provides services to 2500 readers as opposed to only 500 in 1964. The service is free of charge to anyone who is visually handicapped and includes talking books, talking book machines, mail service, servicing of machines at regular intervals and any modifications that may be required. Over 1600 cassettes are handled daily. The library currently holds over 3500 individual titles. Catalogues are available in print, audio and braille format. Once selection is made, borrowers may receive at least 3 books at any one time. Other services include current magazines, foreign language books, newspapers and magazines and regional country newspapers. Many books are recorded at the R.V.I.B. by our volunteer readers while others are bought from similar agencies in Australia and overseas. The department of the R.V.I.B. relies almost entirely on voluntary donations from the public. Other services provided by the Royal Victorian Institute for the Blind Community Resources Section, Aids & Equipment Shop, Tertiary Resource Service, Industrial Department, Retired Personnel Allowance, Children's Services, Social Services, Housing Loans, Vocational Development1 digital image of typewritten pageroyal victorian institute for the blind, talking books -
 Vision Australia
Vision AustraliaBook - Text, Basil Shaw, Vision Queensland, QBIC and the Queensland Industrial Institution for the Blind : a history, 1883-1999 by Basil Shaw, 1999
Brief outline of the development of services to blind and vision impaired Queenslanders since 1883, with more focus on the changes that occurred in the last 20 years.65 pages with illustrations on development of servicesvision queensland, qbic industries, queensland industrial institute for the blind, john puttick, santo santoro -
 City of Greater Bendigo - Civic Collection
City of Greater Bendigo - Civic CollectionMedal - 1873 International Exhibition Medal, G. T Morgan, 1873
In 1791 Prague organized the first World's Fair, Bohemia (modern-day Czech Republic). The first industrial exhibition was on the occasion of the coronation of Leopold II as a king of Bohemia, which took place in Clementinum, and celebrated the considerable sophistication of manufacturing methods in the Czech lands during that time period. The French tradition of national exhibitions culminated with the French Industrial Exposition of 1844 held in Paris. This fair was followed by other national exhibitions in Europe. In 1851, under the title "Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations", the World Expo was held in The Crystal Palace in Hyde Park, London, the United Kingdom. The Great Exhibition, as it is often called, was an idea of Prince Albert, Queen Victoria's husband, and is usually considered to be the first international exhibition of manufactured products. It influenced the development of several aspects of society, including art-and-design education, international trade and relations, and tourism. This expo was the precedent for the many international exhibitions, later called World Expos, that have continued to be held to the present time. (source; Wikipedia) Commemorative medal. Featuring the bust of Edward, Prince of Wales by G. Morgan with the Welsh plume behind and a scene from within the City of London.Front; Draped bust of the Prince of Wales left, plumes to right. ALBERT . EDWARD . PRINCE . OF . WALES . PRESIDENT . Verso; View of the Horticultural Society's arcades and the Albert Hall. MDCCCLXXIII below, LONDON . ANNUAL . INTERNATIONAL . EXHIBITION . OF . ALL . FINE . ARTS . INDUSTRIES AND INVENTIONSworld fairs, international exhibition, prince albert, expo -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesDocument, West Melton: A preview of tomorrow, c.1969
"In April 1969, the first major residential development in Melton began with the release of 148 homes for purchase. This was the first stage of a staggered release of a planned 30,000 homes for 100,000 people by 1990. The development, called Westmelton Satellite City, was described as ‘a preview of tomorrow’.101 It was the first estate built in a ‘modern’ style, with curved streets, and dozens of culs de sac. Westmelton was also the first major development in Victoria to build all the supply lines to the houses – including electricity and telephone lines – underground. The six different home designs in Westmelton were ‘specially designed for the future’, and with allotments ten feet wider than regulations required, there was plenty of ‘space for gracious living’ and for a family swimming pool. The developers of this new estate were active in promoting Westmelton as a new community within the Shire of Melton. By 1971, the Westmelton City News reported that Ian McIntosh, General Manager of Westmelton, had given away $100,000 on behalf of the company ‘to aid community projects’. This included a $72,000 donation towards building a community centre in Westmelton, and $25,000 for the shire’s Olympic-sized swimming pool. Ian McIntosh and his family moved to Melton and Ian said he was ‘very much aware of the needs of [the] Westmelton community’. By the end of 1971, Westmelton was home to 100 new families. The modern residences were obviously an appealing drawcard, but so was the country feel that characterised Melton. Mrs C. Allen, described as a ‘housewife’, said she and her husband chose to move to Westmelton because of ‘the quality homes ... and we both love the clean, fresh, natural environment that surrounds us’. Similarly, Mr W. Coxhead, insurance consultant, moved to Westmelton because of the ‘clean, fresh country air’. Accountant Mr B. Swanton echoed their sentiments, describing Westmelton as ‘far enough away from the industrial pollution carried over Melbourne suburbs by prevailing westerly winds’. The new development attracted an increasing number of young, professional couples and families, representing the beginning of a significant shift from the predominantly rural and farming community of the district’s past. The Westmelton development had four different ‘neighbourhoods’ designed to cater to a variety of different lifestyle needs. Westmelton was the first to be established, followed by Brookfield, which offered ‘superb land in a rustic setting’. Brookfield Acres offered ‘wide open spaces with lots of room for a pool and even a tennis court’ on huge one-acre blocks, while Westlake was an innovative development with ‘different sized homesites’ and ‘lakeside living’.Westmelton was the first of many residential developments that would come to play a huge role in shaping the shire in the decades to follow".A marketing brochure for the Westmelton Satellite City developmentlocal significant events, council -
 Melton City Libraries
Melton City LibrariesNewspaper, Lack of support may close hall, 1977
"The Mechanics Institute movement flourished in Victoria from 1839 to 1950. It was based on the development of Mechanics’ Institutes in Scotland and England from the 1820s, which were intended to educate and enlighten the working classes. The term ‘mechanic’ in those days meant an artisan, craftsman or working man, especially those who had moved from rural areas to work in new city factories during the Industrial Revolution. The early Institutes were usually equipped with a reading room, a library and a lecture room. Although enjoying mixed success in Britain, they contributed to the development of public education and library services. The movement was adopted more enthusiastically in the colonies. It began slowly in Victoria but its expansion after the gold rushes population influx was rapid, especially in rural areas. Every suburb and town wanted to have a Mechanics’ Institute. During the 1850s approximately forty Institutes were established, with even greater growth in the period 1860 to 1900. By 1900 there were 400 Institutes in Victoria. The establishment of a Mechanics’ Institute was often a great achievement for a local community, requiring organising committees to raise substantial funds for a building site (where this had not been granted by the Government), and the building. Once built, the committee then had to purchase books, provide a caretaker or librarian, and finance the ongoing use of and improvements to the building. ‘The history of many Institutes is a story of tremendous community effort, and often, financial difficulties’. In addition to being monuments to local enterprise and community life, the Mechanics’ Institutes played a vital role as an intellectual forum, and in contributing to an informed and participatory democracy in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. They provided journals and other reading matter on local, state, national and international issues, and hosted of lectures and held debates about wider issues such as Federation, colonial nationalism, defence, female suffrage, the price of land and labour. With the development of the school and technical education in the latter part of the nineteenth century, the need for community technical and adult education declined. As a result of the introduction of government library grants in 1867, many Mechanics’ Institutes incorporated a free library in their buildings to finance collection of their books. By 1884-85, there were 257 free libraries in Victoria. However, government support and library grants dropped off in the 1890s depression. Entertainment took on a greater role in the 1890s, with the introduction of moving pictures, billiards rooms, games rooms (chess), concerts and dances. The First World War had a devastating impact on many rural communities, and some Mechanics’ Institutes were no longer viable. On the other hand the early twentieth century was also a time of agricultural development, and many country towns were growing in this period. The 1930s depression further limited growth of many libraries and reduced grants substantially. In response many Mechanics’ Institutes were renamed, for example as memorial halls, in order to retain and attract more patrons (eg at nearby Sunbury). The diminishing role for Mechanics’ Institutes and the preference for larger and better appointed halls (with supper rooms, cloak rooms etc) resulted in demolition of some small Institutes. The advent of cars, radios, and television also provided other opportunities for recreation, learning and entertainment. The greater role of municipalities in providing library services also eroded the need for free libraries. While over 500 Mechanics’ Institutes or halls are extant, very few of these retain their original role as ‘diffusers of useful knowledge’. Most are still available for community purposes, as venues for meetings, socials, civic occasions etc, while others are employed as museums, shops and theatres. Most buildings are on Crown land, and managed by a delegated committee of management, who are responsible for raising revenue to maintain aging buildings. Many of those which were originally established on private land, such as Melton, have since reverted back to the Crown, and municipal Councils. The most common Mechanics Institute building form is the simple weatherboard gable building with iron roofs, notable for their ‘honest simplicity’ rather than as ‘monuments of the ancients’. At the other extreme there are some magnificent two storeyed brick and stucco structures with elaborate ornamentation (as was apparently envisaged by some in Melton in 1905-10)". The future of Melton Mechanic Institute Gazette articlelocal architecture -
 Australian Nursing & Midwifery Federation
Australian Nursing & Midwifery FederationAustralian Nursing Federation ratios campaign badge, 2001
Button distributed to and worn by Australian Nursing Federation (ANF) members and staff as part of a campaign to secure minimum nurse staffing in the public healthcare sector. This badge was accompanied by a booklet 'Nursing the system back to health : Nurse patient ratios 2001', published in April 2002. The booklet describes some of the rationale for minimum staffing ratios and developments in 2000-2001 regarding campaigning for ratios, particular the landmark decision of the Australian Industrial Relations Commission in 2000 that saw the ANF securing the world's first mandated minimum nurse-to-patient ratios. After decades of campaigning from the ANF/ANMF, ratios were legislated for the public sector in Victoria with the passing of the Safe Patient Care (Nurse to Patient and Midwife to Patient) Bill in 2015. The web address on the badge was active from 1999 to 2004, and the shortcut 'anfvic.asn.au' was active from April 2001, suggesting this badge dates from 2001.Circular yellow, blue and white badge. Silver metal, plastic-coated, with safety pin fastener adhered to back. Badge printed with a blue and white ANF [Australian Nursing Federation] logo, the text 'Nurses Nursing the system back to health' and the (then) website of the ANF (Victorian Branch), 'www.vicnet.net.au/~anfvb/'.nursing, ratios, workforce, staffing, nurses, unionism, badges, buttons, pins, campaigning, trade unions, labour history, safe patient care (nurse to patient and midwife to patient ratios) act 2015, australian nursing federation, victoria, enterprise bargaining -
 Australian Nursing & Midwifery Federation
Australian Nursing & Midwifery FederationAustralian Nursing Federation ratios campaign bumper sticker, 2001
Sticker distributed to and used by Australian Nursing Federation (ANF) members and staff as part of a campaign to secure minimum nurse staffing in the public healthcare sector. This sticker was accompanied by a booklet 'Nursing the system back to health : Nurse patient ratios 2001', published in April 2002. The booklet describes some of the rationale for minimum staffing ratios and developments in 2000-2001 regarding campaigning for ratios, particular the landmark decision of the Australian Industrial Relations Commission in 2000 that saw the ANF securing the world's first mandated minimum nurse-to-patient ratios. After decades of campaigning from the ANF/ANMF, ratios were legislated for the public sector in Victoria with the passing of the Safe Patient Care (Nurse to Patient and Midwife to Patient) Bill in 2015. The web address on the sticker was active from 1999 to 2004, and the shortcut 'anfvic.asn.au' was active from April 2001, suggesting this sticker dates from around 2001.Rectangular yellow, blue and white bumper sticker. Badge printed with a blue and white ANF [Australian Nursing Federation] logo, the text 'Nurses Nursing the system back to health' and the (then) website of the ANF (Victorian Branch), 'www.vicnet.net.au/~anfvb/'.nursing, ratios, workforce, staffing, nurses, unionism, stickers, campaigning, trade unions, labour history, safe patient care (nurse to patient and midwife to patient ratios) act 2015, australian nursing federation, enterprise bargaining, victoria -
 Wodonga & District Historical Society Inc
Wodonga & District Historical Society IncBook - Wodonga Australia - Victoria's Top Industrial Town, Wodonga Promotions Committee, 1966
... award for "Industrial Development" in the Victorian Premier Town ...Winning the top award for "Industrial Development" in the Victorian Premier Town Contest 1964, Wodonga was recognised and declared the chief industrially developing town outside the Melbourne metropolitan area. This publication outlines the key features of Wodonga supplemented with photos and maps.non-fictionWinning the top award for "Industrial Development" in the Victorian Premier Town Contest 1964, Wodonga was recognised and declared the chief industrially developing town outside the Melbourne metropolitan area. This publication outlines the key features of Wodonga supplemented with photos and maps.wodonga description and travel, wodonga development -
 City of Kingston
City of KingstonPhotograph - Colour, c. 1982
... development in terms of people, housing construction, industrial ...This aerial photograph of South Road and Nepean Highway, Moorabbin shows the area where houses and shops on the south side of the Nepean Highway have demolished for the widening of the highway. The pressures of rapid urban development in Moorabbin and beyond, especially to the south of Moorabbin caused bottlenecks and delays, especially at the South Road and Nepean Highway intersection, hence the scheme to widen Nepean Highway.The pressures of rapid urban development in terms of people, housing construction, industrial development and commercial activity, in Moorabbin and beyond, especially to the south would put pressure on road infrastructure in the region. In the early 1980s, a major road expansion of the Nepean Highway was implemented to increase capacity on this major thoroughfare for vehicle commuters. Car use had also increased with commuters from the increasingly populous southern suburbs travelling to their place of work in the Melbourne CBD.Colour photograph of an aerial view of South Road and Nepean Highway, Moorabbin. The image shows houses on the south side of the Nepean Highway that have demolished for widening of road. It features housing and commercial buildings looking north towards Cummins Road.Handwritten blue ink: 82 - 5452 - 11 Handwritten red ink: 112% Handwritten black ink: Ch. 7nepean highway, south road, moorabbin, roads, transport, infrastructure -
 City of Kingston
City of KingstonPhotograph - Black and white, 5 January 1984
Moorabbin, Cheltenham and Highett are suburbs in the City of Kingston with a diverse mix of development and zoning. The market gardens, farms and paddocks have gradually been sub-divided into housing and industrial estates and associated infrastructure such as schools and shopping facilities. The area includes many parks, reserves and golf courses.This aerial image covers a diverse section of the City of Kingston, taking in the suburbs of Cheltenham, Moorabbin, Beaumaris and Highett. By 1984, the market gardens of the district have been replaced by housing and factories. The Gas and Fuel state-of-the-art Scientific Services Department is visible on Nepean Highway Highett. The CSIRO Highett site can also be seen. Both sites have now been demolished and have undergone remediation. The Southland site is visible and yet to be redeveloped by Westfield. This image portrays the diversity of development in the City of Kingston with a mixture of green spaces, housing and commercial and industrial features.Aerial photograph of Cheltenham, Beaumaris, Moorabbin and Highett within the City of Kingston. The area depicted in the 1984 aerial view includes Eden Street and Edward Street, Cheltenham (top left), Weatherall Road and Reserve Road, Cheltenham/Beaumaris (top right), Turner Road and Chesterville Road, Moorabbin (bottom left), Nepean Highway (left section), Graham Road and Middleton Street, Highett (bottom right). A large section of this image includes Cheltenham Park and Victoria Golf Club.White text: 3831-219 Lens information [indecipherable] RINGWOOD M/S 7922-3 RUN 15 Clockface image 5,300' ASL VIC DLS© 5-1-84cheltenham, highett, industrialisation, urbanisation, moorabbin, beaumaris -
 City of Kingston
City of KingstonPhotograph - Black and white, 3 March 1954
Cheltenham and Moorabbin are suburbs within the City of Kingston that were originally established as rural market gardening communities The area is bordered by Highett and Mentone. The market gardens, farms and paddocks have gradually been sub-divided into housing and industrial estates. Highett is developed with residential homes but was also the site of major facilities such as the Highett Gas Works. This aerial image covers a diverse section of the City of Kingston, taking in the suburbs of Moorabbin, Cheltenham, Highett and Mentone Residential housing development is prominent along the Frankston Railway line and the area still retains extensive market gardens and paddocks yet to be converted to a large industrial and commercial zone.Aerial photograph of Mentone, Cheltenham and Moorabbin within the City of Kingston. The area depicted in this 1954 aerial view includes Warrigal Road and Centre Dandenong Road intersection (top left); Charman Road, Patty Street, Bourke Street, Collins Street Mentone (top right); Keys Road Moorabbin (bottom left); Bay Road, Cheltenham (bottom right), Friendship Square, Cheltenham Park, Victoria Golf Club and Jack Barker Oval are visible. Nepean Highway and the Frankston railway line run centrally through the image. Highett Gasworks is also evident.White handwriting and type [indecipherable]. White image of clockface White image of compass White type 42956 Black handwriting 3/3/54 Williams [indecipherable] Black pencil: S [arrow] Black ink: 3/3/1954cheltenham, moorabbin, mentone, highett, market gardens -
 City of Kingston
City of KingstonPhotograph - Black and white, 20 December 1945
This photograph depicts a section of Cheltenham with a mix of housing and market gardens. The visible market gardens, farms and paddocks have gradually been sub-divided into housing, commercial and industrial estates. A large part of Cheltenham was originally established as a rural market gardening community. The railway line and station brought urban development to the area and the gradual subdivision of farmland and large land holdings for the development of housing. Aerial photograph dated 1945 of the Cheltenham area in the City of Kingston. Sydney Street (bottom left); Sinclair Street (top left); Weymar Street area off Wilson Street, Charles Street (botton right).White print VIC-170; 57197; RUN5; PROJ.No.5; MELB.METROP AREA Lens information [indecipherable] Small photograph: clockface Black ink: 57197cheltenham, market gardens, urbanisation -
 City of Kingston
City of KingstonPhotograph - Black and white, 20 December 1945
This aerial image covers a section of Cheltenham, with a large paddock yet to be converted to an industrial and later a commercial zone.This aerial photograph provides evidence of the changing landscape of Cheltenham and Highett since WWII. Photographed in 1945, the image features a large block of land now the site of site the major transformation of Cheltenham with the development of the Southland shopping centre in the 1960s and expansion in the 1990s.Aerial photograph of the Cheltenham area in the City of Kingston. This 1945 image is concentrated on the area between Bay Road and Garfield Lane with the distinctive bend into Jean Street. A large block of land runs between the Nepean Highway and the rail line. This is now the area occupied by the extension of Southland in the 1990s.cheltenham, southland, aerial photograph, highett -
 City of Kingston
City of KingstonPhotograph - Black and white, 20 December 1945
This aerial image covers a section of Cheltenham, with a large paddock yet to be converted to an industrial and later a commercial zone.This aerial photograph provides evidence of the changing landscape of Cheltenham and Highett since WWII. Photographed in 1945, the image features a large block of land now the site of site the major transformation of Cheltenham with the development of the Southland shopping centre in the 1960s and expansion in the 1990s.Aerial photograph of the Cheltenham area in the City of Kingston. This 1945 image is concentrated on the area between Bay Road and Garfield Lane with the distinctive bend into Jean Street. A large block of land runs between the Nepean Highway and the rail line. This is now the area occupied by the extension of Southland in the 1990s. It is a negative version of VKHC124.cheltenham, southland, market garden -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionDisplay board
The Forests Commission and its successors continuously encouraged bushfire research and innovation. In 1946 a large parcel of industrial land was purchased at North Altona as a fire cache and workshop. The Altona workshop became a hotbed of new technological innovation… an exhilarating place where lots of things were invented and tested. In fact, a lot of Australia’s pioneering equipment development was led by staff from Altona, often in collaboration with other State forestry and fire authorities. The CSIRO also contributed significantly. The US Forest Service, the US Bureau of Land Management and US State agencies such as the California Department of Forestry and Fire (CalFire) as well as the Canadian Forest Service faced similar challenges and proved strong and willing partners in sharing knowledge, ideas, equipment and expertise over many decades. This collection of badges is testament to the relationships that were forged across the globe with the Altona workshop. Large display panel featuring many fire service badgesforests commission victoria (fcv), bushfire, bushfire aviation -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (Item) - (SP) CAC History Boomerang Description WS Robinson File No 1 7.1.1935 to 18.8.1942 Various Correspondence R3
Correspondence Notes on the "Boomerang" Interceptor 18/8/42 Correspondence re setting up aircraft industry in Australia - between W S Robinson, A G Brown (CAC), S A Middleton (Austral Development Ltd London.), Douglas Aircraft Company, F Mitchell, BHP,, Essiungton Lewis BHP, Australian William S. Robinson had been Managing Director of Broken Hill Associated Smelters, based in London. He had played a key roll in negotiating the British Zinc Corporation’s investment in mining at Broken Hill NSW and formation of the resultant Australian business The Zinc Corporation. Returning to Australia, he was appointed to high levels of Australian Government during the Second World War to formulate policy on wartime demands for Australia's industrial and metals supply. Robinson was held in high regard by successive Prime Ministers and was a close associate of Essington Lewis, head of Broken Hill Pty Ltd (BHP). W.S. Robinson was a strong believer in aviation and business and air transportation having backed the purchase of two DH.84 Dragons in 1933 by associate company Western Mining Corporation to carry out a 12-month aerial photographic survey. He promoted the formation of Commonwealth Aircraft Corporation at Fishermans Bend, Melbourne to ensure Australian production of military aircraft. -
 Moorabbin Air Museum
Moorabbin Air MuseumDocument (Item) - (SP) CAC History Aviation Syndicate Minutes and Agenda
Correspondence Notes on the "Boomerang" Interceptor 18/8/42 Correspondence re setting up aircraft industry in Australia - between W S Robinson, A G Brown (CAC), S A Middleton (Austral Development Ltd London.), Douglas Aircraft Company, F Mitchell, BHP,, Essiungton Lewis BHP, Australian William S. Robinson had been Managing Director of Broken Hill Associated Smelters, based in London. He had played a key roll in negotiating the British Zinc Corporation’s investment in mining at Broken Hill NSW and formation of the resultant Australian business The Zinc Corporation. Returning to Australia, he was appointed to high levels of Australian Government during the Second World War to formulate policy on wartime demands for Australia's industrial and metals supply. Robinson was held in high regard by successive Prime Ministers and was a close associate of Essington Lewis, head of Broken Hill Pty Ltd (BHP). W.S. Robinson was a strong believer in aviation and business and air transportation having backed the purchase of two DH.84 Dragons in 1933 by associate company Western Mining Corporation to carry out a 12-month aerial photographic survey. He promoted the formation of Commonwealth Aircraft Corporation at Fishermans Bend, Melbourne to ensure Australian production of military aircraft. -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Administrative record (Collection) - Collection of Ledgers and other material of the Warrnambool Chamber of Commerce, 20th century
... years it was a major influence in the development of Warrnambool ...Warrnambool Chamber of Commerce administrative material archivePreservation of an historical collectionLedgers and other material kept in 5 A3 archival boxes and archival folders.Ledgers containing Minutes, Newspaper Cuttings, Constitution, Annual Reports etcwarrnambool chamber of commerce, marcus saltauwarrnambool chamber of commerce, marcus saltau -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncNegative - Photograph, View towards Main Road, Research from Maroondah Aqueduct Trail showing mudbrick manufacture, Research Industrial Estate, 1991
Eltham Little Theatre in centre distance and new housing estate development off Reynolds Road in distanceRoll of 35mm colour negative film, 9 strips Colour print 10 x 15 cmFuji HG 200 CA-1eltham little theatre, houses, main road, maroondah aqueduct, maroondah aqueduct trail, mudbrick, mudbrick construction, research (vic.), research industrial estate, reynolds road -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - MCCOLL, RANKIN AND STANISTREET COLLECTION: REPORT ON CASTLEMAINE, MALDON & OTHER AREAS
Copy of a typewritten report on Castlemaine, Maldon, and other areas of the main Bendigo District by H.W. Gepp Consultant on Development to the Commonwealth Government. W. Baragwanath Director of the Geological Survey of Victoria and F.L. Stillwell D.Sc. Council for Scientific and Industrial Research. Mentions Castlemaine, Fryertown, Maldon, South German Mine, Mt. Tarrengower Tunnel, Raywood, Sebastian, Wedderburn, Inglewood, Whipstick, Lightning Hill, Black Forest Mine, Old Tom Mine. Trentham. Dated 17th September 1931. Consists of 19 Foolscap PagesH.W. Gepp, W. Baragwanath, F.L. Stillwell.gold, mining, report, gold mining, bendigo, castlemaine, maldon -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumBook, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), "MMTB Its Progress and Development - 1919 - 1929", 1960's
Book , green / brown stippled cover, with 32 pages on gloss paper centre stapled titled "MMTB Its Progress and Development - 1919 - 1929". Looks at the first ten years of the Board from its formation by an Act of Parliament starting on 2/7/1919 - includes notes on the General Scheme, Industrial, The Board, power, traffic, medical examination, training, Workshops, tram noises, Wattle Park, replacement of Trams by Buses, buses, community services, finances, statistics and appendices. pdf file text searchable when opened separately.Has "H S McComb" in ink along the top of the cover.trams, tramways, mmtb, buses, training, traffic control, statistics, wattle park, medical, finances -
 Department of Energy, Environment and Climate Action
Department of Energy, Environment and Climate ActionAltona Collection Photography and Cataloguing - November 2024
In November 2024, a small group of cheerful volunteers from the Forests Commission Retired Personnel Association (FCRPA) toiled over nine days to dust-off, photograph and record nearly 300 artifacts in DEECA's Altona Museum. It followed a similar project at the FCRPA's Beechworth Museum in February 2024. The Altona project was generously supported by DEECA / FFMVic to engage professional photographer Mark Jesser from Wodonga whose boundless energy and good humour helped to create these amazing images. Special thanks go to the FFMVic Chief Fire Officer, Chris Hardman, as well as Andrew Stanios and Kat Jensen for making it happen. FFMVic crews and the ever-patient staff from Altona took a strong interest and also helped to shift some of the heavy items like pumps and the Bedford tanker which was very welcome. The Forests Commission and its successors continuously encouraged bushfire research and innovation. In 1946 a large parcel of industrial land was purchased at North Altona as a fire cache and workshop. The Altona workshop became a hotbed of new technological thingumajigs… a marvellous blend of Aladdin’s Cave of Wonders coupled with Wallace and Gromit’s madcap contraptions… an exhilarating place where lots of gizmos were invented and tested… mostly with astounding results... but nearly always with some head-scratching frustrations… and thankfully not too much explosive mayhem. In fact, a lot of Australia’s pioneering equipment development was led by staff from Altona, often in collaboration with other State forestry and fire authorities. The CSIRO also contributed significantly. The US Forest Service, the US Bureau of Land Management and US State agencies such as the California Department of Forestry and Fire (CalFire) as well as the Canadian Forest Service faced similar challenges and proved strong and willing partners in sharing knowledge, ideas, equipment and expertise over many decades. The collection at Altona started in the 1970s by fire equipment wizard Barry (Rocky) Marsden. As obsolete equipment was returned to the Fire Protection Workshop for auction, Rocky began the process of selecting some which would be interesting to retain and display. The items at Altona represent just a small sample of the amazing story of Victoria's forestry and bushfire heritage. The largest item was undoubtedly the Bedford tanker which took two days and nearly 1000 photos which were later stitched together with photoshop. The oldest item is probably the Ericsson wall telephone from 1904. There are also many unique items, but the CSIRO incendiary machine and ping-pong incendiary machine developed at Altona probably had the most significant impact on fire management in Australia. There are plenty of gaps in the collection, but some items are in regional DEECA offices. It’s hoped to merge the FCRPA's Beechworth collection to Altona one day and rename the site to honour Rocky Marsden. There may be some additions to the Altona museum over time, but space is limited. The museum is available to visit by appointment. Peter McHugh - January 2025 forests commission victoria (fcv) -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - LONG GULLY HISTORY GROUP COLLECTION: HISTORICAL GUIDE TO BENDIGO
Brochure with an invitation to visit Historical and Mining Museum in Mechanic's Institute, Eaglehawk. Drawing of poppet legs on the front with The Royal Historical Society of Victoria Bendigo Branch. Historical Guide to Bendigo including Self Tours of Bendigo's Famous Goldfields. Forward by John Hattam. Contributors are: H Biggs, Miss L J Parry, A Richardson, L C Bennetts and Edith Checcucci. Credits - The Bendigo Advertiser, Cambridge Press, Mines Department (Bendigo) and J R W Purves. Items include Bendigo Tramways Compiled by H Biggs, Early Bendigo Hotels Compiled by L C Bennetts, Eaglehawk Compiled by H Biggs, Noted Events Compiled by June Parry, The Bendigo Post Office Compiled by LC Bennetts, The Bendigo Goldfield. Introduction to Field and Guide to Some Famous Mines Compiled by A Richardson. Photos include: Pall Mall Bendigo, Ravenswood Homestead, An Early Battery at Kangaroo Flat, Historic High Street Golden Square, The Lonely Grave, Battery Tram c1888, Steam Tram c1892, Electric Tram c1903, The New Chum Railway Golden Square, United Hustlers and Redan Mine Sandhurst Road, Central Deborah Violet Street, Deborah Mine Quarry Hill, Deborah Mine 1000 ft level, First Motion Winding Engine at Central Deborah, Victoria Hill Area, and Looking south from New Chum Hill in 1890's. Also 11010.254, 255, 268, 288a, 288b, and 289.bendigo, history, long gully history group, the long gully history group - historical guide to bendigo, the royal historical society of victoria bendigo branch, historical and mining museum, mechanic's institute eaglehawk, librarian mechanic's institute, miss j parry, john hattam, h biggs, a richardson, l c bennetts, edith checcucci, bendigo advertiser, cambridge press, mines department (bendigo), j r w purves, mr a o'keefe, shire of marong, the sandhurst and eaglehawk tramway company, mr j taylor, mr j hanson, the bendigo tramway company, electric supply company, coliban water suply, juvenile industrial exhibition, geo lansell, cr a harkness, salvation army, vine and fruitgrowers association, decentralisation league, constable thomas ryan, miners association, art gallery, post office, miss broadfoot, bendigo hospital, opera company, bendigo development league, victorian women's franchise league, ana hall, the bendigonian, law courts, temperance hall, trades hall (old wardens court), roman catholic cathedral, shamrock hotel, bendigo philosophical society, old bendigonian society, bendigo fire brigade, bendigo volunteers to south african war, hawkins, porcupine inn, criterion hotel, royal hotel, bendigo hotel, black swan hotel, gillies bakery, hibernian hotel, sandhurst hotel, freemasons hotel, courthouse hotel, shamrock hotel, governor hotham, heffernan & crowley, new chum railway, victoria quartz, shenandoah, shamrock mine, hercules no 1 (originally pearl east), hercules new chum (late pearl), carlisle mine, mr arblaster, meurer, sandhurst bee, benevolent asylum, bendigo gas company, a lloyd, coliban water supply scheme, cr w v simons, eaglehawk council, j mouat, sir henry barkly, agricultural and horticultural exhibition, sandhurst and eaglehawk boroughs, cr john mcintyre, latham and watson's mine, galatea (model ship), st paul's church of england, rev g p despard, fine arts exhibition and exposition, bendigo rifle association, strathfieldsaye shire hall, corporate high school, bendigonian society, richard andrews, easter fair, g aspinall, j burnsides, sir h manners sutton, beehive stores, mining exchanges, bendigo water works, city family hotel, bendigo united friendly society medical institute and dispensary, benevolent asylum, jewish synagogue, masonic hall, school of mines, mr j h abbott, australian natives association, royal princess theatre, albion hall, central state school, high school, gravel hill state school, electricity commission, james mouat, warring natives, the rocks, joseph crook, gold discovery, marong district roads board, camp hotel, mr charles sherratt, city of bendigo, mt alexander north run, grice and heape, ravenswood, gibson and fenton, mrs john kennedy, mrs patrick farrel, mr j a paton, mr lachlan mclachlan, theatre royal, sir charles and lady hotham, harney's bridge, e j ennor, sandhurst fire brigade, the health of towns act, mr townsend, cornish & co, bendigo pottery, bendigo agricultural society, pike or pyke, baby health centre, sandhurst post office, government survey office, sandhurst trustees company, mr h b briston, savings bank, telegraph office, sir henry brougham lock, hon sir john nimmo, sandhurst public offices, the new prince of wales mine, new prince of wales no 2, the whip and jersey, lansell's big 180, new chum and victoria mine and battery, new chum railway, koch's pioneer, south new moon, catherine reef united, new moon, virginia mine, south belle vue, new chum railway, central nell gwynne, north nell gwynne, ironbark mine, new chum syncline, hercules, herculesl energetic, roberts & sons, harkness & co, horwoods, great southern, ulster, carlisle, cornish, new st mungo, duchess tribute, south devonshire, hopewell mine, saxby mine, mcnair & co, mr king, bourke and wills, sandhurst hotel, the dascombe nugget, victoria nugget, r r haverfield, ballerstedt, rae, wittscheibe, lazarus, cave and amos, bendigo amalgamated goldfields, bendigo mines limited, the deborah, north deborah, central deborah, the new red white and blue consolidated (big blue), union, lansell's new red white and blue 9later no 3 shaft), h harkness & co, thompson & co, central deborah, lansell's bendigo battery, north red white and blue, central red white and blue, roberts and sons, little 180 (originally lansell's 180 no 2 shaft), john brown knitwear factory, south ironbark originally victoria consols east shaft, ironbark (originally ironbark east shaft), manchester arms hotel, wattle gully mine chewton, hercules, old wheal-owl, central nell gwynne, gold mines hotel, bendigo city council, jack barker, the new chum syncline, the courier of the mines, telegraph office, bendigo cemetery, white hills cemetery, eaglehawk cemetery, kangaroo flat cemetery, new moon, suffolk united, north new moon, fortuna hustlers, buckell & jeffrey's, royal hustlers reserve no 2 (city and park shafts), jonathan harris, latham and watson, great hustlers, great extended hustlers, j hustler, latham, watson, tribute or pups shaft, bendigo's worst mining disaster, hustlers reef (old hustlers), hustlers reef no 1, lansell's comet, the old comet (cooper's claim), united hustlers and redan, comet hill state school, k k shaft, north or new hustlers (agnew hustler), johnson's no 3, south johnson's, lansell's sandhurst needle, cleopatra needle top, british american, collman and tacchi, south virginia, saddle reefs and spurs, pall mall bendigo, ravenswood homestead, an early battery at kangaroo flat, historic high street golden square, the lonely grave, battery tram c1888, steam tram c1892, electric tram c1903, teh new chum railway golden square, united hustlers and redan mine sandhurst road, central deborah violet street, deborah mine quarry hill, deborah mine 1000 ft level, first motion winding engine at central deborah, victoria hill area, looking south from new chum hill in 1890's -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyBook, Kate Shaw et al, Ewan Ogilvy's Bayside Papers, Box Three - Bayside Views - A Collection of critical perspectives on the Bayside Development, 1988
... Papers' relating to the proposed development of Port Melbourne... development of Port Melbourne industrial land in the late 1980s ...Ewan OGILVY, former Melbourne Councillor and also of Community Services Victoria, Inner Urban Ministerial Advisory Committee and Uniting Church's Centre for Urban Research and Action (CURA), was instrumental in social justice approaches to town planning. He and CURA's Social Justice and the City Project funded Port Melbourne community groups protesting against the SCDC development in 1987. His files were presented to the Society in May 2001 on his preparation for leaving Victoria.From Ewan OGILVY'S chronologically organised 'Bayside Papers' relating to the proposed development of Port Melbourne industrial land in the late 1980s: Bayside Views - A Collection of critical perspectives on the Bayside Development, a book of essays on Bayside issues, 1988 - funded by the Justice in the City projectSigned 'Ewan Ogilvy'town planning, town planning - proposals shelved - bayside, public action campaigns, environmental issues, public housing, missions to seamen, centre for urban research and action (cura), uniting church, sandridge city development co pty ltd, scdc, linton r lethlean, barry pullen, ewan ogilvy
