Showing 171 items matching "school of metallurgy"
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, Ballarat School of Mines Diploma Course, 1947, 1947
Typed list of diploma courses at the Ballarat School of Mines.ballarat school of mines, courses, diplomas, mathematics, physics, english, applied mechanics, engineering drawing, chemistry, assaying, metallurgy, graphics, heat engines, machine shop practice, geology, ore dressing -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionExercise Book, Metallurgy 111A, A.G Hale
... metallurgy ballarat school of mines and industries ballarat a.g. hale ...Black covered exercise book with notes on inside pagesmetallurgy, ballarat school of mines and industries, ballarat, a.g. hale -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Geology, Chemical, Physical, and Stratigraphical, 1886
These books were added to the library of the School of Mines Ballaarat in 1889. The author was Joseph Prestwich, who was a Professor of Geology at the University of Oxford.Two brown hard cloth covered books, Vol 1 & vol 2 with gold printing on the front cover and on the spine. .1) has a coloured fold out map of the World opposite the title page .20 has a coloured fold out map of Europe..1) A label is attached to the inside front cover with The School of Mines Ballaarat and the no. 955 and date purchased 14/3/89 (1889) as well as the institutions stamp in several places throughout the book. .2) As above but with no. 956 and on the inside fly is written in pencil 'Stamped in Error' with a Ballarat School of Mines Student Library stamp crossed out.geology, bookplate, library plate, ballarat school of mines library, joseph prestwich, geological map of the world, geological map of europe, hieropolis thermal springs, rockss, ice, volvanoes, earthquakes, metallurgy, shakespeare's cliff dover, wapley, gloucestershire, redruth mining district, fossils, reptilian footprints, chalk, london clay -
 Victorian Interpretive Projects Inc.
Victorian Interpretive Projects Inc.Book, Theodore Jesse Hoover, The Economics of Mining, 1938
Theodore Jesse Hoover, brother of the 31st President of the United States, was born in West Branch, Iowa, on January 28, 1871. He attended Stanford and received the Bachelor of Arts degree in Geology and Mining in 1901. Following graduation his professional career started with the position of assayer for the Keystone Consolidated Mining Company. After one year, he became assistant manager for the Standard Consolidated Mine, and a year later he was promoted to manager of the operation. In 1907 Hoover went to London as general manager of Minerals Separation, Ltd. This company was developing the froth flotation process for recovering minerals from ores. Hoover took an active part in the development of the flotation concentration process and authored one of the first books on the concentration of ores by flotation. After four years with Minerals Separation, Ltd., Hoover entered private practice as a consulting mining and metallurgical engineer with offices in London and in San Francisco. He was very successful and held positions of consulting engineer, managing director, director, and president of many mining companies in America, Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australia. He returned to Stanford in 1919 as Professor of Mining and Metallurgy and Executive Head of the Department of Mining and Metallurgy. His experience and ability in organization made him a natural leader. He was influential in the formation of the School of Engineering at Stanford. The School was formed in 1925 and he was made dean, a position he held until his retirement in 1936. As dean of engineering, he promoted a broad fundamental training program for undergraduate engineering students. Under his guidance, emphasis was placed upon graduate work and he was responsible for developing strong graduate engineering curricula at Stanford. While dean he continued teaching and his course, "The Economics of Mining," developed into a book which was published in 1933. He became interested in the functions of engineers and, with Professor Fish, wrote a book entitled "The Engineering Profession" which was published in 1940 and revised in 1950. In addition to his academic activities he was generous in his hospitality. Faculty and students alike enjoyed the annual field day and barbecue at his Rancho del Oso, near Santa Cruz. He was widely read and had a lively interest in all the things he encountered. He speculated on the antiquity of man and man's early production processes. To verify an idea regarding flint tools, he studied their shapes and became proficient in making arrow heads. He was also interested in wild life, and was one of the founding members of the Cooper Ornithological Society. (http://engineering.stanford.edu/about/bio-hoover)Blue hard covered book of 547 pages including an index. Contents include mine valuation (sampling, ore deposits, ore reserves, financial provisions, sale of mineral product, metal prices, reports) and Mining Organization (Co-operative effort, Mining Companies, Promoting Mining Enterprises, fluctuations of share prices, valuation of mining shares, fakes and fallacies, the mining Engineer and the law) and Mine Management (Organization of staff, mine manager, efficiency, industrial relations, training and discipline, safety).inside cover 'Charles Bacon Mackay School of Mines'.mining, economics, hoover, stanford, mackay school of mines, mackay, bacon -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumBook, Percy, John, Percy's Metallurgy - Iron & Steel, 1894
Dowlais is a former Iron/steel making and coal mining town in Wales, United Kingdom.1 Hardcover book light brown embossed cover, gold lettering on spine, 1864, subject matter, the art of extracting metals from their ores and adapting them to various purposes of manufacture. With illustrations, chiefly from original drawings, carefully laid down to scale. .2 Newspaper Article "Dr. Percy on Iron and Steel" published in The Times Tuesday, May 17, 1864 .3 Plan for Dowlais New Mills Gold Lettering on spine: "Percy's Metallurgy Iron & Steel London John Murray Faded Maroon stamp page 2 - Clunes School of Mines No. 24 16 Jun 93metallurgy, mining -
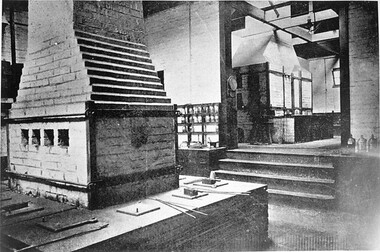 City of Ballarat Libraries
City of Ballarat LibrariesPostcard - Card Box Photographs, Possible Metallurgy Laboratory, School of Mines
... Possible Metallurgy Laboratory, School of Mines.... Possible Metallurgy Laboratory, School of Mines. Postcard Card Box ...school of mines, ballarat, education, mining -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionSculpture - Marble sculpture, 'Professor Alfred Mica Smith' by Paul Montford, 1924
... -loved Professor of Chemistry and Metallurgy at the Ballarat... of Chemistry and Metallurgy at the Ballarat School of Mines between ...Paul Raphael MONTFORD (1868 - 1938) Paul Montford moved to Australia to carve four buttress groups in granite for the Melbourne Shrine of Remembrance. In 1924 he was teaching at Geelong Technical College. Professor Alfred Mica Smith was a long term lecturer at the Ballarat School of Mines. The sculpture was commissioned by former Students of the Ballarat School of Mines working in Western Australia. One of those former students, William Corbould, remembered his first encounter with the professor fondly:- 'From the Registrar's Office I was led to be introduced to the Professor of Chemistry, one Mica Smith. The initial encounter gave me little encouragement - his large laboratory was filled with hundreds of bottles bearing strange labels with queer symbols on them. My heart sank. At the first opportunity I grabbed my hat and made for the door, but the good professor called me back. I pointed out that I was never any good at school ... so it was no use pretending to be clever enough to understand all those weird symbols! The Professor told me not to worry about that and took me to one of the benches where he found a blowpipe and a charcoal block. Mixing together two powders from bottles on the shelf he transferred a sample to the charcoal and directed the bunsen flame onto it. Soon it began to melt and a white bead appeared in front of my eyes. He then took a test tube and added a little colourless liquid from each of two bottles. A beautiful dark blue colour appeared. My interest was won.' Alfred Mica Smith was the well-loved Professor of Chemistry and Metallurgy at the Ballarat School of Mines between 1881 and 1922. Upon reaching the age of 78 Mica Smith retired having influenced generations of miners. At the time of his death Ballarat School of Mines Students’ Magazine reported: "In the annals of the School, the year 1922 will be noted chiefly as the last year in which Professor Mica Smith taught here. With his retirement, a memorable epoch closed. The Professor has served the School for 42 years with a service, the length and thoroughness of which are unique. … It is not quite realised in this city how famous the School became throughout the world, nor to what extent the Professor was responsible for its high position in the mining and metallurgical world. … This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 2000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.Marble bust of Ballarat School of Mines Professor Alfred Mica Smith by Paul Montford. The bust is mounted on a jarrah pedestal made from timber donated by the Millar Timber and Trading Company. The bust was formally presented to the Ballarat School of Mines on Saturday 13 December1924 in front of Alfred Mica Smith and a large gathering. It is signed 'Paul R. Montford, Sc, 1924' at the back.Professor A. Mica Smith, 1924, Presented by His Old Students Associated with Western Australia as a Token of Affectionate Esteemart, artwork, ballarat school of mines, montford, paul montford, alfred mica smith, mica smith, marble, bust, sculpture -
 City of Greater Bendigo - Civic Collection
City of Greater Bendigo - Civic CollectionLetter - Correspondence from School of Mines and Industries, Bendigo to R.H. S Abbott, Bendigo School of Mines and Industries, 17th September, 1901
The Bendigo School of Mines was opened in 1873 following the first report of the Technological Commission in 1869 which recommended the establishment of schools of design and science to meet the scientific and technical needs of the mining industry on the local gold fields. Initially mining, chemistry, geology, metallurgy and art were taught while a separate school of design was established in c. 1870 but incorporated into the School of Mines around 1883 when it was renamed as the School of Mines and Industry. In 1904 The Mechanics Institute was liquidated and its assets and buildings acquired by the School of Mines. Around 1907 a Junior Technical School commenced to operate at the School of Mines and Industry but ceased operating in 1961 with that function being transferred to the White Hills and Kangaroo Flat Technical Schools. The Bendigo School of Mines and Industry became known as the Bendigo Technical College from the 1st July 1959. It operated under that name until February 1967 when it became the Bendigo Institute of Technology (B.I.T.). Construction work commenced in c.1965 which saw the Institute progressively re-locate to new buildings at Flora Hill. (Fn: https://prov.vic.gov.au/archive/VA3091) Richard Hartley Smith Abbott was the step son of Joseph Henry Abbott and continued on in the family tradition of entering into business. He was elected a representative in the Mandurang riding in the Shire of Strathfieldsaye in 1887, served as Mayor of the City of Bendigo from 1917 - 1918 and was Secretary of the Bendigo Art Gallery for over 20 years. His father Joseph Abbot had been a member of the School of Mines Administrative Council and RH Abbott served as President of the School of Mines for two years and was a highly regarded business man within the local community. The School of Mines and Industries would have written to him asking him to intervene to ensure that their reputation remained intact.Handwritten letter by the registrar from the School of Mines to R H S Abbott on lightly lined writing paper.city of greater bendigo education, city of greater bendigo mining, mayor rhs abbott, shire of strathfieldsaye, bendigo art gallery -
 City of Greater Bendigo - Civic Collection
City of Greater Bendigo - Civic CollectionMedal, School of Mines Silver Jubilee 1873 - 1923, 1923
The Bendigo School of Mines was opened in 1873 following the first report of the Technological Commission in 1869 which recommended the establishment of schools of design and science to meet the scientific and technical needs of the mining industry on the local gold fields. Initially mining, chemistry, geology, metallurgy and art were taught while a separate school of design was established in c. 1870 but incorporated into the School of Mines around 1883 when it was renamed as the School of Mines and Industry. In 1904 The Mechanics Institute was liquidated and its assets and buildings acquired by the School of Mines. Around 1907 a Junior Technical School commenced to operate at the School of Mines and Industry but ceased operating in 1961 with that function being transferred to the White Hills and Kangaroo Flat Technical Schools.Obverse; Ornate relief design made up of a coat of arms with mining icons in each quarter flanked by flags on either side. Per varios usus artem experientia fecit written in scroll underneath. Translation: Practice has brought skill through different exercises. (Manilius) Reverse; Outer wheel Bendigo School of Mines and Industries. Inner; 1873 /Jubilee /1923Obverse; Per varios usus artem experientia fecit Reverse; Outer wheel Bendigo School of Mines and Industries. Inner; 1873 /Jubilee /1923city of greater bendigo education, bendigo school of mines -
 University of Melbourne, School of Chemistry
University of Melbourne, School of ChemistryGold Assay Balance
Born in Ireland, John Drummond Kirkland trained as a chemical analyst through apprenticeship in a medical laboratory in Dublin, before migrating to Australia in 1852 and moving to Melbourne in 1855. While still an undergraduate medical student at the University of Melbourne, he was appointed lecturer in chemistry following the sudden death of John Macadam in 1865. Due to the enthusiastic support of his fellow students this temporary role became a permanent appointment the following year. Kirkland continued his studies, graduating in medicine in 1873 and surgery in 1880. His son, John Booth Kirkland, was appointed as his assistant in 1878, later leading to accusations of nepotism. In 1882 John Drummond Kirkland became the University?s first professor of chemistry and metallurgy, continuing until his death in 1885. Today?s researchers use a high performance computing facility named ?Kirkland? after the first Professor of Chemistry at the University of Melbourne. Chemistry was still controlled by the medical school during Kirkland?s career, but became part of the science degree from 1886, along with the appointment of David Orme Masson as professor. Kirkland struggled for University funding to buy new apparatus. To compensate, he bought much from his own personal funds, including analytical chemistry equipment. Chemistry was first taught at Melbourne in the medical school, located in the area now occupied by Physics and the Ian Potter Museum of Art.Gold Assay Balance, almost certainly Kirkland's own. -
 University of Melbourne, School of Chemistry
University of Melbourne, School of ChemistryCombustion Demonstration
John Macadam was a Scottish born analytical chemist, medical practitioner and politician. As a student he soon showed a flair for analytical chemistry, and later also studied medicine. He arrived in Melbourne in 1855 to take up an appointment as lecturer in chemistry and natural science at Scotch College, a position he held until 1865. In 1857 Ferdinand von Mueller named the Macadamia nut after him. He officiated as one of two umpires at one of the earliest recorded games of Australian rules football, between Scotch College and Melbourne Grammar in 1858. Macadam was appointed government analytical chemist in 1858 and health officer to the City of Melbourne in 1860. He represented Castlemaine in the Legislative Assembly between 1859 and 1864. Appointed secretary of the Royal Society of Victoria in 1860 and vice-president in 1863, he was also the secretary of the exploration committee of the Burke and Wills expedition. When the Medical School of the University of Melbourne opened in 1862 Macadam was appointed lecturer in chemistry. He was a skilled, popular and eloquent lecturer, learned and generous with his knowledge. Sadly, just three years later, and aged only 38, he died at sea on the way to give evidence at a murder trial in New Zealand, leaving his widow Elizabeth (n�e Clark), and a son. He was accompanied on that voyage by his assistant, the medical student John Drummond Kirkland, who later became the University?s first Professor of Chemistry. Born in Ireland, John Drummond Kirkland trained as a chemical analyst through apprenticeship in a medical laboratory in Dublin, before migrating to Australia in 1852 and moving to Melbourne in 1855. While still an undergraduate medical student at the University of Melbourne, he was appointed lecturer in chemistry following the sudden death of John Macadam in 1865. Due to the enthusiastic support of his fellow students this temporary role became a permanent appointment the following year. Kirkland continued his studies, graduating in medicine in 1873 and surgery in 1880. His son, John Booth Kirkland, was appointed as his assistant in 1878, later leading to accusations of nepotism. In 1882 John Drummond Kirkland became the University?s first professor of chemistry and metallurgy, continuing until his death in 1885. Today?s researchers use a high performance computing facility named ?Kirkland? after the first Professor of Chemistry at the University of Melbourne. Chemistry was still controlled by the medical school during Kirkland?s career, but became part of the science degree from 1886, along with the appointment of David Orme Masson as professor. Kirkland struggled for University funding to buy new apparatus. To compensate, he bought much from his own personal funds, including analytical chemistry equipment. Chemistry was first taught at Melbourne in the medical school, located in the area now occupied by Physics and the Ian Potter Museum of Art.Demonstration of combustion Mid 19th century, used by McCoy, MacAdam,and Kirkland -
 University of Melbourne, School of Chemistry
University of Melbourne, School of ChemistryDiethylene Disulphide Methyl Iodide
Born in Ireland, John Drummond Kirkland trained as a chemical analyst through apprenticeship in a medical laboratory in Dublin, before migrating to Australia in 1852 and moving to Melbourne in 1855. While still an undergraduate medical student at the University of Melbourne, he was appointed lecturer in chemistry following the sudden death of John Macadam in 1865. Due to the enthusiastic support of his fellow students this temporary role became a permanent appointment the following year. Kirkland continued his studies, graduating in medicine in 1873 and surgery in 1880. His son, John Booth Kirkland, was appointed as his assistant in 1878, later leading to accusations of nepotism. In 1882 John Drummond Kirkland became the University?s first professor of chemistry and metallurgy, continuing until his death in 1885. Today?s researchers use a high performance computing facility named ?Kirkland? after the first Professor of Chemistry at the University of Melbourne. Chemistry was still controlled by the medical school during Kirkland?s career, but became part of the science degree from 1886, along with the appointment of David Orme Masson as professor. Kirkland struggled for University funding to buy new apparatus. To compensate, he bought much from his own personal funds, including analytical chemistry equipment. Chemistry was first taught at Melbourne in the medical school, located in the area now occupied by Physics and the Ian Potter Museum of Art. (Sir) David Orme Masson was Professor of Chemistry at the University of Melbourne from 1886 to1923. As well as being a distinguished teacher and researcher, he contributed significantly to Australian scientific and public life, being instrumental in the establishment and governance of many important bodies including the CSIRO. Masson supported Antarctic research for 25 years, beginning with Douglas Mawson?s expedition of 1911. Born in England and receiving an MA, BSc and DSc from the University of Edinburgh, he was a gifted, elegant and disciplined lecturer and a researcher of substance. His research work included the theory of solutions, from which emerged the term ?critical solution temperature?; the periodic classification of the elements; and the velocity of migration of ions in solutions. Much of his research was done in collaboration with talented students such as David Rivett and his own son Irvine Masson. Masson was knighted in 1923. He is commemorated by the Masson Theatre and Masson Road at the University of Melbourne; a mountain range and island in Antarctica; a portrait painting by William McInnes in the foyer of the School of Chemistry; the Masson lectureship from the Australian National Research Council; and the Masson memorial scholarship from the Royal Australian Chemical Institute.Stocks used in the Blackie - Masson - J.B.Kirkland work. -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - SANDHURST SCHOOL OF MINES COLLECTION: ACQUITTANCE BOOK
... Metallurgical Works SANDHURST SCHOOL OF MINES Acquittance Book -t School ...Acquittance Book -t School of Mines/ thick cardboard cover 31x19x2 cm / purple binding / worn front and back covers containing records of the ACQUITTANCE BOOK -of the SCHOOL OF MINES showing entries from January 1887 June 1889 / numbered entries from 1 to 397 showing columns - Number, Name , Service and period , Amount , Acknowledged having received the sum set opposite my name for the services rendered -the latter column in some entries have a green Victoria one penny stamp stuck to the page - stamp duty , some have receipts attached for railway tickets, etc. other receipts include for , /// regular Payments include the Bendigo Gas company .//SANDHURST SCHOOL OF MINESdocument, sandhurst school of mines/the edward's metallurgical works -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionMagazine - Booklet, Ballarat School of Mines Students' Magazine, 1952-1961, 1952-1961
1957 - Art Lending Library, Neville Bunning, Dana Street Primary School - The Original Ballarat Junior Technical School, ATC, Flight Cadets; Ballarat Junior Girls' Technical School, Ballarat North Junior Technical School, Roll Call 1960 - Ballarat School of MNes Literary Sociaty, begonia parade, Efficient reading, enter the modern, Lois Morris, sheetmetal, G. Cornell Obituary, I. Menz Obituary, metallurgists' Society, Olympic games 1961- Red, black and white soft covered magazine of the Ballarat School of Mines Information outlined in the magazine includes: The Richard W. Richards Medal, Philips Electrical Industries scholarship, A.F. Heseltine scholarship, Hong Kong To-Day (by Daniel Yung), A Treatise on Mount Morgan, Bath Push, The Stud Room, A Gentlemen's Excursion to Beaufort House, Electrical Laboratory, Metallurgical Laboratory, The Australian Aboriginal in Modern Civilization (J. Kavanagh) , The history of Electricity ballarat school of mines, ballarat junior technical school, cadets, flight cadets, airforce cadets, ballarat school of mines students' association, noel delosa, noel whiticher, bob coutts, noel kelly, les dobie, noel murphy, malcolm peel, peter agrums, ian weir, sue mole, val baker, neil bromley, kevin oscar rogers, h.e. arblaster, richard w. richards, dick richards medal, keith hindson, james tinney, walter tooth, john bethune, vilma sansom, betty clark, travers duncn, joyce wilson, lex lockhart, jim beattie, joyce stevens, slim ingleton, john skuja, murray gillan, graeme willey, diana mainwaring, eureka stockade, east africa, canada, sumatra, chris sanos, greece, malaya, bee-keeping, worshipful company of plumbers, hong kong, daniel yung, mount morgan, history of electricity, peter robinson, john clelland, davis schmist, harry brue, harry brew, rex hollioake, broken hill, excusions, john wolfe, beverly selkirk, barry singleton, mara jekabsons, bill widdop, frank pomeroy, art lending library, john mckenzie, ballarat girls' technical school, robert norton, graeme williams, alan bethuse, janis erdmanis, alan rock, gail trewanack, tony white, ching thung tay, jack tay, noel whitcher, norm nash, helen ross, eric mcgrath, g. cornell death, i menz death, john wolffe, brian duthie, bill durant, w.g. durant, heather walton, heather durant, beverly singleton, neville bunning -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBooklet, The School of Mines Ballarat: A Statement of the Objects and Present Resources of the School, 1873, 1873
The Ballarat School of Mines was the first School of Mines in Australia and was established in 1870. 22 page booklet titles 'The Ballarat School of Mines: A Statement of the Objects and Resources of the School.' The book has a number of illustrations including the interior of the Ballarat School of Mines Laboratory, and the former Ballarat Circuit Court House. It includes a statement of the formation, progress, and present position of the School of Mines, Ballaarat. The image of the Ballarat School Mines Assay Room shows assay furnaces, crucibles, chimney, and teacher Joseph Flude on the far right. This room is now is a building known as the 'Old Chemistry Building'. Plan and elevation of the new Metallurgical Laboratory and Proposed Chemical Laboratory is depicted.On front cover "Recorded in M-A" "1873"ballarat school of mines, assay, courthouse, joseph flude, crucible, furnace, flude, warrington rogers, brough smyth, harrie wood, wood, james bickett, bickett, redmond barry, somerville learmonth, metallurgy, chemistry, laboratory, examinations, mining engineer, assayer, inorganic chemistry, underground managers, captains of shift, engieners, enginedrivers, louis balhausen, james campbell, l.s. christie, j.j. casey, alexander dempster, g. higinbotham, james martin, alexander millan, malcolm morrison, band of hope and albion, city of ballarat mining company, city of canterbury gold mining company, egerton mining company, el dorado gold mining company, golden reef gold mining company, happy valley company, hope quartz mining company, long tunnel gold mining company walhalla, hopewell quartz mining company, imperial quartz mining company, student numbers, fees, magdala quartz mining company stawell, mariners and sloane's quartz mining company, new north clunes company, park company, temperence quartz company, tookey quartz company new zealand, walhalla gold mining company, matthew seal, harrie woodmuseum, duke of cornwall claim, john lynch, robert m. sergeant, engineers, f.w. niven, william henry barnard, ballarat school of mines museum, museum, ballarat school of mines library, donations of specimens, mining -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Ballarat School of Mines, Ballarat School of Mines Annual Reports 1895-1902, 1902 (estimated); Bound copies of reports from 1895-1902
The Ballarat School of Mines was established in 1970 and was the first school of Mines in Australia.A number of Ballarat School of Mines Annual General reports bounds in a dark blue hardcover with black leather spine. Includes some illustrations such as the Ballarat School of Mines Senior Staff.mining, mining alumni, geometry, steam, botany, ballarat school of mines, alfred mica smith, j f usher, andrew anderson, chemistry, metallurgy, a e c kerr, henry j hall, veterinary science, robert e weir, assaying, mineralogy, petrography, algebra, trigonometry, applied, mechancis, land surveying, mine surveying, dynamics and heat, sound and light, magnetism and electricity, carpentry and joinery, architecture, photography, john warrington rogers, james bickett, thomas wanliss, henry cuthbert, museum, william huey, steele, and, gas, engines, mine managers certificate, john m sutherland, charles e campbell, cyanide plant, mining laboratory, samuel thornton, daniel walker, percy osborne, robert allan, hubert murphy, charles deane, ernest trend, thomas evans, alfred johnston, boer war, richard maddern, underground, ferdinand krause -
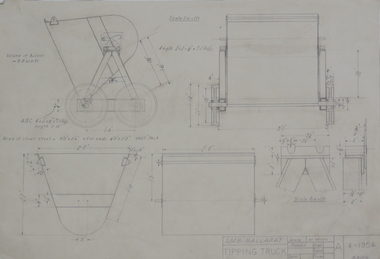 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDrawing - Student's Technical Drawings, Technical drawings, 1954
... technical drawing metallurgy murray gillen School of Mines ...pencil on paper student's technical drawings: .1) Tipping truck dimensions, parts and assembly views .2) A design-in-progress drawing of bucket and frame technical drawing, metallurgy, murray gillen, school of mines ballarat -
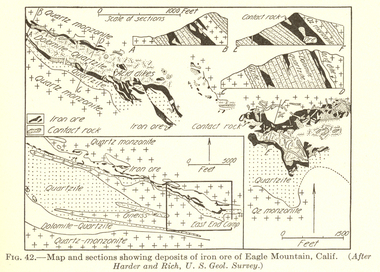 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, William Harvey Emmons, The Principles of Economic Geology, 1940, 1940
... mining engineering metallurgy university of nevada mackay school ...The book was used by Charles Bacon who studied at the University of Nevada in the late 1930s/early 1940s. Bacon worked at Bunker Hill Mines and Kellogg Idaho, before arriving in Australian in 1951. He worked for CN Myers, a company involved with paper converting. CN Myers was a family business (on Charles Bacon's maternal line). William Emmons was Professor and head of Geology and Mineralogy at the University of Minnesota; Director of Minnesota geological Survey; and previously Geologist, Section of Metalliferous Deposits, United States Geological Survey.Maroon soft covered book of 529 pages. Chapters include Magmatic Segregations, Pegmatities, Hypothermal Deposits, Sedimentary Depostis, Openings in Rocks, Metasomatic Processes, Mineral Associations and more.Inside front cover "Charles Bacon 1940 Lincoln Hall Ass. University of Nevada Reno, Nevada"charles bacon, mining engineering, metallurgy, university of nevada, mackay school of mines, geology, california -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - SANDHURST SCHOOL OF MINES COLLECTION: LETTER: RE THE EDWARD'S METALLURGICAL WORKS BENDIGO
SANDHURST (BENDIGO) SCHOOL OF MINES LETTER -Re the Edward's Metallurgical Works Bendigo -Memo number 416, dated 7.12.1907 'Dr to SCHOOL OF MINES (Annie Lawrie Coy) by The Edward's Metallurgical Works / 720 - re 4 bags Pyrites (paper damaged) photo - Edward's Metallurgical Works Bendigo at top of Memo showing factories, open fields, horse and buggydocument, the edward's metallurgical works bendigo / ( annie lawrie coy) / pyrites -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDocument, List of Subjects
School of Mines Ballarat is predecessor of Federation University Foolscap sized list of Subjects from Ballarat School of Mines with handwritten names.8S3S in large writng on the back school of mines ballarat, practical chemistry, mr. walker, theoretical chemistry, theoretical agricultural chemistry, practical agricultural chemistry, technical chemistry, metallurgy, alfred mica smith, metallurgical calculations, metallurgy of gold and ore dressing, assaying practical, assaying dry, mr. murphy, ore dressing practical, mining, mining geology, mineralogy, geology, petrology, botany, applied mechanics, mr hart, mine surveying, land surveying, steam and gas engines, mr gilchrist, elementry electricity & magnetism, electrical technology, mr sutherland, turning and fitting, mr connon, engineering drawing, mr kerr, geometry, algebra, trigonometry, physics, conics, calculus, mr whitington, building construction, plane and solid geometry, plumbing grade, mr hall, mr mullins, carpentry, wool classing, materia medica, mr gutheil, technical arithmatic, mr hutchison, telegraphy, mr williams, sloyd, mr slater, photography, mr campbell, manual training, cyanide, mr deane, mr brittain, mr martell, english, astronomy, list of subjects -
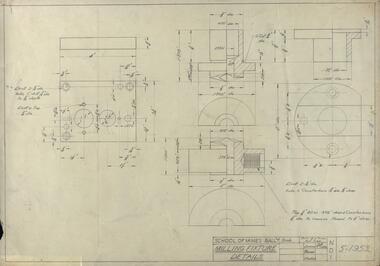 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDrawing - Student's Technical Drawing, Technical drawing, 1953
... technical drawing metallurgy g. heyes School of Mines ...pencil on paper student's technical drawing of Milling Fixtures Detailstechnical drawing, metallurgy, g. heyes, school of mines ballarat
