Showing 1656 items
matching small family
-
 Hymettus Cottage & Garden Ballarat
Hymettus Cottage & Garden BallaratPhotograph, 1938
One of a series of small photographs from the Ballarat Centenary celebrations on an old photo album page donated to the family from the Martin collection in 2012. This photo features the float from The City of Melbourne with that city's coat of arms on the side.This is one of a series of images from the Centenary of Ballarat 1938 collection. It demonstrates the involvement of municipalities across the state in the 1938 centenary celebrations and also fashions of the era being worn by subjects in the photographs.Small black and white photograph on page of photo album with several similar from the Ballarat Centennial celebrations of 1938. centenary of ballarat, 1938, city of melbourne, float, parades, fashion, apparel, -
 Hymettus Cottage & Garden Ballarat
Hymettus Cottage & Garden BallaratBooklet, Boomerang Songster
small booklet of popular song lyrics -
 Falls Creek Historical Society
Falls Creek Historical SocietyPhotograph - Axtrack oversnow vehicle Falls Creek Hotel
This vehicle, an Axtrack is located outside the Falls Creek Museum. It was built by Axel Andre who worked in Falls Creek as a mechanic for several years in the early 1970s. Axel was an engineer by trade. He built this small twin track vehicle for Ivan Spargo at the Falls Creek Hotel and then progressed to building bigger and better models. This included one for Ziggy Doer at Koki and Neville Mashford at Snowland purchased two of them. Some of these machines were also exported to America. Axel Andre later established a company Axtrack Engineering in Melbourne. There are still three of these Axtrack vehicles on the hill at Falls Creek in 2024. The vehicles were used for commercial purposes such as transporting supplies and staff around the mountain. The Spargo family from the Falls Creek Hotel used this vehicle for oversnow transport and it advertised Harvey Wallbanger Happy Hour. Ivan and Joy Spargo relocated from Melbourne to Falls Creek in 1965. They purchased a piece of leasehold land and built Spargo Lodge. This was a dorm style chalet built to accommodate large groups and families. Their son Rob Spargo met his future wife Blanche in 1967 when she was on holiday in Falls Creek. They married and purchased the site where the Falls Creek Hotel is today. The steep gradient of the site was a challenge to build on but was the best location available in the village. In 1970 Rob’s sister Leonie and her husband Glenn joined the business, and they started operating the hotel in 1972. The family played a critical role in the growth of the Falls Creek community and were involved in the foundation of Falls Creek Primary School and Falls Creek Search & Rescue. Rob was also involved in the start-up of Ski Victoria and has served as a member of the Chamber and Resort Management Board. Rob’s eldest daughter Lisa competed with the Australian Ski Team from 1985 to 1989 and has worked as a ski instructor in Australia, Austria & Colorado. In 2010 Lisa and her husband Damien Allport joined the family business and her parents retired to Tawonga South in 2014. Their children are now the fourth generation of the Spargo family living at Falls Creek enjoying the alpine lifestyle and providing outstanding hospitality. The 40 year tradition of the Harvey Wallbanger Happy Hour held on Tuesdays and Thursdays continues at Falls Creek Hotel in 2024.This item is significant because it depicts an important form of transport at Falls Creek, VictoriaA coloured photo of a black Axtrack oversnow vehicle decorated with red and yellow advertising.FALLS CREEK HOTEL APRES ENTERTAINMENT HARVEY HOUR TUES & THURS 3.30 PM LIVE ENTERTAINMENTaxtrack, oversnow vehicles, falls creek transport, spargo lodge, falls creek hotel -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - Photographs of Lewis Lewis and others
Photographs of Lewis Lewis and Reg Ansett in various locations with family and friends. 3 photocopies of photographs and 1 real photograph. They all have Lewis Lewis in them as well as others. The real photograph is a black and white photo of Lewis Lewis and his family beside a fence looking over the sea with large sea cliffs behind them (Image 3a). One of the photographs is a copy of this photo (Image 3b). Another photocopy is black and white photo of a different group of people in the same location by the sea (Image 3c). The last photocopy is black and white of a small plane with a group of people beside it (Image 3d). The real photograph has an attachment on the back that says, '1930 - 1940 on tour with Bus owner Booter and Bendigo (Image 3a). His Mother, his grandfather, his wife, Reg Ansett, his Aunty and Lewis Lewis.' The photocopy of the real photograph has black pen written on it that says, 'His mother, his grandfather, wife, Reg Ansett, his Aunty, Lewis Lewis, Garage Boort and Bendigo Bus owner 1920 - 1940. Built Medical Centre he left behind Rosanna,' (Image 3b). The last photocopy has blue pen written above the photo saying, 'History Lewis Lewis and Reg Ansett,' (Image 3d). lewis lewis, seaside, reg ansett, plane, buses -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Equipment - Camera & Lenses, 1984
Used by the donor's family for family photosCanon MC Camera with separate flash in black case - as well as two lenses in smaller black case complete with instruction book. Total of six items.Canon MCphotography, cameras -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Garden Hill, Eltham-Yarra Glen Road, Kangaroo Ground, 3 February 2008
The original house was built around 1850 was one of Kangaroo Ground's earliest homes, part of which remains today. Built by Scottish farmer Andrew Harkness who acquired the property in 1849 at the top of the hill with magnificent panoramic views as far as Kinglake, the same year he married Sarah Oswin. The property was known as Garden Hill from at least 1865. Andrew and Sarah had four sons and five daughters. Harkness was a founder of the Kangaroo Ground School and one of the first to suggest establishing the Eltham District Road Board (1858-71) of which he was a member, the pre-cursor to the Shire of Eltham (1871-1994). He was also a Trustee of the Kangaroo Ground Cemetery. His daughter Fanny married farmer Alexander White who purchased the property in 1893. Alexander White died in 1906 and ownership transferred to Fanny White. Son, Robert White was a Councillor of the Shire of Eltham at the time the Shire acquired two acres of land on the adjacent property from the Mess brothers for the creation of the Shire of Eltham Memorial Park (1921) in which the Shire of Eltham War Memoirial tower was erected (1926). Fanny White donated a small section of land from the Garden Hill property to facilitate entry access to the park. The White family sold the property to Sir Herbert Gepp in 1925. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p29This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, kangaroo ground -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Garden Hill, Eltham-Yarra Glen Road, Kangaroo Ground, 3 February 2008
The original house was built around 1850 was one of Kangaroo Ground's earliest homes, part of which remains today. Built by Scottish farmer Andrew Harkness who acquired the property in 1849 at the top of the hill with magnificent panoramic views as far as Kinglake, the same year he married Sarah Oswin. The property was known as Garden Hill from at least 1865. Andrew and Sarah had four sons and five daughters. Harkness was a founder of the Kangaroo Ground School and one of the first to suggest establishing the Eltham District Road Board (1858-71) of which he was a member, the pre-cursor to the Shire of Eltham (1871-1994). He was also a Trustee of the Kangaroo Ground Cemetery. His daughter Fanny married farmer Alexander White who purchased the property in 1893. Alexander White died in 1906 and ownership transferred to Fanny White. Son, Robert White was a Councillor of the Shire of Eltham at the time the Shire acquired two acres of land on the adjacent property from the Mess brothers for the creation of the Shire of Eltham Memorial Park (1921) in which the Shire of Eltham War Memoirial tower was erected (1926). Fanny White donated a small section of land from the Garden Hill property to facilitate entry access to the park. The White family sold the property to Sir Herbert Gepp in 1925. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p29 Garden Hill, on Yarra Glen Road, Kangaroo Ground, near the War Memorial is well named. The old house and gardens overlook a magnificent panorama extending to Kinglake. The original house, built around 1850, was one of Kangaroo Ground’s earliest, and part of it remains in today’s timber house. The house was built by the early and prominent settler Andrew Harkness. Later it was occupied for a long time by Sir Herbert Gepp, renowned Australia wide.1 Harkness and Gepp are buried in the Kangaroo Ground Cemetery. Scottish farmer Harkness, who was born in 1817, acquired this property in 18492 and he and his family occupied it until the early 1920s. Harkness cleared its 152 acres (61.4 ha), fenced it and grazed sheep and cattle. Harkness proved a valuable community member. When only ten families lived in the district, he and other settlers set up a school in 1852, with Andrew Ross as the first teacher. Harkness was also one of the first to suggest establishing the Eltham District Road Board, of which he was a member for around 15 years. He was also a trustee of the Kangaroo Ground Cemetery. Harkness married in 1854 and had four sons and five daughters. The first part of the timber house he built included a kitchen-living room and a parlor. The living room’s large fireplace was bricked-in and modernised in 1940. Beside it is the old baker’s oven with its original iron door replaced by a wooden one. It is thought two wattle-and-daub huts, used for a bedroom and bathroom, were built to the west. Harkness’ son-in-law, farmer Alexander White, who had seven sons, bought the property in 1893. Harkness’ grand-daughter Flora married Ewen Cameron who became Minister for Health and was later knighted; he was not related to Ewen Hugh Cameron, a Member of the Legislative Assembly. In 1923 the White family sold the property, called Kilby Park, to Sir Herbert Gepp, who renamed it Garden Hill. Gepp used the property, which was still on the original New South Wales title, as a hobby farm. Robert White stayed on to manage the farm for a while, living in a house on the property. Gepp was born in 1877 and at 16 years began working as a junior chemist with the Australian Explosives and Chemical Company at Deer Park near Melbourne. Gepp was a pioneer in applying enlightened labour policies in industry. He initiated the Broken Hill Progress Association, to improve living conditions. It laid the ground work for the welfare schemes pursued by companies after World War One. During the mid 20th century Gepp was the most prominent liberal thinker associated with conservative politics. As a friend of Prime Minister John Curtin, he contributed to post-war reconstruction. Gepp returned to private industry and retired in 1950. Gepp made significant contributions to the solution of the great metallurgical problems of the mining industry. He was an advocate of the role of science in industry, government and the economy and helped to establish several organizations including the CSIR and the Institute of Public Affairs.3 After Sir Herbert died in 1954 his son Orwell continued to farm the property part-time. When Lady Gepp died in 1963, the land was divided among the five children, although Orwell continued to farm it as a hobby. In 1966, a daughter, Mardi Gething, now married, settled in the house. Another daughter, Kathleen, built her house close by on the property. After the Board of Works designated the property as part of a reserve for a possible reservoir, the family sold all, except the minimum 20 acres allowed, to the Board in the 1970s. Orwell then leased what was the family property from the Board to continue grazing. The two sisters and brother continued to live on the property.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, kangaroo ground -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Graves of Thomas Sweeney and family, Eltham Cemetery, Victoria, 27 January 2008
The grave of Thomas Sweeney, former convict turned respectable citizen. The Murray and Sweeney families were both early settlers of the Eltham district and connected by marriage. Their family plots are located side by side in the Catholic section of the Eltham Cemetery. Irish-born Thomas Sweeney is regarded as the first settler in Eltham. He was transported to Sydney in 1823 after being convicted of arson. He was granted his freedom in 1838 and married Margaret Meehan in the same year. They moved to Melbourne and in 1842 Thomas purchased 110 acres beside the Yarra River in the vicinity of present-day Sweeneys Lane. He called the property ‘Culla Hill’ and built a small slab hut (reputedly with Wurundjeri help; Margaret is said to have run an informal hospital for them in return). This was followed in 1846 by more substantial buildings consisting of a three-roomed Irish-style ‘longhouse’ and a barn made of stone and handmade bricks, with doors large enough to accommodate a fully loaded wagon. When the gold rush came, Thomas prospered by selling meat and potatoes to the prospectors, enabling him to purchase a further 308 acres in 1856. He promoted the construction of a bridge over the Plenty River and the establishment of a school at Eltham. Roman Catholic Church services were held at Culla Hill in the early years. When he died in 1867, he was regarded as a respected member of the community. Thomas and Margaret are buried in Eltham Cemetery with many of their descendants. Their first son John continued to farm Culla Hill until his death in 1909. Culla Hill passed out of the Sweeneys' possession in 1939. The house and barn remain today, though lesser outbuildings have gone. The facade of the house is much the same as it was in the 1840s. Sacred To the memory of Thomas Sweeney Who died Sep 6th 1867 Aged 65 years May his soul res in peace Also his wife Margaret Died Oct 3rd 1884 aged 73 years And their daughters Annie Died Aug 22nd 1860 aged 21 years Johanna Died Aug 19th 1872 aged 22 years Margaret Died 7th Sep 1913 aged 72 years R.I.P. Also In Memory Of John Sweeney Died 24th May 1909 Aged 65 years Also of his wife Ellen Died 8th March 1910 Aged 64 years R.I.P Also In Memory Of Caroline Infant daughter of John & Ellen Sweeney Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p55 From the piety and poverty of 19th century Eltham, 20th century artists and environmentalists, to today’s comfortable middle class, Eltham Cemetery records it all — and more. A visit to Eltham Cemetery reveals an important social record since its beginnings in 1858. The cemetery was situated on about six acres (2.4ha) (now around 4.8ha) at the corner of Mount Pleasant and Metery Roads.1* It is thought that Metery Road was originally called Cemetery Road, but in the early 1940s, a resident, possibly a councillor, objected to the name resulting in the change.2 Much can be gleaned about the developing Eltham community from burial styles and the names of former local residents. Originally the cemetery was divided into Christian denominations, like others of that time, following the United Kingdom burial system. In 1861 the cemetery included Church of England, Presbyterian, Roman Catholic and Wesleyans (later Methodist) sites. Graves also indicated social class. Some had grand tombstones, perhaps fenced with ornamental cast iron railing, but most in the 1860s and 1870s were constructed of modest stone slabs.3 This indicated the poverty of the district, which was largely inhabited by farmers on small landholdings. A poignant reminder of the high rates of infant mortality of those times, are the many infants and young children recorded on the headstones. Major changes occurred in the cemetery in the late 20th century as Christian adherence weakened and society became more egalitarian and informal. In the early 1970s a non-denominational lawn section for burials was established. Since then all new areas have been non-denominational to accommodate the more diverse local community. Now, instead of large ornamental headstones, some mourners have chosen boulders, reflecting the natural Eltham style, while others choose graves in the lawn areas or niches in walls. In the late 1970s, the University Donor Section was established north-west of Candlebark Lawn for those who donated their bodies for The University of Melbourne medical research. In the early 1980s the natural Australian garden style, popular in Eltham, was mirrored in a new section called Ashes Walk. Local landscape architect Gordon Ford, who had popularised this style, designed the Walk using boulders shaded by native plants beside curved pathways. Landscape architect Robert Boyle later redesigned Ashes Walk and developed other parts of the cemetery in keeping with this style.4 Appropriately Ford, who died in 1999, was interred in the Native Garden Section in a cluster of sites shaded by a large eucalyptus tree.5 By 2007, about 6400 interments were recorded in the Eltham Cemetery. Close inspection reveals notable names in the district’s history. The grave of Thomas Sweeney, a former convict who became a respected citizen, can be found in the Roman Catholic section near the path. Eltham Primary School’s first headmaster, David Clark, is buried in a modest grave in the Church of England section to the east of the path from the main entrance. Sir William Irvine, Victorian Premier from 1900 to 1902, whose grave is in the north-east Presbyterian section was at various times Victoria’s Chief Justice, Deputy Governor and Treasurer.6 Further south is the grave of social reformer Bertram Wainer, born in Scotland in 1928 and died in 1987. He campaigned to legalise abortion and exposed police corruption in allowing illegal ‘backyard’ abortions. Other prominent local residents interred in the cemetery include: Justus Jörgensen, who founded Montsalvat; Alistair Knox, the mud-brick housing pioneer and Eltham Shire Councillor from 1971 to 1975 and President in 1975; Clem and Nina Christensen, who had a major influence on the literary development of post World War Two Australia. Others were: composer Dorian Le Gallienne; artist Peter Glass; Stephen Dattner, a prominent Melbourne furrier; ALP parliamentarian for Greensborough, Pauline Toner and political scientist and commentator, Professor William Macmahon Ball.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, annie sweeney, caroline sweeney, ellen sweeney, eltham cemetery, graves, gravestones, johanna sweeney, john murray, john sweeney, margaret sweeney, mary ellen drain, mary murray, thomas murray, thomas sweeney -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Kangaroo Ground Presbyterian Church, 28 December 2007
Built in 1878, the orange polychromatic brick structure replaced a slab building which had been used since 1951. The building has changed little with its handsome bricks buttressed on both sides, a slate roof and a Celtic cross on top of the front gable. The carved wooden pulpit and 18 pews are original. The cathedral-style ceiling is fully lined with tongue-and-groove pine boards and the floor is also pine. The walls have arched oblong leadlight windows. In 1977 the congregaton decided not to join the Uniting Church, whcih amalgamated some Presbyterian churches with all the Methodist and Congregational churches in Australia. Together with the store and school, the church is one of Kangaroo Ground's three public buildings. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p91 The small Presbyterian church in Main Road, Kangaroo Ground, has been a spiritual centre for more than a century. Built in 1878, the orange polychromatic brick structure replaced a rude slab building, which had been used as both a church and school since 1851. Earliest settlers, who were Scottish farmers, had worshipped together since 1841 in a barn owned by farmer James Donaldson and led by a layman called Smith.1 However, from 1843, the Reverend Peter Gunn conducted church services. Prominent early church members include the Donaldson, Bell and Cameron families. In 1851, Samuel Furphy (father of author Joseph) built their first church building, a 30 feet x 18 feet (9m x 5.5m) slab structure on half an acre (0.2ha) donated by Mr Donaldson. Conditions could be very uncomfortable in extreme weather.The green slabs of timber and sapling logs, covered partly with mud, had centimetre-wide cracks, allowing rain and wind through, when not blocked out by folds of paper.2 However this did not deter the first couple marrying there in 1857: John Wilson of Nillumbik and Christina Macpherson of Christmas Hills. The Reverend Peter Gunn seldom visited so it was usually left to Andrew Ross, the settlement’s first teacher and founder of the newspaper The Evelyn Observer, to lead the divine services instead.3 In 1877 the settlers raised £355/19/- and hired architect, Charles Maplestone and builder, Mr Self, to construct today’s church building. Each family rented a pew or pews for ten shillings a half-year; they also paid quarterly subscriptions for the minister’s stipend.4 It was not until 1886 that the church celebrated its first wedding, that of John Bell (junior) from Violet Bank and Elizabeth Charlton of Cunis Nillen. The Sunday School’s first recorded meeting was also held that year. In 1892 a weatherboard vestry was built, and the following year John Bell donated a church bell, which the fire brigade used as a warning for several years. Conditions have varied greatly during the century. In 1893 the Reverend Darroch had to travel more than 2000 miles (3220km) to attend to his scattered parishioners. Then in the Depression, the minister Mr Brown, subsisted only on lodgings with no stipend. The Sunday School ceased for many years because of the small population, but reopened in 1949. The building has changed little with its handmade bricks buttressed on both long sides, a slate roof and a Celtic cross on top of the front gable. The carved wooden pulpit and 18 pews are original and in fine condition. The cathedral-style ceiling is fully lined with tongue-and-groove pine boards and the floor is also of pine. The walls have arched oblong leadlight windows. One window has stained glass commemorating Mrs Jessie Agnes Cameron and her ancestors – the pioneering Bell family. It depicts The Sower because the family comprised farmers who came to a strange land to sow the seeds of their faith as much as their crops. Thistles signify their Scottish ancestry and the pigeons are a symbol of Pigeon Bank, the Kangaroo Ground farming property where Jessie Cameron was born.5 Other historical ties are seen on two marble memorial tablets and carved wooden chairs dedicated to former members. The Church still has the original Bible with gold edged paper, presented by the women of the congregation in 1871, although it is no longer used. In 1977 the Presbyterian congregation decided not to join the Uniting Church, which amalgamated some Presbyterian churches with all the Methodist and Congregational churches in Australia. Together with the store and school, the church is one of Kangaroo Ground’s three public buildings.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, kangaroo ground presbyterian church -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Strathewen Public Hall, 20 August 2008
Strathewen Public Hall, social and spiritual centre was later lost in the Black Saturday fires 2009. The Strathewen Community decided a community hall was needed in 1901. In 1902 locals built the hall with messmate trees. It was located on the Cottlesbridge-Strathewen Road. The first function was a Grand concert and Balll attended by about 120 people. Several denominations held Church services and Sunday School services in the Hall. It survived several bushfires until after this photo was taken when it was destroyed in Black Saturday, 9 February 2009. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p89 Strathewen was settled late, largely because it was difficult to access.1 Early selectors found it a struggle to survive. They had to do everything themselves, from felling trees for buildings, to taking produce to market along bush tracks that they had helped cut. Small dairy farms were typical but fruit became the district’s prime produce. The first settlers east of Arthurs Creek were brothers John and Duncan Smith whose station Glen-Ard was probably operated as a sheep run. Other early settlers were the Mann family, who were to donate land for the hall, provide postal services and John Mann was an Eltham Shire councillor from 1916 to 1919.2 In 1873 James Mann, his wife Jane and their six children, settled on 207 acres (83.7) (Lang Fauld Farm) on both sides of Eagles Nest Road, from the foot of Mount Sugarloaf to the bank of the Arthurs Creek. In 1883 James took up another selection on Chads Creek. It was very hard work and at times he was well behind with his rent. However the family had a good social life, attending the Primitive Methodist Church at the Arthurs Creek Township and on New Year’s Eve throwing a party for all the locals. By 1874 James Mann’s younger brother, John, selected 311 acres (125.8ha) between Eagles Nest Road and upper Arthurs Creek. He called it Carseburn after his home parish in Scotland. Tragically in 1875 John drowned in the Yarra River, at Richmond.3 John Mann’s oldest son, also John, later purchased Duncan Smith’s land, which he named Violet Glen. He was to give one acre (0.4ha) of this land for the Strathewen Hall site. A Mann family diary written at Carseburn in 1897, tells how the district’s name was selected. Strathewen is derived from ‘strath’ meaning ‘broad mountain valley’ and from the name of Ewen H. Cameron, the local parliamentarian for almost 40 years. ‘George Brain came around to get a petition signed to get a post office up here and we had to vote for a name—Strathewen, Glen-Ard, or Headcorie’.4 It was at Carseburn that a public meeting in 1901, decided to build the Strathewen Hall on the Cottlesbridge-Strathewen Road. In 1902 the locals built the hall with messmate trees. The first function was a Grand Concert and Ball attended by around 120 people and several Protestant denominations took turns to hold church services and Sunday School there. Fortunately the hall has survived bushfires to be the town’s spiritual and social centre.5 The area continued to develop and in 1909 a post office operated somewhere at Strathewen and from around 1916 at Carseburn.6 It was not until 1914 that land was bought to establish the Strathewen State School on School Ridge Road. The residents paid £100 to build it on two acres (0.8 ha) while the Education Department contributed £30 and leased the building annually for £1. When teacher Miss Mary Golding opened the school in 1917, it had no equipment.7 But in 1921 the Education Department provided desks and a hexagonal shelter shed (now a rare style in Victoria) and took control in 1925.8 By 1917 Strathewen was booming.9 George Apted had built a coolstore in 1916, and local orchardists bought storage space until the 1950s. This allowed the area to supply the market in and out of season. Guesthouses catered for growing tourism. In the mid 1920s Mrs Eleanor Sparkes built the guest-house Singing Waters, which operated through the 1930s. Her daughter Mrs Vera McKimmie, ran it until the 1950s and the house remains in Chads Creek Road. In the Great Depression land was cleared for timber to be sold as firewood and there was small scale sawmilling. However the orchard industry diminished for several reasons including the 1939 bushfires and rapid changes in production methods. Today the Apteds still operate an orchard and farm at Glen-Ard, which straddles the border between Strathewen and Arthurs Creek. It includes the southern part of Duncan Smith’s original Glen-Ard selection.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, strathewan public hall -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Art Gallery at Clifton Pugh's Artists' Colony, Dunmoochin, Barreenong Road, Cottles Bridge, 5 February 2008
Art Gallery with mural painted by Clifton Pugh (1924-1990) at his Artists' Colony, Dunmoochin, Barreenong Road, Cottles Bridge. Following military service in the second world war, Clifton Pugh studied under artist Sir William Dargie at the National Gallery School in Melbourne as well as Justus Jorgensen, founder of Montsalvat. For a while he lived on the dole but also worked packing eggs for the Belot family saving sufficient to purchase six acres (2.4 ha) of land at Barreenong Road, Cottles Bridge. He accumulated more land and persuaded several other artists and friends to buy land nearby, resulting in a property of approximately 200 acres, stablishing it as one of the first artistic communes in Australia alongside Montsalvat in Eltham. It was around 1951 that Pugh felt he had '"done moochin' around" and so the name of the property evolved. He bought timber from Alistair Knox to build his house on the crest of a hill. Inspired by local goldminer's huts, it was a one room wattle-and-daub structure with dirt floor. Over the years it expanded with thick adobe walls made from local clay, high ceilings and stone floors. All materials other than the local earth were sourced from second hand materials, most found at wreckers' yards. Artists from across the nation were drawn to Dunmoochin, with several setting up houses and shacks on the property, maintaining their independence but sharing their artistic zeal. Artists who worked or resided at Dunmoochin included Mirka Mora, John Perceval, Albert Tucker, Fred Williams, Charles Blackman, Arthur Boyd and John Olsen. In 2002, Pugh's house along with its treasure trove of art and a library of some 20,000 books was destroyed by fire. Traces of Pugh's home remain with the presence of the Victorian doorframe archway with leadlight of intricate design, procured from a demolished Melbourne mansion; and two bronze life-sized female statues created by Pugh and cast by Matcham Skipper. In place of Pugh's house rose two double-storey mud-brick artists' studios topped with corrugated iron rooves curved like the wings of a bird with accommodation for seven. The original studios, gallery and other buildings survived the fire. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p153 It’s not surprising that artist Clifton Pugh was drawn to Cottles Bridge to establish his artists’ colony Dunmoochin. Undisturbed by the clamour of modern life at Barreenong Road, Pugh was surrounded by the Australian bush he loved, and where his ashes were later scattered. The 200 acres (81ha) of bushland, broken by glimpses of rolling hills, has more than 50 species of orchids and Pugh shared his property with native animals including kangaroos, emus, phascogales, wombats, and diverse bird life. Pugh encouraged these creatures to join him in the bush by creating, with Monash University, a holding station where the animals were raised. Dunmoochin inspired Pugh for such paintings as in a book on orchids and the Death of a Wombat series.1 But his love for the bush was accompanied by the fear that Europeans were destroying it and much of his painting illustrated this fear and his plea for its conservation.2 However it was his house rather than the surrounding bush that was to be destroyed. Tragically in 2002 Pugh’s house, with its treasure of art and library of 20,000 art books, was destroyed by fire. Traces of the beauty of Pugh’s home still remain, however, in the magnificent Victorian doorframe archway with leadlight of intricate design procured from a demolished Melbourne mansion; and two bronze life-sized female statues created by Pugh and cast by Matcham Skipper. Now in place of Pugh’s house, are two double-storey mud-brick artists’ studios topped with corrugated roofs curved like birds’ wings, with accommodation for seven. The original studios, gallery and other buildings remain.3 Pugh grew up on his parents’ hobby farm at Briar Hill and attended the Briar Hill Primary School, then Eltham High School and later Ivanhoe Grammar. At 15 he became a copy boy for the Radio Times newspaper, then worked as a junior in a drafting office. Pugh was to have three wives and two sons. After serving in World War Two in New Guinea and Japan, Pugh studied under artist Sir William Dargie, at the National Gallery School in Melbourne.4 Another of his teachers was Justus Jörgensen, founder of Montsalvat the Eltham Artists’ Colony. Pugh lived on the dole for a while and paid for his first six acres (2.4ha) at Barreenong Road by working as an egg packer for the Belot family. Pugh accumulated more land and persuaded several other artists and friends to buy land nearby, resulting in the 200 acre property. They, too, purchased their land from the Belot family by working with their chickens. Around 1951 Pugh felt he had ‘Done moochin’ around’ and so the name of his property was born. Pugh bought some used timber from architect Alistair Knox to build his house on the crest of a hill. Inspired by local goldminers’ huts it was a one-room wattle-and-daub structure with a dirt floor. It was so small that the only room he could find for his telephone was on the fork of a tree nearby.5 Over the years the mud-brick house grew to 120 squares in the style now synonymous with Eltham. It had thick adobe walls (sun-dried bricks) made from local clay, high ceilings and stone floors with the entire structure made of second-hand materials – most found at wreckers’ yards. Pugh’s first major show in Melbourne in 1957, established him as a distinctive new painter, breaking away from the European tradition ‘yet not closely allied to any particular school of Australian painting’.6 Pugh became internationally known and was awarded the Order of Australia. He won the Archibald Prize for portraiture three times, although he preferred painting the bush and native animals. In 1990 not long before he died, Pugh was named the Australian War Memorial’s official artist at the 75th anniversary of the landing at Gallipoli. Today one of Pugh’s legacies is the Dunmoochin Foundation, which gives seven individual artists or couples and environmental researchers the chance to work in beautiful and peaceful surroundings, usually for a year. By November 2007, more than 80 people had taken part, and the first disabled artist had been chosen to reside in a new studio with disabled access.1 In 1989, not long before Pugh died in 1990 of a heart attack at age 65, he established the Foundation with La Trobe University and the Victorian Conservation Trust now the Trust for Nature. Pugh’s gift to the Australian people – of around 14 hectares of bushland and buildings and about 550 art works – is run by a voluntary board of directors, headed by one of his sons, Shane Pugh. La Trobe University in Victoria stores and curates the art collection and organises its exhibition around Australia.2 The Foundation aims to protect and foster the natural environment and to provide residences, studios and community art facilities at a minimal cost for artists and environmental researchers. They reside at the non-profit organisation for a year at minimal cost. The buildings, some decorated with murals painted by Pugh and including a gallery, were constructed by Pugh, family and friends, with recycled as well as new materials and mud-bricks. The Foundation is inspired by the tradition begun by the Dunmoochin Artists’ Cooperative which formed in the late 1950s as one of the first artistic communes in Australia. Members bought the land collaboratively and built the seven dwellings so that none could overlook another. But, in the late 1960s, the land was split into private land holdings, which ended the cooperative. Dunmoochin attracted visits from the famous artists of the day including guitarists John Williams and Segovia; singer and comedian Rolf Harris; comedian Barry Humphries; and artists Charles Blackman, Arthur Boyd and Mirka Mora. A potters’ community, started by Peter and Helen Laycock with Alma Shanahan, held monthly exhibitions in the 1960s, attracting local, interstate and international visitors – with up to 500 attending at a time.3 Most artists sold their properties and moved away. But two of the original artists remained into the new millennium as did relative newcomer Heja Chong who built on Pugh’s property (now owned by the Dunmoochin Foundation). In 1984 Chong brought the 1000-year-old Japanese Bizan pottery method to Dunmoochin. She helped build (with potters from all over Australia) the distinctive Bizan-style kiln, which fires pottery from eight to 14 days in pine timber, to produce the Bizan unglazed and simple subdued style. The kiln, which is rare in Australia, is very large with adjoining interconnected ovens of different sizes, providing different temperatures and firing conditions. Frank Werther, who befriended Pugh as a fellow student at the National Gallery Art School in Melbourne, built his house off Barreenong Road in 1954. Werther is a painter of the abstract and colourist style and taught art for about 30 years. Like so many in the post-war years in Eltham Shire, as it was called then, Werther built his home in stages using mud-brick and second-hand materials. The L-shaped house is single-storey but two-storey in parts with a corrugated-iron pitched roof. The waterhole used by the Werthers for their water supply is thought to be a former goldmining shaft.4 Alma Shanahan at Barreenong Road was the first to join Pugh around 1953. They also met at the National Gallery Art School and Shanahan at first visited each weekend to work, mainly making mud-bricks. She shared Pugh’s love for the bush, but when their love affair ended, she designed and built her own house a few hundred yards (metres) away. The mud-brick and timber residence, made in stages with local materials, is rectangular, single-storey with a corrugated-iron roof. As a potter, Shanahan did not originally qualify as an official Cooperative member.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, art gallery, clifton pugh, dunmoochin, cottlesbridge, cottles bridge, barreenong road -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Doorway of Clifton Pugh's former house at Dunmoochin, Barreenong Road, Cottles Bridge, 5 February 2008
Following military service in the second world war, Clifton Pugh studied under artist Sir William Dargie at the National Gallery School in Melbourne as well as Justus Jorgensen, founder of Montsalvat. For a while he lived on the dole but also worked packing eggs for the Belot family saving sufficient to purchase six acres (2.4 ha) of land at Barreenong Road, Cottles Bridge. He accumulated more land and persuaded several other artists and friends to buy land nearby, resulting in a property of approximately 200 acres, stablishing it as one of the first artistic communes in Australia alongside Montsalvat in Eltham. It was around 1951 that Pugh felt he had '"done moochin' around" and so the name of the property evolved. He bought timber from Alistair Knox to build his house on the crest of a hill. Inspired by local goldminer's huts, it was a one room wattle-and-daub structure with dirt floor. Over the years it expanded with thick adobe walls made from local clay, high ceilings and stone floors. All materials other than the local earth were sourced from second hand materials, most found at wreckers' yards. Artists from across the nation were drawn to Dunmoochin, with several setting up houses and shacks on the property, maintaining their independence but sharing their artistic zeal. Artists who worked or resided at Dunmoochin included Mirka Mora, John Perceval, Albert Tucker, Fred Williams, Charles Blackman, Arthur Boyd and John Olsen. In 2002, Pugh's house along with its treasure trove of art and a library of some 20,000 books was destroyed by fire. Traces of Pugh's home remain with the presence of the Victorian doorframe archway with leadlight of intricate design, procured from a demolished Melbourne mansion; and two bronze life-sized female statues created by Pugh and cast by Matcham Skipper. In place of Pugh's house rose two double-storey mud-brick artists' studios topped with corrugated iron rooves curved like the wings of a bird with accommodation for seven. The original studios, gallery and other buildings survived the fire. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p155 It’s not surprising that artist Clifton Pugh was drawn to Cottles Bridge to establish his artists’ colony Dunmoochin. Undisturbed by the clamour of modern life at Barreenong Road, Pugh was surrounded by the Australian bush he loved, and where his ashes were later scattered. The 200 acres (81ha) of bushland, broken by glimpses of rolling hills, has more than 50 species of orchids and Pugh shared his property with native animals including kangaroos, emus, phascogales, wombats, and diverse bird life. Pugh encouraged these creatures to join him in the bush by creating, with Monash University, a holding station where the animals were raised. Dunmoochin inspired Pugh for such paintings as in a book on orchids and the Death of a Wombat series.1 But his love for the bush was accompanied by the fear that Europeans were destroying it and much of his painting illustrated this fear and his plea for its conservation.2 However it was his house rather than the surrounding bush that was to be destroyed. Tragically in 2002 Pugh’s house, with its treasure of art and library of 20,000 art books, was destroyed by fire. Traces of the beauty of Pugh’s home still remain, however, in the magnificent Victorian doorframe archway with leadlight of intricate design procured from a demolished Melbourne mansion; and two bronze life-sized female statues created by Pugh and cast by Matcham Skipper. Now in place of Pugh’s house, are two double-storey mud-brick artists’ studios topped with corrugated roofs curved like birds’ wings, with accommodation for seven. The original studios, gallery and other buildings remain.3 Pugh grew up on his parents’ hobby farm at Briar Hill and attended the Briar Hill Primary School, then Eltham High School and later Ivanhoe Grammar. At 15 he became a copy boy for the Radio Times newspaper, then worked as a junior in a drafting office. Pugh was to have three wives and two sons. After serving in World War Two in New Guinea and Japan, Pugh studied under artist Sir William Dargie, at the National Gallery School in Melbourne.4 Another of his teachers was Justus Jörgensen, founder of Montsalvat the Eltham Artists’ Colony. Pugh lived on the dole for a while and paid for his first six acres (2.4ha) at Barreenong Road by working as an egg packer for the Belot family. Pugh accumulated more land and persuaded several other artists and friends to buy land nearby, resulting in the 200 acre property. They, too, purchased their land from the Belot family by working with their chickens. Around 1951 Pugh felt he had ‘Done moochin’ around’ and so the name of his property was born. Pugh bought some used timber from architect Alistair Knox to build his house on the crest of a hill. Inspired by local goldminers’ huts it was a one-room wattle-and-daub structure with a dirt floor. It was so small that the only room he could find for his telephone was on the fork of a tree nearby.5 Over the years the mud-brick house grew to 120 squares in the style now synonymous with Eltham. It had thick adobe walls (sun-dried bricks) made from local clay, high ceilings and stone floors with the entire structure made of second-hand materials – most found at wreckers’ yards. Pugh’s first major show in Melbourne in 1957, established him as a distinctive new painter, breaking away from the European tradition ‘yet not closely allied to any particular school of Australian painting’.6 Pugh became internationally known and was awarded the Order of Australia. He won the Archibald Prize for portraiture three times, although he preferred painting the bush and native animals. In 1990 not long before he died, Pugh was named the Australian War Memorial’s official artist at the 75th anniversary of the landing at Gallipoli. Today one of Pugh’s legacies is the Dunmoochin Foundation, which gives seven individual artists or couples and environmental researchers the chance to work in beautiful and peaceful surroundings, usually for a year. By November 2007, more than 80 people had taken part, and the first disabled artist had been chosen to reside in a new studio with disabled access.1 In 1989, not long before Pugh died in 1990 of a heart attack at age 65, he established the Foundation with La Trobe University and the Victorian Conservation Trust now the Trust for Nature. Pugh’s gift to the Australian people – of around 14 hectares of bushland and buildings and about 550 art works – is run by a voluntary board of directors, headed by one of his sons, Shane Pugh. La Trobe University in Victoria stores and curates the art collection and organises its exhibition around Australia.2 The Foundation aims to protect and foster the natural environment and to provide residences, studios and community art facilities at a minimal cost for artists and environmental researchers. They reside at the non-profit organisation for a year at minimal cost. The buildings, some decorated with murals painted by Pugh and including a gallery, were constructed by Pugh, family and friends, with recycled as well as new materials and mud-bricks. The Foundation is inspired by the tradition begun by the Dunmoochin Artists’ Cooperative which formed in the late 1950s as one of the first artistic communes in Australia. Members bought the land collaboratively and built the seven dwellings so that none could overlook another. But, in the late 1960s, the land was split into private land holdings, which ended the cooperative. Dunmoochin attracted visits from the famous artists of the day including guitarists John Williams and Segovia; singer and comedian Rolf Harris; comedian Barry Humphries; and artists Charles Blackman, Arthur Boyd and Mirka Mora. A potters’ community, started by Peter and Helen Laycock with Alma Shanahan, held monthly exhibitions in the 1960s, attracting local, interstate and international visitors – with up to 500 attending at a time.3 Most artists sold their properties and moved away. But two of the original artists remained into the new millennium as did relative newcomer Heja Chong who built on Pugh’s property (now owned by the Dunmoochin Foundation). In 1984 Chong brought the 1000-year-old Japanese Bizan pottery method to Dunmoochin. She helped build (with potters from all over Australia) the distinctive Bizan-style kiln, which fires pottery from eight to 14 days in pine timber, to produce the Bizan unglazed and simple subdued style. The kiln, which is rare in Australia, is very large with adjoining interconnected ovens of different sizes, providing different temperatures and firing conditions. Frank Werther, who befriended Pugh as a fellow student at the National Gallery Art School in Melbourne, built his house off Barreenong Road in 1954. Werther is a painter of the abstract and colourist style and taught art for about 30 years. Like so many in the post-war years in Eltham Shire, as it was called then, Werther built his home in stages using mud-brick and second-hand materials. The L-shaped house is single-storey but two-storey in parts with a corrugated-iron pitched roof. The waterhole used by the Werthers for their water supply is thought to be a former goldmining shaft.4 Alma Shanahan at Barreenong Road was the first to join Pugh around 1953. They also met at the National Gallery Art School and Shanahan at first visited each weekend to work, mainly making mud-bricks. She shared Pugh’s love for the bush, but when their love affair ended, she designed and built her own house a few hundred yards (metres) away. The mud-brick and timber residence, made in stages with local materials, is rectangular, single-storey with a corrugated-iron roof. As a potter, Shanahan did not originally qualify as an official Cooperative member.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, art gallery, clifton pugh, dunmoochin, cottlesbridge, cottles bridge, barreenong road -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Rice House, 69 Ryans Road, Eltham, 27 March 2007
Built in 1953, the Rice House was leading Melbourne architect Kevin Borland's first commssion and was one of two houses of its kind. The design of the shell-like structure was inspired by the Arch of Ctesiphon, built in the second century south of Baghdad. Cement with a waterproofing agent was applied in layers to a form of regularly spaced timber arches covered in hessian. This ctesiphon system was developed in the United Kingdom by engineer J.H. de Waller in 1947. Commissioned in 1951 by Harrie and Lorna Rice, after Harrie, then an art student, met Borland at The Age Small Homes Service. Borland suggested they buy land in Eltham because at that time it was the only council in Melbourne that would grant a permit for such an innovative house. Covered under Victorian Heritage. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p157 Inspired by an ancient arch in Iraq, a house stands on top of a hill in a private position, off Ryans Road, Eltham. One of only two houses of its kind, it was leading Melbourne architect Kevin Borland’s first commissioned house, which he built in 1953. The shell-like structure, partially screened by giant trees and cacti, was inspired by the Arch of Ctesiphon south of Baghdad, built in the second century.1 Cement with a waterproofing agent was applied in layers to a form of regularly spaced timber arches tightly covered by hessian. This ctesiphon system was developed in the United Kingdom by engineer J H de Waller in 1947. This house was the first of three such structures built in Victoria, of which only one other remains, although substantially altered.2 It is the Wood House and supermarket, at the corner of Cleveland Road and High Street Road, Ashwood, designed by Robin Boyd in 1952. The Rice House demonstrates Kevin Borland’s innovative and experimental work. It is an outstanding example of the post-war period of experimentation in domestic architecture in Melbourne – by Robin Boyd, Kevin Borland and others – for The Age Small Homes Service from 1947 to 1953. This was partly an expression of late-Modernism and also necessitated by the post-war shortage of building materials. In Eltham, the post-war shortage of building materials largely resulted in mud-brick houses. Examples of Borland’s public work include contributions to the Olympic Swimming Pool in Melbourne and the Preshil Junior School in Kew. After more than 50 years of living in the house, Harrie and Lorna Rice still love it. Facing north-east with large windows overlooking the garden and two courtyards, it is well lit and benefits from a through breeze. The couple commissioned the extraordinary house after Harrie, then an art student, met Borland in 1951 at The Age Small Homes Service. Harrie was so impressed by the recently graduated Borland’s enthusiasm, that he asked him to design them an interesting house for a low budget.3 The unusual design presented several hurdles for the young couple before they could construct it. Borland suggested that they buy land in Eltham, because at that time it had the only council in Melbourne that would allow such an innovative house. Another hurdle was to gain finance for this remarkable house. The State Savings Bank Manager refused finance on the grounds that it was ‘unliveable’ and a ‘disgrace’. Fortunately, through a family connection, the couple borrowed money from the National Bank. But they discovered years later, that the bank’s evaluation stated the two ‘concrete sheds’ were of no value!4 The house built in off-white concrete, consists of two sections. The main house has four arches supported by brick and concrete walls that create a series of inter-connected rooms. Inside, the ceiling follows the roofline. Originally this section was only ten square metres, because of building restrictions at the time. But in 1973 Borland added two rooms and a carport. The second structure of two arches was originally a garage and a studio for art teacher Harrie Rice. To accommodate the growing family, in the mid 1950s, Borland converted the second structure into two children’s bedrooms, a kitchenette, a bathroom and a living room. The two structures were originally linked by a covered way of suspended draped-concrete, but this collapsed in the 1980s. The design has several maintenance problems. Cracks developed where two halves of the shells were joined. Then the material sprayed over the cracks became brittle, causing leaks. Fortunately Harrie found another material he could use. The valleys between the arches collect water, requiring annual painting with a waterproof material to prevent leaking. Lorna framed the house with native and exotic plants, which provide privacy and as a bonus, the garden attracted the rare Eltham Copper Butterfly.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, eltham, rice house, ryans road -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Eltham Retirement Centre (Judge Book Memorial Village), Diamond Street, Eltham, 23 October 2006
Thousands of elderly people at this centre have contributed much. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p161 Thousands of elderly people, who have contributed much to Nillumbik and beyond, have made their home in the treed Eltham Retirement Centre. The centre, which opened in 1956, has housed the disadvantaged in particular, through good times and hard, including floods, fire and even burglaries. As part of the Melbourne Citymission, a non-denominational Christian organisation that cares for people living with disadvantage, the centre was built to celebrate 100 years of the Melbourne Citymission’s work since 1854.1 Standing on a former poultry farm called Willandra (Still Waters), the centre includes independent units, hostel, nursing home accommodation and a Day Therapy Centre, which is available for non-residents as well.2 Despite being metres from the busy Main Road and railway station, the centre provides a quiet oasis on 6.8 hectares bordered by the Diamond Creek to the west, and the railway line to the east. The centre was originally named Judge Book Memorial Village after Judge Clifford Book, Deacon of the Collins Street Baptist Church. Book was also President of the Baptist Union of Victoria and Grand Master of the Masonic Lodge. He was so respected that, at his death, several Pentridge prisoners asked to attend his funeral. In 1993 the centre’s name was changed to clarify that it was part of the Melbourne Citymission. However Judge Book’s name continues in the Judge Book Memorial Garden, opened in 2006. The Diamond Creek has flooded the centre several times, however rarely causing serious damage. Volunteer Alan Field recalls a flood in 1974 when the resident manager Reverend Norman Pearce and his wife, were rescued by boat from their home with their budgerigar. On February 3, 2005, when the creek almost flooded Metzner Hall, 35 ambulances evacuated residents to nearby nursing homes, hostels and local homes. Residents were also evacuated during the 1965 bush fire, but fortunately a change of wind direction saved the centre. Residents have also endured several burglaries. Despite much rebuilding and modernisation over the years, traces of the original farmhouse remain in the administration areas. In 1991 the Willandra Hostel was built and in 2001 the Eltham Lodge Nursing Home with each room having a garden view. Several buildings are named after people who have given special service to the centre including the Norman Pearce Day Hospital after general manager and pastor Rev Pearce. Metzner Hall was named after the Metzner family who had been active in the auxiliary since it began and had donated generously to the Recreation Hall fund.3 A bridge was named after Sister Lila Murray who had worked at the village for 42 years in various capacities including as relieving manager. Field remembers Sister Murray as ‘the Mother Teresa and soul of what the village aspired to, with love and care’. Since 1957 the Eltham Auxiliary, later called the Residents’ Association, has worked to improve the residents’ quality of life by volunteering and raising funds. An outstanding volunteer, Field, who was drawn to the centre in 1971 with his wife Chris, has held positions on the early Eltham boards, auxiliaries and Residents’ Association. Much of his work has been supporting people with no family and those of limited means. He says he and his wife look at their work as having shared ‘our lives with amazing people’. The wealth of experience and wisdom in the Retirement Village has benefited many people, including local school children. Residents have acted as proxy grand-parents at local schools, by assisting small learning groups or telling their life stories. Conversely, students from local schools have visited to perform, or to assist in programs like craft activities. Resident Val Bell, whose mother Rose Bullock lived at the centre before her, sums up the centre’s most important attribute for her: ‘The Christian care. They could not be more caring’.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, diamond street, eltham, eltham retirement centre, eltham retirement village, judge book memorial village -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Marguerite Marshall, Stuchbery Farm dairy, 14 March 2008
Stuchbery Farm was situated on the Plenty River bounded by Smugglers Gully to the north and La trobe Road, Yarrambat, to the east. Alan and Ada Stutchbery moved to the valley in 1890, first living in a tent where four children were born. Alfred built a home and outbuildings around 1896. They planted an orchard, then a market garden and developed a dairy. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p179 The dramatic steep-sided Plenty Gorge lies along the divide of two geological areas, and separates the Nillumbik Shire and the City of Whittlesea. On the Nillumbik side are undulating hills and sedimentary rock, and in Whittlesea, lies a basalt plain formed by volcanic action up to two million years ago. This provides the Plenty Gorge Park with diverse vegetation and habitats, making it one of Greater Melbourne’s most important refuges for threatened and significant species. The park, established in 1986, consists of around 1350 hectares, and extends 11 kilometres along the Plenty River, from Greensborough to Mernda. It provides a wildlife corridor for around 500 native plant and 280 animal species.1 The area’s plentiful food and water attracted the Wurundjeri Aboriginal people and then European settlers. By 1837 squatters had claimed large runs of land for their sheep and cattle. The Plenty Valley was among the first in the Port Phillip District to be settled - mainly in the less heavily timbered west - and was proclaimed a settled district in 1841.2 But by the late 1880s, the settlers’ extensive land clearing for animal grazing, then agriculture, depleted the Wurundjeri’s traditional food sources, which helped to drive them away. Many Wurundjeri artefacts remain (now government protected), and so far 57 sites have been identified in the park, including scarred trees, burial areas and stone artefacts. Pioneer life could be very hard because of isolation, flooding, bushfires and bushrangers. Following the Black Thursday bushfires of 1851, basalt was quarried to build more fire-resistant homes. Gold discoveries in the early 1850s swelled the population, particularly around Smugglers Gully; but food production made more of an impact. In the late 1850s wheat production supplanted grazing. In the 1860s the government made small holdings available to poorer settlers. These had the greatest effect on the district, particularly in Doreen and Yarrambat, where orchards were established from the 1880s to 1914. Links with a prominent early family are the remains of Stuchbery Farm, by the river’s edge bounded by Smugglers Gully to the north and La Trobe Road, Yarrambat, to the east. The Stuchberys moved to the valley in 1890, and the family still lives in the area. In 1890, Alfred and Ada first lived in a tent where four children were born, then Alfred built the house and outbuildings around 1896. They planted an orchard, then a market garden, and developed a dairy. The family belonged to the local Methodist and tennis communities. Their grandson Walter, opened the Flying Scotsman Model Railway Museum in Yarrambat, which his widow, Vi, continues to run. Wal was also the Yarrambat CFA Captain for 22 years until 1987. Walter sold 24 hectares in 1976 for development - now Vista Court - and in 1990, the remaining 22.6 hectares for the park. Remaining are an early stone dairy and remnants of a stone barn, a pig sty and a well.3 Until it was destroyed by fire in 2003, a slab hut stood on the Happy Hollow Farm site, at the southern end of the park. The hut is thought to have been built in the Depression around 1893. This was a rare and late example of a slab hut with a domestic orchard close to Melbourne. Emmet Watmough and his family first occupied the hut, followed by a succession of families, until the Bell family bought it around 1948. There they led a subsistence lifestyle for 50 years, despite encroaching Melbourne suburbia.4 The Yellow Gum Recreation Area includes the Blue Lake, coloured turquoise at certain times of the year. Following the 1957 bushfires, this area was quarried by Reid Quarries Pty Ltd for Melbourne’s first skyscrapers, then by Boral Australia. However in the early 1970s water began seeping into the quarry forming the Blue Lake and the quarry was closed. The State Government bought the site in 1997 and opened it as a park in 1999.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, ada stuchbery, alan stuchbery, dairy, stuchbery farm, farm buildings, yarrambat, plenty gorge park -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Diamond Creek, Barak Bushlands, Eltham, 2008
A habitat corridor and it strengthens the community. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p185 Barak Bushlands lie west of the Diamond Creek on the corner of Falkiner Street and busy, noisy Main Road. They form part of an important habitat corridor linking the Yarra River to the Kinglake National Park.1 Manna Gums, tawny frogmouths and platypuses are some of the indigenous plants and animals that have made their home there. The bushlands are the result of more than nine years of hard work by the local community with the Nillumbik Council, to transform a degraded flood plain into this refuge of natural beauty. In 1997, shortly after moving into the new Riverside Estate on Falkiner Street, Eltham, several residents noticed the sorry state of the Diamond Creek and surrounding area. Part of it was used as a cow paddock and although small patches of vegetation survived, the area was infested with weeds, rabbits, rubbish and drainage from the housing estate. At various times the 4.4 hectares had been used as a market garden and for shire stock piles. The residents began to restore the area by revegetating land along the Diamond Creek. In 1998 they established the Friends of the Diamond Creek Falkiner Street Reserve2 and 35 families joined from the 90-house Estate. Carolyn Mellor, as the Friends’ Land Manager, undertook a four-year horticulture course to guide this massive project for a volunteer organisation. Since 1999, she has been the Friends’ President. In 1999 the Friends urged the Nillumbik Council to undertake a feasibility study into establishing a wetland system and urban forest. Work began in 2002 with Nillumbik Council funding the project, supplemented by government grants. The Friends also received grants from Melbourne Water and Parks Victoria.3 Aided by the Friends and other community members, the Council created the Barak Bushlands consisting of a forest, a wetland, a bridge, a path and open space. The beautiful wetland treats most of the estate’s stormwater runoff. Storm water is filtered through plants in the wetland ponds then is released slowly into the billabong, before flowing into the Diamond Creek. The wetland also helps to minimise flooding and the improved water quality provides a flora and fauna habitat. The Friends and other volunteers planted more than 27,000 plants, more than one third of which they grew from seeds they collected at Lower Eltham and Wingrove Parks. Eltham High School students planted thousands of these through a Year Eight program introduced for this purpose. Other groups who assisted were: Green Corps, local Scouts and Guides – 2nd Montmorency, 1st Diamond Creek and 1st Eltham Cub Packs, Eltham College students, Eltham East Primary School, Landcare members, Eltham Lions Club and the Eltham Baptist Church. To maintain enthusiasm for the mammoth task, the Friends and other volunteers ‘adopted’ trees to water and wrote their names on the stakes. In 2004, to recognise the area’s original occupiers, the reserve was named Barak Bushlands. William Barak, who lived from 1824 to 1903, was the last chief of the Yarra Yarra tribe of the Wurundjeri-willam people.4 Traces of these original inhabitants remain in scar trees (bark sections removed to make a shield or canoe). That same year the Friends’ group was a finalist in the prestigious Federal Government, Banksia Environmental Awards. The Friends have also participated in Clean Up Australia, removing tonnes of rubbish and regularly testing the billabong, wetland and creek, for pollutants. For years the Friends, together with the Australian Platypus Conservancy, have tagged, measured and checked the health of platypuses from the Diamond and Mullum Mullum Creeks. With Latrobe University the Friends have conducted night walks to view owls, possums, bats and sugar gliders.5 Challenges for the council and the Friends continue with a large rabbit population, some vandalism, weed eradication and maintenance. However, thanks to this community effort, locals can now escape confined urban living on small blocks of land and enjoy the beauty of indigenous plants and animals. Working together has also strengthened the local community,This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, barak bushlands, diamond creek (creek), eltham -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Blue Lake, Plenty Gorge Park, 2008
A quarry was transformed into the Blue Lake. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p179 The dramatic steep-sided Plenty Gorge lies along the divide of two geological areas, and separates the Nillumbik Shire and the City of Whittlesea. On the Nillumbik side are undulating hills and sedimentary rock, and in Whittlesea, lies a basalt plain formed by volcanic action up to two million years ago. This provides the Plenty Gorge Park with diverse vegetation and habitats, making it one of Greater Melbourne’s most important refuges for threatened and significant species. The park, established in 1986, consists of around 1350 hectares, and extends 11 kilometres along the Plenty River, from Greensborough to Mernda. It provides a wildlife corridor for around 500 native plant and 280 animal species.1 The area’s plentiful food and water attracted the Wurundjeri Aboriginal people and then European settlers. By 1837 squatters had claimed large runs of land for their sheep and cattle. The Plenty Valley was among the first in the Port Phillip District to be settled - mainly in the less heavily timbered west - and was proclaimed a settled district in 1841.2 But by the late 1880s, the settlers’ extensive land clearing for animal grazing, then agriculture, depleted the Wurundjeri’s traditional food sources, which helped to drive them away. Many Wurundjeri artefacts remain (now government protected), and so far 57 sites have been identified in the park, including scarred trees, burial areas and stone artefacts. Pioneer life could be very hard because of isolation, flooding, bushfires and bushrangers. Following the Black Thursday bushfires of 1851, basalt was quarried to build more fire-resistant homes. Gold discoveries in the early 1850s swelled the population, particularly around Smugglers Gully; but food production made more of an impact. In the late 1850s wheat production supplanted grazing. In the 1860s the government made small holdings available to poorer settlers. These had the greatest effect on the district, particularly in Doreen and Yarrambat, where orchards were established from the 1880s to 1914. Links with a prominent early family are the remains of Stuchbery Farm, by the river’s edge bounded by Smugglers Gully to the north and La Trobe Road, Yarrambat, to the east. The Stuchberys moved to the valley in 1890, and the family still lives in the area. In 1890, Alfred and Ada first lived in a tent where four children were born, then Alfred built the house and outbuildings around 1896. They planted an orchard, then a market garden, and developed a dairy. The family belonged to the local Methodist and tennis communities. Their grandson Walter, opened the Flying Scotsman Model Railway Museum in Yarrambat, which his widow, Vi, continues to run. Wal was also the Yarrambat CFA Captain for 22 years until 1987. Walter sold 24 hectares in 1976 for development - now Vista Court - and in 1990, the remaining 22.6 hectares for the park. Remaining are an early stone dairy and remnants of a stone barn, a pig sty and a well.3 Until it was destroyed by fire in 2003, a slab hut stood on the Happy Hollow Farm site, at the southern end of the park. The hut is thought to have been built in the Depression around 1893. This was a rare and late example of a slab hut with a domestic orchard close to Melbourne. Emmet Watmough and his family first occupied the hut, followed by a succession of families, until the Bell family bought it around 1948. There they led a subsistence lifestyle for 50 years, despite encroaching Melbourne suburbia.4 The Yellow Gum Recreation Area includes the Blue Lake, coloured turquoise at certain times of the year. Following the 1957 bushfires, this area was quarried by Reid Quarries Pty Ltd for Melbourne’s first skyscrapers, then by Boral Australia. However in the early 1970s water began seeping into the quarry forming the Blue Lake and the quarry was closed. The State Government bought the site in 1997 and opened it as a park in 1999.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, blue lake, plenty gorge park -
 Linton and District Historical Society Inc
Linton and District Historical Society IncPhotograph, Mrs. Harriett Wilson ("Granny Wilson")
Harriett Wilson was the wife of William Wilson, an active member of and preacher with the Linton Methodist congregation. This is one of two photographs of Mrs Wilson in the collection. This one appears to have been taken earlier than the other. The other photograph is Registration no. 480 (Box 14, also Mounted photograph 21), and shows a somewhat older Mrs Wilson, although Mrs Wilson is wearing the same dress in both photographs. An inscription on the back of the photograph says that this photograph was given by Mrs Wilson to F. Bryant on December 16, 1890. Mrs Wilson died in a fire in 1900 and is buried in Linton cemetery. See notes in Wilson family file.Small sepia photograph of a woman with hair drawn back from face, wearing a long-sleeved, full-skirted gown with beaded detail on bodice and white collar, seated with left hand resting on lap, right arm crooked on back of a chair, holding a book in her hand.In faded pencil on reverse of photograph: "James / Wilson / Linton / Given by Mrs Wilson / to F Bryant Dec. 16, 1890". Written in darker pencil over the top of this: "Mrs Wilson / (Granny)".mrs w. wilson, harriett wilson ("granny" wilson), old lintonian collection -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Sweeney's Cottage, Sweeneys Lane, Eltham, 30 January 2008
Part of the original cottage named Culla Hill built by Thomas Sweeney (a former convict) remains as a small section of today’s house. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme National Estate National Trust of Australia (Victoria) Local Sifgnificance Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p19 Thomas Sweeney, a former convict who became a respected citizen, once lived on a property at what is now the corner of Sweeneys Lane and Culla Hill, Eltham. As Sweeney was one of the district’s first settlers, the property is registered by the National Trust. Thomas Sweeney was born in 1802, son of impoverished tenant farmers in Tipperary County, Ireland. He became a ploughman, then at 21 he was sentenced to hang for setting on fire the house of Patrick Guyder at Gullshill. It is said the arson was due to a dispute over undelivered guns to a social justice guerilla group, the White Boys, of which Sweeney was a member. But the sentence was commuted to life transportation to Australia in 1823.1 Apparently in Sydney he became a servant to James Chandler at Botany. Soon James Chandler leased his farm and became a catechist on the Hawkesbury River, so Sweeney was reassigned to a former convict, John Brown, at Liverpool. Later Sweeney was assigned to George Brown of Lake Illawarra. In 1831, Sweeney was granted a ticket-of-leave and bought a boat to carry goods between Illawarra district and Sydney Town. He married his first wife who had come to Australia as a free woman. However she drowned after bearing him a daughter. In 1838, one month after he had received a conditional pardon, Sweeney married a blacksmith’s daughter, Margaret Meehan, newly arrived from Ireland. They then moved to Port Phillip and squatted on the south side of the Yarra River, about seven miles (11km) from Melbourne. Around 1842, Sweeney bought 110 acres (44.5ha) in the parish of Nillumbik for £110. He built a slab hut 12 x 10 feet (3.6m x 3m) and then his homestead, Culla Hill, a typical Tipperary style cottage, now known as Sweeney’s Cottage. It was here that many generations of Sweeneys lived for almost 100 years. Culla Hill became a social centre for the district and the Catholic community used it as a church. Sweeney was apparently on good terms with a tribe of Aborigines living on the river nearby, who helped him build his house.2 Sweeney proved himself a civic-minded leader. In 1844, he led a call for a bridge over the Plenty River. He was on the first school board and supplied the first grain for Eltham’s mill. Sweeney profited during the gold rush, not by gold digging, but by providing supplies for nearby fields and others as far away as Beechworth.3 Thomas Sweeney died in 1867 and was buried at the Eltham Cemetery, leaving two sons, five daughters, and 300 acres (121.4ha), as well as Culla Hill. Culla Hill – by then reduced to 75 acres (30ha) – was sold out of the family in 1939, then renamed Sweeneys. The present Sweeneys Lane, running diagonally through the original holding, was the track to the house. Part of the original cottage remains as a small section of today’s house. The dining-family room fronted by a veranda is original, and although there have been some changes, the cedar door and most of the small 12-paned wooden-framed windows are original. The walls are made of the original hand-made brick. After buying the property in 1952 Mr and Mrs Burston demolished a dilapidated slab hut, a three-roomed detached kitchen and cellar, as materials needed to restore them were very difficult to obtain so soon after the war.4 However the barn remains almost in its original condition. It is believed to have been built from stone quarried on the property. Now roofed with iron sheets it was probably originally thatched. The sandstone barn has a peaked roof supported by the original saplings and a doorway large enough to accommodate a fully loaded wagon.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, culla hill, eltham, sweeney's cottage, sweeneys lane, thomas sweeney -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, St Andrews Anglican Church, St Andrews, 30 January 2008
Built c.1868, St Andrew’s Anglican Church is Nillumbik Shire’s oldest timber church and is historically, socially, and spiritually significant to the Shire of Nillumbik. The church is historically significant because it may have given its name 'St Andrews' to the town (another suggestion is that the name came from the local hotel), it is also historically significant as one of only four buildings that remain from the Caledonian goldfields era of Queenstown (now St Andrews) and one of only a handful of buildings that survived the 1960s bushfires. The church is historically, socially, and spiritually significant because it has played an important part in community life for more than 150 years; a proposal to move the church in 1984 met with strenuous opposition. Much of the fires on Black Saturday 2009 were the north of the town. The town itself remained intact - as did this heritage building. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. National Trust of Australia (Victoria) Local significance Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p69 The St Andrews Anglican Church and former St Andrews Primary School, are two reminders of the district’s early days, when it was founded on gold. St Andrews, then called Queenstown, was the earliest goldfield in the Caledonia Diggings.1 It was the Upper Diamond Gold Mining and Administrative Centre, with 3000 miners. Queenstown was also the seat of the Court of Petty Sessions. The church and school then stood close to European and Chinese stores, three hotels, a brewery and a quartz mill.2 In 1861, Queenstown was officially proclaimed a township. From 1865, the name Queenstown was interchangeable with St Andrews, until 1952, when the town was officially named St Andrews. As gold declined from the early 1880s, Queenstown changed dramatically into a settlement of small farms. St Andrew’s Anglican Church, built in 1868, is the Shire’s oldest timber church and possibly gave its name to the township.3 The small timber church was opened on November 1, 1869, by the Dean of Melbourne. Anniversary tea meetings helped raise funds, and in 1889, a three-bedroom parsonage was built alongside. In 1910, the vicar, the Rev Selwyn Chase (and friend of the Scouting Movement’s founder, Baden Powell), established the 1st Queenstown Scout Troop, only two years after Scouting began in Australia. The church was important to the lives of many local residents who were baptised, married and had funeral services there. But by the 1950s the population had decreased and so did the weekly attendances. Around the mid-1960s the church closed, then fell into disrepair. So in the mid 1980s it was sold to the Education Department and was under threat of relocation or demolition. However this caused such opposition from locals,4 that instead, the Anglican church leased it as part of the Panton Hill parish5 and it was reconsecrated in 1987. Queenstown’s first school was held in a tent after transferring from Andersons Creek, Warrandyte.6 From 1858 a church school, Caledonia Diggings, stood west of the main road, a quarter of a mile (0.4km) before Buttermans Track. In 1882 the school was moved from a leased building, owned by headmaster Robert Harris, into a larger building on the corner of the School and the Heidelberg-Kinglake Roads. It had been moved from Smiths Gully and included a teacher’s three-roomed residence.7 In 1887 the school was replaced by the Queenstown State School No 128, although it was also called Caledonia Diggings until 1891. In 1956 it was renamed St Andrews. Still standing, this building is now used as the St Andrews Community Centre and the residence is leased for private use. The original timber-lined room remains alongside the extensions, and is distinctive with its high ceiling and tall small-paned windows. In 1984 a new school was built 500 metres west of the old school. Many residents have contributed much to St Andrews but one family that has done so for several generations is the Harris family. Robert Harris was an active member of the St Andrew’s Anglican Church, and worked hard at improving the town’s amenities until his death in 1887. He was a signatory to the successful 1863 petition to the Chief Commissioner of Police, against the proposed removal of the Court of Petty Sessions and police station at the Caledonia Diggings. The police station stayed in the town until 1917. Harris was Head Teacher of Queenstown State School from 1864 to 1874, then of the Smiths Gully school until it closed in 1882, and he continued teaching at Panton Hill until his death. His son, Robert Charles Harris, was editor and printer of the local newspaper, The Evelyn Observer, from 1873 until 1915. Robert’s son, William Shelley Harris, served in the Boer War and in World War One. In 1928 he became Kinglake National Park’s first park ranger. Robert’s daughter Elizabeth, taught needlework at Queenstown State School, and later ran the post office in Kinglake.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, st andrews, st andrews anglican church -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Alistair Knox Park, Eltham, 2008
Alistair Knox Park, an oasis of peace and beauty. Covered under National Trust of Australia (Victoria) Landscape Significance and Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p173 It is hard to imagine that the Alistair Knox Park, an oasis of peace and beauty beside busy Main Road, Eltham, was once the township’s rubbish dump. It was only in the 1970s that the tip was transformed into this beautiful six hectare space, which later earned it a National Trust Landscape classification. Before its life as a dump, the area was used for small farms. Thanks largely to the foresight and efforts of local environmental builder Alistair Knox, the park was designed sympathetically with the character of the wider Eltham landscape. Then, appropriately, the park was named after Knox, who was an Eltham Shire Councillor from 1971 to 1975 and Shire President in 1975. The park designers were four major forces in the urban bush landscape garden –Knox, landscape designer Gordon Ford, artist Peter Glass and landscaper Ivan Stranger.1 The National Trust citation for the park, originally called Eltham Town Park, includes the Eltham railway trestle bridge and the Shillinglaw Cottage. The citation states ‘the semi-natural setting of the parkland provides a landscape which is evocative of the history of the area’. Manna Gums (Eucalyptus viminalis) and Candlebarks (Eucalyptus rubida) are significant features. Most of the park’s construction was directed by Bob Grant, Superintendent of the Parks and Gardens Department for the Eltham Shire Council. First plantings occurred in Arbour Week in 1973, then the lake and botanic area were completed in 1975, with Federal Government funding, and the toilet block in 1978. Bounded by the Eltham railway line, Panther Place, Main Road, Bridge and Susan Streets, the park is in a valley about a kilometre wide overlooked by steep hills at the east and west. The Diamond Creek flows through it and the picturesque historic timber trestle railway bridge edges the north. Informal plantings of Australian indigenous and native species in open and undulating grassed settings blend with the natural landscape of the Diamond Creek to the west. The bush-style plants, particularly around the creek, balance with open lawns, paths and a cascade flowing from a small lake to another below. A footbridge over the creek leads to the park’s west. The park includes an adventure playground and barbecue areas. The park stands on part of the land bought from the Crown in 1851 by Josiah Holloway, who subdivided it into allotments and which he called Little Eltham. Most of the land was subdivided into residential lots, but the creek valley, on which the park stands, was subdivided into farm-size lots, used mainly for orchards and grazing. One of the earliest owners was John Hicks Petty, who in 1874 bought a plot from Holloway. Other families who owned properties in that area, included Rees, Clark, Waterfall, Graham, Hill and Morant.2 In 1901 the railway was built through the area. Jock Read, an Eltham resident since around 1920, remembers several farms in the 1920s and ’30s that occupied the site of today’s park. A poultry farm, which extended from present day Panther Place, was owned by the Gahan family. Next to that farm was another for grazing cattle owned by Jack Carrucan. Beside this was land owned by John Lyon. A doctor lived beside this, and at the north-west corner of Bridge Street and Main Road stood a memorial to the soldiers who died in World War One, which was later moved to the RSL site. Mr Read also remembers other farms and orchards west of the creek In the early 1960s the Eltham Council began buying these farms and in the late 1960s turned the areas east of the Diamond Creek into a garbage tip. When this was filled above the creek’s flood plain, the tip was moved to the west of the creek.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, alistair knox park, eltham -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncDocument - Property Binder, 1184 Main Road, Eltham
Newspaper article: A sustainable award, Diamond Valley Leader, 1 November2006, Architect and building Llewellyn Pritchard won resource Efficiency Housing Award, finalist in HIA Greensmart Building of the Year Award. House – Environmental Leader (Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p186) In 2006 environmental awareness was mushrooming in the community, which is reflected in the award-winning house at Main Road near Wattletree Road, Eltham. At first sight, the building appears a mix of a classic Eltham mud-brick house and an avant-garde building style. The crown of solar panels stretching along the width of the curved roof, indicates that this is no ordinary house. In fact it signals a new building trend of minimal impact on the environment. Yet it utilises the environment with high technical expertise to achieve comfort and cut running and maintenance costs. In recognition of this, its designer/builder, Conscious Homes, won the 2006 National HIA Greensmart Resource Efficiency Award. For Conscious Homes director, Llewellyn Pritchard, this house reflects a philosophy, strengthened by his connection with Aboriginal culture, through his foster siblings. Pritchard believes the sustainable way indigenous Australians lived and their spiritual connection with land, demonstrates how humanity is part of the ecology. His interest in environmental design stemmed from growing up in bushy Eltham Shire, with its mud-brick tradition. This was followed by studying Architecture at RMIT in the early 1980s, and learning about passive solar design. Pritchard says this house demonstrates that environmental sustainability is not about sacrifice, but about exceptional levels of occupant comfort, savings in running costs and modern fittings and appliances.1 The solar panels on the north roofs are intentionally obvious to make a statement about what the building is doing. But inside the systems are hidden and interactive with conventional services, such as the underground water tank. The house is water and energy self-sufficient and at 12 squares is much smaller than conventional houses, to minimise resources. Yet it accommodates his family of four with three bedrooms, a living/dining and kitchen area and a bathroom/laundry. Importantly the building is designed to last hundreds of years, by being able to be modified as the need arises, such as for commercial use. In this way the structure minimises its environmental impact. The solid double mud-brick walls (which are insulated) include steel beams and supporting frame, allowing the future removal or alteration of any section. The materials are local, recycled and of low toxicity where possible.2 Inside and out, the mud-brick is rendered and sealed with a combination of cement and sand and a mud-based coating in a soft golden hue increases its life. Inside, the golden-brown timber is plantation Mountain Ash and the concrete floors throughout – of local stone aggregate with a clear seal – have a natural looking random stone appearance. The house sustains a stable temperature of around 20 degrees, assisted by the concrete slab floor. The many large double-glazed windows and highlights (windows set high on walls) provide cross-flow ventilation. The north-facing living area maximises heating from the lower winter sun and is cooler in summer, because the sun is higher. Heating comes from a solar hydronic slab system. All appliances and fittings are high efficiency energy or water rated. Appliances in the timber kitchen include a gas stove and a dishwasher, using the building’s own power and water. French doors open from the living area to a deck, concealing the treatment system for all waste water. This is pumped through sub-soil drippers to the indigenous garden beds and no-dig vegetable patch. Below the carport is the 80,000-litre rainwater tank and at the back, the boiler room houses the solar boiler, water tank access, domestic water supply pump, filter gear and hydronic slab heating controls. The solar system is backed up with gas, which is needed to heat water only in winter. Gas used is less than one quarter of that for an average home with ducted heating. Excess power is fed back to the grid and the building uses about one quarter of the mains electricity of an average home. Other local builders have followed Pritchard’s lead in resource efficiency for minimal environmental impact.main road, eltham, businesses, llewellyn pritchard, hia greensmart building of the year award., efficiency housing award, conscious homes australia pty ltd -
 Bacchus Marsh & District Historical Society
Bacchus Marsh & District Historical SocietyPhotograph, Stone Villa house 4 Bennett Street Bacchus Marsh 1883
The house depicted in this image was constructed in 1865 for James Young a prominent local businessman and participant in community affairs. James Young left Bacchus Marsh in 1869. In 1870 Stone Villa was purchased by local solicitor Francis Gell. In 1872 it was bought by William Collyer. For a time before 1883 it was used as a school operated by Mr Thomas Kissock and his wife. From 1883 until 1922 it was used as a parsonage by the Church of England. In 1922 it was sold to Frederick Slack as a private residence. Since Slack's ownership there have been other owners. As of April 2024 it remains as a private residence and is listed as a heritage property in the Moorabool Shire planning scheme. The identity of the two women and young girl in the foreground of the image has not been established. One of the women, and the child are possibly the wife and daughter of the Rev A.C. McCausland who was the Church of England Vicar in Bacchus Marsh from 1872 until 1885 and would have resided in this house in 1883 when this picture was produced.An early visual record of one of the most culturally and architecturally significant nineteenth century stone houses in Bacchus Marsh.Small sepia 'carte de visite' style unframed photograph on card with gold border framing photograph. Housed in the album, 'Photographs of Bacchus Marsh and District in 1883 by Stevenson and McNicoll', the Jeremeas Family Album. The photo is of a stone dwelling with an ornate gable above the inset front door which is flanked by two double windows, one of which is a bay window. The gable roof line bears ornate woodwork. A weatherboard extension with verandah has been added to the rear of the house, running north-south. A picket fence lines the block to the side of the dwelling. Two elegantly dressed women, both holding a furled umbrella, stand at the front, one holding the hand of a little girl.Printed On the front: Stevenson & McNicoll. Photo. 108 Elizabeth St. Melbourne. COPIES CAN BE OBTAINED AT ANY TIME. On the back: LIGHT & TRUTH inscribed on a banner surmounted by a representation of the rising sun. Copies of this Portrait can be had at any time by sending the Name and Post Office Money Order or Stamps for the amount of order to STEVENSON & McNICOLL LATE BENSON & STEVENSON, Photographers. 108 Elizabeth Street, MELBOURNE. Hand written on the reverse: 'Stone Villa built by James Young 1860 (sic) as his private residence, later as a school (Mr and Mrs Kissock proprietors) bought by CofE for Vicarage 1883-1922. Courtesy of Mrs J Jeremeas, Photo 1883' james young 1816-1871, houses, stone villa bacchus marsh, clergy residences, bacchus marsh vic. history, schools bacchus marsh, stevenson and mcnicoll 1883 photographs of bacchus marsh and district -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Document - Ledger 1883-1892 repurposed
This ledger was used between 1883 and 1892 to record returns and activities on a farming property including numbers of sheep shorn, chaff cut, fencing contracted and people employed. One envelope within the ledger is addressed to Mrs J Edwards, Morven via Branxholme. The Edwards family, lived on the MORVEN property situated about 11 kilometres west of Branxholme in the Western District of Victoria. This property was sub divided in 1911 into 25 farms. The not fully used ledger has later been repurposed as a recipe book with a collection of newspaper cuttings (1924-1929) inserted and recipes handwritten on 16 pages at the rear. The pages also include some household hints including instructions on how "To prepare sheep skins for mats"This ledger is typical of farming records kept in the period 1883 to 1892. The repurposing of the ledger as a recipe book was a common practice. This ledger has cardboard patterned covers. The paper pages are bound with cotton. Some pages are handwritten in ink. There are loose newspaper cuttings within the ledger as well as two addressed envelopes and a small red recipe booklet.ledger, farming records, recipes, morven, edwards family morven, canvassing department of the australian dried fruits association -
 Hymettus Cottage & Garden Ballarat
Hymettus Cottage & Garden BallaratDomestic object - tea set
Remnant Staffordshire porcelain tea set consisting of milk jug, cup, saucers and plates from a tea set presented as a wedding present to Julia Berkery and Michael Taffe at Bungaree in 1893.Unmarked Staffordshire tea set typical of small wedding present for the working classes in the 1890s. This example although a remnant and damaged has a good provenance and remains in the family home with other family wedding presents.Gilder's mark on base of each piece.jug, floral decoration,, bungaree, cup saucer & plate, staffordshire, wedding gift, taffe, present, tea set -
 Linton and District Historical Society Inc
Linton and District Historical Society IncPhotograph, The Wise Family at Their Property at Linton, circa 1869, 1869
... the layout of what a small family holding in the second half ...Family members in this photograph are identified in the book "Dare to be Wise" - L-R: Thomas Wise, born 1858; William Bell Wise, born 1857; John Mardling Wise, born 1860; Thomas Mardling Wise holding baby Joseph James Jonah Wise, born 1868; Mary Bell Wise; Emily Rosina Wise, born 1866; Sarah Ann Wise, born 1854. The girl standing second from right is not identified but is probably Mary Wise, born 1859.Image shows the layout of what a small family holding in the second half of nineteenth century looked like. It also shows cultural and musical items important to the family along with their pets.Black and white copy of original photograph, which shows nine members of the Wise family standing in a row, at their property along Carngham Road at Linton. The photograph shows the layout of the property, with house and stables at rear, animals pens to one side, and orchard at the front. The three young boys in the photograph are holding flutes. The family's dog is lying down in front of the children to the right of the photo.wise family, houses, rural life, thomas mardling wise, mary wise (nee bell), sarah ann wise, william bell wise, thomas wise, mary wise, john mardling wise, joseph james jonah wise, emily wise -
 Linton and District Historical Society Inc
Linton and District Historical Society IncInstrument - Cornet, Brass, Cased, Cornet, Owned and Used by W H Nicholls, Linton Brass Band
The cornet was owned and used by W H Nicholls, a member of the Linton Brass Band, most likely in the 1890s or early 1900s. The cornet was donated to Linton & District Historical Society in 2017 by Robyn Nicholls, of Blackburn. It is understood in the Nicholls family that Robyn's late husband, Graeme Nicholls, inherited the cornet from his great-grandfather, William Henry Nicholls (1845-1902). However it is also possible that the cornet was owned and played by Graeme's grandfather, also named William Henry Nicholls (1880-1943).Brass cornet with mouthpieces, in original dark wooden case which has red fabric lining. Instrument is approximately 30cm in length, has a 12 cm bell and three valves. A small portable sheet-music holder is also in the carrying case. The manufacturer's name "Gautrot Brevete, Paris" is imprinted on the bell, along with the inscription "Exposition Universelle de Paris, 1889, Medaille d'Or". EXHIBITION / UNIVERSELLE / DE PARIS / 1889 / MEDAILLE D'OR / Gautrot Brevete / PARIS.linton brass band, musical instruments -
 Bacchus Marsh & District Historical Society
Bacchus Marsh & District Historical SocietyPhotograph, Harvest Home Hotel Main Street Bacchus Marsh 1883
The Harvest Home Hotel was licensed as a beer shop in 1866. Patrick Vallence was the licensee. On his death in 1874 his widow Mrs M. A. Vallence obtained the license. At the time this image was taken George Marshall was leasing the hotel. Following a decrease in the population of Bacchus Marsh, by 1911 the hotel had lost its licence.The Vallence family still owned the building after the loss of the hotel licence in 1911and it was used for some years after this as a private residence by some members of the Vallence family. Small sepia unframed photograph on card with gold border framing photograph. Housed in the album, 'Photographs of Bacchus Marsh and District in 1883 by Stevenson and McNicoll', the Jeremeas Family Album. The image depicts the Harvest Home Hotel situated in Main Street Bacchus Marsh. The name of the hotel can be seen above the verandah roof. The building appears to be of stone with decorative stonework corners. A verandah is inset to the left of a gabled front section which has its own door and window. On either side of the door beneath the verandah can be seen boot or shoe scrapers. A deep gutter runs along the front of the hotel, with a slab acting as a bridge to the road. Situated in the gutter at the front of the hotel is a water trough which has an arch above it with an ornate lantern, probably to light the front entry and to enable horses to be watered at night. A hitching post is nearby.On the front: Stevenson & McNicoll. Photo. 108 Elizabeth St. Melbourne. COPIES CAN BE OBTAINED AT ANY TIME. On the back: LIGHT & TRUTH inscribed on a banner surmounted by a representation of the rising sun. Copies of this Portrait can be had at any time by sending the Name and Post Office Money Order or Stamps for the amount of order to STEVENSON & McNICOLL LATE BENSON & STEVENSON, Photographers. 108 Elizabeth Street, MELBOURNE. hotels bacchus marsh, stevenson and mcnicoll 1883 photographs of bacchus marsh and district, vallence family bacchus marsh, harvest home hotel bacchus marsh -
 Lakes Entrance Regional Historical Society (operating as Lakes Entrance History Centre & Museum)
Lakes Entrance Regional Historical Society (operating as Lakes Entrance History Centre & Museum)Photograph - Harbeck's Store, 1900c
Harbeck family settled in Lakes Entrance 1892Sepia photograph of Harbecks Store, Esplanade, Lakes Entrance, Victoria, showing a small general store and feed store. Signs above building are Havelock Tobacco, P Harbeck General Merchant, Grocery, Drapery, Iron Mongery, Timber, Crockery. In front of the store, horse and cart with driver, four men on the veranda, horse tethered to post. Lakes Entrance Victoriaretail trade, transport, animals -
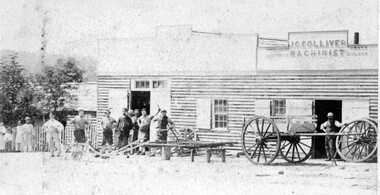 Linton and District Historical Society Inc
Linton and District Historical Society IncPhotograph, J.G. Colliver, Machinist Workshop, 1902, 1902
James Garland Colliver lived and worked in Linton between 1863 and 1875, when he moved to Donald. He was actively involved in Linton's business and community life. (See Colliver family file at LDHS.) This photograph may show two adjacent business premises on the east side of Sussex Street, north of Clyde Street: Edwin Ball or Ball Brothers, blacksmiths, and J.G. Colliver, "Machinist". The Ball and Colliver families were related and are understood to have worked collaboratively. A plan of Sussex Street drawn up in 1871 (in LDHS collection -Reg. no. 2013-25) shows an allotment on the east side owned by 'Colliver' next to a slightly larger allotment owned by 'Ball'.Original small, sepia photograph showing premises of "J G Colliver - Machinist" with workmen in front."J G Collivers shop about 100 years ago".j. g. colliver, wheelwright, carpenter, coachbuilder, workers
