Showing 221 items
matching technical teaching.
-
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionPhotograph, Federation University Centre for Gippsland Studies, 2016, 12/05/2016
Federation University Australia was established on 1 January 2014. Formerly known as the University of Ballarat, its enabling legislation was the University of Ballarat Amendment (Federation University Australia) Act 2013. On 1 January 2014, the University of Ballarat amalgamated with the Monash University Gippsland Campus to form Federation University Australia. The Gippsland Campus also had a long lineage dating back to 1928 with the establishment of the Yallourn Technical School which became a predecessor institution to the Gippsland College of Advanced Education formed in 1968. In 1990, it was renamed the Monash University College and in 1993 became the Gippsland Campus of Monash University. In 2016, Federation University Australia announced plans to take possession, over a two-year period, of Monash’s Berwick Campus in the south-east corridor of Melbourne. Federation University Australia, or FedUni, is headquartered in Ballarat and offers programs in Higher Education and Vocational Education and Training to regional Victoria and beyond. The University’s commitment to educational and social equity, teaching excellence, research distinction, environmental sustainability and regional capacity building has enabled it to develop in a way that draws on its proud heritage to inform its future. Its regional character sets a framework for the University’s priorities but does not constrain it from serving wider community interests, nationally and internationally. The name Federation University Australia was chosen to convey the scope and capacity of an expanded regional university with a federated network of campuses. Photographs of the Centre for Gippsland Studies located at the Churchill campus of Federation University.centre for gippsland studies, churchill campus, gippsland campus, grsc, gippsland campus collection -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionTransparency, University of Ballarat Mace, c1994
Federation University Australia was established on 1 January 2014. Formerly known as the University of Ballarat, its enabling legislation was the University of Ballarat Amendment (Federation University Australia) Act 2013. Although formally created as a University in 1994, the University of Ballarat has a lineage back to 1870 with the establishment of the School of Mines Ballarat, making it the third institution of higher learning to be established in Australia and the first to be established in regional Australia. On 1 January 1994, Ballarat University College became the University of Ballarat and in 1998 the University merged with three TAFE Institutes to become a dual sector institution with multiple campuses. On 1 January 2014, the University of Ballarat amalgamated with the Monash University Gippsland Campus to form Federation University Australia. The Gippsland Campus also had a long lineage dating back to 1928 with the establishment of the Yallourn Technical School which became a predecessor institution to the Gippsland College of Advanced Education formed in 1968. In 1990, it was renamed the Monash University College and in 1993 became the Gippsland Campus of Monash University. In 2016, Federation University Australia announced plans to take possession, over a two-year period, of Monash’s Berwick Campus in the south-east corridor of Melbourne. Federation University Australia, or FedUni, is headquartered in Ballarat and offers programs in Higher Education and Vocational Education and Training to regional Victoria and beyond. The University’s commitment to educational and social equity, teaching excellence, research distinction, environmental sustainability and regional capacity building has enabled it to develop in a way that draws on its proud heritage to inform its future. Its regional character sets a framework for the University’s priorities but does not constrain it from serving wider community interests, nationally and internationally. The name Federation University Australia was chosen to convey the scope and capacity of an expanded regional university with a federated network of campuses.Transparency for the Univesity of Ballarat Mace by Trefor Prestuniversity of ballarat, mace, trefor prest, graduation, federation university -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - OLIVE PELL COLLECTION: NEWSPAPER CLIPPINGS, 1947 on photo
Newspaper clippings and a photograph. Death notices for THOMPSON, Edward (Ted) Colton, died 15/12/1988, formerly of Bendigo, husband of Queenie and a photo of Ted, dated 1947. Newspaper clippings of 'Chemistry Teacher dies', Mr Richard Gaston Walker, died 14/01/?? A chemistry instructor, 50 years of teaching, he was known world wide, during WW1, he was given an important post in England handling chemistry projects in the war effort. On his return to Australia, he became attached to the Bendigo Technical College,(known as the School of Mines) for more than 40 years. On file there is a Richard Gaston Walker died 1965, aged 72, Death Reg.No.1953). Newspaper photo of Richard's son, David G.Walker, Member of the Order of Australia in the Australia Day Honours List. Also newspaper cutting of Two student members of the Faraday Club gave a lecture at the School of Mines.person, group, olive pell collection. edward(ted) colton thompson. richard gaston walker. -
 NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)
NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)Photograph: CTS 1944 Defence trainees with teaching staff
Black and white photograph from Allan Studios which according to Scott's history includes AIF, RAAF, USAF trainees with Principal Strang and other staff 1944 (Scott p.55)collingwood technical school, defence forces training scheme, students, nmit -
 NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)
NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)Photograph: Mr. George Thomas Teacher and Councillor CTS 1937-1972
Mr. George Thomas' connection with Collingwood Technical School began as a junior technical student at Collingwood in 1913. He then became an apprentice in the electrical trades during which time he also undertook a Diploma course in Electrical Engineering. Mr Thomas was appointed as a teacher (part-time) of Electrical Wiring at Collingwood in 1922 having had previous experience teaching in Geelong at the Gordon Institute of Technology. In 1930 Mr Thomas became a full-time teacher in Electrical Trades, the year of the commencement of the Apprenticeship Commission in Victoria. In 1937 he was instrumental in introducing electroplating as a trade whereas it had previously only been taught as a section of the Electrical Trades. This was a period of severe economic constraints following the Great Depression and spending on education was limited. Needing the latest knowledge of industrial practices, Mr Thomas canvassed electroplating industries around Melbourne seeking employment opportunities and met with favourable responses. He approached Quinton’s electroplating firm in North Melbourne with the proposal to work for them on Saturday mornings without payment. In return for his labour, he asked to be taught the basics of the trade. During the week he was able to impart his knowledge to his students. Initially, he wanted to develop electroplating as an outlet for the Youth Employment Training Scheme. Once the class was firmly established, he submitted a proposal to the Education Department to establish an Electroplating Department, and this became the first of its kind in the southern hemisphere. He gave up teaching in 1939 to become the Northcote City Electrical Engineer where he served for 26 years. During this time he was also a Consulting Electrical Engineer to Box Hill and Port Melbourne Councils. His association with Collingwood Technical School (and later, College) continued, first as an examiner on the State Electricity Commission (SEC) panel and from 1947 as a member of the School Council. He was president of the Council in 1961 and 1962. He also represented the College on the Northern Regional Council and participated in the selection of Electrical Trades teachers. For four years, 1967-1971, he represented the metropolitan Technical Schools and Colleges on the Council of the Monash University, in which capacity he gave outstanding service to technical education. George H. Thomas attended his first Council meeting on June 12, 1947 and remained on the Council until the secondary and post-secondary sections were separated in 1981 – a period in excess of 34 years. (See Scott p36).Black and white photographs of Mr. George Thomas who had a long association with Collingwood Technical School and Collingwood Technical College, spanning the years 1937-1972. He began his connection with the school as a teacher and went on to become a member of the School Council. He introduced Electroplating as a trade to be taught at Collingwood Technical School in 1937. (Scott p36) The photographs include one of Mr. George Thomas in Monash University regalia 1971. Another of Collingwood Technical School Council 1972 with Mr. Thomas. Images also include an excerpt from Mr. Scott's history.collingwood technical school, george h. thomas, electroplating course, nmit -
 NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)
NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)Photographs: CTS 1961 Alex Cowmeadow Farewell 20 October 1961
Black and white photographs of the Farewell to Alex Cowmeadow on 10 October 1961. On the reverse of two photos is written '10/10/61 A. Cowmeadow Farewell'. Another photo has on reverse a handwritten note 'Dear Alex / In / memory of happy / days at Collingwood. / Seasons greetings / to Mrs Cowmeadow. / 'Dick'.' Alex Cowmeadow started at Collingwood as a teacher of carpentry and cabinet making in 1927 and stayed there for 34 years until his retirement in 1961 when he was head of the Cabinetmaking and Chair and Couch Making Departments. Besides his trade teaching activity, Alex was involved in the sporting activities of the school and also organised interchange visits between students of Collingwood and Goodwood Technical School in South Australia. After his death in 1970 it was discovered that he had left his property for the benefit of Collingwood Technical School. This generous gesture enabled the development of a much better school camp at Camp Westlake in Buxton, where two wings of the camp were named after Alex and his wife Doris Cowmeadow – reminders to the students of the generosity of their former teacher. (George Eraclides, 2013). collingwood technical school, camp westlake, alex cowmeadow, nmit -
 NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)
NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)Plumbing tools: CTS and PTS 1920s onwards, Plumbing tools and texts used in teaching 1920s
... in teaching at Collingwood Technical School then also at Preston... Technical School Preston Technical School Northern Metropolitan ...A number of Plumbing tools dating from 1880s-1970s and used in teaching at Collingwood Technical School then also at Preston Technical School and at Northern Metropolitan College of TAFE's Heidelberg campus. Includes: Kerosene blow torch X 2 (1930s-); Stillson Grips; Pipe Cutter; Mash hammer; Adjustable spanner X 3 different sizes; Caulking tool; 5 way tee, 2X3 way tee, 4 way tee (1930s-); Old Handmade lead traps (student work) X 2; Metal tool tray holding; Offset adjustable spud spanner; Pear shaped lead working mallet; Bossing tool for lead work (1880s-1920s); Soldering iron (1920s-); Set square; Large screwdriver; Also Plumbing texts: • Problems for elementary physics, new rev. edn., by Thomas Tasker and Alexander Boden, Science Press, Sydney, 1966. • Gasfitting. Printed and published by McCarron Bird Pty. Ltd. [Melbourne] • Trade science for plumbing apprentices, Education Dept. Victoria, 1954 • Sanitary Plumbing and water supply, Dept. of Labour • Gasfitting, produced by members of the Colonial Gas Association Limited, Gas and Fuel Corporation of Victoria, and the Technical Division of the Education Department of Victoria. Rev metric edn. 1976 • Mechanical world year book 1953, Manchester Emmott & Co., 1953 collingwood technical school, preston technical school, northern metropolitan college of tafe, plumbing tools, plumbing texts, nmit -
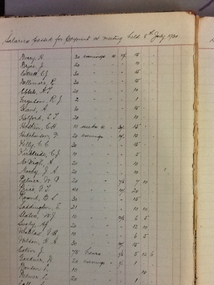 NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)
NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)Account Book - CTS, Account book - Salaries 1920-1934
... teaching at Collingwood Technical School in the 1920s as well ...This account book contains the "Salaries passed for payment..." and details the salary for each staff member, number of classes taught, weeks worked, etc.This is a significant account of both the people teaching at Collingwood Technical School in the 1920s as well as an indication of the rates of pay at the time.Grey cloth-covered cardboard cover with red spine. Pages are ruled for accounts. Label on cover "Journal"Handwritten on cover label "Salaries"collingwood technical school, cts, salaries, teachers, account books, nmit, -
 NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)
NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)Book - CTS, Lectures on education, Early 20th century
This set of 20 lecture notes outlines the theory and practice of teaching. Covers a range of subjects and disciplines.A written account of educational theory in the early 20th century.A series of lecture notes bound into one volume. Black cover with gold lettering on spine.Stamped on spine in gold lettering: "C'WD/TECH./SCH./LECTURES ON EDUCATION"education, educational theory, cts, collingwood technical school, nmit, -
 NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)
NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)Book: A Bricklayer's journey by Frank Upfill, Book: A Bricklayer's journey by Frank Upfill, 2003
Book published in 2003 by the author spanning years in the 1970s and 1980s when he taught Bricklaying at Preston Technical College which later became Preston College of TAFE.Book of 37 pages with photos and bibiliography. Bricklayers--Victoria--Biography. Bricklaying -- Study and teaching. Geelong (Vic.) -- Biography preston techinical school, preston college of tafe, bricklaying study and teaching 1970s-1980s, frank upfill, staff 1970s-1980s, inmit -
 NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)
NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)Book: Tom Thrupp's war: July 1940-June 1941, Book: Tom Thrupp's war: July 1940-June 1941, by his daughter Rosalie Bray (Thrupp), June 26, 2011
... Technical School Thomas Thrupp Teaching Staff 1930s Second World War ...Book of 109 pages, with images. preston technical school, thomas thrupp, teaching staff, 1930s, second world war, nmit -
 NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)
NMIT (Northern Melbourne Institute of TAFE)Certificate: Foundation student, Preston Technical School 1937
Buff coloured card certifying that the named student was a Foundation Student of Preston Technical School which was officially opened on 21st April, 1937. Lists the members of the School Council, the Teaching staff of 1937 and the Evening School staff. Also held are copy of Foundation Certificate for Foundation student Kenneth Fyffe who was at Preston Technical School from 1937 to 1939; Ken Fyffe's Junior School report; Ken's Merit Certificate dated 21 December 1937; Ken's Junior Technical Certificate dated 6 June 1939; and letter from the Principal regarding Timetable for Supplementary Examinations for Intermediate Certificate.preston technical school, students, certificates, awards, kenneth fyffe, nmit -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesCD-ROM, Board of Studies New South Wales, Winangaylanha Dhayn-gu Gaay : understanding Aboriginal languages : working with the Aboriginal languages K-10 syllabus : a guide for Aboriginal community collaboration for school based languages programs, 2004
A guide for Aboriginal community collaboration for school-based programs. Supporting the Aboriginal languages K-10 syllabus, this resource assists Aboriginal community participation in the teaching of Aboriginal languages in schools. Technical Details System requirements (PC): 64 Mb RAM; Windows 98; 800x600 screen; thousands of colours.CD-ROMmulticultural education, multilingualism -
 Duldig Studio museum + sculpture garden
Duldig Studio museum + sculpture gardenSculpture, Karl Duldig, Mask by Karl Duldig 1921, 1921
Karl Duldig carved this marble sculpture of a mask in the Vienna Kunstgewerbeschule (School of Applied Arts) in 1921. His teacher, Anton Hanak, the Professor of Sculpture at the School, encouraged him to carve directly into the stone. It was an accomplished work for the 19 year-old student and was selected by Hanak to represent the students of the School at the Deutschen Gewerbeschau (German Applied Art exhibition) in Munich in 1922, an early accolade for the young artist. The sculpture and another Kneeling Nude were reproduced in the journal Deustche Kunst and Dekoration in 1923-24 in an article on the Hanak-Klasse. In 2011 Mask was exhibited in the National Gallery of Victoria exhibition Vienna: Art and Design. The sculpture is one of ten substantial sculptures in marble and stone, and a larger group terracotta sculptures and masks, portrait busts and small stone sculptures created by Karl Duldig in Vienna that are held in the Museum collection. These art works are complemented by an archive of contemporary documents including letters, photographs, documents and ephemera. In 1938 Duldig’s Viennese sculptures were sent to Paris in 1938 for a proposed exhibition, and were hidden in Paris by Slawa Duldig’s sister Rella, throughout the Second World War, and arrived in Australia post-war over 5 decades. Karl Duldig was a student of the Kunstgewerbeschule from 1921 until 1925, and then attended the Akademie Der Bildenden Künste (Academy of Fine Arts) from 1929 until 1933. He was accepted into the Professor Josef Mullner’s “Meisterschule” at the Academy of Fine Arts from 1929 until 1933. His teacher at the Kunstgwerebeschule was Austria’s foremost contemporary sculptor Anton Hanak, and he was a formative influence on Duldig’s work. Hanak had been a member of Viennese Secession, and worked with Josef Hoffman on architectural commissions prior to the First World War. Hanak shared both his love of the expressive quality of materials and a humanist vision with his students. Various writers have written about Duldig’s interest in masks. His interest may have been stimulated by his classical education, the Greek and Roman antiquities in the Kunsthistoriches Museum in Vienna, or the ethnological collections in Vienna’s Museum of Ethnology (now known as the Weltmuseum). The mask was a motif explored by expressionist and cubist artists whose work was exhibited at the Vienna Secession. Duldig would have been familiar with the psychological investigations of the neurologist and founder of psychoanalysis Sigmund Freud, who established his practice in Vienna. In the Duldig Studio library, Duldig’s keen interest in the arts of a myriad of visual cultures is apparent. Of particular note are two well-thumbed copies Rudolf Utzinger’s, Masken, published by Ernst Wasmuth in Berlin in 1923, depicting masks from around the world. It is likely that a multitude of influences were at play. Slawa Duldig also worked with this motif, and also carved a smaller mask in Salzburg marble as well as a remarkable mask in clay, and these are held in the collection. Ann Carew 2016The Mask has national and international aesthetic significance. It is one of the earliest works by Karl Duldig in the Studio collection, and is a subject that he would continue to explore throughout his working life. The sculpture demonstrates a high degree of technical skill and mastery at an early age. It is evidence of Duldig’s engagement with the art of his peers during this period – the mask is a motif that inspired contemporary expressionist and cubist artists. It also demonstrates his interests in portraiture, human psychology, and the creation of identity and transformation of personalities. The Mask also provides an important link to the studio practice in the Vienna Kunstgwerbeschule, the teaching of Anton Hanak, and the program of international art exhibitions in Europe during the period. It is also of historical significance: the story of its survival and eventual recovery provides a counterpoint to the story of the Nazis’ confiscation of art during the Second World War. Ann Carew 2016Carving in Salzburg Marble. Holes for eyes and mouth cut through the block. Highly polished finish at front contrasting with rough finish at back and stylised curled hair. Marble base separate (75 x 275 x 198, wt 9000) and added later by artist. Karl Duldig 1921 incised on back -
 Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.
Whitehorse Historical Society Inc.Functional object - Illustration, Woodwork Illustrations, 1970's
Eight Illustrative charts issued by Commonwealth of Australia.Eight Illustrative charts issued by Commonwealth of Australia - Department of Labour and National Service - Industrial Training Division for teaching woodwork to students.Eight Illustrative charts issued by Commonwealth of Australia.blackburn technical school, woodworking tools -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesDrawing - Artwork - Painting, Portrait by Jean Appletom
Jean APPLETON (1911-2003) Jean Appleton was a painter and craftworker who studied at East Sydney Technical College and at the Westminster School, London. After seeing French sculptor Maillol's work 'The Cyclist' she was inspired to try sculpture and consequently studied under Eric Schilsky in London. With the outbreak of war she returned to Australia, thereafter teaching at high schools in the ACT and NSW and at the Julian Ashton and National Art Schools in Sydney. The first of her thirteen solo exhibitions was held at Sydney’s Macquarie Galleries in 1940. Resident in England from 1969 to 1981, she continued to teach intermittently into the late 1970s. After a difficult first marriage to artist Eric Wilson, who died, she married painter Tom Green and they settled in Moss Vale. Though her work is now represented in major state and regional collections, Appleton was like many women artists of her generation in that recognition of her work came late in life: she was in her eighties when a public gallery first presented a retrospective exhibition of her art. (https://www.portrait.gov.au/portraits/2013.92/self-portrait, accessed 15 September 2019) Jean Appleton won the inaugural Portia Geach Memorial Award in 1965 with this work. She dies in 2003.A sketched portrait of a man's head by Jean Apppleton. It may be Jean Appleton's first husband, Eric Wilson. drawing, portrait, jean appleton -
 RMIT Design Archives
RMIT Design ArchivesDomestic object - Object, General Electric KE12 Kettle, designed by Barry Hudson
The GE12 Electric Kettle was designed by Barry Hudson for General Electric and in 1978 won the Australian Design and the Prince Philip Prize awards for Australian Design. The kettle was innovative in many ways; it was an early example of an all plastic electric kettle with a single-handed opening-spout. According to design historian Ian Wong ‘The use of an integral hinge for the spout opening mechanism utilised the unique live hinge property of polypropylene, now common but at the time a novel use and very efficient to manufacture.’ The kettle was available in Carpentaria Orange, Blaze Yellow and Lime Green with a contrasting base. Barry Hudson (1935-2008) studied Mechanical Engineering at the Melbourne Technical College (MTC). In the 1970s he was Research and Development Manager at General Electric, and he also worked with the industrial design practice Rosenfeldt, Gherardin and Associates. He established Barry Hudson Industrial Design in the 1980s and began a teaching career at the former MTC, now known as RMIT University. Ann Carew, 2020 1978 the Kettle won an Australian Design Award and the Prince Philip Prize for Australian Design.Orange and brown electric kettlekettle, industrial design, rmit university, domestic appliances -
 Wangaratta High School
Wangaratta High SchoolWTC Teaching Service regulations, 1974
Green folder with silver text reading WANGARATTA TECHNICAL COLLEGE containing document outlining the Victorian teaching service regulationsTEACHING SERVICE REGULATIONS -
 Expression Australia
Expression AustraliaReport, Final Report, Overseas Study Tour, To Examine Curricula and Teaching Strategies Used in the Vocational Training of Deaf Students in the U.S.A
Winston Churchill Memorial Trust; Written by Barry Clyne, Churchill Fellow 1983, Richmond College of Technical and Further EducationThis report is significant as it led to the setting up of the Auslan Program at Kangan Batman TAFE.Yellow cover, Size 28cmHx22cmW, 71 pagesvocational training, barry clyne, richmond college of technical and further education -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionPainting - Portrait, Laurence Scott Pendlebury, 'The Artist's Wife' by Laurence Scott Pendlebury, 1978
... between 1941 and 1945. Teaching at Swinburne Technical College... and 1938 and then at Swinburne Technical College. He served during ...Laurence SCOTT PENDLEBURY (1914 - 1986) Born Melbourne Laurence Scott Pendlebury studied at the National Gallery of Victoria School between 1932 and 1938 and then at Swinburne Technical College. He served during World War Two with the AIF between 1941 and 1945. Teaching at Swinburne Technical College between 1946 and 1963 Laurence Scott Pendlebury was head of the art school from 1963 until his retirement in 1974. He was president of the Victorian Artists’ Society from 1961 to 1963. Awards include: Dunlop Prize in 1950, 1951, 1953 and 1954; Gibson Prize, Victorian Artists’ Society in 1956; Wynne Prize in 1956, 1957, 1960 (shared with John Perceval) and 1968; Caltex Prize in 1957; Victorian Artists’ Society Artist of the Year (shared) in 1975. Portrait of Nornie Gude, the artist's wife, holding a violin. Nornie Gude was a student of the Ballarat Technical Art School, a division of the Ballarat School of Mines. Nornie Gude was the daughter of Walter Gude, a leding musician, and highly regarded teacher. She grew up in Ballarat and was educated at Loreto College. From 1931 to 1936 Nornie Gude attended the Ballarat Technical Art School, a division of the Ballarat School of Mines. She was accepted into the School at the age of 15 because she was so advanced in painting. Nornie Gude studied at Ballarat for five years before progressing to Melbourne’s National Gallery of Victoria School. As a violinist Nornie Gude played for more than a decade with the Zelman Orchestra. This work was a finalist in the 1978 Archibald Prize.artists, artwork, laurence scott pendlebury, pendlebury, nornie gude, gude, available, alumni -
![Ceramic, Ino Kiyoshi, [Vase] by Ino Kiyoshi, c1982](/media/collectors/530576742162ef0fa09a2288/items/5566bbdf2162f113608fc669/item-media/60f41b51b06f0c13a9354719/item-fit-380x285.jpg) Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionCeramic, Ino Kiyoshi, [Vase] by Ino Kiyoshi, c1982
Ino KIYOSHI (b 1946, Kyoto Japan, d. 2008) Worked in Australia from 1973–76 and 1978–2008 Ino Kiyoshi was to a family that has been involved in the production of pottery for some 160 years. Working in the family studio while studying at the Kyoto School of Arts and Crafts, he completed his diploma of Ceramic Art in 1969. He then attended the KyotoTechnical School for a post-graduate course in glazing. then lectured in ceramics at the KyotoTechnical School. Following in the footsteps of the famous Japanese potter, Shoji Hamada who had visited Australia in 1965, Kiyoshi Ino visited Sydney in 1973, where he worked with Japanese potter Shigeo Shiga). Kiyoshi took up an appointment as Visiting Lecturer in Ceramics at the Gippsland Institute of Technical Education, Churchill, Victoria, from 1974 to 1976 and returned there as Assistant to the Senior Lecturer in Ceramics in 1979. He ceased teaching at the Gippsland Institute in 1988. Ino was involved in the establishment of a space for artists in the old butter factory at the nearby township of Yinnar and in 1982 the Yinnar Art Resource Collective, commonly known as Yinnar ARC, was established. Ino has exhibited extensively throughout Australia.Australian Studio Ceramics Gift of the artist, 1982Impressed seal for Kiyoshi Ino on baseceramics, gippsland campus, jan feder memorial ceramics collection, ino kiyoshi, japanese ceramics -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionCeramic, [Untitled] by Ino Kiyoshi, c1982
Ino KIYOSHI (b 1946, Kyoto Japan, d. 2008) Worked in Australia from 1973–76 and 1978–2008 Ino Kiyoshi was to a family that has been involved in the production of pottery for some 160 years. Working in the family studio while studying at the Kyoto School of Arts and Crafts, he completed his diploma of Ceramic Art in 1969. He then attended the KyotoTechnical School for a post-graduate course in glazing. then lectured in ceramics at the KyotoTechnical School. Following in the footsteps of the famous Japanese potter, Shoji Hamada who had visited Australia in 1965, Kiyoshi Ino visited Sydney in 1973, where he worked with Japanese potter Shigeo Shiga). Kiyoshi took up an appointment as Visiting Lecturer in Ceramics at the Gippsland Institute of Technical Education, Churchill, Victoria, from 1974 to 1976 and returned there as Assistant to the Senior Lecturer in Ceramics in 1979. He ceased teaching at the Gippsland Institute in 1988. Ino was involved in the establishment of a space for artists in the old butter factory at the nearby township of Yinnar and in 1982 the Yinnar Art Resource Collective, commonly known as Yinnar ARC, was established. Ino has exhibited extensively throughout Australia. Gift of the artist, 1982impressed seal for Kiyoshi Ino on baseceramics, shikuhu ino, jan feder memorial ceramics collection, gippsland campus, yinnar, yinnar art resource collective -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionCeramic, Ian Sprague, [Ceramic Panel] by Ian Sprague, c1977
Ian SPRAGUE (1920 - 18 April 1994) Born Geelong, Victoria Ian Broun Sprague's initial training was in Architecture, completing a degree at the University of Melbourne in 1950. After a serious car accident in England, Sprague was encouraged to take up a craft to restore the strength in his arms. He studied at the Central School of Arts and Crafts, London for three years, and spent two months at the David Leach Pottery in Devon, before returning to Australia in 1962. In 1964 Ian Sprague established the Craft Centre in Toorak Road, South Yarra, and the Mungeribar Pottery in Upper Beaconsfield, with Robin Welch, Mungeribar being an Aboriginal word meaning 'red clay'. In 1981, he moved to Mooney-Mooney, NSW (Mungeribar was gutted by bushfires shortly after he left), and to Noosa in 1992. The Mungeribar Pottery mark is an impressed 'm', and Sprague's own mark is an impressed 'IS' with the S rendered in Morse code. Ian Sprague's Mungeribar apprentices were Grattan Burley, Victor Greenaway (1969–73), Christopher Sanders (1976-78}, Trevor Hanby (1978–80). In 1981, he moved to Mooney-Mooney, NSW , and Noosa in 1992. Greenaway's mark in his Mungeribar years was an impressed capital G. Grattan Burley (for six months), The Craft Centre in South Yarra was owned and stocked entirely by Ian Sprague, and he travelled all over Australia in search of the best possible textiles, glassware, woodwork and jewellery, not just pottery. The opening exhibition showed the pottery of Robin Welch. Sprague sold the Centre in 1967, but soon started a campaign for a government funded centre, eventually established as the Meat Market Craft Centre in North Melbourne. In 1971 Sprague became president of the recently created Craft Association of Victoria. Dismayed by the quality of teaching in art schools and technical colleges, he ran many workshops around the country on the textural treatment of clay. This work is part of the Jan Feder Memorial Ceramics Collection. Jan Feder was an alumna of the Gippsland Campus who studied ceramics on the campus. She passed away in the mid 1980s. Her student peers raised funds to buy ceramic works in her memory. They bought works from visiting lecturers who became leading ceramic artists around the world, as well as from many of the staff who taught there.Contemporary ArtTexture fire clay slab and partly glazed wall panel. Ian Sprague produced his hand modeleed wall panels by cutting them from fireclay blocks, heating and scraping them, and applying bold simplified motifs. A strong solution of salted wated was poured onto the rugged clay surfaceswhich produced a warm toasted surface effect. The panels show a clear understanding of the modulation of two dimensional relief sculpture. Artists stamp on lower RH cornerceramics, ian sprague, gippsland campus, jan feder memorial ceramics collection, mungeribar, meat markery craft centre, craft centre south yarra -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionSculpture - Marble sculpture, 'Professor Alfred Mica Smith' by Paul Montford, 1924
... Shrine of Remembrance. In 1924 he was teaching at Geelong.... In 1924 he was teaching at Geelong Technical College. Professor ...Paul Raphael MONTFORD (1868 - 1938) Paul Montford moved to Australia to carve four buttress groups in granite for the Melbourne Shrine of Remembrance. In 1924 he was teaching at Geelong Technical College. Professor Alfred Mica Smith was a long term lecturer at the Ballarat School of Mines. The sculpture was commissioned by former Students of the Ballarat School of Mines working in Western Australia. One of those former students, William Corbould, remembered his first encounter with the professor fondly:- 'From the Registrar's Office I was led to be introduced to the Professor of Chemistry, one Mica Smith. The initial encounter gave me little encouragement - his large laboratory was filled with hundreds of bottles bearing strange labels with queer symbols on them. My heart sank. At the first opportunity I grabbed my hat and made for the door, but the good professor called me back. I pointed out that I was never any good at school ... so it was no use pretending to be clever enough to understand all those weird symbols! The Professor told me not to worry about that and took me to one of the benches where he found a blowpipe and a charcoal block. Mixing together two powders from bottles on the shelf he transferred a sample to the charcoal and directed the bunsen flame onto it. Soon it began to melt and a white bead appeared in front of my eyes. He then took a test tube and added a little colourless liquid from each of two bottles. A beautiful dark blue colour appeared. My interest was won.' Alfred Mica Smith was the well-loved Professor of Chemistry and Metallurgy at the Ballarat School of Mines between 1881 and 1922. Upon reaching the age of 78 Mica Smith retired having influenced generations of miners. At the time of his death Ballarat School of Mines Students’ Magazine reported: "In the annals of the School, the year 1922 will be noted chiefly as the last year in which Professor Mica Smith taught here. With his retirement, a memorable epoch closed. The Professor has served the School for 42 years with a service, the length and thoroughness of which are unique. … It is not quite realised in this city how famous the School became throughout the world, nor to what extent the Professor was responsible for its high position in the mining and metallurgical world. … This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 2000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.Marble bust of Ballarat School of Mines Professor Alfred Mica Smith by Paul Montford. The bust is mounted on a jarrah pedestal made from timber donated by the Millar Timber and Trading Company. The bust was formally presented to the Ballarat School of Mines on Saturday 13 December1924 in front of Alfred Mica Smith and a large gathering. It is signed 'Paul R. Montford, Sc, 1924' at the back.Professor A. Mica Smith, 1924, Presented by His Old Students Associated with Western Australia as a Token of Affectionate Esteemart, artwork, ballarat school of mines, montford, paul montford, alfred mica smith, mica smith, marble, bust, sculpture -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionArtwork, other - Artwork, 'College Logo' by Henry Moritz, 1979
Henry MORITZ (1931- ) Born Mainz, Germany Arrived Australia c1952 Henry Moritz was an experienced commercial artist when he left Germany for Australia. After working as a railwayman, coal miner, fruit picker and steelworker, he started teaching commercial art at the Ballarat School of Mines Technical Art School in 1963. He moved to the Mount Helen Tertiary Division, and was head of the Art School at the Ballarat College of Advanced Education (BCAE) when he produced this work. The Ballarat College of Advanced Education logo was derived from the Southern Cross depicted on the Eureka Flag, which was adopted by Ballarat College of Advanced Education in 1978. The logo was designed by former student Debra Garton, who graduated with a Diploma of Art and Diploma of Education. This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 1000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.Farmed marquetry using fine woods chosen for their grains and reflective properties: silver ash, cedar, queensland walnut, grey bird's eye maple and African gaboon.art, artwork, henry moritz, marquetry, logo, southern cross, ballarat college of advanced education, available, stars -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionSculpture - Bust, Greenhalgh, Victor, Dick Richards by Victor Greenhalgh
Victor GREENHALGH (1900-1983) Born Australia Victor Greenhalgh studied at at the Ballarat School of Mines, and was appointed to the staff in 1938. He was the commissioned sculptor for the King George V statue located in Ballarat's Sturt Street Gardens, as well as eight of the portrait busts of Australian Prime Ministers which line the "Avenue of Prime Ministers" in the Ballarat Botanical Gardens. From 1938 he taught at the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology (RMIT). The bust of Dick Richards was Victor Greenhalgh's last work, and was cast after the sculptors death. It was donated to the Ballarat School of Mines by Victor Greenhalgh's wife Violet Greenhalgh (Hambly). Dick Richards and Victor Greenhalgh were brothers-in-law. Dick Richards was a member of Shackleton's ill-fated Trans-Antarctic Expedition, and was awarded the Albert Medal for his heroic contribution as a member of the Ross Sea Shore party. In 1972 the Albert Medal was exchanged for the more widely recognised George Cross. Speaking at the unveiling of the sculpture in Dick Richards said that on his return fro the expedition in 1917 he had little inclination for a sedentary or a teaching career. By the time he retired in 1958 he was not at all sorry that he had spent his life as a teacher. Victor Greenhalgh died in Queensland in 1983. This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 2000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.Bronze bust of Antarctic Explorer and former Principal of the Ballarat School of Mines, Richard W. Richards.art, artwork, dick richards, r.w. richards, richard w. richards, victor greenhalgh, antarctic explorer, alumni, violet greenhalgh, violet hambly, sculpture, staffmember, ballarat technical art school, school of mines ballarat -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionCeramic - Ceramic - Stoneware, Pilven, Peter, Autumn Vessel, 1998
Peter PILVEN (1956- ) Born Ballarat Peter Pilven is acknowledged by his peers for his high level of tacit skills, including throwing, and for his sound technical knowledge of materials.Training with John Gilbert's Edinborough Pottery from 1972-1975, Pilven trained with Joan Campbell in Fremantle in 1976. In 1977 Peter Pilven obtained a Diploma of Fine Art (Ceramics) from Ballarat College of Advanced Education (now Federation University). The following year he worked with Ian Dowling at Geraldton, WA, and with the Western Australian Aboriginal Education Unit in 1979. He next trained with Alan Cagier-Smith in England between 1980 and 1981. Peter Pilven established his own studio in 1982. He has been teaching ceramics at Federation University since 1983, and is considered by his students, to be a living treasure. This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 1000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.art, artwork, ceramics, peter pilven, pilven, stoneware, wheelthrown, madeinballarat -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionPainting - Watercolour, Albert E. Williams, 'Study of Kangaroo Apple', 05/07/1928
Albert E. WILLIAMS (1899-1986) Victoria, Australia Albert Edward Williams was among the first to undertake the five-year, Technical Art Teacher’s Certificate (TATC) at the Ballarat Technical Art School in 1915, with work placement at the Ballarat Lithographic company. Williams taught for several years before he was selected to undertake further teacher training at the Working Men’s College, Melbourne, in 1926. He returned to teach at Ballarat in 1928, facilitating many student activities, while pursuing the arduous Art Teacher’s Certificate. From its inception in 1914, it was 30 years before the first candidate achieved the certificate’s exhaustive requirements. This artwork was completed for the Drawing Teachers' Secondary Certificate at the Ballarat Technical Art School, a division of the Ballarat School of MInes. It is part of the Federation University Art Collection which features over 2000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.Three design motifs inspired by the Kangaroo Apple for undertaken for the Drawing Teacher's Secondary Certificate."Study of Kangaroo Apple - with two designs based thereon. For Drawing Teacher's Secondary Certif. By Albert E. Williams. Tech. Art School, Ballt."art, artwork, albert e williams, a e williams, williams, ballarat technical art school, secondary art teaching, drawing, a.e. williams, available, alumni -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionInk on card, 'Bill Durant in Neville Bunning's Chair' by Henry Moritz, 2002
Henry MORITZ (1931- ) Born Mainz, Germany Arrived Australia c1952 Henry Moritz was an experienced commercial artist when he left Germany for Australia. After working as a railwayman, coal miner, fruit picker and steelworker, he started teaching commercial art at the Ballarat School of Mines Technical Art School in 1963. He moved to the Mount Helen Tertiary Division, and was head of the Art School at the Ballarat College of Advanced Education (BCAE) when he produced this work. This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 2000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.Original caricature of Bill Durant. Both Bill Durant and artist Henry Moritz were staff members at the Ballarat College of Advanced Education (later Federation University). Neville Bunning ceremoniously presented the chair to Bill Durant in the Art Department at Neville Bunnings Retirement function.Verso "Bill Durant in 'Nev Bunning's Chair' which was ceremoniously presented to Bill in Art SChool Staffroom at Neville's retirement function. Drawing by Hner Moritz Donated by Heather (walton) Durant Heather (SMB Library) married Bill (SMB Physics Head) in December 1960. KC (Ken Clements) July 2002art, artwork, henry moritz, bill durant, caricature, available -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionEtched metal, Henry Moritz, [Jack Barker's Farewell] by Henry Moritz
Historical Information Henry MORITZ (1931- ) Born Mainz, Germany Arrived Australia c1952 Henry Moritz was an experienced commercial artist when he left Germany for Australia. After working as a railwayman, coal miner, fruit picker and steelworker, he started teaching commercial art at the Ballarat School of Mines Technical Art School in 1963. He moved to the Mount Helen Tertiary Division, and was head of the Art School at the Ballarat College of Advanced Education (BCAE) when he produced this work. This item is part of the Federation University Art Collection. The Art Collection features over 1000 works and was listed as a 'Ballarat Treasure' in 2007.art, artwork, henry moritz, jack barker
