Showing 33 items matching "airstrip"
-
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Photograph, A Typical Airstrip In The Delta Region
Two black and white photograph in a frame - Top photo is an aerial photo of an unknown airstrip in the Delta Region. Bottom photo depicts tyre tracks on the muddy airstrip during the wet seasonTop photo - 'A Typical Airstrip In The Delta Region' Bottom photo - 'During the wet season a test of pilot skill and aircraft durabilityairstrip, wet season, photograph -
 Department of Health and Human Services
Department of Health and Human ServicesMenyamya Village and airstrip about 175 aeronautical miles North West of Port Moresby. Papua New Guinea - Department of Health – National Fitness Office (Sports & Recreation) – Historical Press Release Photo Collection
Department of Health – National Fitness Office (Sports & Recreation) – Historical Press Release Photo - Empire Youth Day & Royals on Tour CollectionDepartment of Health – National Fitness Office (Sports & Recreation) – Historical Press Release Photo - Empire Youth Day & Royals on Tour Collection -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - AULSEBROOK COLLECTION: NOTES ABOUT FLYING CLUB BENDIGO 1950'S - 60'S
Aulsebrook Collection: Notes about the flying club in Bendigo during the 1950's - 1960's -Scribbled notes on two fools gap pages -Refers to history of flying club, how many students and details about airstrip and planes involvedflying club, airstrip -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Photograph, Pilatus Porter
Framed Coloured Photograph of Pilatus Porter Aircraft parked at an unknown Airstrip.S/N A14 - 692, Australian Air Force Rondelphotograph, planes, pilatus porter -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Photograph, Sioux G3R1
Coloured Photograph in a black frame of SIOUX G3R1 Helicopter parked at an unknown Airstrip.Armyphotograph, sioux helicpoter -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPapers - Mt Beauty Airport Development
The SECV began investigating four possible sites for an airstrip in Mt Beauty in 1965. The land was owned by the SEC and leased by Mr J. Sharp. It became available on the condition that the land would only be available to the Municipal shire. This land was officially opened as an Airport as an official tourist activity in 1977. It continues to be available to tourists, fire fighters, the air ambulance and the local gliding club.The opening of Mt Beauty Airport has enhanced Mt Beauty township by enabling fire fighters to access the surrounding bush during bush fires, by enabling Ambulance helicopters to rush emergency patients to city hospital, by giving tourists the opportunity to fly in and to give the local Gliding Club the opportunity to store and fly their gliders. 1. Set of papers titled 'History Mt Beauty Airport Development' held together by large steel clip by Alex McCullough. 2. Set of papers titled 'Department of Transport' and 'Alpine Shire' both held together by one staple. 3.Mt Beauty Township Survey Plan of Airstrip 1975 4. Large folder titled Mr J. R. Sharp 1975 - Mt Beauty Airfieldmt beauty airport history, alex mccullough, transport, tourism -
 National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)
National Vietnam Veterans Museum (NVVM)Photograph, Kiowa OH58A
Framed coloured Photograph in a black frame of Australian Army Kiowa Helicopter parked at an unknown Airstrip.Australian Rondel, S/N 15236photograph, oh58a, helicopter -
 Tramways/East Melbourne RSL Sub Branch - RSL Victoria Listing id: 27511
Tramways/East Melbourne RSL Sub Branch - RSL Victoria Listing id: 27511Photograph, Iroquois flying over Caribou at Vung Tau Airfield
Framed image of the 9th Squadron Iroquois Helicopters flying over the 35th Squadron Caribou Jet at Vung Tau Airstrip. Information sheet on images states '9SQN IROQUOIS flying over 35SQN CARIBOU flight line VUNG TAU AIRFIELD 1970. iroquois, helicopter, caribou, jet, 9 squadron, 35 squadron, vung tau, 1970, vietnam, iroquis -
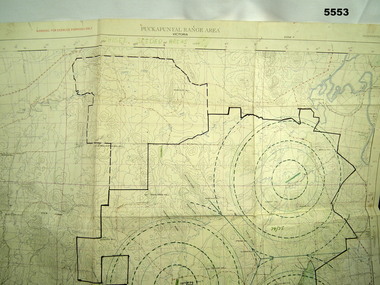 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumMap - MAP of PUCKAPUNYAL, RAAF et al, 1958
Refer to Cat 5547, Matheson.This is a large map, printed in colour on one side only. Scale 1:25,999. The grid squares are 1000 x 1000 metres. it shows the camp, ranges and bush areas used by the military.This map is covered in a large number of added colour shadings, nav lines, airstrips and circles.puckapunyal army base, military training, map -
 Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation Society
Port Melbourne Historical & Preservation SocietyProgramme - Fishermen's Bend Classic, Airstrip races, Feb 1956
Official souvenir programme Fishermen's Bend Classic airstrip races 11 & 12 February 1956. Details of races. 36 pages black and red cover. Digital image of cover on computer.sport - motor racing, fishermans bend airstrip, port melbourne speedway, light car club of australia -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchPhotograph, c1945
Prior to the Second World War Tarakan Island was part of the Dutch East Indies and an important oil-producing centre. In early 1942 it was occupied by the Japanese. The primary objective for the Allied attack on Tarakan (code-named "Oboe One") was to secure and develop the island's airstrip so that it could be used to provide air cover for subsequent landings in Brunei, Labuan and Balikpapan. The secondary objective for the operation was to secure Tarakan's oilfields and bring them into operation as a source of oil for the Allied forces. As part of the 26th Brigade the 2/24 Battalion landed at Tarakan on May1 1945. The task of capturing Tarakan's airstrip was assigned to the 2/24th Battalion. The Battalion's initial attack on the airstrip on the night of 2 May was delayed when the Japanese set off large explosive charges, and the airstrip was not secured until 5 MayThe 2/24th Battalion was an infantry battalion of the Australian Army, which served during World War II .A unit of all-volunteers, it was formed in July 1940 from primarily Victorian volunteers and was known as "Wangaratta's Own" because of the time the battalion spent in the town during its formative period prior to deployment overseas. It served in North Africa in 1941–1942 as part of the 26th Brigade, which was assigned to the 7th Division, before being reassigned to the 9th Division. In early 1943, the battalion returned to Australia and later took part in campaigns against the Japanese in New Guinea in 1943–1944 and Borneo in 1945, before being disbanded in 1946. The 2/24th suffered the highest number of casualties of any 2nd AIF infantry battalion. The Unit was granted the Freedom of the City by the Rural City of Wangaratta in 1996 and one of the first, if not the first, to receive this type of honour. Reproduced black and white photograph of metal pylon structures with man standing in bombed foreground Handwritten on rear - Oil wells on Tarakan2/24th battalion, tarakan, ww2 -
 Hume City Civic Collection
Hume City Civic CollectionPhotograph, Late 1990's
Riddell Road is the continuation of Macedon Street and is on the west side of the town centre. It is the main road to Riddells Creek, the Sunbury airstrip, Sunbury tip and water towers.A coloured photograph of Riddell Road looking west. A red car is in the foreground travelling north and is at the T intersection of Riddell Road and Ligar Street. There are houses along the north side of Riddell Road and the football ground is on the south side of the road.sunbury football club, riddell road, ligar street, george evans collection -
 South Gippsland Shire Council
South Gippsland Shire CouncilPhotograph, Framed, Cape Wom 13 Sept 1945, 1995
Framed B & W photograph titled: "CAPE WOM, NEW GUINEA, 13 SEPTEMBER 1945". Grey card window mount with title and text below the image. Image features the commander of the Japanese Army in New Guinea handing over his sword during a formal surrender ceremony held at Cape Wom Airstrip. -
 Lilydale RSL Sub Branch
Lilydale RSL Sub BranchNewspaper - Framed newspaper copies of Liberators 21 SQN
Framed copies of newspaper photos of Liberators of 21 SQN -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - JENNY FOLEY COLLECTION: SURVIVOR
Darwin was bombed a total of 64 times during the war. The biggest and most deadly air-raids occurred on19/1/1943. Two hundred and forty two Japanese aircraft bombed the township, harbour and 2 airstrips. There were 235 deaths, 9 ships sunk in the harbour and 9 aircraft destroyed.Bendigo Advertiser ''The way we were'' from Monday, December 30, 2002. Survivor: more from the Darwin series of photos from 1942 during World War 2. This one shows the Darwin hospital. The hospital was one of the few buildings to survive both the Japanese bombing and the devastation of cyclone Tracy. The clip is in a folder.newspaper, bendigo advertiser, the way we were -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - JENNY FOLEY COLLECTION: WAR TORN
Darwin was bombed a total of 64 times during the war. The biggest and most deadly air-raids occurred on19/1/1943. Two hundred and forty two Japanese aircraft bombed the township, harbour and 2 airstrips. There were 235 deaths, 9 ships sunk in the harbour and 9 aircraft destroyed.Bendigo Advertiser ''The way we were'' from 2003. War torn: a house in Darwin after the Japanese bombing during World War 2, circa 1942. The clip is in a folder.newspaper, bendigo advertiser, the way we were -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - JENNY FOLEY COLLECTION: DAMAGED
Darwin was bombed a total of 64 times during the war. The biggest and most deadly air-raids occurred on19/1/1943. Two hundred and forty two Japanese aircraft bombed the township, harbour and 2 airstrips. There were 235 deaths, 9 ships sunk in the harbour and 9 aircraft destroyed.Bendigo Advertiser ''The way we were'' from 2002. Damaged: a Commercial Bank in Darwin shortly after the Japanese bombed the city in 1942. The clip is in a folder.newspaper, bendigo advertiser, the way we were -
 Waverley RSL Sub Branch
Waverley RSL Sub BranchRSL Photo Album, RSL Photo Album Section 3
During World War II the Japanese attacked New Britain soon after the outbreak of hostilities in the Pacific Ocean. During January 1942, Japanese heavily bombed Rabaul. On 23 January, Japanese marines landed by the thousands, starting the Battle of Rabaul. The Japanese used Rabaul as a heavy base until 1944; it served as the key point for the failed invasion of Port Moresby (May to November, 1942) Note: these photos are incorrectly labelled as Nth. Britain Photograph of "OIRE LUNG " airfield is in fact "WUNUNG, JACQUINOT BAY, NEW BRITAIN, 1945-08-28. A FULL PARADE OF 37/52 INFANTRY BATTALION AND 29/46 INFANTRY BATTALION, BOTH OF 4 BRIGADE, WAS HELD ON WUNUNG AIRSTRIP. THIS PARADE WAS TO PREPARE TROOPS FOR A PARADE TO BE HELD ON 1945-09-03. SHOWN, 37/52 INFANTRY BATTALION PRESENTING ARMS." Airstrip was maintained by 1 ACSPhoto Album 360 Pocket "Photo Safe" divided for cataloguing purposes into 4 sections. Section 1 Recent Colour Photos of RSL and commemoration services Section 2 Black and white photos of earlier commemoration services, Section 3 WWII photos mainly of New Britain 1945, Section 4 Early photos of Memorabilia display.new britain, wwii, japanese surrender, pow, rms aquitania, ss nieuw amsterdam, rms mauritania, rabaul, wunung airfield, jaquinot bay, 1 acs -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumPhotograph - PHOTOGRAPHS FRAMED, C. WWII
William Leslie Tibbett No VX28381 enlisted on 19.6.40 in 2/21st Batt AIF age 20 years. As part of Gull Force they were posted on the Island of Ambon to defend the Harbour and Airstrip. In January 1942 some 20,000 Japanese troops invaded the Island. Off the Gull Force of 1131 men 779 were either KIA or died as POW’s. His death is listed as 1.10.43. Refer 503P also 930..1) 2/21st Batt A.I.F marching through Melbourne prior to leaveing for Darwin, black and white photo mounted on perspex, khaki on metal brass coloured stand. .2) Photo of Pte. W.L Tibbett, black and white photo mounted on perspex (fawn coloured) on metal backed frame. .3) Photo of Pte W.L Tibbett's war grave, black and white photo.1) Handwritten on back in black, 2/21 Btn Gull Force marching in Melb prior to leaving for Darwin , Pte. W.L. Tibbett VX28381 , K.I.A .2) On back handwritten in black pen - Pte W.L. Tibbett, VX28381, 2/21 Btn Gull force, K.I.A. .3) On back handwritten in black pen - Gull Force.photography - photographs,, frames, frame accessories, graves -
 Peterborough History Group
Peterborough History GroupPhotograph - Surf Carnival, Newfield Bay, Jocelyn Burt
Unusual choice of location by Port Campbell Surf club due to Port Campbell beach being too small. The Surf Carnival was held at Newfield Bay (possibly for two years running). Eyewitness accounts advise that one year the surf was so rough that the event was abandoned. This photograph appears to show calmer sea. In order to get the surf boats onto the beach a track was bulldozed over the sand dunes. Spectators cars were parked in the area which is now the airstrip, on the corner of the Port Campbell Peterborough Road and the Timboon Peterborough road.Town eventOriginal photograph of the surf carnival, taken from the west looking towards the east, with the Crown of thorns visible in the background. Surf boats are on the beach and umbrellas are visible. Occurred in the early 1970's.Written on the back is Jocelyn Burt, who is a photographer.newfield bay, surf lifesaving carnival, peterborough, jocelyn burt, crown of thorns rock formation -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - Kangaroo Flat Gold Mine Collection: Deadhorse Gully, Sydney Flat Creek March 1986
Colour photographs, seventeen images on nine page. Images labelled as follows : 1. North New Moon shaft - natural discharge point of Garden Gullly line 2. Actual exit to surface from beneath mullock at North New Moon shaft. 3. Looking into Deadhorse Gully from mullock heap at North New Moon site. 4. Deadhorse Gully downstream of WMC Weir. 5. Sydney Creek track crossing - impassable ford. 6. Sydney Creek looking downstream from ford. 7. Sydney Creek looking upstream from road near Recreation Reserve (12 inch pipe under road). 8. Sydney Creek looking downstream from same point. 9. Sydney Creek - Camp Road, looking upstream.. 10. Sydney Creek - Camp Road, looking downstream. 11. Sydney Creek - Camp Road Culverts. 12. Sydney Creek - Pyramid Road Bridge, looking upstream. 13. Sydney Creek - Pyramid Road Crossing looking downsteam. 14. Sydney Creek - rail crossing, looking upstream. 15. Sydney Creek - rail crossing, looking downstream. 16. Sydney Creek - Airstrip road, looking upstream. 17. Sydney Creek - Airstrip Road, looking downstream 12 inch pipe under road. Lined paper, in blue pen 'Deadhorse Gully-Sydney Flat Creek, March 1986, Photos of Deadhorse Gully/Sydney Flat Creek'kangaroo flat gold mine, deadhorse gully, sydney flat creek, unity mining, water discharge, north new moon, camp road, pyramid hill road, eaglehawk -
 Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub Branch
Dandenong/Cranbourne RSL Sub BranchMemorabilia, Aircraft propeller
The Stinson L - 5 Sentinel was a World War 11- era liaison aircraft used by the United States Army Air Forces, U.S Army Ground Forces, U>S Marine Corps and the British Royal Air Force. It was produced by the Stinson Division of the Vultee Aircraft Company (Consolidated - Vultee from mid- 1943). Capable of operating from short unimproved airstrips the L - 5 Sentinel delivered personnel, intelligence, and supplies to the front line. On return flights it carried wounded soldiers who were evacuated to rear area field hospitals for treatment. The L - 5 carried a pilot and observer. It had a length of 24.1 feet, wingspan of 34 feet, It had a maximum speed of 130 mph, a cruise speed of 100 mph with a range of 375 miles.The L - 5 was a significant asset to the allied war effort.Wooden propeller from Lycoming engine, with photograph of aircraft. Stinson L 5 Sentinal reconnaissance plane used in Korea and Vietnam. Propeller displayed from a similar plane. -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchPhotograph, SGT A R Wills
Image of burial site of Sgt Albert Robert WILLS born 16.11.1917 at Bendigo -VX 5275 He enlisted in 1939 embarked on HMT 'Ettrick" on 14/4/1940 after basic training at Puckapunyal. Disembarked in Egypt on 18/5/1940 and saw action at Bardia, Greece and Syria. Spent time in Lebanon and Ceylon before returning to Australia on 4/8/1942. On 13/10/42 disembarked at Milne Bay New Guinea and took part in the battle for Wau securing the airstrip and surrounding area after heavy fighting. Between 6-9 Feb 2/5 Bn C and D companies supported by A company spearheaded the attack engaged and defeated the enemy thus ending the battle of Wau Sgt WILLS was one of 28 men killed in action in the Crystal Creek area on 7/2/1943 and is buried at Lae War Cemetery. Black and white image of grave with white cross Cof E VX 5275 SGT A R WILLS 2/5 Aust. Inf. Bn. 7.2.43 Rear is stamped with Photograph supplied by Directorate of Graves Registration Victoria Barracks Melbourne - Buried at Laea.r. wills, vx 5275, 2/5th aust. inf. bn, new guinea -
 Wangaratta RSL Sub Branch
Wangaratta RSL Sub BranchLetter, 2/5 Australian Infantry Battalion Assoc, 2000
Letter lists the service history of Sgt A R WILLS VX 5275 2/5 Infantry Battalion. He enlisted in 1939 embarked on HMT 'Ettrick" on 14/4/1940 after basic training at Puckapunyal. Disembarked in Egypt on 18/5/1940 and saw action at Bardia, Greece and Syria. Spent time in Lebanon and Ceylon before returning to Australia on 4/8/1942. On 13/10/42 disembarked at Milne Bay New Guinea and took part in the battle for Wau securing the airstrip and surrounding area after heavy fighting. Between 6-9 Feb 2/5 Bn C and D companies supported by A company spearheaded the attack engaged and defeated the enemy thus ending the battle of Wau Sgt WILLS was one of 28 men killed in action in the Crystal Creek area on 7/2/1943 and is buried at Lae War Cemetery.Letter consisting of letterhead above black typing on white paperAt top 2/5 Australian Infantry Battalion Association 1939-1945 Dated 27 April 2000 At bottom "Sans regret"a r wills, 2/5th aust. inf. bn, lae, new guinea, battle for wau, kia, crystal creek -
 Returned Nurses RSL Sub-branch
Returned Nurses RSL Sub-branchMagazine - Magazine clipping, The nurse: sister at the front, [Aug 26th 1989]
The story is mostly a quote from Mollie Edwards, who was a captain in the 2nd/5th Australian General Hospital. She served in a 1200 bed field hospital tent, near the front in the Middle East, Greece, Crete, Syria, New Guinea, and Morotai. Mollie talks about her evacuation from the hospital in Greece. She was one of the forty nurses told to leave, leaving forty to be taken as POWs. Leaving her patients was one of the hardest things she had to do during the war. Mollie goes on to detail her most horrific war experience, in New Guinea, when a bomber laden with bombs and fuel crashed into the 33rd Battalion as it waited on the edge of the airstrip. Eighty men were incinerated with many more horribly burned. Despite her experiences, Mollie says she was privileged to serve, gaining lifelong friendships.An a4 page from a magazine of an inset story that features a medium black and white photo of women in the back of an an army truck above two columns of text.' 'The Age' WEEKEND / Aug 26[carrot]th 1989' [blue ink, along top of page]german, ww2, wwii, athens, hmas voyager -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, 1948
The Schweizer SGS 2-12 or TG-3A as officially certificated is a glider that was designed in 1941-1942 and produced in United States of America from 1942 for training of military glider pilots. It is understood that over 100 TG-As were supplied to the USA military and at the end of the war many were sold off as surplus. Fred Hoinville imported the Museum’s TG-3A into Australia in August 1950. It is understood that it had been built in 1948 and given construction number G15. On arrival in Australia it was assembled at Bankstown aerodrome and delivered by aero-tow behind a DH Tiger Moth to Camden where Hoinville’s club, the Hinkler Soaring Club, was based. Hoinville’s TG-3A performed well at the Hinkler club in 1950-1951. Several altitude records (including a solo flight to 8000 feet by Grace Roberts – a national women’s record) were set and many soaring flight made over Camden. However, it was badly damaged in a crash landing on 15 April 1951. The glider was repaired after the crash at Camden. It is likely that modifications were made to the cockpit canopy at this time. There were three configuration tried at various times: the original dual cockpit canopy as was standard for TG3As; an unusual dual bubble canopy set up; and a single canopy over the forward seating position (in effect converting the glider to a single seater). When the glider was flown by Hoinville at the 1958 Australian Gliding Championships at Benalla, Victoria in January 1959 (refer The Age Newspaper, January 10, 1959 p.21) it had a single canopy. Records show that the glider was entered on the Australian register as VH-GDI on 6 May 1957. And the Logbook commencing in 1959 shows that ownership passed to the Port Augusta Gliding Club in South Australia on 16 August 1959. Inspections were carried out at that club and airworthiness certificates renewed in 1965. The logbook record indicates that VH-GDI had 1191 flights with an aggregate time in the air of 197 hours at the Wilmington Road Airstrip used by the Port Augusta Club. The glider was transferred to the Cooma Gliding Club, New South Wales. Flying at Cooma began in November 1966 and continued until August 1969: the glider was in the air a further 108 hours from 1067 flights. The last recorded technical inspection of the glider was conducted on 28 September 1968. The glider then passed on to Bill Riley on 20 March 1980 who stored the glider until March 2004 when it was collected by the Australian Gliding Museum. It is not clear whether the current poor state of the airframe is due to accident damage or the conditions under which it has been stored over many years or a combination of factors. Although in poor condition, this exhibit is the sole example of a TG3A ex-US military aircraft in Australia. Further the connection with the story of well-known power and glider pilot Fred Hoinville adds to its historical significance. Tubular metal framed fuselage (without covering and fittings), wooden rudder (no covering) and in damaged condition, wooden fuselage component (formers for fuselage top), Parts of control mechanism, Wooden stringers, Wooden wings without fabric covering and in damaged condition, Ailerons, Tailplane /Elevator without fabric covering, Perspex bubble canopies.australian gliding, glider, sailplane, schweizer, tg 3a, hoinville, roberts, hinkler soaring club, port augusta gliding club, cooma gliding club, riley -
 Waverley RSL Sub Branch
Waverley RSL Sub BranchPhoto Album, Charles Harold Dix 119700 RAAF Photos of the War Years
Photos taken by Charles Dix 119700 RAAF 2 SQN. at Darwin Adelaide River Morotai and Balikpapan during WWII and 2 photos of later dateCharles Dix 119700 RAAF 2 Sqn. was a member of RSL Waverley Sub Branch for many years. He Joined the RAAF on 8th October 1942 and was discharged from the 83rd. Operational base unit on 30th. January 1946. During WWII and served at Darwin, Adelaide River Morotai Island and made a "beach Landing" under fire at Balikpapan to set up RAAF signals station at the newly captured airstrip Vic Morgan is thought to be MORGAN, Victor Allen - (Leading Aircraftman); Service Number - 88726; File type - Casualty - Repatriation; Aircraft - Mitchell A47-37; Place - Arafura Sea; Date - 14 August 1945Photo Album of mainly black and white photos from WWII Darwin Morotai Island and Balikpapancharles harold dix, darwin wwii, adelaide river wwii, frognal air base, raaf, balikpapan, dix, photos wwii, darwin hospital, jeep, morotai island, 2 squadron r.a.a.f., 2nd squadron raaf, wwii -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph of Snow Covered Catchment Area Vic, Snow Covered Catchment Area Victorian Alps - 1950s, Circa 1950
This photograph details (early to mid1950s), the Victorian Alpine region when this remote area was part of a "lay back" rural landscape,occasionally visited by recreational adventurers and some wayward tourists. The mountain ranges had provided an adequate barrier against the way-would traveller, but with the opening up of this region by the provision of improved roadways and accommodation facilities, courtesy of the Kiewa Valley Hydro Electricity Scheme, changes such as tourism and its impact upon the "natural" state started to show its side effects (clearing of the land). The expansion of the European immigration numbers (1950s) coming into Australia was increasing after World War II which not only provided increased construction workers to the region but also immigrants who appreciated alpine regions. Some of these immigrants contributed to the expansion of the region and provided for a greater degree of diverse professions and rural related work force.This photograph depicts the borderline in time between an exclusively rural based population and respective activities(early 1900s)to the present (2000 on wards) integrated village, tourist and retiree/holiday area. The time when land was exclusively used in agriculture and Alpine grazing lands is over. The Kiewa Valley is loosing its hiding place and is becoming more and more a source of untapped residential land and winter time recreational adventure lands. The changes brought about by modern technologies involving recreational activities such as hang gliding, gliding (local airstrip), mountain bikes, car rallies and their associated clubs is providing for an increased short term population boost. These together with the attractions for retirees is changing not only the physical nature of the Kiewa valley but also its "soul".This item is a black and white photograph of a section of snow covered catchment area in the Victorian Alps in the mid 1900. It is on 200 gms paper but not on photographic paper and has a white boarder (3 mm).kiewa valley tourism, victorian alps, alternate energy supplies, alpine population growth -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionReports, Big Cats Sightings and Stock Kills 2000-2011, 2000-2011
The folder or correspondence is the result of a Freedom of Informaition request made to the Department of Primary Industries in 2011. The folder was collected for research being conducted by David Waldron.Folder of reports of Big Cat by rangers. australian mythical animals collection, david waldron, department of primary industries, rangers, peter walsh, warragul creek, binginwarri, coongulla, straford, licola, blanket hill, darramin, blanket hill, woodside beach, heyfield, puma, panther, cowwarr, glenmaggie, bolands bluff, darrimen, bolands bluff, binginnwarri, dawson, the springs, mt taylor, black range, driffield west, snowy plains airstrip, glenmaggie north, jack smith lake, munro, briagaling, dutson downs, connors plain, giffard west, darriment, joyces road junction, giffard west, wallaby creek, south gippsland highway, avon river, orbost, four mile creek -
 Australian Commando Association - Victoria
Australian Commando Association - VictoriaBook, The Private War of the Spotters: A history of the New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company, February 1942-April 1945
The history of the New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company. This reprinted version contains a map of the dispositions of Spotting Stations August 1943, additional MID awards listed and some additions to the nominal roll. The New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company was formed in Port Moresby in late January 1942 and was granted “Separate Independent Establishment” status in October 1943. The company’s “founding father” was Major Don Small, who had witnessed Japanese air raids on Rabaul and realised that having lacked an effective early-warning system around New Britain meant that the defenders were taken by surprise. At the time, gaps had also appeared in the coast-watching communications network because the territory administration ordered the withdrawal of civilian wireless operators when Japan entered the war. The first influx of men into the company consisted largely of volunteers from the 39th Infantry Battalion, which was stationed at Port Moresby. Initial training was rudimentary, hasty, and was sometimes even carried out on en route to a new station. The first party of company personnel, or “spotters”, left Port Moresby as early as 1 February 1942, bound for the strategically important Samarai area, at the tip of Papua. In the first month of the company’s existence 16 spotter stations were established on the coast of Papua and in the mountains around Port Moresby. At the end of 1942 there were 61 operational stations being run by 180 men. The company’s high-water mark was in late 1944, by which time over 150 stations had been set up in Papua and New Guinea behind enemy lines. On 3 February 1942 the company issued its first air warning in Papua, when spotters at Tufi saw Japanese aircraft about to attack Port Moresby for the first time. The following month the company was responsible for the first Japanese killed in action in Papua by Australian ground forces, when spotters from Gona engaged the crew of a downed Japanese bomber. And in July 1942 the station at Buna signalled Port Moresby with news of the Japanese landings in Papua, marking the beginning of the Kokoda campaign. The dangers involved in the company’s work had also been made clear by this time. In July 1942 a party of spotters attempting to set up a station at Misima Island, off Milne Bay, was intercepted by a Japanese destroyer, resulting in the company’s first operational losses. Anticipating the direction of the campaign as a whole, the company’s focus moved north and north-west over the three years of its existence. In May 1942 a network was set up in the Wau area in association with the activities of Kanga Force. As part of the Wau network, spotter Ross Kirkwood audaciously constructed an observation post overlooking the Japanese airstrip at Salamaua. Kirkwood’s position was photographed by Damian Parer on the understanding that the pictures would not be published. They nevertheless appeared in a Sydney newspaper. The day after the publication of the photographs the observation post was attacked by the Japanese and Kirkwood was lucky to escape. In June 1944 the company’s headquarters were moved to Nadzab. By that time, spotter stations existed behind Japanese lines, as far north as Hollandia, and the company began to train Americans to perform similar work in the Philippines. In early 1945 the company moved to Balcombe, Victoria, where its members were posted to other units of the Australian Corps of Signals.gray plasticnon-fictionThe history of the New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company. This reprinted version contains a map of the dispositions of Spotting Stations August 1943, additional MID awards listed and some additions to the nominal roll. The New Guinea Air Warning Wireless Company was formed in Port Moresby in late January 1942 and was granted “Separate Independent Establishment” status in October 1943. The company’s “founding father” was Major Don Small, who had witnessed Japanese air raids on Rabaul and realised that having lacked an effective early-warning system around New Britain meant that the defenders were taken by surprise. At the time, gaps had also appeared in the coast-watching communications network because the territory administration ordered the withdrawal of civilian wireless operators when Japan entered the war. The first influx of men into the company consisted largely of volunteers from the 39th Infantry Battalion, which was stationed at Port Moresby. Initial training was rudimentary, hasty, and was sometimes even carried out on en route to a new station. The first party of company personnel, or “spotters”, left Port Moresby as early as 1 February 1942, bound for the strategically important Samarai area, at the tip of Papua. In the first month of the company’s existence 16 spotter stations were established on the coast of Papua and in the mountains around Port Moresby. At the end of 1942 there were 61 operational stations being run by 180 men. The company’s high-water mark was in late 1944, by which time over 150 stations had been set up in Papua and New Guinea behind enemy lines. On 3 February 1942 the company issued its first air warning in Papua, when spotters at Tufi saw Japanese aircraft about to attack Port Moresby for the first time. The following month the company was responsible for the first Japanese killed in action in Papua by Australian ground forces, when spotters from Gona engaged the crew of a downed Japanese bomber. And in July 1942 the station at Buna signalled Port Moresby with news of the Japanese landings in Papua, marking the beginning of the Kokoda campaign. The dangers involved in the company’s work had also been made clear by this time. In July 1942 a party of spotters attempting to set up a station at Misima Island, off Milne Bay, was intercepted by a Japanese destroyer, resulting in the company’s first operational losses. Anticipating the direction of the campaign as a whole, the company’s focus moved north and north-west over the three years of its existence. In May 1942 a network was set up in the Wau area in association with the activities of Kanga Force. As part of the Wau network, spotter Ross Kirkwood audaciously constructed an observation post overlooking the Japanese airstrip at Salamaua. Kirkwood’s position was photographed by Damian Parer on the understanding that the pictures would not be published. They nevertheless appeared in a Sydney newspaper. The day after the publication of the photographs the observation post was attacked by the Japanese and Kirkwood was lucky to escape. In June 1944 the company’s headquarters were moved to Nadzab. By that time, spotter stations existed behind Japanese lines, as far north as Hollandia, and the company began to train Americans to perform similar work in the Philippines. In early 1945 the company moved to Balcombe, Victoria, where its members were posted to other units of the Australian Corps of Signals.world war ii, special operations, new guinea, new guinea air warning wireless company
