Showing 1129 items
matching number 10
-
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy Railway10 NU - Louvred Truck, 30/12/1911
... Victorian Heritage Register (VHR) Number H2187 NW 10 is a 1972... Register (VHR) Number H2187 NW 10 is a 1972 reclassification of NU ...10 NU Louvre Van - Louvred Truck (11) Untrafficable NUU LOUVRED TRUCK. Seven louvre vans for carrying general goods were built during 1899-1901, with another one in 1906 and a further six in 1911, a total of 14 louvre vans numbered 1-14. The term Louvred Truck describes the sides which consist of fixed louvres for ventilation. The aim was to keep the goods inside cool. VR Service History : *NUU 10.VA - 30/12/1911 NWS Built new - / /1926 - To NU 10.VA - NU 10.VA - / 5/1926 - Modified AC Malco /12/1972 BEL To NW 10.VA Sec72/3400, RS72/9371 NW 10.VA - 26/ 8/1976 CLS Photograph #662.2-.4: and end detail 1/10/1977 - Off Register To ETRB Sec76/3630 RS77/4223 Build Date: 30/12/1911 NWS Built new Victorian Heritage Register (VHR) Number H2187 NW 10 is a 1972 reclassification of NU 10. It is presumed the van was used to store tools and equipment. In 1977, the van was removed from railway records and control handed to the Puffing Billy group.Historic - Victorian Railways Narrow Gauge - Rolling Stock - Louvered Van Victorian Heritage Register (VHR) Number H2187 Puffing Billy Locomotives and Rolling Stock CollectionWooden Louvered Van - Made of Timber on a Wrought iron frame - current condition Untrafficable10 NU puffing billy, louvered van, 10nu, victorian railways, 2'6" gauge, narrow gauge rolling stock -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumBook, State Electricity Commission of Victoria (SECV), "Electric Tramways of the State Electricity Commission of Victoria Amendment to By-Law", 1963
... " Pages are numbered pages 1 to 10, with front cover title... 1963" Pages are numbered pages 1 to 10, with front cover title ...Twelve page booklet, plus medium weight card light orange colour covers centre stapled. Book cover has title "Electric Tramways of the State Electricity Commission of Victoria Amendment to By-Law 1". Along the bottom edge is the date, "June 1963" Pages are numbered pages 1 to 10, with front cover title repeated on cover sheet inside. Document amends the fare schedules for Ballarat and Bendigo. Dated by the SEC 13/6/1963 to come into effect 1/8/1963.. Details names of SEC Commissioners on rear page. Four copies held. No printer details. See Fares in Ballarat – from Alan Bradley 11/4/2005 – appendix for Book Copy 3 - has "Ballarat Tramway Preservation Society No. 206" written in black ink on top of cover over writing the letters "1963" in red ink.. Copy 4 - has "Ballarat Tramway Preservation Society No. 206" written in black ink on top of cover . trams, tramways, secv rules, by laws, tickets, fares, ballarat, bendigo -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph - Folder of Photographs – Photocopied set of 10 black and white photographs (pages 29 - 38) from the display folder put together by KVHS to document life on the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric Scheme
... number 29 2-28/10/54 – Langfords Gap Basalt Hill – Tunnel... Beauty Pondage inlet – Regulating weir Page number 29 2-28/10/54 ...Although the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme was first proposed in 1911, construction did not commence until 1938. As part of the push to cut electricity costs and diversify supply, the Victorian Government (circa 1930) initiated the conversion from primarily brown coal supply to hydro – electricity. Field investigations during the 1940’s resulted in a new proposal for a scheme that had more than double the capacity of the 1938 scheme. The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme became the largest scheme of its kind in the State Of Victoria and the second largest scheme in Australia. The number of personnel involved in the planning and construction of the scheme increased dramatically. During the late 1940’s, most activity centred around the construction of the West Kiewa Power Station, Rocky Valley Reservoir, McKay Creek Power Station and the Bogong Creek Aqueduct.A common thread across all the larger hydro scheme constructions was the need for workers, both qualified and unqualified who came from around the world seeking a new life for themselves and their families. New accommodation and facilities were required for the army of workers engaged in construction in often remote and wild areas. The SEC had a high demand for timber, and set up the first of a number of sawmills at Bogong Creek in 1939 and set up the first hardwood logging in the headwaters of the Kiewa River. These new ‘towns’ such as Mt Beauty and Bogong, survived, serving the needs of operational personnel and their families, and expanding with growth of new industries. Mount Beauty, and to a lesser extent Bogong, are among these places. Large A3 size spiral bound display folder containing 21 pages of photocopied black and white photographs of various aspects of the early days of the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric scheme including equipment, various work sites and photographs of workers and their families. 1-Mt Beauty Pondage inlet-Regulating weir 2-Langfords Gap Basalt Hill-Tunnel in quarry face.3-Rocky Valley Camp-from Engineering Office 4-Basalt Hill tunnel portal 5-No 1 Pressure Shaft Works Bench 6-No 1 Power Station 7-Overturned haulage wagons on the side of an embankment 8- Group of workers dressed in wet weather gear inside a tunnel 9-Workmen and vehicle in tunnel 10-Howman’s Gap campsite at 4,150 feet 1-1954 – Mt Beauty Pondage inlet – Regulating weir Page number 29 2-28/10/54 – Langfords Gap Basalt Hill – Tunnel in quarry face K7860 Page number 30 3-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 17.8.55 Time: No K8132 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works ROCKY VALLEY CAMP – FROM ENGINEERING OFFICE Page number 31 4-28/10/54 – Basalt Hill tunnel portal K7859 Page number 32 5-No.1 Pressure Shaft Works Bench 5.7.56 Page number 33 6- No. 1 Power Station 26.4.59 Page number 34 7- No markings Page number 35 8-No markings (Wooden board on ground printed with - POLAR A.N.GELATINE DYNAMITE “75” DE 28.8.40) Page number 36 9-No markings Page number 37 10-Howman’s Gap campsite at 4,150 feet Page number 38 secv; kiewa hydro electric scheme; mt beauty; bogong; construction area -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph - Folder of Photographs – Photocopied set of black and white photographs (pages 39 - 48) from the display folder put together by KVHS to document life on the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric Scheme
... Dam Core Wall Page number 47 10-No markings Page number 48 ... 46 9-Rocky Valley Dam Core Wall Page number 47 10-No markings ...Although the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme was first proposed in 1911, construction did not commence until 1938. As part of the push to cut electricity costs and diversify supply, the Victorian Government (circa 1930) initiated the conversion from primarily brown coal supply to hydro – electricity. Field investigations during the 1940’s resulted in a new proposal for a scheme that had more than double the capacity of the 1938 scheme. The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme became the largest scheme of its kind in the State Of Victoria and the second largest scheme in Australia. The number of personnel involved in the planning and construction of the scheme increased dramatically. During the late 1940’s, most activity centered around the construction of the West Kiewa Power Station, Rocky Valley Reservoir, McKay Creek Power Station and the Bogong Creek Aqueduct.A common thread across all the larger hydro scheme constructions was the need for workers, both qualified and unqualified who came from around the world seeking a new life for themselves and their families. New accommodation and facilities were required for the army of workers engaged in construction in often remote and wild areas. The SEC had a high demand for timber, and set up the first of a number of sawmills at Bogong Creek in 1939 and set up the first hardwood logging in the headwaters of the Kiewa River. These new ‘towns’ such as Mt Beauty and Bogong, survived, serving the needs of operational personnel and their families, and expanding with growth of new industries. Mount Beauty, and to a lesser extent Bogong, are among these places. Large A3 size spiral bound display folder containing photocopied black and white photographs of various aspects of the early days of the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric scheme including equipment, various work sites and photographs of workers and their families. 1-Breakdown in Circuit Breaker (Isolating Contacts) 2-Big Hill Bench- Site of No 5 Devlopment 3-No 1 Power Station 4-No 1 Pipeline, Anchor No 8 5-Push Dozing-RD8 Tractor 6- Tractor and driver at work 7- Workmen in unnamed tunnel 8- Front page of Journal of SECV Vol 15. Photograph of No 1 pipeline viewed from McKay Portal 9-Rocky Valley Dam Core Wall 10-Workmen working inside tunnel loading rocks into a rail truck. 1-Breakdown in (generator) Circuit Breaker (Isolating Contacts) Handwritten underneath (This is not a picture of any part of a generator. It is a circuit breaker Signed Ron White Ron was the Principal Hydro Engineer of the SEC Kiewa Scheme Page number 39 2-Big Hill Bench – Site of No. 5 Development (abandoned) Page number 40 3-No 1 Power Station Page number 41 4-No. 1 Pipeline, Anchor No. 8 Page number 42 5-Push Dozing – RD8 Tractor, 12 cubic yard Carryall and FD Cletrac Tractor Page number 43 6-No marking Page number 44 7-No marking Page number 45 8-Journal of State Electricity Commission of Victoria SEC Vol 15 No… April-May, 19… No 1 Pipeline-A view from McKay Portal G Hempenstall and D Sutton stiffening pipe section for transport during construction (….indicates missing text) Page Number 46 9-Rocky Valley Dam Core Wall Page number 47 10-No markings Page number 48 secv; kiewa hydro electric scheme; construction area; power stations; reservoirs; aqueduct; mt beauty; bogong -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy Railway1 NNN - Bogie Ballast Hopper Truck, 1954
... 6 tons Capacity 10 tons Number Built Not known... Capacity 10 tons Number Built Not known In use 1 To be restored 3 ...NNN - BALLAST HOPPER, This vehicle was built by the Tasmanian Govt. Railways in 1954 and classified QG. A number were obtained by the Puffing Billy Railway for use on ballast trains but to date, only two have been converted. When the first of these was converted for 2’6” gauge operation it kept the Tasmanian QG but with the addition of an N prefix, and also kept its Tasmanian number of 3. However, to follow traditional V.R. practice, in June 2003 it was reclassified to NNN and numbered 1 as the nearest counterpart on the V.R. was the broad-gauge NN. A second one, numbered 2, has since been converted. 1 NNN - Bogie Ballast Hopper Truck Service History Built 1954 Tasmanian Railways - QR 3 - Bogie Ballast Hopper Truck converted from a 3ft 6 inch (1,068 mm) gauge ex Tasmanian Railways ballast wagon by the Puffing Billy railway. Coupled Length 20 feet 0 inches (6100 mm) Weight 6 tons Capacity 10 tons Number Built Not known In use 1 To be restored 3 Puffing Billy Service History or Notes Historic - Tasmanian Government Railways - 3 QG Bogie Ballast Hopper Truck Puffing Billy Railway - Track maintenance Vehicle - NNN - Bogie Ballast Hopper Truck1 NNN - Bogie Ballast Hopper Truck made of Steel and metal1NNNpuffing billy, pbr, rolling stock , 1 nnn bogie ballast hooper truck, tasmanian government railways, 3 qg bogie ballast hopper truck -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy Railway2 NNN - Bogie Ballast Hopper Truck, 1954
... Capacity 10 tons Number Built Not known In use 1 To be restored 3... Capacity 10 tons Number Built Not known In use 1 To be restored 3 ...NNN - BALLAST HOPPER, This vehicle was built by the Tasmanian Govt. Railways in 1954 and classified QG. A number were obtained by the Puffing Billy Railway for use on ballast trains but to date, only two have been converted. When the first of these was converted for 2’6” gauge operation it kept the Tasmanian QG but with the addition of an N prefix, and also kept its Tasmanian number of 18. However, to follow traditional V.R. practice, it was reclassified to NNN and numbered 2 as the nearest counterpart on the V.R. was the broad-gauge NN. A second one, numbered 1, was also converted. and was reclassified to NNN in June 2003 2 NNN - Bogie Ballast Hopper Truck Service History Built 1954 Tasmanian Railways - QR 18 - Bogie Ballast Hopper Truck converted from a 3ft 6 inch (1,068 mm) gauge ex Tasmanian Railways ballast wagon by the Puffing Billy railway. Coupled Length 20 feet 0 inches (6100 mm) Weight 6 tons Capacity 10 tons Number Built Not known In use 1 To be restored 3 Puffing Billy Service History or Notes Historic - Tasmanian Government Railways - 18 QG Bogie Ballast Hopper Truck Puffing Billy Railway - Track maintenance Vehicle - NNN - Bogie Ballast Hopper Truck2 NNN - Bogie Ballast Hopper Truck made of Steel and metal2NNNpuffing billy railway, pbr, rolling stock , 2 nnn bogie ballast hopper track, tasmanian government railways, 18 qg bogie ballast hopper truck -
 Australian Gliding Museum
Australian Gliding MuseumMachine - Glider – Sailplane, 1972
... . In Australia the number is possibly 10 or 11. The Hall Cherokee VH-GVO.... In Australia the number is possibly 10 or 11. The Hall Cherokee VH-GVO ...The Hall Cherokee II glider is an American design for amateur construction from plans. The designer was Stan Hall (1915-2009), a professional engineer, who gained extensive experience in the United States aviation industry during World War 2 including the programs for military gliders. He continued to work as an engineer for aircraft manufacturers and as a consultant to the industry after the war. He was active in gliding and, in particular, the home built sailplane movement. The Cherokee II was one of about 10 glider designs that he produced: it came out in 1956. It is understood that over 100 Cherokee gliders have been built. In Australia the number is possibly 10 or 11. The Hall Cherokee VH-GVO was built by R.D Meares of Caringbah, New South Wales. The glider was registered as VH-GVO on 11 October 1973 and given serial number “GFA-HB-82” by the Gliding Federation of Australia. The Logbook for VH-GVO appears to be a complete record of the flying history; in aggregate 210 hours 40 minutes in the air from 331 flights. The first test hop occurred on 29 July 1972 at Camden, New South Wales. VH-GVO was last flown on 22 July 1986. Many of the flights recorded are of one or two hours duration. The glider was last inspected and certified as airworthy and in a reasonable condition at the Hunter Valley Gliding Club in July 1986. Since that time, until transferred to the Australian Gliding Museum, the glider was in storage. Structural restoration work has been completed on the fuselage and one wing. However, inspection of the other wing revealed extensive damage to the ribs and spars and consequently a decision was taken to make it a static exhibit. The exhibit is an example of home built construction of a type that has proved popular amongst amateur glider builders.The Hall Cherokee (formerly registered as VH-GVO) is a single seat wooden home built glider. The glider is constructed from wood, plywood, fabric and metal fittings, all commercial grade except for main wing fittings, pulleys, cables and bolts. The fuselage is simple with four main longerons and bulkheads with diagonal bracing. The wing has two identical solid spars which form a geodetic structure, hence the leading edge is non-structural. Registration VH-GVO – serial number GFA-HB-82 australian gliding, glider, sailplane, hall, cherokee, meares, hunter valley gliding club -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumManual - MILITARY REGULATIONS AMENDMENTS, 1939 - 1951
... . Dated Aug 47, Serial No. 52, 10 numbered pages plus blanks. 7... plus blanks. 6. Dated Aug 47, Serial No. 52, 10 numbered pages ...Australian Military Regulations and Orders 1927 were the basis of the Rules for behaviour for the Military Forces. Amendments then issued on a regular basis had to be gazetted to be official. Items in the collection re Lt Col J Swatton, refer Cat No 6719.2P for his service details.Small booklets covering latest amendments to Australian Military Regulations 1927. On faded yellow paper, stapled and no hard cover.1. Dated Mar '39. Serial No. 13, 8 number pages but additional blank loose leaf stapled together in top left corner. 2. Dated Oct 44, Serial No. 47, 18 numbered pages plus blanks. 3. Dated Feb 44, Serial No. 45, 4 numbered pages plus blanks. 4. Dated Dec 44, Serial No. 48, 6 numbered pages plus blanks. 5. Dated Aug 46, Serial No. 51, 16 numbered pages plus blanks. 6. Dated Aug 47, Serial No. 52, 10 numbered pages plus blanks. 7. Dated Apr 51, Serial No. 55. 15 pages. Blanket. A tick and "OK" written on front cover.passchendaele barracks trust, military regulations -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumBook, State Electricity Commission of Victoria (SECV), "Electric Tramways Amendment to By-Law June 1963", Jun. 1963
... Booklet with orange card cover and 12 pages, numbered 1... with orange card cover and 12 pages, numbered 1 to 10, side stapled ...Demonstrates aspects of the SEC governance system in issuing By-laws for the travelling public, as part of their Act. Yields information about fares charged for tram services in Ballarat and Bendigo. Issued to crews.Booklet with orange card cover and 12 pages, numbered 1 to 10, side stapled, off set printed giving details of fares, revised in June 1963 for both Ballarat and Bendigo, to come into force on 1/8/1963. Has details of sections etc. Was shown as being approved by the Governor in Council on 25/6/1963. Adjust the City Section fares only. See Alan Bradley notes in references re this. Full pdf copy added 28/5/2019. Alan Bradley advised 25/4/2005. In the "Courier" of 26/6/1963, the adjustments to fares from 1/8/1963 were announced. They were only for adjustments to city section fares. Fares outside the city area remained unchanged. The SEC promoted these as being cheaper city section fares. Tom Evans gave me a copy of a poster showing a Scotsman boarding a tram. The caption was: "Now! It's cheaper to travel by tram! Beats walking every time!" New economy city fares. From Dawson St to the Railway Station return, & from Dawson St to the east end of Bridge St or return, 4d. From the intersection of Lydiard & Sturt Sts - To Dawson St, east end Bridge St, to Railway Station 3d. trams, tramways, secv rules, by-laws, tickets, fares -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageBell, Before 1837
... . (Diving identification number S.M24/10-73, Accession number 24... Divers on 1 October 1973. (Diving identification number S.M24/10 ...This remnant of a ships bell was recovered from the wreck site of the CHILDREN by Flagstaff Hill Divers on 1 October 1973. (Diving identification number S.M24/10-73, Accession number 24). The artefact had lain in the ocean off Childers Cove since the vessel’s disastrous sinking there on 15 January 1839. Other similarly high value metallic objects raised from the site, and now in the Flagstaff Hill collection, are the ship’s signal cannon (1963), and the ship’s anchor (1974). A ship’s bell was normally struck by the lookout at the foreward part of a vessel, following orders (“Strike the bell”) from the officer of the watch at the helm, or as a warning signal of danger ahead. Its main function was to keep the crew aware of time. Each 24 hour period was divided into 4 hour work-shifts, or watches, and each of these was divided into 8 half hours, or glasses (each half hour being determined by the time it took between each turn of the ship’s hourglass). The six watches were the first watch from 8pm to midnight, the second or middle watch from midnight to 4am, the third or morning watch from 4 to 8am, the fourth of forenoon watch from 8am to midday, the fifth or noon watch from midday to 4pm, and the sixth or dog watch from 4 to 8pm. Within each watch the first half hour would end with one bell, the second with two bells, the third with three bells, and so on until their work-shift ended with the ringing of eight bells. The CHILDREN left Launceston on 11 January 1839 and immediately struck heavy weather. By the evening of 15 January Captain Browne had been continuously on duty for 4 days and needed sleep, his First Mate (T. Gay) was incapacitated with seasickness, and the task of command was given to the Second Mate (W. Wentworth). At two bells into the first watch, or 9 o’clock that night, the captain went below. Two hours later, at six bells into the first watch, or 11 o’clock that night, the lookout cried “Breakers close ahead”. Within a minute the ship struck the rocks at the entrance of Childers Cove. Within twenty minutes the huge seas had taken her stern, three masts and much of her weatherside, leaving survivors clinging to the forecastle. Within two hours the wreck had completely disappeared. If anyone could have rung the bell by then, it would have been to strike two bells into the middle-watch, or one o’clock on the morning of 16 January. An 1859 Victorian Register of Wrecks from 1835 to 1858 remarks the CHILDREN “Ran ashore through an error in the reckoning and a bad lookout [and] Became a total wreck”. 22 passengers and crew survived the tragedy, but 16 lives were lost, including the captain and second mate, and 8 children. The shipwreck of the CHILDREN is of State significance ― Victorian Heritage Register S116A part of a brass ship’s bell, recovered from the wreck of the CHILDREN. The upper part, or dome of the bell, has corroded away, leaving the lower portion, or mouth of the bell, largely intact. However this lower surviving portion has been severed vertically with a clear (saw?) cut, leaving a regular 1cm gap down one side of the bell. It is an evocative relic, attractively aged on the seafloor, bearing layers of aqua-marine verdigris and white limestone accretion on a dull bronze surface. There is no visible ship’s name on the bell. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, the children, bell, ships bell, childers cove, henty brothers, james henty & co, sea-watches, nautical time, james henty & co, bell from the children -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph - Folder of Photographs (KVHS 1150 A - F) – Photocopied set of black and white photographs from the display folder (pages 1 - 8) put together by KVHS to document life on the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric Scheme
... Upstream Page number 7 10- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION... Page number 4 7- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date ...Although the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme was first proposed in 1911, construction did not commence until 1938. As part of the push to cut electricity costs and diversify supply, the Victorian Government (circa 1930) initiated the conversion from primarily brown coal supply to hydro – electricity. Field investigations during the 1940’s resulted in a new proposal for a scheme that had more than double the capacity of the 1938 scheme. The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme became the largest scheme of its kind in the State Of Victoria and the second largest scheme in Australia. The number of personnel involved in the planning and construction of the scheme increased dramatically. During the late 1940’s, most activity centred around the construction of the West Kiewa Power Station, Rocky Valley Reservoir, McKay Creek Power Station and the Bogong Creek Aqueduct.A common thread across all the larger hydro scheme constructions was the need for workers, both qualified and unqualified who came from around the world seeking a new life for themselves and their families. New accommodation and facilities were required for the army of workers engaged in construction in often remote and wild areas. The SEC had a high demand for timber, and set up the first of a number of sawmills at Bogong Creek in 1939 and set up the first hardwood logging in the headwaters of the Kiewa River. These new ‘towns’ such as Mt Beauty and Bogong, survived, serving the needs of operational personnel and their families, and expanding with growth of new industries. Mount Beauty, and to a lesser extent Bogong, are among these places. Large A3 size spiral bound display folder containing 21 of 58 pages of photocopied black and white photographs of various aspects of the early days of the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric scheme including equipment, various work sites and photographs of workers and their families. 1-Front page; 2-Security gate at Mt Beauty Camp; 3-Channel 1 on East Kiewa River; 4-Junction Dam – Diversion Tunnel Inlet; 5-Sawmill; 6- Homan’s Gap Sawmill; 7 Junction Dam: 8-Homan Dam Site-Diamond Drilling on River Buttress; 9- Homan Dam Site View Upstream 10-Homan Dam Investigation Camp 1-Windsor & Newton Visual Diary 60 sheet (120 pages) 11’ x 14’ 280 x 356mm 110 GSM Acid Free Drawing Paper 2-1940-Security Gate on Mt Beauty side of Kiewa River bridge. Part of old Mt Beauty camp and mess in background 3- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date; 11.3.40 Time: 10.30am No K35 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works. Diverting East Kiewa River into Channel Page number 1 4-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 5.4.40 Time: Noon No K58 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works. Junction Dam – Diversion Tunnel Inlet – Normal Flow Page number 2 5- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 19.8.42 Time: 2.30pm No K883 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works. Sawmill – General View Page number 3 6- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 12.1.42 Time: 2.00pm No K540 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works. Homan’s Gap Sawmill – General View Page number 4 7- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 12.1.42 Time: 2.00pm No K540 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works. Junction Dam – General View looking upstream Page number 5 8- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 16.11.45 Time: 10.32amm No K52153 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Homan Dam Site – Diamond Drilling on River Buttress Page number 6 9-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 15.1.45 Time: 4.10pm No K1781 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Homan Dam Site – View Upstream Page number 7 10- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 15.1.45 Time: 4.10pm No K1781 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Homan Dam Investigation Camp 1944 – 1945 Page number 8 secv; kiewa hydro electric scheme; mt beauty; bogong; construction work; -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph - Folder of Photographs – Photocopied set of 10 black and white photographs (pages 19 - 28) from the display folder put together by KVHS to document life on the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric Scheme
... refer to No 4 Headrace Tunnel? Page number 27 10-STATE... Tunnel? Page number 27 10-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION ...Although the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme was first proposed in 1911, construction did not commence until 1938. As part of the push to cut electricity costs and diversify supply, the Victorian Government (circa 1930) initiated the conversion from primarily brown coal supply to hydro – electricity. Field investigations during the 1940’s resulted in a new proposal for a scheme that had more than double the capacity of the 1938 scheme. The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme became the largest scheme of its kind in the State Of Victoria and the second largest scheme in Australia. The number of personnel involved in the planning and construction of the scheme increased dramatically. During the late 1940’s, most activity centred around the construction of the West Kiewa Power Station, Rocky Valley Reservoir, McKay Creek Power Station and the Bogong Creek Aqueduct.A common thread across all the larger hydro scheme constructions was the need for workers, both qualified and unqualified who came from around the world seeking a new life for themselves and their families. New accommodation and facilities were required for the army of workers engaged in construction in often remote and wild areas. The SEC had a high demand for timber, and set up the first of a number of sawmills at Bogong Creek in 1939 and set up the first hardwood logging in the headwaters of the Kiewa River. These new ‘towns’ such as Mt Beauty and Bogong, survived, serving the needs of operational personnel and their families, and expanding with growth of new industries. Mount Beauty, and to a lesser extent Bogong, are among these places. Large A3 size spiral bound display folder containing 21 pages of photocopied black and white photographs of various aspects of the early days of the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric scheme including equipment, various work sites and photographs of workers and their families. 1-Allis Chalmers Tractor School 2- Gardens outside Administrative Office – Mt Beauty 3- Mt Beauty house – 1950 4-Bridge over Pretty Valley River, Bogong 5-Rocky Valley Spillway Tunnel break through 6-Ni 1 Headrace Tunnel drilling face 7-No 4 Power Station Drilling 8-Clover Dam Flood Waters 9-No1 Head Race Tunnel Portal Building 10-Clover Dam 1-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 5.9.49 Time: 10amm No K5174 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Allis Chalmers Tractor School Page number 19 2-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 22.2.50 Time: 3.30pm No K5601 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Gardens outside Administrative Office – Mt Beauty Page number 20 3-Mt Beauty house – 1950 Page number 21 4-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 23.10.50 Time: 11.15am No K6331 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Bogong-Bridge over Pretty Valley River Page number 22 5-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 23.6.50 Time: 2.30pm No K5844 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works ROCKY VALLEY SPILLWAY TUNNEL BREAK THROUGH Page number 23 6-20/3/52 – No. 1 Headrace Tunnel Drilling face (E.E.E. contract) Page number 24 7-6/6/52 – No 4 Power Station – Drilling Page number 25 8-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 6/6/52 Time: No K7113 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Clover Dam Flood Waters Page number 26 9-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: Oct 1952 Time: No K7239 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works No. 1 HEAD RACE TUNNEL PORTAL BUILDING. Handwritten underneath – This information from Ron White-the later Principal Hydro Engineer of the SEC. Oct 1952 Location incorrect? All work on No 1 had ceased after financial crash of 1951. This photo would refer to No 4 Headrace Tunnel? Page number 27 10-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: Jan 1953 Time: No K7307 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works CLOVER DAM Page number 28 secv; kiewa hydro electric scheme; bogong; mt beauty; construction area -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph - Folder of Photographs – Photocopied set of black and white photographs (pages 49 -58) from the display folder put together by KVHS to document life on the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric Scheme
... boss, John McCluskey (c) At No. 5 Bench Page number 56 6- STATE... LANGFORD GAP BASALT HILL TUNNEL FACE Page number 49 10 ...Although the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme was first proposed in 1911, construction did not commence until 1938. As part of the push to cut electricity costs and diversify supply, the Victorian Government (circa 1930) initiated the conversion from primarily brown coal supply to hydro – electricity. Field investigations during the 1940’s resulted in a new proposal for a scheme that had more than double the capacity of the 1938 scheme. The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme became the largest scheme of its kind in the State Of Victoria and the second largest scheme in Australia. The number of personnel involved in the planning and construction of the scheme increased dramatically. During the late 1940’s, most activity centred around the construction of the West Kiewa Power Station, Rocky Valley Reservoir, McKay Creek Power Station and the Bogong Creek Aqueduct.A common thread across all the larger hydro scheme constructions was the need for workers, both qualified and unqualified who came from around the world seeking a new life for themselves and their families. New accommodation and facilities were required for the army of workers engaged in construction in often remote and wild areas. The SEC had a high demand for timber, and set up the first of a number of sawmills at Bogong Creek in 1939 and set up the first hardwood logging in the headwaters of the Kiewa River. These new ‘towns’ such as Mt Beauty and Bogong, survived, serving the needs of operational personnel and their families, and expanding with growth of new industries. Mount Beauty, and to a lesser extent Bogong, are among these places. Large A3 size spiral bound display folder containing photocopied black and white photographs of various aspects of the early days of the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric scheme including equipment, various work sites and photographs of workers and their families. 1-Workmen working inside one of the tunnels. 2-Workman drilling in West Kiewa Tunnel 3-Junction Dam wall construction 4&5-2B&W photographs Kiewa House residents ready to go to a ball in Mt Beauty 6-Workmen warming up in front of a fire at No 1 bench 7-Workmen being hauled in at No 4 P.S Shaft 8-No 4 Power Station – Drilling 9-Workmen eating a hot meal in the tunnel. 10-2 photographs (a)Pretty Valley camp showing workman’s huts and construction materials & (b)Worker in Langford Gap Basalt Hill Tunnel face 11-Tunnel entrance (unlabelled) with rail tracks in foreground 12- Workmen drilling at No 1 Head race tunnel-Drilling face 13- No 1 Power Station 14-Workmen at the entrance to one of the SECV tunnels under construction 1-SECV number at bottom of picture Half obscured possibly K8461 Page number 53 2-In West Kiewa Tunnel Page number 54 3- Construction of Junction Dam wall – approximately 1941 Page number 55 4&5- Residents of Kiewa House at Bogong ready to go to the ball at Mt Beauty-1946. Handwritten on a copy of the photo on opposite page Mrs Lorna Crosset filled out the names *Dad was Des Crossett – his daughter is Gael Petcopoulis Greta engaged to John broke it off. Charlie, Rosalind, Bill, Priscilla, Max Lawrence-Dad’s Boss, Mary & Max married, Mary, Kay, Gwen McPherson Mum’s boss, John McCluskey (c) At No. 5 Bench Page number 56 6- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 27.2.51 Time:2.15pm No K6373 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works No. 4 P.S. Shaft – Haulage of men in buckets (b) As above Handwritten at top of photo Appendix 4 page number 57 7- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 6.6.52 Time:… No K7122 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works No. 4 POWER STATION – DRILLING page number 58 8-No markings page number 59 9-(a)Handwritten under photograph Approx. 1948/49 (b) STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 28.10.54 Time:.. No K7860 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works LANGFORD GAP BASALT HILL TUNNEL FACE Page number 49 10-(a) No markings 11- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 20.3.52 Time: No K6979 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works No. 1 HEAD RACE TUNNEL – DRILLING FACE (E.E.E. CONTRACT) ‘The Frenchies’ (E.E.E) as they were affectionately known Page number 50 12-31.5.56 No. 1 Power Station Aggregate Stock Piles. Page number 51 13&14-No markings Page number 52 secv; kiewa hydro electric scheme; bogong; mt beauty; construction area -
 Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.
Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.Information folder - Germans Gully - Arcady
... -Certificate Of Title (number illegible) dated 10 July 1919, initial... during Plarre ownership -Certificate Of Title (number illegible ...Folder containing items pertaining to the history of Germans Gully - Arcady, Belgrave Heights. Contents: -4 colour photos, c. 2000, showing house and gardens -sketches, photocopied, by Barbara Smith, dated 29 October 2002, showing stone huts at Arcady prior to mid-1950s, with additional comments by Marian Matta -typescript, "Short History Of Arcady also known as German Gully, 'Carinya' & Church Of Freedom", 1 page, 3 copies including one with small photo -typescript, dated 22 June 97, "Plarre Visit to 'Arcady', Originally Known as 'Carinya'", six pages -hand-written letter, addressed to "Sue & Peter" (Downard) from Ralph (Wilson) dated April 02, containing historical information re. Arcady, 4 sheets double-sided -Yarra Ranges Shire Heritage Study Place Nomination Form for Germans Gully, partially completed -obituary, Herald Sun newspaper, undated but 2003, "Raymond Otto Plarre, Baker had passion for quality produce" -4 page Fairfax newspaper wraparound, "A Recipe For Success", advertising feature commemorating Ferguson Plarre Bakehouse Centenary, 1901-2001 -8 sheets of photocopied photos of Arcady, taken during Plarre ownership -Certificate Of Title (number illegible) dated 10 July 1919, initial purchasers being Robert and Bertha Maurer, 3 copies of obverse sheet (copies) (dups. in A3 folio #1) -Certificate of Title, Vol. 5262, Folio 1052392, dated 18 January 1927, initial purchaser being Bernhard Walk (2 copies, one issued 12 Aug 1996, one issued 17 Apr 1997) (dups. in A3 folio #1) -photo (colour) and hand-drawn map of site, prepared by Ralph Wilson, 2006 -Pamphlet, "Our Place, a celebration of where we live", Shire of Yarra Ranges, Oct. 2006 -photos (2, colour) of fire at Arcady, annotated 'Hello Peter & Sue, more pictures taken by Marty of CFA' -article, Australian Post, 6 Jul. 1972, 'Fool around with SCARLETT!', 2 photos of John Wilson (in A3 folio #1)albert hartung, otto plarre, mr stace, john wilson, count felix von lucknor, mr & mrs smart, plarre family, mr hutter, carinya, raymond otto plarre, ferguson plarre bakehouses, keith cooke, hugh ackland, alexander wynnum king, russell & jean smart -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybook, The Cocky Farmer, 1907
Nathan Frederick Spielvogel (1874-1956), teacher, writer and historian, was born on 10 May 1874 at Ballarat, Victoria. as well as his stories he published a number of Books about the history of Ballarat. Nathan Frederick Spielvogel (1874–1956) was a teacher, writer and historian. As a country schoolteacher, he traveled widely in the eastern Australian outback and also made a journey to London. Spielvogel gained distinction as one of the only Australian Jewish writers of his time. Many of his early books were best-sellers. A paper back book with 146 pp.written by Nathan Spielvogel. On the front cover is a drawing of a farm-house in a green paddock. The book is about school life and farming at Sale, Stawell, and the Wimmera district. the-cocky-farmer spielvogel-nathan literature -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societybook, Songs of the Currawongs, 2011
Mary Ann Willis is a member of The Orbost Nixon family and as a child spent time in Orbost. Mrs Marion Dwyer held office at Bairnsdale Golf Club and the East Gippsland Golf Associates Association for many years, being honoured with Life Membership from both. She was also a member of the YGLU (now Golf Victoria) council for 10 years. Mrs Dwyer won a number of titles including: Victorian Country Champion 9 times, Victorian Veteran Champion 3 times, Gippsland Champion 13 times, East Gippsland Champion 16 times, East Gippsland Foursomes' Champion 2 times, Bairnsdale Golf Club Ladies Champion 32 times, Bairnsdale Golf Club Foursomes' Champion 4 times & 106 single tournaments.A large book with a black cover. Book written by Mary Ann Willis. Contains poetry and articles including an oral history of Marion Dwyer. willis-maryann literature dwyer-marion nixon-family orbost -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyblack and white photograph, early 20th century - 1910?
From L-R : Nathan Spielvogel, Hector Young, Percy Watt and George Holden. . Taken on the front porch at Illfracombe in 1908 after the four men had enjoyed a weekend fishing There appears to be a photo hanging on the wall in the background which looks like it could be of a young Marion Watt and the family's dog, a golden retriever In "The Gum Sucker at Home: Bound for Croajingolong 1908" by Nathan Spielvogel, published in Mary Gilbert's Personalities and Stories of the Early Orbost District, 3rd edition, p. 107-116, Spielvogel talks of his trip to Orbost, and fishing with Watt, Bruce and Young aboard Percy Watt's boat, the Maris Stella. Spielvogel's story says Young was the secretary at James & Birds auctioneers and "was one of the builders of the first foot bridge over the Backwater". It says George Holden was a Bank Manager at the Bank of Victoria. (info. from Campbell Watt) This photograph shows Mr Nathan Spielvogel on the left. He was a school teacher at the Orbost State School following Mr Rowe. Nathan Frederick Spielvogel (1874-1956), teacher, writer and historian, was born on 10 May 1874 at Ballarat, Victoria, son of Newman Frederick Spielvogel, pawnbroker, and his wife Hannah, née Cohen. As well as his stories he published a number of books about the history of Ballarat. Spielvogel taught at Orbost for at least a year Nathan Frederick Spielvogel (1874–1956) was a teacher, writer and historian. As a country schoolteacher, he traveled widely in the eastern Australian outback and also made a journey to London. Spielvogel gained distinction as one of the only Australian Jewish writers of his time. Many of his early books were best-sellers. He has an association with the history of Orbost having spent a year as a teacher at Orbost. The Watt family were early Marlo settlers.A black / white photograph / postcard of four men sitting around a small table playing cards. Two of the men have pillows behind their heads. Three are smoking pipes.on back - "On R - N. Spielvogel"spielvogel-nathan-orbost -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Society10/- note, June 1954 to February 1966
The 10/- banknote was first issued on 1 May 1913 as a blue banknote payable in gold. It was equal to a half sovereign gold coin. This is an example of Australian pre-decimal currency.A brown rectangular paper Australian ten shilling note. On the obverse side is Matthew Flinders and on the reverseis Parliament House. The signatories are : H. C. Coombs, Governor, Commonwealth Bank of Australia and Roland Wilson, Secretary to the Treasury. The watermark is Captain Cook in left oval and ’HALF’ behind each signature. The serial number is AE 617665 72currency australian-ten-shilling-note -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societymedallion, Memorial Plaque Factory, after WW1
These medallions were issued after the First World war to the next-of-kin of all British and Commonwealth(Empire) service personnel who were killed as a result of the war. The plaques were made of bronze aand hence popularly known as the "Dead Man's Penny". James Pullar Cameron was killed at Lone Pine during WW1. James Pullar Cameron (Service No 605) enlisted in the 8th Light Horse at Orbost on September 11, 1914 aged 23 years 5 months. His medical was done by Dr James Kerr. He was 6 ft 1 in tall, 11 st 6 lbs, of dark complexion with dark eyes and hair and a chest measurement of 34 ½ / 38 inches. After training, he embarked the Armadale on February 12, 1915. He was shot in the chest at the Dardanelles on May 29, 1915 and taken aboard the HT Neuralia for transfer to Malta. He was admitted to the military hospital ‘Cootenara’ and after 10 days treatment, he re-embarked for Gallipoli aboard the HMT Southland on June 14, 1915. He returned to duty at Gallipoli on June 20, 1915. On August 7, 1915 he was killed in action. His body was not recovered. His name is on the memorial at Lone Pine. His memorial plaque has a wide H and a number behind the back paw of the lion, indicating that this plaque was made at the Acton Factory, one of the later ones cast there.James Pullar Cameron was the son of Robert Cameron one of the earliest settlers on the Orbost flats. He was a trooper in the 8 Light Horse Regiment and died at Gallipoli on 7 August 1915.A bronze commemorative medallion in a wooden frame. The token has an image of Britannia holding trident and standing with a lion. The designer's initials E.Cr.P appear above the front paw. In her left outstretched hand she holds an oak wreath with the name James Pullar Cameron in a rectangle. His memorial plaque has a wide H and a number behind the back paw of the lion, indicating that this plaque was made at the Acton Factory, one of the later ones cast there.Around the picture- He died for freedom and honour.ww1 gallipoli cameron medallion military -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Chair, Early 20th Century
The chair has been used since antiquity, although for many centuries it was a symbolic article of state and dignity rather than an article for ordinary use. "The chair" is still used as the emblem of authority in the House of Commons in the United Kingdom and Canada, and in many other settings. In keeping with this historical connotation of the "chair" as the symbol of authority, committees, boards of directors, and academic departments all have a 'chairman' or 'chair'. Endowed professorships are referred to as chairs. It was not until the 16th century that chairs became common. Until then, people sat on chests, benches, and stools, which were the ordinary seats of everyday life. The number of chairs which have survived from an earlier date is exceedingly limited; most examples are of ecclesiastical, seigneurial or feudal origin. Chairs were in existence since at least the Early Dynastic Period of Egypt (c. 3100 BC). They were covered with cloth or leather, were made of carved wood, and were much lower than today's chairs – chair seats were sometimes only 10 inches (25 cm) high. In ancient Egypt, chairs appear to have been of great richness and splendour. Fashioned of ebony and ivory, or of carved and gilded wood, they were covered with costly materials, magnificent patterns and supported upon representations of the legs of beasts or the figures of captives. Generally speaking, the higher ranked an individual was, the taller and more sumptuous was the chair he sat on and the greater the honour. On state occasions, the pharaoh sat on a throne, often with a little footstool in front of it.[ The average Egyptian family seldom had chairs, and if they did, it was usually only the master of the household who sat on a chair. Among the better off, the chairs might be painted to look like the ornate inlaid and carved chairs of the rich, but the craftsmanship was usually poor. The earliest images of chairs in China are from 6th-century Buddhist murals and stele, but the practice of sitting in chairs at that time was rare. It was not until the 12th century that chairs became widespread in China. Scholars disagree on the reasons for the adoption of the chair. The most common theories are that the chair was an outgrowth of indigenous Chinese furniture, that it evolved from a camp stool imported from Central Asia, that it was introduced to China by Christian missionaries in the 7th century, and that the chair came to China from India as a form of Buddhist monastic furniture. In modern China, unlike Korea or Japan, it is no longer common to sit at floor level. In Europe, it was owing in great measure to the Renaissance that the chair ceased to be a privilege of state and became a standard item of furniture for anyone who could afford to buy it. Once the idea of privilege faded the chair speedily came into general use. Almost at once the chair began to change every few years to reflect the fashions of the day. Thomas Edward Bowdich visited the main Palace of the Ashanti Empire in 1819, and observed chairs engrossed with gold in the empire. In the 1880s, chairs became more common in American households and usually there was a chair provided for every family member to sit down to dinner. By the 1830s, factory-manufactured “fancy chairs” like those by Sears, Roebuck, and Co. allowed families to purchase machined sets. With the Industrial Revolution, chairs became much more available. The 20th century saw an increasing use of technology in chair construction with such things as all-metal folding chairs, metal-legged chairs, the Slumber Chair,[ moulded plastic chairs and ergonomic chairs. The recliner became a popular form, at least in part due to radio and television. The modern movement of the 1960s produced new forms of chairs: the butterfly chair (originally called the Hardoy chair), bean bags, and the egg-shaped pod chair that turns. It also introduced the first mass-produced plastic chairs such as the Bofinger chair in 1966. Technological advances led to moulded plywood and wood laminate chairs, as well as chairs made of leather or polymers. Mechanical technology incorporated into the chair enabled adjustable chairs, especially for office use. Motors embedded in the chair resulted in massage chairs. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ChairThe chair is one of the most commonly used items providing comfort.Chair wooden varnished dark brown. Spokes for back support, front legs and spokes joining legs are patterned turned wood. Back rest has a floral emblem with a kangaroo in the centre.Back rest has a floral emblem with a kangaroo in the centre.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, chair, dining, carpentry -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Chair, Early 20th Century
The chair has been used since antiquity, although for many centuries it was a symbolic article of state and dignity rather than an article for ordinary use. "The chair" is still used as the emblem of authority in the House of Commons in the United Kingdom and Canada, and in many other settings. In keeping with this historical connotation of the "chair" as the symbol of authority, committees, boards of directors, and academic departments all have a 'chairman' or 'chair'. Endowed professorships are referred to as chairs. It was not until the 16th century that chairs became common. Until then, people sat on chests, benches, and stools, which were the ordinary seats of everyday life. The number of chairs which have survived from an earlier date is exceedingly limited; most examples are of ecclesiastical, seigneurial or feudal origin. Chairs were in existence since at least the Early Dynastic Period of Egypt (c. 3100 BC). They were covered with cloth or leather, were made of carved wood, and were much lower than today's chairs – chair seats were sometimes only 10 inches (25 cm) high. In ancient Egypt, chairs appear to have been of great richness and splendour. Fashioned of ebony and ivory, or of carved and gilded wood, they were covered with costly materials, magnificent patterns and supported upon representations of the legs of beasts or the figures of captives. Generally speaking, the higher ranked an individual was, the taller and more sumptuous was the chair he sat on and the greater the honour. On state occasions, the pharaoh sat on a throne, often with a little footstool in front of it.[ The average Egyptian family seldom had chairs, and if they did, it was usually only the master of the household who sat on a chair. Among the better off, the chairs might be painted to look like the ornate inlaid and carved chairs of the rich, but the craftsmanship was usually poor. The earliest images of chairs in China are from 6th-century Buddhist murals and stele, but the practice of sitting in chairs at that time was rare. It was not until the 12th century that chairs became widespread in China. Scholars disagree on the reasons for the adoption of the chair. The most common theories are that the chair was an outgrowth of indigenous Chinese furniture, that it evolved from a camp stool imported from Central Asia, that it was introduced to China by Christian missionaries in the 7th century, and that the chair came to China from India as a form of Buddhist monastic furniture. In modern China, unlike Korea or Japan, it is no longer common to sit at floor level. In Europe, it was owing in great measure to the Renaissance that the chair ceased to be a privilege of state and became a standard item of furniture for anyone who could afford to buy it. Once the idea of privilege faded the chair speedily came into general use. Almost at once the chair began to change every few years to reflect the fashions of the day. Thomas Edward Bowdich visited the main Palace of the Ashanti Empire in 1819, and observed chairs engrossed with gold in the empire. In the 1880s, chairs became more common in American households and usually there was a chair provided for every family member to sit down to dinner. By the 1830s, factory-manufactured “fancy chairs” like those by Sears, Roebuck, and Co. allowed families to purchase machined sets. With the Industrial Revolution, chairs became much more available. The 20th century saw an increasing use of technology in chair construction with such things as all-metal folding chairs, metal-legged chairs, the Slumber Chair,[ moulded plastic chairs and ergonomic chairs. The recliner became a popular form, at least in part due to radio and television. The modern movement of the 1960s produced new forms of chairs: the butterfly chair (originally called the Hardoy chair), bean bags, and the egg-shaped pod chair that turns. It also introduced the first mass-produced plastic chairs such as the Bofinger chair in 1966. Technological advances led to moulded plywood and wood laminate chairs, as well as chairs made of leather or polymers. Mechanical technology incorporated into the chair enabled adjustable chairs, especially for office use. Motors embedded in the chair resulted in massage chairs. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ChairThe chair is one of the most commonly used items providing comfort.Chair wooden varnished dark brown. Spokes for back support, front legs and spokes joining legs are patterned turned' wood. Backrest has a floral emblem with a kangaroo in the centre.Back rest has a floral emblem with a kangaroo in the centre.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, chair, dining, carpentry -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Chair, Early 20th Century
The chair has been used since antiquity, although for many centuries it was a symbolic article of state and dignity rather than an article for ordinary use. "The chair" is still used as the emblem of authority in the House of Commons in the United Kingdom and Canada, and in many other settings. In keeping with this historical connotation of the "chair" as the symbol of authority, committees, boards of directors, and academic departments all have a 'chairman' or 'chair'. Endowed professorships are referred to as chairs. It was not until the 16th century that chairs became common. Until then, people sat on chests, benches, and stools, which were the ordinary seats of everyday life. The number of chairs which have survived from an earlier date is exceedingly limited; most examples are of ecclesiastical, seigneurial or feudal origin. Chairs were in existence since at least the Early Dynastic Period of Egypt (c. 3100 BC). They were covered with cloth or leather, were made of carved wood, and were much lower than today's chairs – chair seats were sometimes only 10 inches (25 cm) high. In ancient Egypt, chairs appear to have been of great richness and splendour. Fashioned of ebony and ivory, or of carved and gilded wood, they were covered with costly materials, magnificent patterns and supported upon representations of the legs of beasts or the figures of captives. Generally speaking, the higher ranked an individual was, the taller and more sumptuous was the chair he sat on and the greater the honour. On state occasions, the pharaoh sat on a throne, often with a little footstool in front of it.[ The average Egyptian family seldom had chairs, and if they did, it was usually only the master of the household who sat on a chair. Among the better off, the chairs might be painted to look like the ornate inlaid and carved chairs of the rich, but the craftsmanship was usually poor. The earliest images of chairs in China are from 6th-century Buddhist murals and stele, but the practice of sitting in chairs at that time was rare. It was not until the 12th century that chairs became widespread in China. Scholars disagree on the reasons for the adoption of the chair. The most common theories are that the chair was an outgrowth of indigenous Chinese furniture, that it evolved from a camp stool imported from Central Asia, that it was introduced to China by Christian missionaries in the 7th century, and that the chair came to China from India as a form of Buddhist monastic furniture. In modern China, unlike Korea or Japan, it is no longer common to sit at floor level. In Europe, it was owing in great measure to the Renaissance that the chair ceased to be a privilege of state and became a standard item of furniture for anyone who could afford to buy it. Once the idea of privilege faded the chair speedily came into general use. Almost at once the chair began to change every few years to reflect the fashions of the day. Thomas Edward Bowdich visited the main Palace of the Ashanti Empire in 1819, and observed chairs engrossed with gold in the empire. In the 1880s, chairs became more common in American households and usually there was a chair provided for every family member to sit down to dinner. By the 1830s, factory-manufactured “fancy chairs” like those by Sears, Roebuck, and Co. allowed families to purchase machined sets. With the Industrial Revolution, chairs became much more available. The 20th century saw an increasing use of technology in chair construction with such things as all-metal folding chairs, metal-legged chairs, the Slumber Chair,[ moulded plastic chairs and ergonomic chairs. The recliner became a popular form, at least in part due to radio and television. The modern movement of the 1960s produced new forms of chairs: the butterfly chair (originally called the Hardoy chair), bean bags, and the egg-shaped pod chair that turns. It also introduced the first mass-produced plastic chairs such as the Bofinger chair in 1966. Technological advances led to moulded plywood and wood laminate chairs, as well as chairs made of leather or polymers. Mechanical technology incorporated into the chair enabled adjustable chairs, especially for office use. Motors embedded in the chair resulted in massage chairs. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ChairThe chair is one of the most commonly used items providing comfort.Chair varnished dark brown. Spokes for back support, front legs and spokes joining legs are patterned turned wood. Back rest has a floral emblem with a kangaroo in the centre.Back rest has a floral emblem with a kangaroo in the centre.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, chair, dining, carpentry -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Needle Pin Case, 1860 to 1900
Knitting, as a household task, has been traced back to 1100 AD where archaeologists in Egypt found remnants of socks. Evidently socks or stockings became a household necessity and creating them by knitting was the easiest way to get a good fit. The Tudors wore hand knit caps and King Henry the VIII made hand knit silk stockings, imported from Spain, a fashion staple. Meanwhile in Paris in 1525, men formed one of the first worker's unions for hand knitters. Knitting by machine first appeared during this same period and with the spread of fashion of the silk stockings and the basic needs of people to keep warm helped to fuel the popularity of knitting. By the 1850's, knitting machines were common place and apprenticing in such a factory, was considered honourable employment. But the main tool of knitting has always remained the needle, that is said to have it's origins in Arabia. The first needles were made of copper and looked more like hooks than needles. In other locations around the world, knitting needles have been found constructed from wood, ivory, bone, bamboo, amber and iron as well. They are also known as woods, skewers or wires depending where in the world they are found. Context: Edwin Rodgers was born in Lincolnshire England estimated at 1830-1832, records document that he was working as a Miller in Jan 1863 and that he resided in Warrnambool until his death in 1887. The knitting needle case is believed to belong to his wife Ellen Amelia (nee Heywood), daughter of George Heywood and Dinah Turton. She had married Mr Edwin Rodgers on 30 Jan 1863 in Warrnambool, and they had continued to resided in Warrnambool. Ellen Amelia Heywood was born Oct to Dec 1839 in Stockport, Cheshire England & christened on 5 Jul 1840 in St Thomas, Stockport, Cheshire. She died on 8 Dec 1922 in 284 Merri Street, Warrnambool, Victoria 10 and was buried on 11 Dec 1922 in the Warrnambool Cemetery.A significant item that belonged to one of the early families of Warrnambool and as such is regarded by the Warrnambool community as significant because it helps to document Warrnambool's development.Medium sized cardboard foldable maroon knitting pin case with numbered sections to fit relevant sized metal pins 10 in all case called the peacock knitting pin case.On lid of case written in italic Mrs E A Rodgers, Warrnambool 1860-1922, Wife of Edwin Rodgersflagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village -
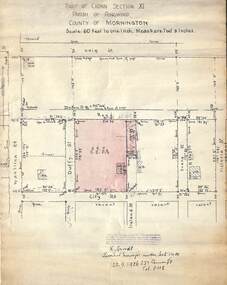 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyDocument, 1926 Land Survey drawing of the area surrounding 1-5 City Road, Ringwood
Drawing on parchmentHand-drawn survey of what is now 1-5 City Road, Ringwood. Drawn by K Arndt, licensed surveyor, 237 Queen Street, Melbourne Tel 5118 on 25 September 1926. The block of land in question was 2 roods, 21 and 8/10 perches in size. The location was between Haig Street in the north, City Road in the south, Wantirna Road in the west and Victoria Road in the east. The Good Shepherd Retirement Village (Lutheran) now occupies the land. The drawing shows a number of existing weatherboard houses, fences and frontage sizes. A number of named roads were defined but no longer exist, these were Duffy Street (to the west), Evans Street (east) and Victoria Street (further east). Ireland Street still exists in the south. -
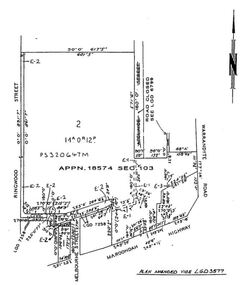 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyDocument - Folder, Commercial and Retail Property Sales Information, Civic Place and Melbourne Street, Ringwood - 1998
45 photocopied pages including - Plan of Subdivision No.LP80718, Parish of Ringwood, Victoria, Crown Portion 12(Part) and part of a former government road Ref Vol 8668 Fol 745. - Vendors Statement, Planning Certificate and Heritage Council (Victoria) Certificate issued for 20 Melbourne Street, Ringwood. - Maroondah City Council Land Information Certificate for 149 149A and 149B Maroondah Highway; number 8 Civic Mall; and numbers 16, 20, 22 & 24 Melbourne Street Mall. - Yarra Valley Water statements relating to encumbrances for Shop 11, 149 Maroondah Highway; Shop 10, 149A Maroondah Highway; Shop 9, 149B Maroondah Highway; numer 8 Civic Place; Unit 3, 20 Melbourne Street; Office 4, 20 Melbourne Street; Shop 7, 22 Melbourne Street; and Shop 8, 24 Melbourne Street. - Land Tax Certificate pertaining to Commonwealth Bank, Civic Place, Ringwood. - Certificate of Title Vol 8892 Fol 906, Lot One on Plan of Subdivision No. 80718, Parish of Ringwood - Hanover Developments P/L - 29th June, 1971. -
 Mission to Seafarers Victoria
Mission to Seafarers VictoriaDocument - Statement of earnings (linked to group certificate registration number 00291), Issued 26 January 1945
Tax certificate of Allan QuinnThis certificate gives an indication of the level of wages in 1945 and the amount of tax paid. Triplicate version of group certificate marked statement of earnings.Issued 26 January 1945 for tax of 2 pounds, 12 shillings and 9 pence on earnings of 79 pounds, 10 shillings. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCard - Recipe Card, Department of Public Instruction, Cookery Instruction Card No. 10, 1910s
This card is one of four in our Collection. The original set of cards was a series of 33 cards published by the Victorian Government to give recipes and instructions for basic meals. This card has recipes for (1) Rissoles of Cold Meat (2) Grilled Chop or Steak The Cookery instruction cards show that in the early 20th century the Victorian Government was concerned about domestic education and produced the set of cards to help meet that need.Cookery Instruction Card No. 10 Author: Department of Public Instruction, Victoria Publisher: Department of Public Instruction, Victoria Printed – By Authority: Albert J. Moffett, Government Printer, Melbourne. Cream coloured card with printed ingredients and instructions for recipes. A number is printed in the top right corner.Overprinted: “(Set of 33 cards, 1s.; 1 card 1/2d.)” “Copyright)”warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, cooking instructions, department of public instruction, food, domestic, cookery, kitchen, recipe, education, training, domestic life, cooking, recipes, food & beverages, domestic work, education and training, card no. 10 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageCard - Recipe Card, Department of Public Instruction, Cookery Instruction Card No. 7, 1910s
This card is one of four in our Collection. The original set of cards was a series of 33 cards published by the Victorian Government to give recipes and instructions for basic meals. This card has recipes for (1) Classes of Soups (2) To Keep Stock (3) Macaroni Soup The Cookery instruction cards show that in the early 20th century the Victorian Government was concerned about domestic education and produced the set of cards to help meet that need.Cookery Instruction Card No. 7 Author: Department of Public Instruction, Victoria Publisher: Department of Public Instruction, Victoria Printed – By Authority: Albert J. Moffett, Government Printer, Melbourne. Cream coloured card with printed ingredients and instructions for recipes. A number is printed in the top right corner.Overprinted: “(Set of 33 cards, 1s.; 1 card 1/2d.)” “Copyright)”warrnambool, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill, maritime museum, maritime village, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, cooking instructions, department of public instruction, food, domestic, cookery, kitchen, recipe, education, training, domestic life, cooking, recipes, food & beverages, domestic work, education and training, card no. 10 -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Cannon, 1813
This 1813 cannon is classified as a carronade, having been made by the Carron Ironworks foundry in Stirling, Scotland in 1813. It is a large calibre, short range, gun mainly used on ships. The carronade model of cannon was first used when introduced into the British Royal Navy in the American War of the Revolution (1775-1883). This cannon was originally a 28pdr, 48cwt, 8ft gun. The date ‘1837’ on the barrel probably indicates the date that the Board of Ordinance accepted the change in size to a 32pdr. It may originally have been a naval gun and the conversion undertaken when it was brought ashore. It is very probably one of the 15 guns that are known to have constituted the defences of Victoria in 1860. This group of 32pdrs was the shorter model of the 4800width and 8ft length cannon and as such are different from the 32pdrs found in NSW. It was originally located on Cannon Hill in Warrnambool when it was the site of the Warrnambool Battery Western Artillery, formed in 1866. It was obsolete by the time of the 1887 fortifications, and was moved from the Warrnambool Fortifications to the Botanic Gardens in 1910, when the Fortifications were declared obsolete. HISTORIC INFORMATION ABOUT THE CANNON IN THE WARRNAMBOOL AREA In the years following the Crimean War (1854-1857J) there was a great concern in the Colony that Imperial Russia would attempt an invasion. Coastal defences in the colony of Victoria were greatly strengthened by the Government as a result. Warrnambool was originally protected by cannons at Cannon Hill, approximately 1 kilometer west of the Flagstaff Hill Fortifications. The cannons included two 1866 guns, both 80 Pound Rifled Muzzle Loaders (RML) purchased by Victoria’s Colonial Government. They were part of a shipment of 26 such guns sent from England in December 1866. They are registered as No. 23 (80cwt-2qr-0lbs) - Gun 1, and No.13 (81cwt-1qr-12lbs) - Gun 2. They were cast at the Royal Gun Factory, Woolwich Arsenal, in 1866 and have a 6.3 inch bore. Both barrels carry the Royal Cypher of Queen Victoria, Insignia of the Royal Engineers, within the Garter and Motto surmounted by the Crown, with the Royal Cypher of Queen Victoria within the Garter (letters in centre “VR”, motto “HONI SOIT QUI MAL Y PENSE”, "Shame be to him who thinks evil of it."). The guns were originally supplied with wooden carriages. (The Royal Arsenal at Woolwich, England, was established eleven years after the Restoration of King Charles II. It was the principal supplier of armaments to the British and Empire Governments. At the height of its operations during World War One the factory covered 1300 acres and employed very nearly 80,000 workers. Woolwich was the Headquarters of the Royal Artillery since the raising of that Regiment in 1716. The Arsenal was closed in the late 1960’s.) The two 80pdr cannons were transferred to the Warrnambool Garrison Artillery Battery Fortifications erected at Flagstaff Hill in 1887 as part of Victoria’s Coastal Defences. The original wooden carriages were subsequently replaced with the present iron garrison carriages in 1888. They are a “C” pivot. The ‘racers’ or curved track set into the floor of the gun emplacement (which enabled the guns to be traversed more quickly) are as specified for guns up to 10 inch, being of wrought iron 2.78 inches wide. A temporary third gun, now no longer on Flagstaff Hill’s site, was a 5 inch Rifled Breech Loading (BL) Armstrong gun mounted on an Elswick hydro pneumatic disappearing carriage It was faster to load and fire than the 80 pound RMLs and its arrival spelt the end of the older 80 pound guns’ useful life, apart from being used for practice sessions. The 5 inch BL gun was the main defensive weapon of the Warrnambool Battery until the Battery was downgraded in importance and the gun was recalled to Melbourne in 1910. The gun emplacement still remains in place set between the 2 80pdr cannon. The State of Victoria took over the ownership of the guns at the time of Australian Federation in 1901. In about 1901/1902 the Garrison Battery was converted to the Warrnambool Battery of the Australian Field Artillery (No 4 Field Battery). It was equipped with 4.7 inch naval guns mounted on field carriages. They were now a mobile unit but continued to use the Warrnambool Garrison area at Flagstaff Hill for practice. When the Fortifications were declared obsolete the two 80 Pounder RML were relocated to Cannon Hill in 1910. On the outbreak of World War 1 the 4.7 inch guns were recalled to Melbourne, and the Battery was disbanded. Most of the personnel probably re-enlisted in the local 4th Australian Light Horse Regiment. The two 80 Pounder RML were moved back to the Fortifications in 1973. They were both fully restored by Army First Year Apprentices at the Ordinance Factory in Bendigo in time for the centenary year of the fortifications in 1987. The guns are capable of firing 80 pound (32.3kg) armour piercing exploding shells 3.65kms out to sea. They were original manned by volunteers before a paid Garrison was established. Now the Guns are again fired by volunteers on Special Event days. Since restoration the Gun Number 1 had been fired on a regular basis but Gun Number 2 hadn’t been fired since the mid 1990’s. In April 2015 Gun Number 2 was serviced in preparation for the firing of both cannons on the ANZAC Centenary commemorations on April 25th 2015. Other guns from the original Cannon Hill location were obsolete by the time the 1887 Warrnambool Garrison Artillery Battery was built. These guns are (1) a 32 Pounder Muzzle Loading Smooth Bore (SB) cast in 1813 at the famous Carron Foundry, number 80837 and now located in the Warrnambool Botanic Gardens. It is now mounted on a replica carriage due to the original carriage being in a fragile condition (the original carriage stored under cover at Flagstaff Hill). (2) a 68 Pounder Muzzle Loading Smooth Bore cast in 1861 at the equally august Low Moor Foundry, number 10310 and now located on the lawn area at the entrance to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. It is still mounted on its original wooden garrison carriage. Its wooden slide compressor mechanism is fragile and now kept in Flagstaff Hill’s storage. There are only seven 32 Pounder SB made by Carron and fifteen 68 Pounder SB made at Low Moor known to exist in the State of Victoria Plaque attached to the carriage “This replica carriage was constructed by the Warrnambool Tritan Woodworkers club in conjunction with the generosity of local businesses and the Warrnambool community. The original carriage (circa 1860) was removed for restoration and is now located at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. The timber used for the replica carriage is Monterey Cypress, which was an early planting in the gardens. 2010 marked the centenary of the cannon’s relocation in the Warrnambool Botanic Gardens.” (Reference; Victorian Guns and Cannons, South Western Victoria Assessment, May 2008, item W/B/01; Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village datasheets and archives). There are only seven 32 Pounder SB made by Carron known to exist in the State of Victoria and this is one of them. On a world level, this cannon represents a high level of rarity. Further, as it has been modified (bored up) it is representative of the historical process of amending artillery in order to ensure a longer usefulness of each piece despite rapidly advancing artillery technology. The number of surviving carriages with traversing slides in this group in South Western Victoria is unique in Australia and probably in the World. Out of 10 such platforms surviving in Australia, the South Western Victorian group has half. Several survive around the world but probably not in such a large group. The wooden sliding compressor mechanism belonging to this cannon is extremely rare, and the only one in this South Western Victorian group of Guns and Cannons. As a whole, this cannon has undergone very little restoration or modification, giving it a high level of integrity. The City of Warrnambool is one of several custodians of a collection of artillery pieces of heritage significance at a state, national and international level. These pieces are directly related to the defence of south-west Victoria in the 19th century. The care and preservation come under the Heritage Act 1995. (Reference; Victorian Guns and Cannons, South Western Victoria Assessment, May 2008).Cannon, or carronade, 32pdr with wheels. Muzzle loading smooth bore (SB) cannon. Cannon has original wooden Burmese Teak carriage and slide with wrought iron fittings and iron wheels. Manufactured by Carron in Scotland, in 1813. It has been converted from a 28pdr. There is a loop for a rope on the cascabel, which was part of the original casting. Re-bored in 1837. Marks include Serial Number, Royal Cypher of King George III, broad arrow of proofing, and numbers to represent the weight. NOTE: The cannon is displayed in the Warrnambool Botanic Gardens and is mounted on a replica wooden carriage; the original wooden carriage is now stored under cover at Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village. This carriage has 4 wheels on swivel attachments and a central gear that allows the wheels to turn on rails. Pressed into left trunnion “80837 / CARRON / 1813”, cast on barrel“symbol (Royal Cypher of King George III”, “symbol (broad arrow of proofing)” and numbers “45-3-24 / 1837” . Cascable “CV” and marks with gradations from nought to three in quarters on each side, On the carriage the end of one of the main slide members carries the mark “W symbol (broad arrow) D” incised into the timber. Plaque attached to the carriage by the Warrnambool Tritan Woodworkers club, 2010, marking the centenary of the cannon’s relocation in the Warrnambool Botanic Gardens and the addition of the replica carriage. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, victoria’s coastal defences, warrnambool fortification, warrnambool garrison battery, ordinance, armaments, cannon hill fortifications, victorian colonial government, carron ironwroks foundary, 32pdr smooth bore cannon, 28pdr smooth bore cannon, 1813 cannon, carronade -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDecorative object - Sewing Machine, c 1914-1930
Sewing Machine, Medium C S. (item has 10 parts), treadle operated, in wooden cabinet. Machine body is black with floral decals in gold, cream and red. Cabinet has wheels, 4 drawers containing cylinder shuttle, 2x bobbins, handle from a drawer and a bundle of horse hair. Drive belt is missing, cabinet has evidence of borer. Ironwork on right upright has 2 splits, name on plate of treadle is worn off. Decals include English Made and Approved to Her Majesty Queen Victoria. Machine has Serial Number.Pencilled inside machine support " 11/11/10 H M X" Serial Number "66389" Decals include "MEDIUM C.S / APPOINTED TO HER MAJESTY / QUEEN VICTORIA", "ENGLISH MADE".flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, sewing machine, cylinder shuttle sewing machine, dressmaker's equipment, taylor, jones sewing machine, medium c.s. machine, medium cylinder shuttle machine
