Showing 149 items matching "spear"
-
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - ''PROGRAMME: FOR ABORIGINE CAMP''
''Programme for Aborigine Camp''. Single page typed programme (undated - and no actual location referred to) re 17 activities for a 'demonstration' of how aborigines were supposed to live/have lived? - e.g. #3 One boy to be fishing in the space between the tree at the edge of the creek; # 11 When coach drives through Park, aborigines to rush from all quarters and point their spears at the coach, and jabber. War crys in order.bendigo, history, aboriginal, aboriginal camp. mia mia. -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncFolder, Commercial Bank of Australia Eltham Branch Hold-Up, 15 December 1949
Thursday, December 15, 1949, the quiet little bank was embroiled in an infamous wild shoot-out between a daring thief and two bank officers. Today, the building still carries the scars ; a bullet hole remains visible in a cedar bench testifying to the events that played out that day. 3.30 a.m., Friday, December 9. The manager of the Commercial Bank branch at Greensborough, Mr Harry Wallace and his wife are asleep in their bedroom of the little house behind the branch. Harry is awakened by a noise and sees an intruder in a corner of the bedroom. He calls out but the intruder who has switched off the power in anticipation flees through a side door and scarpers down Main Street. Harry summons the police but a search by First Constable Thomas of the Greensborough Police assisted by a wireless patrol car is unsuccessful. A report is filed noting the theft of a .25 calibre pistol from the wardrobe. Thursday, December 15th. It is 1pm and the Commercial Bank has just opened. The branch is only open Mondays and Thursdays from 1-3pm. The morning started off a little cool with some scattered showers but it has fined up and the temperature is now around 61 degrees (16 C). A new grey Singer sports car with soft-top pulls up on the opposite side of the road and a young man, neatly dressed in a dark blue suit, wearing a grey hat and carrying a brief case exits the vehicle. He looks around then crosses the road and walks up the steps and through the door into the bank. There are three people inside; Mr. Jack Burgoyne whose grocery store is situated just 50 yards up the road, Mr. Lindsay A. Spears, the Eltham Agency Receiving Officer and by chance, Mr Harry Wallace, manager of the Greensborough branch. Jack Burgoyne takes note of the young stranger; thinking to himself he appears nervous. The man approaches the counter and introduces himself as John Henderson of Greensborough and explains that he wishes to open a new account. He places his hat and £3 on the counter. Mr Spears attends to the paperwork. He asks the young man to sign two forms, which he does but then he withdraws from the counter and starts walking towards the door. Suddenly he spins around pulling an automatic pistol from his right-hand pocket. He exclaims forcefully; “The game’s on! I’ll take the lot!” Spears appears to comply by pretending to open a drawer. The man shouts loudly, “Keep your hand away from that drawer.” Spears instead reaches for a pistol in his pocket and challenges the man, “Here it is. Come and get it!” At the same time, Harry Wallace pulls a pistol from his pocket as well. The bandit fires a shot but misses, the bullet striking the counter. Both Spears and Wallace open fire and Jack Burgoyne ducks for cover. As the bandit turns and runs for the door leaving his £3 behind, he fires another shot, which strikes the ceiling. Spears fires back, and thinks he may have hit him in the foot. The bandit flees the bank and heads for the grey Singer car, registration NO-106, parked opposite. Wallace and Spears pursue him to the door and open fire again, striking the car three times around the driver’s door. Spears lets off eight shots and Wallace, seven before his gun jams. The getaway car initially heads slowly down Main Road towards Bridge Street. About 100 yards down the road, Dave Adams, a PMG employee, who has heard the shots, throws a steel manhole step at the driver. It hits the roof of the car nine inches above the driver’s head and tears the hood. Another witness claims to have seen the door blow open and the driver raise his hand. The car gathers speed and swings left into Bridge Street racing along at about 60 miles an hour careering recklessly past council employee, Mr. Percy Williams, who is driving a dray along Smarts Road [believed to be Bridge Street]. At the end of the road the Singer fails to get round the sharp turn and crashes into an embankment skidding to a stop outside the home of Mr John Clifford. One side of the car is wrecked. Mr Clifford, an aircraft engineer hears the fast travelling car bump heavily into the road bank at about 1.25 p.m. Hearing the whine of an engine he goes outside to find the grey Singer parked at the side of the road. Jack George also lives at the corner and hears the car crash. “The bandit opened the car door, ran 50 yards, and suddenly turned back,” exclaims Jack. “He took something from the car. It might have been a gun.” In his haste, the bandit drops his grey felt hat, size 6 7/8, on the road and dashes up Sherbourne Road for about 200 yards then disappears into the scrub carrying a brief case and a bundle in which a sailor’s cap can be seen. About 3 p.m., Mr H.D. Pettie of Mountain View Road, Montmorency is looking through his field glasses and notices a young man walking through thick scrub on private property some distance from his house. The man is wearing a sailor’s cap and disappears along the railway track toward Montmorency. As the day progresses, ten police cars, one motor cycle, and about 40 police led by Det. Sgt. McMennemin of Malvern CIB are searching for him. They believe he is hiding in thick scrub along the bank of the creek about half-a-mile outside Eltham township. Wireless patrol cars, four mobile traffic cars and the CIB area cars from Malvern and Kew are taking part. Police check the thief’s car and discover it was stolen from Helen Baxter, of Doncaster Road, North Balwyn from outside Victoria Barracks. Harry Wallace informs the police that he believes he recognised the bandit as the man who took his pistol from his bedroom the previous Friday morning. As night falls, armed police are posted at strategic points in the Eltham-Greensborough district. Police in cars are watching the roads. Others are searching the bush and checking passengers on trains. Little do they realise the young man has already slipped out of the net. SEQUEL YOUTH OF 19 CHARGED WITH ATTEMPTED ARMED ROBBERY OF BANK AT ELTHAM Weekly Times, Wednesday 15 February 1950, page 6 Detectives who raided a house in Bell St., Coburg, Melbourne, charged a 19-year-old youth, of South Yarra, with attempted armed robbery at the Commercial Bank’s Eltham (Vic.) receiving depot on Dec. 15. Police say they recovered a loaded automatic pistol, diamond and signet rings worth more than £200, a complete set of house-breaking instruments, a sailor’s uniform, and chloroform gauze in the raid. The youth was charged that while armed with an offensive weapon, he attempted to rob Lindsay George Spears of a sum of money. He was further charged on six counts of breaking, entering and stealing. Police allege that the person who tried to hold up Mr Spears in the Commercial Bank receiving depot at Eltham on December 15. escaped in a stolen car, after Mr Spears and Mr Henry Wallace, manager of the bank’s Greensborough branch, had fired at him. After the car crashed, he escaped into thick scrub and is alleged to have changed into a sailor’s uniform. On December 9 an automatic pistol was stolen from Mr Wallace’s bedroom at the Greensborough bank. The chloroform pad recovered is alleged to have been stolen from the Dental Supply Company, Plenty Road, Preston. The rings are alleged to have been taken in a £513 burglary from the shop of James Paton. Sydney Road, Coburg. Det. Sgt. H. McMennemin conducted the investigations with Senior Dets. R. Newton and M Downie, Detectives l. Dent, R. Rayner, P. Pedersen and M. Handley and First Constable A. Thomas. The youth will appear at Eltham Court on February 22. Manager’s Gun Used in Holdup at Bank The Age, Thursday 23 February 1950, page 4 It was stated in Eltham court yesterday that a youth who robbed a bank manager of his pistol, later used it in an attempt to hold-up the bank. Kay Arthur Morgan, 19, draftsman, of Castle-street, South Yarra, was committed for trial on charges of breaking and entering, and stealing a pistol and attempted robbery while armed with an offensive weapon. He pleaded guilty. The manager of Eltham branch of the Commercial Bank of Australia Ltd., Henry Clifton Cabot Wallace, said he disturbed someone in the bedroom, in which he and his wife were sleeping, at 3 a.m. on December. 9, 1949. Later he found that his automatic- pistol was missing. On December 15 a youth, who said his name was John Henderson, entered the bank and opened a new account. As the youth was leaving the bank he turned round with a pistol in his hand and said: — “I want the lot.” Spear indicated a drawer under the counter; and said.— “Here it is. Come and get it.” The youth said:— “Keep your hand away from that drawer.” Witness said Spear then drew his pistol from his hip pocket. The youth fired at them, and Spear returned the fire. “I pulled my pistol and fired, too” said witness. The youth fired again, ran out to a car and drove off. Witness and Spear fired several shots at the car. The youth was the accused Morgan, sitting in court, witness said. Evidence was given that one bullet was found in the celling and the other in the bank. Morgan was allowed £100 bail on each charge. Morgan ended up serving three years for the failed armed robbery and became a notorious criminal. He had twin sons, Peter and Doug and even though only ten years old, Morgan would get his sons to act as lookouts whilst he committed burglaries. The lads became building contractors but when the industry suffered a downturn in 1977 and they were short on cash, they returned to the family business. Over the following 23 months they undertook 24 raids on country and outer-suburban TABs and banks. Whilst robbing one country bank for the third time, just like their father, it all went wrong ending up with a police officer shot. They were nick-named the “After-dark” bandits and are considered to be Australia’s last bushrangers. They were convicted and served 17 years in prison.5 x A4 photocopied pagesbank hold-up, cba bank, det sgt mcmennemin, eltham, h.d. pettie, harry wallace, jack burgoyne, kay arthur morgan, lindsay a. spears, main road -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Painting - NORMAN PENROSE COLLECTION: BORDER PAINTINGS
Artwork. Norman Penrose collection: 2 border paintings. One has black, red and yellow stripes at the top. A spear shaped design with a red spot in the centre. Yellow, green, red and blue squares separated by two black and a white strip and black and yellow stripes at the bottom. The second one has red, white and black stripes at the top. A black, red and green geometric design in the centre and a black stripe at the bottom. The background is unpainted.drawing, print, norman penrose collection, artwork, border paintings -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Ephemera - SHOWBAGS COLLECTION: GOOD PFELLA LICORICE SHOWBAG
A paper showbag. A mainly green showbag with a black and white design, within a square made of black and white lines and 8 smiling faces of what appear to be an African or aborigine youth, we read: delicious soft eating Licorice and licorice all sorts. There is also a design of 7 stick figure holding a spear and dancing around a camp fire. Underneath the square the words: " Good Pfella Licorice" Packed by tafes sweets, Strathpine QLD. The same design on both sides.business, retail, advertising, business advertising usually found at agricultural shows and other promotional activities. -
 Melbourne Royal
Melbourne RoyalMemorabilia - Showbag, Life Savers and Beechies gum Showbag, 1955-1970
Together with 6 traditional rolls of Life Savers, this showbag offered the new lollipop version. Beechies gum is advertised on the verso of the showbag.Life Savers and Beechies gum showbag, no content: paper bag (printed in yellow, blue, red, green and pink) with handle, one side advertising the Life Savers range (Pep-o-Mint, Spear-o-Mint, musk, raspberry, thirst, and five flavor, and the new Life Savers lollipop); the other side advertising Beechies gum, with a yellow smiley face and five packs of gum showing the range of available flavours (strawberry, musk, orange, lime, spearmint, peppermint)[obverse] Reach for a beechies and smile! / [reverse] Life Savers, the cand with a hole / New! lollipops - the giant Life Saver on a stick / [sides] look at life through a Life Saverconfectionery, life savers, showbag, lifesavers, lollipops, commercial -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumAnimal specimen - Eastern Meadowlark, Trustees of the Australian Museum, 1860-1880
Eastern Meadowlarks live throughout the grasslands and farms in eastern North America. On the ground, their brown-and-black dappled upperparts camouflage the birds among dirt clods and dry grasses. When in flight or perching, they reveal bright-yellow breasts and bellies, and a striking black chevron across the chest. The Eastern Meadowlark has a diet which consists of mainly insects and seeds. These birds forage by walking on the ground and taking insects and seeds from the ground and from low plants. In winter, these birds may choose to forage in flocks. This specimen is part of a collection of almost 200 animal specimens that were originally acquired as skins from various institutions across Australia, including the Australian Museum in Sydney and the National Museum of Victoria (known as Museums Victoria since 1983), as well as individuals such as amateur anthropologist Reynell Eveleigh Johns between 1860-1880. These skins were then mounted by members of the Burke Museum Committee and put-on display in the formal space of the Museum’s original exhibition hall where they continue to be on display. This display of taxidermy mounts initially served to instruct visitors to the Burke Museum of the natural world around them, today it serves as an insight into the collecting habits of the 19th century.This specimen is part of a significant and rare taxidermy mount collection in the Burke Museum. This collection is scientifically and culturally important for reminding us of how science continues to shape our understanding of the modern world. They demonstrate a capacity to hold evidence of how Australia’s fauna history existed in the past and are potentially important for future environmental research. This collection continues to be on display in the Museum and has become a key part to interpreting the collecting habits of the 19th century. This Eastern Meadowlark has a yellow breast and throat with black plumage in the shape of a 'V' on it's throat. This particular specimen has a long pointed bill which is in the shape of a spear. The crown of the bird is a dark brown and it also has lighter brown/yellow stripes on the brow. The back, wings, and tail are light brown with dark brown mottling. This specimen stands upon a wooden platform and has an identification tag tied around its leg. The legs are long and the specimen has been styalised in an upright position.Label: [illegible] Ant-Eating Thrush / Catalogue, Page 66. /taxidermy mount, taxidermy, animalia, burke museum, beechworth, australian museum, skin, reynell eveleigh johns, bird, american birds, eastern meadowlark, meadowlark -
 Frankston RSL Sub Branch
Frankston RSL Sub BranchLance
Wooden standard bearers lance used by Australian colonial era Mounted Militia and, after Federation, Australian Light Horse formations. This lance is in the form of a straight wooden staff (made from ash timber) fitted with a spear-shaped pointed steel lance head (attached to the staff by rivets) and a steel shoe fitted to the base of the staff. The lance has an overall length of 2765 mm (108 inches). This lance is an example of a British 1846 Pattern mounted cavalry lance and was manufactured at the Enfield Arms Works, England, in 1848.the lance head is stamped 'ENFIELD 1848' and, on the opposite side, the characters 'C, E, 6' (vertically aligned). -
 Clunes Museum
Clunes MuseumEphemera - FIREMARKS
.1 Black plaque, raised teardrop with building, crown on top, red background with number .2 Black plaque, raised oval, showing castle and lion .3 Black plaque, rectangular, gold sun with face on blue, lion, a circular raised section with name below .4 Black rectangular plaque, spearhead shape raised, gold border, crown on top. Building depicted in spear head .5 Black plaque, circle shape raised, gold with lion and unicorn, sheild with lute/harp on top in centre.1 Royal Exchange .2 Norwich .3 Bath Sun .4 Royal Exchange .5 ABERDEEN ASSURANCE COMPANY, SCOTLAND 1825firemark, fire office, plaque -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumTextile - Cloak, Dr Deanne Gilson, Banksia Tree Cloak (water and fire business), 2022
Standing proud, still here, the spirit of ten ancestral matriarchs adorned in contemporary ceremonial cloaks. Representing our women past, present and future, her Spirit, our culture, our Country (spelt with a capital for its importance and this is part of First Peoples protocols on acknowledging Country, our strength, our resilience and healing towards a sustainable future).The sacred banksia tree was a favourite for Wadawurrung people. Flowering before deep Winter, the banksia was used for spear making and other wooden tools. The sap was drunk as a sweet drink and the seed pods used for water straining and fire sticks. The banksia tree flowers at the time when fire sticks farming is practiced marking the days before the coldest days and nights and the hotter days.White, orange, and yellow banksia design on outer cloak, yellow and white circle and diamond design in lining. Solid black trimming. Cloak is machine sewn and handstitched with hand stitching on shoulder seam.deanne gilson, wadawurrung dja, first nations art, cloak -
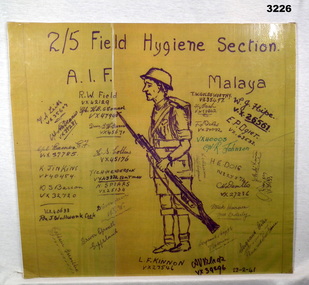 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumMemorabilia - SKETCH WW2, 23 April 1941
VX35607 PTE F. A. LEITH, VX39281 CPL A. W. DENNIS, VX 37785 CPL E F EAMES, VX40454 K. JINKINS, VX32720 D S BARTON, VX40633 COOK J. WALLWONK, CAPT GREVILLE, DRIVER SPROULL (GIPPSLAND), DRIVER KEENE (NSW), VX25134 PTE N. SPEARS, VX49884 BATMAN TICH HENDERSON, VX45176 H.S. COLLINS, VX45671 DRIVER L.W. GARRIE, VX47945 CPL H.B. O'CONNOR, VX42129 F. NASH, VX 39092 F.J. GILES, VX40003 CPL R. JOHNSON, VX25874 H.E. DOIG, VX27236 C.H. DEMILLO, MESS ORDERLY MICK HEARNEE, SGT L. ATKINSON, SGT BIGGS (VICTORIA), VX 39296 A.V. BLACK, SGT GILES (China & New Guinea), VX 26561 W.J. HIPE, VX 43532 E.P. OGIET, J.H. McKINNON, VX35133 O.A. JOYCE.Sketch - In centre in black ink is a sketch of a soldier in uniform with helmet, back pack & rifle with fixed bayonet in L hand . Khaki background. Plastic coated with white cardboard backingWritten at top: “2/5 Field Hygiene Section AIF Malaya” Written underneath: Names & numbers of Section Members2/5th field hygiene section, malaya, ww2, memorabilia -
 Melbourne Royal
Melbourne RoyalMemorabilia - Showbag, Wilmers & Gladwin Pty Ltd, Life Savers Showbag, c. 1959
Life Savers were invented in America in 1912 and produced under an agreement in Australia from 1921. The name refers to the fact that the hole in the middle will prevent choking if the sweet is swallowed whole.Life Savers showbag, no content: paper bag with string cord handle, printed in colour; one side showing a roll of Butter Scotch Life Savers and two Scottish children dancing under it; the other, a roll of Pep-O-Mint Life Savers, set against an Arctic background[obverse] 3 PACKETS FOR 1-' EVERYWHERE / BUTTER SCOTCH / LIFE SAVERS / THE CANDY WITH THE HOLE / Also obtainable / in following flavours: / Crystomint - Stick-O-Pep - Orange - Lemon - Lime" [reverse] Cooling Pep-O-Mint Life Savers, the candy mint with the hole / Also obtainable in following flavours: Spear-O-Mint - Assorted floral - Vi-O-Let - Musk - Clove - Thirst - An-O-Sed / 3 packets for 1'- everywhere / [bottom] Wilmers & Gladwin Pty Ltdconfectionery, lifesavers, showbag, commercial -
 Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages
Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for LanguagesBook, Aldo Massola, The Aborigines of south-eastern Australia : as they were, 1971
Contents: p.1-3; Origins, arrival in Australia; p.4-9; How they lived - camp sites, dating (including carbon dating); p.10-27; Physical appearance, skin colour, hair, clothing, body ornaments, cicatrization; exchange system, distribution of food, marriage &? sexual relations; the tribe - structure, relationship to land, territory, gives map showing locations of tribes, New South Wales, Victoria &? eastern South Australia, leadership, government, division of labour, status of women, estimated population at white settlement, density of population (Victoria); p.28-31; Language - names &? naming, reproduces Wembawemba vocabulary, notes use of secret languages, gives 12 rules for pronounciation; p.32-53; Religion, spirit beliefs, totemism, moieties, phratries, marriage rules; mythology, gives eaglehawk &? crow myth from Lake Victoria &? other myths illustrating origins of fire &? natural rock formations, mythical beasts (Bunyip, Mindie), stellar beliefs; magic, medicine men, powers, native remedies for sickness, describes ceremony held in Melbourne, 1847 to avert evil, sorcery, pointing bone, love magic, rain makers; messengers, appearance, etiquette, message sticks; p.54-71; Rock art, motifs, colours, decorative art, engraving of utensils, rock engravings, manufacture &? use of pigments, engraving techniques; trade system, objects bartered, meeting places for trade (Victoria), map shows possible routes (south east Australia); corroborees, purpose, body ornaments &? decorations, musical instruments; p.72-93; Ceremonial life, marriage, punishment for infidelity, birth, childhood, games &? amusements, initiation, etiquette of visiting tribes, details of ceremony, womens role, earth figures &? ground designs, bull roarers, female puberty ceremonies; p.94-133; Shelters, fire making, cooking, construction of canoes, wooden implements, use of reeds, animal skins &? sinews, shells; stone tools, cylindro conical stones, scrapers, knives &? microliths; hunting weapons, spear, other methods pits, nets; fishing methods &? spears, traps; food sharing, womens responsibilities for collecting, digging stick, cooking methods, insect foods, plant foods, water resources; manufacture &? use of spears, spear throwers, shields, clubs, boomerangs; inter- &? intratribal fighting; p.134-147; Death, disposal of body - eating of the dead, burial, cremation, platform exposure, dendroglyphs (N.S.W.), Aboriginal burial grounds (Darling &? Murray Rivers), mourning, widowhood, kopi caps (N.S.W.), causes of death, inquest ceremonies, revenge expedition, after death beliefs; p.148-157; The end of the tribes white settlement &? its impact on Aboriginal life, friction between natives &? settlers, establishment of Protectorates; copiously illustrated throughout.maps, b&w illustrations, b&w photographswemba wemba, murray river, darling river, lake victoria -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumCeremonial object - 67th BATTALION COLOURS, c. 1912
The 67th Battalion was raised in mid 1912 as a local militia training battalion in Bendigo. During World War One, many of its members enlisted in the newly formed 38th Battalion which was raised in Bendigo in 1916. At one point it was a garrison battalion stationed at Queenscliff. It was disbanded in 1918 and became the area 38th Battalion. The colours were laid up in St Paul's Cathedral in Bendigo on October 25th 1929. In 2006, with the cathedral needing to carry out repairs and alterations, the colours were offered to Bendigo's Soldiers Memorial Institute Military Museum. On 17th April, 2007 under direction from RSM Ceremonial, the colours were re-laid up in the museum in a ceremony conducted by the Reverend Peta Sherlock and witnessed by church and RSL members after 12 months of planning and putting together..1) Middle banner in the photograph. Rectangular banner representing the colours of the 67th Battalion on an olive green background. In the centre is a circular red medallion featuring an embroidered battalion badge. A purple circular border with 'Bendigo Infantry' on it surrounds the red medallion. All are surrounded by a gold and silver wreath depicting the flowers and leaves of the golden wattle. '67' is embroidered on the top right hand corner. The banner is fringed on three sides in gold. Two cords with gold and olive tassels are attached to the top right hand corner. A sewn sleeve for the pike is on the right hand side. .2) Wooden pike with metal spear head on end. A metal ring encircles the handle of the pike.battalion colours, 67th battalion, military banners, unit badges -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Newspaper - JENNY FOLEY COLLECTION: ALL TOGETHER NOW
Bendigo Advertiser '' The way we were'' from 2002. All together now, smile: Huntly School (No306), gathers in 1937 for school photos. Back row: George Nan, Neil Hamilton, Alan Bacon, Kevin Hamilton, Alex Paul, Ronnie Strauch, Neil Rutherford, Keith Bacon and Mr. Rutherford. Middle row: Miss Scamel, Ruth Boldinston, Nancy Poulter, Jessie Spears, Pat Poulter, Gwen Brown, Elva Munro, Lorna Munro and Joan Hewett. Front row: Bryan Egan, Yvonne Paul, Linda Boldiston, Lexie Munro, Win Hamilton, Joyce Nan Tie, Edie Worcester and Alan Strauch. The clip is in a folder.newspaper, bendigo advertiser, the way we were -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Booklet - Frontier Life in the Loddon Protectorate, 1967
95-page light cover booklet of Episodes from Early Days 1837-1842 in the Loddon Aboriginal Protectorate in Victoria. By Edgar Morrison. Map showing the approximate limits of the Protectorate in Victoria on title page. Map of early station boundaries on page iv. Sketch of an Aborigine holding a spear on front cover. Illustrated with B&W photos. B&W photo of Edward Stone Parker (1802-1865) Protector of Aborigines in the Loddon District. A reprint of Parker's Lecture on the Aborigines of Australia, May 10, 1854, is given in a 31-page section at the back. Foreword by Edgar Morrison Feb. 1967. Hugh McColl, Printer, 'Banner' Office, Latrobe StreetHandwritten in ink on front page. 'To Mr A. Chisholm from Alan J. Hardy (?)aborigines, loddon protectorate, edgar morrison, edward stone parker -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - HARRY BIGGS: STABLES ON GODGREYS HOMESTEAD
Black and white photo of Mr Henry Godfrey and his sons along with Prince Charlie of the Jajoweroung or Loddon Tribe. The group are standing in front of wooden stables with a window in the roof above the open door. One son is on a horse and the other is holding the reins. The boys are both wearing hats and are dressed in stockings and breeches. Mr Godfrey is the background wearing a hat riding boots, breeches and a 3/4 coat. In the front to the left is Prince Charlie holding two spears and is in native costume. At the bottom of the photo written in black ink is: Stables on Godfreys Homestead - Lake Boort - On the back of the Photo is written in clue Ink "Stables on Godfrey's Boort Homestead, Lake Boort, November 1863. W. Henry Godfrey and his sons, with "Prince Charlie" of the jajoweroung or Loddon Tribe.photo, group, godfreys homestead, stables on godfreys homestead, lake boort, prince charlie, henry godfrey and his sons. -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Harpoon, Early to mid 19th Century
A harpoon is a long spear-like instrument used in fishing, whaling, sealing and other marine hunting to catch large fish or marine mammals such as whales. It accomplishes this task by impaling the target animal and securing it with barb or toggling claws, allowing the fishermen to use a rope or chain attached to the projectile to catch the animal. The earliest known harpoons, have been recorded as having been made and used 90,000 years ago. In the early whaling industry the two flue harpoon was the primary weapon used around the world. This two fluke harpoon tended to penetrate no deeper than the soft outer layer of a whales blubber. Thus it was often possible for the whale to escape by struggling or swimming away forcefully enough to pull the shallowly embedded barbs out backwards. This flaw was corrected in the early nineteenth century with the creation of the one fluke harpoon. By removing one of the flukes, the head of the harpoon was narrowed, making it easier for it to penetrate deep enough to hold fast. In the Arctic, the indigenous people used the more advanced toggling harpoon design and by the mid-19th century, the toggling harpoon was adapted by Lewis Temple, using iron. The Temple toggle was widely used, and quickly came to dominate the whaling industry around the world.A hand forged harpoon demonstrating the blacksmiths art for fashioning an item used during the early 19th century in the significant industry of whaling. Used during a time when the world depended on the natural resources derived from whales, oil for lighting, lubrication, margarine, candles, soaps and cosmetics as well as the use of the whales bones for various other items such as corsets, umbrellas,fertiliser and animal feed. The item is significant as it was probably made between 1820-1850 after which a single fluke and toggle harpoon began to be use extensively in the whaling industry. Also coming in to general use was a black powder gun to fire the harpoon rather than the early type that had to be manually thrown by a mariner from a row boat of which the subject item is an example.Hand forged double fluke steel whaling harpoon with an arrowhead tip atop a square shank that tapers to a narrow round shaft with a split metal cone to accommodate a wooden harpoon pole.Noneharpoon, whaling, whaling harpoon, fishing industry, whales, flukes, lewis temple, marine technology, flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageSign - Hudson's Soap Enamel Advertising Sign, Patent Enamel Co Ltd, c. late 19th century- early 20th century
Hudson's Soap Powder, was the first satisfactory and commercially successful soap powder and was made in Liverpool by Robert Spear Hudson. He was also an innovator in using advertising, commissioning striking images from professional artists and paid for publicity , something which few other businesses did, and as such Hudson's soap became a household name. Horse, steam and electric tramcars, print periodicals and chemist shops carried his advertisements. This sign was manufactured by Patent Enamel Co Ltd was a company built in 1889 at Selly Oak, Borough of Birmingham, West Midlands, England, United Kingdom. The business was the first factory specifically devoted to enameled iron sign making. It had twelve furnaces for fusing the enamel, two scaling furnaces, and a large printing room, plus a huge area for steampipe drying. The company also smelted its own enamels and colour oxides. It is believed that the factory was decommissioned and demolished in the 1960's.the first factory specifically devoted to enameled iron sign making. It had twelve furnaces for fusing the enamel, two scaling furnaces, and a large printing room, plus a huge area for steampipe drying. The company also smelted its own enamels and colour oxides.The factory was decommissioned and demolished in the 1960s.The signage demonstrates the increasing demand for domestic soap products and new forms of advertising. The soap business was apart of the flourishing export trade between Australia and Britain during the height of the British Empire.Enamel advertising sign for Hudson's soapflagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime museum, hudson's soap, advertising signage, patent enamel co ltd, selly oak, borough of birmingham, robert spear hudson -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - HARRY BIGGS COLLECTION: PHOTO OF ABORIGINAL CAMP
Black and white photo of a group of Jajoweroung or Loddon Aboriginal people in front of their camp. The group consists of four women sitting behind some wooden branches and four men all in native dress. Two men are standing holding spears and two are sitting. The male standing to the left is Prince Charlie and standing to the right is Batten. Behind them is a hut made of bark and sticks. On the bottom of the photo is printed in black ink 'Aboriginal Camp - on - Boort Creek - 1863 -' Photo is inside envelope 2400 418a. On the back of photo 2400 419a the following is hand written in blue ink. The Jajoweroung or Loddon Tribe of Blacks. Aboriginal Camp - on Boort Creek, 1863. Names of Aborigines - Left to Right. Women sitting in front row - Lizzie, Caroline, Maryanne, Kitty. The two men sitting behind the women - Adam, Nero. The two men standing back row - Prince Charlie, Batten. Photo is in envelope 2400.418aphoto, group, aboriginal camp boort creek, boort creek, prince charles, jajoweroung or loddon tribe -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageArticle - Ointment, Bates & Co. (William Usher), 1851 - mid-1900s
Bates' Salve has been used as a home remedy for the treatment of boils, skin infections, splinters, pimples and insect bites for decades, from the mid-1800s to the mid-1900s. It is a drawing application for bringing out foreign bodies and pusses from a wound. There are still many families who remember using it and others who have been using it and are down to their last ‘inch’. One comment from a reader from Queensland tells how his Dad was a sleeper cutter in the 1950s and on school holidays his brother and he used to help their Dad. When doing this task after a wet season they would be confronted with spear grass about a metre high. Sometimes the spears would enter their skin, and when the spears were wet they would screw like a corkscrew into their flesh. If they left them for too long it was impossible to dig them out with a needle. That's when the Bates Salve was put into action to draw the spearhead out. "It worked wonders. It was a marvellous invention." Many people say that they would love to be able to purchase more of it today and hope that someone will produce a ‘safe’ version of it. There are several versions of a recipe for the salve available online. It appears that the salve is named after Daisy Bates, wife of the Bates’ Salve proprietor, William Usher. William’s son Victor continued making Bates’ Salve well into the mid-1900s, with the business being carried on by Victor’s only son, Alan. There are still descendants in the family home in Norwood, Adelaide. William’s great-grandchild has stated that, despite being subject to the salve during childhood, there have been no noticeable ill effects. A small notice in the Adelaide Advertiser in 1915 made a suggestion “It is said that Bates’ Salve is the popular line with OUR BOYS in Gallipoli. They recently sent to the Adelaide Red Cross for a supply, so it would be a good line to put in soldiers’ Christmas Billies.“ Over 700 ‘Christmas Billies’ were sent from generous Warrnambool citizens to our soldiers in the trenches in Gallipoli. The average cost of filling a billy with gifts was Ten Shillings, calculated at about Fifty-four Dollars in 2021. The contents included Christmas puddings and tobacco. The huge project was coordinated by a local Committee and involved generous businesses and hundreds of kind-hearted community members, with recognition sown by naming many of those involved in an article in the Warrnambool Standard. The project’s idea was initiated by Australia’s Department of Defence and all states were involved in supporting the soldiers in this way. Mr Bates (Theopholis) of Hull, England, was the original owner of the Bates’ Salve recipe. When he died he left his business to William Usher, his son-in-law. William arrived in South Australia in 1851 after he had sold his recipe to an English firm, giving them the rights to make and sell it all over the world, except in Australia. Bates then became the registered proprietor of Bates’ Salve for the Commonwealth and still had a large market for his product. William Usher made the salve at his Norwood home, in a wood-fired copper in the garden within a three-sided enclosure. The ointment was then taken to a room in the house where it was divided, labelled and packaged. It was then sent to Faulding’s Wholesale Chemist for distribution. William and his wife May (or Mary) had three children; Jack, Victor and Ivy. When May died, William married Mary Williams (May’s maid, from Tasmania, twenty years younger than William) and had seven more children. The treatment’s packaging labels it as a POISON. It seems that its active ingredient was lead oxide (22 per cent), which is no longer considered unsafe. A member of the public mentioned that in 2016 they found some Bates’ Salve in an old family medicine chest. Its label stated that the product “contains a minimum of 25.8 per cent of red lead oxide”. That particular sample was made at 470 Wallon Road, West Molesey, Surrey, England. Some people would love to be able to use the product still and even take the risk of poisoning. Instructions for its use are included on the wrapper. Here is a transcription - "Bates' Salve. Bee Brand. POISON. This Preparation contains 22 parts per centum [lead oxide]… Made by Descendants of the Inventor and Original Proprietor. For use as a medicated plaster. Melt over a slight flame or use a heated knife to spread the salve on a piece of linen. If away from a joint it will not need tying as, when put on lukewarm, the plaster will hold itself. When the salve adheres to the skin moisten it with oil and wipe it off with a dry cloth. Manufactured by the direct descendants of the inventor and the original proprietor since 1833."This package of Bates' Salve has been used as a home remedy since the mod-1800s and even up to now in 2019 by those who consider themselves lucky to still have some at home. It was promoted as a 'cure all' treatment and kept handy for use at home and away. It represents our early industry and health management when medical treatment was often difficult to access. The product is the part of many childhood memories of those alive today.Bates’ Salve ointment; oblong stick of firm, brown waxy substance wrapped in waxed paper, with an outer printed wrapper. Text on wrapper warns that it is POISON and includes instructions for use as a medicated plaster, to be heated and spread onto linen then applied to the injury. Made by Bates & Co., Adelaide. The wrapper shows an emblem of a bee. The formula has been used since 1833.Text on wrapper includes "POISO[N]", "BATES' SALVE", "BEE BRAND", "BATES & CO., ADELAIDE". "This Preparation contains 22 parts per centum [lead oxide]" There is an emblem of a bee with wings outstretched.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, bates’ salve, bates’ salve medicated plaster, bates and co adelaide, bee brand, medicated plaster, medical treatment, remedy, drawing treatment for infection, medicine cabinet, home remedy, pharmacy treatment, mid 1800s – mid 1900s remedy, topical application, treatment for boils, bites, splinters and infections, poison, preparation for treatment, ointment -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyBottle - Liquid Wax, mid 1900's
This bottle of liquid floor polish was manufactured before 1960(taken over by Wattyl) in a period when most of the floors in high traffic areas were covered in linoleum. Most of the floors using this product during this period would have been kitchens and laundries. During this period the cleanliness of the kitchen, hallways and eateries had to appear clean (cleanliness was a sign of a bacteria free area). This was a priority for kitchens, mess areas(SEC Hydro Scheme facilities) and connecting walkways. The cleanliness attitude was enhanced in the rural areas due to the "dirty" farm work not impinging upon the residential home.When Mount Beauty was first inhabited all the residential and worker's facilities were a prime area for linoleum floor surfaces. The liquid floor polish was in great demand, "a polished floor is a clean floor".This bottle of liquid floor polish is very significant to the Kiewa Valley, not only that it covers the floors of every home and residential barracks of the first major development of a "town" now known as Mount Beauty but also it demonstrates that the "cleanliness" approach of early Australians living areas in the rural regions was "on par" with its city cousins. It is the smaller types of mores that underlie the "mushrooming" cultural and psyche "wholeness" of an ever expanding Australian culture.This brown opaque glass bottle with an oblong shape has a blue coloured "screw on" cap. It has a "wrap around" label glued firmly on the bottle and covers the front and sides.On the front main label under a red line, "SPARTAN" underneath in smaller print "For use on" below this, "LINOLEUM, RUBBER, COMPOSITION AND HARDWOOD FLOORS" besides this is an encircled Trade Mark of a "Spartan Warrior holding a spear and shield" these word follow the curviture of the circle and are below it "TRADE MARK REGISTERED" Below this are "SUPER FLOOR GLOSS" to the left in very small print "Nett Contents 16 Fluid Ounces". Below this on a blue background and in white print"LIQUID FLOOR WAX WATER REPELLENT". On the bottom of the label "Made under licence by HARDIE TRADING LIMITED for SPARTAN PAINTS PTY, LIMITED" below this in small print "Melbourne, Sydney, Adelaide, Brisbane, Perth, Hobart, Launceston, Geelong. Embossed on the bootm of the glass is" G/Mfloor cleaners, liquid polish, "hygienic" clean floors. -
 Ringwood and District Historical Society
Ringwood and District Historical SocietyMixed media - Video, RDHS Guest Speaker Presentation - "Heathmont 2020 Highlights" - Gerry Robinson and Peter Le Get
Digitised video (1.11GB). Duration: 20 minutes. Recorded March, 2021. (Video is available for viewing at Ringwood & District Historical Society Archives by appointment)Presenters: Gerry Robinson and Peter Le Get of Heathmont History Group (HHG) look back over developments in the area over the previous year. HEATHMONT HIGHLIGHTS FOR 2020 Summary - "Of course for 2020 the Covid 19 virus dominated. Other finalists included roadworks on Bedford Road corner, new Wards for MCC and their elections, 100th birthday and death of Rita James, opening of Milk & Wine Co. café replacing Barclays, election of Kylie Spears as Mayor, closure of Heathmont Medical Centre, demolition of Miller homestead in Coven Avenue, final edition of Maroondah Leader local newspaper, opening of HE Parker Sports pavilion, 50 more bollard arts, and the ugliness of the former Anglican Church and other local sites." -
 University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus Archives
University of Melbourne, Burnley Campus ArchivesAlbum - Colour slides, Miscellaneous Burnley
Garden views, newly planted Melaleuca styphelioides, Garden view "BHC". "Spear Thistle Flowers". "Orchard Weed Control Terbacil?" "Feeding Hay to Merino X" "Baleo? Lucerne." 1. "Glasshouse Display." 2. Fitzroy Gardens excursion? 3. "Rose Pruning Day." 4. "Cut Flowers" growing in the Orchard. "B.H.C. Gardens" Jan 8? 5. Sequoia sempervirens & Jacaranda. 7. Student spraying in the Orchard. 8. Poly tunnel. 6, 10. Inside a greenhouse. 9. Sign "Plant Science Laboratory Lecture Room 5 →". Poly tunnel Jan? 11. Student Representative Council? 12. an unreadable sign near the Plant Research Institute. 13. Plant Research Institutue. 14. Students in Class.15. "Citrus Burnley Orchard. 16. " Student being taught how to lay irrigation pipe (Burnley?) Students in class . 17, 18..Students in Science Laboratory. 19, 20. a student on a ride-on-mower in the Gardens "Burnley" 21. Tap in the ground - irrigation?garden views, bhc, weed control, merino, lucerne, glasshouses, displays, fitzroy gardens, flowers, jacaranda, nurseries, equipment, spraying, poly tunnel, plant science laboratory, plant research institute, irrigation pipe, mower, melaleuca styphelioides, spear thistle, orchard, greenhouse, rose pruning day, greenhouses, students in class, students working outside -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumNewspaper, The Courier Ballarat, City Honored by six Royal Visits, Mar. 1938
Yields information about Ballarat and its locations or environs late 1938.Pages 11,12, 19 and 20 of the centenary of settlement in the Ballarat district by the Ballarat Courier - March 1938. See also items 186, 198 and 199. Page 11 Royal visits, banking in Ballarat, photos - NW section of Ballarat, railway station in foreground. Ads for J.McKay and Son, Roy Reeds (Men's store) and Ballarat Gas Co. Also photo of "The Corner" in Sturt St. - old Mining Exchange. Page 12 - full page ad for Morseheads, women's store. Page 19 - articles - Ballarat Lighting and Power, ESCo, SEC, electric trams. photos of the Arch of Victory, first electric tram, Lake Wendouree. Advertisements for Austin Spears (cycles), McDougall and Chisholm (drapers), W.E. Longhurst (bread) and the ES&A bank. Also article on South St. Society - music and elocution. Page 20 - articles - Ballarat Gas Co., horse and electric trams, agriculture in district and Ballarat's war record (WWI). Photos of work at Gong Gong Reservoir and Committeemen of the Ballarat Horticultural Society - 1859 to 1885. Ads for Ballarat College, Clarendon, Queens (girls) and Ballarat Grammar schools, Ern Craig Motors (Vauxhall) and Snows men's wear. Record reviewed and images of pages added 7-9-2013 and 10-9-2013trams, tramways, ballarat electricity, centenary, banking, transport, trams, esco -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Knife
From the early days of our race, the knife represented one of the first and most important tools that enabled rise of our technology, military, culture, science and all other things that brought us to this point of modern civilisation. As a vital tool for survival, combat, construction and food preparation, the knife quickly became the most basic tool from which all others were born. In those ancient times, 500,000 years ago, sharpened stones started slowly evolving, becoming more and more like their modern counterpart. Before the time when fire enabled the melting of the various metals, and forging them into modern knives, their stone counterparts received several visual upgrades. Double bladed knives were most popular, and their wooden or stone hilts were decorated with animal skins and feathers. Those knives represented a great deal of pride for the warriors and elders who owned them, and that tradition continued to be practised with the arrival of the Bronze Age. The appearance of metallurgy brought the ability to create knives from softer types of metal. Even though knives from bronze did not provide durability over longer periods of time [easily dulled, and susceptible to corrosion), their sharpness and slim designed proved to be superior to any stone knife tool. As the centuries went on, iron and then steel became commonplace across the entire world. Knives created from those materials were much more durable and easier to maintain their sharpness after prolonged use. During medieval times in Europe, steel metallurgy managed to evolve knives from small single or double-bladed edges to larger sizes - swords, spears and axes. Even with all those advancements, the use of knives as an eating utensil continued to be used in some small circles. Even as early as the 15th century, wealthy circles of people started carrying personal knives, intended for double use - both eating and defending against threats. During those times the host were not obliged to provide their guest with any kind of eating utensil in addition to plates, so wealthy males used their eating knives for cutting their own meals, and the meals of nearby female guests. Slim double-bladed knives were good for cutting and piercing foods. As the use of forks became widespread in the whole of Europe by the late 17th century, most people used this kind of small knife on a regular basis (a combination of two knives, one for stabilising and other for cutting the meal). http://www.eatingutensils.net/history-of-cutlery/knife-history/The knife is one of the most important items that has enabled the development of civilisation over thousands of years.Carving knife with wooden handle and rusted slender metal blade.None.flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked-coast, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, knife, kitchen equipment, dining -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionDrawing - Image - black and white, Angus McMillan, c1835
Angus McMillan named the Avon River after the river of the same name in his native Scotland. In 1840 he established a pastoral run at Bushy Park, north-west of the township. William Odell Raymond established a run in the area in 1842, and built his house, Strathfieldsaye, during 1848–54. European settlement did not take place without resistance, and in return, massacres were inflicted by Angus McMillan and others on Gunai people, especially between the years of 1840 and 1850. (wikipedia) The first application for the 'Bushy Park' run appears in the “Port Phillip Gazette” on 13 August 1843. It was taken up by Angus McMillan, who also took up the 'Boisdale' run for his employer Lachlan Macalister at the same time. In March 1844 a Licence to occupy the 16,000 acre 'Bushy Park' was granted to McMillan. In the late 1840s Andrew Martin and Matt McCraw built Angus McMillan's Bushy Park homestead. Aboriginal killings in Gippsland area most often were never formally recorded, but lived on in folklore, mainly in place names pinpointing what some historians now refer to as "massacres", and others as "conflicts". There is Boney Point, on Lake Wellington, Butchers Creek, near Metung, Slaughterhouse Gully, at Buchan, Skull Creek, at Lindenow, and, notoriously, Warrigal Creek, at Woodside. "Here, according to a couple of contemporary - though not eyewitness - reports, between 50 and 150 blacks were killed in an orgy of revenge after the murder and mutilation of a leading Scots settler, Ronald Macalister. If anybody had any doubts about the fitness of commemorating McMillan's name, no one voiced them then. Gippsland was, and still is, dotted with stone cairns tracing his route from Omeo, down the Tambo Valley to the fertile plains where he was to make (and lose) his fortune. And where, according to a growing body of opinion, he was to lead the "Highland Brigade", a band of armed settlers, against the Kurnai. History is fiction agreed on, and it is written by the winners. For most of the past 150 years, McMillan has been hailed as a trail-blazing pioneer. The legend began to crumble 20 years ago with publication of new histories, which at first outraged Gippsland historical societies and old residents, but which have gradually changed the way McMillan is viewed. ... Still, not all McMillan's contemporaries agreed with the "Highland Brigade" and its methods. Henry Meyrick, an English-born squatter, wrote to relatives in disgust about his neighbours. He estimated that 450 had been killed, and wrote: "Men, women and children are shot down whenever they can be met with. Some excuse might be found for shooting the men by those who are daily getting their cattle speared, but what they can urge in their excuse who shoot the women and children I cannot conceive." (http://www.theage.com.au/articles/2002/04/26/1019441303552.html, accessed 20 September 2016.) The Gippsland electorate is called 'McMillan' in his honour. Black and white image of a man wearing a coat and beret. He is Scottish born Victorian Squatter Angus McMillan of Bushy Park, Gippsland.angus mcmillan, squatter, aboriginal massacre, bushy park, gunai, avon river, pioneer -
 Federation University Art Collection
Federation University Art CollectionPainting - Artwork - Painting, Bonnie Fagan (Chew), 2013
Bonnie Fagan's County is Wadawurrung. Most of her early learning about her Aboriginality came from the father.Aboriginal dot painting telling the artist's learning journey. Bonnie Fagan wrote of this work: "Ochres reflect my connection with the land of my traditional Wadawurrung Country. Yellow ochre forms the background and white ochre defines my pathway, showing where I have traveled from my past and where I am heading in my future. I use reddish ochres for the larger dots along my pathway to show my footprint and for the smaller dots that ripple outwards to show how I've had some influence, either good or bad. The white lines show my pathway with an entry point from my past marking the start of my journey, a middle part showing were my life will continue. Through the middle part, my teenage years, the pathway is very windy. These years were sometime quite difficult and I struggled. The two circle areas symbolize two chapters in my life, first as a child and then as an adult, when I've felt mostly positive and safe. They are periods when I've been very open to learning, gathering knowledge from people and experiences that I trusted, and the circles within the circles symbolize the layers of support, of experience, of connection and of learning that I experienced. Strong visual symbols at the base of the painting under the first circle area represent the key figures in my learning through my childhood: my father (represented by the traditional symbol, of a man with a spear) and my mothers with me as a small child, The spirit of my paternal grandmother, my Nan, hovers above my childhood circle and near the pathway through to my teenage years, showing the strength of her influence and how she was always there guiding me." (Robyn Brandenburg and Jacqueline Z, Wilson [Eds] Pedagogies for the Future: Leading Quality Learning and Teaching in Higher Education, Sense Publishers, The Netherlands, 2013, pp40-41)bonnie fagan, bonnie chew, wadawurrung, artists, artwork, aboriginal -
 City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)
City of Moorabbin Historical Society (Operating the Box Cottage Museum)Photographs, x 3 Black & White Cheltenham Football Club 1909,1913, 1946, 20thC
Known as the Rosellas, the early Cheltenham Football Club sides began playing on a regular basis in 1890, and would travel long distances by steam train to play country teams, such as Ballarat where they would arrive at their destination, play the match, socialize then return to the station. Opposition players and supporters would give three hearty cheers on their departure. The Cheltenham home games were played on a paddock on the corner of Park and Charman roads in Cheltenham. In 1907 the Cheltenham progress committee made an application to the board of land works for land in Weatherall Road for recreational service to the public. That application was received and granted, then developed where Cheltenham Recreational Reserve now stands. The land in the early days was virgin bush and the response for voluntary help to clear the area was outstanding. Nearly all the market gardeners in the district along with horses, ploughs, axes, shovels completely cleared the area in three weeks. The Moorabbin council then leveled the playing area and erected a post and rail fence around the ground. Pine tree shrubs were then planted on the west side of the ground. The ground was opened in 1909 and the first Cheltenham side entered in the newly formed Federal Football Association along with seven other foundation members, Mordialloc, Mentone, Moorabbin, Frankston, Glenhuntly, Elsternwick, and Ellindale. The grand final for that year, 1909 was a hard encounter between Cheltenham and Ellindale with Cheltenham coming out victors, thus becoming the inaugural Federal Football Association premiers. Cheltenham went onto win five senior premierships in the Federal Football Association by the end of the 1920s, they won the flags in 1909, 1911, 1913, 1922 and 1925, with the late Percy Woff playing in all 5 premiership sides and was captain in 1922. 1928 saw the start of an outstanding career from our oldest living player Tom Connor. Cheltenham continued to win premierships in the 1920’s and 1930’s with juniors taking out the 1929 and 1933 flags, under the guidance of Woff, and that continued in 1934 when Cheltenham took out the 1st XVIII and 2nd XVIII premierships. Cheltenham produced its only Brownlow medallist in Peter Box who played in the late 1940s, before going to Footscray where he became a champion. The 3rd XVIII went through the season undefeated in 1974 winning the premiership, with Trevor Barker a key player before going to St Kilda the following year. The club won three senior premierships under coach Barry White in 1992, 1993 and 1995. ( from CFNC website 2019) Cheltenham Football Club was formed 1890 and succeeded in winning many Premierships as a member of the Federal Football Association, Outstanding players Peter Box Brownlow Medalist 1956 Footscay VFL, , Trevor Barker and Kevin Roberts St Kilda VFL.3x Black & White photographs of the players in the Australian Rules Cheltenham Football Club 1909, 1913 and 1946 extra photo of Peter Box Folio 10 MAV 01059a) CHELTENHAM FOOTBALL CLUB 1909 Cheltenham Football Club 1909. Back row: A Chandler, committee member; R. Robertson, back-pocket; J. Harris, half back flank; J Adams, ruck and forward-pocked; M. J. Monk, club president; L. Woff, back-pocket; W. Adams, ruck and back-pocket; P. Woff, rover and forward-pocket; A Monk, committee member. Middle row: W. Hore, back pocket and ruck; A. Towns, half-forward flank; W. Carson, full back; F. Andrews, captain-half forward flank; H. Butler, centre half back; J. Warburton, centre half-forward; A. Slater, half-back flank; F. Fisher, half-forward flank; C. Sherwood, trainer. Front Row: G Gouldthorpe, wing; H. King, full-forward; W. Johnston, ruck and forward-pocket; P Spears, rover and forward-pocket; F. Bichl, wing; A. Bichl. rover and forward-pocket; F. Butler, centre player. Courtesy, Lionel Seal. ( from CFC website 2019) b) CHELTENHAM 1913 PREMIERS c) CHELTENHAM -1946 / Back row - J. Fisher, G.Corrigan, N.Hocking, F.Virtue, R.Craven, L.Baker, M.Blundell / 2nd Row - J.Phillips, T.Connor, E.Hawkins, A.Blakely, G.Baker, A.Dark, J.Barker, D.Craven, J.Pickering, P.Cameron,/ W.Hicks, G.Hoskings, R.Beihl, A.Hubbard, R.Kier, C.Russell. / Front Row - Clark Taylor, J.Slade, N.Niel, J.Brooks, T,Butler, H.Hosking, C.Hacusler, E.Hornibrook, W.Briggs, B.Russell, L.Biehl, / W Ripponcheltenham football club, australian rules football, victorian football association, victorian football league, smith j l; smith mary ann, stanley helen, , chaff cutter, horse drawn carts, toll gates brighton, motor cars 1900, steam engines, early settlers, bentleigh, parish of moorabbin, city of moorabbin, county of bourke, moorabbin roads board, shire of moorabbin, henry dendy's special survey 1841, were j.b.; bent thomas, o'shannassy john, king richard, charman stephen, highett william, ormond francis, maynard dennis, market gardeners, vineyards, orchards, cheltenham, two acre village, holloway josiah,, woff percy, connor tom, box peter, barker trevor, white barry, browlow charles, -
 Ballarat Heritage Services
Ballarat Heritage ServicesPhotograph - Photograph - Colour, Lisa Gervasoni, Remains of Angus McMillan's Bushy Park Home, 2014, 07/06/2014
Angus McMillan was born in 1810 at Glenbrittle in the Isle of Skye. He was one of fourteens sons of Ewan McMillan. Angus McMillan arried i New South Wales in January 1839, and became an overseer for Captai nLachlan Macalister. I n 1839 Angus McMillan travelled south. He settled for a time on Jame MacFarlane's statin at Currawong. IOn 28 May 1839 Angus MacMillan stated travelling southward toward the coast. Angus Macmillan named the Avon River after the river of the same name in his native Scotland. In 1840 he established a pastoral run at Bushy Park, near Maffra. William Odell Raymond established a run in the area in 1842, and built his house, Strathfieldsaye, during 1848–54. European settlement did not take place without resistance, and in return, massacres were inflicted by Angus McMillan and others on Gunai people, especially between the years of 1840 and 1850. (wikipedia) The first application for the 'Bushy Park' run appears in the “Port Phillip Gazette” on 13 August 1843. It was taken up by Angus McMillan, who also took up the 'Boisdale' run for his employer Lachlan Macalister at the same time. In March 1844 a Licence to occupy the 16,000 acre 'Bushy Park' was granted to McMillan. In the late 1840s Andrew Martin and Matt McCraw built Angus McMillan's Bushy Park homestead. Aboriginal killings in Gippsland area most often were never formally recorded, but lived on in folklore, mainly in place names pinpointing what some historians now refer to as "massacres", and others as "conflicts". There is Boney Point, on Lake Wellington, Butchers Creek, near Metung, Slaughterhouse Gully, at Buchan, Skull Creek, at Lindenow, and, notoriously, Warrigal Creek, at Woodside. "Here, according to a couple of contemporary - though not eyewitness - reports, between 50 and 150 blacks were killed in an orgy of revenge after the murder and mutilation of a leading Scots settler, Ronald Macalister. If anybody had any doubts about the fitness of commemorating McMillan's name, no one voiced them then. Gippsland was, and still is, dotted with stone cairns tracing his route from Omeo, down the Tambo Valley to the fertile plains where he was to make (and lose) his fortune. And where, according to a growing body of opinion, he was to lead the "Highland Brigade", a band of armed settlers, against the Kurnai. History is fiction agreed on, and it is written by the winners. For most of the past 150 years, McMillan has been hailed as a trail-blazing pioneer. The legend began to crumble 20 years ago with publication of new histories, which at first outraged Gippsland historical societies and old residents, but which have gradually changed the way McMillan is viewed. ... Still, not all McMillan's contemporaries agreed with the "Highland Brigade" and its methods. Henry Meyrick, an English-born squatter, wrote to relatives in disgust about his neighbours. He estimated that 450 had been killed, and wrote: "Men, women and children are shot down whenever they can be met with. Some excuse might be found for shooting the men by those who are daily getting their cattle speared, but what they can urge in their excuse who shoot the women and children I cannot conceive." (http://www.theage.com.au/articles/2002/04/26/1019441303552.html, accessed 20 September 2016.) The Gippsland electorate is called 'McMillan' in his honour. Photographs of the remains of a timber home used by squatter Angus McMillan at his "Bushy Park" property on the Avon River. angus mcmillan, bushy park, avon river, squater -
 Eltham District Historical Society Inc
Eltham District Historical Society IncPhotograph - Digital Photograph, Alan King, Former CBA bank, Main Road, Eltham, 26 January 2008
This tiny picturesque building near the corner of John Street has served the community since 1878. At that time it served as an agency of the Heidelberg branch of the Commonwelath Bank of Australia. It has a small space inside measuring about 3.6 metres by 4.5 metres. It was built by George Stebbing who was also responsible for other heritage buildings nearby in Eltham. Covered under Heritage Overlay, Nillumbik Planning Scheme. Published: Nillumbik Now and Then / Marguerite Marshall 2008; photographs Alan King with Marguerite Marshall.; p93 The tiny picturesque building on Main Road, Eltham, near the corner of John Street, has served the community since 1878. At that time the building, which inside measures only about 3.6m by 4.5m served as an agency of the Heidelberg branch of the Commercial Bank of Australia. The yellow and orange Victorian brick structure was built by Mr George Stebbing.1 Mr Stebbing, who also built the Anglican and former Methodist churches and the Shillinglaw Cottage, had come from England and lived in Pitt Street. The bank is a fine example of a once common but now rare building style – the single room bank. It compares with another in the municipality, also a former Commercial Bank of Australia branch, the timber Little Bank Building in Hurstbridge, built around the early 1900s.2 The Eltham bank, which was said to store gold from the Eltham - Research mining areas, has had exciting moments. A bullet hole still visible in a cedar bench testifies to the drama in 1949 when a youth held up the bank. After the 19-year-old opened an account as John Henderson, he walked to the door and then turned pointing a pistol. But it was shots fired by the clerk, Lindsay Spear, that saved the day, frightening the youth, who drove off empty-handed in a grey sports car. He was later apprehended and given a two-year sentence. Soon afterwards the agency was upgraded to a branch. However by 1954 the bank no longer needed the branch and the adjoining Methodist Church bought the building. It proved useful for the Church’s young people who furnished it and used it for their meetings. A youth club developed, led by young adult member, Ross Gangell. The building was also used as a Sunday School, which with junior membership numbered 27.3 Around 1960, Mrs Alma Bell, of the Methodist Church Women’s Guild, suggested using the building as an opportunity shop to raise funds for a chaplain at the Eltham High School. The women later asked the nearby St Margaret’s Anglican Church to help them in the shop. In 1960 the Eltham Combined Churches Opportunity Shop was established and staffed by Methodist and Anglican parishioners, notably Methodist Mrs Gwen Miller. The shop originally opened on Child Endowment Days to help the needy, but later for years, it opened twice a week. In 1962 it donated clothing and shoes to the Eltham Bushfire Appeal. By 1963 the chaplaincy scheme ceased. So the £450 raised was then donated to the Council for Christian Education and to the participating churches. Funds were also donated to local charities including the Eltham and Research Fire Brigades, the Austin Hospital Auxiliary, the Benevolent Society, the Red Cross and the Diamond Valley Hospital.4 In 2008 the Opportunity Shop volunteers continue to work together to help the local community. Although crammed with second-hand goods, the simple, almost stark interior, is still evident and is relieved only by a front rectangular window and an unused fireplace. Outside, the chimney, the corrugated iron peaked roof, and the surrounding varied plants, add to the charm of this sound building which continues to serve the community well.This collection of almost 130 photos about places and people within the Shire of Nillumbik, an urban and rural municipality in Melbourne's north, contributes to an understanding of the history of the Shire. Published in 2008 immediately prior to the Black Saturday bushfires of February 7, 2009, it documents sites that were impacted, and in some cases destroyed by the fires. It includes photographs taken especially for the publication, creating a unique time capsule representing the Shire in the early 21st century. It remains the most recent comprehenesive publication devoted to the Shire's history connecting local residents to the past. nillumbik now and then (marshall-king) collection, cba bank
