Showing 82 items matching "electric conversion"
-
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumPhotograph - Cable tram dummy outide Myer Lonsdale St, 1924-1925
... electric conversion... of the track in this section of Lonsdale St and the electric conversion... of the track in this section of Lonsdale St and the electric conversion ...Postcard of cable tram dummy stationary outside the double story "Myers" Parcels Office in Lonsdale Street, demolished late in 1925, between Elizabeth and Swanston Streets. Three boys in shorts sit or stand on the dummy. The dummy's destination reads "Brighton Rd", which dates the photograph as between February 1924 and December 1925, (not c1929 as written) between the construction of the track in this section of Lonsdale St and the electric conversion of the Brighton Rd line. Also in the street are horse drawn carts and motor cars.Yields information about cable trams in Lonsdale St and MyerBlack and white postcard print with note on rear.In print on rear: "c1929 Lonsdale Street Warehouse, later to become 11-storey store. MYER - GROWING WITH AUSTRALIA since 1901 - today employs over 32,000 staff throughout the country in its Department Stores, Target Discount Stores and Supermarkets, speciality fashion stores, liquor and fast food outlets. AFFIX STAMP HERE"myers, lonsdale st, cable dummy, brighton rd line, electric conversion, horse drawn carts, warehouse, boys, shorts -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumNewspaper, The Leader, “The trams that gave a better service”, 15/04/1981 12:00:00 AM
... of conversion to electric trams. Conversion took 15 years. "...lost... Government ordered a start of conversion to electric trams ...Newspaper clipping titled: “The trams that gave a better service” The Leader, Wednesday, April 15, 1981 Photo and text Alf Twentyman, cable trams Expert on cable trams. Purchased 2 cable tram cars for 20 pounds each in 1940. Also bought one of the dummies that pulled the cars for 30 shillings. Vehicles renovated and stored in his backyard in Bastings St Northcote. Spends hours each day restoring trams to their 1890 condition. Life member of Tramway Museum Society. End of cable tram era began in 1925, when State Government ordered a start of conversion to electric trams. Conversion took 15 years. "...lost frequency of service with electric trams...cable trams would come every 2 minutes..."trams, tramways, cable trams, enthusiasts, restoration -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumDocument - Manuscript, "Ballarat Tramways", 1950's
... history in Ballarat, opening of the electric routes, (conversion..., opening of the electric routes, (conversion of horse trams ...Each copy consists of a chapter, one page titled "Early History", five pages titled "Part 1 - Horse Trams - Ballarat 1887 - 1905, Sebastopol 1893 - 1912, Ballarat East Nil" Notes on the construction of the tramway, opening, personalities, Julien Battery tram, and half a page titled "Bits of Interest". The 3rd chapter, 3 pages, titled "Part 2 - Electric Trams - Ballarat 1905, Ballarat East, Sebastopol 1912". Notes the early power supply history in Ballarat, opening of the electric routes, (conversion of horse trams to electric), and the purchase of new trams ex Melbourne 1930. Chapter ends with 3 short paragraphs notes on the SEC taking over, Conductresses during the war and reconstruction. Author - unknown - possibly the SEC, Les Denmead and others - notes the scrubber car still in service in 1969? See also item 106 and 6419 for similar documents.Yields detailed information about the history of Ballarat's tramways.Three copies of a typed manuscript titled "Ballarat Tramways" - 18 foolscap pages. Each document has been typed, 1.5 line spacing on foolscap paper, 2nd and 3rd copies are carbon copies.On front cover of copy 1 hand written in black ink "BTPS No. 419". Copy 3 has "Incomplete" on the top right hand corner.trams, tramways, manuscript, ballarat tramways, ballarat, horse trams, esco, statistics -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Report, Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), Statement by the Chairman (MMTB) to the Committee of Public Accounts of the Parliament, c1927
... with the electric system, costs, conversion of the cable car routes..., comparison with the electric system, costs, conversion of the cable ...Report - duplicated - 12 foolscap sheets pinned with a brass clip in the top left hand corner, titled "Statement by the Chairman (MMTB) to the Committee of Public Accounts of the Parliament of the State of Victoria", not formally dated, but c1927. Report looks at the establishment of the Board, operation of the cable tram system, failures, accidents, comparison with the electric system, costs, conversion of the cable car routes, a summary of the cable stoppages, issues with cable trams, shunting, ropes, accidents and operational matters.trams, tramways, mmtb, parliament, victorian government, finances, buses, cable trams, conversion, accidents -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumNewspaper, The Courier Ballarat, "From horse-buses to Trams and back to buses?", 24/08/1968 12:00:00 AM
... , electric trams and possible conversion back to buses. Has three..., trams and electric trams. Horse Trams Buses ESCo SEC Newspaper ...Yields information about the public transport methods in Ballarat from horse cabs, buses, trams and electric trams.Newspaper clipping from The Courier, Sat. 24/8/1968, Saturday Magazine, titled "From horse-buses to Trams and back to buses?". Written by K. Mackenzie, looks at the history of public transport in Ballarat, the construction of the horse trams, electric trams and possible conversion back to buses. Has three well known photos of horse trams and a horse drawn, two wheeler cab.horse trams, buses, esco, sec -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumBook, Denver Tramway Corporation, "As U Go", 1950
... of the conversion of electric streetcar systems to buses - forward by Mayor... of the conversion of electric streetcar systems to buses - forward by Mayor ...12 page printed booklet, titled "As-U-Go", Souvenir edition, issued for the retirement of Denver's USA streetcar system, June 3 1950, by the Denver Tramway Corp. Features horse trams, short history, cable trams, steam trams, electric tram, funeral car, sight seeing and buses. Shows viewpoints of the conversion of electric streetcar systems to buses - forward by Mayor of Denver, Quigg Newton. trams, tramways, denver, usa -
 Melbourne Tram Museum
Melbourne Tram MuseumDocument - Report, Parliament of Victoria, "Report of the Royal Commission - Railway and Tramway systems on Melbourne and Suburbs", Nov. 1911
... for Melbourne, operational speeds, use of cable conduits for electric..., operational speeds, use of cable conduits for electric traction ...Report - 42 pages, 3 sections, stapled on the left hand edge, titled "Report of the Royal Commission appointed to inquire into and report upon the Railway and Tramway systems on Melbourne and Suburbs" - dated 1911. Looks at the state of the Suburban rail system, finances, electrification's, costs, evidence of Mr. Merz, advantages of the electrification, power supply and standards, whether AC or DC, duplication, Glen Iris line, conclusions and recommendations. Tramway - summarises the current tramways operating, cable system and operational stats, the current tramway systems, other cities, relative merits, future tramways for Melbourne, operational speeds, use of cable conduits for electric traction, conversion, municipal control , control of the tramways by the railways, a general scheme, formation of a larger tramway trust and its management, purchase of the cable tramways and recommendations. Note: This document is available as a pdf on the Parliament of Victoria website. 2nd copy added 2-1-2019 from donation of Norm Cross.In ink in the top right hand corner "TB"trams, tramways, tramways, cable trams, finances, conversion, railways, royal commission, costs -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - BASIL MILLER COLLECTION: TRAMS - 'RUNNING JOURNAL', June 1972
... when the line was back to conversion to electric traction... when the line was back to conversion to electric traction ...Journal of the Tramway Museum society of Victoria. Ltd. Volume 9, No. 3, June 1972. Thirty five cents. Twenty pages. Front cover (right) shows photo of Swanston Street Melbourne in the era of the American system of painless dentistry,cobbled streets, verandah posts and cable tram. From 1888 the brightly painted car from city to Prahran and St. Kilda until December 1925 when the line was back to conversion to electric traction. History of document: part of 'Basil Miller Tramways Collection'.document -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumNewspaper, The Courier Ballarat, "Fifty years of electric trams in Ballarat", 30/04/1955 12:00:00 AM
... of electric trams in Ballarat, conversion of horse trams, trams ex... of electric trams in Ballarat, conversion of horse trams, trams ex ...Newspaper Clipping from The Courier, Ballarat Sat. 30 April 1955, titled "Fifty years of electric trams in Ballarat". Features photo of the opening of the tramway to Lydiard St. North, Norman St in 1937 and Leo Grant, depot worker, working on the undergear of Ballarat No. 19. Notes the number of staff employed, Mr. L. J. Denmead as Superintendent, 67 motormen or conductors, four inspectors, a senior inspector, 12 track men and 12 depot workers and a number of traffic clerks. Gives a history of electric trams in Ballarat, conversion of horse trams, trams ex Sydney, fares, replacement trams, trailers, conductresses, bogie trams, gold tram, reconditioning of the system. ballarat, sec, esco, reconstruction -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph - Kiewa River in flood at Clover Dam
As part of the push to cut electricity costs and diversify supply, the Victorian Government (circa 1930) implemented the conversion strategy from mainly brown coal supply to hydro - electricity. The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme became the largest scheme of its kind in the State Of Victoria and the second largest scheme in Australia. Clover Dam and Power Station were built by the State Electricity Commission of Victoria as part of the Kiewa Hydro Electric Scheme from the late 1930's to the early 1940's. This dam was constructed to supply water to feed four turbines (62 mega watts) at the West Kiewa Power Station. This was at the forefront of sustainable "Green" energy. Costs associated with power supplies is still a major incentive of governments, however environmentally friendly alternatives such as wind and nuclear have also made inroads. The Kiewa valley and its surrounding alpine catchment were looked at(Victorian State Government), from the beginning of the twentieth century as a source of alternate power for an ever-increasing demand for electricity by growing population and heavy industrial areas within Melbourne City and State regions. Construction of dams, such as Clover Dam provided the large quantity holding areas of water required to turn the turbines at the various power stations to provide the electricity needed. The impact of these controls by moderating water run-off from the alpine regions is beneficial in reducing flooding from thawing of snow on the alps. This by-product allows agriculture and grazing to be less vulnerable to seasonal flooding thereby resulting in a more stable annual production level.Black and white photograph of Clover Dam with Kiewa River in flood. .5mm white boarder on 3 sides of photo.Handwritten on back of photograph in black pen - Kiewa in flood. Clover Dam.clover dam, secv -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph - Clover Dam
As part of the push to cut electricity costs and diversify supply, the Victorian Government (circa 1930) implemented the conversion strategy from mainly brown coal supply to hydro - electricity. The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme became the largest scheme of its kind in the State Of Victoria and the second largest scheme in Australia. Clover Dam and Power Station were built by the State Electricity Commission of Victoria as part of the Kiewa Hydro Electric Scheme from the late 1930's to the early 1940's. This dam was constructed to supply water to feed four turbines (62 mega watts) at the West Kiewa Power Station. This was at the forefront of sustainable "Green" energy. Costs associated with power supplies is still a major incentive of governments, however environmentally friendly alternatives such as wind and nuclear have also made inroads. The Kiewa valley and its surrounding alpine catchment were looked at(Victorian State Government), from the beginning of the twentieth century as a source of alternate power for an ever-increasing demand for electricity by growing population and heavy industrial areas within Melbourne City and State regions. Construction of dams, such as Clover Dam provided the large quantity holding areas of water required to turn the turbines at the various power stations to provide the electricity needed. The impact of these controls by moderating water run-off from the alpine regions is beneficial in reducing flooding from thawing of snow on the alps. This by-product allows agriculture and grazing to be less vulnerable to seasonal flooding thereby resulting in a more stable annual production level.Black and white photograph of Clover Dam buildings and Kiewa River. Has a .4cm white border around photograph Printed on bottom left corner of photograph in white - Clover Flatclover dam, secv -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotographs x 2 - Clover Dam, Circa 1940's
As part of the push to cut electricity costs and diversify supply, the Victorian Government (circa 1930) implemented the conversion strategy from mainly brown coal supply to hydro - electricity. The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme became the largest scheme of its kind in the State Of Victoria and the second largest scheme in Australia. Clover Dam and Power Station were built by the State Electricity Commission of Victoria as part of the Kiewa Hydro Electric Scheme from the late 1930's to the early 1940's. This dam was constructed to supply water to feed four turbines (62 mega watts) at the West Kiewa Power Station. This was at the forefront of sustainable "Green" energy. Costs associated with power supplies is still a major incentive of governments, however environmentally friendly alternatives such as wind and nuclear have also made inroads. The Kiewa valley and its surrounding alpine catchment were looked at(Victorian State Government), from the beginning of the twentieth century as a source of alternate power for an ever-increasing demand for electricity by growing population and heavy industrial areas within Melbourne City and State regions. Construction of dams, such as Clover Dam provided the large quantity holding areas of water required to turn the turbines at the various power stations to provide the electricity needed. The impact of these controls by moderating water run-off from the alpine regions is beneficial in reducing flooding from thawing of snow on the alps. This by-product allows agriculture and grazing to be less vulnerable to seasonal flooding thereby resulting in a more stable annual production level. Photographs also document early engineering and building techniques used in the construction of dams and power stations during the 1940’s and 1950’s. Note the lack of safety equipment and suitable work attire worn by construction workers on the sites 1. Black and white photograph of Clover Dam under construction. Has a .5cm white border around photo 2. Black and white photograph of Clover Dam under construction showing workmen at work. Has a .5cm white border around photo Written in pencil on back of both photographs - Clover Damclover dam, secv -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph - Folder of Photographs (KVHS 1150 A - F) – Photocopied set of black and white photographs from the display folder (pages 1 - 8) put together by KVHS to document life on the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric Scheme
Although the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme was first proposed in 1911, construction did not commence until 1938. As part of the push to cut electricity costs and diversify supply, the Victorian Government (circa 1930) initiated the conversion from primarily brown coal supply to hydro – electricity. Field investigations during the 1940’s resulted in a new proposal for a scheme that had more than double the capacity of the 1938 scheme. The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme became the largest scheme of its kind in the State Of Victoria and the second largest scheme in Australia. The number of personnel involved in the planning and construction of the scheme increased dramatically. During the late 1940’s, most activity centred around the construction of the West Kiewa Power Station, Rocky Valley Reservoir, McKay Creek Power Station and the Bogong Creek Aqueduct.A common thread across all the larger hydro scheme constructions was the need for workers, both qualified and unqualified who came from around the world seeking a new life for themselves and their families. New accommodation and facilities were required for the army of workers engaged in construction in often remote and wild areas. The SEC had a high demand for timber, and set up the first of a number of sawmills at Bogong Creek in 1939 and set up the first hardwood logging in the headwaters of the Kiewa River. These new ‘towns’ such as Mt Beauty and Bogong, survived, serving the needs of operational personnel and their families, and expanding with growth of new industries. Mount Beauty, and to a lesser extent Bogong, are among these places. Large A3 size spiral bound display folder containing 21 of 58 pages of photocopied black and white photographs of various aspects of the early days of the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric scheme including equipment, various work sites and photographs of workers and their families. 1-Front page; 2-Security gate at Mt Beauty Camp; 3-Channel 1 on East Kiewa River; 4-Junction Dam – Diversion Tunnel Inlet; 5-Sawmill; 6- Homan’s Gap Sawmill; 7 Junction Dam: 8-Homan Dam Site-Diamond Drilling on River Buttress; 9- Homan Dam Site View Upstream 10-Homan Dam Investigation Camp 1-Windsor & Newton Visual Diary 60 sheet (120 pages) 11’ x 14’ 280 x 356mm 110 GSM Acid Free Drawing Paper 2-1940-Security Gate on Mt Beauty side of Kiewa River bridge. Part of old Mt Beauty camp and mess in background 3- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date; 11.3.40 Time: 10.30am No K35 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works. Diverting East Kiewa River into Channel Page number 1 4-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 5.4.40 Time: Noon No K58 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works. Junction Dam – Diversion Tunnel Inlet – Normal Flow Page number 2 5- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 19.8.42 Time: 2.30pm No K883 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works. Sawmill – General View Page number 3 6- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 12.1.42 Time: 2.00pm No K540 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works. Homan’s Gap Sawmill – General View Page number 4 7- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 12.1.42 Time: 2.00pm No K540 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works. Junction Dam – General View looking upstream Page number 5 8- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 16.11.45 Time: 10.32amm No K52153 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Homan Dam Site – Diamond Drilling on River Buttress Page number 6 9-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 15.1.45 Time: 4.10pm No K1781 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Homan Dam Site – View Upstream Page number 7 10- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 15.1.45 Time: 4.10pm No K1781 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Homan Dam Investigation Camp 1944 – 1945 Page number 8 secv; kiewa hydro electric scheme; mt beauty; bogong; construction work; -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph - Folder of Photographs – Photocopied set of black and white photographs (pages 9 - 18) from the display folder put together by KVHS to document life on the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric Scheme
Although the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme was first proposed in 1911, construction did not commence until 1938. As part of the push to cut electricity costs and diversify supply, the Victorian Government (circa 1930) initiated the conversion from primarily brown coal supply to hydro – electricity. Field investigations during the 1940’s resulted in a new proposal for a scheme that had more than double the capacity of the 1938 scheme. The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme became the largest scheme of its kind in the State Of Victoria and the second largest scheme in Australia. The number of personnel involved in the planning and construction of the scheme increased dramatically. During the late 1940’s, most activity centred around the construction of the West Kiewa Power Station, Rocky Valley Reservoir, McKay Creek Power Station and the Bogong Creek Aqueduct.A common thread across all the larger hydro scheme constructions was the need for workers, both qualified and unqualified who came from around the world seeking a new life for themselves and their families. New accommodation and facilities were required for the army of workers engaged in construction in often remote and wild areas. The SEC had a high demand for timber, and set up the first of a number of sawmills at Bogong Creek in 1939 and set up the first hardwood logging in the headwaters of the Kiewa River. These new ‘towns’ such as Mt Beauty and Bogong, survived, serving the needs of operational personnel and their families, and expanding with growth of new industries. Mount Beauty, and to a lesser extent Bogong, are among these places. PHYSICAL: Large A3 size spiral bound display folder containing 21 pages of photocopied black and white photographs of various aspects of the early days of the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric scheme including equipment, various work sites and photographs of workers and their families. 1-Bridge across Tailrace Channel 1946 2-New Mess building, Mt Beauty 3-Homan’s Gap Saw Mill 4- Diamond Drilling Plant – Big Hill 5-Rocky Valley Camp-Mess Building 6-Parlimentary Party at Rocky Valley 7-No.4 Headrace Tunnel 8- Allis-Chalmers Tractor School 9- SECV Heavy Machinery lined up by road 10- No. 5 Raceline – Balasting Track with improvised truck 1-1946 – Bridge across tailrace channel Page number 9 2-New mess building, Mt Beauty 6.4.46 Page number 10 3- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 10.1.47 Time: 11.40am No K2271 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Homan’s Gap Saw Mill – Rip Saw Page number 11 4- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 5.10.47 Time: 11am No K4111 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Diamond Drilling Plant – Big Hill Page number 12 5- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 11.2.48 Time: 3pm No K4277 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Rocky Valley Camp-Mess Building Page number 13 6- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 15.4.48 Time: 4.30pm No K4397 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Parlimentary Party at Rocky Valley Page number 14 7- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 22.8.48 Time: 9am No K4668 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works General view of No.4 Headrace Tunnel Page number 15 8-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 5.9.49 Time: 10am No K5180 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Allis-Chalmers Tractor School – HD 19, Mr I Crossthwaite at Controls Page number 16 9- No markings Page number 17 10- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 7,12.49 Time: 4pm No K5423 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works No. 5 Raceline – Balasting Track with improvised truck. Page number 18 secv; kiewa hydro electric scheme; mt beauty; bogong; construction area -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph - Folder of Photographs – Photocopied set of 10 black and white photographs (pages 19 - 28) from the display folder put together by KVHS to document life on the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric Scheme
Although the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme was first proposed in 1911, construction did not commence until 1938. As part of the push to cut electricity costs and diversify supply, the Victorian Government (circa 1930) initiated the conversion from primarily brown coal supply to hydro – electricity. Field investigations during the 1940’s resulted in a new proposal for a scheme that had more than double the capacity of the 1938 scheme. The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme became the largest scheme of its kind in the State Of Victoria and the second largest scheme in Australia. The number of personnel involved in the planning and construction of the scheme increased dramatically. During the late 1940’s, most activity centred around the construction of the West Kiewa Power Station, Rocky Valley Reservoir, McKay Creek Power Station and the Bogong Creek Aqueduct.A common thread across all the larger hydro scheme constructions was the need for workers, both qualified and unqualified who came from around the world seeking a new life for themselves and their families. New accommodation and facilities were required for the army of workers engaged in construction in often remote and wild areas. The SEC had a high demand for timber, and set up the first of a number of sawmills at Bogong Creek in 1939 and set up the first hardwood logging in the headwaters of the Kiewa River. These new ‘towns’ such as Mt Beauty and Bogong, survived, serving the needs of operational personnel and their families, and expanding with growth of new industries. Mount Beauty, and to a lesser extent Bogong, are among these places. Large A3 size spiral bound display folder containing 21 pages of photocopied black and white photographs of various aspects of the early days of the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric scheme including equipment, various work sites and photographs of workers and their families. 1-Allis Chalmers Tractor School 2- Gardens outside Administrative Office – Mt Beauty 3- Mt Beauty house – 1950 4-Bridge over Pretty Valley River, Bogong 5-Rocky Valley Spillway Tunnel break through 6-Ni 1 Headrace Tunnel drilling face 7-No 4 Power Station Drilling 8-Clover Dam Flood Waters 9-No1 Head Race Tunnel Portal Building 10-Clover Dam 1-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 5.9.49 Time: 10amm No K5174 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Allis Chalmers Tractor School Page number 19 2-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 22.2.50 Time: 3.30pm No K5601 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Gardens outside Administrative Office – Mt Beauty Page number 20 3-Mt Beauty house – 1950 Page number 21 4-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 23.10.50 Time: 11.15am No K6331 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Bogong-Bridge over Pretty Valley River Page number 22 5-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 23.6.50 Time: 2.30pm No K5844 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works ROCKY VALLEY SPILLWAY TUNNEL BREAK THROUGH Page number 23 6-20/3/52 – No. 1 Headrace Tunnel Drilling face (E.E.E. contract) Page number 24 7-6/6/52 – No 4 Power Station – Drilling Page number 25 8-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 6/6/52 Time: No K7113 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works Clover Dam Flood Waters Page number 26 9-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: Oct 1952 Time: No K7239 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works No. 1 HEAD RACE TUNNEL PORTAL BUILDING. Handwritten underneath – This information from Ron White-the later Principal Hydro Engineer of the SEC. Oct 1952 Location incorrect? All work on No 1 had ceased after financial crash of 1951. This photo would refer to No 4 Headrace Tunnel? Page number 27 10-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: Jan 1953 Time: No K7307 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works CLOVER DAM Page number 28 secv; kiewa hydro electric scheme; bogong; mt beauty; construction area -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph - Folder of Photographs – Photocopied set of 10 black and white photographs (pages 29 - 38) from the display folder put together by KVHS to document life on the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric Scheme
Although the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme was first proposed in 1911, construction did not commence until 1938. As part of the push to cut electricity costs and diversify supply, the Victorian Government (circa 1930) initiated the conversion from primarily brown coal supply to hydro – electricity. Field investigations during the 1940’s resulted in a new proposal for a scheme that had more than double the capacity of the 1938 scheme. The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme became the largest scheme of its kind in the State Of Victoria and the second largest scheme in Australia. The number of personnel involved in the planning and construction of the scheme increased dramatically. During the late 1940’s, most activity centred around the construction of the West Kiewa Power Station, Rocky Valley Reservoir, McKay Creek Power Station and the Bogong Creek Aqueduct.A common thread across all the larger hydro scheme constructions was the need for workers, both qualified and unqualified who came from around the world seeking a new life for themselves and their families. New accommodation and facilities were required for the army of workers engaged in construction in often remote and wild areas. The SEC had a high demand for timber, and set up the first of a number of sawmills at Bogong Creek in 1939 and set up the first hardwood logging in the headwaters of the Kiewa River. These new ‘towns’ such as Mt Beauty and Bogong, survived, serving the needs of operational personnel and their families, and expanding with growth of new industries. Mount Beauty, and to a lesser extent Bogong, are among these places. Large A3 size spiral bound display folder containing 21 pages of photocopied black and white photographs of various aspects of the early days of the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric scheme including equipment, various work sites and photographs of workers and their families. 1-Mt Beauty Pondage inlet-Regulating weir 2-Langfords Gap Basalt Hill-Tunnel in quarry face.3-Rocky Valley Camp-from Engineering Office 4-Basalt Hill tunnel portal 5-No 1 Pressure Shaft Works Bench 6-No 1 Power Station 7-Overturned haulage wagons on the side of an embankment 8- Group of workers dressed in wet weather gear inside a tunnel 9-Workmen and vehicle in tunnel 10-Howman’s Gap campsite at 4,150 feet 1-1954 – Mt Beauty Pondage inlet – Regulating weir Page number 29 2-28/10/54 – Langfords Gap Basalt Hill – Tunnel in quarry face K7860 Page number 30 3-STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 17.8.55 Time: No K8132 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works ROCKY VALLEY CAMP – FROM ENGINEERING OFFICE Page number 31 4-28/10/54 – Basalt Hill tunnel portal K7859 Page number 32 5-No.1 Pressure Shaft Works Bench 5.7.56 Page number 33 6- No. 1 Power Station 26.4.59 Page number 34 7- No markings Page number 35 8-No markings (Wooden board on ground printed with - POLAR A.N.GELATINE DYNAMITE “75” DE 28.8.40) Page number 36 9-No markings Page number 37 10-Howman’s Gap campsite at 4,150 feet Page number 38 secv; kiewa hydro electric scheme; mt beauty; bogong; construction area -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph - Folder of Photographs – Photocopied set of black and white photographs (pages 49 -58) from the display folder put together by KVHS to document life on the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric Scheme
Although the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme was first proposed in 1911, construction did not commence until 1938. As part of the push to cut electricity costs and diversify supply, the Victorian Government (circa 1930) initiated the conversion from primarily brown coal supply to hydro – electricity. Field investigations during the 1940’s resulted in a new proposal for a scheme that had more than double the capacity of the 1938 scheme. The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme became the largest scheme of its kind in the State Of Victoria and the second largest scheme in Australia. The number of personnel involved in the planning and construction of the scheme increased dramatically. During the late 1940’s, most activity centred around the construction of the West Kiewa Power Station, Rocky Valley Reservoir, McKay Creek Power Station and the Bogong Creek Aqueduct.A common thread across all the larger hydro scheme constructions was the need for workers, both qualified and unqualified who came from around the world seeking a new life for themselves and their families. New accommodation and facilities were required for the army of workers engaged in construction in often remote and wild areas. The SEC had a high demand for timber, and set up the first of a number of sawmills at Bogong Creek in 1939 and set up the first hardwood logging in the headwaters of the Kiewa River. These new ‘towns’ such as Mt Beauty and Bogong, survived, serving the needs of operational personnel and their families, and expanding with growth of new industries. Mount Beauty, and to a lesser extent Bogong, are among these places. Large A3 size spiral bound display folder containing photocopied black and white photographs of various aspects of the early days of the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric scheme including equipment, various work sites and photographs of workers and their families. 1-Workmen working inside one of the tunnels. 2-Workman drilling in West Kiewa Tunnel 3-Junction Dam wall construction 4&5-2B&W photographs Kiewa House residents ready to go to a ball in Mt Beauty 6-Workmen warming up in front of a fire at No 1 bench 7-Workmen being hauled in at No 4 P.S Shaft 8-No 4 Power Station – Drilling 9-Workmen eating a hot meal in the tunnel. 10-2 photographs (a)Pretty Valley camp showing workman’s huts and construction materials & (b)Worker in Langford Gap Basalt Hill Tunnel face 11-Tunnel entrance (unlabelled) with rail tracks in foreground 12- Workmen drilling at No 1 Head race tunnel-Drilling face 13- No 1 Power Station 14-Workmen at the entrance to one of the SECV tunnels under construction 1-SECV number at bottom of picture Half obscured possibly K8461 Page number 53 2-In West Kiewa Tunnel Page number 54 3- Construction of Junction Dam wall – approximately 1941 Page number 55 4&5- Residents of Kiewa House at Bogong ready to go to the ball at Mt Beauty-1946. Handwritten on a copy of the photo on opposite page Mrs Lorna Crosset filled out the names *Dad was Des Crossett – his daughter is Gael Petcopoulis Greta engaged to John broke it off. Charlie, Rosalind, Bill, Priscilla, Max Lawrence-Dad’s Boss, Mary & Max married, Mary, Kay, Gwen McPherson Mum’s boss, John McCluskey (c) At No. 5 Bench Page number 56 6- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 27.2.51 Time:2.15pm No K6373 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works No. 4 P.S. Shaft – Haulage of men in buckets (b) As above Handwritten at top of photo Appendix 4 page number 57 7- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 6.6.52 Time:… No K7122 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works No. 4 POWER STATION – DRILLING page number 58 8-No markings page number 59 9-(a)Handwritten under photograph Approx. 1948/49 (b) STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 28.10.54 Time:.. No K7860 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works LANGFORD GAP BASALT HILL TUNNEL FACE Page number 49 10-(a) No markings 11- STATE ELECTRICITY COMMISSION OF VICTORIA Date: 20.3.52 Time: No K6979 Kiewa Hydro Electric Works No. 1 HEAD RACE TUNNEL – DRILLING FACE (E.E.E. CONTRACT) ‘The Frenchies’ (E.E.E) as they were affectionately known Page number 50 12-31.5.56 No. 1 Power Station Aggregate Stock Piles. Page number 51 13&14-No markings Page number 52 secv; kiewa hydro electric scheme; bogong; mt beauty; construction area -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPhotograph - Folder of Photographs – Photocopied set of black and white photographs (pages 39 - 48) from the display folder put together by KVHS to document life on the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric Scheme
Although the Kiewa Hydro-Electric Scheme was first proposed in 1911, construction did not commence until 1938. As part of the push to cut electricity costs and diversify supply, the Victorian Government (circa 1930) initiated the conversion from primarily brown coal supply to hydro – electricity. Field investigations during the 1940’s resulted in a new proposal for a scheme that had more than double the capacity of the 1938 scheme. The Kiewa Hydroelectric Scheme became the largest scheme of its kind in the State Of Victoria and the second largest scheme in Australia. The number of personnel involved in the planning and construction of the scheme increased dramatically. During the late 1940’s, most activity centered around the construction of the West Kiewa Power Station, Rocky Valley Reservoir, McKay Creek Power Station and the Bogong Creek Aqueduct.A common thread across all the larger hydro scheme constructions was the need for workers, both qualified and unqualified who came from around the world seeking a new life for themselves and their families. New accommodation and facilities were required for the army of workers engaged in construction in often remote and wild areas. The SEC had a high demand for timber, and set up the first of a number of sawmills at Bogong Creek in 1939 and set up the first hardwood logging in the headwaters of the Kiewa River. These new ‘towns’ such as Mt Beauty and Bogong, survived, serving the needs of operational personnel and their families, and expanding with growth of new industries. Mount Beauty, and to a lesser extent Bogong, are among these places. Large A3 size spiral bound display folder containing photocopied black and white photographs of various aspects of the early days of the Kiewa Valley Hydro-electric scheme including equipment, various work sites and photographs of workers and their families. 1-Breakdown in Circuit Breaker (Isolating Contacts) 2-Big Hill Bench- Site of No 5 Devlopment 3-No 1 Power Station 4-No 1 Pipeline, Anchor No 8 5-Push Dozing-RD8 Tractor 6- Tractor and driver at work 7- Workmen in unnamed tunnel 8- Front page of Journal of SECV Vol 15. Photograph of No 1 pipeline viewed from McKay Portal 9-Rocky Valley Dam Core Wall 10-Workmen working inside tunnel loading rocks into a rail truck. 1-Breakdown in (generator) Circuit Breaker (Isolating Contacts) Handwritten underneath (This is not a picture of any part of a generator. It is a circuit breaker Signed Ron White Ron was the Principal Hydro Engineer of the SEC Kiewa Scheme Page number 39 2-Big Hill Bench – Site of No. 5 Development (abandoned) Page number 40 3-No 1 Power Station Page number 41 4-No. 1 Pipeline, Anchor No. 8 Page number 42 5-Push Dozing – RD8 Tractor, 12 cubic yard Carryall and FD Cletrac Tractor Page number 43 6-No marking Page number 44 7-No marking Page number 45 8-Journal of State Electricity Commission of Victoria SEC Vol 15 No… April-May, 19… No 1 Pipeline-A view from McKay Portal G Hempenstall and D Sutton stiffening pipe section for transport during construction (….indicates missing text) Page Number 46 9-Rocky Valley Dam Core Wall Page number 47 10-No markings Page number 48 secv; kiewa hydro electric scheme; construction area; power stations; reservoirs; aqueduct; mt beauty; bogong -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionObject, Synchronome Co. Ltd, Synchronome Frequency Checking Master Clock No. 2191, c1930
Information from Norman F. Dalton: Ballarat had a reticulated DC supply in the early part of last century and in 1905 had sufficient generating capacity to enable the trams to be changed from horse drawn to DC electricity. The use of electricity increased with the main power station located on Wendouree Parade, near Webster Street, under the ownership of The Electric Supply Company of Victoria. AC generating plant was installed in 1925 and conversion to AC proceeded. In 1934 the company was taken over by the State Electricity Commission Victoria (SECV) and more AC generation was installed and the changeover of customers was accelerated. This is around the time that the Synchronome Frequency Checking Mast Clock was installed at the Wendouree Parade Power Station. The SECV Annual Report of 1921 states: ::Section 11 of the act directed the COmmission to enquire into the question of securing the adoption of such standards of plant and equipment of a system, frequency and pressure for the generation and distribution of electricity as will admit of the efficient interconnection of undertakings throughout the State. In 1934 when the SECV took over the Ballarat operations the question of linking with the State grid had been a planned operation for some years but due to financial considerations had hindered it and in fact would continue to do so for a further 10 years. So while the need for close frequency control for interconnection was hardly an issue, the need to keep electric clocks correct was important, particularly as this item was a frequent sales point to cover the inconvenience and sometimes expense of converting from DC to AC. The clock is a very accurate pendulum clock with provision for varying effective length during operation for precise time regulation. There are two normal time dials and one is controlled by the pendulum and the other is operated by the system frequency. When the clock was in use it was installed by the MEter and Tests Laboratory and the time was checked daily by radio time signals. The two dials were repeated in the operators control panel in the Power Station. A maximum deviation between the two dials was set in the operating instructions (eg 5 seconds) and the operator would correct this when necessary by remote manual alteration of the turbine governor set point. The clock was used to drive and regulate a system of "slave" clocks which were used to display the time in various locations around the power station. A slave clock is a simple clock which is driven by a small electric motor, its accuracy is regulated by the master clock every 30 seconds to ensure that it and all the other slave clocks in the station are on exactly the right time; slave clocks were placed in various locations, from common rooms to workshops. A master clock could potentially run thousands of slave clocks at one plant. The clock also contains a rectifier. A rectifier is a device that is used to convert AC power to more stable DC current.Two clocks in a timber case. Both are electric, one is powered by the main pendulum mechanism, the other is a self contained electric clock. The main mechanism is of the gravity arm and roller type, which sends an impulse to the slave clocks every 30 seconds. The This Synchronome Frequency Checking Master Clock was used at the Ballarat Power Station. Below the main section of the case is a smaller cabinet containing a rectifier to provide consistent DC power for the clock. The rectifier was made by the Victorian company Hilco, which was located in Burwood. There is a high chance this is not the original rectifier from this clock as there appears to be brackets to hold a larger device in the space the rectifier occupies.Front below main clock face on front of case: "Patented Sychronome Brisbane" Lower left-hand clock face: "Frequency time" Lower right-hand clock face: "Standard Seconds" Synchronous electric clock mechanism on door (Frequency time clock): >200/250 V. 50~ >"Synchronomains" Made in England >Direction indicator for clock starting switch >"To start move lever in direction of arrow and release" >"Patent applied for" Mechanism for "standard seconds" clock: >"English Made" >"Patented" >Serial number "321" >0 above right-hand pillar on front-plate Mechanism for "standard seconds" clock: >"English Made" >"Patented" >Serial number "321" >0 above right-hand pillar on front-plate Mechanism for main clock face: >"English Made" >"Patented" >Serial number "8751" >0 above right-hand pillar on front-plate Inside case, back panel, top enamel plate: >Seconds Battery + Pos. > Battery Common or - Neg. >1/2 min dials Inside case, back panel, bottom enamel plate: external seconds dial Inside case, right hand side, electrical knobs: two switches, both "A.C. mains" Pendulum rod, below suspension spring: Serial number (?) 0000005 Rectifier in bottom cabinet: >"Hilco Rectifier" >"A.C. Volts 230/240" >"Model 1060/S" >"A.C. Amperes" >"Serial No. 1060/S >"Phases 1" >"D.C. Volts 6" >"C.P.S. 50" >"D.C. Amperes 1" >"Made in Australia by Hilco Transformers McIntyre St., Burwood, Victoria." Bakelite electrical plug: makers mark Lower cabinet, RH side panel, pressed tin plate: "AC" (upside down) Brass speed adjustment, outer right RH side: "S" and "F" Ivory and wood pendulum beat ruler: >Ruler, with 0 in centre and numbers 1-5 in ascending order from centre on left and right. > "Synchronome Patent." Steel plate, back panel, inside case, right hand side: >N R A" (descending) >"2191" serial number/part number Face of main clock: "Synchronome Electric" synchronome frequency checking master clock, electricity, state electricity commission, wendouree parade power station, secv, clock, time, pendulum, electric supply company of victoria, norman f. dalton, ballarat power station, rectifier, slave clock -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumBook, Metropolitan Transit Authority (MTA), "Light Rail Transit System - Inner Area North-South Link", c1986
Sixteen page book, A4 portrait format, saddle stapled, titled "Light Rail Transit System - Inner Area North-South Link", published by the Metropolitan Transit Authority detailing the conversion of the former heavy electric suburban railway lines to St Kilda and Port Melbourne to electric trams or Light Rail. Has foreword by Tom Roper, Minister for Transport, Describes the proposed system, vehicles, development of articulated vehicles (2001, 2002), interchange with rail services, travel times and a map showing the proposed route, including a possible extension along Mitford St. and Broadway to Glenhuntly Road. Has a number of artists impressions of the vehicles at Station Pier and South Melbourne station. Includes colour photographs of the vehicles, conductors and photos of other light rail systems in Hanover and Amsterdam. Published c1986.trams, tramways, melbourne, light railways, mta, st kilda, port melbourne, articulated trams -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumMagazine, Jack Richardson, "Tram Tracks - The Electric Traction Monthly", Feb. 1949 to August 1949
2467.1 - Vol. 4 No. 2, February 1949 of "Tram Tracks - The Electric Traction Monthly" of the Australian Electric Traction Association. Magazine consists of 16 printed pages with a 12 page supplement titled "Fifty Questions and Answers about trams in Australia". Has a single staple on the saddle. Incorporated within the magazine are articles or editorials on Tramways and Tramway Experts (Sydney and bus replacement), Interurban to St Kilda (conversion of VR St. Kilda line). General news items on Brisbane, Geelong, Launceston closure, Hobart, Bourke St routes, Perth, Adelaide, NSW, Christchurch, Overseas tramways and railways. Also has letters to the Editor, plans of a Birney tram for model makers and AETA Notes. Issue has advertisements for the Model Dockyard, ARLHS, The Hobby Shop, Barnes Tennis Centre, Fleet, Christie Model Railway Equipment of Sydney, Meadmore Model Engineering, Austral Bronze, Wattle Park, Traction Publications and Robilt "O" gauge locomotives. 2467.2 - Vol 4, No. 5 - May 1949 - 20 pages - red cover, 4th year, article by Peter Duckett with photos of Board members, "PCC Trucks here", MMTB advert for staff, news from Sydney, Newcastle, Melbourne (applications for new Chairman to replace Mr. Bell), Bendigo, Perth, Christchurch, Wellington, Wanganui, Bourke St construction work (photo of poles), Brisbane tramway history, map of CBD Melbourne, Melbourne and Sydney suburban railways, AETA News. 2467.3 - Vol 4, No. 6 - June 1949 - 16 pages - green pages, tramways and private cats, news from Sydney, Newcastle, Melbourne, Launceston, Hobart, article "Scrap Sydney Tams by 1960 - Newcastle this years say London experts", buses tackle football crowds (Sydney), Fremantle (Wal Jack letter), and Melbourne and Sydney suburban railways, AETA News. 2467.4 - Vol 4, No. 7 - July 1949 - 16 pages - tramways and the public, news from Sydney, Newcastle, Melbourne, appointment of R. Risson as new chairman, Perth, Adelaide, Launceston, tramcar solenoid brakes, National City Lines USA, and Melbourne and Sydney suburban railways, AETA News. 2467.5 - Vol 4, No. 8 - August 1949 - 8 pages - tramways and politics, photo of new points for Latrobe and William Sts, East Hills Line by C. C. Singleton, general tramway news, and advertisement for Robilt model railways. .2 to .4 added 15-2-2016 from the collection of Ian Stanley. .5 added 24-3-18 - from consolidation of Melbourne Tram Museum and BTM collections)trams, tramways, electric traction, aeta, australian tramways, mmtb, pcc, closure, sydney, newcastle, brisbane -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumMagazine, Wellington Tramway Museum, "Tramway Topics", Oct. 1968
... Horse trams and the conversion to electric. Trams tramways ...Yields information primarily about New Zealand tram and bus city systems and what the various NZ Museums were doing at the time. Has an article on Ballarat Horse trams and the conversion to electric.Magazine - Tramway Topics - Vol. 7, No. 5 Sep - Oct 1968 - 28 wax cut stencil duplicated pages with printed centre page of photos and printed covers, which are slightly larger in size than the internal sheets. Published by Wellington Tramway Museum, Tramway Historical Society and Tramway Division of MOTAT jointly - editor J. Wilkinson. Contains articles on Brisbane trams for Queen Elizabeth Park, Peak Tram, Auckland, Horse trams in Ballarat, Napier, Wellington and News of Museums etc.On inside of front cover in black ink "Ballarat Tramway Preservation society Catalogue No. 111". In red ink on front cover "Ballarat p9"trams, tramways, ballarat, wellington, auckland, napier -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumBook, David Chantrell, "Duncan & Fraser Ltd. 'Legacies Left Untold' ", 2008
Provides information about the company and its history that built many of the tram bodies within the BTM collection and photographsBox - 268 pages within blue colour soft covers titled "Duncan & Fraser Ltd. 'Legacies Left Untold' ", written and published by David Chantrell of Adelaide, 2008. Details the story of the coach building firm of Duncan and Fraser of Adelaide who built horse drawn vehicles, horse trams, electric tramcar bodies, motor cars and other vehicles. Tells the story of the company from its founding days, the family and people involved, the conversion to motor car manufacturing and its demise when the Ford Motor car company commenced manufacturing in Geelong. Details known D&F tramcars, provides some lists of existing bodies. Has a copy of the letter that accompanied the book by the authortrams, tramways, duncan fraser, tramcar construction, ford motor company, motor vehicles -
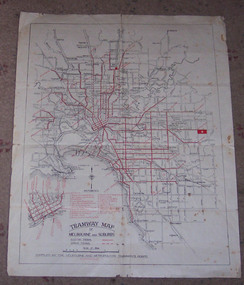 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumMap, Melbourne and Metropolitan Tramways Board (MMTB), "Tramway Map of Melbourne and Suburbs", 1930c
Two colour map of Melbourne tramway Network, undated, but post the conversion of Collins St to electric trams (late 1929), c1930. Shows both electric and cable lines, various locations, eg the Motordrome, railway lines and primary streets. Compiled by the MMTB.On rear in pencil over three locations "Young Asst Mgr", "Young" and "L Calder? 6 Inglis? Wahroonga"trams, tramways, mmtb, map, cable trams, conversion -
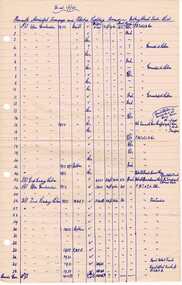 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumDocument - List, "Fremantle Municipal Tramways and Electric Lighting Board - Rolling Stock Data List", 1950
Handwritten list titled ""Fremantle Municipal Tramways and Electric Lighting Board - Rolling Stock Data List" listing the tramcars of Fremantle, builder, date, motors, length, car type and history of conversions. Dated as at 1/1/1950. Handwritten on lined foolscap paper with four punch holes on left hand edge. Contained originally within Reg Item 5623 at the front of this note book. For items see BTM5623 loose items list.pdf. See also Reg Item 152 for other information obtained by Wal and also Reg item 136 for a list prepared by Wal Jack.fremantle, tramcars -
 Queenscliffe Maritime Museum
Queenscliffe Maritime MuseumEquipment - Light, electric
Removed from HMAS Canberra before being scuttled. HMAS Canberra was an Adelaide class guided missile frigate of the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). Based on the Oliver Hazard Perry class design, Canberra was one of four Adelaide class ships constructed in the United States of America, and one of six to serve in the RAN. The frigate entered service in 1981. During her career, Canberra was assigned to escort the Royal Yacht Britannia during Queen Elizabeth II's visit in 1988, helped enforce the post-Gulf War United Nations' sanctions against Iraq during 1992 and 1993, was part of the Australian responses to the 1998 Indonesian riots and the 2000 Solomon Islands Civil War, and returned to the Persian Gulf in 2002 as part of the War in Afghanistan. In 2005, Canberra became the first ship of her class to be decommissioned. The frigate was marked for conversion into a dive wreck and artificial reef off Barwon Heads, Victoria, and was scuttled on 4 October 2009. Electric emergency light, fixed mountedwarning lights, hmas canberra -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Bendigo - tram 17 at depot
Photo shows Electric supply Co. toast rack or cross bench type No. 17 outside the depot prior to its coversion to the track cleaner in 1953. The Bendigo trust returned the tram to its toast rack or cross bench type.Yields information about Bendigo tram 17 prior to its conversion in 1953 to the track cleaner.Black and white photograph of Bendigo - tram 17 at depotOn rear in red pencil is "Dup JBS"tramways, trams, sec tramways, bendigo, tram 17, bendigo depot -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumFunctional Object - Tramcar, Duncan and Fraser and Ballarat Tramway Preservation Society, Horse Tram No 1, 1887 - original, reconstruction 1986-1992
A double deck horse drawn tram with single saloon. drop ends, stairs, longitudinal seats, sliding doors, wheels of cast iron, hand brakes - see notes. Originally built by Duncan & Fraser in 1887. Rebuilt by BTPS 1991. From the BTM Fleet page on the website: Built in 1887 by Duncan and Fraser for the Ballaarat Tramway Company Ltd. as a double-decked horse tramcar. One of eight cars which ran as trailers behind electric trams at times of heavy patronage, after takeover and conversion of the horse lines by the Electric Supply Company of Victoria Ltd. in 1905. Withdrawn in the late 1920's when the body shell became a residential outbuilding locally, until retrieved in 1985. Fully reconstructed to its original form and placed on a modified Melbourne saloon cable car truck. See attached notestrams, horse trams, tram 1 -
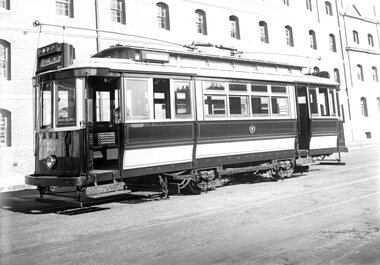 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Geelong Tram No. 18
Geelong Tramcar No. 18, freshly painted, in Corio Tce. with Strachan & Co's wool store in the background. The car has been converted for one man operation but retains the MESCo's double lineouts that were replaced by single yellow lines in the 1940s. It is likely that the photographs were taken to display the conversion in 1939. See also Item 9242.Black and white print on paper12-6 and GRS170/12/1/6 printed on reverse in pencil. No. 1 in a circle printed on the reverse in pen.geelong tramcar, geelong tramcar no. 18, strachan and co. wool store, geelong, tramcar one-man operator conversion -
 Ballarat Tramway Museum
Ballarat Tramway MuseumPhotograph - Geelong Tram No. 18
Geelong Tramcar No. 18, freshly painted, in Corio Tce. with Strachan & Co's wool store in the background. The car has been converted for one man operation but retains the MESCo's double lineouts that were replaced by single yellow lines in the 1940s. It is likely that the photographs were taken to display the conversion in 1939. See also Item 9230.Black and white print on paper.No. 1 inside a circle and 13-8 printed on the reverse in ink. GSR710/13/1/8 printed on the reverse in pencil.geelong tramcar no. 18, geelong tramcar conversion to one man operation, mesco lineouts
