Showing 135 items matching "scribbling"
-
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book, Meditations & Contemplations, 1807
This book belonged to Charity Lamerton Phillips and may have belonged to her parents before her. On the inside front cover are the names of George Phillips and Jessie Kerr, giving their marriage date and the birth dates of four of their children. Charity Lamerton Phillips (1872-1942) was the daughter of George and Jessie Phillips of Nirranda and she married Frederick Bonnett and farmed in the Mepunga district. This book is of interest because of its age and because it contains family information on the Phillips family of Nirranda. Many 19th century people recorded family information in a Bible or other old book kept in the home. This is a hard cover book of 325 pages. The cover is brown leather with some sections eroded away. The spine has gold lettering. The book contains several black and white illustrations. Some of the pages are stained and torn at the edges. There are two loose sheets – an undated newspaper cutting and a notice regarding an anniversary service at the Westdown Congregational Chapel. The inscriptions are handwritten in black ink. There is also pencil scribble on some pages. Inside front cover: Details of the marriage of George Phillips and Jessie Kerr and the birth dates of four of their children. charity phillips, george and jessie phillips of nirranda, history of warrnambool -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book, Warrnambool Standard Almanac 1913, 1913
This booklet was given to subscribers to the Warrnambool Standard newspaper as an almanac for the year 1913. Warrnambool Standard Almanacs were produced annually from 1875 to 1930. They contain much local information on Warrnambool and district about businesses, government officials, harbour management, churches, schools, banks, large landowners, societies and organizations etc. The Warrnambool Standard newspaper was established in 1872 and continues to this day. Ths booklet is of high significance as it contains much valuable information on Warrnambool and district for the year 1913. It is an important resource tool for those studying and writing the history of Warrnambool and district. The original owner of this booklet is not known. This is a booklet of 113 pages. Most of the original advertisements that were at the front and back of the booklet are missing. The original front cover is missing and has been replaced with a photocopy of the original front cover and a plain piece of cardboard at the back. These have been bound with a plastic strip and covered with a sheet of clear plastic. The booklet contains some black and white photographs and some other illustrations. There is some scribble in pencil on the back page. warrnambool standard newspaper, history of warrnambool, standard almanac 1913 -
 Ballarat Clarendon College
Ballarat Clarendon CollegeBook, Philomena, 1957
Phillippa (Tarrant) Rowland attended Clarendon Presbyterian Ladies College 1956 - 1967, Kindergarten to Leaving. The Prize was awarded for good academic progress during the second grade. Phillippa has provided the following reminiscences from her years at CPLC: [Principal] Miss McPherson used to come once a week to the prep school to read to us and the books chosen were then presented as prizes at the end of the year. Mrs Langham was the head of the junior school, Mrs Tolliday and Mrs Alexander (who used to play the piano for our morning assemblies) the other teaching staff. We would gather, at the bell, in the concrete yard at the back of the school, in rows on the concrete lines, have our fingernails and uniform inspected, we had to show a handkerchief before filing in to the large room for assembly. We also had lunch and afternoon naps in this large room, folk dancing, plays, other special occasions. Book in English language. Large 8vo; hbk ; 1st edition; book has bright yellow cloth covers with red vignette on front cover and red lettering to spine; school crest in gold at bottom right corner of front cover; brightly illustrated endpapers; book plate fixed to front endpaper; illustrated throughout in sepia; brown pencil scribbling on book plate and half title page; Book plate: Clarendon Presbyterian / Ladies College / Ballarat / Crest / Awarded to / PHILLIPPA TARRANT / Prize PROGRESS / Form IIB / Margaret McPherson / Principal / December / 1959phillippa-tarrant-rowland, clarendon-presbyterian-ladies-college, 1959, book-prize -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - NORMAN OLIVER COLLECTION: MAYOR'S NOTES 6 FEB 1965
The Norman Oliver collection. Norman Oliver was three times Mayor of Bendigo - 1950-51, 1964-65, 1970-71. Three pages of typed notes titled Mayor Speaks. The date, 6/2/65, is written in pen across the top. There is some scribbled calculations in blue pen on the first page. Topics include : traffic infringements, classes in life saving for school children, cemetery management, and the Country Swimming Championships.bendigo, council, report, norman joseph oliver , councillor norman oliver. mayor of bendigo. -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book, Warrnambool Standard Almanac 1887, 1887
This booklet was given to subscribers to the Warrnambool Standard newspaper as an almanac for the year 1887. These Standard almanacs were produced from 1875 to 1930. They contain much local information on Warrnambool and district about the businesses, government officials, schools, societies and organizations, harbour management, churches, banks etc. The Warrnambool Standard newspaper was established in 1872 and continues to this day. This booklet is of high significance as it contains much valuable information on Warrnambool and district for the year 1887. It is a very important research tool for those studying and writing the history of Warrnambool and district. This copy has the name ‘Barber’ on the front cover and probably refers to George Barber, the son of George Barber, a well-known solicitor who opened a legal practice in Warrnambool in 1855. He died in 1879 and it appears that a member or members of his family went to live in the Maryborough district. This copy came into the collection of the Warrnambool and District Historical Society via the Midlands Historical Society. This is a soft cover booklet of 73 pages, plus several pages of advertisements. The section on the tourist’s guide to Warrnambool is printed in pink. There is a fold-out page with a map of the railway routes in Victoria. The cover is buff-coloured with black lettering and is slightly frayed. There is some scribble on the first page and the back cover. There are many black and white illustrations and several sketches of Warrnambool and district printed in pink. The name ‘Barber’ is handwritten in black ink on the front cover. ‘Barber’ ‘Miss Duff c/o Mrs Hyslop Farquar Lodge Lysle Street Ladysmith South Africa’warrnambool standard newspaper, history of warrnambool, standard almanac1887 -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - THOMAS JAMES CONNELLY COLLECTION: MEMO DATED 17 SEPT 1870, 174/09/1870
The Thomas James Connelly collection. T. J. Connelly - Brassfounder, Coppersmith, Plumber and Gasfitter. Located in High St. Bendigo. Items of correspondence. Memo headed Sandhurst Sept 17th 1870. Memo for Mr Connelly. Please send up to Benevolent Asylum and repair Steam exhaust pipe from Kitchen Range also, Hot water pipes and pump, etc. Vahland & Getzschmann, Architects. There are some numbers scribbled on the left side and on the reverse.trades, plumbing, thomas james connelly, connelly, thomas james. bendigo plumbers. vahland & getzschmann. bendigo benevolent asylum. -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Booklet, Victorian Country Football League Constitution and Rules, 1955
This booklet lists the Constitution and Rules of the Victorian Country Football League in 1955. The Victorian Country Football League was founded in 1927 and merged with AFL Victoria in 2012 to form AFL Victoria Country. In 1955 the Victorian Country Football League had eight delegates elected by the League and one District Councillor from each of the fifteen designated country districts. The object of the League was to promote the game in the Victorian country areas. This booklet is of some interest as it details the Constitution and Rules of the Victorian Country Football League in 1955. The Hampden League centred around the Warrnambool area was one of the districts covered at that time by the Victorian Country Football League.This is a small soft-covered booklet of 64 pages. It has a pale green cover with ruled black lines and printed information on the front and the name of the printer on the back. The pages have been stapled but the staples are now removed. The cover is torn at the spine and the cover is somewhat scuffed with some scribble on the cover edge. The back cover and one of the pages have biro annotations on them. The booklet has an index at the back and a couple of blank pages for notes. Back cover: ‘189936’victorian country football league, warrnambool -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyBook, L.Zions, Zions' Hours and Wages Record Book, c 1960's
An Hours and Wages Record Book for the Silvan Fruit Processors business in the Wandin area, Victoria.A faded square grey coloured Silvan Fruit Processors Zions' Hours and Wages Record Book bound with red tape on the stapled spine. The cover has the title, the business who used it stamped at the top as well as a full list of other publications and place of printing and publishing details. At the top of the front cover is written in blue biro, the dates of records - from Dec 1960 to Jan 1963. Inside are full column listings of Names, Hours Worked Daily, Total Hours, Rate,Total earnings, Tax Deductions, Net Payment and a Signature or Other Particulars column.non-fictionAn Hours and Wages Record Book for the Silvan Fruit Processors business in the Wandin area, Victoria. wages books, business records, books, wages tables, wages calculators, wages -
 Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.
Warrnambool and District Historical Society Inc.Book, The history of ancient Greece pub 1812, 1812
This book has the signature of Joseph Ware of Minjah, Caramut, Victoria. Joseph Ware came, with his parents, from England to Van Diemen’s Land (Tasmania) in 1822. With his brother, Jeremiah, he came to the Port Phillip Colony (Victoria) in 1838 and settled in the Colac area (Wooriwyrite and Koort-Koort-Nong stations). With his brothers or alone Joseph then held the runs of Minjah, Mustons Creek (Barwidgee), Sinclair West and Springburn. Joseph Ware was a highly successful pastoralist, breeding sheep, cattle and horses and importing Shorthorn cattle. Ware was connected with Minjah from 1845 to his death in 1895. The homestead at Minjah which still stands today was built by Joseph Ware in 1870. This book is of interest because of its antiquarian nature. But it is far more important because it was once the property of Joseph Ware. He and his brothers were most influential pastoralists in South Western Victoria in the 19th century. This is a hard cover book of 630 pages. It has a Preface, an Introduction, five Books with Chapters on the history of Greece and an Index. The cover is dark brown leather, now stained and mottled, with ‘Robertson’s Greece’ embossed in red and gold lettering on the spine. The top of the first page has been cut out and there is considerable staining throughout the book. There is one insert map of ancient Greece and some scribble (perhaps a signature) on the first and last pages. The inscription is handwritten in black ink. ‘Joseph Ware, Minjah, Caramut’ ‘Dec.24…’ ware brothers, joseph ware, minjah, pioneers of s.w. victoria -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumAdministrative record - MEMBERSHIP RECORDS, BENDIGO RSL, C.mid 1940's
Membership index Bendigo RSL Sub - Branch 1) This full tray of memberships date back to mid 1940's through to 1964 in alphabetical order. 2) This tray has membership dates back to 1944 to 1961/62. i.e. members deceased, moved on or become un financial members. There is no membership index pre these records. A new membership index type began after this one. The card shown in the photo's is Frederick Gardiner Davey DFC, refer Cat No 3536P for his collection.1) Membership Index tray, wood construction with slide out tray with metal pull out handle, the handle has a section for a card with details. The tray is full of membership cards, brownish in colour. Print is in black and the majority have typed entries in black. 2) Membership index tray, metal construction with metal slide out tray and pull out handle, the handle has a section for a card with details. The tray is approx 30/40% full of cards - same as item .1)1) On pull out tray handle in red pen "Financial from 1962 whose names have gone in folder ________ _________ _________ ________" 2) On pull out tray handle in red pen "Unfinancial (scribble)" then in blue "Not in Register".brsl, index, membership, smirsl -
 Box Hill RSL Inc.
Box Hill RSL Inc.Functional object - AFV Periscope, Minneapolis-Honeywell, c. 1943
This periscope was used during WW2 extensively made for armoured vehicles.Minneapolis-Honeywell was approached by the US military for engineering and manufacturing projects. In 1941, Minneapolis-Honeywell developed this superior tank periscope and camera stabilizers, as well as the C-1 autopilot.Rectangular periscope with screw & clip device to hold in position, painted olive drab.On one label: PERISCOPE M6/ MINNEAPOLIS HONEYWELL REGULATOR COMPANY/ No 4XO/ 1943. On paper label: Periscope Adjustments Knob Settings (indecipherable). On one side handmade scribbling unable to analyse: PVNCAN/HARE/838 4551periscope, armoured vehicles, tanks, ww2, us army, chaffee, stuart, shermann, minneapolis -
 Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.
Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society Inc.Medical diary and visiting list, Wellcome's Medical Diary and Visiting List (Australasian Edition) 1909, 1908
Diary was owned by Evelyn White and was found in the estate of Neil Russell. It was donated to Museum Victoria in 2006 by Neil's son, Barry. MV passed on the diary to Southern Sherbrooke Historical Society who kept it after ascertaining that Healesville Historical Society didn't want it.A leatherbound diary with closing flap and press stud closure, and an expanding pocket at the front. There is a pencil holder. The first 254 pages have been torn out. Pages 255 to 318 have printed information of benefit to GPs. The remaining pages, 1-150, are a diary plus engagements list. There are pencil scribble marks on some pages. Handwritten lists of women patients and dates, presumably when women gave birth. Also lists of patients and death dates. 'Healesville' is mentioned alongside some names. -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph, Caldwell, c1950/60s
A photo of the original Burke Library building between two medium sized trees, a lamp post sits between them and a large tree is behind the building. This photo was taken c1950/60s.This photo is of both historical and social significance to the people and community of Beechworth because it shows the development of the Burke Museum from what it was in this picture, to what can be seen today. It also shows the Burke Museum's prominent architecture marking it as a particular point of interest within Beechworth. Along with the aspects of the building that the Burke museum is known for today, such as the façade and the central lamp post, all of which are significant to the town of Beechworth and its people.Black and white rectangular photograph printed on photographic paper.Obverse: 1856 / Library Reverse: Beechworth Library / 33 1/3% / Caldwell / 19 eu (illegible) / 11 eu (illegible) / 729 / 3 1/6 / BMM 8691 / S / T / E / T (Scribbles and arrows across the page)burke museum, beechworth, 1950s, architecture, landscaping, development -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionArtwork, other - Painting, Neville Touzeau, Eclipse 3, 1972
UnknownAbstract composition of 24 circles, evenly spaced across image. In orange, yellow, brown, green, blue and white, with each alternate circle taking on aspects of the colours beside it. Set in dark blue background. Mounted in dark green matt. In wooden frame with glass glazing.Front: (no inscriptions) Back: "Eclipse 3" Neville Touzeau $40 '72 Touzeau 276 (lower right)(blue pen) Touzeau (black felt pen) Flight IV 50 Touzeau (blue pen, scribbled out in blue felt pen) -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - Badge/Shield designs
Manilla envelope containing three pieces of paper with hand drawn designs for crests. Written on the front of the envelope "3 Crests" and "Mssrs Prescott + Dawe". After 1904. One is a shield shape that has been scribbled over. One has a shield and banner as part of the design. Written in the top LH corner are the words "Leaves", "Gold", "Back Ground white". Words on the banner and written below the design "ROBUR IN FIDE".(Translation "Strength in Faith".) One is drawn in green ink with "FAITH HOPE CHARITY" on the banner. Prescott & Dawe Collection prescott & dawe, jewellers, designs -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyBook, The Religious Tract Society, Show Your Colours and Other True Narratives, late 1800's
A collection of three short stories for young children of family and school life with strong religious themes in the late 1800's.A small blue cloth covered storybook for young children titled - Show Your Colours and Other True Narratives. There are gold and black patterns all over the front cover and the back is embossed. A Merit Bookplate is glued to the front endpaper. The full colour illustrated frontispiece picture is of an old man seated at a table with a younger one standing behind him. It has grey pencil scribble all over it and a large tear. There are three short stories all with strong religious themes. At the back is a list of 40 of The "Little Dot" Series - New Sixpenny Books. The spine is broken from the pages. 62p.fictionA collection of three short stories for young children of family and school life with strong religious themes in the late 1800's.religious stories, children's stories, school life -
 Kilmore Historical Society
Kilmore Historical SocietyBook, WHITCOMBE'S FEDERAL GEOGRAPHY, c1920
School text, Grade 8 geographyGrey cover, stained & torn, brown paper cover, pages torn & ink-marked. 160pp. Fair conditionnon-fictionSchool text, Grade 8 geographychildren, textbook, glanville, geography -
 City of Kingston
City of KingstonPhotograph - Black and white, 1903
The Scantlebury family moved to Cheltenham from Linton. The father, George, was a medical practitioner. His daughter, Vera, became an early woman graduate of medicine at the University of Melbourne. His son, Clifford, also became a medical practitioner.Black and white image of a man (Dr George Scantlebury) driving an early car along Charman Road, Cheltenham. There are two women in the car as well. Cheltenham Cemetery can be seen in the background.Handwritten in black ink on round red sticker: X17 [scribbled over] Handwritten in black ink inside a circle: A4 Handwritten in red ink inside a black ink circle: 60% Handwritten in black ink: Dr Scantlebury's motor car Handwritten in blue ink: Ch4scantlebury, cheltenham, medicine, cars -
 Broadmeadows Historical Society & Museum
Broadmeadows Historical Society & MuseumBook - Published book, Judith Faulds, Broadmeadows : Two Decades of Community change 1981-2001, 2002
A companion volume to Andrew Lemon's Broadmeadows: A Forgotten HistoryHard cover book - Ex Moreland city libraries - Associated library stickers, Pages yellowing at edges, cover shows signs of usenon-fictionA companion volume to Andrew Lemon's Broadmeadows: A Forgotten Historyhistory, book, judith faulds, broadmeadows -
 National Wool Museum
National Wool MuseumEnvelope, 1940
Envelope was part of a larger donation by Mrs Robyn Adams and was addressed to her father Victor Clyde. Envelope contained books from various years. Envelope is from c1940-1969, most likley the latter. Mostl likely associated with way bill books on which wool clip details were recorded.Dark cream coloured envelope, bound on left short end, torn open at right torn end with piece loose. Dark blue text on top left front corner -ELDER SMITH / GOLDBROUGH MORT / LIMITED- -WOOL WAY BILLS- Black printed text in middle front of envelope reads - Mr. V.T. Clyde, / Killawarra Park, / WANGARATTA..VIC.-. Dark blue printed text at bottom front reads - PLEASE USE THIS WOOL WAY BILL FOR THIS SEASON'S CLIP- Faded red stamp top right corner. Rear is blank apart from pen ink note of the word -CLYDE- and a scribble.wool waybill, mrs robyn adams, wool clip, elder smith goldsbrough mort limited, dalgety and company limited elder smith goldsbrough mort limited -
 Mont De Lancey
Mont De LanceyBook, William Gillies, M.A, Stories in British History for Young Australians, 1920
A simple study in British History for secondary school students with a fold out map of the British Empire at the time - published in 1920. There is a list of the dynasties and kings and queens and a table of Periods in British History which can be referred to.A badly damaged red cloth covered hardcover book with the title: Stories in British History for Young Australians printed in black lettering on the front cover with the publisher, a round publisher symbol and 2/6 at the bottom. The title is printed on the spine. This is a First Course in British History by William Gillies, M.A. Inside, opposite the title page, is a lined sketch of Oliver Cromwell. Black white illustrations, maps and photographs are included. At the back is an Index as well as three additional recommended titles of other history books. Considerable markings, lists and a love poem is scribbled at the back. It is quite damaged and worn through use. Pp.315.non-fictionA simple study in British History for secondary school students with a fold out map of the British Empire at the time - published in 1920. There is a list of the dynasties and kings and queens and a table of Periods in British History which can be referred to.great britain - history, history, textbooks -
 Friends of Ballarat Botanical Gardens History Group
Friends of Ballarat Botanical Gardens History GroupWork on paper - National Trust of Australia (Vic), Register of Significant Trees. Ballarat Botanical Gardens. c1983, Unknown
This National Trust Register of Significant Trees in the Ballarat Botanical Gardens is an important part of Ballarat's history. Unfortunately, since 1983, some of the trees listed have died or been removed.The Ballarat Botanical Gardens has a unique collection of trees which testify to the knowledge and enthusiasm of the Curators, City fathers and Gardeners in their development of the Gardens in earlier years, especially in the nineteenth century.1 sheet of paper with three lists of the trees and the number of them in the Gardens. (1 copy)Draft printed in red under main heading. In black biro, written on the first entry, "no on map". 10th entry (Sierra Redwood) number scribbled over and "outside gate" written. 14th entry (Horizontal Elm) "3 on list, 1dead". 15th entry (Horizontal Elm) "W of 17". ballarat botanical gardens, national trust of australia (vic), register of significant trees, trees, john garner collection, gardens, ballarat -
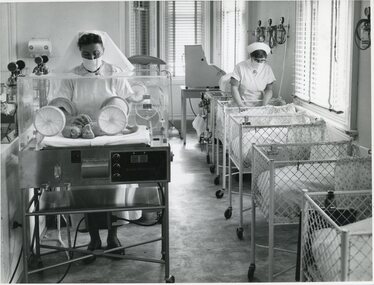 Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic History
Geoffrey Kaye Museum of Anaesthetic HistoryPhotograph
Black and white photograph depicting a maternity ward or neonatal intensive care unit at the Royal Women's Hospital. On the left of the photo is an incubator with a newborn infant lying inside. A female nurse is standing behind the incubator holding the infant through the incubator. On the right of the photograph is a row of five infant cradles, and a second female nurse is standing behind a cradle. Both nurses are dressed in an apron, cap and mask.•Handwritten on reverse in blue ink: Royal Womens Hospital - 6 [indecipherable] •Handwritten scribble on reverse in blue ink in too left corner •Stamped on reverse in black ink: Reproduction by / NOEL RUBIE PTY. LTD. / 24 JAMIESON ST. / SYDNEY •Handwritten on reverse in blue ink: B9762royal women's hospital, neonatal care, nurse, infant, incubator -
 Bendigo Military Museum
Bendigo Military MuseumUniform - UNIFORM, CAMOUFLAGE, 6) & .7) et al, c.1990
Uniform worn by Kieran Dole..1) Trousers, jungle pattern, heavy cotton shades of khaki, brown & green. Belt keepers same design. Pockets in legs at front. .2) Shirt, front buttoning, jungle patterned cotton. Corporal's stripes on sleeves. Breast pockets with flap fastenings. .3) Helmet, Kevlar camouflage pattern. .4) & .5) Gloves, pair, green khaki knit fabric with false leather PVC? insert down front. Gathered at writs, label inside. .6) & .7) Boots, pair, light khaki, leather combat with moulded composite soles, cotton laces. .8) United Nations beret, blue. Gold gilt & white enamel UN badge pinned on front. Black cotton fabric lined. Edge bound through which is threaded a drawstring black tape. .9) Wide brimmed UN sun hat, blue with black chin strap. Metal edged ventilation holes around crown. White embroidered UN badge on front of crown. Cotton hat band sewn at intervals. Close circles of stitching around brim to stiffen. .10) Jacket, heavy, camouflage, twill weave cotton. Front fastened with zipper. Breast & side pockets fastened with heavy press studs. .2) Breast pockets name: DOLE .3) Written inside in texta: DOL 312 Scribbled out: Ball 4100612 Written inside in pen: DOLE 3805312 Written inside on back: DOLE .10) Label inside centre back: Logo & AVA Victoria 1998 Washing instructions Made in Australia uniforms, camouflage, jungle pattern -
 Returned Nurses RSL Sub-branch
Returned Nurses RSL Sub-branchNewspaper - Newspaper clipping, [Pakenham-Berwick Gazette], Welfare work rewarded, [Wednesday, 7 February 1990]
Article about why Wilma Young [Wilma Elizabeth Forster Oram] received the Advance Australia Award 1989. This award was conferred because of her contributions to veteran welfare. She was also a POW during WWII on Bangka Island and Sumatra. Newspaper clipping with a headline and large black and white photograph of a elderly woman holding an award in her lap. The article has three columns of text.'Pakenham-Berwick Gazette / 100-106 Main St. P. / Wed. 7th Feb. 1990 Phone 059412 666' [blue ink at top of page] 'Page 25' [blue ink lower right hand corner] [article at end of main clipping article scribbled/crossed out with blue ink]wwii, world war two, ww2, wilma young, wilma elizabeth forster oram, advance australia award, bangka island, sumatra -
 Tramway Heritage Centre
Tramway Heritage CentrePhotograph Album (part of), Ray Pearson's Photo Album - Trams of Victorian Railways, Ballarat, Bendigo, Geelong
Page 2 of Ray Pearson's Photo Album. Brown card page with two photographs (landscape format) placed on page with plastic photo corners. The bottom photograph also has decorative metallic card photo corners beneath the newer plastic ones. Both photographs depict trams in streetscapes. The photo corner plastic is perishing and one photograph (top left) is loose on the page. Hand written inscriptions are written under the both photographs and also appear on the back of the loose photograph. One inscription beside the bottom photo is scribled out. Hand written inscription in biro under photographs. Top photo: VICTORIA ST TERMINUS Bottom photo: LYDIARD ST BALLARAT Beside bottom photo, scribbled out: SORRENTO STEAM TRAM To back of loose photograph - In top left corner with an underline: 8 To centre: Victoria St Terminus / Ent Route to Sardess / 20th Aug 1971 -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - SCRAP BOOK WITH 'PRESS OUT' ILLUSTRATIONS
Scrap Book (4 pages) with 'press-out' illustrations. These are inserted loosely in between the hard covers of a business book issued by the Commercial Union Assurance Co Ltd (Agent for Bendigo: Mr George G McColl printed on front cover). Printed on inside back cover is ''Record of Fire Policies and unused columns for such information - there are 'scribbles' on both inside front and back covers with the repeated (child's?) initials of EJH. A printed date may have been altered to be 1892. The rhyme ''Ten Little Nigger Boys'' (12 illustrations) are on four of the loose pages and three English monarchs are grouped on the other loose page. The ''Ten Little Nigger Boys'' is notable in that it is now politically incorrect and it is also brilliantly coloured and appears to be a very fine example of this type of 'press-out' illustration available for scrapbooks.business, retail, insurance, commercial union assurance co ltd., bendigo. mr george g mccoll -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Document - NEW CHUM & VICTORIA LINES OF REEF - NOTES ON NEW CHUM & VICTORIA
Handwritten notes on New Chum & Victoria. Winding Engine Pair 22 in cylinders. Two valves to each cylinder (Corliss?). One boiler - steel. 26 ft x 6 ft 6 ins diameter. Reference: T. M. Hooper, Mining Manager, Sth Bellevie United Mine in machinery. Report to His Directors probably 7 /11/1885. On the back with scribble over it, are some notes re Bendigo was making its own winding engines, air compressors and crushing machinery so efficiently that the Senior Inspector of Mines, Mr. E. R. Neekison in a report to the Secretary for Mines in 1884 was emphatic that the best batteries, winding engines and gear have all been made in Sandhurst. Machinery made in Sandhurst was superior to any others in the colony for this class of work.document, gold, new chum & victoria lines of reef, notes on new chum & victoria, t m hooper, sth bellevu united mine, mr e r meekison, new chum, garden gully, hustler's, sheepshead line -
 City of Kingston
City of KingstonPhotograph - Black and white, c. 1930
This image is part of a larger collection of images from the Public Transport Corporation displaying train stations and streetscapes in what is now the City of Kingston.The Nepean Highway is a major highway running through the City of Kingston. This image is one of many that depicts its importance to the local community as it undergoes many changes over time.Black and white photograph depicting railway crossing at Nepean Highway Moorabbin. The level crossing gates are open and a man is walking through with his dog. To the right of the crossing is a billboard/hoarding promoting what appears to be a brand of radio/wireless.White round sticker with indecipherable black printed text which has been scribbled over with black pen. White round sticker with black printed text: 175 Handwritten in red ink: 50% Blue ink stamped on reverse: COPYRIGHT / Public Transport Corporation / For re-ordering photographs / Please quote negative No ADV 903 / Enquiries C/- PTC Photographic Unit / Telephone switchboard 619 111moorabbin, trains, railway crossing, level crossing, nepean highway -
 The Beechworth Burke Museum
The Beechworth Burke MuseumPhotograph - Two Photographs, Saunders, 1864-1972
Taken some time after 1864, these photographs depict the Star Hotel both directly (8674.1) and from the Hotel north west down Ford Street (8674.2). The images depict the building with its modern exterior, having settled for this brick form after several other building designs. The Star Hotel was the first hotel opened in Beechworth, and would go through a series of dramatic changes under its first three owners. The original timber structure was built by W.H. Neuber, though at the time it was only known as ‘The Beechworth Hotel’. The site was later purchased in 1855 by mining entrepreneur, and prolific business owner, John Alston “Six Stars” Wallace. He would go on to extend the established hotel, rebuilding much of it with weatherboard and a shingled roof, adding a two storey structure with a verandah and a theatre capable of supporting 400-500 people, which was often used for international performances. Renamed as the Star Hotel, it was the second in a chain franchise, eventually leading to the “Six Stars” moniker Wallace went by, with hotels at Rutherglen, Chiltern, Yackandandah, Bright, Snake Valley, and of course, Beechworth. Under his ownership, it developed into a popular location for merchants, wayfarers, and locals alike, with the help of his brother Peter as manager. Situated on a road once synonymous with Melbourne to Sydney roadtrips, and the allure of the gold mines, the popularity of the Star drew all manner of clientele from across the country. As such a central hub, the ‘Star Assembly Rooms’ were used as a meeting place for debates, discussions, festivities, and problem solving among the various working sects of the area. These meetings included shareholder discussions for prospecting companies, railway planning, council meetings, and discussions surrounding the interactions between European and Chinese miners, both good and bad. By late 1856, John had the Beechworth at auction through J.H. Grey & Co. It was most likely due to the high profile murder of the manager, Robert Murdoch, during an altercation in relation to a dine and dash event by a Swedish miner, Charles Jansen, who had been ‘excited by drink’ on November 17th. He had refused to pay for his meal and waiter James Mitchell failed to persuade him otherwise. Mitchell, or possibly Murdoch himself, forced him out as tempers and threats escalated. As the photos tell, there are a number of doors which may be entered through, and Jansen used an alternate entrance to access the building. Murdoch was investigating the noise when he encountered the furious man. He was subsequently stabbed with no warning by a small clasp knife, as he tried to stop the intrusion. His exclamations, "I’m stabbed, I’m stabbed!” alerting other occupants, and Jansen was restrained and arrested. Murdoch died the next day from his injuries, with the inquest carried out on the theatre stage. Some 3000 members of the town attended the funeral, and the Star hung black cloth in memory of Robert and his death. Afterwards, an auction caw the property pass to Messrs Robertson and Quirk, though would return shortly thereafter to Six Stars’ portfolio. Six Stars would later sell off his properties from 1862, with the Beechworth Star purchased by 1864 by John Sitch Clark. This allowed Clark to redevelop a significant portion of the Hotel, stripping a central section and constructing the brick structure that survives today, reopening the Star in July that year. It was after this time that our photographs were taken. Clark would later sell the property to Frank Mitchell, shortly before his own death. The next owner, Frederick Allen, lived on the property before the deed was sold to him in the 1880s. He would later sell the property to William Carroll in 1890, with proprietorship eventually moving to Mr. W.H. Porter, and transferring to a Mr. Marendaz by 1913 and Mr. Holly in 1915. Licensing disputes would arise 1917 between Margaret Carroll and a Mrs. McDonald, before it became delicenced some years prior to 1935. It was around this year that the property was bought by Mr. W.J. Pemberton at the meagre price of £500, down from the £13,000 Six Stars originally auctioned it for. It served as a Youth Hostel for a period of time around 1972, and currently the building serves as a private accommodation on the second floor, with shops taking up the ground floor level.These photographs of the Beechworth Star Hotel as they depict a form of Beechworth's first hotel, and also the site of a high profile murder. Two black and white rectangular photographs printed on matte photographic paper.8674.1 (reverse) Beechworth/ 734/ Tanswell’s Hotel [crossed out]/? Old Star/ Hotel,/[small pencil scratching]/ Saunders/ BMM 8674.1 8674.2 (reverse) Beechworth/ 60%[circled]/ Old Star Hotel/Building etc.,/ 12 ½ cm/ 3"[circled, arrows extending horizontally to edges]/[arrows extending top to bottom mid-right of reverse]/ Saunders/ 734[circled]/ BMM 867.2,/ [thin scribbled bordering around top, right, and bottom edges]star hotel, beechworth hotel, john alston wallace, ja wallace, john sitch clark, frederick allen, robert murdoch, meeting place, tragedy, theatre, mining town
