Showing 40 items matching " cast iron works"
-
 Glen Eira Historical Society
Glen Eira Historical SocietyDocument - Burreel
... Cast iron works... lighting Cast iron works Architectural features gardens Document ...This file contains one item. 1. Auction leaflets for two periods of sale, 5 April and 30 April, years unknown, possibly 1990’s. Articles give same photograph of home, sketch of home and interior plan layout. Also includes history of Burreel to 1982/1983.burreel, biggin and scott, auctions, biggin kevin, lawson graeme, elsternwick, victorian style, mansions, stephen francis, glenhuntly road, buxton family, allen george, music, neate mary, nursing homes, alexander enid, cellars, bricks, bluestone, slate, verandas, fireplaces, plaster moulds, cool stores, gas lighting, cast iron works, architectural features, gardens -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Book - MUSEUM OF VICTORIAN TECHNOLOGY - AN EMPLOYMENT INITIATIVES PROGRAMME, c1983
... cast iron museum gas works tourism Bendigo... BENDIGO History victorian technology cast iron museum gas works ...Museum of Victorian Technology - An Employment Initiatives Programme. Project outline and detail for development of a Museum of Victorian Technology at the Old Gasworks Bendigo. Black and white Illustrations & maps.Bendigo City Council, Bendigo Trust and National Trust of Australia (Victoria)bendigo, history, victorian technology, cast iron museum gas works tourism bendigo -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societyembosser and seal, 1890's
This stamp and seal were collected by Kevin Ingram who cleaned up the Orbost Butter factory in 1981. It is possibly from the original factory in the 1890's.This seal was probably used on official letters.The Orbost Butter and Produce Co. Ltd was registered on June 1st 1893 and was an important source of income to the Orbost district.Cast iron stamp and seal. Stamp (.1) has a wooden handle which works by a lever action. It has a rectangular base plate and is painted black.The main stem is decorated in gold paint. The separate seal (.2) seems to have been attached to the stamp.On seal in centre : ORBOST Around edge of seal : Orbost Butter Factory plus some unreadable print orbost-butter-factory agriculture farming seal embosser stamp -
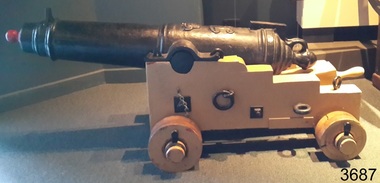 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageWeapon - Carronade, 1840
The carronade was designed as a short-range naval weapon with a low muzzle velocity for merchant ships, but it also found a niche role on warships. It was produced by the Carron Iron Works and was at first sold as a complete system with the gun, mounting, and shot altogether. Carronades initially became popular on British merchant ships during the American Revolutionary War. A lightweight gun that needed only a small gun crew and was devastating at short range was well suited to defending merchant ships against French and American privateers. The invention of the cannon is variously attributed to Lieutenant General Robert Melville in 1759, or to Charles Gascoigne, manager of the Carron Company from 1769 to 1779. In its early years, the weapon was sometimes called a "mellvinade" or a "gasconade". The carronade can be seen as the culmination of a development of naval guns reducing the barrel length and thereby the gunpowder charge. The Carron Company was already selling a "new light-constructed" gun, two-thirds of the weight of the standard naval gun and charged with one-sixth of the weight of the ball in powder before it introduced the carronade, which further halved the gunpowder charge. The theory of its design was to use less powder and had other advantages that were advertised in the company's sales pamphlet of the time, state. The smaller gunpowder charge reduced the barrel heating in action, also reduced the recoil. The mounting, attached to the side of the ship on a pivot, took the recoil on a slider, without altering the alignment of the gun. The pamphlet advocated the use of woollen cartridges, which eliminated the need for wadding and worming, although they were more expensive. Carronades also simplified gunnery for comparatively untrained merchant seamen in both aiming and reloading that was part of the rationale for adopting the gun. Other advantages promoted by the company were. The replacement of trunnions by a bolt underneath, to connect the gun to the mounting, reduced the width of the carriage that enhanced the wide angle of fire. A merchant ship would almost always be running away from an enemy, so a wide-angle of fire was much more important than on a warship. A carronade weighed a quarter as much as a standard cannon and used a quarter to a third of the gunpowder charge. This reduced charge allowed Carronades to have a shorter length and much lighter weight than long guns. Increasing the size of the bore and ball reduces the required length of the barrel. The force acting on the ball is proportional to the square of the diameter, while the mass of the ball rises by the cube, so acceleration is slower; thus, the barrel can be shorter and therefore lighter. Long guns were also much heavier than Carronades because they were over-specified to be capable of being double-shotted, (to load cannons with twice the shot, for increased damage at the expense of range), whereas it was dangerous to do this in a carronade. A ship could carry more carronades, or carronades of a larger calibre, than long guns, and carronades could be mounted on the upper decks, where heavy long guns could cause the ship to be top-heavy and unstable. Carronades also required a smaller gun crew, which was very important for merchant ships, and they were faster to reload. The small bore carronade and carriage is part of a collection of nineteenth Century Flagstaff Hill Guns and Cannon, which is classified as being of significance and was made a few years after the beginning of Queen Victoria's reign in 1837 and fires a 6 lb pound cannon ball. This nineteenth century artillery piece is a rare and representative item of artillery of this era, used predominately on ships, both military and merchant. The artillery piece, individually and as part of the collection, is highly significant for its historical, scientific and aesthetic reasons at the state, national and world level. This carronade represents the methods of artillery technology, its advancement and its modifications to suit dangerous situations that sailors encountered from attacks from free booters (pirates, living from plunder) or others at the time. Carronade firing a 6 lb cast iron ball, with a smooth bore barrel 6.5 cm in dia the item is mounted on stepped wooden carriage with wooden wheels. Cannon barrel can have its elevation adjusted via a wooden wedge. Gun carriage has loops for locating and holding in position to a deck by ropes. Carriage is a replica made 1982Cast into the barrel is the royal emblem of Queen Victoria (VR "Victoria Regina") indicating the carronade was cast during Queen Victoria's reign / 1840 & 4-2-0 denoting the weight of the barrel. Right hand trunnion has a serial number “8708”. Also on top of the barrel is the British "Board of Ordinance" identifying mark a broad arrow indicating the carronade was in military use. flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, colonial defences, victoria’s coastal defences, warrnambool fortification, warrnambool garrison battery, warrnambool volunteer corps, ordinance, armaments, garrison gun, smooth bore cannon, carronade, black powder, 12 pounder, 1840, artillery, lieutenant general robert melville, charles gascoigne, carron company, mellvinade, gasconade -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Post Office Receiving Pillar, 1885
Post Office Receiving Pillar was Collected from Warrnambool City Council’s Scott Street Depot and transported to Flagstaff Hill, stored in the Barracks area Friends of Flagstaff Hill began the project of restoring the Post Office Receiving Pillar in early 2011. The replacement dome required a pattern to be made from paper, then timber, then someone to manufacture it. The cast iron body required sand blasting and undercoating. The pillar was installed in Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village in March 2014. A specialist visited the Village and painted the pillar with 7 coats of ‘post office red’ then completed the job with gold paint on the details. In 2015 an information plate of brass was fitted to the Pillar in the position that would have originally announced the clearing times. It was originally manufactured by G Couch, Engineer, Alliance Iron Works, Melbourne. Gordon Couch passed away in June 1896 and his Works were offered for auction in November 1897. HISTORY OF POST OFFICE RECEIVING PILLARS In 1851 ‘pillar boxes’ were installed at roadside locations in the island of Jersey, England; they had already been successful in several European countries. The use of new prepaid, adhesive postage stamps as well as the roadside pillar boxes meant there was no need for the public to take a trip to the Post Office just to post a letter. By 1855 London had installed its first six Pillar Boxes. In 1856 the pillar boxes were first introduced in Sydney. These were circular with a crown on the dome, supported by leaves. Early Victoria Mail was originally collected by ‘letter carriers’, first appointed in Melbourne in 1841, equipped with leather bag and hand bell. He wore a red coat with brass buttons and a black top hat! In 1844 two wooden receiving boxes were erected in Melbourne. The first cast iron boxes were installed in South Melbourne (Emerald Hill) and were still in service until 1967. They were a fluted circular design and made in England. In the early 1860’s the ‘low door round’ design posting box was introduced, being circular and surrounded by a crown, with two broad embossed bands around its circumference. The clearance door was in front of the box and low down. These were made in Australia. In the early 1870’s square boxes with a tapering top were being used. These too were made in Australia by different manufacturers with slight variations on style such as the orientation and number of slots. Next came the circular boxes again, similar to the ‘low door round’ but with the clearance door extending to just below the posting slot, often referred to as ‘high door round’. These boxes did not have embossed bands. In 1887 small cast iron boxes were introduced, attached to posts and poles and called ‘lamp post receivers’. Around 1930 a ‘London’ model was used in Victoria. It was copied from the flat-domed type in London but made in Tasmania. … [References: Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village records, The Argus, 11th April, 1890, The Argus, 2nd July, 1896, The Argus, 30th Nov. 1897, “Stamps.Au” http://www.stampsau.com, 4th April 2011 (Extracted from “Australian Street Posting Boxes” by Ken Sparks – out of print)] Post Office Receiving Pillar, or letterbox.1885 "High Door Round" design, restored 2014 Tall cast iron sylinder with decorative dome cap, slot in side, hinged door with handle shaped as a fist. Painted red with gold trip..Reconditioned barrel, reconstructed dome. Restored by Friends of Flagstaff Hill, 2014. Now a working letterbox. Made in Melbourne.Oval maker's plate “ - G. COUCH - / ENGINEER / ALLIANCE IRON / WORKS / MELBOURNE”flagstaff hill, warrnambool, shipwrecked coast, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, post office receiving pillar, letterbox, mailbox, australia post -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyIron - Kerosene
Kerosene irons were used c1930 - 1950 especially where electricity wasn't available. Shelite was another fuel that could be used instead of kerosene. The advantage of the kerosene iron was that it didn't require a stove to be lit (especially in summer) to heat the iron and it didn't require electricity.Residents in the Kiewa Valley used kerosene irons.This black iron is made of cast iron with a steel base and a black wooden handle. This Comfort iron has a ball shaped container with a screw-on lid to hold the fuel (kerosene or Shelite). At the bottom of this ball is a pipe going down then meeting another pipe at right angles to it leading into the iron. At the pipe junction there is a handle on a screw to limit the amount of fuel. The Kerosene would flow through this pipe. There is a filler plug air stem on top. This is a self-heating iron.Comfort iron / Self Heating Comfort Iron MFD by / National Stamping and Electric Works / made in U.S.A. Chicago iron, domestic, laundry, pressing clothes, household, kerosene, shelite -
 Glenelg Shire Council Cultural Collection
Glenelg Shire Council Cultural CollectionDomestic object - Try pot, n.d
Believed donated to City of Portland Collection, stored at city works depot for many years.Cast iron, oval shaped pot, 2 flat sides, 2 round lifting or bracing lugs diagonally opposite each other. Circular opening on the top surrounded by collar. Gaps in collar (to fit spout or perhaps to join another pot).Front: on lip "Bishop London"whaling -
 Kiewa Valley Historical Society
Kiewa Valley Historical SocietyPot - Cast Iron, c1900
... on the High Plains used this cooking pot. cast iron. cooking pot ...Cattlemen on the High Plains used this cooking pot.This circular cast iron pot has three legs. The pot has straight sides, 13 cms high and a diameter of 36 cms. The handle is in two pieces joined with a hinged pin with hooks on the ends. These hooks go through the cast iron protruding "eyes" on each side near the top.Albion Stove Works, Maryborough.cast iron. cooking pot. albion stove works. maryborough. -
 Orbost & District Historical Society
Orbost & District Historical Societydolly pot
A dolly pot is used to crush specimens and samples before panning. It works like a large mortar and pestle. A small cast iron dolly pot.dolly-pot gold-mining metal-trades -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageInstrument - Barometer, 1867
Langlands Company History: Langlands foundry was Melbourne's first foundry and iron shipbuilder established in 1842, only 8 years after the founding of the Victorian colony by two Scottish immigrants, Robert Langlands and Thomas Fulton, who had formed a partnership before emigrating (1813–1859). The business was known as the 'Langlands Foundry Co'. Henry Langlands (1794-1863), left Scotland in 1846 with his wife Christian, née Thoms, and five surviving children to join his brother Robert. By the time he arrived in early January of 1847 the partnership of Robert Langlands and Fulton had dissolved as Fulton had gone off to establish his own works. It was at this time that the two brothers took over ownership of Langlands foundry. Several years later Robert retired and Henry became sole the proprietor. The foundry was originally located on Flinders Lane between King and Spencer streets. Their sole machine tool, when they commenced as a business, was a small slide rest lathe turned by foot. In about 1865 they moved to the south side of the Yarra River, to the Yarra bank near the Spencer Street Bridge and then in about 1886 they moved to Grant Street, South Melbourne. The works employed as many as 350 workers manufacturing a wide range of marine, mining, civil engineering, railway and general manufacturing components including engines and boilers. The foundry prospered despite high wages and the lack of raw materials. It became known for high-quality products that competed successfully with any imported articles. By the time Henry retired, the foundry was one of the largest employers in Victoria and was responsible for casting the first bell and lamp-posts in the colony. The business was carried on by his sons after Henry's death. The company was responsible for fabricating the boiler for the first railway locomotive to operate in Australia, built-in 1854 by Robertson, Martin & Smith for the Melbourne and Hobson's Bay Railway Company. Also in the 1860s, they commenced manufacture of cast iron pipes for the Board of Works, which was then laying the first reticulated water supply system in Melbourne. Langlands was well known for its gold mining equipment, being the first company in Victoria to take up the manufacture of mining machinery, and it played an important role in equipping Victoria's and Australia's first mineral boom in the 1850s and 1860s. Langlands Foundry was an incubator for several engineers including Herbert Austin (1866–1941) who worked as a fitter at Langlands and went on to work on the Wolesely Shearing machine. He also founded the Austin Motor Company in 1905. Around the 1890s Langlands Foundry Co. declined and was bought up by the Austral Otis Co. in about 1893. History for Grimoldi: John Baptist Grimoldi was born in London UK. His Father was Domeneck Grimoldi, who was born in Amsterdam with an Italian Father and Dutch mother. Domeneck was also a scientific instrument maker. John B Grimoldi had served his apprenticeship to his older brother Henry Grimoldi in Brooke Street, Holburn, London and had emigrated from England to Australia to start his own meteorological and scientific instrument makers business at 81 Queens St Melbourne. He operated his business in 1862 until 1883 when it was brought by William Samuel and Charles Frederick, also well known scientific instrument makers who had emigrated to Melbourne in 1875. John Grimoldi became successful and made a number of high quality measuring instruments for the Meteorological Observatory in Melbourne. The barometer was installed at Warrnambool's old jetty and then the Breakwater as part of the Victorian Government's insistence that barometers be placed at all major Victorian ports. This coastal barometer is representative of barometers that were installed through this government scheme that began in 1866. The collecting of meteorological data was an important aspect of the Melbourne Observatory's work from its inception. Just as astronomy had an important practical role to play in navigation, timekeeping and surveying, so the meteorological service provided up to date weather information and forecasts that were essential for shipping and agriculture. As a result, instruments made by the early instrument makers of Australia was of significant importance to the development and safe trading of companies operating during the Victorian colonies early days. The provenance of this artefact is well documented and demonstrates, in particular, the importance of the barometer to the local fishermen and mariners of Warrnambool. This barometer is historically significant for its association with Langlands’ Foundry which pioneered technology in the developing colony by establishing the first ironworks in Melbourne founded in 1842. Also, it is significant for its connection to John B Grimoldi who made the barometer and thermometer housed in the cast iron case. Grimoldi, a successful meteorological and scientific instrument maker, arrived in the colony from England and established his business in 1862 becoming an instrument maker to the Melbourne Observatory. Additional significance is its completeness and for its rarity, as it is believed to be one of only two extant barometers of this type and in 1986 it was moved to Flagstaff Hill Maritime Village as part of its museum collection. Coast Barometer No. 8 is a tall, red painted cast iron pillar containing a vertical combined barometer and thermometer. Half way down in the cast iron framed glass door is a keyhole. Inside is a wooden case containing a mercury barometer at the top with a thermometer attached underneath, each with a separate glass window and a silver coloured metal backing plate. Just below the barometer, on the right-hand side, is a brass disc with a hole for a gauge key in the centre. The barometer has a silvered tin backing plate with a scale, in inches, of "27 to 31" on the right side and includes a Vernier with finer markings, which is set by turning the gauge key. The thermometer has a silvered tin backing plate with a scale on the left side of "30 to 140". Each of the scales has markings showing the units between the numbers.Inscription at the top front of the pillar reads "COAST BAROMETER" Inscribed on the bottom of the pillar is "No 8". and "LANGLANDS BROS & CO ENGINEERS MELBOURNE " The barometer backing plate is inscribed "COAST BAROMETER NO. 8, VICTORIA" and printed on the left of the scale, has "J GRIMOLDI" on the top and left of the scale, inscribed "Maker, MELBOURNE". There is an inscription on the bottom right-hand side of the thermometer scale, just above the 30 mark "FREEZING" Etched into the timber inside the case are the Roman numerals "VIII" (the number 8)flagstaff hill, warrnambool, maritime village, maritime museum, flagstaff hill maritime museum & village, shipwreck coast, great ocean road, warrnambool breakwater, coast barometer, coastal barometer, barometer, weather warning, ports and harbours, fishery barometer, sea coast barometer, austral otis co, coast barometer no. 8, henry grimoldi, henry langlands, john baptist grimoldi, langlands foundry co, meteorological instrument maker, robert langlands, scientific instrument maker, thermometer, thomas fulton -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Stove, Cox and Rizzetti Stove Works, ca. 1918-1930s
Cast iron stoves burn solid fuel such as wood or coal, and are used for cooking and warmth. The stoves have a firebox with a grate where the fuel is burned. The hot air flows through flues and baffles that heat the stove top and the oven. Before cast iron stoves were invented, cooking and heating were carried out in outdoor open fires, and later, in fireplaces inside the home. In 1642 the first cast iron stove was manufactured in Lynn, Massachusetts, where molten cast iron was poured into a sand mould to make rectangular plates that were then joined together to make a box. Benjamin Franklin invented the more efficient Pennsylvania stove in 1744, and this efficient design is still used today. After the mid-19th century cast iron stoves were produced with burners in different positions, giving varied temperatures, so a wide variety of foods could be cooked at the same time at the most suitable heat, from slow cooking to baking scones. In contemporary times people the new wood-burning stoves had to meet the anti-pollution standards now in place to protect our environment. By the 1920s gas cookers were being introduced for domestic use, and by the 1930s electric home cookers were being offered to householders. PLANET STOVES In August 1925 the firm Cox and Rizzetti, Stove Works, and also Sydney Road, South Melbourne, advertised in the Brunswick and Coburg Leader of November 11, 1925 as "formerly with Harnwell and Sons" and as "specialists in solid cast iron Planet stoves ... which merit an inspection from builders and householders". The firm continued in business and was mentioned as sponsors in the King Island News in 1971. Harnwell and Sons was listed in the Victorian Government Gazette of 1894. It is curious that the firm was mentioned in an article in the Sunrasia Daily of June 14, 1934 titled 'Planet Stoves' as a manufacturer of Planet Stoves. This Planet No 3 stove is an uncommon example of cooking equipment used in kitchens in the early 20th century, as the firebox is above the oven rather than beside it. The cast iron combustion stove is significant as part of the evolution of domestic cooking. Previously cooking was mostly carried out in outdoors in open fires, and later in fireplaces indoors. Cast iron stoves are still used today and have additional features such as thermostats to monitor and maintain temperature, water heating pipes connected, and environmentally approved anti-pollution fittings. Stove; a compact, blackened cast iron combustion cooker, installed within a fireplace and enclosed by bricks on both sides. The upright rectangular stove has a flat top with three round, removable cook plates and a flue connected at the back. The front has three doors with round knob handles; a swing-down firebox door above a sliding ashtray, and two side-hinged oven doors above a sliding opening. Inside on the side walls are two pairs of runners. Behind the pair of doors is an oven with two pairs of rails and two removable metal shelves. The stove has cast inscriptions on the chimney flue and on the front of the right hand side stove door. The model of the stove is The Planet No 3, made in Melbourne.Chimney flue, "[within rectangle] THE / PLANET" Stove door, "(within oval) PLANET / No 3"flagstaff hill, flagstaff hill maritime museum and village, warrnambool, maritime museum, maritime village, great ocean road, shipwreck coast, stove, cast iron stove, combustion stove, wood-burning stove, wood stove, wood oven, solid fuel stove, cooker, the planet, planet, planet no. 3, kitchen equipment, baking, domestic cooking, cooking equipment, food preparation, planet stove, planet cooker, cooking range, slow combustion stove, antique, range cooker, cox and rizzetti, harnwell and sons, melbourne manufacturer -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageDomestic object - Boiling Copper, Newberry & Walker, Boiling Tub, Circa1900
Francis John Newberry founded the Victoria Foundry and Enameling Works in 1890 with a workmate from the Humbles iron foundry in Lupton Street Geelong where he worked. Newberry & Walker Foundry & Enameling Works was built adjoining a cottage that was to be the home of the Newberry family during the ensuing years. Although Walker soon relocated to New Zealand, the Newberry and Walker foundry had become a local success. The foundry produced numerous cast iron products such as washing copper frames, and friezes, balustrades and verandah columns. Verandah posts are to be found in declining numbers, but the Newberry and Walker mark can sometimes be seen on the few which remain. A certain number of iron culvert posts were also made; some of them were still in place on the road to Cressy as late as 1961. Perhaps half the iron friezes on Geelong West verandahs came from the local firm’s foundry. A significant item made in Geelong giving a snapshot into the early beginnings of Victoria's industrial manufacturing of products that helped to replace previously imported items from England or America.Copper boiling tub, cast iron frame copper bowl inside of 14 gallon capacity Newberry & Walkerflagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, copper, cast iron, newberry & walker, washing copper frame, laundry, dairy, butchering -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Anchor, Henry P Parkes & Co, 1885 - 1904
In about 1820 Henry Pershouse Parkes, from Dudley, established the Tipton Green Chain and Anchor Works (Staffordshire). The firm’s products included cables, chains, anchors and all kinds of forgings. In 1851 some tests were carried out on the company’s chains to demonstrate the tensile strength and fibrous toughness of the iron used in their production. The iron used on this occasion was supplied by Summer Hill Iron Works. Some of the chains were exhibited at the Great Exhibition in 1851 and also at the 1855 French Exhibition in Paris, where they won a prize medal. Henry Pershouse Parkes died in 1867 and appears to have been succeeded by his son, who had the same name. In 1867 the firm produced the largest anchor in the world, at that time. It was built for Brunel’s S. S. Great Eastern to the patented design of Joseph Beterley, of Liverpool. The anchor, which weighed eight tons was twenty six and a half feet long and cast from iron supplied by Bloomfield Iron Works. It was tested at Tipton Proving House and found to be able to stand a strain of 100 tons. Henry Pershouse Parkes junior went into partnership with Alexander Stewart Ross to form Henry P. Parkes and Ross. The partnership came to an end in 1885 and the company became Henry P. Parkes & Company. In 1904 the business was sold and became H. P. Parkes and Company, under the control of N. Hingley & Sons Limited, of Netherton. In 1944 the company’s name was changed to Richard Sykes and Son Limited, then in 1947 it became H. P. Parkes & Company Limited. The business went into liquidation in 1966.The item is significant as an early example of a well known prize winning British anchor and chain maker from the mid 19th century. The company name on the anchor indicate the period of manufacture making it a significant item prized today by collectors.Anchor 5 pronged metal with loop at bottom to attach anti-snag rope. Long shank painted black. Label attached "Henry P Parker and Co"flagstaff hill, warrnambool, flagstaff-hill, flagstaff-hill-maritime-museum, maritime-museum, shipwreck-coast, flagstaff-hill-maritime-village, five pronged anchor, henry p parkes & co, tipton green chain and anchor works -
 Federation University Historical Collection
Federation University Historical CollectionBook, Ballarat Conservation Guidelines, 1981, 1981
The Guidelines were commissioned by the City of Ballarat , Historical Buildings Preservation Council and the Australian Heritage Commission.Cream soft coloured book of 60 pages. Contents include - Contributary Commercial Buildings, New COmmercial Buildings, Contributary residential Buildings, New Residential Development, Public and In stitutiona Buildings, Railways, Cemeteries, Botanic Gardens, Lake Wendouree, Public Open Spaces, Street Works, Fences and Landscaping, Advertising Guidelines, Lydiard/Camp Street Precinct Case Studyballarat, conservation guidelines, lydiard/camp street precinct case study, railway, botanic gardens, guttes, footpaths, signs, signage, fences, robin nuttall, gerald jenzen, ray tonkin, conservation study, architectural styles, verandahs, shopfronts, cast iron, wndy jacobs, miles lewis, gary vines, heritage planning, heritage guidelines -
 Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and Village
Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum and VillageFunctional object - Water standpipe, Langlands Bros. & Co, 1880-1893
This water standpipe is believed to be the only one of its kind in working order. It was originally located in Warrnambool, on the hillside at the corner of Mickle Crescent and Banyan Street, providing water for the Chinese Market Gardens below, on the flats. It was removed from this location on May 2nd, 1979, with the intention to relocate it at the new Flagstaff Hill Maritime Museum & Village. The standpipe lay in storage for years until the Warrnambool Company, Chemblast, offered to restore it for use as a working display. The display was officially opened on March 31, 2014. The water from the adjacent lake is drawn out with a hand operated water pump, and goes up into the standpipe, where flows through the canvas hose and into the top of the Furphy Farm Water Cart. The display is a visual acknowledgement of the years served by Flagstaff Hill volunteer and Friends of Flagstaff Hill Chairperson, Bob Crossman. Warrnambool’s early settlers had no water supply prior to the mid-1850s. They relied on rain water tanks, domestic wells and springs. The town experienced a huge, destructive fire in William Bateman Jnr. & Co.’s large produce store in November 1856, which highlighted the need for both a fire brigade and a good supply of water. In 1863 a volunteer fire brigade was established. In August 1880 the town celebrated the installation of its first water standpipe on the corner of Liebig and Timor streets. The water was pumped from springs at Cannon Hill through the connected pipeline to the standpipe, then distributed to households via horse and cart. Each of the licenced cart drivers were compelled by Council regulations to keep their carts full from sunset to sunrise, ready to cart water to outbreaks of fire. They received a fee for this service. In 1893 the town installed a water supply, sourced from the Merri River, stored in a reservoir basin and tower in north Liebig Street, and distributed throughout the town in a system of pipes. By late 1939 a reticulated supply was installed, with the water piped in under the Otway Scheme. Standpipes are still used in modern times in rural and remote areas for homes, farms, stock, agriculture and firefighting. Many commercial or government owned standpipes are metered, charging a fee for the quantities of water supplied. This water standpipe was made by Langlands Foundry Co. Limited, Melbourne, which was establish in 1842. It was Melbourne’s first foundry and iron shipbuilder, and one of the largest employers in Victoria at the time. Langlands was known for its high quality workmanship and wide range of goods for mining, engineering, marine, railway and other industrial uses. The company made the first cast bell, the first lamp posts in the colony, and the boiler for the first Australian train. In the 1860s it produced cast iron pipes for the Board of Works, which laid the pipes for Melbourne’s first reticulated water supply. The firm was bought by Austral Otis Co. in 1897.This water standpipe is significant historically as it is believed to be the only one of its type in working condition. The standpipe is significant for being manufactured by early colonial firm Langlands Foundry of Melbourne, which was known for high quality, cast iron products. The firm made the boiler for the first Australian train, assembled the first Australian paddle steamer and made the first Australian cast bell and lamp posts. Langlands was one of the largest employers in Victoria at the time. The standpipe is significant historically as it represents the evolution of water supply services in Australia. Standpipe; vertical cast iron water pipe, painted crimson, fixed in position, tapering inward from the round base to the rectangular joint near the finial on top. A hexagonal pipe extends at right angles from the joint, with an outlet fitting and flow-controlling wheel on the end. A length of canvas hose hangs from the outlet fitting. Inscriptions are on one face of the joint. The standpipe was made by Langlands Foundry Company of Melbourne. Embossed “LANGLANDS FOUNDRY CO. / LIMITED / ENGINEERS / MELBOURNE”warrnambool, flagstaff hill maritime museum, maritime museum, shipwreck coast, flagstaff hill maritime village, great ocean road, flagstaff hill, standpipe, stand-pipe, water standpipe, fire standpipe, firefighting equipment, water supply equipment, chinese market gardens, banyan street, liebig street, water tower, bateman’s fire, working display, water supply, town water, rural water, reticulated water, cannon hill spring, merri river, otway water, water carters, horse and cart water supply, volunteer fire brigade, langlands foundry, early melbourne, iron works, bob crossman, late 19th century water supply -
 Bendigo Historical Society Inc.
Bendigo Historical Society Inc.Photograph - CHARLIE BUTTON'S STORE
black and white photo: large weatherboard building with central doorway, 4 arched windows and panelled doorway to right of photo. Two males standing in doorway. Trunks, prams, rocking chairs in front of photo, also cast iron cookware. MP 99 top right hand corner. On paper enclosed with photo : ' this large weatherboard building was Charlie Button's Secondhand Furniture Store at 204 Williamson Street next to Jones Miller's Store formerly Pickles' large rolling stock works' ( BHS Inc. )organization, business, charlie button's store -
 Wannon Water
Wannon WaterCast iron seal embossing press, Excello, Seal
Heywood Waterworks Trust was constituted on 20 November 1962 upon application by Councillors of the Shire of Portland to construct, manage and maintain the works for the supply of water to the township of Heywood. The Trust was abolished on 1 July 1984 under the Water and Sewerage (Restructuring) Act 1983 when it amalgamated with the Heywood Sewerage Authority to form Heywood Water BoardA cast iron seal press, . This was used by Heywood Waterworks Trust to emboss agreements and official documents. Die is still attached to the press. It reads: Heywood Waterworks Trust 1963Small metal machine painted black and mounted onto a black rubber base. Two dies are attached with the seal of Heywood Waterworks Trust. Paper is placed between the dies, the handle depressed and the seal embossed on the paper under pressure as a blind (inkless) embossing. The seal consists of two circles with the wording "Heywood Waterworks Trust".Heywood Waterworks Trust 1963/ Excello / Reg Trade Mark/ Seal Press/ Pat NO 420419/Size No 2/Inscription on rubber base: "EXCELLO SEAL PRESS" / REGD TRADE MARK / 1. PATENT ROLLER BEARING HANDLE PAT. NO. 420419 / 2. DURABLE PLASTIC COUNTER / 3. RUBBER DESK PROTECTOR / STANDARD RUBBER TYPE CO. LTD. / TOKYO JAPAN"heywood, public administration, water supply, amalgamations -
 Wannon Water
Wannon WaterCast Iron Seal Embossing Press, Seal
Mortlake Waterworks Trust – 18 May 1915 to 1 July 1984 Mortlake Waterworks Trust was constituted on 18 May 1915 following application by the Shire of Mortlake to carry out works for the supply of water to the township of Mortlake. The Trust was abolished on 1 July 1984 under the Water and Sewerage Authorities (Restructuring) Act 1983 when authority was transferred to the Mortlake Water Board. A cast iron seal press. This was used by Mortlake Waterworks Trust to emboss agreements and official documents. Die is still attached to the press. It reads: Mortlake Waterworks Trust 1915. Small metal machine painted black , decorated gold . Dies are attached with the seal of Mortlake Waterworks Trust . Paper is placed between the dies, the handle depressed and the seal embossed on the paper under pressure as a blind (inkless) embossing. The seal consists of two circles with the wording "Mortlake Waterworks Trust 1915". Mortlake Waterworks Trust 1915mortlake, public administration, water supply, amalgamations -
 Wannon Water
Wannon WaterPipe, Cast Iron Pipe
This 75 mm cast iron pipe was laid in 1920 and would have been cement lined in the 1960's. It was replaced during modifications of Jamieson Street Roundabout Pipe Works in 2013Cast Iron pipe - rust encrusted on the outside, cement lined on the insidewater, pipe, reticulation, -
 Wannon Water
Wannon WaterPipe, Cast Iron Pipe
This 75 mm cast iron pipe was laid in 1920 and would have been cement lined in the 1960's. It was replaced during modifications of Jamieson Street Roundabout Pipe Works in 2013 Rust encrusted on the outside, cement lined on the insidewater, pipe, reticulation -
 Wannon Water
Wannon WaterPipe, Cast Iron Pipe
This 100 mm cast iron pipe was laid in 1920 and would have been cement lined in the 1960's. It was replaced during modifications of Jamieson Street Roundabout Pipe Works in 2013 Rust Encrusted on the outside - cement lined on the incsidewater, pipe, reticulation -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayV. R. Krupp 1888. IV. Rail, 1888
60lbs rail that was used throughout the Victorian rail network. In 1887 Gibbs, Bright and Co. had a contract with Victorian Railways for railway and canal construction and supply of Krupp Rails. Gibbs, Bright and Co were merchant bankers and shipping agents and merchants who where also Directors of the GWR ( Great Western Railway ) and the Ship The "Great Britain" in England Gibbs, Bright and Company had principally been involved in shipping and trading, mainly in the West Indies, but following the discovery of gold in Victoria they established an office in Melbourne and soon became one of the leading shipping agents and merchants in the Colony. They expanded into passenger shipping and soon established offices in Brisbane, Sydney, Newcastle, Adelaide and Perth as well as launching passenger services between England, Mauritius and New Zealand. Gibbs, Bright also held a number of financial agencies from British mortgage, finance and investment companies as well as representing several British insurance companies in Australia. In addition they conducted a growing import business as well as an export business that included livestock, dairy produce, wool and flour. Also the company played a substantial part in the development of Australia's mineral resources, starting with lead in 1895, and later venturing into tin, gold, copper, cement and super phosphates. In Australia, after WWI, many of the larger companies were managing their own import and export so Gibbs, Bright and Company tended to focus its Agency business on smaller companies while expanding their interest into other markets such as timber, wire netting, zinc, stevedoring, road transport, marine salvage, gold mining as well as mechanical, structural, electrical and marine engineering. The Company's shipping interests continued to grow as well and still formed a major part of its business. In 1948 the parent company in England took the major step from tradition when they changed the business from a partnership into a private limited company. The name was the same, Antony Gibbs and Sons Limited, and in practice the effect of the change was very little. Some of the firm's branches and departments had already become limited companies and the formation of a parent company simplified the structure. The Australian operation was in time changed to Gibbs Bright & Co Pty Ltd in 1963. In 1848 Alfred Krupp becomes the sole proprietor of the company which from 1850 experiences its first major growth surge. In 1849 his equally talented brother Hermann (1814 - 1879) takes over the hardware factory Metallwarenfabrik in Berndorf near Vienna, which Krupp had established together with Alexander Schöller six years earlier. The factory manufactures cutlery in a rolling process developed by the brothers. Krupp's main products are machinery and machine components made of high-quality cast steel, especially equipment for the railroads, most notably the seamless wheel tire, and from 1859 to an increased extent artillery. To secure raw materials and feedstock for his production, Krupp acquires ore deposits, coal mines and iron works. On Alfred Krupp's death in 1887 the company employs 20,200 people. His great business success is based on the quality of the products, systematic measures to secure sales, the use of new cost-effective steel-making techniques, good organization within the company, and the cultivation of a loyal and highly qualified workforce among other things through an extensive company welfare system. From 1878 August Thyssen starts to get involved in processing the products manufactured by Thyssen & Co., including the fabrication of pipes for gas lines. In 1882 he starts rolling sheet at Styrum, for which two years later he sets up a galvanizing shop. The foundation stone for Maschinenfabrik Thyssen & Co. is laid in 1883 with the purchase of a neighboring mechanical engineering company. In 1891 August Thyssen takes the first step toward creating a vertical company at the Gewerkschaft Deutscher Kaiser coal mine in [Duisburg-]Hamborn, which he expands to an integrated iron and steelmaking plant on the River Rhine. Just before the First World War he starts to expand his group internationally (Netherlands, UK, France, Russia, Mediterranean region, Argentina). info from The company thyssenkrupp - History https://www.thyssenkrupp.com/en/company/history/the-founding-families/alfred-krupp.htmlHistoric - Victorian Railways - Track Rail - made by Krupp in 1888Section of VR Krupp 1888 Rail mounted on a piece of varnished wood. Rail made of ironpuffing billy, krupp, rail, victorian railways -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayDouble Headed Rail, circa 1872 - 1883
Double Headed Rail from Ravenswood Station Siding which was dismantled circa 1987 the two rails were stored for a time at Maldon before being donated to Puffing Billy Museum Bearing makers marks of Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield- Steel works Wilson & Cammell made Steel rails at their Dronfield Steel Works, in Dronfield, North East Derbyshire, England from 1872 - 1883 Double-headed rail In late 1830s Britain, railway lines had a vast range of different patterns. One of the earliest lines to use double-headed rail was the London and Birmingham Railway, which had offered a prize for the best design. This rail was supported by chairs and the head and foot of the rail had the same profile. The supposed advantage was that, when the head became worn, the rail could be turned over and re-used. In practice, this form of recycling was not very successful as the chair caused dents in the lower surface, and double-headed rail evolved into bullhead rail in which the head was more substantial than the foot. Info from Wikipedia - Rail Profile https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rail_profile The first records of double headed rail being used In Victoria by Victorian Railways was in 1859, the rails, chairs, oak and trenails were imported from UK. After the 1870’s the Victorian Railways went over to using flat bottom rails, but they still needed replacement double headed rail for lines already laid and this continued up to at least 1883 Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield- Steel works Wilson & Cammell made Steel rails at their Dronfield Steel Works, in Dronfield England from 1872 - 1883 Mount Alexander & Murray River Railway The Melbourne, Mount Alexander & Murray River Railway Company received parliamentary assent in February 1853 to build Victoria's first inland railway from Melbourne to Williamstown, and Melbourne to Bendigo and Echuca. Construction commenced in January 1854 with work on a pier at Williamstown but lack of funds slowed progress, eventually prompting the company to sell out to the government. The 100-mile (162 km) section to Bendigo opened in October 1862. Its cost of £35,000 per mile made it the most expensive railway ever built in Australia. In 1864, the line was extended to Echuca, tapping into the booming Murray-Darling paddlesteamer trade. info from Museums Victoria - Victorian Railways https://museumsvictoria.com.au/railways/theme.aspx?lvl=3&IRN=450&gall=456 1863 Ravenswood Station open on the 1st Feb 1863 Victorian Railways - purchased and imported the Rail and Chairs from Raleigh, Dalgleish, White and Co. London Importation of railway plant : abstract of a return to an order of the Legislative Assembly dated 27th June 1860 for - Copies of the advertisements calling for tenders, the names of the tenderers and the accounts and correspondence with Mr Brunel relating thereto GP V 1859/60 no. C 15 http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoC15.pdf Report from the Select Committee upon the Importation of Railway Plant : together with proceedings of the Committee, minutes of evidence and appendix GP V 1859/60 no. D 38 (2.9 MB) http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoD38.pdf Ravenswood Siding When the Victorian Railways were established in 1856 they adopted one of the popular British permanent way standards - heavy 80lb (36.3kg) double-headed rail held up right in cast iron chairs attached to transverse timber sleepers by wooden pegs called trenails. The Ravenswood Railway siding was constructed in 1862 with 12 feet wrought iron double-head rail held in cast iron chairs with Ransom and May patent compressed keys. Trenails held the chairs to the sleepers and the joints were secured in joint chairs. Joints were subsequently joined using fish plates. It formed part of the Melbourne to Echuca rail line, initially known as the Melbourne, Mt Alexander and Murray River Railway. George Christian Derbyshire, the first Engineer-in-Chair of the Victorian Railways was responsible for the design and construction of the works. No new lines were built in Victoria using double-headed rail after 1870. The siding was disconnected from the main line in 1988. The Ravenswood Railway Siding demonstrates the original 1856 philosophy of the Victorian Railways to adopt British permanent way technology. The siding demonstrates significant aspects in the development of permanent way technology in England and Victoria over the period from the 1830's to the 1880's. The chairs in the Ravenswood siding are physical evidence of early railway technology rendered obsolete 120 years ago, namely joint chairs at rail joints and trenails to secure the chairs to the sleepers. The double-headed rail demonstrates an important stage in the evolution of British rail technology in the 1830s. The old fish plates, square headed bolts and square nuts demonstrate the success of fishing the rail joins. The Ravenswood siding demonstrates the earliest form of rail joint technology developed in England, and existing in Australia, the joint chair. In part of the siding the sequence of joint and intermediate chairs is consistent with the 1856 specifications, that sequence is rare with the joints secured in joint chairs. The survival of chairs in this sequence is rare and almost certainly demonstrates that they remained in continuous use at the same location from 1862 to 1988. This remnant of the Ravenswood siding has survived 126 years. The siding has proved to be the most significant of extant remnant double-headed sidings in Victoria, containing a rare combination of early permanent way technologies. Construction dates 1862, Info from Ravenswood Railway Siding Victorian Heritage Database Report http://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/4693/download-report The remaining section of this siding is significant at the State and National levels in that it demonstrates the use of chaired rail by the Victorian Railways Department for the Trunk Lines and, more particularly, the following stages in the evolution of this long obsolete method of permanent way construction: a) The use of joint chairs and intermediate chairs at regular intervals inferring that the original wrought iron rail lengths were 12 feet, as is known through documentary sources to have been the case. The survival of chairs in this sequence is unique and almost certainly demonstrates that they have remained in continuous use at the same location and in the same sequence from 1862 to 1988 . b) The use of joint chairs and intermediate chairs designed for use with trenails. c) The use of later intermediate chairs designed for use with steel pins and the use of fished joints with steel double head chaired rail, representing a second method of constructing the permanent way using chaired rail technology. info from Ravenswood Siding - Melbourne/Echuca Railway Line - Victorian Heritage Database Report http://vhd.heritagecouncil.vic.gov.au/places/70103/download-report Addition to Citation for Melbourne to EchucaRailway Line 1/10/1990 Double Head Rail The surviving lengths of double head rail with chairs on this railway compare with one surviving similar remnant on the Geelong to Ballarat railway and are representative of permanent way construction techniques applied exclusively to the two trunk railways of the 1860's. In this respect they are rare survivors and may be unique at the national level and of technical importance at the international level to the extent that they enhance contemporary understanding of early railway building technology. Surviving lengths of chaired double head rail survive at Kyneton, Ravenswood and Bendigo on this railway and include a number of different types of cast iron intermediate and joint chairs with hardwood keys and metal pins. The Ravenswood siding is of special significance for the diversity of chair types and for the sequence of chairs recalling rail lengths known to be associated with construction of the line in 1862. Construction of the Railway Tenders closed on 24 March 1858 with no less than 133 tenders being received. A contract was let to Cornish and Bruce for £3,356,937 to commence work on 1 June 1858 and complete the line by 31 July 1861. Cornish and Bruce made quick early progress with the Melbourne to Sunbury section being officially opened on 13 January 1859. The line was officially opened to Bendigo (Sandhurst) on 20 October 1862 by the Governor of Victoria, Sir Henry Barkly. A great banquet was held for 800 guests and this was followed by a grand ball. The extension of the line to Echuca was a relatively simple matter as that part of the line was across plain country without any significant engineering challenges. Tenders were called for the work in 1863 and the work was completed in 1864 by contractors Collier and Barry Apart from the line contractors, other firms directly involved were J Shire law and Co (sleepers), R Fulton, Langlands Brothers and Co, William Crossley (water supply), B Moreland, Langlands Brothers and Co (platelayers lorries), E Chambers (iron pins, traversers), Miller and McQuinstan (luggage vans and steam engines) and various contractors for building works. Info from Engineers Australia Engineering Heritage Victoria Nomination for Recognition under the Engineering Heritage Australia Heritage Recognition Program for the Goldfields Railways - Melbourne , Bendigo & Echuca Railway Page 25 - .2.9.2 Statement from National Trust of Australia (Victoria) Listing number B5323 for Mt Alexander/Murray Valley Rail Line: Page 69 - Theme 3 https://www.engineersaustralia.org.au/portal/system/files/engineering-heritage-australia/nomination-title/Melbourne_%20Bendigo_Echuca%20Railway%20Nomination.pdf The Melbourne, Mount Alexander and Murray River Railway Company was a railway company in Victoria, Australia. It was established on 8 February 1853 to build a railway from Melbourne to Echuca on the Victorian-NSW border and a branch railway to Williamstown. The company struggled to make any progress and on 23 May 1856, the colonial Government took over the Company and it became part of the newly established Department of Railways, part of the Board of Land and Works. The Department of Railways became Victorian Railways in 1859. Construction of the Bendigo line commenced in 1858, but this private consortium also met with financial difficulties when it was unable to raise sufficient funds, and was bought out by the Victorian colonial government. The design work was then taken over by Captain Andrew Clarke, R. E., Surveyor-General of Victoria, with bridge designs completed by Bryson and O'Hara The contract for the first stage of the line from Footscray to Sandhurst (now Bendigo), was let to Cornish and Bruce for £3,356,937.2s.2d ($6.714 million) with work commencing on 1 June 1858. Completion of the permanent way was to be by 31 July 1861 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Melbourne,_Mount_Alexander_and_Murray_River_Railway_Company Victorian Railways - purchased and imported the Rail and Chairs from Raleigh, Dalgleish, White and Co. London Importation of railway plant : abstract of a return to an order of the Legislative Assembly dated 27th June 1860 for - Copies of the advertisements calling for tenders, the names of the tenderers and the accounts and correspondence with Mr Brunel relating thereto GP V 1859/60 no. C 15 http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoC15.pdf Report from the Select Committee upon the Importation of Railway Plant : together with proceedings of the Committee, minutes of evidence and appendix GP V 1859/60 no. D 38 (2.9 MB) http://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1859-60NoD38.pdf Victorian Railways : report of the Board of Land and Works November 1862 GP V 1862/63 no. 21 (2.8 MB) https://www.parliament.vic.gov.au/papers/govpub/VPARL1862-63No21.pdfHistoric - Victorian Railways - Double Headed rail Ravenswood Railway Station and Siding Victorian Heritage Database Reports Victorian Heritage Register VHR H1100 Victorian Heritage Register VHR H1786 National Trust VHR H1100 Mount Alexander and Murray River Rail way Line National Trust2 rail lengths of Double Headed Rail made of Iron makers marks : Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield - Steel and 20 joint chairs with metal rail pins Makers mark Wilson & Cammell - Dronfield - Steel (possible date 187? very hard to read ) puffing billy, double headed rail, wilson & cammell - dronfield - steel works, ravenswood station siding, melbourne to echuca rail line, initially known as the melbourne, mt alexander and murray river railway. -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayEquipment - Victorian Railways Carriage Foot Warmer
During prestige, long distance train journeys some carriages had air-conditioning, and the majority of passengers had to brave unheated carriages. To offer some comfort during the winter months, the non-air-conditioned carriages were provided with footwarmers. These were metal containers roughly 100 mm thick and 300 mm wide, and about 750 mm long, which were filled with salt crystals (concentrated crystalline hydrated sodium acetate). The footwarmers were covered by sleeves of thick canvas, and two footwarmers were usually placed in each compartment of non-air-conditioned carriages. To activate the chemicals, the footwarmers were heated almost to boiling point. This was done by removing the canvas sleeves and placing the footwarmers in a large bath of very hot water. After they had been heated, they were removed from the bath and the sleeves refitted. They were then ready to be placed in the carriages. The McLaren patent foot warmer was used on railways in New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria and South Australia as well as South Africa and New Zealand. It was during the 1901 royal visit by the Duke and Duchess of Cornwall that these foot warmers were first used in New Zealand in the royal carriage. Before railway carriage heating was introduced, McLaren patent foot warmers were placed on the floor of New South Wales government railway carriages from 1891 to provide a little passenger comfort. The rectangular steel container worked a bit like a hot water bottle but instead of water contained six and a half kilograms of loosely-packed salt crystals, (concentrated crystalline hydrated sodium acetate). This was permanently sealed inside the container with a soldered cap. After the foot warmer was heated in vat of boiling water for about one and a quarter hours the crystals became a hot liquid. (The melting point for sodium acetate is 58 degrees). There was a whole infrastructure of special furnaces set up at stations for the daily heating of foot warmers. By 1914 the Victorian railways had 4,000 foot warmers in service and by 1935 there were 33 furnaces at principal stations to heat them. After about 10 hours the container was picked up by the handle and given a good vertical shake which helped the cooled liquid reform into a solid mass of hot crystals. Staff or sometimes passengers shook them en route when the foot warmers began to get cold. However, as they were heavy this was only possible by fit and agile passengers. At the end of the journey the containers were boiled again for reuse on the next trip. Sodium acetate railway foot warmers were introduced in Victoria in 1889, Adelaide to Melbourne express in 1899. "Shaking up" on this service took place at Murray Bridge and Stawell on the tip to Melbourne and at Ballarat and Serviceton on the trip to Adelaide. The use of foot warmers began to decline in New South Wales from the 1930s with the first trial of carriage air-conditioning in 1936, steam heating from 1948 ad LP gas heating from 1961. By the early 1960s the main services using foot warmers were the overnight mail trains. info from : http://www.powerhousemuseum.com/collection/database/?irn=67564#ixzz4UBNzVf6t Under Creative Commons License: Attribution Non-Commercial There was a whole infrastructure set up at stations for the daily heating of foot warmers in special furnaces. In Victoria alone in 1935 there were 33 heating works.Historic - Victorian Railways - Carriage Heater - Foot warmerA rectangular-shaped stainless steel casing with a welded seam down the back and welded ends. There is a handle at one end for carrying and shaking. Inside the foot warmer are two baffle plates and three trays to contain the sodium acetate. There was a cast-iron ball in each internal compartment. puffing billy, victorian railways, carriage haeter, foot warmer, passenger comfort, station furnace, railway ephemera, early heating methods -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayRail Bender No. 3
Rail Bender - Part of Hydraulic Rail Bender Rail Bender – No. 3 Most rails are produced straight. While they to easily bend and appear flexible, they are required to bend for some curves, at rail joins on curves and at point (turn-out) junctions. For a safe transition around curves and in the finer areas of the point, this use to be done with a manual rail bender. Sometimes referred to as a Buddah, the rail bender attaches its two claws to the rail. In the middle of the two claws is a screw that is tightened slowly using large spanner. Historic - Railways Permanent Way and Works - track equipment - Rail Bender large Rail Bender - Part of Hydraulic Rail Bender made of cast wrought iron puffing billy, rail bender -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayBender - Light Rail
Light Rail Bender Most rails are produced straight. While they to easily bend and appear flexible, they are required to bend for some curves, at rail joins on curves and at point (turn-out) junctions. For a safe transition around curves and in the finer areas of the point, this use to be done with a manual rail bender. Sometimes referred to as a Buddah, the rail bender attaches its two claws to the rail. In the middle of the two claws is a screw that is slowly tightened using a crow-bar to bend the rail. Tightening the screw too fast or too tightly may not give the structure of the rail time to redistribute and the rail may break if not done properly. Historic - Railways Permanent Way and Works - track equipment - Light Rail Bender Light Rail Bender made out of cast wrought ironpuffing billy, light rail bender -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayTool - Rail bender
Railway tracks are produced straight. They may appear to be easy to bend and may appear flexible, but are required to be bent for curves, at rail joins on curves and at point (turn-out) junctions. For a safe transition around curves and in the finer areas of the point, this was required to be done with a manual rail bender. Sometimes referred to as a Jim Crow, the rail bender attaches its two claws to the rail. In the middle of the two claws is a screw that is slowly tightened using a crow-bar to bend the rail. Tightening the screw too fast or too tightly may not give the structure of the rail time to redistribute and the rail may break if not done properly.Victorian Railways Permanent Way and Works track equipment Light Rail Bender narrow GaugeCast iron semi-circular tool, with hooked ends and central screw shaft.puffing billy, rail bender, jim crow -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwayTurning Bar, Rail
Rail Turning Bar Rail is heavy, sometimes as much as 120 lbs per yard. To assist in being able to move rail, a special turning bar was developed. Usually a long handle, on one end various features in the head allow rail to be moved Historic - Railway Permanent Way and Works - track equipment - Rail Turning BarRail Turning Bar made from cast wrought iron puffing billy, rail turning bar -
 Puffing Billy Railway
Puffing Billy RailwaySpanner, Ratchet
Ratchet Spanner This spanner is used on track work. Being a ratchet spanner, it allows movement in one direction, with a reverse movement to keep the tool in the same position, but it does not allow the item being tightened to rotate with the spanner in the reverse direction. This allows for longer handles and therefore gives more force to the item that is being tightened or released.Historic - Railway Permanent Way and Works - track equipment - Ratchet SpannerRatchet Spanner made of cast wrought iron puffing billy, ratchet spanner -
 Sunshine and District Historical Society Incorporated
Sunshine and District Historical Society IncorporatedD324 WRENCH - H. V. McKay, H. V. McKay Pty. Ltd, Early 1900's
This type of wrench or spanner was used as a service tool for H. V. McKay Pty. Ltd. manufactured agricultural machinery. This specific tool belonged to Albert (Bert) Montgomery of 11 Kamarooka St, Albion. Bert Montgomery was born in Sunshine and in 1910 was apprenticed as a carpenter with Sunshine Harvester Works, where he worked as a wood machinist. On 19 August 1914, while still an apprentice, he enlisted in the First AIF. He left McKay's and started business as a builder probably just prior to WW2. After the war he joined the Shire of Braybrook as Assistant Building Surveyor until he retired. In 1962 Bert and his friend Jack Causon (proprietor of an Anderson Road second hand store that previously was Les James grocery) were on a fishing trip to Lake Tooliorook (aka Ettrick) near Lismore, Victoria. Their boat capsized and both fishermen were drowned. Bert was a Past President of Sunshine RSL and at that time it was reported that his funeral was the largest that Sunshine had seen. The information about Bert Montgomery was supplied by a Committee member of the Sunshine & District Historical Society Inc. who spoke to Montgomery's daughter, who also donated the tool. This tool serves as a reminder of the large H. V. McKay agricultural manufacturing works that once existed in Sunshine. The tool is associated with the works, and the design is significant enough for images of the tool to be used in an artistic mural, which is painted on the Eastern Pillar of the new H. V. McKay Footbridge in Sunshine, Victoria 3020.Curved double ended rusty cast iron wrench with 4 open slots plus 2 closed slots'H V McKAY' on one side and 'D324' on the reverse sideh. v. mckay pty. ltd, d324, d324 wrench, d324 spanner, agricultural spanner, antique wrench, agricultural tool, albert montgomery, jack causon, lake tooliorook
